Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
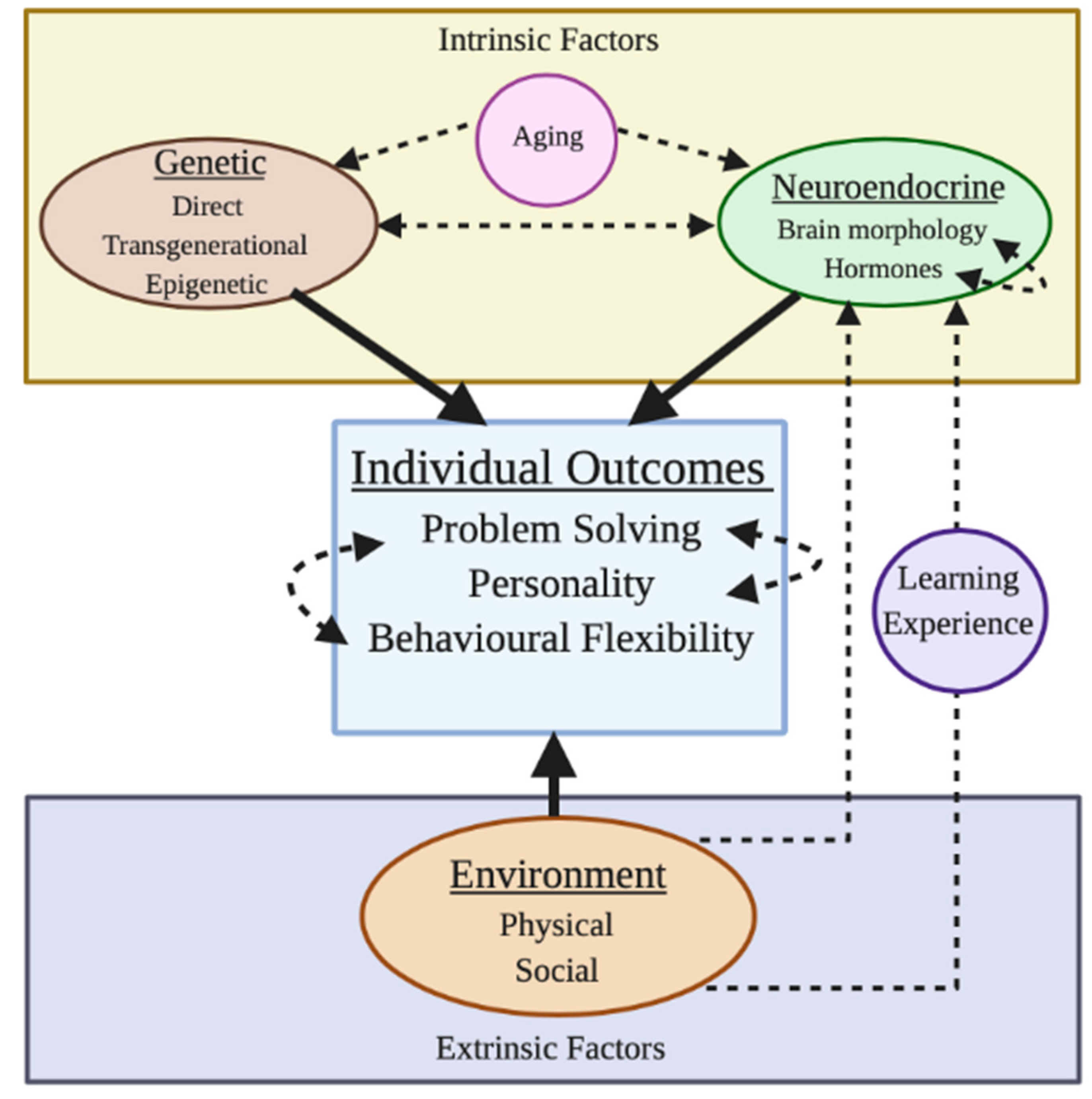
2. Factors Affecting the Development of Problem Solving
2.1. Instrinic Factors
2.1.1. Direct Genetic Effects
2.1.2. Indirect Genetic Effects
2.1.3. Neuroendocrine Effects—Brain Morphology
2.1.4. Neuroendocrine Effects—Hormones
2.2. Extrinsic Factors
2.2.1. Physical Environmental Factors
2.2.2. Social Environmental Factors
3. Interacting Factors that Influence the Development of Problem Solving
3.1. Gene × Environment Interactions
3.2. Neuroendocrine × Environment Interactions
3.3. Age Effects
3.4. Learning and Experience
3.5. Behavioural Flexibility and Personality
4. Forgotten Components Limiting Our Understanding of Problem Solving and Its Development
5. An Individual-Centric Focus can be Beneficial
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rymer, T.L.; Pillay, N.; Schradin, C. Extinction or survival? Behavioral flexibility in response to environmental change in the African striped mouse Rhabdomys. Sustainability 2013, 5, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson-Amram, S.; Dantzer, B.; Stricker, G.; Swanson, E.M.; Holekamp, K.E. Brain size predicts problem-solving ability in mammalian carnivores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.L.; Jacobs, I.; Osvath, M.; von Bayern, A.M. Birds of a feather? Parrot and corvid cognition compared. Behaviour 2019, 156, 505–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.H. Corvid cognition. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2014, 5, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, B.; Noble, D.W.; Whiting, M.J. Learning in non-avian reptiles 40 years on: Advances and promising new directions. Biol. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, A.M.; Starnberger, I.; Pašukonis, A.; Bugnyar, T.; Hödl, W.; Fitch, W.T. Take the long way home: Behaviour of a neotropical frog, Allobates femoralis, in a detour task. Behav. Process. 2016, 126, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laland, K.N.; Reader, S.M. Foraging innovation in the guppy. Anim. Behav. 1999, 57, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dussutour, A.; Deneubourg, J.L.; Beshers, S.; Fourcassié, V. Individual and collective problem-solving in a foraging context in the leaf-cutting ant Atta colombica. Anim. Cogn. 2009, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keagy, J.; Savard, J.-F.; Borgia, G. Male satin bowerbird problem-solving ability predicts mating success. Anim. Behav. 2009, 78, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchard, L.; Boogert, N.J.; Lefebvre, L.; Dubois, F.; Doligez, B. Problem-solving performance is correlated with reproductive success in a wild bird population. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, S.M.; Laland, K.N. Animal Innovation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kummer, H.; Goodall, J. Conditions of innovative behaviour in primates. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 1985, 308, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, L.G.; Hoppitt, W.; Laland, K.N.; Kendal, R.L. Sex ratio affects sex-specific innovation and learning in captive ruffed lemurs (Varecia variegata and Varecia rubra). Am. J. Primatol. 2011, 73, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.E.; Fanelli, R.E.; Gilbert, A.; Benson-Amram, S. Behavioral flexibility of a generalist carnivore. Anim. Cogn. 2019, 22, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, R. Generativity theory. Encycl. Creat. 1999, 1, 759–766. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, A.M.; Call, J. Problem-solving in tool-using and non-tool-using animals. Encycl. Anim. Behav. 2010, 2, 778–785. [Google Scholar]
- Duncker, K.; Lees, L.S. On problem solving. Psychol. Monogr. 1945, 58, i-113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerer, M. Problem-solving. Sci. Am. 1963, 208, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.F. The Complete Thinker: A Handbook of Techniques for Creative and Critical Problem Solving; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Heppner, P.P.; Krauskopf, C.J. An information-processing approach to personal problem solving. Couns. Psychol. 1987, 15, 371–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.D.; Kralik, J.; Botto-Mahan, C. Problem solving and functional design features: Experiments on cotton-top tamarins, Saguinus oedipus oedipus. Anim. Behav. 1999, 57, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, C.; Putrino, N.; Helbling, J.; Tognetti, S.; Bentosela, M. Individual differences in social and non-social behaviors in domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) during the acquisition, extinction and reacquisition of a problem solving task. Behav. Process. 2015, 113, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, P.K.Y.; Lea, S.E.G.; Hempel de Ibarra, N.; Robert, T. How to stay perfect: The role of memory and behavioural traits in an experienced problem and a similar problem. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sol, D.; Duncan, R.P.; Blackburn, T.M.; Cassey, P.; Lefebvre, L. Big brains, enhanced cognition, and response of birds to novel environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5460–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sol, D.; Lefebvre, L. Behavioural flexibility predicts invasion success in birds introduced to New Zealand. Oikos 2000, 90, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlovsky, D.Y.; Branch, C.L.; Pravosudov, V.V. Problem-solving ability and response to novelty in mountain chickadees (Poecile gambeli) from different elevations. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2015, 69, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.; Samson, J. Innovative problem solving in wild meerkats. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, B.; Bugnyar, T. Testing Problem Solving in Ravens: String-Pulling to Reach Food. Ethology 2005, 111, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.J.; Lefebvre, L. Problem solving and neophobia in a columbiform–passeriform assemblage in Barbados. Anim. Behav. 2001, 62, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducatez, S.; Audet, J.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Kayello, L.; Lefebvre, L. Innovativeness and the effects of urbanization on risk-taking behaviors in wild Barbados birds. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, E.V.; Matthews, L.J.; Hare, B.A.; Nunn, C.L.; Anderson, R.C.; Aureli, F.; Brannon, E.M.; Call, J.; Drea, C.M.; Emery, N.J.; et al. How does cognition evolve? Phylogenetic comparative psychology. Anim. Cogn. 2014, 15, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.O.; Weaver, M.J.; Hutton, P.; McGraw, K.J. The effects of urbanization and human disturbance on problem solving in juvenile house finches (Haemorhous mexicanus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2017, 71, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holekamp, K.E.; Dantzer, B.; Stricker, G.; Yoshida, K.C.S.; Benson-Amram, S. Brains, brawn and sociality: A hyaena’s tale. Anim. Behav. 2015, 103, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamps, J. Behavioural processes affecting development: Tinbergen’s fourth question comes of age. Anim. Behav. 2003, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, M.J.; Wilczynski, W. An Introduction to Animal Behaviour; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Groothuis, T.G.G.; Trillmich, F. Unfolding Personalities: The Importance of Studying Ontogeny. Dev. Psychobiol. 2011, 53, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, D.F.; Gilliam, J.F. Feeding under predation hazard: Response of the guppy and Hart’s rivulus from sites with contrasting predation hazard. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1987, 21, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Finkemeier, M.-A.; Trillmich, F. The ontogeny of personality in the wild guinea pig. Anim. Behav. 2014, 90, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymer, T.L.; Pillay, N. An integrated understanding of paternal care in mammals: Lessons from the rodents. J. Zool. 2018, 306, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, E.F.; Cram, D.L.; Quinn, J.L. Individual variation in spontaneous problem-solving performance among wild great tits. Anim. Behav. 2011, 81, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.; Healy, S.D. Measuring variation in cognition. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, G. Bird Minds: Cognition and Behaviour of Australian Native Birds; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, O.; Scott, J.P. The analysis of breed differences in maze performance in dogs. Anim. Behav. 1965, 13, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A.; Sweatt, J.D. Covalent Modification of DNA Regulates Memory Formation. Neuron 2007, 53, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bókony, V.; Lendvai, A.Z.; Vagasi, C.I.; Patras, L.; Pap, P.L.; Nemeth, J.; Vincze, E.; Papp, S.; Preiszner, B.; Seress, G.; et al. Necessity or capacity? Physiological state predicts problem-solving performance in house sparrows. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.C. Testing cognition in the wild: Factors affecting performance and individual consistency in two measures of avian cognition. Behav. Process. 2017, 134, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, B.R.; Vitousek, M.N.; Hubbard, J.K.; Safran, R.J. An experimental analysis of the heritability of variation in glucocorticoid concentrations in a wild avian population. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rymer, T.; Pillay, N. Transmission of parental care behavior in African striped mice, Rhabdomys pumilio. J. Exp. Zool. 2011, 315, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Both, C.; Drent, P.J.; van Oers, K.; van Noordwijk, A.J. Repeatability and heritability of exploratory behaviour in great tits from the wild. Anim. Behav. 2002, 64, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, W.D.; Russell, J.L.; Schaeffer, J. Chimpanzee intelligence is heritable. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudde, A.; Krause, E.T.; Matthews, L.R.; Schrader, L. More Than Eggs—Relationship Between Productivity and Learning in Laying Hens. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upchurch, M.; Wehner, J.M. Inheritance of spatial learning ability in inbred mice: A classical genetic analysis. Behav. Neurosci. 1989, 103, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumer, I.B.; Bugnyar, T.; Reber, S.A.; Auersperg, A.M. Can hook-bending be let off the hook? Bending/unbending of pliant tools by cockatoos. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audet, J.N.; Kayello, L.; Ducatez, S.; Perillo, S.; Cauchard, L.; Howard, J.T.; O’Connell, L.A.; Jarvis, E.D.; Lefebvre, L. Divergence in problem-solving skills is associated with differential expression of glutamate receptors in wild finches. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolman, E.C. The Inheritance of Maze-Learning Ability in Rats. J. Comp. Psychol. 1924, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heron, W.T. The inheritance of maze learning ability in rats. J. Comp. Psychol. 1935, 19, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagzi, I.; Soh, S.; Wesson, P.J.; Browne, K.P.; Grzybowski, B.A. Maze Solving by Chemotactic Droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.L.; Cole, E.F.; Reed, T.E.; Morand-Ferron, J. Environmental and genetic determinants of innovativeness in a natural population of birds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bókony, V.; Pipoly, I.; Szabó, K.; Preiszner, B.; Vincze, E.; Papp, S.; Seress, G.; Hammer, T.; Liker, A. Innovative females are more promiscuous in great tits (Parus major). Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonduriansky, R.; Day, T. Nongenetic Inheritance and Its Evolutionary Implications. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.J.; Junier, M.P.; Costa, M.E.; Ojeda, S.R. Transforming growth factor-α gene expression in the hypothalamus is developmentally regulated and linked to sexual maturation. Neuron 1992, 9, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräff, J.; Mansuy, I.M. Epigenetic codes in cognition and behaviour. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 192, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, D.; Hallbook’, F.; Persson, H.; Vennstrom, B. Distinct functions for thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta in brain development indicated by differential expression of receptor genes. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Diorio, J.; Day, J.C.; Francis, D.D.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, M.K.; Rymer, T.L. Memory enhances problem solving in the fawn-footed mosaic-tailed rat Melomys cervinipes. Anim. Cogn. in review.
- Champagne, F.A. Epigenetic mechanisms and the transgenerational effects of maternal care. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skinner, M.K.; Anway, M.D.; Savenkova, M.I.; Gore, A.C.; Crews, D. Transgenerational Epigenetic Programming of the Brain Transcriptome and Anxiety Behavior. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, X.; Hartley, D.M.; Feig, L.A. The environment versus genetics in controlling the contribution of MAP kinases to synaptic plasticity. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, E.I. Sensitive Periods in the Development of the Brain and Behavior. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.F.; Repa, J.C.; Mauk, M.D.; LeDoux, J.E. Parallels between cerebellum-and amygdala-dependent conditioning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenka, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Long-term potentiation—A decade of progress? Science 1999, 285, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherry, D.F.; Hoshooley, J.S. Seasonal hippocampal plasticity in food-storing birds. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniuk, A.A.; Lefebvre, L.; Wylie, D.R. The comparative approach and brain-behaviour relationships: A tool for understanding tool use. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. /Rev. Can. De Psychol. Exp. 2009, 63, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefebvre, L.; Whittle, P.; Lascaris, E.; Finkelstein, A. Feeding innovations and forebrain size in birds. Anim. Behav. 1997, 53, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehlhorn, J.; Hunt, G.R.; Gray, R.D.; Rehkämper, G.; Güntürkün, O. Tool-making New Caledonian crows have large associative brain areas. Brain Behav. Evol. 2010, 75, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Abdallah, N.M.-B.; Fuss, J.; Trusel, M.; Galsworthy, M.J.; Bobsin, K.; Colacicco, G.; Deacon, R.M.J.; Riva, M.A.; Kellendonk, C.; Sprengel, R.; et al. The puzzle box as a simple and efficient behavioral test for exploring impairments of general cognition and executive functions in mouse models of schizophrenia. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meethal, S.V.; Atwood, C.S. The role of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal hormones in the normal structure and functioning of the brain. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiri-Hänninen, T.; Sankilampi, U.; Dunkel, L. Activation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Infancy: Minipuberty. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2014, 82, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, E.A.; Zuber, T.J. Management of Precocious Puberty. Hosp. Pract. 1998, 33, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, D.; Hampson, E. Cognitive pattern in men and women is influenced by fluctuations in sex hormones. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1994, 3, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.B. Testosterone and estradiol produce different effects on cognitive performance in male rats. Horm. Behav. 2005, 48, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.; Skvarenina, A.; Pottier, J. Effects of neonatal androgens on open-field behavior and maze learning in the prepubescent and adult rat. Physiol. Behav. 1975, 14, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belz, E.E.; Kennell, J.S.; Czambel, R.K.; Rubin, R.T.; Rhodes, M.E. Environmental enrichment lowers stress-responsive hormones in singly housed male and female rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 76, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmandari, E.; Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G. Endocrinology of the stress response. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joëls, M.; Pu, Z.; Wiegert, O.; Oitzl, M.S.; Krugers, H.J. Learning under stress: How does it work? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapman, A.; Heinzmann, J.-M.; Hellweg, R.; Holsboer, F.; Landgraf, R.; Touma, C. Increased stress reactivity is associated with cognitive deficits and decreased hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a mouse model of affective disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Guo, M.; Garza, J.; Rendon, S.; Sun, X.-L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.-Y. Cognitive and neural correlates of depression-like behaviour in socially defeated mice: An animal model of depression with cognitive dysfunction. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLay, R.N.; Freeman, S.M.; Zadina, J.E. Chronic Corticosterone Impairs Memory Performance in the Barnes Maze. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 63, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozendaal, B. Stress and Memory: Opposing Effects of Glucocorticoids on Memory Consolidation and Memory Retrieval. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2002, 78, 578–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashaly, M.M. Effect of exogenous corticosterone on chicken embryonic-development. Poult. Sci. 1991, 70, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.S.; Haug, A.; Torjesen, P.A.; Bakken, M. Prenatal exposure to corticosterone impairs embryonic development and increases fluctuating asymmetry in chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Br. Poult. Sci. 2003, 44, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaro, A.; Huber, R.; Panksepp, J. Behavioral Functions of the Mesolimbic Dopaminergic System: An Affective Neuroethological Perspective. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 56, 283–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brisch, R.; Saniotis, A.; Wolf, R.; Bielau, H.; Bernstein, H.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Braun, K.; Jankowski, Z.; Kumaratilake, J.; et al. The role of dopamine in schizophrenia from a neurobiological and evolutionary perspective: Old fashioned, but still in vogue. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszy, J.; Laszlovszky, I.; Gyertyán, I. Dopamine D3 receptor antagonists improve the learning performance in memory-impaired rats. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.S.; Guez, D. Innovation and problem solving: A review of common mechanisms. Behav. Process. 2014, 109, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, S.; Vincze, E.; Preiszner, B.; Liker, A.; Bókony, V. A comparison of problem-solving success between urban and rural house sparrows. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2015, 69, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Horik, J.O.; Madden, J.R. A problem with problem solving: Motivational traits, but not cognition, predict success on novel operant foraging tasks. Anim. Behav. 2016, 114, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lermite, F.; Peneaux, C.; Griffin, A.S. Personality and problem-solving in common mynas (Acridotheres tristis). Behav. Process. 2017, 134, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, N.; Gaines, M. Social carnivores outperform asocial carnivores on an innovative problem. Anim. Behav. 2016, 114, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieoullon, A. Dopamine and the regulation of cognition and attention. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemoto, S.; Panksepp, J. The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: A unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 31, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghzouti, K.; Louilot, A.; Herman, J.P.; le Moal, M.; Simon, H. Alternation behaviour, spatial discrimination, and reversal disturbances following 6-Hydroxydopamine lesions in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Behav. Neural Biol. 1985, 44, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabadayi, C.; Krasheninnikova, A.; O’neill, L.; van de Weijer, K.; Osvath, M.; von Bayern, A.M. Are parrots poor at motor self-regulation or is the cylinder task poor at measuring it? Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.M. A History of Animal Welfare Science. Acta Biotheor. 2011, 59, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; De Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J.; Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, A.; Newman, T.K.; Higley, J.D.; Murray, E.A. Genetic modulation of cognitive flexibility and socioemotional behavior in rhesus monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14128–14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallender, E.J.; Lynch, L.; Novak, M.A.; Miller, G.M. Polymorphisms in the 3 ′UTR of the serotonin transporter are associated with cognitive flexibility in rhesus macaques. Am. J. Med Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 150, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, P.J. A neurochemical yin and yang: Does serotonin activate and norepinephrine deactivate the prefrontal cortex? Psychopharmacology 2011, 213, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delion, S.; Chalon, S.; Guillotaeu, D.; Besnard, J.-C.; Durand, G. α -Linolenic acid deficiency alters age-related changes of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat frontal cortex. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, I.; Hembert, S.; Dward, G.; Breton, P.; Guilloteau, D.; Besnard, J.-C.; Chalon, S. Chronic n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid diet-deficiency acts on dopamine metabolism in the rat frontal cortex: A microdialysis study. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 240, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, P.C.; Osenberg, C.W.; Mittelbach, G.G. Trophic Polymorphism in the Pumpkinseed Sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus Linnaeus): Effects of Environment on Ontogeny. Funct. Ecol. 1991, 5, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.A. Ecological heterogeneity: An ontogeny of concepts and approaches. In The Ecological Consequences of Heterogeneity; Hutchin, M.J., John, E.A., Stewart, A.J.A., Eds.; Oxford: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 9–31. [Google Scholar]
- Eccard, J.A.; Walther, R.B.; Milton, S.J. How livestock grazing affects vegetation structures and small mammal distribution in the semi-arid Karoo. J. Arid Environ. 2000, 46, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, J.A.; Swaisgood, R.R. Someplace like home: Experience, habitat selection and conservation biology. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 102, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, T.; Shine, R. Seasonal migration of predators and prey—A study of pythons and rats in tropical Australia. Ecology 1996, 77, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztainberg, Y.; Chen, A. An environmental enrichment model for mice. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husband, A.J.; Bryden, W.L. Nutrition, stress and immune activation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. Aust. 1996, 20, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, C.P.; Lill, A.; Reina, R.D. Does habitat fragmentation cause stress in the agile antechinus? A haematological approach. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2012, 182, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genaro, G.; Schmidek, W.R. Exploratory activity of rats in three different environments. Ethology 2001, 106, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Perfilieva, E.; Johansson, U.; Orwar, O.; Eriksson, P.S. Enriched environment increases neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus and improves spatial memory. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 39, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liker, A.; Bókony, V. Larger groups are more successful in innovative problem solving in house sparrows. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7893–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, T.J.; Beehner, J.C. Measuring social complexity. Anim. Behav. 2015, 103, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittleman, J.L.; Thompson, S.D. Energy allocation in mammalian reproduction. Am. Zool. 1988, 28, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebelsmann, U.; Roberts, J.M.; Jaffe, R.B. Placental transfer of 3H-oestriol-3-sulphate-16-glucosidur-onate and 3H-oestriol-16-glucosiduronate-14C. Acta Endocrinol. 1972, 70, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.M.; Pearson, J.N.; Neeley, E.W.; Berger, R.; Leonard, S.; Adams, C.E.; Stevens, K.E. Maternal stress during pregnancy causes sex-specific alterations in offspring memory performance, social interactions, indices of anxiety, and body mass. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pillay, N.; Rimbach, R.; Rymer, T. Pre-and postnatal dietary protein deficiency influences anxiety, memory and social behaviour in the African striped mouse Rhabdomys dilectus chakae. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 161, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheney, D.L.; Seyfarth, R.M. Nonrandom dispersal in free-ranging vervet monkeys: Social and genetic consequences. Am. Nat. 1983, 122, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, D.A.; Brown, G.R. The ontogeny of exploratory behavior in male and female adolescent rats (Rattus norvegicus). Dev. Psychobiol. 2009, 51, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boogert, N.J.; Reader, S.M.; Laland, K.N. The relation between social rank, neophobia and individual learning in starlings. Anim. Behav. 2006, 72, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.K.; Touzot, L.; Brummer, S.P. Persistence and conspecific observations improve problem-solving abilities of coyotes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drea, C.M.; Wallen, K. Low-status monkeys ‘play dumb’ when learning in mixed social groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12965–12969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drea, C.M.; Carter, A.N. Cooperative problem solving in a social carnivore. Anim. Behav. 2009, 78, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, L.M.; Sheldon, B.C.; Morand-Ferron, J. Milk bottles revisited: Social learning and individual variation in the blue tit, Cyanistes caeruleus. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, S.M.; Laland, K.N. Primate Innovation: Sex, Age and Social Rank Differences. Int. J. Primatol. 2001, 22, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, B.J.; Thornton, A.; Ridley, A.R. Larger group sizes facilitate the emergence and spread of innovations in a group-living bird. Anim. Behav. 2019, 158, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, P.E.; Weber, P.G.; Weber, S.P. Effect of group size on avoidance learning in zebra fish, Brachydanio rerio (Pisces: Cyprinidae). Anim. Learn. Behav. 1977, 5, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasheninnikova, A.; Schneider, J.M. Testing problem-solving capacities: Differences between individual testing and social group setting. Anim. Cogn. 2014, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrod, J.D.; Hartdegen, R.; Burghardt, G.M. Rapid solving of a problem apparatus by juvenile black-throated monitor lizards (Varanus albigularis albigularis). Anim. Cogn. 2008, 11, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.K.Y.; Lea, S.E.G.; Leaver, L.A. How practice makes perfect: The role of persistence, flexibility and learning in problem-solving efficiency. Anim. Behav. 2016, 112, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tecwyn, E.C.; Thorpe, S.K.; Chappell, J. What cognitive strategies do orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus) use to solve a trial-unique puzzle-tube task incorporating multiple obstacles? Anim. Cogn. 2012, 15, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, M.A.; Steer, C.D.; Newman, T.K.; Gibson, N.; Goldman, D. Early life stress, MAOA, and gene-environment interactions predict behavioral disinhibition in children. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, T.K.; Syagailo, Y.V.; Barr, C.S.; Wendland, J.R.; Champoux, M.; Graessle, M.; Suomi, S.J.; Higley, D.; Lesch, K.-P. Monoamine Oxidase A Gene Promoter Variation and Rearing Experience Influences Aggressive Behavior in Rhesus Monkeys. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Sananbenesi, F.; Wang, X.; Dobbin, M.; Tsai, L.-H. Recovery of learning and memory is associated with chromatin remodelling. Nature 2007, 447, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.B.; Brodie, E.D.I.I.I.; Cheverud, J.M.; Moore, A.J.; Wade, M.J. Evolutionary consequences of indirect genetic effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakovsky, R.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Pan, Y.X. Gestational high fat diet programs hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression and histone modification in neonatal offspring rats. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyaev, A.V.; Uller, T. Parental effects in ecology and evolution: Mechanisms, processes and implications. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. BBiol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, D.; Diorio, J.; Liu, D.; Meaney, M.J. Nongenomic Transmission across Generations of Maternal Behavior and Stress Responses in the Rat. Sci. New Ser. 1999, 286, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fish, E.W.; Shahrokh, D.; Bagot, R.; Caldji, C.; Bredy, T.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic Programming of Stress Responses through Variations in Maternal Care. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1036, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bredy, T.W.; Diorio, J.; Grant, R.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal care influences hippocampal neuron survival in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Diorio, J.; Tannenbaum, B.; Caldji, C.; Francis, D.; Freedman, A.; Sharma, S.; Pearson, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care, Hippocampal Glucocorticoid Receptors, and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Responses to Stress. Science 1997, 277, 1659–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caldji, C.; Tannenbaum, B.; Sharma, S.; Francis, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5335–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bredy, T.W.; Humpartzoomian, R.A.; Cain, D.P.; Meaney, M.J. The influence of maternal care and environmental enrichment on hippocampal development and function in the rat. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herczeg, G.; Gonda, A.; Merilä, J. Predation mediated population divergence in complex behaviour of nine-spined stickleback (Pungitius pungitius). J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, A.; Herczeg, G.; Merilä, J. Habitat-Dependent and -Independent Plastic Responses to Social Environment in the Nine-Spined Stickleback (Pungitius pungitius) Brain. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonda, A.; Herczeg, G.; Merila, J. Adaptive brain size divergence in nine-spined sticklebacks (Pungitius pungitius)? J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallet, J.; Mars, R.B.; Noonan, M.P.; Andersson, J.L.; O’Reilly, J.X.; Jbabdi, S.; Croxson, P.L.; Jenkinson, M.; Miller, K.L.; Rushworth, M.F.S. Social Network Size Affects Neural Circuits in Macaques. Science 2011, 334, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, L.C.; Schutte, S.R.M.; Koch, M.; Schwabe, K. Effect of “enriched environment” during development on adult rate behaviour and response to the dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlucchi, G.; Buchtel, H.A. Neuronal plasticity: Historical roots and evolution of meaning. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 192, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, J.A.; Feig, L.A. Long-lasting and transgenerational effects of an environmental enrichment on memory formation. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, A.M.; Burton, T.J.; Leamey, C.A.; Sawatari, A. The Use of the Puzzle Box as a Means of Assessing the Efficacy of Environmental Enrichment. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 94, e52225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Aniello, B.; Scandurra, A. Ontogenetic effects on gazing behaviour: A case study of kennel dogs (Labrador Retrievers) in the impossible task paradigm. Anim. Cogn. 2016, 19, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Barnes, C.A.; McNaughton, B.L.; Skaggs, W.E.; Weaver, K.L. The effect of aging on experience-dependent plasticity of hippocampal place cells. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 6769–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.K.; White, C.W.; Villeda, S.A. The systemic environment: At the interface of aging and adult neurogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milgram, N.W. Cognitive Experience and Its Effect on Age-Dependent Cognitive Decline in Beagle Dogs. Neurochem. Res. 2003, 28, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workel, J.O.; Oitzl, M.S.; Fluttert, M.; Lesscher, H.; Karssen, A.; de Kloet, E.R. Differential and Age-Dependent Effects of Maternal Deprivation on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis of Brown Norway Rats from Youth to Senescence. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2001, 13, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, K.M.; Baxter, M.G.; Markowska, A.L.; Olton, D.S.; Price, D.L. Age-related spatial reference and working memory deficits assessed in the water maze. Neurobiol. Aging 1995, 16, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H. Interaction between isolation rearing and social development on exploratory behavior in male rats. Behav. Process. 2005, 70, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, L.M.; Bó, M.S.; Vassallo, A.I. Inter-individual and age differences in exploration, neophobia and problem-solving ability in a Neotropical raptor (Milvago chimango). Anim. Cogn. 2010, 13, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, M.A. “String-pulling” in birds. (2) Differences related to age in greenfinches, chaffinches and canaries. Anim. Behav. 1958, 6, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.J.; Marshall, H.H.; Heinsohn, R.; Cowlishaw, G. Personality predicts the propensity for social learning in a wild primate. PeerJ 2014, 2, e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loepelt, J.; Shaw, R.C.; Burns, K.C. Can you teach an old parrot new tricks? Cognitive development in wild kaka (Nestor meridionalis). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2016, 283, 20153056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellis, S.M.; Pellis, V.C.; Bell, H.C. The function of play in the development of the social brain. Am. J. Play 2010, 2, 278–296. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, A.S.; Diquelou, M.C. Innovative problem solving in birds: A cross-species comparison of two highly successful passerines. Anim. Behav. 2015, 100, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson-Amram, S.; Holekamp, K.E. Innovative problem solving by wild spotted hyenas. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasher, S.; Evans, J.C.; Thompson, M.J.; Morand-Ferron, J. Characterizing innovators: Ecological and individual predictors of problem-solving performance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.E. Learning about danger: Chemical alarm cues and local risk assessment in prey fishes. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnstedt, O.M.; McCormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.G.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Chivers, D.P. Learn and live: Predator experience and feeding history determines prey behaviour and survival. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katz, M.; Lachlan, R.F. Social learning of food types in zebra finches (Taenopygia guttata) is directed by demonstrator sex and feeding activity. Anim. Cogn. 2003, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, R.; Kopin, I.J. Changes in Plasma Catecholamines and Behavior of Rats during the Anticipation of Footshock. Horm. Behav. 1978, 11, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugatkin, L.A.; Godin, J.-G.J. Predator inspection, shoaling and foraging under predation hazards in the Trinidadian guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1992, 24, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, C.D.; Emery, N.J. Insightful problem solving and creative tool modification by captive nontool-using rooks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10370–10375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Range, F.; Huber, L. Attention in common marmosets: Implications for social-learning experiments. Anim. Behav. 2007, 73, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragaszy, D.M.; Visalberghi, E. Social processes affecting the appearance of innovative behaviors in capuchin monkeys. Folia Primatol. 1990, 54, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, C.M. Imitation, culture and cognition. Anim. Behav. 1993, 46, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diatchenko, L.; Slade, G.D.; Nackley, A.G.; Sigurdsson, K.B.A.; Belfer, I.; Goldman, D.; Xu, K.; Shabalina, S.A.; Shagin, D.; Max, M.B.; et al. Genetic basis for individual variations in pain perception and the development of a chronic pain condition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tello-Ramos, M.C.; Branch, C.L.; Kozlovsky, D.Y.; Pitera, A.M.; Pravosudov, V.V. Spatial memory and cognitive flexibility trade-offs: To be or not to be flexible, that is the question. Anim. Behav. 2019, 147, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kappeler, P.; Kraus, C. Levels and mechanisms of behavioural variability. In Animal Behaviour: Evolution and Mechanisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 655–684. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, M.; Powell, B.J. Behavioural flexibility and problem-solving in a tropical lizard. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Storks, L.; Leal, M. Thinking outside the box: Problem-solving in free-living lizards. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2020, 74, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auersperg, A.M.; Von Bayern, A.M.; Gajdon, G.K.; Huber, L.; Kacelnik, A. Flexibility in problem solving and tool use of kea and New Caledonian crows in a multi access box paradigm. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bebus, S.E.; Small, T.W.; Jones, B.C.; Elderbrock, E.K.; Schoech, S.J. Associative learning is inversely related to reversal learning and varies with nestling corticosterone exposure. Anim. Behav. 2016, 111, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, R.; Laskowski, K.L.; Schiestl, M.; Bugnyar, T.; Schwab, C. Socially Driven Consistent Behavioural Differences during Development in Common Ravens and Carrion Crows. PLoS ONE 2016, e0148822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Ziemba, R.E. Behavioral syndromes: An integrative overview. Q. Rev. Biol. 2004, 79, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Reader, S.M.; Sol, D.; McDougall, P.T.; Dingemanse, N.J. Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biol. Rev. 2007, 82, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couchoux, C.; Cresswell, W. Personality constraints versus flexible antipredation behaviors: How important is boldness in risk management of red shanks (Tringa totanus) foraging in a natural system? Behav. Ecol. 2012, 23, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koolhaas, J.; Korte, S.; De Boer, S.; Van Der Vegt, B.; Van Reenen, C.; Hopster, H.; De Jong, I.C.; Ruis, M.A.W.; Blokhuis, H. Coping styles in animals: Current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1999, 23, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyomo, T.O.; Watt, P.J. Effect of hunger level and time of day on boldness and aggression in the zebrafish Danio rerio hunger level, time of day and behaviour. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 86, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relyea, R.A. Predators come and predators go: The reversibility of predator-induced traits. Ecology 2003, 84, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wat, K.K.; Banks, P.B.; McArthur, C. Linking animal personality to problem-solving performance in urban common brushtail possums. Anim. Behav. 2020, 162, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, M.K.; Rymer, T.L. Personality influences problem solving in the fawn-footed mosaic-tailed rat (Melomys cervinipes). Ethology. in review.
- Overington, S.E.; Cauchard, L.; Côté, K.A.; Lefebvre, L. Innovative foraging behaviour in birds: What characterizes an innovator? Behav. Process. 2011, 87, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, F.; Caicoya, A.L.; Majolo, B.; Widdig, A. Innovation in wild Barbary macaques (Macaca sylvanus). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasheninnikova, A.; Bräger, S.; Wanker, R. Means-end comprehension in four parrot species: Explained by social complexity. Anim. Cogn. 2013, 16, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oritz, S.T.; Maxwell, A.; Krasheninnikova, A.; Wahlberg, M.; Larsen, O.N. Problem-solving capabilities of peach-fronted conures (Eupsittula aurea) studied with the string-pulling test. Behaviour 2019, 156, 815–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Wilson, J.; Horskins, K. The role of adjacent habitats in rodent damage levels in Australian macadamia orchard systems. Crop Prot. 1997, 16, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautier, L.; Lebrun, R.; Saksiri, S.; Michaux, J.; Vianey-Liaud, M.; Marivaux, L. Hystricognathy vs. sciurognathy in the rodent jaw: A new morphometric assessment of hystricognathy applied to living fossil Laonastes (Rodentia, Diatomyidae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmides, L.; Tooby, J. Beyond intuition and instinct blindness: Toward an evolutionarily rigorous cognitive science. Cognition 1994, 50, 41–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbich, S.; Griffin, A.S.; Peschl, M.F.; Sterelny, K. From mechanisms to function: An integrated framework of animal innovation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wainwright, P.E. Dietary essential fatty acids and brain function: A developmental perspective on mechanisms. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2002, 61, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.W.; Wrege, P.H.; Allen, P.E.; Kast, T.L.; Senesac, P.; Wasson, M.F.; Llambias, P.E.; Ferretti, V.; Sullivan, P.J. Breeding dispersal and philopatry in the tree swallow. Condor 2004, 106, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fone, K.C.F.; Porkess, M.V. Behavioural and neurochemical effects of post-weaning social isolation in rodents—Relevance to developmental neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, K.M.; Weiss, D.J. Pulling to scale: Motor planning for sequences of repeated actions by cotton-top tamarins (Saguinus oedipus). J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 2013, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Dickinson-Anson, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: Age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, D.; Rimmer, L.B.; Pritchard, V.L.; Butlin, R.K.; Krause, J. Inter and intra-population variation in shoaling and boldness in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.J.; Bennett, A.F. Behavioural variation in natural populations. III: Antipredator displays in the garter snake Thamnophis radix. Anim. Behav. 1984, 32, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromswold, K. Why aren’t identical twins linguistically identical? Genetic, prenatal and postnatal factors. Cognition 2006, 101, 333–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Terminology | Drivers | Animal Properties | Definition | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation | Internal and External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | A new or modified learned behaviour not previously found in the population | [12] |
| Innovation | Internal and External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | The ability to invent new behaviours, or to use existing behaviours in new contexts A new or modified learned behaviour not previously found in the population A process that results in new or modified learned behaviour and that introduces novel behavioural variants into a population’s repertoire | [11] |
| Innovation | Internal and External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | The devising of new solutions | [13] |
| Innovation | Internal and External | Cognitive | An animal’s ability to apply previous knowledge to a novel problem or apply novel techniques to an old problem | [14] |
| Novel behaviour | Internal | Cognitive | The result of an orderly and dynamic competition among previously established behaviours, during which old behaviours blend or become interconnected in new ways | [15] |
| Physical problem solving | External | Mechanical/Morphology | Use of novel means to reach a goal when direct means are unavailable | [16] |
| Problem solving | Internal | Cognitive | Overcoming an obstacle that is preventing animals from achieving their goal immediately | [17] |
| Problem solving | External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | A problem exists when the goal that is sought is not directly attainable by the performance’ of a simple act available in the animal’s repertoire; the solution calls for either a novel action or a new integration of available actions | [18] |
| Problem solving | Internal | Cognitive | Any goal-directed sequence of cognitive operations | [19] |
| Problem solving | Internal and External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | A goal-directed sequence of cognitive and affective operations as well as behavioural responses for the purpose of adapting to internal or external demands or challenges | [20] |
| Problem solving | Internal | Cognitive | An analysis of means–end relationships | [21] |
| Problem solving | External | Mechanical/Morphology and Cognitive | A subset of instrumental responses that appear when an animal cannot achieve a goal using a direct action; the subject needs to perform a novel action or an innovative integration of available responses in order to solve the problem | [22] |
| Problem solving | Internal | Mechanical/Morphology | The ability to overcome obstacles and achieve a goal | [23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rowell, M.K.; Pillay, N.; Rymer, T.L. Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective. Animals 2021, 11, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030866
Rowell MK, Pillay N, Rymer TL. Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective. Animals. 2021; 11(3):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030866
Chicago/Turabian StyleRowell, Misha K., Neville Pillay, and Tasmin L. Rymer. 2021. "Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective" Animals 11, no. 3: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030866
APA StyleRowell, M. K., Pillay, N., & Rymer, T. L. (2021). Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective. Animals, 11(3), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030866





