First Data on the Helminth Community of the Smallest Living Mammal on Earth, the Etruscan Pygmy Shrew, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Hosts
2.2. Parasitological Techniques
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Helminth Populations
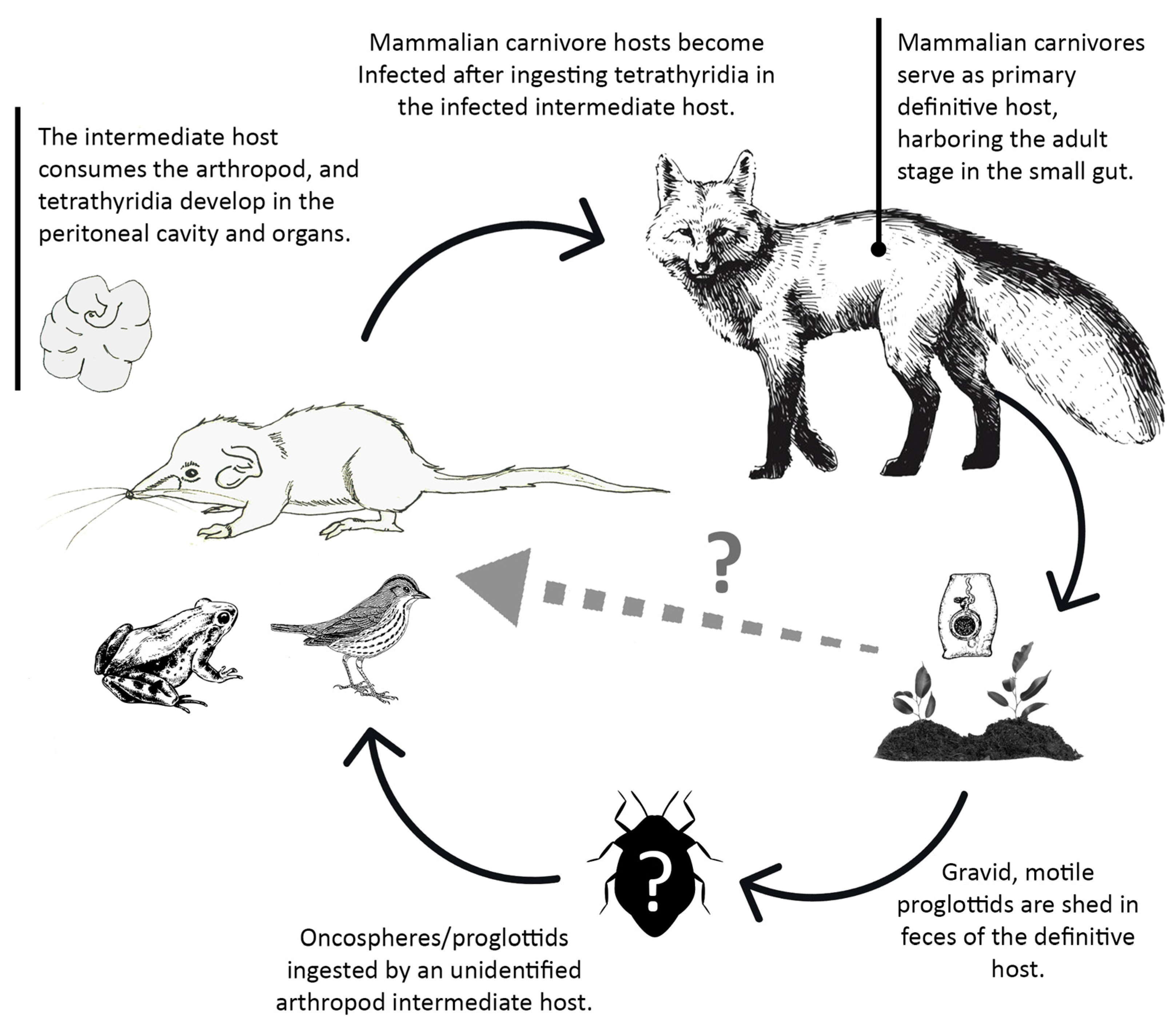
4.1.1. Tapeworm Metacestodes
- Mesocestoides sp.
- Joyeuxiella pasqualei
4.1.2. Tapeworm Adult Stages
- Staphylocystis Species
- Pseudhymenolepis sp.
4.1.3. Nematodes
4.2. Helminth Community
4.3. Helminth Diversity and S. etruscus Body
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowak, R.N. Suncus: Musk Shrews, or Pygmy Shrews. In Walker’s Mammals of the World, 6th ed.; Novak, R.M., Ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Libois, R.; Fons, R. Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822), the pygmy white-toothed shrew. In The Atlas of European Mammals; Mitchell-Jones, A.J., Amori, G., Bogdanowicz, W., Krystufek, B., Reijnders, P.J.H., Spitzenberger, F., Stubbe, M., Thissen, J.B.M., Vohralik, V., Zima, J., Eds.; Poyser Natural History: London, UK, 1999; pp. 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, S.K.; Sheftel, B.I. The pygmy white-toothed shrew, (Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822)): A species new to the fauna of Russia. Biol. Bull. 2018, 96, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fons, R. Méthodes de capture et d’élevage de la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822). Z. Säugetierkd. 1974, 39, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Contribution à la connaissance de la Pachyure étrusque Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822). Bull. Soc. Ecol. 1976, 7, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Contribution à la connaissance de la Musaraigne étrusque Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) Mammifère, Soricidae. Vie Milieu 1970, 21, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R.; Saint Girons, M.C. Notes sur les Mammifères de France. XIV. Donées morphologiques concernant la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822). Mammalia 1975, 39, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans Coma, V.; Fons, R.; Vesmanis, I.E. Eine morphometrische untersuchung and Schädel der Etruskerspitzmaus Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) aus Süd-Frankreich (Mammalia, Insectivora). Abh. Staatl. Mus. TierkdeDresden 1981, 37, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Vesmanis, I.E.; Sans-Coma, V.; Fons, R. Bermerkungen über die Moephologische Variation des P4 bei verschiedenen rezenten Crocidura—Arten und Suncus etruscus im Mittelmeergebiet. Afr. Small Mamm. Newsl. 1979, 3, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Vesmanis, I.E.; Fons, R.; Sans-Coma, V. Die Etruskerspitzmaus Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) in Tunesien (Mammalia, Insectivora). Afr. Small Mamm. Newsl. 1980, 3, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hartge, R.; Fons, R.; Schneider, J. Uber die Feinstruktur der Plazenta des Kleinsten Säugetirs der Welt der Etruskerspitzmaus Suncus etruscus Was unterscheidet sie von jener des Gröften Säugers des Blauwals (Balena, Cetacea)? Physiol. Pathol. Fortpfl. Verhandl. 1982, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R.; Mas-Coma, S.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Valero, M.A.; Moutou, F. Parasitological suggestions on the evolution and systematics of Suncus and other genera of Soricidae (Mammalia: Insectivora). Zool. Jahr. Abt. Systematik. 1994, 121, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Modalités de la reproduction et development post-natal en captivité chez Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822). Mammalia 1973, 37, 288–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fons, R. Rythmes circadiens d’activité d’une petite musaraigne Suncus etruscus (Mammalia—Insectivora). Bull. Gr. Etud. Rhythm. Biol. 1973, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. La mue chez les Crocidurinae: I—Changement de pelage dans la nature et captivité chez la Pachyure étrusque S. etruscus. Mammalia 1974, 38, 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Premières données sur l’écologie de la Pachyure étrusque Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822)—Comparison avex deux autres Crocidurinés, Crocidura russula (Hermann, 1780) et Crocidura suaveolens (Pallas, 1881) (Insectivora, Soricidae). Vie Milieu 1975, 25, 315–359. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Durée de vie chez la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) dans la nature et en captivité (Insectivora, Soricidae). Z. Säugetierkd. 1978, 44, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R. Le répertoire comportemental de la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822). Rev. Ecol. (Terre Vie) 1974, 28, 131–157. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R.; Saint-Girons, R. Horaire et intensité de l’activité locomotrice spontanée chez un petit mammifère, la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Insectivora, Soricidae). Bull. Gr. Etud. Rhythm. Biol. 1976, 8, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Saint Girons, M.C.; Fons, R. Activité locomotrice spontanée chez un mâle senile de Pachyure étrusque, S. etruscus (Savi, 1822). Mammalia 1978, 42, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Fons, R.; Sicart, R. Contribution à la connaissance du métabolisme énergétique chez deux Crocidurinés: Suncus etruscus et Crocidura russula (Mammifère, Insectivora). Mammalia 1976, 40, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fons, R.; Sablé, R.; Sicart, R. Quelques aspects des métabolismes glucidique et lipidique chez deux Insectivores Crocidurinae, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) et Crocidura russula (Hermann, 1780) (Mammifère–Soricidae). Vie Milieu 1977, 21, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Sicart, R.; Sablé, R.; Fons, R. Comparative aspect of lipid metabolism in two shrews (Suncus etruscus and Crocidura russula). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1978, 61, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, H.R.; Baumann, R.; Fons, R.; Jürgens, K.D.; Wright, P. La fonction respiratoire du sang et poids relatif de certains organes chez deux espèces de Musaraigne: Crocidura russula et Suncus etruscus (Mammifère, Soricidae). C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1978, 286, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, H.R.; Baumann, R.; Fons, R.; Jürgens, K.D.; Wright, P. Blood oxygen transport function in Etruscan shrews. Pflügers Archiv. 1978, 373, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, H.R.; Baumann, R.; Fons, R.; Jürgens, K.D.; Wright, P. Blood oxygen transport and oxygens weights of two shrews, Suncus etruscus and Crocidura russula. Am. J. Physiol. 1979, 236, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens, K.D.; Peter, T.; Sender, S.; Fons, R.; Gros, G. Carbonic anhydrase activities of blood, lung and heart of the smallest mammal, the Etruscan shrew (Suncus etruscus). Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1994, 426, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens, K.D.; Fons, R.; Peter, T.; Sender, S. Heart and respiratory rates and their significance for convective oxygen transport rates in the smallest mammal, the Etruscan shrew Suncus etruscus. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 2579–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fons, R.; Sender, S.; Peters, T.; Jürgens, K.D. Rates of rewarming, heart and respiratory rates and their significance for oxygen transport during arousal from torpor in the smallest mammal, the Etruscan shrew Suncus etruscus. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.; Kubis, H.P.; Wetzel, P.; Sender, S.; Asmussen, G.; Fons, R.; Jurgens, K.D. Contraction parameters, myosin composition and metabolic enzymes of skeletal muscles of the Etruscan shrew Suncus etruscus and of the Common European white-toothed shrew Crocidura russula. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 2461–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Fons, R.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Valero, M.A. Hymenolepis claudevaucheri n. sp. (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae), first record of a helminth in the smallest known living mammal, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Insectivora: Soricidae). Critical revision of the Cyclophyllidea in Suncus murinus (Linnaeus, 1766). Vie Milieu 1984, 34, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Fons, R.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Valero, M.A. Description de Hymenolepis cerberensis n. sp. (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae) et premières considérations générales sur la faune de Cestodes parasites de la Pachyure étrusque, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Insectivora: Soricidae). Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1986, 4, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Fons, R.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Valero, M.A. Hymenolepis banyulsensis n. sp. (Hymenolepididae), un nouveau Cestode parasite de la Musaraigne étrusque (Soricidae) dans la région de Banyuls-sur-Mer (France). Rev. Suisse Zool. 1986, 93, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, B.B.; Bray, R.A.; Littlewood, D.T.J. Cestodes of small mammals: Taxonomy and life cycles. In Micromammals and Macroparasites. From Evolutionary Ecology to Management; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 29–62. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, B.C.; Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Fuentes, M.V. Normal and aberrant Mesocestoides tetrathyridia from Crocidura spp. (Soricimorpha) in Corsica and Spain. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos-Frank, B. One or two intermediate hosts in the life cycle of Mesocestoides (Cyclophyllidea, Mesocestoididae)? Parasitol. Res. 1991, 77, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, S.G.H.; Bradbury, R.S. The forgotten exotic tapeworms: A review of uncommon zoonotic Cyclophyllidea. Parasitology 2020, 147, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, C.T.; Tkach, V.V.; Bruce, D.B. Morphological and molecular characterization of post-larval pre-tetrathyridia of Mesocestoides sp. (Cestoda: Cyclophyllidea) from Ground Skink, Scincella lateralis (Sauria: Scincidae), from southeastern Oklahoma. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T. Contribución al Conocimiento de la Fauna de Plathelmintos Parásitos de Crocidurinae (Insectivora: Soricidae) en el Marco Europeo Continental e Insular del Mediterráneo Occidental. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, D.B. The rarity of asexual reproduction among Mesocestoides tetrathyridia (Cestoda). J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Fuentes, M.V.; Conn, D.B. A new type of endogenous asexual proliferation in cyclophyllidean metacestodes. Acta Parasitol. 2002, 47, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, R.K. Cestodes of the genera Diplopylidium and Joyeuxiella (Eucestoda: Dipylidiiae)—A review of historical data, species inventory and geographical distribution. Sci. Parasitol. 2020, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Esteban, J.G.; Fuentes, M.V.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A.; Galán-Puchades, M.T. Helminth parasites of small mammals (Insectivores and Rodents) on the Pityusic Island of Eivissa (Balearic Archipelago). Res. Rev. Parasitol. 2000, 60, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, R.; Montag, A. Joyeuxiella pasqualei—An unusual tapeworm in an indigenous domestic cat. Kleintierpraxis 2000, 11, 867–870. [Google Scholar]
- Joyeux, C. Recherches sur la fauna helminthologique Africaine. 2. Cestodes. Arch. Inst. Pasteur Tunis 1923, 14, 119–167. [Google Scholar]
- Czaplinski, B.; Vaucher, C. Family Hymenolepididae. In Keys to the Cestode Parasites of Vertebrates; Khalil, L.F., Bray, R.A., Eds.; CAB International: Oxon, UK, 1994; pp. 595–663. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S. Helminthes de micromammifères. Spécificité, évolution et phylogénie des Cestodes Arostrilepididae Mas-Coma et Tenora, 1981 (Cyclophyllidea: Hymenolepidoidea). Mém. Mus. Nat. Hist. Nat. Ser. A Zool. 1982, 123, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Vaucher, C. Les Cestodes parasites des Soricidés d’Europe. Etude anatomique, révision taxonomique et biologie. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1971, 78, 1–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunkeler, P. Les Cestodes parasités des petits mammifères (Rongeurs et Insectivores) de Côte-d’Ivoire et de Haute-Volte. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1974, 80, 809–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaucher, C. Cestodes parasites de Crocidura suaveolens (Pallas) en Grèce, avec description de Pseudhymenolepis graeca n. sp. et remarques sur Pseudhymenolepis solitaria (Meggit, 1927) n. comb. Bull. Soc. Neuchâtel. Sc. Nat. 1984, 107, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, I.; Koyasu, K. Pseudhymenolepis nepalensis sp. nov. (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae) parasitic on the house shrew, Suncus murinus (Soricidae) from Nepal. Zool. Sci. 1991, 8, 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, I.; Harada, M. A new species of the genus Pseudhymenolepis (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae) from Insectivora of Central Japan with record of the known Cestoda species. Proc. Jpn. Soc. Syst. Zool. 1991, 44, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Velikanov, V.P. New species of the genus Pseudhymenolepis (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae) from the white-toothed shrew. Parazitologia 1997, 31, 210–222. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tkach, V.V.; Velikanov, V.P. Pseudhymenolepis turkestanica sp. N. (Cestoda: Hymenolepididae), a new cestode from shrews. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1991, 66, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawada, I.; Ohono, N. Some cestodes parasites of the Indian House Mausk Shrew, Suncus murinus. Jpn. J. Parasitol. 1993, 42, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Veciana, M.; Chaisiri, K.; Morand, S.; Ribas, A. Helminths of the Asian House shrew Suncus murinus from Cambodia. Cambodian J. Nat. Hist. 2012, 2012, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.P.; Sinha, N. On a new cestode Pseudhymenolepis suncusi sp. N. (Fam. Hymenolepididae Railliet et Henry, 1909) from a common shrew, Suncus striatus Lucknow. Ind. J. Helminth. 1984, 36, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.; Singh, S.R. On a new species Pseudhymenolepis guptai sp. n. (Cyclophyllidea: Hymenolepididae) from Suncus striatus from Khurja, U.P. Ind. J. Helminth. 1987, 39, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tkach, V.V.; Zhumabekova, B.K. Helminth fauna of shrews in southeastern Kazakhstan. In Proceedings of the Paraztologiya v Ukraini: Vchora, Sogodni, Zavta. Mat Yuvil. Konf. UNTP 16-17, Travnya, Ukraine, 16–17 May 1995; pp. 101–110. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Quentin, J.-C.; Beaucournu, J.-C. Cysticercoides d’Hymenolepididae parasites d’insectivores chez les Siphonapteres. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1966, 262, 2059–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrion, C. Presence de cysticercoides d’un cestode cysclophillidae chez un arachnide, Phalangium opilio. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1977, 52, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beaucournu, J.-C.; Lorvelec, O. Mise à jour taxonomique et répartition des puces du genre Ctenothalmus Kolenati 1856 en région paléarctique occidentale (Insecta: Siphonaptera: Ctenophthalmidae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2014, 50, 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, F. Proposal of a new systematic arrangement of the nematodes of the family Capillariidae. Folia Parasitol. 1982, 29, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Galán-Puchades, M.T. Consideraciones sobre el género Aonchotheca López-Neyra, 1947 (Nematoda: Trichuridae). Circ. Farm. 1985, 286, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa, M.; Kamiya, H.; Ohbayashu, M. Studies on the parasite fauna of Insectivora. II. Four new capillarid nematodes from the Japanese shrews, genera Suncus and Crocidura. J. Coll. Dairy. Nat. Sci. Jpn. 1988, 12, 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Umur, S.; Moravec, F.; Gurler, A.; Bolukbas, C.; Acici, M. First report on Aonchotheca annulosa Dujardin, 1845 (Nematoda, Capillariidae) in a Hamadrya baboon (Papio hamadryas) from a zoo in northern Turkey. J. Med. Primatol. 2012, 41, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.C. (Ed.) Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Their Development and Transmission; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000; 650p. [Google Scholar]
- Ribas, A.; Casanova, J.C. Acanthocephalans. In Micromammals and Macroparasites. From Evolutionary Ecology to Management; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Morand, S.; Bouamer, S.; Hugot, J.P. Nematodes. In Micromammals and Macroparasites. From Evolutionary Ecology to Management; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Koprivnikar, J.; Randhawa, H.S. Benefits of fidelity: Does host specialization impact nematode parasite life history and fecundity. Parasitology 2016, 140, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berg, M. A minuscule model for research. Nature 2016, 45, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiman, S.E.; Tkach, V.V. Description and phylogenetic relationship of Rodentolepis gnoskei n. sp. (Cyclophyllidea: Hymenolepididae) from a shrew Suncus varilla minor in Malawi. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojmanska, T.; Niewiadomska, K. New trends in research on parasite host specificity: A survey of current parasitological literature. Ann. Parasitol. 2012, 58, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krasnov, B.R.; Poulin, R.; Morand, S. Patterns of macroparasites diversity in small mammals. In Micromammals and Macroparasites. From Evolutionary Ecology to Management; Morand, S., Krasnov, B.R., Poulin, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 197–231. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Regulation and stability of host-parasite population interactions. I. Regulatory processes. J. Anim. Ecol. 1978, 7, 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.; Burt, A. The comparative biology of parasite species diversity: Intestinal helminths of freshwater fishes. J. Anim. Ecol. 1991, 60, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, M.; Naumann, R.; Anjum, F.; Wolfe, J.; Munz, M.; Mende, C.; Roth-Aleperman, C. The neurobiology of Etruscan shrew active touch. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2011, 366, 3026–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morand, S.; Harvey, P.H. Mammalian metabolism, longevity and parasite species richness. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2000, 267, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Helminth Species | Microhabitat | n | p (%) | 95% CI |
| Mesocestoides sp. larvae | abdominal cavity | 1 | 0.60 | 0.10–3.96 |
| Joyeuxiella pasqualei larvae | liver | 2 | 1.20 | 0.10-3.96 |
| Staphylocystis claudevaucheri | intestine | 31 | 18.67 | 13.42–25.72 |
| Staphylocystis cerberensis | intestine | 5 | 3.01 | 1.01–6.85 |
| Staphylocystis banyulsensis | intestine | 14 | 8.43 | 4.46–13.13 |
| Hymenolepididae gen. sp. indet. | intestine | 9 | 5.42 | 2.27–9.47 |
| Pseudhymenolepis sp. | intestine | 47 | 28.31 | 21.42–35.39 |
| Overall cestodes | 80 | 48.19 | 40.30–55.78 | |
| Aonchotheca sp. | stomach | 2 | 1.20 | 0.10–3.96 |
| Nematoda gen. sp. larvae | stomach/abdominal cavity | 6 | 3.61 | 1.61–8.18 |
| Overall nematodes | 8 | 4.82 | 2.27–9.47 | |
| Overall parasitism prevalence | 84 | 50.60 | 43.00–58.21 |
| Helminth Species | B/C (N = 150) n/p (%) | 95% CI | Corsica (N = 16) n/p (%) | 95% CI |
| Mesocestoides sp. larvae | - | - | 1/6.25 | 0.16–30.00 |
| Joyeuxiella pasqualei larvae | 2/1.33 | 0.01–4.20 | - | - |
| Staphylocystis claudevaucheri | 29/19.33 | 13.17–26.10 | 2/12.50 | 1.56–37.96 |
| Staphylocystis cerberensis | 3/2.00 | 0.45–5.71 | 2/12.50 | 1.56–37.96 |
| Staphylocystis banyulsensis | 14/8.43 | 4.30–13.46 | - | - |
| Hymenolepididae gen. sp. indet. | 7/4.67 | 2.17–9.76 | - | - |
| Pseudhymenolepis sp. | 43/28.67 | 22.00–36.85 | 4/25.00 | 7.31–51.69 |
| Aonchotheca sp. | 2/1.33 | 0.01–4.20 | - | - |
| Nematoda gen. sp. larvae | 6/4.00 | 1.53–8.46 | - | - |
| Overall prevalence | 78/52.00 | 44.00–60.00 | 6/37.50 | 15.31–63.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Fuentes, M.V. First Data on the Helminth Community of the Smallest Living Mammal on Earth, the Etruscan Pygmy Shrew, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). Animals 2021, 11, 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072074
Galán-Puchades MT, Mas-Coma S, Valero MA, Fuentes MV. First Data on the Helminth Community of the Smallest Living Mammal on Earth, the Etruscan Pygmy Shrew, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). Animals. 2021; 11(7):2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072074
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalán-Puchades, María Teresa, Santiago Mas-Coma, María Adela Valero, and Màrius V. Fuentes. 2021. "First Data on the Helminth Community of the Smallest Living Mammal on Earth, the Etruscan Pygmy Shrew, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae)" Animals 11, no. 7: 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072074
APA StyleGalán-Puchades, M. T., Mas-Coma, S., Valero, M. A., & Fuentes, M. V. (2021). First Data on the Helminth Community of the Smallest Living Mammal on Earth, the Etruscan Pygmy Shrew, Suncus etruscus (Savi, 1822) (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). Animals, 11(7), 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072074









