An N-ethyl-N-Nitrosourea Mutagenesis Screen in Mice Reveals a Mutation in Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (Nrf1) Altering the DNA Methylation State and Correct Embryonic Development
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Embryo Dissections
Determination of GFP Expression in Erythrocytes
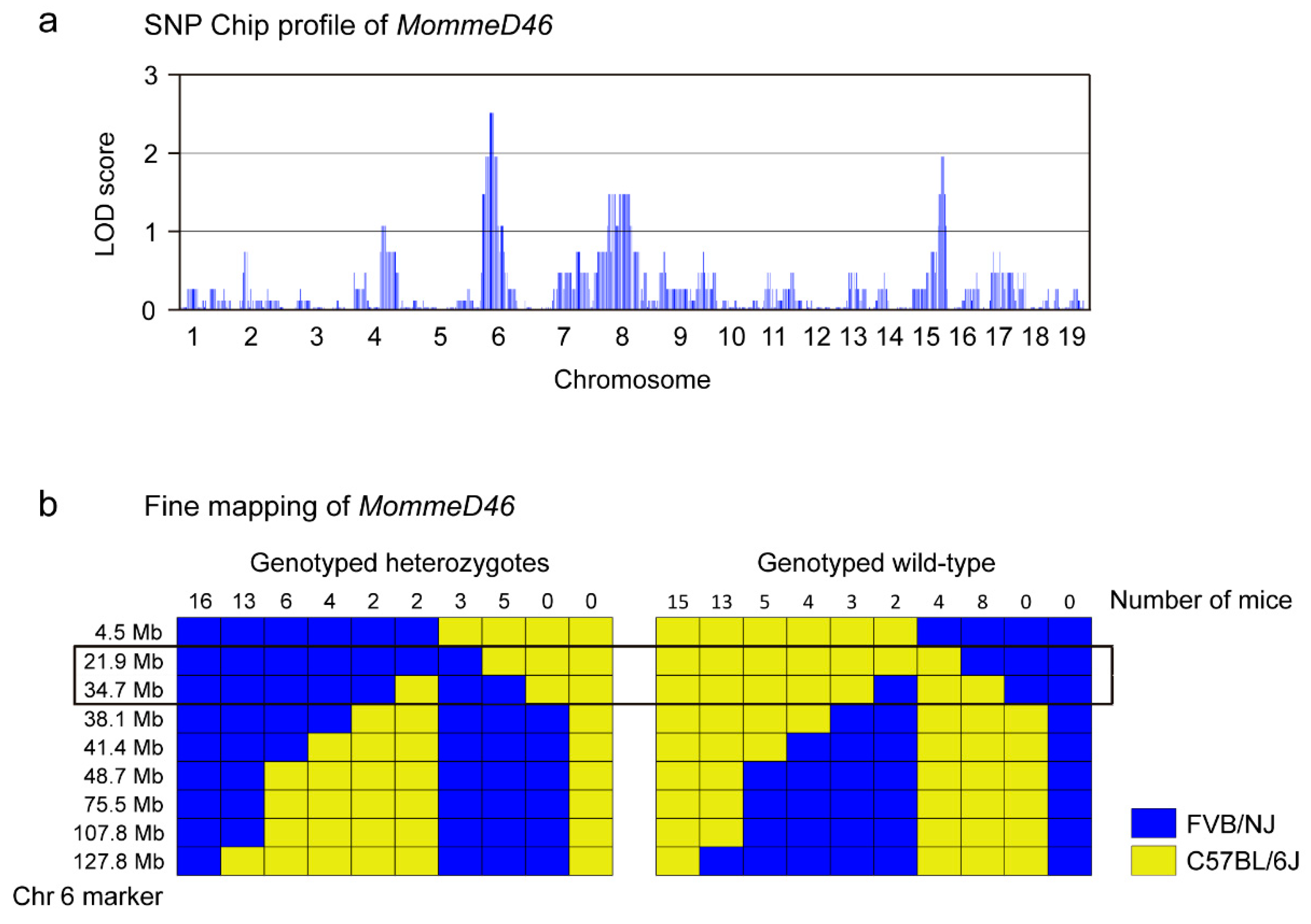
2.3. Linkage Analysis by SNP Chip
2.4. Whole Exome Sequencing
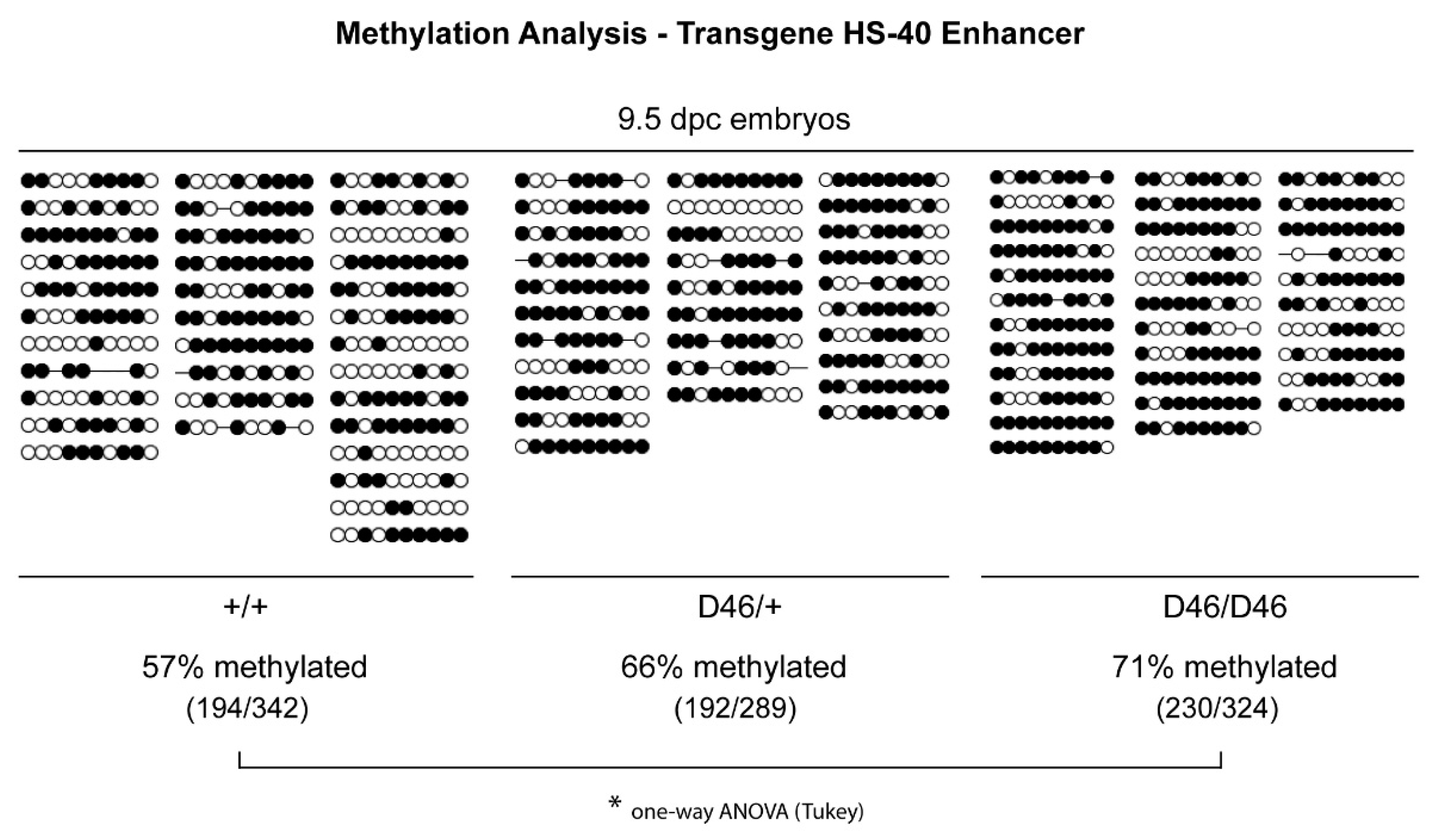
2.5. Methylation Analysis in the Transgene HS-40 Enhancer
2.6. Genotyping
2.7. Determination of Nrf1 mRNA Levels by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Determination of Nrf1 Protein Levels by Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MommeD46 Is an Enhancer of Variegation
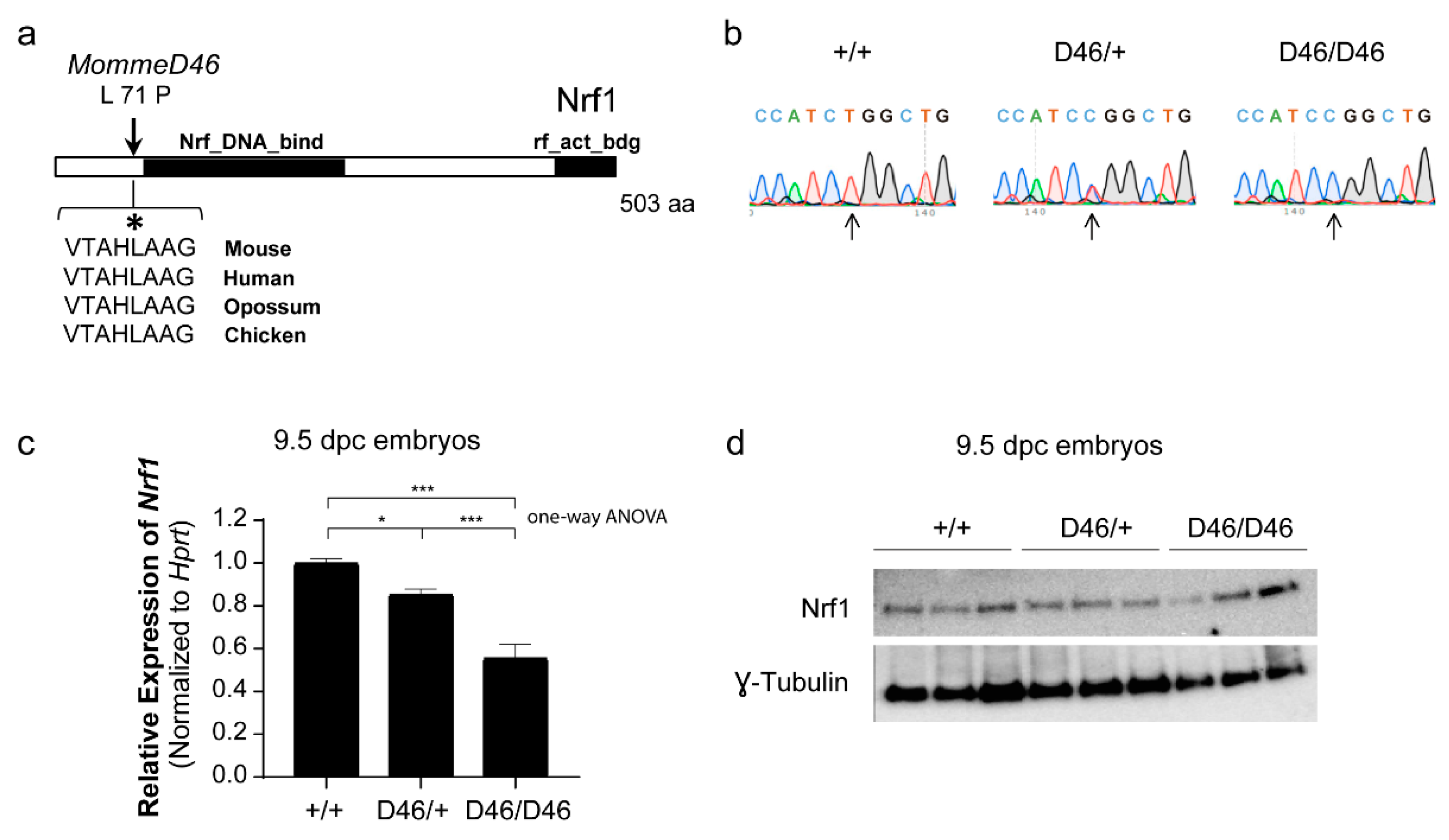
3.2. MommeD46 Carries a Point Mutation in the Nrf1 Gene
3.3. Nrf1 Mutants Display Enhanced DNA Methylation
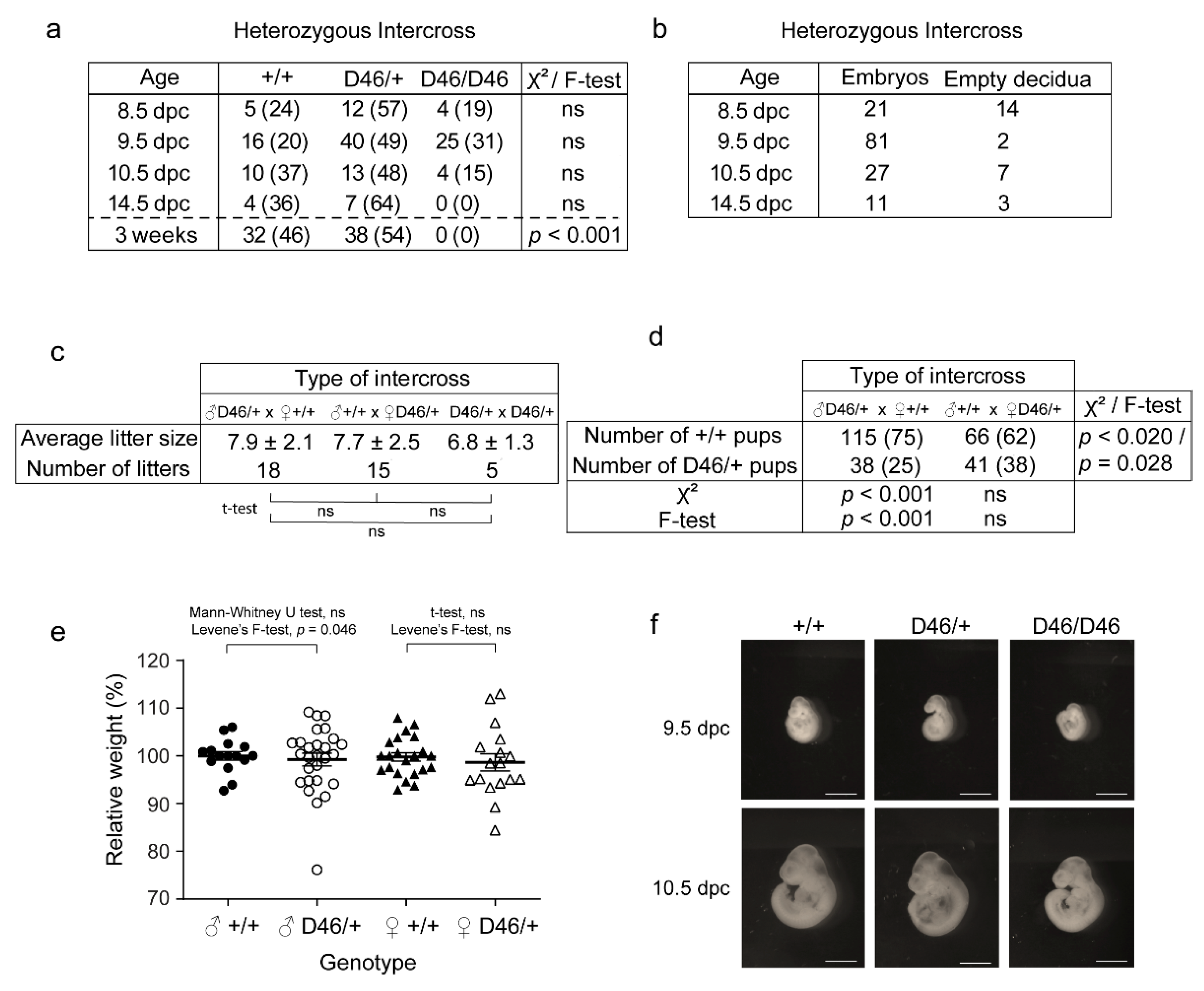
3.4. The Observed Hereditability of the Nrf1 Suggests Paternal Imprinting and Haploinsufficiency, and Normal Nrf1 Is Required for Normal Embryonic Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henikoff, S. Position-effect variegation after 60 years. Trends Genet. 1990, 6, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, R.; Szidonya, J.; Korge, G.; Sehnert, M.; Taubert, H.; Archoukieh, E.; Tschiersch, B.; Morawietz, H.; Wustmann, G.; Hoffmann, G.; et al. P transposon-induced dominant enhancer mutations of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1993, 133, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, G.; Wolff, I. Isolation of dominant suppressor mutations for position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1981, 182, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blewitt, M.E.; Vickaryous, N.K.; Hemley, S.J.; Ashe, A.; Bruxner, T.J.; Preis, J.I.; Arkell, R.; Whitelaw, E. An N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea screen for genes involved in variegation in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7629–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Preis, J.I.; Downes, M.; Oates, N.A.; Rasko, J.E.; Whitelaw, E. Sensitive flow cytometric analysis reveals a novel type of parent-of-origin effect in the mouse genome. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorolla, A.; Tallack, M.R.; Oey, H.; Harten, S.K.; Daxinger, L.C.; Magor, G.W.; Combes, A.N.; Ilsley, M.; Whitelaw, E.; Perkins, A.C. Identification of novel hypomorphic and null mutations in Klf1 derived from a genetic screen for modifiers of alpha-globin transgene variegation. Genomics 2015, 105, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daxinger, L.; Harten, S.K.; Oey, H.; Epp, T.; Isbel, L.; Huang, E.; Whitelaw, N.; Apedaile, A.; Sorolla, A.; Yong, J.; et al. An ENU mutagenesis screen identifies novel and known genes involved in epigenetic processes in the mouse. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blewitt, M.E.; Gendrel, A.V.; Pang, Z.; Sparrow, D.B.; Whitelaw, N.; Craig, J.M.; Apedaile, A.; Hilton, D.J.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; Brockdorff, N.; et al. SmcHD1, containing a structural-maintenance-of-chromosomes hinge domain, has a critical role in X inactivation. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Vickaryous, N.; Ashe, A.; Zamudio, N.; Youngson, N.; Hemley, S.; Stopka, T.; Skoultchi, A.; Matthews, J.; Scott, H.S.; et al. Modifiers of epigenetic reprogramming show paternal effects in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashe, A.; Morgan, D.K.; Whitelaw, N.C.; Bruxner, T.J.; Vickaryous, N.K.; Cox, L.L.; Butterfield, N.C.; Wicking, C.; Blewitt, M.E.; Wilkins, S.J.; et al. A genome-wide screen for modifiers of transgene variegation identifies genes with critical roles in development. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harten, S.K.; Bruxner, T.J.; Bharti, V.; Blewitt, M.; Nguyen, T.M.; Whitelaw, E.; Epp, T. The first mouse mutants of D14Abb1e (Fam208a) show that it is critical for early development. Mamm. Genome 2014, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harten, S.K.; Oey, H.; Bourke, L.M.; Bharti, V.; Isbel, L.; Daxinger, L.; Faou, P.; Robertson, N.; Matthews, J.M.; Whitelaw, E. The recently identified modifier of murine metastable epialleles, Rearranged L-Myc Fusion, is involved in maintaining epigenetic marks at CpG island shores and enhancers. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isbel, L.; Srivastava, R.; Oey, H.; Spurling, A.; Daxinger, L.; Puthalakath, H.; Whitelaw, E. Trim33 Binds and Silences a Class of Young Endogenous Retroviruses in the Mouse Testis; a Novel Component of the Arms Race between Retrotransposons and the Host Genome. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isbel, L.; Prokopuk, L.; Wu, H.; Daxinger, L.; Oey, H.; Spurling, A.; Lawther, A.J.; Hale, M.W.; Whitelaw, E. Wiz binds active promoters and CTCF-binding sites and is required for normal behaviour in the mouse. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemmers, R.J.; Tawil, R.; Petek, L.M.; Balog, J.; Block, G.J.; Santen, G.W.; Amell, A.M.; van der Vliet, P.J.; Almomani, R.; Straasheijm, K.R.; et al. Digenic inheritance of an SMCHD1 mutation and an FSHD-permissive D4Z4 allele causes facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy type 2. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leong, H.S.; Chen, K.; Hu, Y.; Lee, S.; Corbin, J.; Pakusch, M.; Murphy, J.M.; Majewski, I.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Alexander, W.S.; et al. Epigenetic regulator Smchd1 functions as a tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourke, L.M.; Del Monte-Nieto, G.; Outhwaite, J.E.; Bharti, V.; Pollock, P.M.; Simmons, D.G.; Adam, A.; Hur, S.S.; Maghzal, G.J.; Whitelaw, E.; et al. Loss of Rearranged L-Myc Fusion (RLF) results in defects in heart development in the mouse. Differentiation 2017, 94, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.J.; Scarpulla, R.C. Interaction of nuclear factors with multiple sites in the somatic cytochrome c promoter. Characterization of upstream NRF-1, ATF, and intron Sp1 recognition sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 14361–14368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, B.; Yu, G.; Gulick, T. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 controls myocyte enhancer factor 2A transcription to provide a mechanism for coordinate expression of respiratory chain subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11935–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virbasius, J.V.; Scarpulla, R.C. Activation of the human mitochondrial transcription factor A gene by nuclear respiratory factors: A potential regulatory link between nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression in organelle biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Puigserver, P.; Andersson, U.; Zhang, C.; Adelmant, G.; Mootha, V.; Troy, A.; Cinti, S.; Lowell, B.; Scarpulla, R.C.; et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 1999, 98, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gugneja, S.; Scarpulla, R.C. Serine phosphorylation within a concise amino-terminal domain in nuclear respiratory factor 1 enhances DNA binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18732–18739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Cuadrado, A.; Martín, M.; Noël, M.; Ruiz-Carrillo, A. Initiation binding repressor, a factor that binds to the transcription initiation site of the histone h5 gene, is a glycosylated member of a family of cell growth regulators [corrected]. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 6670–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhar, S.S.; Ongwijitwat, S.; Wong-Riley, M.T. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 regulates all ten nuclear-encoded subunits of cytochrome c oxidase in neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3120–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domcke, S.; Bardet, A.F.; Adrian Ginno, P.; Hartl, D.; Burger, L.; Schubeler, D. Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1. Nature 2015, 528, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, Q.; Su, J.; Ni, T.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; et al. NRF1 coordinates with DNA methylation to regulate spermatogenesis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Wan, J.; Su, Y.; Song, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Nguyen, H.N.; Shin, J.; Cox, E.; Rho, H.S.; Woodard, C.; et al. DNA methylation presents distinct binding sites for human transcription factors. eLife 2013, 2, e00726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, N.; Talib, S.Z.A.; Ratnacaram, C.K.; Low, D.; Bisteau, X.; Lee, J.H.S.; Pfeiffenberger, E.; Wollmann, H.; Tan, J.H.L.; Wee, S.; et al. CDK2 regulates the NRF1/Ehmt1 axis during meiotic prophase I. J. Cell. Biol. 2019, 218, 2896–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huo, L.; Scarpulla, R.C. Mitochondrial DNA instability and peri-implantation lethality associated with targeted disruption of nuclear respiratory factor 1 in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Jato, S.; Nicholls, R.D.; Driscoll, D.J.; Yang, T.P. Characterization of cis- and trans-acting elements in the imprinted human SNURF-SNRPN locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4740–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Jato, S.; Shan, J.; Khadake, J.; Heggestad, A.D.; Ma, X.; Johnstone, K.A.; Resnick, J.L.; Yang, T.P. Regulatory elements associated with paternally-expressed genes in the imprinted murine Angelman/Prader-Willi syndrome domain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyama, T.; Chen, C.K.; Wang, S.W.; Pan, P.; Ju, Z.; Wang, J.; Takada, S.; Klein, W.H.; Mao, C.A. Essential roles of mitochondrial biogenesis regulator Nrf1 in retinal development and homeostasis. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSimone, S.M.; White, K. The Drosophila erect wing gene, which is important for both neuronal and muscle development, encodes a protein which is similar to the sea urchin P3A2 DNA binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, T.S.; Burgess, S.M.; Amsterdam, A.H.; Allende, M.L.; Hopkins, N. not really finished is crucial for development of the zebrafish outer retina and encodes a transcription factor highly homologous to human Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1 and avian Initiation Binding Repressor. Development 1998, 125, 4369–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, D.; Usdin, K. Interaction of the transcription factors USF1, USF2, and alpha -Pal/Nrf-1 with the FMR1 promoter. Implications for Fragile X mental retardation syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4357–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Cogswell, M.; Hixson, K.; Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Russek, S.J. Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (NRF-1) Controls the Activity Dependent Transcription of the GABA-A Receptor Beta 1 Subunit Gene in Neurons. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.T.; Chen, H.I.; Chiou, R.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, A.M. A novel function of transcription factor alpha-Pal/NRF-1: Increasing neurite outgrowth. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.W.; Wang, J.L.; Jiang, M.S.; Hsu, C.H.; Chang, W.T.; Huang, A.M. Novel genes that mediate nuclear respiratory factor 1-regualted neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma IMR-32 cells. Gene 2013, 515, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, S.B.; Hong, C.H.; Liao, W.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, G.S.; Wei, Y.H.; Yu, H.S. Aberrant cell proliferation by enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis via mtTFA in arsenical skin cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Quan, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, T.; Hou, S.; Qiao, H.; Harismendy, O.; Wang, J.Y.J.; et al. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 promotes spheroid survival and mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6152–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Bhat, T.A.; Walsh, E.M.; Chaudhary, A.K.; O’Malley, J.; Rhim, J.S.; Wang, J.; Morrison, C.D.; Attwood, K.; Bshara, W.; et al. Cytochrome c Deficiency Confers Apoptosome and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in African-American Men with Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Leung, L.; Yen, T.S.; Lee, C.; Chan, J.Y. Liver-specific inactivation of the Nrf1 gene in adult mouse leads to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic neoplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4120–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohrin, M.; Shin, J.; Liu, Y.; Brown, K.; Luo, H.; Xi, Y.; Haynes, C.M.; Chen, D. Stem cell aging. A mitochondrial UPR-mediated metabolic checkpoint regulates hematopoietic stem cell aging. Science 2015, 347, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diman, A.; Boros, J.; Poulain, F.; Rodriguez, J.; Purnelle, M.; Episkopou, H.; Bertrand, L.; Francaux, M.; Deldicque, L.; Decottignies, A. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 and endurance exercise promote human telomere transcription. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veeranki, S.; Winchester, L.J.; Tyagi, S.C. Hyperhomocysteinemia associated skeletal muscle weakness involves mitochondrial dysfunction and epigenetic modifications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, N.; Pushpakumar, S.B.; Givvimani, S.; Kundu, S.; Metreveli, N.; James, D.; Bratcher, A.P.; Tyagi, S.C. Epigenetic regulation of aortic remodeling in hyperhomocysteinemia. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3411–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baar, K.; Song, Z.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Jones, T.E.; Han, D.H.; Nolte, L.A.; Ojuka, E.O.; Chen, M.; Holloszy, J.O. Skeletal muscle overexpression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 increases glucose transport capacity. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorolla, M.A.; Marqués, M.; Parisi, E.; Sorolla, A. An N-ethyl-N-Nitrosourea Mutagenesis Screen in Mice Reveals a Mutation in Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (Nrf1) Altering the DNA Methylation State and Correct Embryonic Development. Animals 2021, 11, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072103
Sorolla MA, Marqués M, Parisi E, Sorolla A. An N-ethyl-N-Nitrosourea Mutagenesis Screen in Mice Reveals a Mutation in Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (Nrf1) Altering the DNA Methylation State and Correct Embryonic Development. Animals. 2021; 11(7):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072103
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorolla, Maria Alba, Marta Marqués, Eva Parisi, and Anabel Sorolla. 2021. "An N-ethyl-N-Nitrosourea Mutagenesis Screen in Mice Reveals a Mutation in Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (Nrf1) Altering the DNA Methylation State and Correct Embryonic Development" Animals 11, no. 7: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072103
APA StyleSorolla, M. A., Marqués, M., Parisi, E., & Sorolla, A. (2021). An N-ethyl-N-Nitrosourea Mutagenesis Screen in Mice Reveals a Mutation in Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (Nrf1) Altering the DNA Methylation State and Correct Embryonic Development. Animals, 11(7), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072103




