Activity of Mannose-Binding Lectin on Bacterial-Infected Chickens—A Review
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Brief Overview of the Chicken Innate Immune System
3. Mannose-Binding Lectin
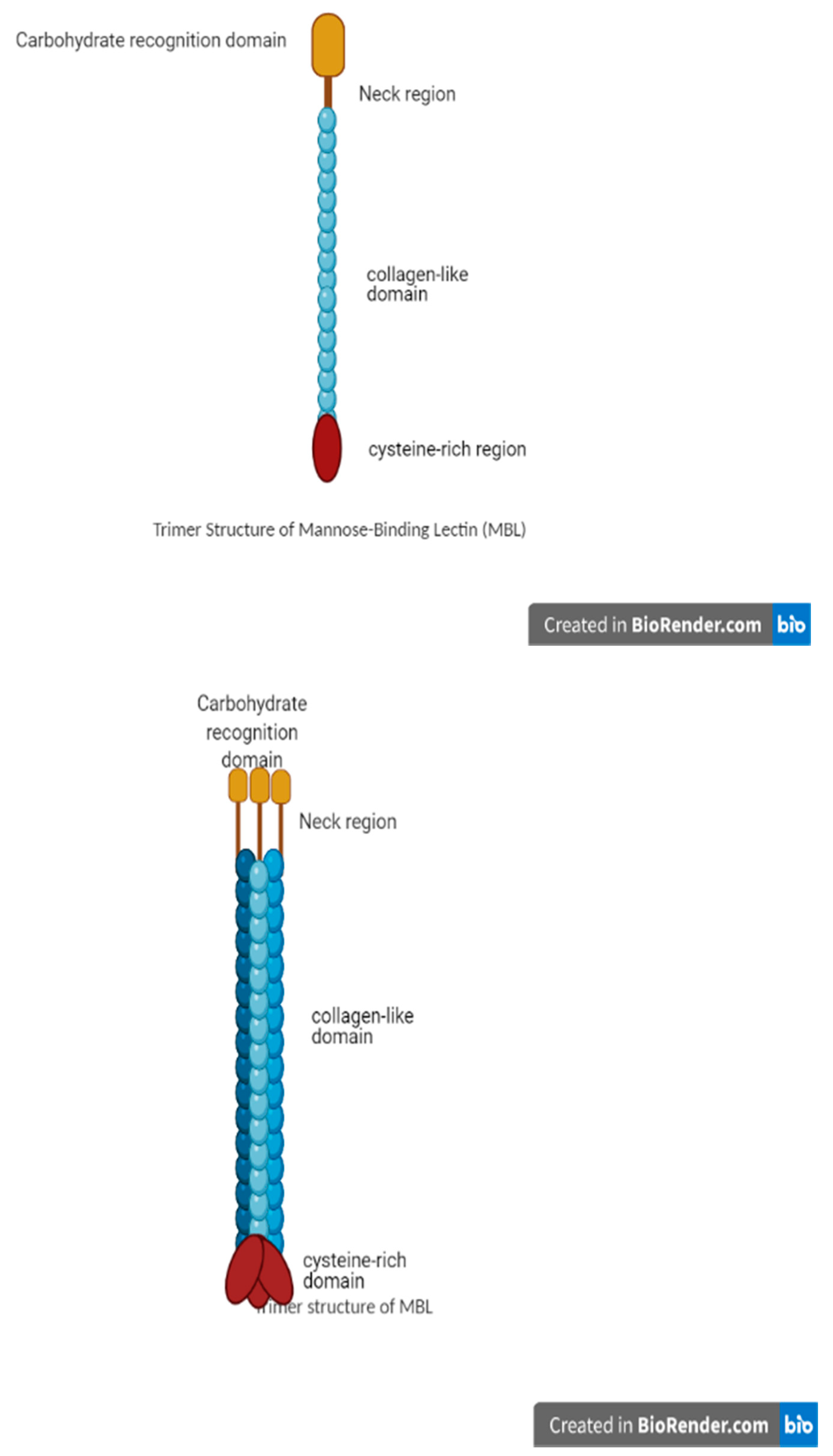
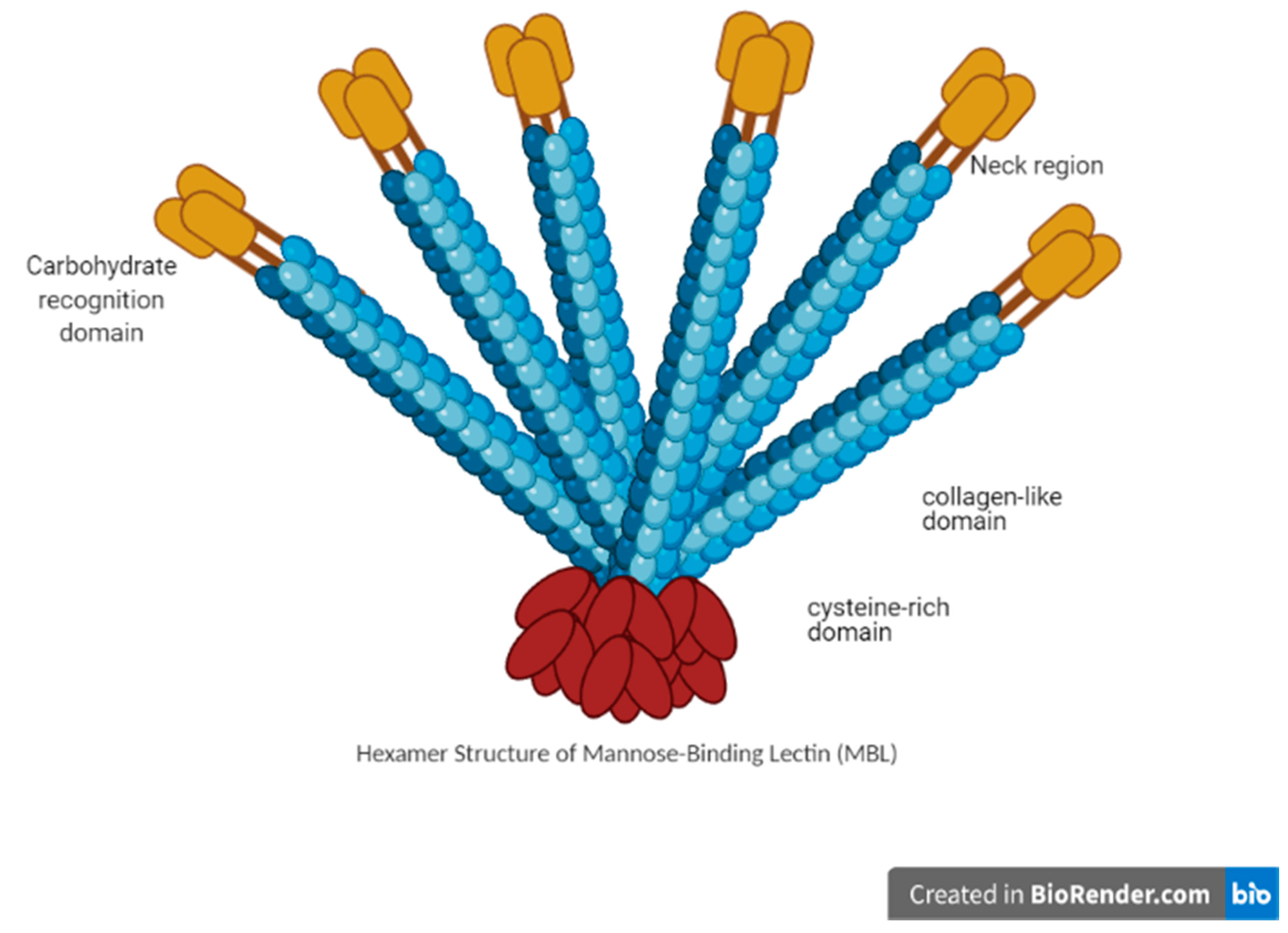
3.1. MBL Structure
3.2. MBL Mode of Action
3.3. MBL Ligand Binding
4. Complement System
The Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation
5. Applicable Methods for Detecting and Quantifying MBL
5.1. Chromatography
5.2. Reverse Phase HPLC
5.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
5.4. DNA Typing
5.5. Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
5.6. Mass Spectrometry
6. MBL Localization/Synthesis
7. MBL Concentration vs. Bacterial Disease Protection
8. Antimicrobial Nature of MBL Concentration and Its Effect on Chicken Growth Rate
9. MBL Deficiency
10. Possible Factors Affecting cMBL Production in Chicken Management Systems
10.1. Effect of Age and Stress on cMBL Production
10.2. Effect of Breed on cMBL Production
10.3. Possible Effect of Feed Manipulation on cMBL Expression
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Idowu, P.A.; Mpayipheli, M.; Muchenje, V. Practices, Housing and Diseases within Indigenous Poultry Production in Eastern Cape, South Africa. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 10, p111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Z.-Z.; Kong, L.-H.; Tang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, A.-Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.-N. Vertical transmission of Salmonella Enteritidis with heterogeneous antimicrobial resistance from breeding chickens to commercial chickens in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkey, P.M. The growing burden of antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, i1–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froebel, L.; Jalukar, S.; Lavergne, T.; Lee, J.; Duong, T. Administration of dietary prebiotics improves growth performance and reduces pathogen colonization in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6668–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, R. Interactions between mannose-binding lectin and MASPs during complement activation by the lectin pathway. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarma, J.V.; Ward, P.A. The complement system. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 343, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K. Mannose-binding lectin and the balance between immune protection and complication. Expert Rev. Antiinfect. Ther. 2011, 9, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.M.; Lynch, N.J.; Haleem, K.S.; Fujita, T.; Endo, Y.; Hansen, S.; Holmskov, U.; Takahashi, K.; Stahl, G.L.; Dudler, T.; et al. The Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation Is a Critical Component of the Innate Immune Response to Pneumococcal Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, P.M.D.S.; De Oliveira, W.F.; Albuquerque, P.B.S.; Correia, M.T.D.S.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. Insights into anti-pathogenic activities of mannose lectins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenthal, J.; Bean, A.; Kogut, M. What’s so special about chicken immunology? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, F.T.; Bed’Hom, B.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Dalgaard, T.S. Identification and tissue-expression profiling of novel chicken c-type lectin-like domain containing proteins as potential targets for carbohydrate-based vaccine strategies. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghfouri, A.H.; Zarrin, R.; Maleki, V.; Payahoo, L.; Bishak, Y.K. A comprehensive mechanistic review insight into the effects of micronutrients on toll-like receptors functions. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, D.K.; Chang, Y.S.; Sung, S.I.; Yoo, H.S.; Ahn, S.Y.; Park, W.S. Antibacterial effect of mesenchymal stem cells against Escherichia coli is mediated by secretion of beta-defensin-2 via toll-like receptor 4 signalling. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loh, S.H.; Park, J.-Y.; Cho, E.H.; Nah, S.-Y.; Kang, Y.-S. Animal lectins: Potential receptors for ginseng polysaccharides. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, O.L.; Jensenius, J.C.; Jørgensen, P.H.; Laursen, S.B. Serum levels of chicken mannan-binding lectin (MBL) during virus infections; indication that chicken MBL is an acute phase reactant. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 70, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norup, L.; Dalgaard, T.; Friggens, N.; Sørensen, P.; Juul-Madsen, H. Influence of chicken serum mannose-binding lectin levels on the immune response towards Escherichia coli. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, T.; Permin, A.; Christensen, J.; Cu, H.; Juul-Madsen, H. Mannan-binding lectin (MBL) in two chicken breeds and the correlation with experimental Pasteurella multocida infection. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 33, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lynge, S.L.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Norup, L.R.; Song, X.; Sørensen, P.; Juul-Madsen, H.R. Chicken mannose-binding lectin function in relation to antibacterial activity towards Salmonella enterica. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Van Eijk, M.; Guo, H.; Van Dijk, A.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Verheije, M.H.; Wang, G.; Haagsman, H.P.; Veldhuizen, E.J. Expression and characterization of recombinant chicken mannose binding lectin. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Idowu, P.A.; Mpayipheli, M.; Muchenje, V. Can Mannose-Binding Lectin Activation Help in Fighting Bacterial Pathogen in Poultry Production Systems?—A Review. Preprints 2018, 201811, 0350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Yamashina, I. Isolation and characterization of mannan-binding proteins from chicken liver. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1985, 241, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, S.B.; Hedemand, J.E.; Nielsen, O.L.; Thiel, S.; Koch, C.; Jensenius, J.C. Serum levels, ontogeny and heritability of chicken mannan-binding lectin (MBL). Immunology 1998, 94, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, N.J.; Khan, S.-U.-H.; Stover, C.M.; Sandrini, S.M.; Marston, D.; Presanis, J.S.; Schwaeble, W.J. Composition of the Lectin Pathway of Complement inGallus gallus: Absence of Mannan-Binding Lectin-Associated Serine Protease-1 in Birds. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4998–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yongqing, T.; Drentin, N.; Duncan, R.C.; Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Pike, R.N. Mannose-binding lectin serine proteases and associated proteins of the lectin pathway of complement: Two genes, five proteins and many functions? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norup, L.; Juul-Madsen, H. An Assay for Measuring the Mannan-Binding Lectin Pathway of Complement Activation in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2322–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebremeskel, M.; Brah, G.S.; Mukhopadhyay, C.S.; Dipak, D.; Ramneek, R. Molecular characterization of mannose-binding lectin protein in chickens. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 84, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asbeck, E.C.; Hoepelman, A.I.; Scharringa, J.; Herpers, B.L.; Verhoef, J. Mannose binding lectin plays a crucial role in innate immunity against yeast by enhanced complement activation and enhanced uptake of polymorphonuclear cells. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Van Eijk, M.; Haagsman, H.P. The carbohydrate recognition domain of collectins. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3930–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, D.L.; Klein, N.J.; Turner, M.W. Mannose-binding lectin: Targeting the microbial world for complement attack and opsonophagocytosis. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 180, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitved, L.; Holmskov, U.; Koch, C.; Teisner, B.; Hansen, S.; Skjødt, K. The homologue of mannose-binding lectin in the carp family Cyprinidae is expressed at high level in spleen, and the deduced primary structure predicts affinity for galactose. Immunogenetics 2000, 51, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, C.; Schaerer, B.; Kohn, M.; Pendl, H.; Weigend, S.; Kaspers, B.; Härtle, S. A rapid high-precision flow cytometry based technique for total white blood cell counting in chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 145, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenkamp, A.; Van Eijk, M.; Van Dijk, A.; Van Asten, A.J.; Veldhuizen, E.J.; Haagsman, H.P. Characterization and expression sites of newly identified chicken collectins. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juul-Madsen, H.R.; Norup, L.R.; Jørgensen, P.H.; Handberg, K.J.; Wattrang, E.; Dalgaard, T.S. Crosstalk between innate and adaptive immune responses to infectious bronchitis virus after vaccination and challenge of chickens varying in serum mannose-binding lectin concentrations. Vaccine 2011, 29, 9499–9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, B.T.; Cartwright, M.; Dinis, A.L.M.; Duffy, S.; Lombardo, P.; Cartwright, D.; Super, E.H.; Lanzaro, J.; Dugas, K.; Super, M.; et al. Broad-spectrum capture of clinical pathogens using engineered Fc-mannose-binding lectin enhanced by antibiotic treatment. F1000Research 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisen, D.P.; Minchinton, R.M. Impact of Mannose-Binding Lectin on Susceptibility to Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrame, M.H.; Catarino, S.J.; Goeldner, I.; Boldt, A.B.W.; De Messias-Reason, I.J. The Lectin Pathway of Complement and Rheumatic Heart Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2015, 2, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heesterbeek, D.A.; Angelier, M.L.; Harrison, R.A.; Rooijakkers, S.H. Complement and Bacterial Infections: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Applications. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Sannoh, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Yamashina, I. Serum lectin with known structure activates complement through the classical pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 7451–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héja, D.; Kocsis, A.; Dobó, J.; Szilágyi, K.; Szász, R.; Závodszky, P.; Pál, G.; Gál, P. Revised mechanism of complement lectin-pathway activation revealing the role of serine protease MASP-1 as the exclusive activator of MASP-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10498–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kjærup, R.M.; Norup, L.R.; Skjødt, K.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Juul-Madsen, H.R. Chicken mannose-binding lectin (mannose-binding lectin) gene variants with influence on mannose-binding lectin serum concentrations. Immunogenetics 2013, 65, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich-Lynge, S.L.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Norup, L.R.; Kjærup, R.M.; Olsen, J.E.; Sørensen, P.; Juul-Madsen, H.R. The consequence of low mannose-binding lectin plasma concentration in relation to susceptibility to Salmonella Infantis in chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 163, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, S.B.; Nielsen, O.L. Mannan-binding lectin (MBL) in chickens: Molecular and functional aspects. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, S.B.; Hedemand, J.E.; Thiel, S.; Willis, A.C.; Skriver, E.; Madsen, P.S.; Jensenius, J.C. Collectin in a non-mammalian species: Isolation and characterization of mannan-binding protein (MBP) from chicken serum. Glycobiology 1995, 5, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, R.; Tsiftsoglou, S. Proteases of the complement system. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedzyński, M.; Świerzko, A.S. Components of the Lectin Pathway of Complement in Haematologic Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, R.; Thiel, S.; Jensenius, J.C. Mannan-binding-lectin-associated serine proteases, characteristics and disease associations. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2005, 27, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-M.; Martinez, A.W.; Gong, J.; Mace, C.R.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Mirica, K.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-Based ELISA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4771–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, B.; Ramos-Fernández, A.; Calvo, E.; López-Ferrer, D.; Camafeita, E. Mass spectrometry technologies for proteomics. Briefings Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2006, 4, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulrich-Lynge, S.L.; Juul-Madsen, H.R.; Kjærup, R.B.; Okimoto, R.; Abrahamsen, M.S.; Maurischat, S.; Sørensen, P.; Dalgaard, T.S. Broilers with low serum Mannose-binding Lectin show increased fecal shedding of Salmonella enterica serovar Montevideo. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Kuhlenschmidt, T.B.; Lee, Y.C. Isolation and characterization of the major mannose-binding protein in chicken serum. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5932–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromberg, Z.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Kilbourne, J.; Van Goor, A.; Curtiss, R.; Mellata, M. Evaluation of Escherichia coli isolates from healthy chickens to determine their potential risk to poultry and human health. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neth, O.; Jack, D.L.; Dodds, A.W.; Holzel, H.; Klein, N.J.; Turner, M.W. Mannose-Binding Lectin Binds to a Range of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms and Promotes Complement Deposition. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norup, L.R.; Jensen, K.H.; Jørgensen, E.; Sørensen, P.; Juul-Madsen, H.R. Effect of mild heat stress and mild infection pressure on immune responses to an E. coli infection in chickens. Animal 2008, 2, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenes, A.; Roura, E. Essential oils in poultry nutrition: Main effects and modes of action. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2010, 158, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdeano, C.M.; PerdigónG. The Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus casei Induces Activation of the Gut Mucosal Immune System through Innate Immunity. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pascal, G.; Denery, S.; Bodinier, M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: Impact on the gut immune system and allergic reactions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Petrova, M.I.; Imholz, N.C.E.; Verhoeven, T.L.A.; Noppen, S.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Liekens, S.; Balzarini, J.; Schols, D.; Vanderleyden, J.; et al. High mannose-specific lectin Msl mediates key interactions of the vaginal Lactobacillus plantarum isolate CMPG5300. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyofo, B.; Deloach, J.; Corrier, D.; Norman, J.; Ziprin, R.; Mollenhauer, H. Prevention of Salmonella typhimurium Colonization of Broilers with D-Mannose. Poult. Sci. 1989, 68, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, P.; Wenk, C.; Dawson, K.A.; Newman, K.E. The effects of dietary mannaoligosaccharides on cecal parameters and the concentrations of enteric bacteria in the ceca of salmonella-challenged broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Ghosh, T.; Toshiwati; Bedford, M. Effects of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and yeast protein concentrate on production performance of broiler chickens exposed to heat stress and challenged with Salmonella enteritidis. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2011, 168, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiihonen, K.; Kettunen, H.; Bento, M.; Saarinen, M.; Lahtinen, S.; Ouwehand, A.; Schulze, H.; Rautonen, N. The effect of feeding essential oils on broiler performance and gut microbiota. Br. Poult. Sci. 2010, 51, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placha, I.; Takacova, J.; Ryzner, M.; Cobanova, K.; Laukova, A.; Strompfova, V.; Venglovska, K.; Faix, S. Effect of thyme essential oil and selenium on intestine integrity and antioxidant status of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2014, 55, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Identification Method | Mode of Action and Sensitivity | Price and Sample Size | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affinity chromatography | Less sensitive Possibility of interfering with MBL structure, ligand leakage. | Small sample ranging from 1–10 samples, consumes time, less reliable and less reproducible | [22,48] |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | Specific monoclonal and polyclonal detection Very sensitive and reliable | Expensive and medium sample size | [23] |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Real time PCR Multiplex PCR | Use of suitable primers Flourescent reporter signal Sequence specific probe Proper genotyping of MBL gene | Extremely expensive, highly reproducible and Highly reliable with large sample size. | [49] |
| Mass spectrophotometry | mass of heterogeneously glycosylate protein; molecular weight of MBL | Highly reproducible with high sample size | [19] |
| Treatment | Age of Chicken | Site of MBL | Detection Method | Outcome/Result | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consequence of low mannose-binding lectin plasma concentration in relation to susceptibility to Salmonella infantis in chickens | Day-old | Serum and Ceca | ELISA, RT-PCR and Flow Cytometry | Higher average body weight gain and MBL expression in L10H. Higher bacteria count in caecum swab of L10L | [42] |
| Escherichia coli ISA, LSL, LB, HE | 16–52 weeks old | Serum | ELISA and PCR | Increased body weight in high MBL. Low MBL chicken are more prone to E. coli | [16] |
| Effect of Pasteurella multocida inoculation on MBL level | 16 weeks | Serum | ELISA | Significant low MBL in systemic infected chicken with Pasteurella multicoda (acute phase) | [17] |
| Broilers with low serum mannose-binding lectin show increased fecal shedding of Salmonella enterica serovar Montevideo | Day old | Serum | ELISA and RT-PCR | L/H chickens had significantly less salmonella counts/cloacal swab at week 3and 5 post infection than L/L chicken. Chicken with low MBL are more susceptible to Salmonella thanhigh MBL chicken. | [50] |
| Chicken mannose-binding lectin function in relation to antibacterial activity towards Salmonella enterica | NA | Serum | ELISA and Flow-Cytometry | S. enterica S. enterica is the only C1 serotypes that bound to cMBL.Serum with high cMBL exhibited a greater bactericidal activity to S. aureus than serum with low concentrations of cMBL activity to S. aureus than serum with low concentrations of cMBL | [18] |
| Bacteria Strain | Site of Binding | References |
|---|---|---|
| Pasteurella multocida | Liver, spleen, serum | [17] |
| Escherichia coli | Liver, serum | [16,32,34] |
| Salmonella enterica | Liver, serum | [18] |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Ceca, serum | [33,35] |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | Serum | [34] |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Serum | [34] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Serum | [34] |
| Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | Serum | [34] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Serum | [19] |
| Salmonella Montevideo | Serum | [41] |
| Enterobacter cloacae | Serum | [34] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idowu, P.A.; Idowu, A.P.; Zishiri, O.T.; Mpofu, T.J.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Nephawe, K.A.; Mtileni, B. Activity of Mannose-Binding Lectin on Bacterial-Infected Chickens—A Review. Animals 2021, 11, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030787
Idowu PA, Idowu AP, Zishiri OT, Mpofu TJ, Veldhuizen EJA, Nephawe KA, Mtileni B. Activity of Mannose-Binding Lectin on Bacterial-Infected Chickens—A Review. Animals. 2021; 11(3):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030787
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdowu, Peter A., Adeola P. Idowu, Oliver T. Zishiri, Takalani J. Mpofu, Edwin J. A. Veldhuizen, Khathutshelo A. Nephawe, and Bohani Mtileni. 2021. "Activity of Mannose-Binding Lectin on Bacterial-Infected Chickens—A Review" Animals 11, no. 3: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030787








