Polymorphisms of Codons 110, 146, 211 and 222 at the Goat PRNP Locus and Their Association with Scrapie in Greece
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
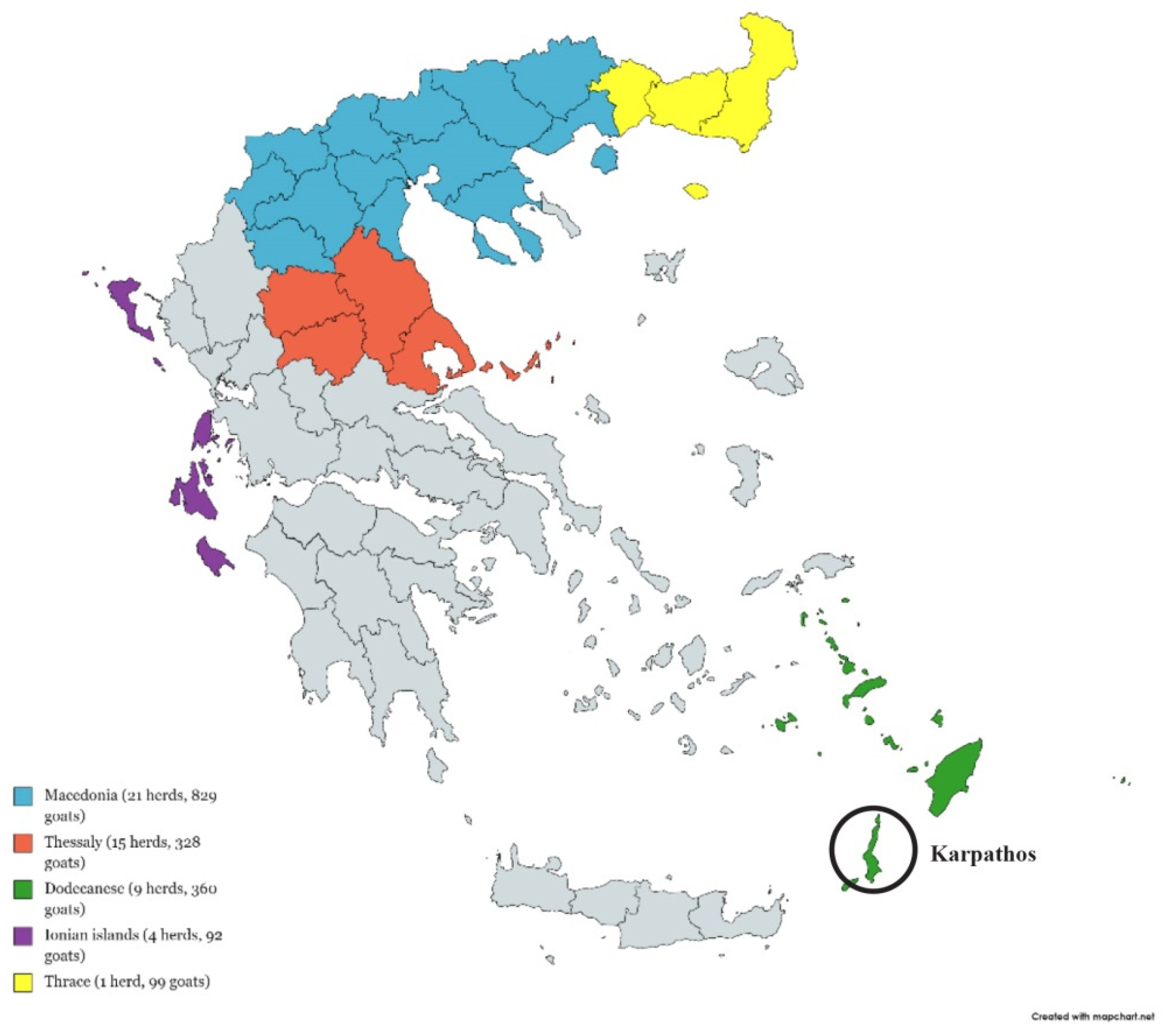
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Detection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethics Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FaoStat. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/?#data/QC (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Billinis, C.; Panagiotidis, C.H.; Psychas, V.; Argyroudis, S.; Nicolaou, A.; Leontides, S.; Papadopoulos, O.; Sklaviadis, T. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in natural goat scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.; Martin, S.; Jeffrey, M. Distinct profiles of PrPd immunoreactivity in the brain of scrapie- and BSE-infected sheep: Implications for differential cell targeting and PrP processing. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelle, P.L. Un cas de tremblante chez la chevre. Bull. Acad. Vet. Fr. 1942, 15, 294–295. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccari, G.; Panagiotidis, C.H.; Acin, C.; Peletto, S.; Barillet, F.; Acutis, P.L.; Bossers, A.; Langeveld, J.; Van Keulen, L.; Sklaviadis, T.; et al. State-of-the-art review of goat TSE in the European Union, with special emphasis on PRNP genetics and epidemiology. Veter. Res. 2009, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, C. and Groschup, M.H. Classical and Atypical Scrapie in Sheep and Goats. In Prions and Diseases; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boukouvala, E.; Katharopoulos, E.; Christoforidou, S.; Babetsa, M.; Ekateriniadou, L.V. Analysis of the PRNP gene polymor-phisms in healthy Greek sheep during 2012–2016. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2018, 69, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Espinosa, J.-C.; Andréoletti, O.; González, L.; Orge, L.; Juste, R.; Torres, J.-M. Goat K222-PrPC polymorphic variant does not provide resistance to atypical scrapie in transgenic mice. Veter. Res. 2016, 47, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detwiler, L.; Baylis, M. The epidemiology of scrapie. Rev. Sci. Tech. l’OIE 2003, 22, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotherston, J.; Renwick, C.; Stamp, J.; Zlotnik, I.; Pattison, I. Spread of scrapie by contact to goats and sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 1968, 78, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.; Martin, S.; Sisó, S.; Konold, T.; Ortiz-Peláez, A.; Phelan, L.; Goldmann, W.; Stewart, P.; Saunders, G.; Windl, O.; et al. High prevalence of scrapie in a dairy goat herd: Tissue distribution of disease-associated PrP and effect of PRNP genotype and age. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konold, T.; Thorne, L.; Simmons, H.A.; Hawkins, S.A.C.; Simmons, M.M.; González, L. Evidence of scrapie transmission to sheep via goat milk. BMC Veter. Res. 2016, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 999/2001, The TSE Regulation. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02001R0999-20150805 (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Bossers, A.; Schreuder, B.E.C.; Muileman, I.H.; Belt, P.B.G.M.; Smits, M.A. PrP genotype contributes to determining survival times of sheep with natural scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossers, A.; Belt, P.B.G.M.; Raymond, G.J.; Caughey, B.; De Vries, R.; Smits, M.A. Scrapie susceptibility-linked polymorphisms modulate the in vitro conversion of sheep prion protein to protease-resistant forms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4931–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, N.; Foster, J.D.; Goldmann, W.; Stear, M.; Hope, J.; Bostock, C. Natural scrapie in a closed flock of cheviot sheep occurs only in specific PrP genotypes. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, M.; Hoinville, L.J.; Hosie, B.D.; Hunter, N. Guidance on the use of PrP genotyping as an aid to the control of clinical scrapie. Scrapie Information Group. Veter. Rec. 1998, 142, 623–625. [Google Scholar]
- Elsen, J.-M.; Amigues, Y.; Schelcher, F.; Ducrocq, V.; Andreoletti, O.; Eychenne, F.; Khang, J.V.T.; Poivey, J.-P.; Lantier, F.; Laplanche, J.-L. Genetic susceptibility and transmission factors in scrapie: Detailed analysis of an epidemic in a closed flock of Romanov. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgeirsdottir, S.; Sigurdarson, S.; Thorisson, H.M.; Georgsson, G.; Palsdottir, A. PrP gene polymorphism and natural scrapie in Icelandic sheep. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tranulis, M.A.; Osland, A.; Bratberg, B.; Ulvund, M.J. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in sheep with natural scrapie and healthy controls in Norway. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, M.B.; Windig, J.J.; Hagenaars, T.J.; Bossers, A.; Davidse, A.; Van Zijderveld, F.G. Eradication of scrapie with selective breeding: Are we nearly there? BMC Veter. Res. 2010, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Pelaez, A.; Thompson, C.; Dawson, M. The impact of the national scrapie plan on the PRNP genotype distribution of the british national flock, 2002–2012. Veter. Rec. 2014, 174, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenaars, T.J.; Melchior, M.B.; Windig, J.J.; Bossers, A.; Davidse, A.; Van Zijderveld, F.G. Modelling of strategies for genetic control of scrapie in sheep: The importance of population structure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmann, W.; Hunter, N.; Chong, A.; Foster, J.; Hope, J. The shortest known prion protein gene allele occurs in goats, has only three octapeptide repeats and is non-pathogenic. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 3173–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Billinis, C.; Psychas, V.; Leontides, L.; Spyrou, V.; Argyroudis, S.; Vlemmas, I.; Leontides, S.; Sklaviadis, T.; Papadopoulos, O. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in healthy and scrapie-affected sheep in Greece. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Fan, B.; Fang, M.; Xu, W. PRNP polymorphisms in Chinese ovine, caprine and bovine breeds. Anim. Genet. 2004, 35, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.R.; Yu, S.L.; Yeon, S.H.; Le, J.H. Identification of single nucleotide polymorhisms in PRNP gene of korean native goats. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2009, 51, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Papasavva-Stylianou, P.; Windl, O.; Saunders, G.; Mavrikiou, P.; Toumazos, P.; Kakoyiannis, C. PrP gene polymorphisms in Cyprus goats and their association with resistance or susceptibility to natural scrapie. Veter. J. 2011, 187, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torricelli, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Ciullo, M.; Ceccobelli, S.; Chiappini, B.; Vaccari, G.; Capocefalo, A.; Conte, M.; Giovannini, S.; Lasagna, E.; et al. PRNP Polymorphisms in eight local goat populations/breeds from central and southern Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, J.J. Review: Update on Classical and Atypical Scrapie in Sheep and Goats. Veter. Pathol. 2019, 56, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccari, G.; Di Bari, M.A.; Morelli, L.; Nonno, R.; Chiappini, B.; Antonucci, G.; Marcon, S.; Esposito, E.; Fazzi, P.; Palazzini, N.; et al. Identification of an allelic variant of the goat PrP gene associated with re-sistance to scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papasavva-Stylianou, P.; Kleanthous, M.; Toumazos, P.; Mavrikiou, P.; Loucaides, P. Novel polymorphisms at codons 146 and 151 in the prion protein gene of Cyprus goats, and their association with natural scrapie. Veter. J. 2007, 173, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barillet, F.; Mariat, D.; Amigues, Y.; Faugeras, R.; Caillat, H.; Moazami-Goudarzi, K.; Rupp, R.; Babilliot, J.M.; Lacroux, C.; Lugan, S.; et al. Identification of seven haplotypes of the caprine PrP gene at codons 127, 142, 154, 211, 222 and 240 in French Alpine and Saanen breeds and their association with classical scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzalas, I.G.; Dovas, C.; Banos, G.; Papanastasopoulou, M.; Kritas, S.; Oevermann, A.; Papakostaki, D.; Evangelia, C.; Papadopoulos, O.; Seuberlich, T.; et al. Caprine PRNP polymorphisms at codons 171, 211, 222 and 240 in a Greek herd and their association with classical scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkiadaki, E.G.; Vaccari, G.; Ekateriniadou, L.V.; Agrimi, U.; Giadinis, N.D.; Chiappini, B.; Esposito, E.; Conte, M.; Nonno, R. PRNP genetic variability and molecular typing of natural goat scrapie isolates in a high number of infected flocks. Veter. Res. 2011, 42, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipanyula, M.; Chuma, I.; Brundtland, E.; Bårdsen, K.; Msalya, G.; Kifaro, G.; Ulvund, M. Prion protein (PrP) gene polymorphisms in small east african and norwegian white goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2014, 121, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.N.; Reynolds, J.O.; Waldron, D.F.; Schneider, D.; O’Rourke, K.I. Extended scrapie incubation time in goats singly heterozygous for PRNP S146 or K222. Gene 2012, 501, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrale, C.; Cancedda, M.G.; Pintus, D.; Masia, M.; Nonno, R.; Ru, G.; Carta, A.; Demontis, F.; Santucciu, C.; Ligios, C. Genetic and Pathological Follow-Up Study of Goats Experimentally and Naturally Exposed to a Sheep Scrapie Isolate. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10044–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kdidi, S.; Yahyaoui, M.; Conte, M.; Chiappini, B.; Hammadi, M.; Khorchani, T.; Vaccari, G. Genetic Variation in the prion protein gene (PRNP) of two tunisian goat populations. Animals 2021, 11, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acín, C.; Martín-Burriel, I.; Monleón, E.; Lyahyai, J.; Pitarch, J.L.; Serrano, C.; Monzón, M.; Zaragoza, P.; Badiola, J.J. Prion Protein Gene Variability in Spanish Goats. Inference through Susceptibility to Classical Scrapie Strains and Pathogenic Distribution of Peripheral PrPsc. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Fernandez Escamez, P.R.; Gironayes, R.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lindqvist, R.; et al. Genetic resistance to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE) in goats. EFSA J. 2017, 5, 4962. [Google Scholar]
- Migliore, S.; Puleio, R.; Loria, G.R. Scrapie Control in EU Goat Population: Has the Last Gap Been Overcome? Front. Veter. Sci. 2020, 7, 581969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouraki, S.; Gelasakis, A.; Alexandri, P.; Boukouvala, E.; Ekateriniadou, L.V.; Banos, G.; Arsenos, G. Genetic profile of scrapie codons 146, 211 and 222 in the PRNP gene locus in three breeds of dairy goats. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanata, E.; Humphreys-Panagiotidis, C.; Giadinis, N.D.; Papaioannou, N.; Arsenakis, M.; Sklaviadis, T. Perspectives of a scrapie resistance breeding scheme targeting Q211, S146 and K222 caprine PRNP alleles in greek goats. Veter. Res. 2014, 45, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonno, R.; Marin-Moreno, A.; Espinosa, J.C.; Fast, C.; Van Keulen, L.; Spiropoulos, J.; Lantier, I.; Andreoletti, O.; Pirisinu, L.; Di Bari, M.A.; et al. Characterization of goat prions demonstrates geographical variation of scrapie strains in Europe and reveals the composite nature of prion strains. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermeyer, S.; Eiden, M.; Toumazos, P.; Papasavva-Stylianou, P.; Ioannou, I.; Sklaviadis, T.; Panagiotidis, C.; Langeveld, J.; Bossers, A.; Kuczius, T.; et al. Identi-fication of prion protein gene polymorphisms in goats from Italian scrapie outbreaks. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Acutis, P.L.; Colussi, S.; Santagada, G.; Laurenza, C.; Maniaci, M.G.; Riina, M.V.; Peletto, S.; Goldmann, W.; Bossers, A.; Caramelli, M.; et al. Genetic variability of the PRNP gene in goat breeds from Northern and Southern Italy. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corbiere, F.; Perrin-Chauvineau, C.; Lacroux, C.; Costes, P.; Thomas, M.; Bremaud, I.; Martin, S.; Lugan, S.; Chartier, C.; Schelcher, F.; et al. PrP-associated resistance to scrapie in five highly infected goat herds. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroux, C.; Perrin-Chauvineau, C.; Corbière, F.; Aron, N.; Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Torres, J.M.; Costes, P.; Brémaud, I.; Lugan, S.; Schelcher, F.; et al. Genetic resistance to scrapie infection in experimentally challenged goats. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Espinosa, J.C.; Pintado, B.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Alamillo, E.; Miranda-Bedate, A.; Prieto, I.; Bossers, A.; Andreoletti, O.; Torres, J.M.; et al. Role of the goat K222-PrPC polymorphic variant in prion infection resistance. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.; Guglielmetti, C.; Ingravalle, F.; Brusadore, S.; Langeveld, J.P.M.; Ekateriniadou, L.V.; Andréoletti, O.; Casalone, C.; Acutis, P.L. Low fraction of the 222K PrP variant in the protease-resistant moiety of PrPres in heterozygous scrapie positive goats. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, J.P.M.; Pirisinu, L.; Jacobs, J.G.; Mazza, M.; Lantier, I.; Simon, S.; Andréoletti, O.; Acin, C.; Esposito, E.; Fast, C.; et al. Four types of scrapie in goats differentiated from each other and bovine spongiform encephalopathy by biochemical methods. Veter. Res. 2019, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmann, W.; Marier, E.; Stewart, P.; Konold, T.; Street, S.; Langeveld, J.; Windl, O.; Ortiz-Pelaez, A. Prion protein genotype survey confirms low frequency of scrapie-resistant K222 allele in british goat herds. Veter. Rec. 2016, 178, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattison, I.; Gordon, W.; Millson, G. Experimental Production of Scrapie in Goats. J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1959, 69, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acín, C.; Bolea, R.; Monzón, M.; Monleón, E.; Moreno, B.; Filali, H.; Marín, B.; Sola, D.; Betancor, M.; Guijarro, I.; et al. Classical and atypical scrapie in sheep and goats. Review on the etiology, genetic factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and control measures of both diseases. Animals 2021, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Codon for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) | Primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| 110(T/P) | TCAGTGGAACAAGCCCAGTAAG | AGCAGCTCCTGCCACATG |
| 146(N/S) | GCCATGAGCAGGCCTCTTATA | GGGTAACGGTACATGTTTTCACGAT |
| 146(N/D) | GCCATGAGCAGGCCTCTT | GGGTAACGGTACATGTTTTCACGAT |
| 211(R/Q) | GAACTTCACCGAAACTGACATCAAG | ACTGGGTGATGCACATTTGCT |
| 222(Q/K) | TGGTGGAGCAAATGTGCATCA | GGGAAGAAAAGAGGATCACACTTG |
| Probe * | ||
| FAM | VIC® | |
| 110(T/P) | TCATGTTGGGTTTTGG | CTTCATGTTGGTTTTTGG |
| 146(N/S) | TTTTGGCAGTGACTATG | CATTTTGGCAATGACTATG |
| 146(N/D) | CATTTTGGCAATGACT | ATACATTTTGGCGATGACT |
| 211(R/Q) | AATGGAGCAAGTGGTG | ATAATGGAGCGAGTGGTG |
| 222(Q/K) | CTGGGATTCTCTCTTGTACTG | TGGGATTCTCTCTGGTACTG |
| Brain Samples | Blood Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I. Scrapie-Positive | II. Scrapie-Negative | III. Scrapie-Positive Herds | IV. Scrapie-Negative Herds | ||
| Count (%) | Count (%) | Count (%) | Count (%) | ||
| Codon 110 * | n = 282 | n = 167 | n = 241 | n = 727 | |
| Genotype | TT | 282 (100.0) | 158 (94.6) | 227 (94.2) | 662 (91.1) |
| TP | 0 (0.0) | 9 (5.4) | 14 (5.8) | 63 (8.7) | |
| PP | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.3) | |
| Allele | T | 564 (100.0) | 325 (97.3) | 468 (97.1) | 1387 (95.4) |
| P | 0 (0.0) | 9 (2.7) | 14 (2.9) | 67 (4.6) | |
| Codon 146 | n = 282 | n = 243 | n = 241 | n = 1467 | |
| Genotype | NN | 281 (99.6) | 237 (97.5) | 235 (97.5) | 1394 (95.0) |
| ND | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 26* (1.8) | |
| NS | 1 (0.4) | 6 (2.5) | 6 (2.5) | 44 (3.0) | |
| DD | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.1) | |
| SS | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.1) | |
| DS | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Allele | N | 563 (99.8) | 480 (98.8) | 476 (98.8) | 2860 (97.5) |
| S | 1 (0.2) | 6 (1.2) | 6 (1.2) | 46 (1.6) | |
| D | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 28 (0.9) | |
| Codon 211 * | n = 282 | n = 243 | n = 241 | n = 1467 | |
| Genotype | RR | 270 (95.7) | 230 (94.7) | 197 (81.7) | 1406 (95.8) |
| RQ | 12 (4.3) | 13 (5.3) | 44 (18.3) | 61 (4.2) | |
| 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Allele | R | 552 (97.9) | 473 (97.3) | 438 (90.9) | 2873 (97.9) |
| Q | 12 (2.1) | 13 (2.7) | 44 (9.1) | 61 (2.1) | |
| Codon 222 * | n = 282 | n = 243 | n = 241 | n = 1467 | |
| Genotype | 269 (95.4) | 226 (93.0) | 232 (96.3) | 1418 (96.7) | |
| QK | 13 (4.6) | 17 (7.0) | 9 (3.7) | 49 (3.3) | |
| KK | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Allele | Q | 551 (97.7) | 469 (96.5) | 473 (98.1) | 2885 (98.3) |
| K | 13 (2.3) | 17 (3.5) | 9 (1.9) | 49 (1.7) | |
| Brain Samples (n = 525) | ||||||||
| Codon | Genotype | % (Number of Animals) | B | SE | p-Value | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| 146 | NS | 1.3 (7) | −2.00 | 1.08 | 0.065 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 1.13 |
| NN | 98.7 (518) | Ref. | ||||||
| 211 | RQ | 4.8 (25) | −0.27 | 0.41 | 0.507 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 1.70 |
| RR | 95.2 (500) | Ref. | ||||||
| 222 | QK | 5.7 (30) | −0.47 | 0.38 | 0.216 | 0.63 | 0.30 | 1.32 |
| 94.3 (495) | Ref. | |||||||
| Constant | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.024 | 1.24 | - | - | ||
| Blood samples (n = 1708) | ||||||||
| Codon | Genotype | % (Number of animals) | B | SE | p-value | Odds ratio | 95% CI | |
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| 146 | DD | 0.1 (1) | NV | |||||
| SS | 0.1 (2) | NV | ||||||
| ND | 1.5 (26) | NV | ||||||
| NS | 2.9 (50) | −0.16 | 0.45 | 0.716 | 0.85 | 0.35 | 2.05 | |
| NN | 95.4 (1629) | Ref. | ||||||
| 211 | RQ | 6.1 (105) | 1.73 | 0.22 | 0.000 | 5.62 | 3.68 | 8.59 |
| RR | 93.9 (1603) | Ref. | ||||||
| 222 | QK | 3.4 (58) | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.659 | 1.18 | 0.57 | 2.46 |
| 96.6 (1650) | Ref. | |||||||
| Constant | −1.95 | 0.08 | 0.000 | 0.14 | - | - | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gelasakis, A.I.; Boukouvala, E.; Babetsa, M.; Katharopoulos, E.; Palaska, V.; Papakostaki, D.; Giadinis, N.D.; Loukovitis, D.; Langeveld, J.P.M.; Ekateriniadou, L.V. Polymorphisms of Codons 110, 146, 211 and 222 at the Goat PRNP Locus and Their Association with Scrapie in Greece. Animals 2021, 11, 2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082340
Gelasakis AI, Boukouvala E, Babetsa M, Katharopoulos E, Palaska V, Papakostaki D, Giadinis ND, Loukovitis D, Langeveld JPM, Ekateriniadou LV. Polymorphisms of Codons 110, 146, 211 and 222 at the Goat PRNP Locus and Their Association with Scrapie in Greece. Animals. 2021; 11(8):2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082340
Chicago/Turabian StyleGelasakis, Athanasios I., Evridiki Boukouvala, Maria Babetsa, Efstathios Katharopoulos, Vayia Palaska, Dimitra Papakostaki, Nektarios D. Giadinis, Dimitrios Loukovitis, Jan P. M. Langeveld, and Loukia V. Ekateriniadou. 2021. "Polymorphisms of Codons 110, 146, 211 and 222 at the Goat PRNP Locus and Their Association with Scrapie in Greece" Animals 11, no. 8: 2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082340
APA StyleGelasakis, A. I., Boukouvala, E., Babetsa, M., Katharopoulos, E., Palaska, V., Papakostaki, D., Giadinis, N. D., Loukovitis, D., Langeveld, J. P. M., & Ekateriniadou, L. V. (2021). Polymorphisms of Codons 110, 146, 211 and 222 at the Goat PRNP Locus and Their Association with Scrapie in Greece. Animals, 11(8), 2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082340







