Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. II. Sharks and Chimaeras
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origins of the Specimens
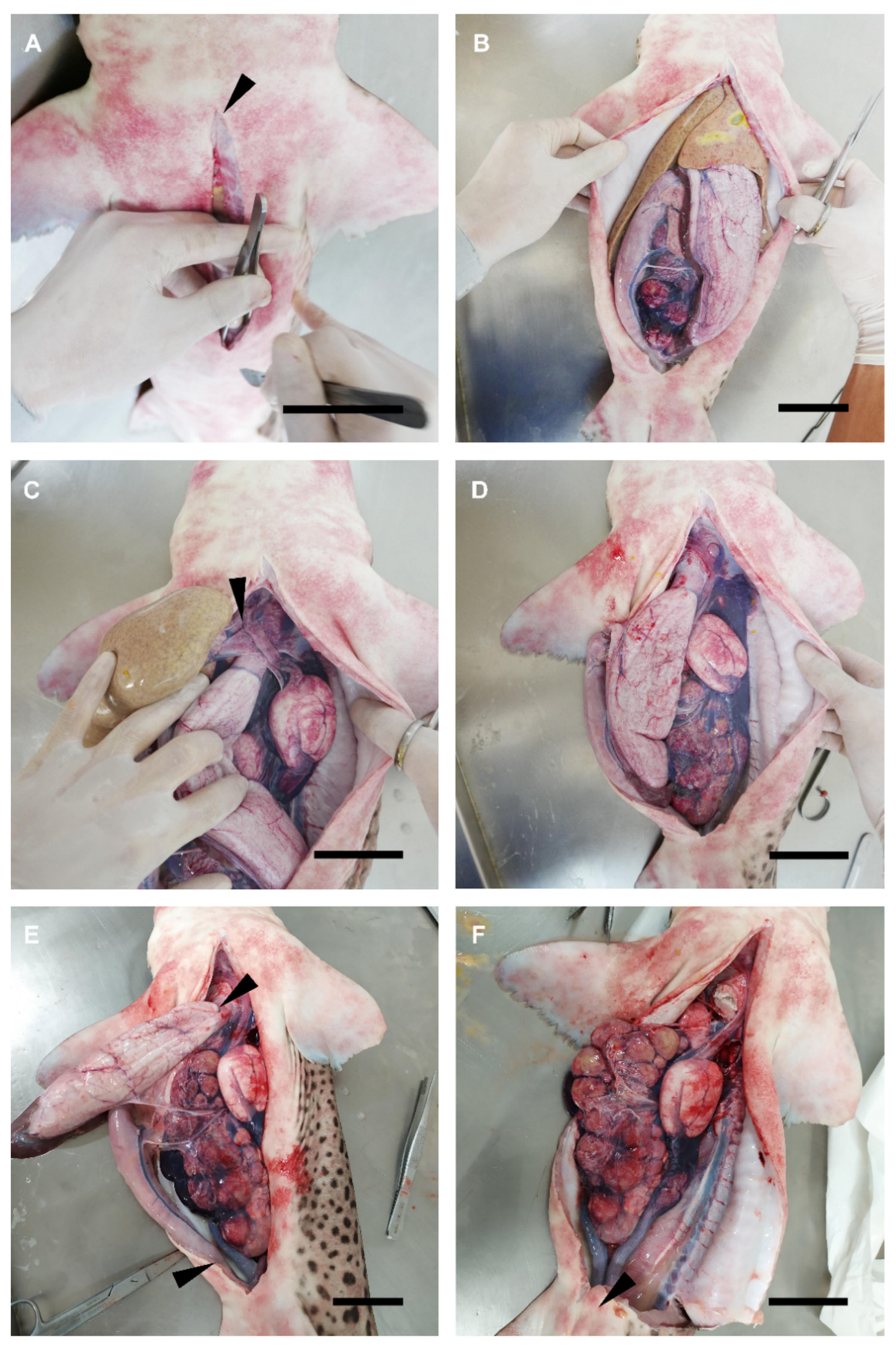
2.2. Dissection Procedure
2.3. Description of Reproductive Structures
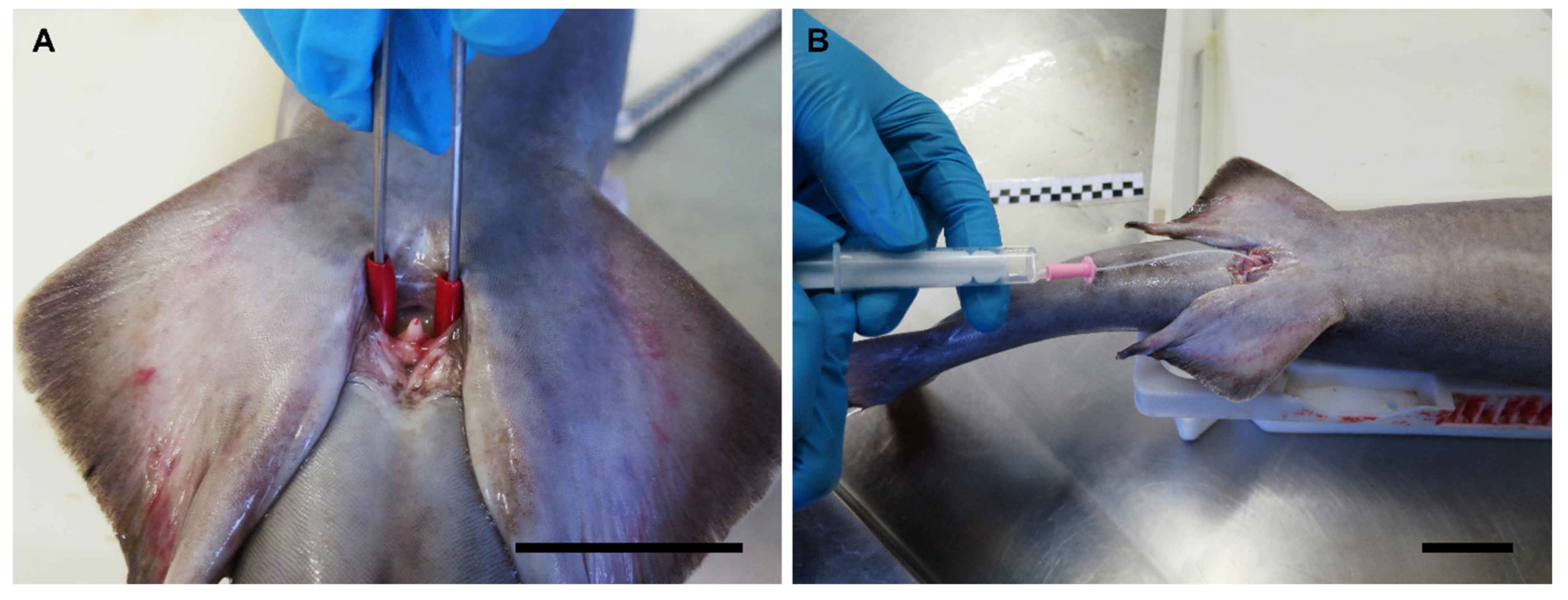
2.4. Sperm Collection
2.4.1. In Vivo Sperm Extraction
2.4.2. Postmortem Sperm Extraction
3. Results and Discussion
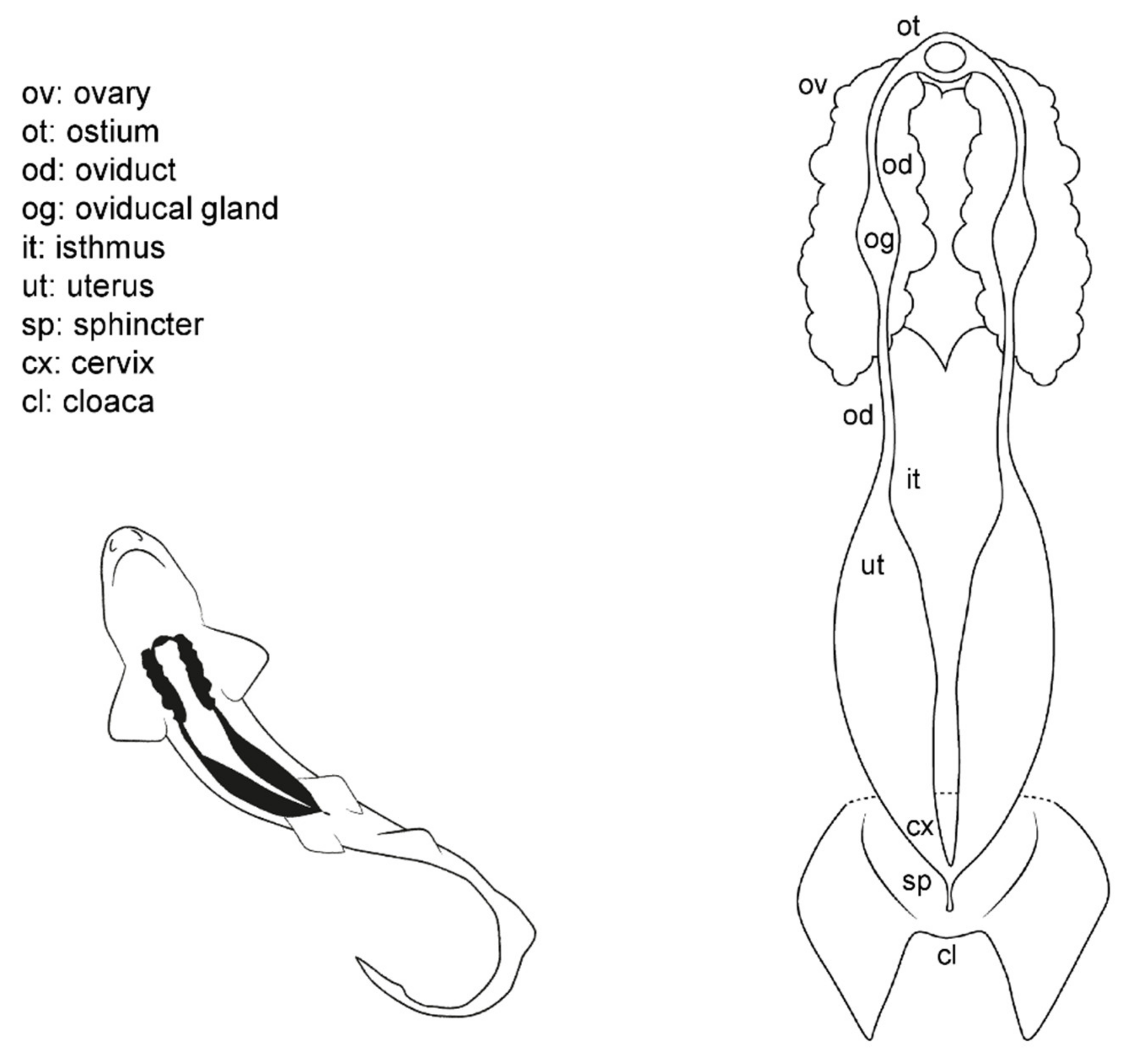
3.1. Female General Anatomy: Sharks
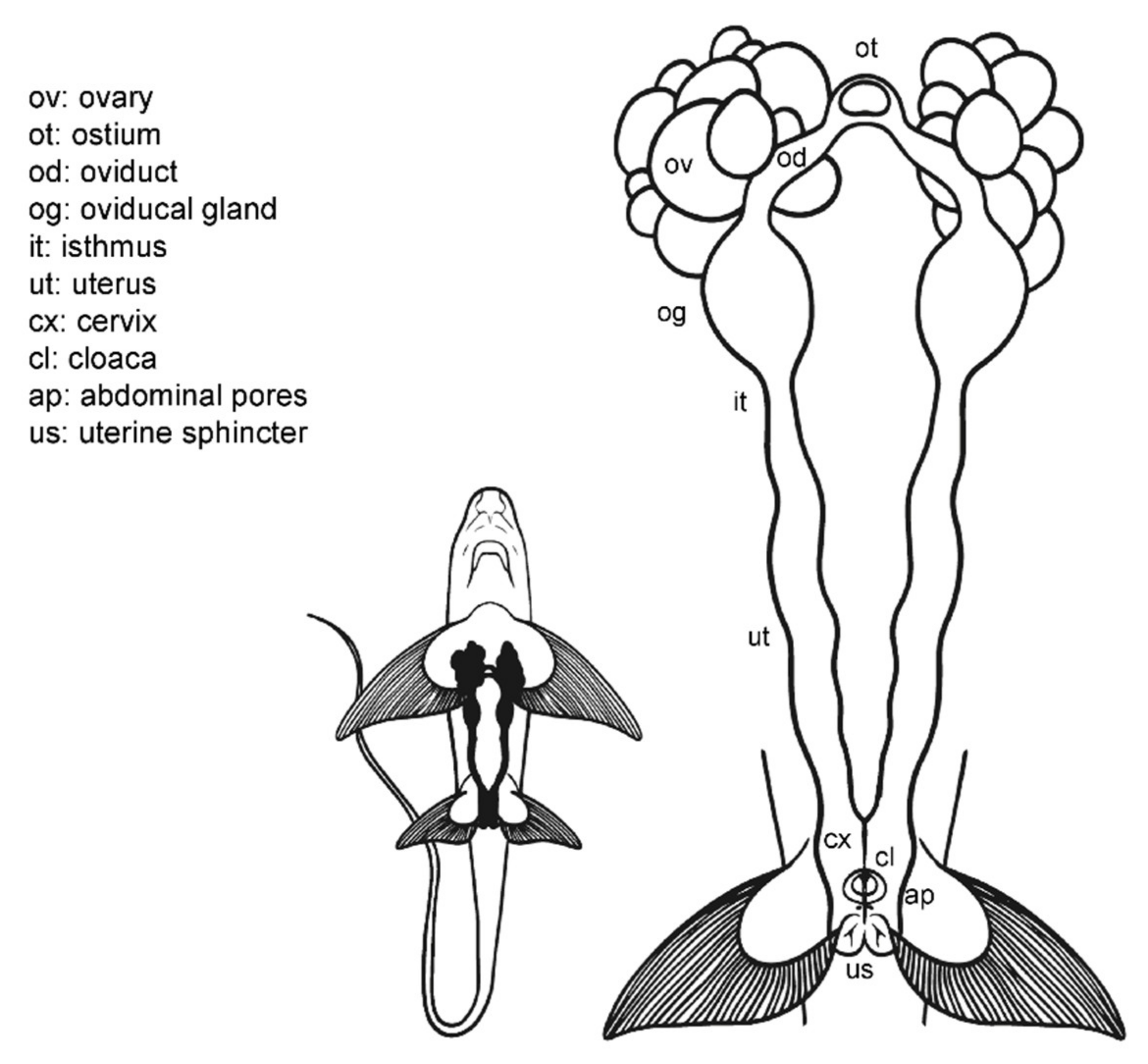
3.2. Female Anatomy: Chimaera monstrosa
3.3. Female Comparative Anatomy
3.4. Anatomic Notes for Artificial Insemination
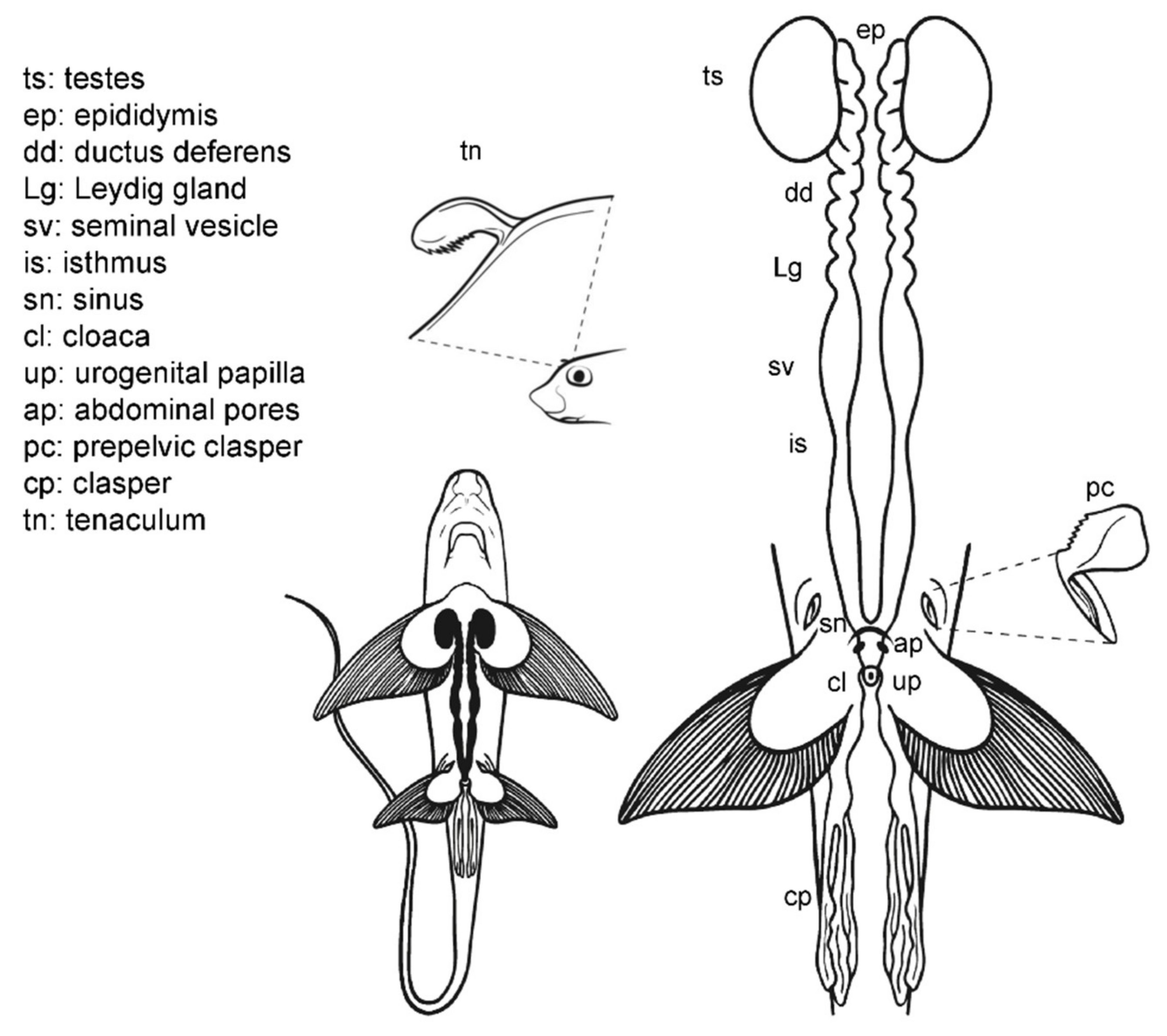
3.5. Male General Anatomy: Sharks
3.6. Male Anatomy: Chimaera monstrosa
3.7. Male Comparative Anatomy
3.8. Anatomic Notes for Sperm Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compagno, L.J.V. Alternative life-history styles of cartilaginous fishes in time and space. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1990, 28, 33–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J. The effects of fishing on sharks, rays, and chimaeras (chondrichthyans), and the implications for marine ecosystems. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 476–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Van der Laan, R. CAS-Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes. Available online: https://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Didier, D.A. Phylogeny and classification of extant Holocephali. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Heithaus, M.R., Musick, J.A., Carrier, J.C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Weigmann, S. Annotated checklist of the living sharks, batoids and chimaeras (Chondrichthyes) of the world, with a focus on biogeographical diversity. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 88, 837–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.L.; Cavanagh, R.D. Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras: The Status of the Chondrichthyan Fishes: Status Survey; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2005; Volume 63, ISBN 2831707005. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.B.; Lucifora, L.O.; Myers, R.A. The importance of habitat and life history to extinction risk in sharks, skates, rays and chimaeras. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Forrest, R.E. Life histories, population dynamics and extinction risks in chondrichthyans. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 639–679. [Google Scholar]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Fowler, S.L.; Musick, J.A.; Cavanagh, R.D.; Kyne, P.M.; Harrison, L.R.; Carlson, J.K.; Davidson, L.N.; Fordham, S.V.; Francis, M.P.; et al. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. Elife 2014, 3, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulvy, N.K.; Allen, D.J.; Ralph, G.M.; Walls, R.H.L. The Conservation Status of Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras in the Mediterranean Sea (Brochure); IUCN: Malaga, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pacoureau, N.; Rigby, C.L.; Kyne, P.M.; Sherley, R.B.; Winker, H.; Carlson, J.K.; Fordham, S.V.; Barreto, R.; Fernando, D.; Francis, M.P. Half a century of global decline in oceanic sharks and rays. Nature 2021, 589, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, E. Life History Patterns and Correlations in Sharks. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2000, 8, 299–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.I. Reproduction of Chondrichthyans. In Reproduction in Aquatic Animals; Yoshida, M., Asturiano, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 193–223. [Google Scholar]
- Musick, J.A.; Ellis, J.K.; Hamlett, W. Reproductive evolution of chondrichthyans. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes, Sharks, Batoids and Chimaeras; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2005; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Conrath, C.L.; Musick, J.A. Reproductive biology of elasmobranchs. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; Carrier, J.D., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 291–311. [Google Scholar]
- Janse, M.; Zimmerman, B.; Geerlings, L.; Brown, C.; Nagelkerke, L.A.J. Sustainable species management of the elasmobranch populations within European aquariums: A conservation challenge. J. Zoo Aquar. Res. 2017, 5, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Henningsen, A.D.; Smale, M.J.; Gordon, I.; Garner, R.; Marin-Osorno, R.; Kinnunen, N. Captive breeding and sexual conflict in elasmobranchs. In The Elasmobranch Husbandry Manual: Captive Care of Sharks, Rays and Their Relatives; Smith, M., Warmolts, D., Thoney, D., Hueter, R., Eds.; Special Publication of the Ohio Biological Survey: Columbus, OH, USA, 2004; pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, L.A.K.; Earley, R.L.; Ebert, D.A.; Cailliet, G.M. Maturity, fecundity, and reproductive cycle of the spotted ratfish. Mar. Biol. 2009, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.; Jones, R. The use of reproductive technologies in breeding programs for elasmobranchs in aquaria. In The Elasmobranch Husbandry Manual II: Recent Advances in the Care of Sharks, Rays and Their Relatives; Smith, M., Warmolts, D., Thoney, D., Hueter, R., Murray, M., Ezcurra, J., Eds.; Special Publication of the Ohio Biological Survey: Columbus, OH, USA, 2017; pp. 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Luer, C.A.; Walsh, C.J.; Bodine, A.B.; Wyffels, J.T. Normal embryonic development in the clearnose skate, Raja eglanteria, with experimental observations on artificial insemination. In Biology of Skates; Ebert, D.A., Sulikowski, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Daochai, C.; Keschumras, N.; Chansue, N.; Haetrakul, T. Preliminary of intra-vagina artificial insemination using fresh semen in Ocellate river stingray (Potamotrygon motoro). Thai J. Vet. Med. 2020, 50, 383–385. [Google Scholar]
- Penfold, L.M.; Wyffels, J.T. Reproductive science in sharks and rays. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1200, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Izawa, Y.; Kametuta, S.; Ikuta, H.; Isogai, T. Artificial insemination of the cloudy catshark. J. Jpn. Assoc. Zool. Gard. Aquar. 2003, 44, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, M.; Izawa, Y.; Kametsuta, S.; Ikuta, H.; Isogai, T. Artificial insemination of the white-spotted bamboo shark, Chiloscyllium plagiosum. J. Jpn. Assoc. Zool. Gard. Aquar. 2005, 46, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wyffels, J.T.; Adams, L.M.; Bulman, F.; Fustukjian, A.; Hyatt, M.W.; Feldheim, K.A.; Penfold, L.M. Artificial insemination and parthenogenesis in the whitespotted bamboo shark Chiloscyllium plagiosum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamikawa, S.; Morisawa, M. Acquisition, initiation and maintenance of sperm motility in the shark, Triakis scyllia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1996, 113, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.L.; Tanaka, S.H.O. Sperm Storage in Male Elasmobranchs: A Description and Survey. J. Morphol. 1994, 308, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyffels, J.T.; George, R.; Adams, L.; Adams, C.; Clauss, T.; Newton, A.; Hyatt, M.W.; Yach, C.; Penfold, L.M. Testosterone and semen seasonality for the sand tiger shark Carcharias taurus. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 102, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Salinas, P.; Gallego, V.; Asturiano, J.F. Development of Sperm Cryopreservation Protocols for Sharks and Rays: New Tools for Elasmobranch Conservation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 689089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wourms, J.P. Reproduction and development in chondrichthyan fishes. Am. Zool. 1977, 17, 379–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luer, C.A. Elasmobranchs (sharks, skates, and rays) as animal models for biomedical research. In Nonmammalian Animal Models for Biomedical Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Coolen, M.; Menuet, A.; Chassoux, D.; Compagnucci, C.; Henry, S.; Lévèque, L.; Da Silva, C.; Gavory, F.; Samain, S.; Wincker, P. The dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula: A reference in jawed vertebrates. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriano, E.R.; Pergolizzi, S.; Gangemi, J.; Kuciel, M.; Capillo, G.; Aragona, M.; Faggio, C. Immunohistochemical colocalization of G protein alpha subunits and 5-HT in the rectal gland of the cartilaginous fish Scyliorhinus canicula. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luer, C.A.; Walsh, C.J. Potential human health applications from marine biomedical research with elasmobranch fishes. Fishes 2018, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leigh-Sharpe, W.H. The comparative morphology of the secondary sexual characters of Holocephali and elasmobranch fishes. The claspers, clasper siphons, and clasper glands. J. Morphol. 1922, 36, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungersen, H.F.E. On the Appendices Genitales in the Greenland Shark, Somniosus Microcephalus (BL. Schn.), and Other Selachians. In Danish Ingolf-Expedition, 1895-1896; Luno, B., Dreyer, F., Eds.; Bianco Luno: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1899; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, P.W.; Gordon, W.H. The clasper-siphon sac mechanism in Squalus acanthias and Mustelus canis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1972, 42, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.J.P.; Walker, T.I.; Bell, J.D.; Reardon, M.B.; Ambrosio, C.E.; Almeida, A.; Hamlett, W.C. Male genital ducts and copulatory appendages in chondrichthyans. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes: Sharks, Batoids and Chimaeras; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2005; pp. 361–393. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, J.M. 2 Reproduction in Cartilaginous Fishes (Chondrichthyes). In Reproduction; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Donaldson, E.M.B.T.-F.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; Volume 9, pp. 31–95. ISBN 1546-5098. [Google Scholar]
- Del Mar Pedreros-Sierra, T.; Arrieta-Prieto, D.M.; Mejía-Falla, P.A. Reproductive system of females of the Magdalena river endemic stingray P otamotrygon magdalenae: Anatomical and functional aspects. J. Morphol. 2016, 277, 680–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-T.; Teshima, K.; Mizue, K. Studies on Sharks―IV Testes and Spermatogeneses in Selachians. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 1973, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, G.R.; Grier, H.J. Seasonal changes in shark testicular structure and spermatogenesis. J. Exp. Zool. 1992, 261, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, I.R.; Weaver, A.L.; Wourms, J.P. A novel set of structures within the elasmobranch, ovarian follicle. J. Morphol. 2011, 272, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutton, B.V. The elasmobranch ovary. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 247–276. ISBN 0429062907. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, H.L., Jr. Elasmobranch gonad structure: A description and survey. Copeia 1988, 1988, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B. Chimæeroid Fishes and Their Development; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1906. [Google Scholar]
- García-Salinas, P.; Gallego, V.; Asturiano, J.F. Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. I. Rays and Skates. Animals 2021, 11, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, D.A.; Dando, M. Field Guide to Sharks, Rays & Chimaeras of Europe and the Mediterranean; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 0691205981. [Google Scholar]
- Gillian, M.; King, D.R.N. Colour Atlas of Vetebrate Anatomy; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, G.L.; Brock, J.A. Necropsy Methods and Procedures for Elasmobranchs. In The Elasmobranch Husbandry Manual: Captive Care of Sharks, Rays and Their Relatives; Smith, M., Warmolts, D., Thoney, D., Hueter, R., Eds.; Special Publication of the Ohio Biological Survey; Ohio Biological Survey, Inc.: Columbus, OH, USA, 2004; pp. 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- De Iuliis, G.; Pulerà, D. The Dissection of Vertebrates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; ISBN 0124105009. [Google Scholar]
- Henningsen, A.D. Tonic immobility in 12 elasmobranchs: Use as an aid in captive husbandry. Zoo Biol. 1994, 13, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Marshall, A.; Correia, J.P.; Rupp, P. Elasmobranch Transport Techniques and Equipment. In Elasmobranch Husbandry Manual: Captive Care of Sharks, Rays, and Their Relatives; Smith, M., Warmolts, D., Thoney, D., Hueter, R., Eds.; Special Publication of the Ohio Biological Survey: Columbus, OH, USA, 2004; pp. 105–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kessel, S.T.; Hussey, N.E. Tonic immobility as an anaesthetic for elasmobranchs during surgical implantation procedures. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlett, W.C.; Knight, D.P.; Koob, T.J.; Jezior, M.; Luong, T.; Rozycki, T.; Brunette, N.; Hysell, M.K. Survey of oviducal gland structure and function in elasmobranchs. J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 282, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlett, W.C.; Koob, T.J. Female reproductive system. In Sharks, Skates and Rays: The Biology of Elasmobranch Fishes; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 398–443. [Google Scholar]
- Musick, J.A. Chondrichthyan reproduction. In Reproduction and Sexuality in Marine Fishes: Patterns and Processes; Cole, K.S., Ed.; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 3–19. ISBN 9780520264335. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.E.; Erzini, K.; Borges, T.C. Reproductive biology of the blackmouth catshark, Galeus melastomus (chondrichthyes: Scyliorhinidae) off the south coast of Portugal. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2005, 85, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.L. Reproduction in the blue shark, Prionace glauca. Fish. Bull. 1979, 77, 445–470. [Google Scholar]
- Capape, C.; Bradai, M.N.; Seck, A.A.; Diata, Y.; Tomasin, J.A.; Quignard, J.P. Aspects of the reproductive biology of the velvet belly, Etmopterus spinax (Elasmobranchii: Squalidae). Bull. Inst. Natn. Scien. Tech. Mer Salammbô 2001, 28, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Porcu, C.; Marongiu, M.F.; Follesa, M.C.; Bellodi, A.; Mulas, A.; Pesci, P.; Cau, A. Reproductive aspects of the velvet belly Etmopterus spinax (Chondrichthyes: Etmopteridae), from the central western Mediterranean Sea. Notes on gametogenesis and oviducal gland microstructure. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasse, P.P. Super-order des holocephali: Anatomie, ichtyologie, systematique. Trait. Zool. Anat. Syst. Biol. 1958, 13, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.D. Reproduction and Ageing of Australian Holocephalans and White-Fin Swell Shark. Ph.D. Thesis, Deakin University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giacomo, E.E.; Perier, M.R. Reproductive biology of the cockfish, Callorhynchus callorhynchus (Holocephali: Callorhynchidae), in Patagonian waters (Argentina). Fish. Bull. 1994, 92, 531–539. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez-Farías, J.F.; Lara-Mendoza, R.E. Notas sobre la morfología del aparato reproductor de la quimera, Hydrolagus melanophasma (Chondrichthyes, Holocephali), de la costa oeste de Baja California, México. Hidrobiológica 2014, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, T.; Prosser, L.C. Uterine response to 5-Hydroxytryptamine in clasper-siphon secretion of spiny dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Biological Bulletin: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 1963; Volume 125, pp. 384–385. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, H.L.; Carrier, J.C. Elasmobranch Courtship and Mating Behavior. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes: Sharks, Batoids, and Chimaeras; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2005; pp. 129–169. [Google Scholar]
- Whitney, N.M.; Pratt, H.L.; Carrier, J.C. Group courtship, mating behaviour and siphon sac function in the whitetip reef shark, Triaenodon obesus. Anim. Behav. 2004, 68, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, B.G.M.; Hamlett, W.C. Chondrichthyan spermatozoa and phylogeny. In Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Chondrichthyes: Sharks, Batoids, and Chimaeras; Hamlett, W.C., Ed.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2005; pp. 201–236. [Google Scholar]
- Malagrino, G.; Takemura, A.; Mizue, K. Studies on Holocephali―II On the Reproduction of Chimaera phantasma Jordan et Snyder Caught in the Coastal Waters of Nagasaki. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 1981, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, D.A. Some observations on the reproductive biology of the sixgill shark Hexanchus griseus (Bonnaterre, 1788) from South African waters. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 24, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daly, J. Clinical Studies. Available online: https://www.theaquariumvet.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/Jon-Daly-PhD-Clinical-Studies.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Stanley, H.P. Urogenital morphology in the chimaeroid fish Hydrolagus colliei (Lay and Bennett). J. Morphol. 1963, 112, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, L.H. Reproduction in the basking shark, Cetorhinus maximus (Gunner). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1950, 234, 247–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marongiu, M.F.; Porcu, C.; Bellodi, A.; Cuccu, D.; Mulas, A.; Follesa, M.C. Oviducal gland microstructure of Raja miraletus and Dipturus oxyrinchus (Elasmobranchii, Rajidae). J. Morphol. 2015, 276, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, H.L. The storage of spermatozoa in the oviducal glands of western North Atlantic sharks. In The Reproduction and Development of Sharks, Skates, Rays and Ratfishes; Wourms, J.P., Demski, L.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Follesa, M.C.; Carbonara, P. Atlas of the maturity stages of Mediterranean fishery resources. Gen. Fish. Comm. Mediterr. Stud. Rev. 2019, 99, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Field, I.C.; Meekan, M.G.; Buckworth, R.C.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Susceptibility of Sharks, Rays and Chimaeras to Global Extinction. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2009, 56, 275–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN/SSC IUCN Species Survival Commission Guidelines on the Use of Ex Situ Management for Species Conservation; Version 2; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–7.
- Grassmann, M.; McNeil, B.; Wharton, J. Sharks in captivity: The role of husbandry, breeding, education, and citizen science in shark conservation. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2017, 78, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.A.; Crook, D.A.; Pillans, R.D.; Smith, L.; Kyne, P.M. Sustainability of threatened species displayed in public aquaria, with a case study of Australian sharks and rays. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyffels, J.; Coco, C.; Schreiber, C.; Palmer, D.; Clauss, T.; Bulman, F.; George, R.; Pelton, C.; Feldheim, K.; Handsel, T. Natural environmental conditions and collaborative efforts provide the secret to success for sand tiger shark Carcharias taurus reproduction in aquaria. Zoo Biol. 2020, 39, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Common Name | Scientific Name | NM | NF | IUCN | Source | Range (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small-spotted catshark | Scyliorhinus canicula | 7 | 5 | LC | AQ/FM/BC | 38–57 |
| Nursehound | Scyliorhinus stellaris | 7 | 3 | NT | AQ | 75–144 |
| Blackmouth catshark | Galeus melastomus | 4 | 6 | LC | BC/FM | 48–69 |
| Blue shark | Prionace glauca | 2 | 1 | CR | ST | 290–297 |
| Velvet belly lanternshark | Etmopterus spinax | - | 4 | LC | BC | 33–40 |
| Little gulper shark | Centrophorus uyato | 1 | - | NE | BC | 86 |
| Bluntnose sixgill shark | Hexanchus griseus | 1 | - | LC | ST | 250 |
| Rabbitfish | Chimaera monstrosa | 2 | 2 | NT | BC | 104/112 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Salinas, P.; Gallego, V.; Asturiano, J.F. Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. II. Sharks and Chimaeras. Animals 2021, 11, 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082191
García-Salinas P, Gallego V, Asturiano JF. Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. II. Sharks and Chimaeras. Animals. 2021; 11(8):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082191
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Salinas, Pablo, Victor Gallego, and Juan F. Asturiano. 2021. "Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. II. Sharks and Chimaeras" Animals 11, no. 8: 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082191
APA StyleGarcía-Salinas, P., Gallego, V., & Asturiano, J. F. (2021). Reproductive Anatomy of Chondrichthyans: Notes on Specimen Handling and Sperm Extraction. II. Sharks and Chimaeras. Animals, 11(8), 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082191








