Differential Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in the Ovaries of Low and High Fecundity Hanper Sheep
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Selection of Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction and Library Construction
2.4. Sequence Mapping and CircRNA Prediction
2.5. Differential Expression Analysis of CircRNAs
2.6. STEM Cluster and Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) Analysis of CircRNAs
2.7. Functional Analysis of CircRNAs in Follicular and Luteal Period
2.8. Analysis of MiRNA Target Sites
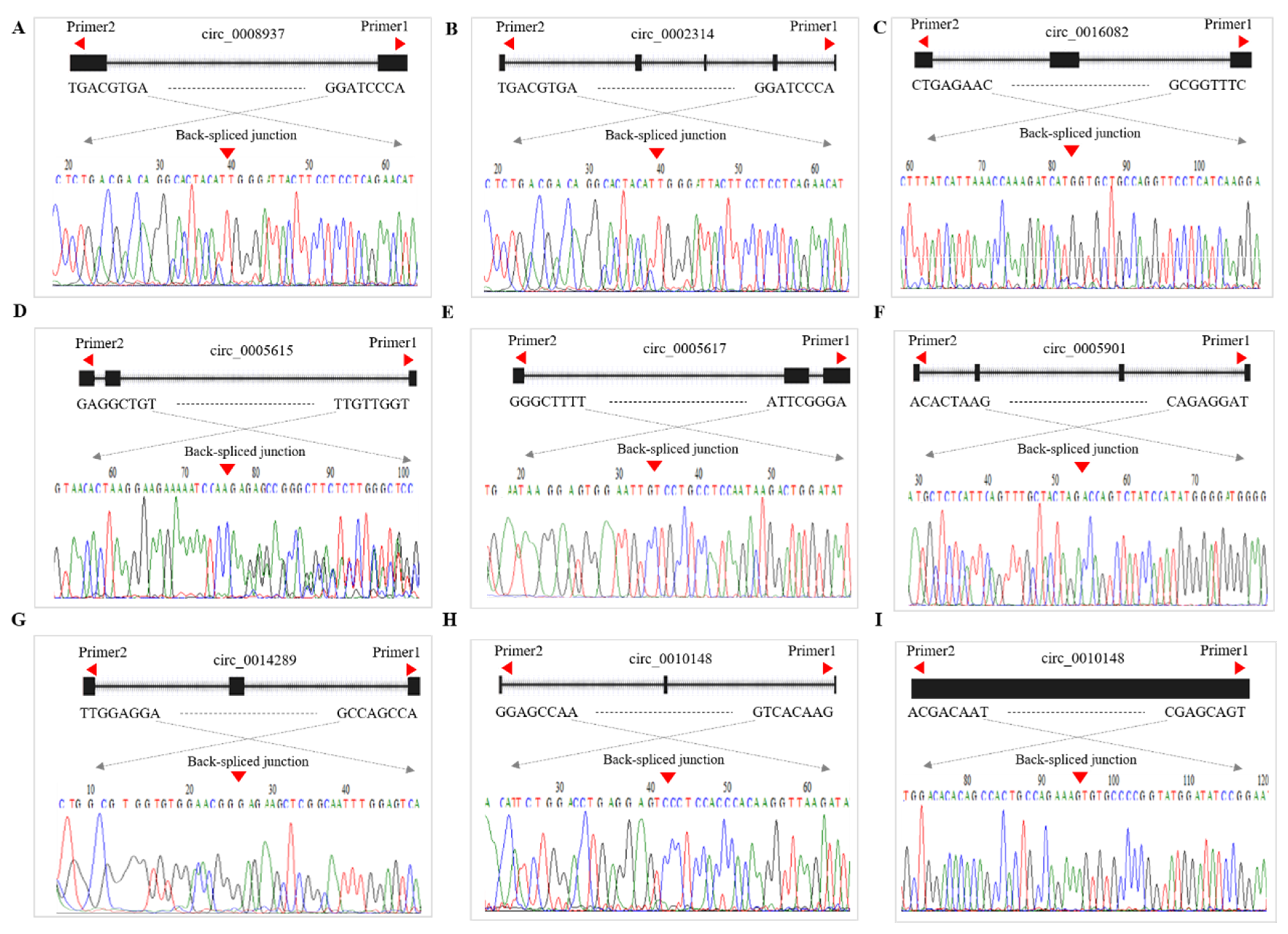
2.9. Validation of CircRNA Expression
3. Results
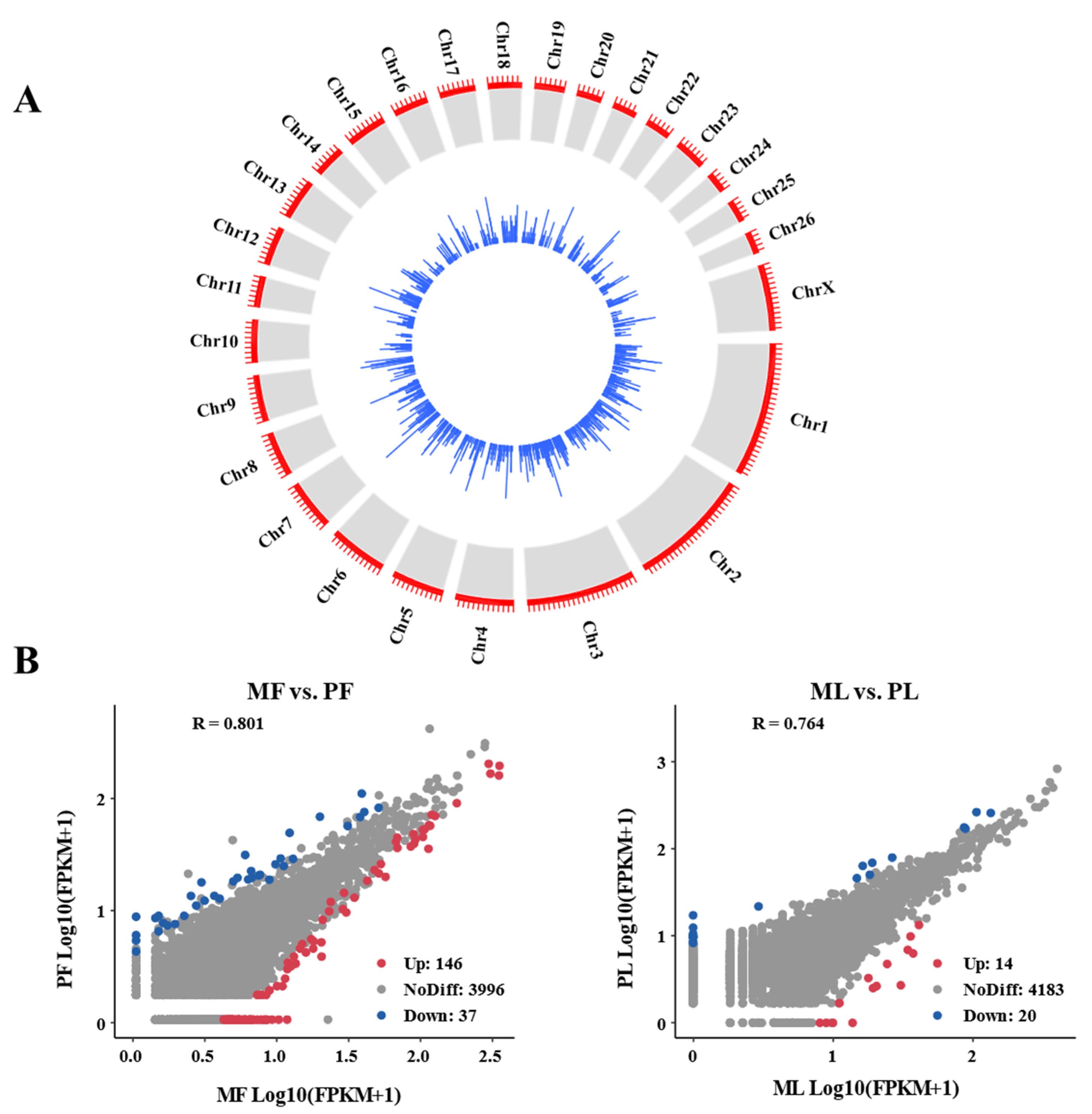
3.1. Genomic Characteristics of CircRNA in Sheep Ovaries
3.2. Diversity of CircRNA Isoforms and Circularization Forms
3.3. Identification of DE-CircRNAs
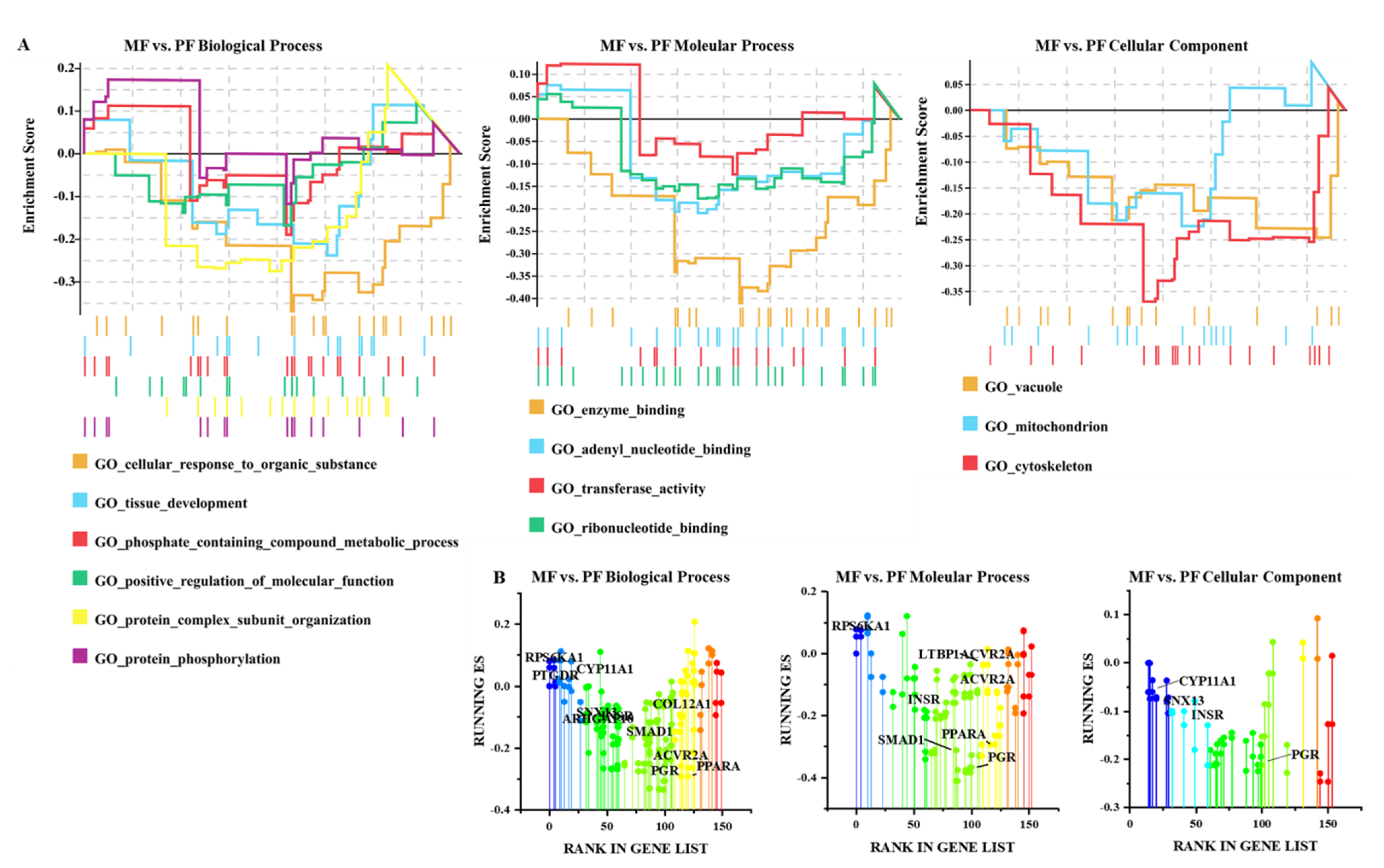
3.4. Functional Analysis of CircRNAs in Sheep of Varying Fecundity in the Follicular and Luteal Phases
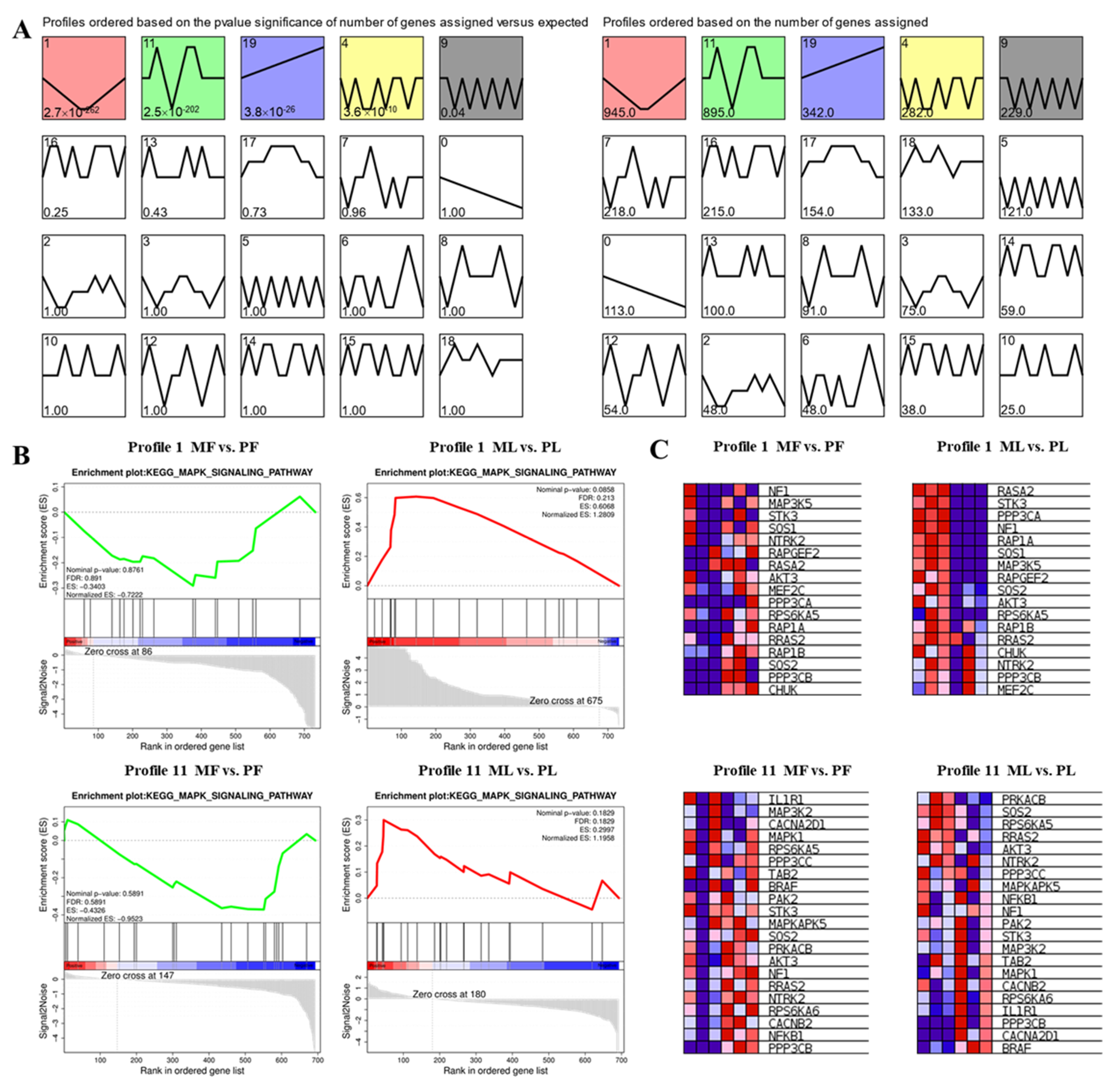
3.5. STEM Cluster Analysis of DE-CircRNAs
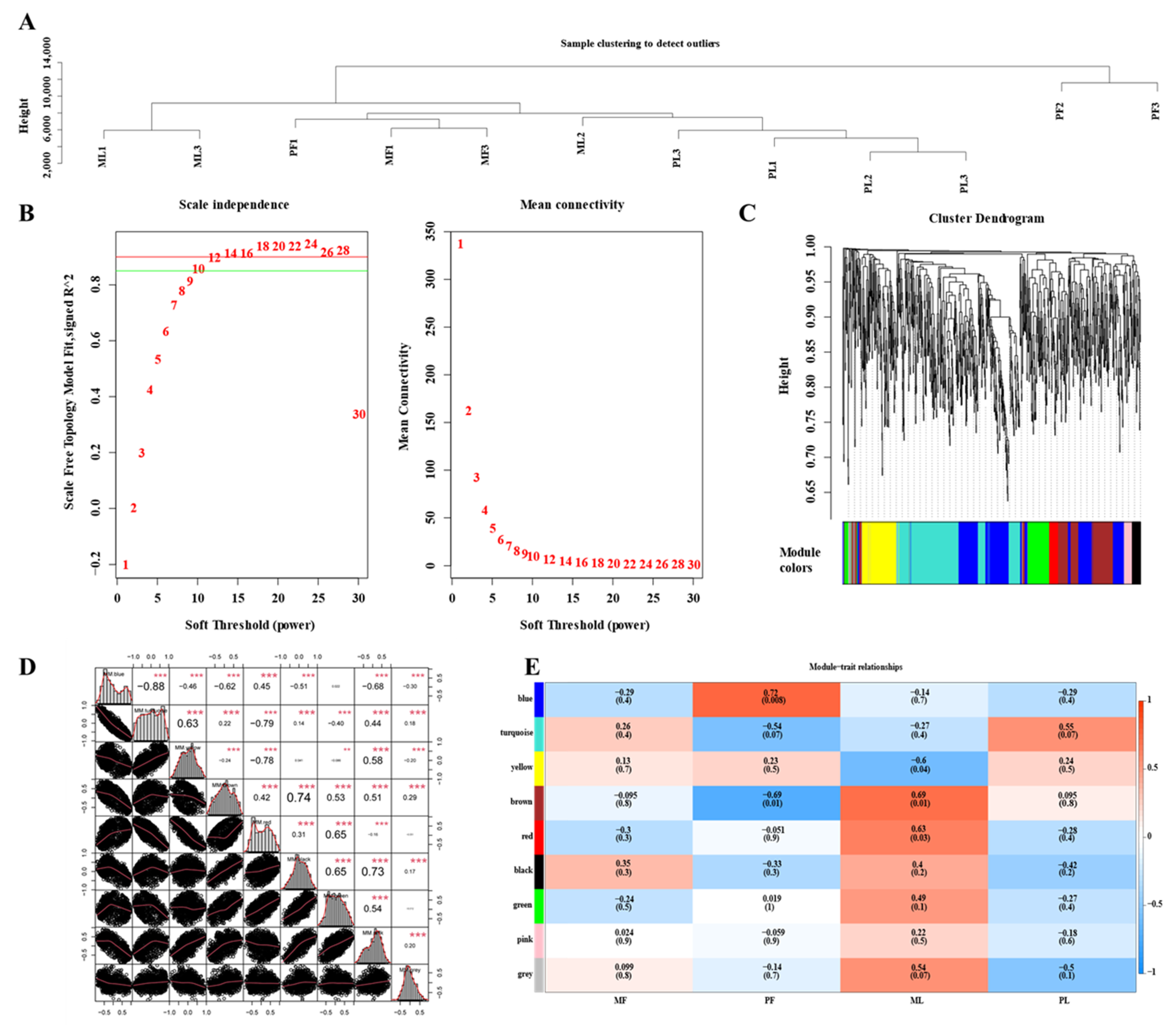
3.6. Construction of WGCNA Network
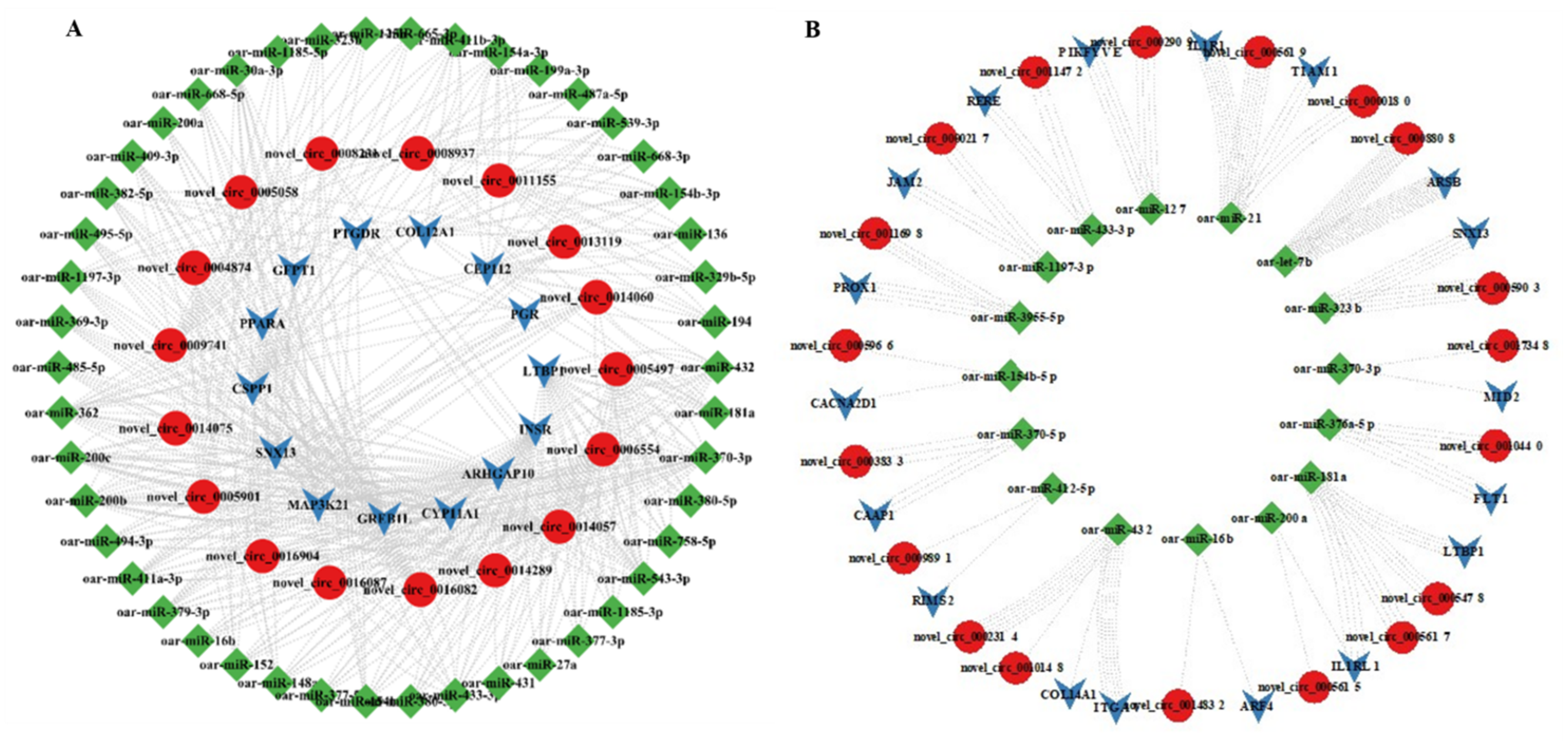
3.7. MiRNA Targets of DE-CircRNAs
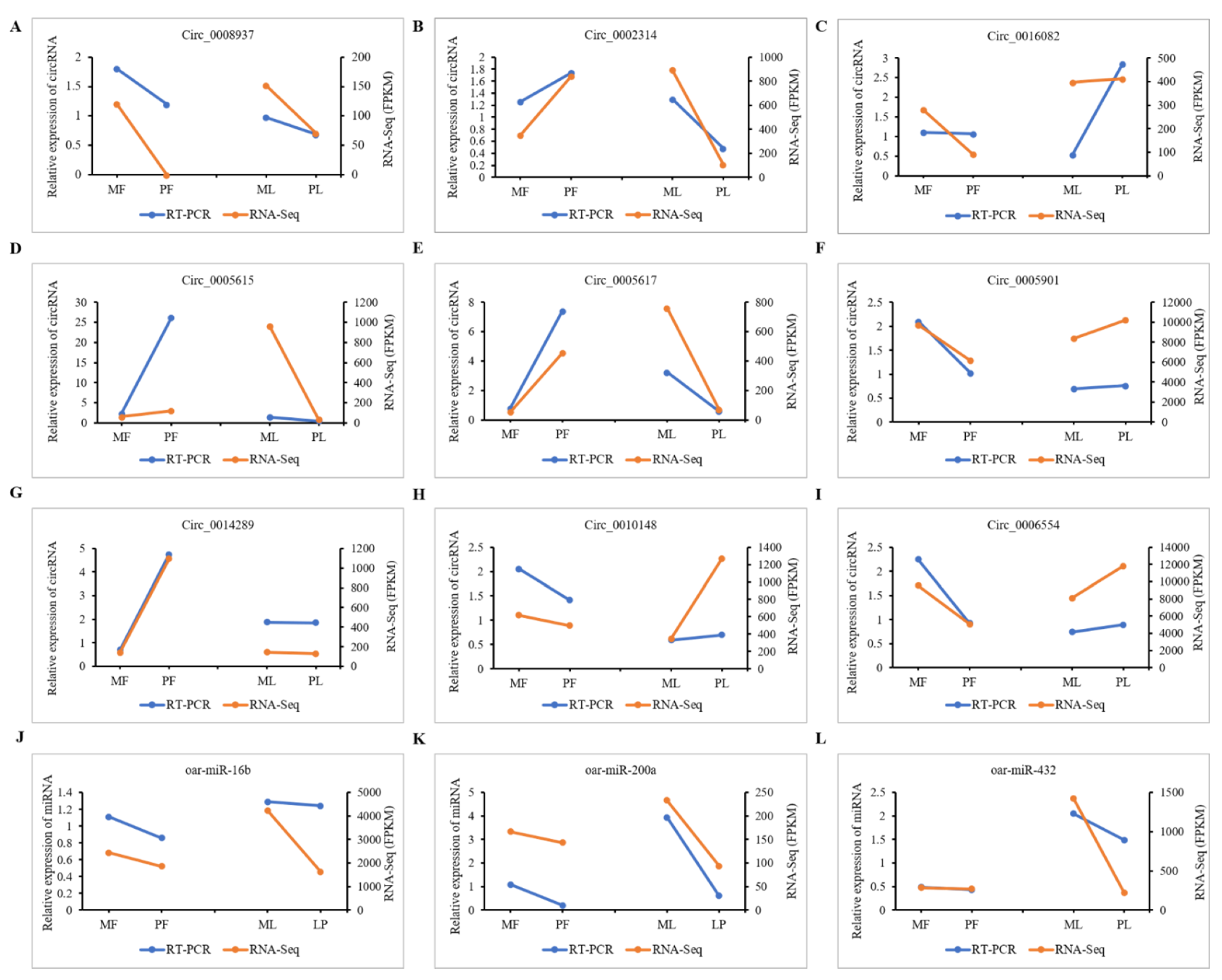
3.8. qRT-PCR Validation of DE-CircRNAs in the Regulatory Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Di, R.; Liu, Q.; Hu, W.; He, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Broniowska, K.; et al. Metabolic Effects of FecB Gene on Follicular Fluid and Ovarian Vein Serum in Sheep (Ovis aries). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, X.; Luo, Q.; Qin, X. Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of mRNAs and microRNAs in Dorset and Small Tail Han sheep to explore the regulation of fecundity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, H.; Qin, X. Ovarian transcriptomic study reveals the differential regulation of miRNAs and lncRNAs related to fecundity in different sheep. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Sui, M.; Zheng, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhang, X. Identification and analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs between multiparous and uniparous goat (Capra hircus) ovaries. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, S. Differential expression and prediction of function of lncRNAs in the ovaries of low and high fecundity Hanper sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.-H.; Ren, C.-H.; Guo, X.-F.; Xu, L.-N.; Huang, Y.-F.; Luo, J.-C.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zhang, Z.-J. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in the ovaries of multiple and uniparous goats (Capra hircus) during follicular phase. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Pang, J.; Ren, C.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Genome-wide differential expression profiling of mRNAs and lncRNAs associated with prolificacy in Hu sheep. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, S.; Di, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Gan, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. The genetic mechanism of high prolificacy in small tail han sheep by comparative proteomics of ovaries in the follicular and luteal stages. J. Proteom. 2019, 204, 103394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, H.; Qin, X. Co-expression analysis and identification of fecundity-related long non-coding RNAs in sheep ovaries. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V.; Elegans, J.C. Heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 116, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulitsky, I.; Bartel, J.C. lincRNAs: Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell 2013, 154, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shi, W.; Chen, C. Differential circular RNAs expression in ovary during oviposition in honey bees. Genomics 2019, 111, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Yao, Y.; You, S.; Wang, D.; Quan, R.; Hou, X.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of circular RNAs in prenatal and postnatal pituitary glands of sheep. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; He, X.; Zhu, M.; Gan, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Chu, M. Comparative Transcriptomics Identify Key Hypothalamic Circular RNAs that Participate in Sheep (Ovis aries) Reproduction. Animals 2019, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ni, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Hazi, W.; Wang, D.; Quan, R.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of circular RNAs in prenatal and postnatal muscle of sheep. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97165–97177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; You, S.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.-J.; Hazi, W.; Li, C.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Hou, X.-X.; Wei, J.-C.; Li, X.-Y.; et al. Expression profiles of circular RNAs in sheep skeletal muscle. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zou, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; et al. Changes in circRNA expression profiles related to the antagonistic effects of Escherichia coli F17 in lamb spleens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.; Sharpless, N. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conn, S.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA Binding Protein Quaking Regulates Formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starke, S.; Jost, I.; Rossbach, O.; Schneider, T.; Schreiner, S.; Hung, L.-H.; Bindereif, A. Exon Circularization Requires Canonical Splice Signals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, S.P.; Wang, P.L.; Salzman, J.J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. eLife 2015, 4, e07540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Bartolomei, M.S. X-Inactivation, Imprinting, and Long Noncoding RNAs in Health and Disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1308–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thore, S.; Arieti, F.; Huet, T.; Gabus-Darlix, C. Structural views on the steroid receptor RNA activator. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallen, A.; Zhou, X.-B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.-S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Imprinted H19 LncRNA Antagonizes Let-7 MicroRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, R.; Jia, D.; Xue, P.; Cui, X.; Li, K.; Zheng, S.; He, X.; Dong, K. Genome-Wide Analysis of Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Expression in Hepatoblastoma Tissues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Hugouvieux, V.; Nayak, A.; Conos, S.A.; Capovilla, G.; Cildir, G.; Jourdain, A.; Tergaonkar, V.; Schmid, M.; Zubieta, C.; et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, Y.; Tang, F.; Huang, Y. Single-cell RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of linear and circular RNAs in mouse preimplantation embryos. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legnini, I.; di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. CIRI: An efficient and unbiased algorithm for de novo circular RNA identification. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houtgast, E.J.; Sima, V.-M.; Bertels, K.; Al-Ars, Z. Hardware acceleration of BWA-MEM genomic short read mapping for longer read lengths. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 75, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquinelli, A.E. MicroRNAs and their targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Di, R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Gan, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Chu, M. Comparative Transcriptomics Reveal Key Sheep (Ovis aries) Hypothalamus LncRNAs that Affect Reproduction. Animals 2019, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La, Y.; Tang, J.; Di, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W.; Chu, M. Differential Expression of Circular RNAs in Polytocous and Monotocous Uterus during the Reproductive Cycle of Sheep. Animals 2019, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, G.; Yang, Y.; Niu, G.; Tang, Z.; Li, K. Genome-wide profiling of Sus scrofa circular RNAs across nine organs and three developmental stages. DNA Res. 2017, 24, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, J.N.; Cieslik, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shukla, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.-M.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Engelke, C.G.; Cao, X.; et al. The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell 2019, 176, 869–881.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhu, S.Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Fang, X.T. Circular RNA of cattle case in genes are highly expressed in bovine mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4750–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Wu, P.; Li, T.; Wu, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, L.; Xie, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Transcriptome Analysis of circRNA and mRNA in Theca Cells during Follicular Development in Chickens. Genes 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Kjems, J.; Hansen, T.B. Circular RNAs: Identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2016, 1859, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keski, J. Latent transforming growth factor-beta binding proteins (LTBPs)-structural extracellular matrix proteins for targeting TGF-beta action. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tatti, O.; Vehviläinen, P.; Lehti, K.; Keski-Oja, J. MT1-MMP releases latent TGF-beta1 from endothelial cell extracellular matrix via proteolytic processing of LTBP-1. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2501–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Teerds, K.; Tao, J.; Wei, H.; Jaklofsky, M.; Zhao, Z. Characteristics of Circular RNA expression profiles of porcine granulosa cells in healthy and atreticantral follicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Yan, J.; Guo, J.; Tang, Z. Identification of Ovarian Circular RNAs and Differential Expression Analysis between MeiShan and Large White Pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Xu, B.; Wu, J. Circular RNA expression profiles of mouse ovaries during postnatal development and the function of circular RNA epidermal growth factor receptor in granulosa cells. Metabolism 2018, 85, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, S.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tsang, S.Y.; Li, X. MicroRNA-27a-3p affects estradiol and androgen imbalance by targeting Creb1 in the granulosa cells in mouse polycytic ovary syndrome model. Reprod. Biol. 2017, 17, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Xiong, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Suo, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M. Circular RNA profiling reveals chi_circ_0008219 function as microRNA sponges in pre-ovulatory ovarian follicles of goats (Capra hircus). Genomics 2018, 110, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Without Pregnancy Sheep (Earmark) | Litter Size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Parity | Second Parity | Third Parity | Four Parity | ||
| Polytocous group | 3E202 | 3 | 3 | 5 | |
| 6T01 | 3 | 4 | 2 | ||
| 6T06 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
| CE104 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 3E161 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
| CE103 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |
| Monotocous group | 9M06 | 1 | |||
| MY91 | |||||
| MY86 | |||||
| 3E146 | |||||
| 3E79 | |||||
| MY66 | |||||
| Type | Gene Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CircRNA | novel_circ_0006554 | F: ACGACAATGAGGAGTGTGGG | 198 |
| R: GTCCTTCAATGACCGAGCAGT | |||
| novel_circ_0005901 | F: ACACTAAGTGATGACGAATCTTTTC | 190 | |
| R: CCACCCACAAAGCAGAGGAT | |||
| novel_circ_0008937 | F: TGACGTGAATGTCTATGCTCAGT | 153 | |
| R: GGAGAGGGTGAAGGATCCCA | |||
| novel_circ_0016082 | F: CTGAGAACCAACAGCAGTGGA | 187 | |
| R: AGCTCTTCCAGGCGGTTTC | |||
| novel_circ_0002314 | F: GCTGCTGATGCAACAGGGTT | 198 | |
| R: CAGGCAGAGGGCAGGTTTTA | |||
| novel_circ_0005615 | F: GAGGCTGTAACGGAAGAGGA | 199 | |
| R: AGCACGTTAGGTTTGTTGGT | |||
| novel_circ_0005617 | F: GGGCTTTTCTTTGCCTCCTG | 199 | |
| R: TTGTGGGACAAAATATTCGGGA | |||
| novel_circ_0010148 | F: GGAGCCAAAACCCAGAGTCAA | 187 | |
| R: ACCTGAAGCTGGAGTCACAAG | |||
| novel_circ_0014289 | F: TTGGAGGATGTCAAGGCCAA | 180 | |
| R: TACTGGTGATAGGCCAGCCA | |||
| Control | GADPH | F: ACAGTCAAGGCAGAGAACGG | 107 |
| R: CCAGCATCACCCCACTTGAT | |||
| miRNA | oar-miR-16b | GCGCGTAGCAGCACGTAAA | |
| oar-miR-200a | CGCGCGAACACTGTCTGGT | ||
| oar-miR-432 | CGCGTCTTGGAGTAGGTCATT | ||
| Control | U6 | AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| ID | Host_Gene_Name | MF. TPM | PF. TPM | ML. TPM | PL. TPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| novel_circ_0005901 | SNX13 | 527 | 151 | 377 | 663 |
| novel_circ_0006554 | INSR | 533 | 122 | 343 | 774 |
| novel_circ_0014057 | ARHGAP10 | 457 | 129 | 330 | 615 |
| novel_circ_0008317 | SLTM | 444 | 150 | 220 | 504 |
| novel_circ_0012048 | ZEB1 | 410 | 221 | 165 | 264 |
| novel_circ_0014135 | UBE3A | 334 | 164 | 135 | 335 |
| novel_circ_0008261 | USP3 | 426 | 207 | 291 | 450 |
| novel_circ_0009916 | ANKRD46 | 273 | 94 | 212 | 335 |
| novel_circ_0010401 | PDS5B | 271 | 69 | 199 | 292 |
| novel_circ_0001969 | SLC30A7 | 189 | 103 | 118 | 175 |
| novel_circ_0001127 | CEP70 | 254 | 82 | 288 | 397 |
| novel_circ_0016729 | HERC4 | 198 | 89 | 159 | 249 |
| novel_circ_0003675 | KDM4C | 190 | 107 | 109 | 223 |
| novel_circ_0013646 | ELF2 | 221 | 78 | 158 | 264 |
| novel_circ_0006681 | CEP120 | 168 | 88 | 169 | 238 |
| novel_circ_0009038 | REV3L | 133 | 29 | 70 | 156 |
| novel_circ_0004301 | RAP1B | 191 | 50 | 109 | 233 |
| Pathway Name | p-Value | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | 0.01 | ITGAV, JAM2 |
| Glycosaminoglycan degradation | 0.02 | ARSB |
| Dorso-ventral axis formation | 0.02 | SPIRE1 |
| Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | 0.06 | ITGAV |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | 0.06 | ITGAV |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | 0.07 | ITGAV |
| ECM-receptor interaction | 0.07 | ITGAV |
| Small cell lung cancer | 0.08 | ITGAV |
| Protein digestion and absorption | 0.09 | COL14A1 |
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 0.10 | ITGAV |
| Lysosome | 0.10 | ARSB |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 0.10 | JAM2 |
| Tight junction | 0.11 | JAM2 |
| Phagosome | 0.13 | ITGAV |
| Focal adhesion | 0.16 | ITGAV |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | 0.17 | ITGAV |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 0.17 | ITGAV |
| Pathways in cancer | 0.25 | ITGAV |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.26 | ITGAV |
| Metabolic pathways | 0.66 | ARSB |
| Module Color | KEGG Term | p-Value | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 3.50 × 10−2 | FBXW7, HUWE1, BIRC6, UBE2Q2, UBA6 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 4.40 × 10−2 | RAB5C, TIAM1, PDGFD, RRAS2, STK4 | |
| Black | Leishmaniasis | 9.40 × 10−2 | TAB2, TGFB2 |
| Brown | Wnt signaling pathway | 5.90 × 10−2 | APC, LRP6, ROCK2 |
| Green | Focal adhesion | 3.20 × 10−2 | AKT3, DOCK1, ITGB1, LAMC1, MAPK1 |
| Toxoplasmosis | 5.60 × 10−2 | AKT3, ITGB1, LAMC1, MAPK1 | |
| mTOR signaling pathway | 1.30 × 10−2 | AKT3, RICTOR, MAPK1 | |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 1.90 × 10−2 | AKT3, ITGB1, LAMC1, MAPK1, PPP2R2A | |
| Estrogen signaling pathway | 3.50 × 10−2 | AKT3, FKBP5, MAPK1 | |
| TNF signaling pathway | 4.20 × 10−2 | AKT3, MAPK1, RIPK1 | |
| Turquoise | Endocytosis | 1.50 × 10−2 | WASL, LDLRAP1, NEDD4L, PSD3, RABEP1, STAM2 |
| Insulin resistance | 2.70 × 10−2 | GFPT1, PPARA, PIK3R1, PRKAA2, PRKCE | |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 3.70 × 10−2 | ABL1, RAP1B, NTRK2, PIK3R1, RPS6KA5 | |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | 5.60 × 10−2 | WASL, PIK3R1, PLPP1, PRKCE | |
| Notch signaling pathway | 9.90 × 10−2 | NUMBL, SNW1, RBPJ | |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | 0.012 | FYN, SOS1, DLG1, TEC | |
| Yellow | Focal adhesion | 0.018 | FYN, ARHGAP5, SOS1, IGF1R |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 0.025 | RHEB, SOS1, GYS1, IGF1R | |
| Adherens junction | 0.044 | FYN, IGF1R, PTPRM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, A.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Tian, S. Differential Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in the Ovaries of Low and High Fecundity Hanper Sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071863
Liu A, Chen X, Liu M, Zhang L, Ma X, Tian S. Differential Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in the Ovaries of Low and High Fecundity Hanper Sheep. Animals. 2021; 11(7):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071863
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Aiju, Xiaoyong Chen, Menghe Liu, Limeng Zhang, Xiaofei Ma, and Shujun Tian. 2021. "Differential Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in the Ovaries of Low and High Fecundity Hanper Sheep" Animals 11, no. 7: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071863
APA StyleLiu, A., Chen, X., Liu, M., Zhang, L., Ma, X., & Tian, S. (2021). Differential Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in the Ovaries of Low and High Fecundity Hanper Sheep. Animals, 11(7), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071863





