Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Treatment with Antibiotics or Nutraceuticals on Clinical Activity and the Fecal Microbiome of Dogs with Acute Diarrhea
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Clinical Procedures
2.4. Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
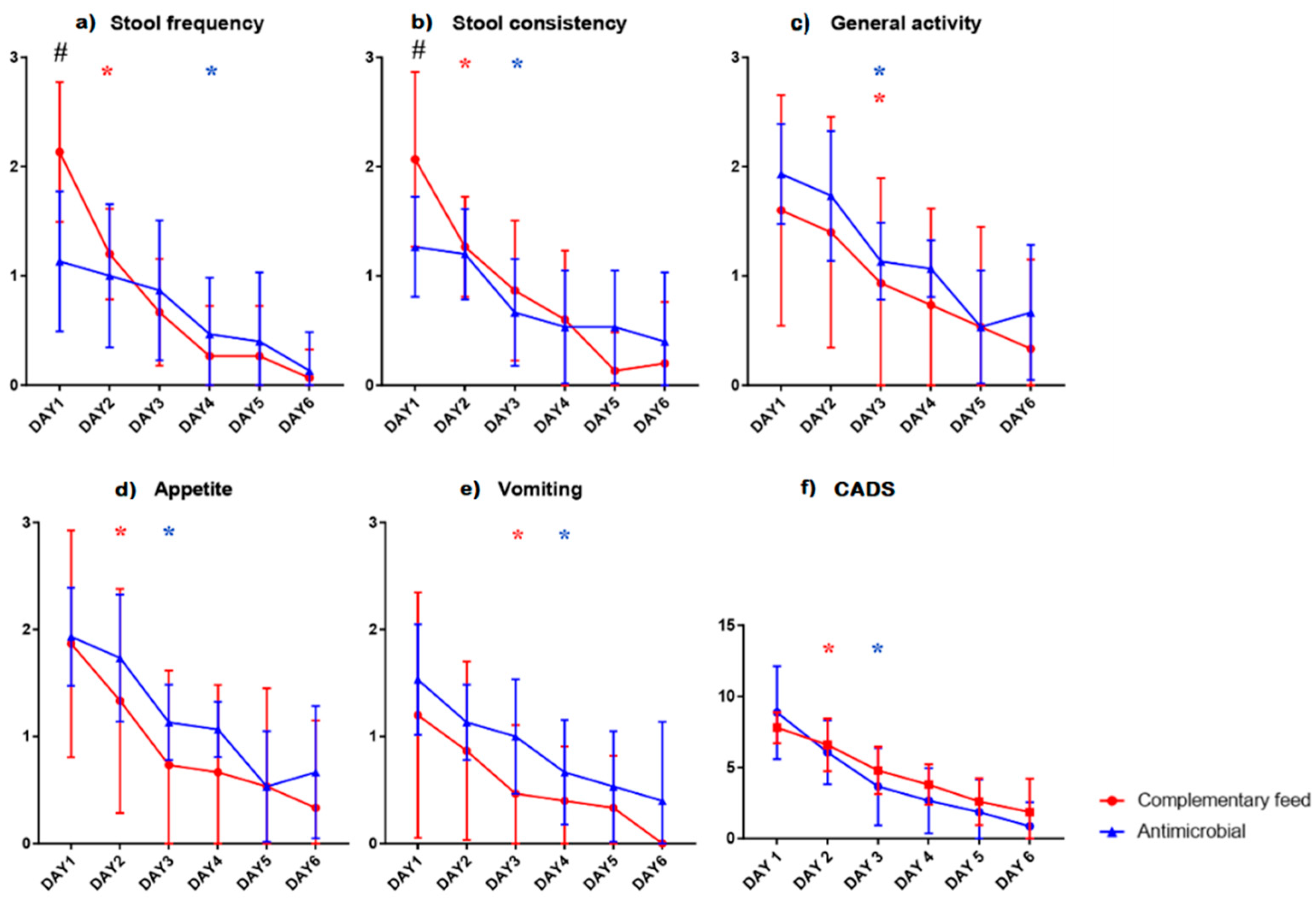
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelley, R.L.; Minikhiem, D.; Kiely, B.; O’Mahony, L. Clinical Benefits of Probiotic Canine-Derived Bifidobacterium Animalis Strain AHC7 in Dogs with Acute Idiopathic Diarrhea. Vet. Ther. 2009, 10, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Markel, M.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.; Unterer, S.; Heilmann, R.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Minamoto, Y.; Dillman, E.M.; et al. The Fecal Microbiome in Dogs with Acute Diarrhea and Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0051907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herstad, H.K.; Nesheim, B.B.; L’Abée-Lund, T.; Larsen, S.; Skancke, E. Effects of a probiotic intervention in acute canine gastroenteritis—A controlled clinical trial. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 51, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, A.J.; Halladay, L.J.; Noble, P.-J.M. First-choice therapy for dogs presenting with diarrhoea in clinical practice. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, A.D.; Noble, P.J.; Coyne, K.P.; Gaskell, R.M.; Jones, P.H.; Bryan, J.G.E.; Setzkorn, C.; Tierney, Á.; Dawson, S. Antibacterial prescribing patterns in small animal veterinary practice identified via SAVSNET: The small animal veterinary surveillance network. Vet. Rec. 2011, 169, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anholt, R.M.; Berezowski, J.; Ribble, C.S.; Russell, M.L.; Stephen, C. Using Informatics and the Electronic Medical Record to Describe Antimicrobial Use in the Clinical Management of Diarrhea Cases at 12 Companion Animal Practices. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.; Dawson, S.; Gaskell, R.; Coyne, K.; Tierney, Á.; Setzkorn, C.; Radford, A.; Noble, P.-J. Surveillance of diarrhoea in small animal practice through the Small Animal Veterinary Surveillance Network (SAVSNET). Vet. J. 2014, 201, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, D.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, F.; Dawson, S.; Jones, P.; Noble, P.; Pinchbeck, G.; Williams, N.; Radford, A. Patterns of antimicrobial agent prescription in a sentinel population of canine and feline veterinary practices in the United Kingdom. Vet. J. 2017, 224, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krentz, T.; Allen, S. Bacterial translocation in critical illness. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weese, J.; Giguère, S.; Guardabassi, L.; Morley, P.; Papich, M.; Ricciuto, D.; Sykes, J. ACVIM Consensus Statement on Therapeutic Antimicrobial Use in Animals and Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guard, B.C.; Barr, J.W.; Reddivari, L.; Klemashevich, C.; Jayaraman, A.; Steiner, J.M.; Vanamala, J.; Suchodolski, J.S. Characterization of Microbial Dysbiosis and Metabolomic Changes in Dogs with Acute Diarrhea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelley, R.; Levy, K.; Mundell, P.; Hayek, M.G. Effects of Varying Doses of a Probiotic Supplement Fed to Healthy Dogs Undergoing Kenneling Stress. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2012, 10, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, S.S. Value of Probiotics in Canine and Feline Gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 171–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary Modulation of the Human Colonic Microbiota: Introducing the Concept of Prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K. Responses of feeding prebiotics on nutrient digestibility, faecal microbiota composition and short-chain fatty acid concentrations in dogs: A meta-analysis. Animal 2011, 5, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vickers, R.J.; Sunvold, G.D.; Kelley, R.L.; Reinhart, G.A. Comparison of fermentation of selected fructooligosaccharides and other fiber substrates by canine colonic microflora. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.M. Mannan oligosaccharides in poultry nutrition, mechanisms and benefits. In Science and Technology in the Feed Industry, Proceedings of the Alltech’s 17th Annual Symposium; Lyons, T.P., Jacques, K.A., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2001; pp. 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Spring, P.; Wenk, C.; Dawson, K.A.; Newman, K.E. The effects of dietary mannaoligosaccharides on cecal parameters and the concentrations of enteric bacteria in the ceca of salmonella-challenged broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carra, R. Boosting immune response in dogs, A role for dietary mannan sugars. In Proceedings of the Alltech’s 14th Annual Symposium on Biotechnology in the Feed Industry; Lyons, T.P., Jacques, K.A., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 1998; pp. 563–572. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, K.; Grieshop, C.M.; Flickinger, E.A.; Bauer, L.L.; Healy, H.-P.; Dawson, K.A.; Merchen, N.R.; Fahey, G.C. Supplemental Fructooligosaccharides and Mannanoligosaccharides Influence Immune Function, Ileal and Total Tract Nutrient Digestibilities, Microbial Populations and Concentrations of Protein Catabolites in the Large Bowel of Dogs. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Steed, H.; Macfarlane, S. Bacterial metabolism and health-related effects of galacto-oligosaccharides and other prebiotics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 104, 305–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkins, A.; Behrens, R.; Roy, S. The role of zinc and vitamin A deficiency in diarrhoeal syndromes in developing countries. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1993, 52, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunez, M.C.; Ayudarte, M.V.; Morales, D.; Suarez, M.D.; Gil, A. Effect of Dietary Nucleotides on Intestinal Repair in Rats with Experimental Chronic Diarrhea. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1990, 14, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Straubinger, R.K.; Wolf, G.; Steiner, J.M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Neuerer, F.; Hartmann, K.; Unterer, S. Effect of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid on clinical scores, intestinal microbiome, and amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli in dogs with uncomplicated acute diarrhea. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alshawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A dysbiosis index to assess microbial changes in fecal samples of dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavazza, A.; Rossi, G.; Lubas, G.; Cerquetella, M.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S. Faecal microbiota in dogs with multicentric lymphoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 16, E169–E175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziese, A.-L.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Hartmann, K.; Busch, K.; Anderson, A.; Sarwar, F.; Sindern, N.; Unterer, S. Effect of probiotic treatment on the clinical course, intestinal microbiome, and toxigenic Clostridium perfringens in dogs with acute hemorrhagic diarrhea. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guard, B.C.; Suchodolski, J.S. HORSE SPECIES SYMPOSIUM: Canine intestinal microbiology and metagenomics: From phylogeny to function1. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 2247–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Gaschen, F.; Barr, J.W.; Olson, E.; Honneffer, J.; Guard, B.C.; Blake, A.B.; Villanueva, D.; Khattab, M.R.; Alshawaqfeh, M.K.; et al. Effects of metronidazole on the fecal microbiome and metabolome in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1853–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Maeda, S.; Ohno, K.; Horigome, A.; Odamaki, T.; Tsujimoto, H. Effect of Oral Administration of Metronidazole or Prednisolone on Fecal Microbiota in Dogs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0107909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Props, R.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Rubbens, P.; De Vrieze, J.; Sanabria, E.H.; Waegeman, W.; Monsieurs, P.; Hammes, F.; Boon, N. Absolute quantification of microbial taxon abundances. ISME J. 2017, 11, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbeele, P.V.D.; Moens, F.; Pignataro, G.; Schnurr, J.; Ribecco, C.; Gramenzi, A.; Marzorati, M. Yeast-Derived Formulations Are Differentially Fermented by the Canine and Feline Microbiome As Assessed in a Novel In Vitro Colonic Fermentation Model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13102–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videlock, E.J.; Cremonini, F. Meta-analysis: Probiotics in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 1355–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Dowd, S.E.; Westermarck, E.; Steiner, J.M.; Wolcott, R.D.; Spillmann, T.; Harmoinen, J.A. The effect of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin on microbial diversity in the canine small intestine as demonstrated by massive parallel 16S rRNA gene sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suchodolski, J.S. COMPANION ANIMALS SYMPOSIUM: Microbes and gastrointestinal health of dogs and cats1. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Engelhardt, W.; Bartels, J.; Kirschberger, S.; Meyer zu Düttingdorf, H.D.; Busche, R. Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Hind Gut. Vet. Q. 1998, 20, S52–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzman, J.R.; Conlin, V.S.; Jobin, C. Diet, Microbiome, and the Intestinal Epithelium: An Essential Triumvirate? BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 425146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vermeire, S. The intestinal barrier: A fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.L.; Rose, L.; Muller, A.T. Efficacy of an orally administered anti-diarrheal probiotic paste (Pro-Kolin Advanced) in dogs with acute diarrhea: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shmalberg, J.; Montalbano, C.; Morelli, G.; Buckley, G.J. A Randomized Double Blinded Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of a Probiotic or Metronidazole for Acute Canine Diarrhea. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Active Ingredient | Unit | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| ZT455C 1 | mg/tab | 500 |
| Mannanoligosaccharides | mg/tab | 300 |
| Carob flour | mg/tab | 140 |
| Nucleotides | mg/tab | 50 |
| Enterococcus faecium (35 billion CFU/g) DSM 10663/NCIMB 10415 | mg/tab | 40 |
| Vitamin B12 (0.1%) | mg/tab | 5 |
| Excipients | Unit | Quantity |
| Dicalcium phosphate | mg/tab | 190 |
| Vegetable appetizing | mg/tab | 75 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | mg/tab | 40 |
| Potassium citrate | mg/tab | 30 |
| Silicon dioxide | mg/tab | 15 |
| Magnesium salts of fatty acids | mg/tab | 15 |
| Parameter | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severely decreased |
| Appetite | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severely decreased |
| Vomiting | Normal | 1 ×/d | 2–3 ×/d | > 3 ×/d |
| Stool consistency | FeSc 1 2–3/7 | FeSc 4–5/7 | FeSc 6/7 | FeSc 7/7 |
| Stool frequency | Normal | 3 ×/d | 4–5 ×/d | > 5 ×/d |
| Activity | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severely decreased |
| Variable | Group A | Group B | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 6.2 ± 3 | 7.9 ± 3.3 | 0.13 |
| Sex (male/female) | 10/5 | 9/6 | 0.57 |
| Weight (kg) | 20.4 ± 10.8 | 17.8 ± 13.1 | 0.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pignataro, G.; Di Prinzio, R.; Crisi, P.E.; Belà, B.; Fusaro, I.; Trevisan, C.; De Acetis, L.; Gramenzi, A. Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Treatment with Antibiotics or Nutraceuticals on Clinical Activity and the Fecal Microbiome of Dogs with Acute Diarrhea. Animals 2021, 11, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061484
Pignataro G, Di Prinzio R, Crisi PE, Belà B, Fusaro I, Trevisan C, De Acetis L, Gramenzi A. Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Treatment with Antibiotics or Nutraceuticals on Clinical Activity and the Fecal Microbiome of Dogs with Acute Diarrhea. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061484
Chicago/Turabian StylePignataro, Giulia, Roberta Di Prinzio, Paolo Emidio Crisi, Benedetta Belà, Isa Fusaro, Carlo Trevisan, Luigi De Acetis, and Alessandro Gramenzi. 2021. "Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect of Treatment with Antibiotics or Nutraceuticals on Clinical Activity and the Fecal Microbiome of Dogs with Acute Diarrhea" Animals 11, no. 6: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061484







