Effect of Interleukin-7 on In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes and Subsequent Developmental Potential after Parthenogenetic Activation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Measurement of IL-7 in Porcine Follicular Fluid (FF)
2.3. Oocyte Collection and IVM
2.4. Assessment of Nuclear Maturation
2.5. Measurement of Intracellular GSH and ROS Levels
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis Using Real-Time qPCR
2.7. Parthenogenetic Activation and In Vitro Culture of Porcine Embryos
2.8. Evaluation of Developmental Competence and Total Cell Count
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of IL-7 in Porcine FF
3.2. Effect of IL-7 Supplementation during IVM on Oocyte Nuclear Maturation
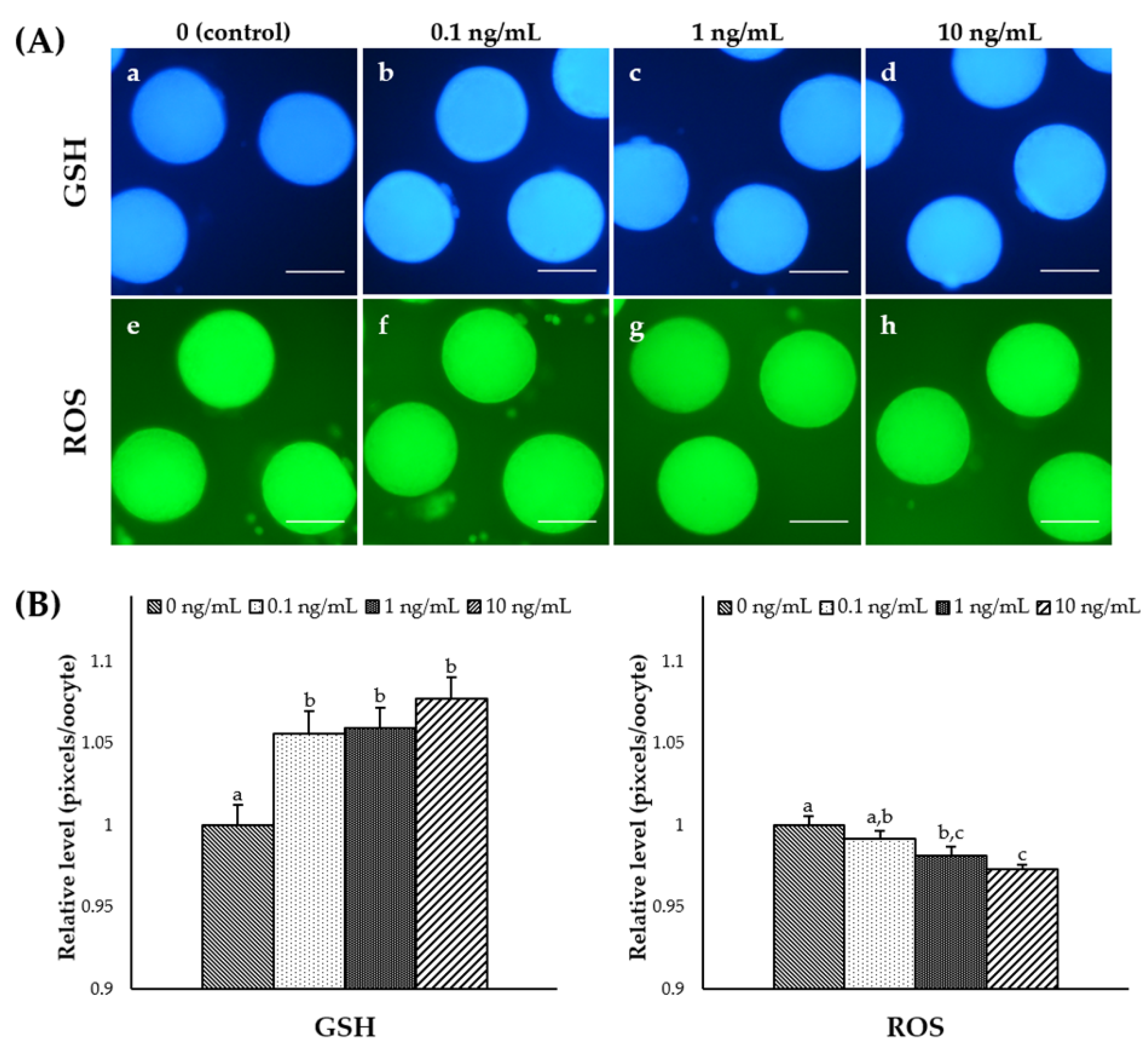
3.3. Effect of IL-7 Supplementation during IVM on Cytoplasmic Maturation
3.4. Effect of IL-7 Supplementation on Gene Expression Levels in CCs and Oocytes during IVM
3.5. Effect of IL-7 Supplementation in IVM Media on Developmental Potential after PA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Day, B.N. Reproductive biotechnologies: Current status in porcine reproduction. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2000, 60–61, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, R.A.; Simond, D.M.; Burns, H.; Patel, A.T.; O’Connell, P.J.; Gunton, J.E.; Hawthorne, W.J. Transplantation sites for porcine islets. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, D.K.; Bottino, R. Recent advances in understanding xenotransplantation: Implications for the clinic. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiebig, U.; Fischer, K.; Bähr, A.; Runge, C.; Schnieke, A.; Wolf, E.; Denner, J. Porcine endogenous retroviruses: Quantification of the copy number in cell lines, pig breeds, and organs. Xenotransplantation 2018, 25, e12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, C.G.A.; Byrne, G.W. Porcine to human heart transplantation: Is clinical application now appropriate? J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 2534653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendriksen, P.J.; Vos, P.L.; Steenweg, W.N.; Bevers, M.M.; Dieleman, S.J. Bovine follicular development and its effect on the in vitro competence of oocytes. Theriogenology 2000, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Uchida, M.; Shimatsu, Y.; Miyake, M.; Nagao, Y.; Minami, N.; Yamada, M.; Imai, H. Developmental competence of somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos reconstructed from oocytes matured in vitro with follicle shells in miniature pig. Cloning Stem Cells 2005, 7, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.D.; Hwang, S.-U.; Kim, E.; Jin, M.; Kim, S.; Hyun, S.-H. GDF8 activates p38 MAPK signaling during porcine oocyte maturation in vitro. Theriogenology 2017, 101, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-E.; Hyun, H.; Shin, M.-Y.; Park, Y.-G.; Jeong, S.-G.; Kim, E.-Y.; Park, S.-P. Fibroblast growth factor 10 markedly improves in vitro maturation of porcine cumulus-oocyte complexes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Xia, G. Natriuretic peptides improve the developmental competence of in vitro cultured porcine oocytes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2017, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton, M.L.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Thompson, J.G. Effects of in-vivo and in-vitro environments on the metabolism of the cumulus–oocyte complex and its influence on oocyte developmental capacity. Hum. Reprod. Update 2003, 9, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumesic, D.A.; Meldrum, D.R.; Katz-Jaffe, M.G.; Krisher, R.L.; Schoolcraft, W.B. Oocyte environment: Follicular fluid and cumulus cells are critical for oocyte health. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Lane, M.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte-secreted factors: Regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum. Reprod. Update 2008, 14, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, F.; McTavish, K.J.; Shimasaki, S. Integral role of GDF-9 and BMP-15 in ovarian function. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2011, 78, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Albertini, D.F.; Nishimori, K.; Kumar, T.R.; Lu, N.; Matzuk, M.M. Growth differentiation factor-9 is required during early ovarian folliculogenesis. Nature 1996, 383, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wang, P.; DeMayo, J.; DeMayo, F.J.; Elvin, J.A.; Carino, C.; Prasad, S.V.; Skinner, S.S.; Dunbar, B.S.; Dube, J.L.; et al. Synergistic roles of bone morphogenetic protein 15 and growth differentiation factor 9 in ovarian function. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Xu, Y.-N.; Wang, Q.-L.; Namgoong, S.; Cui, X.-S.; Kim, N.-H. Effects of growth differentiation factor 9 and bone morphogenetic protein 15 on the in vitro maturation of porcine oocytes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2014, 49, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Luckey, M.A.; Park, J.-H. Intrathymic IL-7: The where, when, and why of IL-7 signaling during T cell development. Semin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovanen, P.E.; Leonard, W.J. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases: Critical roles of the γc-dependent cytokines interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, 15, and 21, and their signaling pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakajima, H.; Saito, Y.; Saito, T.; Leonard, W.J.; Iwamoto, I. Janus kinase 3 (Jak3) is essential for common cytokine receptor γ chain (γc)-dependent signaling: Comparative analysis of γc, Jak3, and γc and Jak3 double-deficient mice. Int. Immunol. 2000, 12, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kittipatarin, C.; Khaled, A.R. Interlinking interleukin-7. Cytokine 2007, 39, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.T.; Dudl, E.; LeRoy, E.; Murray, R.; Sprent, J.; Weinberg, K.I.; Surh, C.D. IL-7 is critical for homeostatic proliferation and survival of naive T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8732–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. Homeostasis of naive and memory T cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Yata, A.; Klein, C.; Cho, J.-H.; Deguchi, M.; Hsueh, A.J. Oocyte-expressed interleukin 7 suppresses granulosa cell apoptosis and promotes oocyte maturation in rats. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cakmak, H.; Franciosi, F.; Zamah, A.M.; Cedars, M.I.; Conti, M. Dynamic secretion during meiotic reentry integrates the function of the oocyte and cumulus cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2424–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Javvaji, P.K.; Dhali, A.; Francis, J.R.; Kolte, A.P.; Mech, A.; Sathish, L.; Roy, S.C. Interleukin-7 improves in vitro maturation of ovine cumulus-oocyte complexes in a dose dependent manner. Cytokine 2019, 113, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.-S.; Yoon, J.D.; Cheong, S.-A.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, E.; Hyun, S.-H. The new system of shorter porcine oocyte in vitro maturation (18 hours) using≥ 8 mm follicles derived from cumulus-oocyte complexes. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, K.; Toyoda, Y. Fluctuation of histone H1 kinase activity during meiotic maturation in porcine oocytes. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1991, 93, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, J.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Lee, E. Anthocyanin stimulates in vitro development of cloned pig embryos by increasing the intracellular glutathione level and inhibiting reactive oxygen species. Theriogenology 2010, 74, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Kwak, S.-S.; Cheong, S.-A.; Seong, Y.H.; Hyun, S.-H. Effect of trans-ε-viniferin on in vitro porcine oocyte maturation and subsequent developmental competence in pre-implantation embryos. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mito, T.; Yoshioka, K.; Yamashita, S.; Suzuki, C.; Noguchi, M.; Hoshi, H. Glucose and glycine synergistically enhance the in vitro development of porcine blastocysts in a chemically defined medium. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2012, 24, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidder, G.M.; Vanderhyden, B.C. Bidirectional communication between oocytes and follicle cells: Ensuring oocyte developmental competence. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 88, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.-Q.; Ou, S.-B.; Zhang, N.-F.; Ren, L.; Wei, L.-N.; Zhang, Q.-X.; Yang, D.-Z. Increased GDF9 and BMP15 mRNA levels in cumulus granulosa cells correlate with oocyte maturation, fertilization, and embryo quality in humans. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2014, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostanin, A.A.; Aizikovich, B.I.; Aizikovich, I.V.; Kozhin, A.Y.; Chernykh, E.R. Role of cytokines in the regulation of reproductive function. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Xia, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, A. Follicular fluid cytokine composition and oocyte quality of polycystic ovary syndrome patients with metabolic syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilization. Cytokine 2017, 91, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, P.G.; Glister, C. TGF-β superfamily members and ovarian follicle development. Reproduction 2006, 132, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, S.L.; Dasgupta, T.; Cummings, M.; Orsi, N.M. Cytokines in ovarian folliculogenesis, oocyte maturation and luteinisation. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 81, 284–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.-W.; Shin, T.-Y.; Park, J.-I.; Roh, S.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, B.-C.; Hwang, W.-S.; Lee, E.-S. Development of porcine oocytes from preovulatory follicles of different sizes after maturation in media supplemented with follicular fluids. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2000, 12, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, R.; Vigneron, C.; Perreau, C.; Bali-Papp, A.; Mermillod, P. Effect of follicular size on meiotic and developmental competence of porcine oocytes. Theriogenology 2002, 57, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Sun, Q.-Y. Oocyte meiotic maturation. In The Ovary, 3rd ed.; Leung, P.C.K., Adashi, E.Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 181–203. [Google Scholar]
- Poniedziałek-Kempny, K. In vitro production of porcine embryos: Current status and possibilities. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2020, 20, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, H.; Cantley, T.C.; Stumpf, T.T.; Terlouw, S.L.; Day, B.N. Use of low-salt culture medium for in vitro maturation of porcine oocytes is associated with elevated oocyte glutathione levels and enhanced male pronuclear formation after in vitro fertilization. Biol. Reprod. 1994, 51, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luberda, Z. The role of glutathione in mammalian gametes. Reprod. Biol. 2005, 5, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, S.; Tiwari, M.; Pandey, A.N.; Shrivastav, T.G.; Chaube, S.K. Impact of stress on oocyte quality and reproductive outcome. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moustafa, M.H.; Sharma, R.K.; Thornton, J.; Mascha, E.; Abdel-Hafez, M.A.; Thomas, A.J.; Agarwal, A. Relationship between ROS production, apoptosis and DNA denaturation in spermatozoa from patients examined for infertility. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.; Girio, A.; Cebola, I.; Santos, C.I.; Antunes, F.; Barata, J.T. Intracellular reactive oxygen species are essential for PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent IL-7-mediated viability of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2011, 25, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, I.; Mannervik, B. Glutathione reductase. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 113, pp. 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Uzbekova, S.; Roy-Sabau, M.; Dalbiès-Tran, R.; Perreau, C.; Papillier, P.; Mompart, F.; Thelie, A.; Pennetier, S.; Cognie, J.; Cadoret, V.; et al. Zygote arrest 1 gene in pig, cattle and human: Evidence of different transcript variants in male and female germ cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2006, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orsi, N.M.; Leese, H.J. Protection against reactive oxygen species during mouse preimplantation embryo development: Role of EDTA, oxygen tension, catalase, superoxide dismutase and pyruvate. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2001, 59, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matos, D.G.; Furnus, C.C.; Moses, D.F.; Martinez, A.G.; Matkovic, M. Stimulation of glutathione synthesis of in vitro matured bovine oocytes and its effect on embryo development and freezability. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1996, 45, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, T.; Zheng, W.; Sun, R.; Shen, W.; Sha, J.; et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) regulates primordial follicle assembly by promoting apoptosis of oocytes in fetal and neonatal mouse ovaries. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zheng, P.; Dean, J. Maternal control of early mouse development. Development 2010, 137, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, K.-A. Maternal effect genes: Findings and effects on mouse embryo development. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2014, 41, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L. Versican expression level in cumulus cells is associated with human oocyte developmental competence. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2020, 66, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Amano, T.; Shimizu, H. Roles of gap junctional communication of cumulus cells in cytoplasmic maturation of porcine oocytes cultured in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chian, R.C.; Niwa, K.; Sirard, M.A. Effects of cumulus cells on male pronuclear formation and subsequent early development of bovine oocytes in vitro. Theriogenology 1994, 41, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høst, E.; Gabrielsen, A.; Lindenberg, S.; Smidt-Jensen, S. Apoptosis in human cumulus cells in relation to zona pellucida thickness variation, maturation stage, and cleavage of the corresponding oocyte after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 77, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chaudhury, P.; Osmond, D.G. Regulation of cell survival during B lymphopoiesis: Apoptosis and Bcl-2/Bax content of precursor B cells in bone marrow of mice with altered expression of IL-7 and recombinase-activating gene-2. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, E.; Aflatoonian, R.; Moeini, A.; Yamini, N.; Asadi, E.; Khosravizadeh, Z.; Tarzjani, M.D.; Harat, Z.N.; Abolhassani, F. Apoptotic biomarkers in cumulus cells in relation to embryo quality in polycystic ovary syndrome. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 296, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, F.J.; Tait, S.W. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thundathil, J.; Filion, F.; Smith, L.C. Molecular control of mitochondrial function in preimplantation mouse embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 71, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Chu, C.T.; Kaufman, B.A. The mitochondrial transcription factor TFAM in neurodegeneration: Emerging evidence and mechanisms. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Block, K.; Gorin, Y.; Abboud, H.E. Subcellular localization of Nox4 and regulation in diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14385–14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Cytokine | Size of Follicles (n* = 25) | M199 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (1–2 mm) | Medium (3–7 mm) | Large (≥8 mm) | ||
| IL-7 (pg/mL) | 6.8 ± 5.0 a | 64.2 ± 39.2 b | 44.0 ± 22.8 a,b | ND |
| IL-7 Concentration (ng/mL) | No. of Oocytes Cultured for Maturation | Mean ± SEM (%) Oocytes at the Stage of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germinal Vesicle | Metaphase I | Anaphase and Telophase I | Metaphase II | ||
| 0 | 192 | 3.2 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 1.8 | 91.6 ± 1.8 a |
| 0.1 | 179 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 1.1 | 92.2 ± 1.0 a |
| 1 | 188 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 97.3 ± 0.5 b |
| 10 | 191 | 2.7 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 92.1 ± 1.1 a |
| IL-7 Concentration (ng/mL) | No. of Embryos Cultured, N* | No. (%) of Embryos Developed to | Total Cell Number in Blastocyst (n**) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 2-Cell | Blastocyst | |||
| 0 | 116 | 49 (42.3 ± 1.4) a | 32 (27.6 ± 2.0) a | 90.1 ± 6.9 (32) a |
| 0.1 | 114 | 72 (62.9 ± 4.3) b | 53 (46.0 ± 5.8) b | 89.4 ± 5.1 (53) a |
| 1 | 121 | 79 (65.3 ± 2.6) b | 67 (55.4 ± 1.1) b | 114.7 ± 5.8 (67) b |
| 10 | 121 | 76 (62.8 ± 1.5) b | 56 (46.3 ± 4.5) b | 98.0 ± 5.1 (56) a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Hwang, S.-U.; Yoon, J.-D.; Cai, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, G.; Choi, H.; Hyun, S.-H. Effect of Interleukin-7 on In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes and Subsequent Developmental Potential after Parthenogenetic Activation. Animals 2021, 11, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030741
Oh D, Lee J, Kim E, Hwang S-U, Yoon J-D, Cai L, Kim M, Kim G, Choi H, Hyun S-H. Effect of Interleukin-7 on In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes and Subsequent Developmental Potential after Parthenogenetic Activation. Animals. 2021; 11(3):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030741
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Dongjin, Joohyeong Lee, Eunhye Kim, Seon-Ung Hwang, Junchul-David Yoon, Lian Cai, Mirae Kim, Gahye Kim, Hyerin Choi, and Sang-Hwan Hyun. 2021. "Effect of Interleukin-7 on In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes and Subsequent Developmental Potential after Parthenogenetic Activation" Animals 11, no. 3: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030741
APA StyleOh, D., Lee, J., Kim, E., Hwang, S.-U., Yoon, J.-D., Cai, L., Kim, M., Kim, G., Choi, H., & Hyun, S.-H. (2021). Effect of Interleukin-7 on In Vitro Maturation of Porcine Cumulus-Oocyte Complexes and Subsequent Developmental Potential after Parthenogenetic Activation. Animals, 11(3), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030741








