Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals Handling, Drug Administration, and Blood Collection
2.2. In Vitro Incubation of Whole Blood with Lornoxicam
2.3. Separation of Blood Leukocytes
2.4. Monoclonal Antibodies
2.5. Membrane Immunofluorescence and Flow Cytometry
2.6. Analysis of Cell Viability and Apoptosis
2.7. Phagocytosis Assay
2.8. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation Assay
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
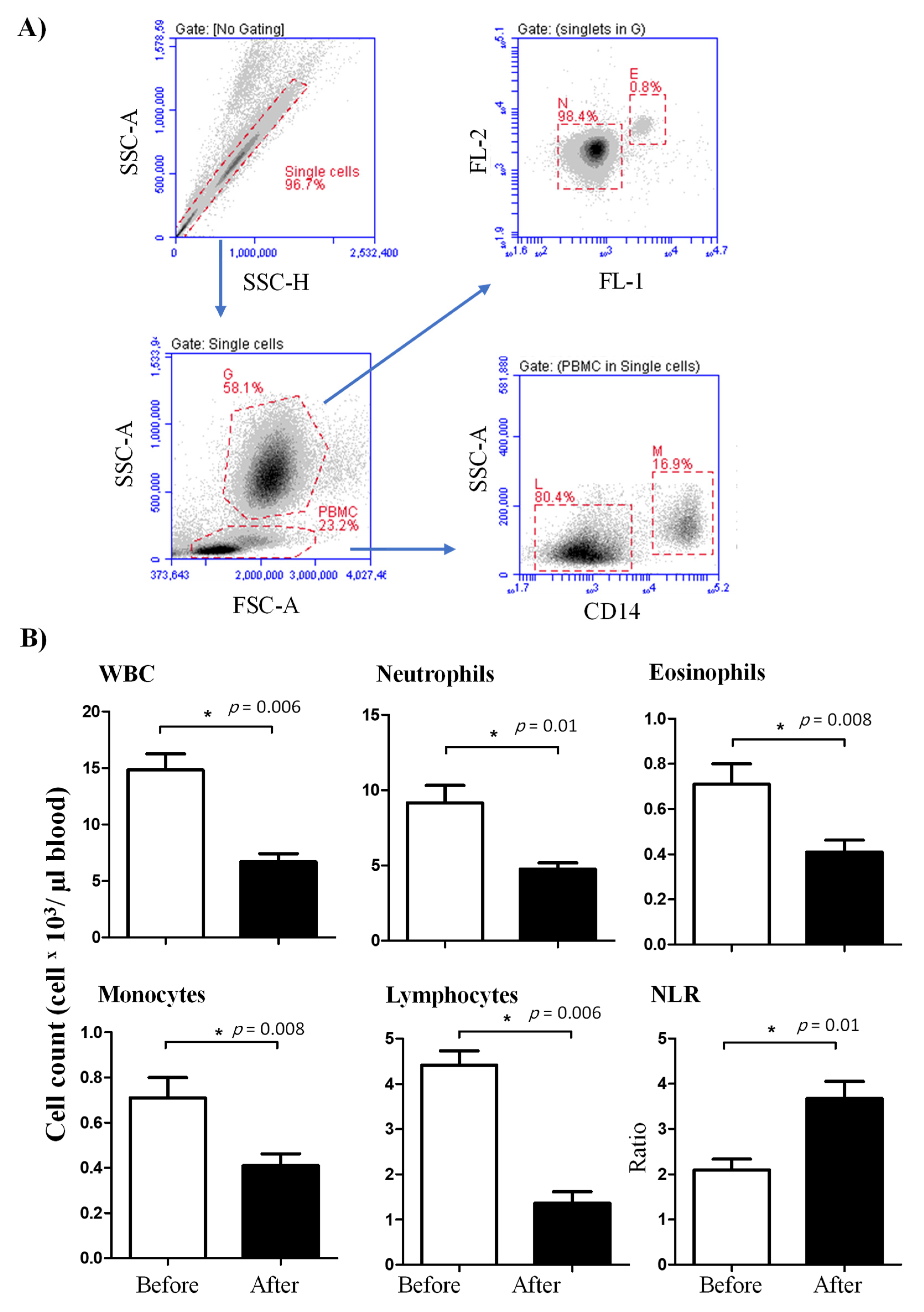
3.1. The Impact of Lornoxicam on the Leukogram of Dromedary Camels
3.2. Lymphocyte Composition in the Blood of Lornoxicam-Injected Camels
3.3. Lornoxicam Modulates the Phenotype of Blood Monocytes
3.4. Lornoxicam Injection Reduces the Phagocytosis and ROS Generation Capacity of Blood Phagocytes
3.5. Impact of In Vitro Incubation with Lornoxicam on Cell Vitality of Camel Leukocytes
3.6. Impact of In Vitro Incubation with Lornoxicam on Bacterial Phagocytosis and ROS Production Capacity of Camel Granulocytes and Monocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guedes, A. Pain Management in Horses. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pr. 2017, 33, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, K.R.; Hector, R.C. Therapeutic developments in equine pain management. Vet. J. 2019, 247, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Nava, A.; Ramírez-Uribe, J.M.; Recillas, S.; Ibancovichi-Camarillo, J.A.; Venebra-Muñoz, A.; Sánchez-Aparicio, P. Pharmacological Regulation in the USA and Pharmacokinetics Parameters of Firocoxib, a Highly Selective Cox-2, by Pain Management in Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 77, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coetzee, J.F.; Shearer, J.; Stock, M.L.; Kleinhenz, M.; van Amstel, S.R. An Update on the Assessment and Management of Pain Associated with Lameness in Cattle. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pr. 2017, 33, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschoner, T.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Peinhofer, V.; Feist, M. Attitudes of Bavarian bovine veterinarians towards pain and pain management in cattle. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarco, G.J.; Nunamaker, E.A. A Review of the Effects of Pain and Analgesia on Immune System Function and Inflammation: Relevance for Preclinical Studies. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, M.; Dionne, R. Mechanisms of Non-Opioid Analgesics Beyond Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefifard, M.; Zali, A.; Zarghi, A.; Neishaboori, A.M.; Hosseini, M.; Safari, S. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in management of COVID-19; A systematic review on current evidence. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2020, 74, e13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, D.; Craven, M.A. A review of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Can Fam. Physician 1983, 29, 2121–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Rouzer, C.A.; Marnett, L.J. Oxicams, a class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and beyond. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulbert, L.E.; Moisá, S.J. Stress, immunity, and the management of calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3199–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balfour, J.A.; Fitton, A.; Barradell, L.B. Lornoxicam. Drugs 1996, 51, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buritova, J.; Besson, J.M. Potent anti-inflammatory/analgesic effects of lornoxicam in comparison to other nsaids: A c-fos study in the rat. Inflammopharmacology 1997, 5, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buritova, J.; Besson, J.-M. Dose-related anti-inflammatory/analgesic effects of lornoxicam: A spinal c-Fos protein study in the rat. Inflamm. Res. 1998, 47, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruss, T.P.; Stroissnig, H.; Radhofer-Welte, S.; Wendtlandt, W.; Mehdi, N.; Takacs, F.; Fellier, H. Overview of the pharmacological properties, pharmacokinetics and animal safety assessment of lornoxicam. Postgrad. Med. J. 1990, 66, S18-21. [Google Scholar]
- Aabakken, L.; Osnes, M.; Frenzel, W. Gastrointestinal tolerability of lornoxicam compared to that of naproxen in healthy male volunteers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Fellier, H.; Christoph, T.; Grarup, J.; Stimmeder, D. The analgesic NSAID lornoxicam inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX)-1/-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the formation of interleukin (IL)-6 in vitro. Inflamm. Res. 1999, 48, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.; Johnston, A. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies with lornoxicam. Postgrad. Med. J. 1990, 66, S28-29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, D.; Si, D.; Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H. Lornoxicam pharmacokinetics in relation to cytochrome P450 2C9 genotype. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 59, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-I.; Kim, M.-J.; Jang, C.-G.; Park, Y.-S.; Bae, J.-W.; Lee, S.-Y. Effects of the CYP2C9*1/*13 Genotype on the Pharmacokinetics of Lornoxicam. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Qian, Y. Which has the least immunity depression during postoperative analgesia—morphine, tramadol, or tramadol with lornoxicam? Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 369, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussen, J.; Düvel, A.; Sandra, O.; Smith, D.; Sheldon, I.M.; Zieger, P.; Schuberth, H.-J. Phenotypic and Functional Heterogeneity of Bovine Blood Monocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussen, J.; Shawaf, T.; Al-Herz, A.I.; Alturaifi, H.R.; Alluwaimi, A.M. Reactivity of commercially available monoclonal antibodies to human CD antigens with peripheral blood leucocytes of dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius). Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eger, M.; Hussen, J.; Drong, C.; Meyer, U.; von Soosten, D.; Frahm, J.; Daenicke, S.; Breves, G.; Schuberth, H.-J. Impacts of parturition and body condition score on glucose uptake capacity of bovine monocyte subsets. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 166, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussen, J.; Schuberth, H.-J. Recent Advances in Camel Immunology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 614150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, L.; Scott, A.P.; Marfell, B.J.; Boughaba, J.A.; Chojnowski, G.; Waterhouse, N.J. Measuring Cell Death by Propidium Iodide Uptake and Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosin, J.M.; Zamudio, A.; Wang, Z. Application of JC1 for non-toxic isolation of cells with MDR transporter activity by flow cytometry. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, E.; Troiano, L.; Ferraresi, R.; Roat, E.; Prada, N.; Nasi, M.; Pinti, M.; Cooper, E.L.; Cossarizza, A. Characterization of cells with different mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis. Cytom. Part A 2005, 68, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, J. Changes in Cell Vitality, Phenotype, and Function of Dromedary Camel Leukocytes After Whole Blood Exposure to Heat Stress in vitro. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, J.; Koy, M.; Petzl, W.; Schuberth, H.-J. Neutrophil degranulation differentially modulates phenotype and function of bovine monocyte subsets. Innate Immun. 2016, 22, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldeira, M.; Bruckmaier, R.; Wellnitz, O. Meloxicam affects the inflammatory responses of bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 10277–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, S.S.; Jr, P.C.F.; Silva, M.J.B.; de Lima, V.C.; Fontes, W.; Freitas-Junior, R.; Eterovic, A.K.; Forget, P. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A narrative review. ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Sharma, M.; Jain, N.; Sinha, N.; Kaushik, R.; Jash, D.; Chaudhry, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Early and Late Phase of Sepsis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maślanka, T. Dexamethasone inhibits and meloxicam promotes proliferation of bovine NK cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 35, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawer, S.G.; Mawhinney, L.; Chadwick, K.; de Chickera, S.N.; Weaver, L.C.; Brown, A.; Dekaban, G.A. Temporal changes in monocyte and macrophage subsets and microglial macrophages following spinal cord injury in the lys-egfp-ki mouse model. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 261, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, Y.S.; Svistelnik, A.V. Functional phenotypes of macrophages and the M1-M2 polarization concept. Part I. Proinflammatory phenotype. Biochemistry 2012, 77, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, J.; Frank, C.; Düvel, A.; Koy, M.; Schuberth, H.-J. The chemokine CCL5 induces selective migration of bovine classical monocytes and drives their differentiation into LPS-hyporesponsive macrophages in vitro. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 47, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, R.; Francis, H.; Dervish, S.; Li, S.C.; Medbury, H.; Williams, H. Characterization of Human Monocyte Subsets by Whole Blood Flow Cytometry Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, e57941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buechler, C.; Ritter, M.; Orsó, E.; Langmann, T.; Klucken, J.; Schmitz, G. Regulation of scavenger receptor CD163 expression in human monocytes and macrophages by pro- and antiinflammatory stimuli. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, P.; Etzerodt, A.; Deleuran, B.; Moestrup, S.K. Mouse CD163 deficiency strongly enhances experimental collagen-induced arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacerdote, P. Lornoxicam Inhibits Human Polymorphonuclear Cell Migration Induced by fMLP, Interleukin-8 and Substance P. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 1, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainsford, K.D.; Ginsburg, I.; Gadd, S.J. A comparison between the effects of meloxicam and other nsaids on the production of oxyradicals by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Inflammopharmacology 1997, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, D.; Zdzisińska, B.; Kondracki, M.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M. Effect of steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with long-acting oxytetracycline on non-specific immunity of calves suffering from enzootic bronchopneumonia. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 96, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Won, S.-J.; Lin, M.-T. Effects of morphine on immune response in rats with sciatic constriction injury. Pain 2000, 88, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Barke, R.A.; Charboneau, R.; Roy, S. Morphine Impairs Host Innate Immune Response and Increases Susceptibility toStreptococcus pneumoniaeLung Infection. J. Immunol. 2004, 174, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacerdote, P.; Bianchi, M.; Gaspani, L.; Manfredi, B.; Maucione, A.; Terno, G.; Ammatuna, M.; Panerai, A.E. The Effects of Tramadol and Morphine on Immune Responses and Pain After Surgery in Cancer Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 90, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Memiş, D.; Karamanlıoğlu, B.; Turan, A.; Koyuncu, O.; Pamukçu, Z. Effects of lornoxicam on the physiology of severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R474–R482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soehnlein, O.; Lindbom, L. Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Antigen | Antibody Clone | Labeling | Source | Isotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD14 | TÜK4 | - | WSU | Mouse IgG1 |
| MHCII | TH81A5 | - | Kingfisher | Mouse IgG2a |
| CD163 | LND68A | - | WSU | Mouse IgG1 |
| CD4 | GC50A1 | - | WSU | Mouse IgM |
| WC1 | BAQ128A | - | WSU | Mouse IgG1 |
| Mouse IgM | poly | APC | Thermofisher | Goat IgG |
| Mouse IgG1 | poly | FITC | Thermofisher | Goat IgG |
| Mouse IgG2a | poly | PE | Thermofisher | Goat IgG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussen, J.; Kandeel, M.; Shawaf, T.; Al-Mubarak, A.I.A.; Al-Humam, N.A.; Almathen, F. Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes. Animals 2021, 11, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072023
Hussen J, Kandeel M, Shawaf T, Al-Mubarak AIA, Al-Humam NA, Almathen F. Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes. Animals. 2021; 11(7):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072023
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussen, Jamal, Mahmoud Kandeel, Turke Shawaf, Abdullah I. A. Al-Mubarak, Naser A. Al-Humam, and Faisal Almathen. 2021. "Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes" Animals 11, no. 7: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072023
APA StyleHussen, J., Kandeel, M., Shawaf, T., Al-Mubarak, A. I. A., Al-Humam, N. A., & Almathen, F. (2021). Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes. Animals, 11(7), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072023







