From the Andes to the Apennines: Rise and Fall of a Free-Ranging Population of Feral Llamas
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
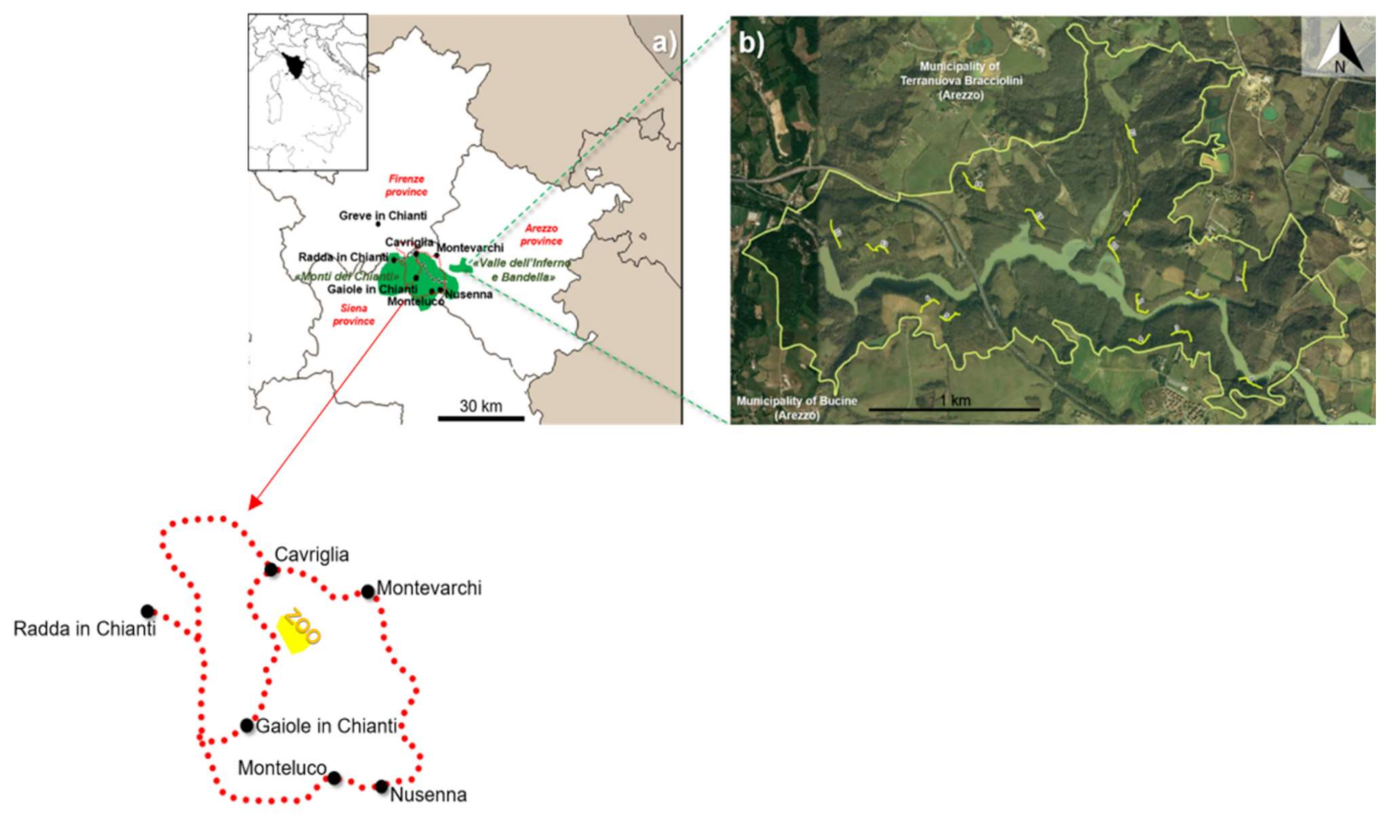
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Social Perception of Feral Llamas
2.4. Media Content Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Llama Records and Population Range
3.2. Social Perception
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mack, R.N.; Simberloff, D.; Londsdale, W.M.; Evans, H.; Clout, M.; Bazzaz, F.A. Biotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 689–710. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Bellard, C.; Ricciardi, A. Alien versus native species as drivers of recent extinctions. Front. Ecol. Environm. 2019, 17, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Manenti, R.; Ghia, D.; Fea, G.; Ficetola, G.F.; Padoa-Schioppa, E.; Canedoli, C. Causes and consequences of crayfish extinction: Stream connectivity, habitat changes, alien species and ecosystem services. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ warning on invasive alien species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, A.; Clutton-Brock, J.; Groves, G.P. The naming of wild animal species and their domestic derivatives. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Essl, F.; Bacher, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kowarik, I.; Kühn, I.; Pyšek, P.; Rabitsch, W.; et al. Which taxa are alien? Criteria, applications, and uncertainties. BioScience 2018, 68, 496–509. [Google Scholar]
- Csurhes, S. How safe are zoos? Newsl. Invasive Species Counc. 2003, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Fàbregas, M.C.; Guillén-Salazar, F.; Garcés-Narro, C. The risk of zoological parks as potential pathways for the introduction of non-indigenous species. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3627–3636. [Google Scholar]
- Cassey, P.; Hogg, C.J. Escaping captivity: The biological invasion risk from vertebrate species in zoos. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 181, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Essl, F.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Booy, O.; Brundu, G.; Brunel, S. Crossing frontiers in tackling pathways of biological invasions. BioScience 2015, 65, 769–782. [Google Scholar]
- Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; Bacher, S.; Essl, F.; Genovesi, P.; Harrower, C.A. Troubling travellers: Are ecologically harmful alien species associated with particular introduction pathways? NeoBiota 2017, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Saul, W.C.; Roy, H.E.; Booy, O.; Carnevali, L.; Chen, H.J.; Genovesi, P.; Harrower, C.A.; Hulme, P.E.; Pagad, S.; Pergl, J.; et al. Assessing patterns in introduction pathways of alien species by linking major invasion data bases. J. App. Ecol. 2017, 54, 657–669. [Google Scholar]
- Hulme, P.E. Invasion pathways at a crossroad: Policy and research challenges for managing alien species introductions. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Escribano-Alacid, J.; Martìnez-Silvestre, A.; Verdaguer, I.; Mac Nally, R. What’s next? The release of exotic pets continues virtually unabated 7 years after enforcement of new legislation for managing invasive species. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 2933–2947. [Google Scholar]
- Clergeau, P.; Yésou, P. Behavioural flexibility and numerous potential sources of introduction for the sacred ibis: Causes of concern in western Europe? Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, E.; Monaco, A.; Sposimo, P.; Genovesi, P. Low establishment success of alien non-passerine birds in a Central Italy wetland (Selva di Paliano: Latium). Ital. J. Zool. 2014, 81, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, S.L.; Cecchetti, M.; McDonald, R.A. Hunting behaviour in domestic cats: An exploratory study of risk and responsibility among cat owners. People Nat. 2019, 1, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Boscherini, A.; Mazza, G.; Menchetti, M.; Laurenzi, A.; Mori, E. Time is running out! Rapid range expansion of the invasive northern raccoon in central Italy. Mammalia 2020, 84, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Scalera, R. How much is Europe spending on invasive alien species? Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Essl, F.; Evans, T.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Kühn, I.; Kumschick, S.M.; Markovà, Z.; Mrugala, A.; Nentwig, W.; et al. A unified classification of alien species based on the magnitude of their environmental impacts. PLoS Biol. 2014, 17, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Mazza, G.; Tricarico, E. Invasive Species and Human Health; Cabi Editions: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, A.L.; Fill, J.M.; Davies, S.J.; Louw, M.; Rebelo, A.D.; Thorp, C.J.; Vimercati, G.; Measey, J. A global meta-analysis of the ecological impacts of alien species on native amphibians. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182528. [Google Scholar]
- Turbè, A.; Strubbe, D.; Mori, E.; Carrete, M.; Chiron, F.; Clergeau, P.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.; Le Louarn, M.; Luna, A.; Menchetti, M.; et al. Assessing the assessments: Evaluation of four impact assessment protocols for invasive alien species. Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.; Macdonald, D.W. A review of the interactions between free-roaming domestic dogs and wildlife. Biol. Cons. 2013, 157, 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, D.; van der Waal, Z.; Pidcock, S.; Gomm, M.; Stephens, N.; Brash Arkvets, M.; White, P.; Mair, L.; Mill, A. Adaptive management of an iconic invasive goat Capra hircus population. Mammal Rev. 2019, 50, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Khayat, R.O.S.; Grant, R.A.; Ryan, H.; Melling, L.M.; Dougill, G.; Killick, D.R.; Shaw, K.J. Investigating cat predation as the cause of bat wing tears using forensic DNA analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 8368–8378. [Google Scholar]
- Seymour, C.L.; Simmons, R.E.; Morling, F.; George, S.T.; Peters, K.; O’Rian, J. Caught on camera: The impacts of urban domestic cats on wild prey in an African city and neighbouring protected areas. Glob. Ecol. Biogeog. 2020, 23, e01198. [Google Scholar]
- Courchamp, F.; Chapuis, J.L.; Pascal, M. Mammal invaders on islands: Impact, control and control impact. Biol. Rev. 2003, 78, 347–383. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, S.C.; Van Vuren, D.H.; Witmer, G.W. Feral Goats and Sheep. In Ecology and Management of Terrestrial Vertebrate Invasive Species in the United States; Pitt, W.C., Beasley, J.C., Witmer, G.W., Eds.; CRC Press, Tayor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 14; pp. 289–309. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, N.D.; Spatz, D.R.; Oppel, S.; Tershy, B.; Croll, D.A.; Keitt, B.; Genovesi, P.; Burfield, I.J.; Will, D.J.; Bond, A.L.; et al. Globally important islands where eradicating invasive mammals will benefit highly threatened vertebrates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212128. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, G.P.; Zeng, B.; Saalfeld, W.K.; Vaarzon-Morel, P. Evaluation of the impacts of feral camels. Rangel. J. 2010, 32, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pople, A.R.; McLeod, S.R. Demography of feral camels in central Australia and its relevance to population control. Rangel. J. 2010, 32, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Saalfeld, W.K.; Edwards, G.P. Distribution and abundance of the feral camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Australia. Rangel. J. 2010, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, G.; Fitzgerald, N.; Davidson, C. Public Attitudes Towards Invasive Animals and Their Impacts. A Summary and Review of Australasian and Selected International Research; Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre: Canberra, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, R.L.; Larson, L.R.; Green, G.T. Factors influencing public preferences for invasive alien species management. Biol. Cons. 2011, 144, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Jarić, I.; Courchamp, F.; Correia, R.A.; Crowley, S.L.; Essl, F.; Fischer, A.; González-Moreno, P.; Kalinkat, G.; Lambin, X.; Lenzner, B.; et al. The role of species charisma in biological invasions. Front. Ecol. Environm. 2020, 18, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzamuto, M.V.; Panzeri, M.; Bisi, F.; Wauters, L.A.; Preatoni, D.; Martinoli, A. When management meets science: Adaptive analysis for the optimization of the eradication of the Northern raccoon (Procyon lotor). Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar]
- Adriaens, T.; Baert, K.; Breyne, P.; Casaer, J.; Devisscher, S.; Onkelinx, T.; Pieters, S.; Stuyck, J. Successful eradication of a suburban Pallas’s squirrel Callosciurus erythraeus (Pallas 1779) (Rodentia, Sciuridae) population in Flanders (northern Belgium). Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, S.L.; Hinchliffe, S.; McDonald, R.A. Conflict in invasive species management. Front. Ecol. Environm. 2017, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Richardson, D.M.; Shackleton, C.M.; Bennett, B.; Crowley, S.L.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Estevez, R.A.; Fischer, A.; Kueffer, C.; Kull, C.A.; et al. Explaining people’s perceptions of invasive alien species: A conceptual framework. J. Environm. Manag. 2019, 229, 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Archibald, J.L.; Anderson, C.B.; Dicenta, M.; Roulier, C.; Slutz, K.; Nielsen, E.A. The relevance of social imaginaries to understand and manage biological invasions in southern Patagonia. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3307–3323. [Google Scholar]
- Cerri, J.; Mori, E.; Zozzoli, R.; Gigliotti, A.; Chirco, A.; Bertolino, S. Managing invasive Siberian chipmunks Eutamias sibiricus in Italy: A matter of attitudes and risk of dispersal. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 603–616. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P.; Ji, R.; Ding, F.; Qi, D.; Gao, H.; Meng, H.; Yu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H. A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the wild two-humped camel (Camelus bactrianus ferus): An evolutionary history of Camelidae. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, J. Evolution and present situation of the South-American Camelidae. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1995, 52, 271–295. [Google Scholar]
- Yacobaccio, H.D.; Vilá, B.L. A model for llama (Lama glama Linnaeus, 1758) domestication in the southern Andes. Anthropozoologica 2016, 51, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dodaro, G.; Battisti, C.; Campedelli, T.; Fanelli, G.; Monaco, A. Unsafe management of a zoological garden as a cause of introduction of an alien species into the wild: First documented case of feral naturalized population of Lama glama in Europe. J. Nat. Cons. 2019, 49, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Pyšek, P.; Bacher, S.; Carlton, J.T.; Duncan, R.P.; Jarosik, V.; Wilson, J.R.U.; Richardson, D.M. A proposed unified framework for biological invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Rovero, F.; Zimmermann, F. Camera Trapping for Wildlife Research; Pelagic Publishing Ltd.: Exeter, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burgman, M.A.; Fox, J.C. Bias in species range estimates from minimum convex polygons: Implications for conservation and options for improved planning. Anim. Cons. 2003, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, D.F.; Luengos Vidal, E.M.; Casaneve, E.B.; Lucherini, M. Habitat selection of Molina’s hog nosed skunks in relation to prey abundance in the Pampas grassland of Argentina. J. Mammal. 2012, 93, 716–721. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.B. The ade4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J. Stat. Soft. 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Calenge, C. Home Range Estimation in R: The adehabitatHR Package. 2011. Available online: http://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/adehabitatHR/ (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. Available online: http://www.Rproject.org/ (accessed on 22 August 2020).
- Lioy, S.; Marsan, A.; Balduzzi, A.; Wauters, L.A.; Martinoli, A.; Bertolino, S. The management of the introduced grey squirrel seen through the eyes of the media. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 3723–3733. [Google Scholar]
- Nanni, V.; Caprio, E.; Bombieri, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; Chiorri, C.; Mammola, S.; Pedrini, P.; Penteriani, V. Social media and large carnivores: Sharing biased news on attacks on humans. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Manville, R.H. Longevity of captive mammals. J. Mammal. 1957, 38, 279–280. [Google Scholar]
- Colautti, R.I.; MacIsaac, H.J. A neutral terminology to define “invasive” species. Divers. Distrib. 2004, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Crooks, J.A. Lag times and exotic species: The ecology and management of biological invasions in slow-motion. Ecoscience 2005, 12, 316–329. [Google Scholar]
- Manenti, R.; Mori, E.; Di Canio, V.; Mercurio, V.; Picone, M.; Caffi, M.; Brambilla, M.; Ficetola, G.F.; Rubolini, D. The good, the bad and the ugly of COVID-19 lockdown effects on wildlife conservation: Insights from the first European locked down country. Biol. Cons. 2020, 249, 108728. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino, S.; Genovesi, P. The application of the European strategy on invasive alien species: An example with introduced squirrels. Hystrix 2005, 16, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Scillitani, L.; Sturaro, E.; Menzano, A.; Rossi, L.; Viale, C.; Ramanzin, M. Post-release spatial and social behaviour of translocated male Alpine ibexes (Capra ibex ibex) in the Eastern Italian Alps. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, Á.; Edelaar, P.; Shwartz, A. Assessment of social perception of an invasive parakeet using a novel visual survey method. NeoBiota 2019, 46, 71. [Google Scholar]



| Year | Min. N Individuals | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Location | Data Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 5 | 43.548432 | 11.397699 | Badia a Coltibuono | [46]; photos by local people |
| 2017 | 4 | 43.541079 | 11.400526 | Badiaccia a Montemuro | [46] |
| 2017 | 1 | 43.534617 | 11.420925 | Cafaggiolo | [46] |
| 2017 | 1 | 43.538865 | 11.420130 | Caiano | [46] |
| 2017 | 2 | 43.545886 | 11.403143 | Caiano | [46] |
| 2017 | 5 | 43.540687 | 11.419126 | Caiano | [46] |
| 2017 | 2 | 43.542622 | 11.408738 | Camping Orlando—Cavriglia | iNaturalist; photos by local people |
| 2017 | 3 | 43.539714 | 11.409792 | Cavriglia | Dodaro et al., 2019; photos by local people |
| 2017 | 3 | 43.540616 | 11.413999 | Cavriglia | iNaturalist |
| 2017 | 3 | 43.544332 | 11.412823 | Cavriglia | [46] |
| 2017 | 2 | 43.541926 | 11.415896 | Cavriglia | iNaturalist; photos by local people |
| 2017 | 3 | 43.539700 | 11.418975 | Cavriglia | [46] |
| 2017 | 2 | 43.541631 | 11.415181 | Cavriglia | [46] |
| 2017 | 1 | 43.546706 | 11.394140 | Monte San Michele | [46] |
| 2017 | 3 | 43.542724 | 11.316486 | Panzano | [46]; Youtube |
| 2018 | 2 | 43.530708 | 11.422933 | Cavriglia | iNaturalist |
| 2018 | 2 | 43.471998 | 11.436921 | Gaiole in Chianti | Facebook and Youtube |
| 2018 | 1 | 43.428363 | 11.410002 | Osteria della Passera | Photos by local people |
| 2018 | 2 | 43.548432 | 11.397699 | Badia a Coltibuono | Facebook; photos by local people/tourists |
| 2018 | 3 | 43.488398 | 11.402336 | Radda in Chianti | Photos by local people |
| 2018 | 4 | 43.443966 | 11.508516 | Monteluco | YouTube; Facebook |
| 2018 | 4 | 43.451299 | 11.530570 | Nusenna | Photos by local people |
| 2019 | 4 | 43.451299 | 11.530570 | Nusenna | Photos by local people |
| 2019 | 1 | 43.442528 | 11.453818 | Castagnoli | Photos by local people |
| 2019 | 5 | 43.519675 | 11.666618 | Valle dell’Inferno e Bandella | iNaturalist |
| 2020 | 3 | 43.444639 | 11.480960 | Castellare | Photos by local people/tourists |
| 2020 | 3 | 43.444908 | 11.507084 | Monteluco | Our survey |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gargioni, C.; Monaco, A.; Francesco Ficetola, G.; Lazzeri, L.; Mori, E. From the Andes to the Apennines: Rise and Fall of a Free-Ranging Population of Feral Llamas. Animals 2021, 11, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030857
Gargioni C, Monaco A, Francesco Ficetola G, Lazzeri L, Mori E. From the Andes to the Apennines: Rise and Fall of a Free-Ranging Population of Feral Llamas. Animals. 2021; 11(3):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030857
Chicago/Turabian StyleGargioni, Carlo, Andrea Monaco, Gentile Francesco Ficetola, Lorenzo Lazzeri, and Emiliano Mori. 2021. "From the Andes to the Apennines: Rise and Fall of a Free-Ranging Population of Feral Llamas" Animals 11, no. 3: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030857
APA StyleGargioni, C., Monaco, A., Francesco Ficetola, G., Lazzeri, L., & Mori, E. (2021). From the Andes to the Apennines: Rise and Fall of a Free-Ranging Population of Feral Llamas. Animals, 11(3), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030857








