Suitability of Protein Content Measured by MilkoScan FT-Plus Milk Analyzer to Evaluate Bovine and Ovine Colostrum Quality
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Colostrum Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, R.L.; Tyler, J.W.; Schultz, L.G.; Tessman, R.K.; Hostetler, D.E. Management strategies to decrease calf death losses in beef herds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beam, A.L.; Lombard, J.E.; Kopral, C.A.; Garber, L.P.; Winter, A.L.; Hicks, J.A.; Schlater, J.L. Prevalence of failure of passive transfer of immunity in newborn heifer calves and associated management practices on US dairy operations. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3973–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S.G.; Siegel, M.J.; Knowlton, B.J. Sheep immunoglobulins and their transmission to the neonatal lamb. N. Z. Vet. J. 1977, 25, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Poindron, P. From birth to colostrum: Early steps leading to lamb survival. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2006, 46, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bovine Alliance on Management and Nutrition. A Guide to Colostrum and Colostrum Management for Dairy Calves; American Feed Industry Association: Arlington, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, A.G.; Reneau, J.K.; Williams, J.B. Factors affecting IgG concentration in day-old lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 45, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turquino, C.F.; Flaiban, K.K.M.C.; Lisbôa, J.A.N. Transferência de imunidade passiva em cordeiros de corte manejados extensivamente em clima tropical. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2011, 31, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godden, S.M.; Haines, D.M.; Konkol, K.; Peterson, J. Improving passive transfer of immunoglobulins in calves. II: Interaction between feeding method and volume of colostrum fed. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, E.C.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Gross, J.J. Short communication: Comparative estimation of colostrum quality by Brix refractometry in bovine, caprine, and ovine colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulliksen, S.M.; Lie, K.I.; Sølverød, L.; Østerås, O. Risk factors associated with colostrum quality in Norwegian dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, K.M.; Conrad, E.; Lago, A.; Campbell, J.; Quigley, J.; Tyler, H. Nationwide evaluation of quality and composition of colostrum on dairy farms in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabatabaei, S.; Nikbakht, G.; Vatankhah, M.; Sharifi, H.; Alidadi, N. Variation in colostral immunoglobulin G concentration in fat tailed sheep and evaluation of methods for estimation of colostral immunoglobulin content. Acta Vet. Brno 2013, 82, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelsinger, S.L.; Smith, A.M.; Jones, C.M.; Heinrichs, A.J. Comparison of radial immunodiffusion and ELISA for quantification of bovine immunoglobulin G in colostrum and plasma. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 4084–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Løkke, M.M.; Engelbrecht, R.; Wiking, L. Covariance structures of fat and protein influence the estimation of IgG in bovine colostrum. J. Dairy Res. 2016, 83, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopreiato, V.; Ceniti, C.; Trimboli, F.; Fratto, E.; Marotta, M.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M. Evaluation of the capillary electrophoresis method for measurement of immunoglobulin concentration in ewe colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6465–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, J. Using the Colostrometer to Measure Colostrum Quality. 1998. Available online: http://www.americanprotein.com/calf/calfnotes/APCCN22.htm (accessed on 12 July 2017).
- Bartier, A.L.; Windeyer, M.C.; Doepel, L. Evaluation of on-farm tools for colostrum quality measurement. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, J.D.; Lago, A.; Chapman, C.; Erickson, P.; Polo, J. Evaluation of the Brix refractometer to estimate immunoglobulin G concentration in bovine colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Carbonara, A.O.; Heremans, J.F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 1965, 2, 235-IN6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, D.E.; Constable, P.D.; Maunsell, F.P.; McCoy, G.C. Factors associated with colostral specific gravity in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, M.J.; Valderrama, X.; Haines, D.; Alomar, D. Prediction of immunoglobulin G content in bovine colostrum by near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsohaby, I.; McClure, J.T.; Hou, S.; Riley, C.B.; Shaw, R.A.; Keefe, G.P. A novel method for the quantification of bovine colostral immunoglobulin G using infrared spectroscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsohaby, I.; McClure, J.T.; Cameron, M.; Heider, L.C.; Keefe, G.P. Rapid assessment of bovine colostrum quality: How reliable are transmission infrared spectroscopy and digital and optical refractometers? J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, A.; Sierra, D.; Luengo, C.; Corrales, J.C.; de la Fe, C.; Morales, C.T.; Contreras, A.; Gonzalo, C. Evaluation of the MilkoScan FT 6000 Milk Analyzer for Determining the Freezing Point of Goat’s Milk Under Different Analytical Conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lérias, J.R.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Suárez-Trujillo, A.; Castro, N.; Pourlis, A.; Almeida, A.M. The mammary gland in small ruminants: Major morphological and functional events underlying milk production—A review. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mech, A.; Dhali, A.; Baruah, K.K.; Singh, R.K.; Mondal, S.K.; Rajkhowa, C. Effect of method and time of first colostrum feeding on serum immunoglobulin concentration, health status and body weight gain in mithun (Bos frontalis) calves. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 95, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolinec, M.; Bíro, D.; Gálik, B.; Šimko, M.; Juráček, M.; Kanka, T.; Schubertová, Z. Changes in the nutrient content of colostrum of sows during parturition. Res. Pig. Breeds 2012, 6, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bielmann, V.; Gillan, J.; Perkins, N.R.; Skidmore, A.L.; Godden, S.; Leslie, K.E. An evaluation of Brix refractometry instruments for measurement of colostrum quality in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3713–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, S.I.; Jayarao, B.M.; Heinrichs, A.J. A survey of bovine colostrum composition and colostrum management practices on Pennsylvania dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chigerwe, M.; Tyler, J.W.; Middleton, J.R.; Spain, J.N.; Dill, J.S.; Steevens, B.J. Comparison of four methods to assess colostral IgG concentration in dairy cows. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 233, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sabbagh, T.A.; Swanson, L.V.; Thompson, J.M. The effect of ewe body condition at lambing on colostral immunoglobulin G concentration and lamb performance. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 2860–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, T.J.; Hammer, C.J.; Luther, J.S.; Carlson, D.B.; Taylor, J.B.; Redmer, D.A.; Neville, T.L.; Reed, J.J.; Reynolds, L.P.; Caton, J.S. Effects of gestational plane of nutrition and selenium supplementation on mammary development and colostrum quality in pregnant ewe lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, R.P.; Gaskins, C.T.; Hillers, J.K.; Parker, C.F.; McGuire, T.C. Genetic and environmental factors affecting immunoglobulin G1 concentrations in ewe colostrum and lamb serum. J. Anim. Sci. 1988, 66, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Zamiri, M.J.; Safdarian, M. Effects of nutritional level during late pregnancy on colostral production and blood immunoglobulin levels of Karakul ewes and their lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 75, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleenor, W.A.; Stott, G.H. Hydrometer Test for Estimation of Immunoglobulin Concentration in Bovine Colostrum1. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapper, L.W.; Copestake, D.E.J.; Otter, D.E.; Indyk, H.E. Analysis of bovine immunoglobulin G in milk, colostrum and dietary supplements: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirk, S.M.; Collins, M. Managing the production, storage, and delivery of colostrum. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2004, 20, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, D.J.; Murray, L. Making the most of colostrum at lambing. Vet. Rec. 1986, 118, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.C.C.; Alves, N.G.G.; Ascari, I.J.J.; Junqueira, F.B.B.; Coutinho, A.S.S.; Lima, R.R.R.; Pérez, J.R.O.R.O.; De Paula, S.O.O.; Furusho-Garcia, I.F.F.; Abreu, L.R.R. Colostrum composition of Santa Inês sheep and passive transfer of immunity to lambs. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3706–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrill, K.M.; Robertson, K.E.; Spring, M.M.; Robinson, A.L.; Tyler, H.D. Validating a refractometer to evaluate immunoglobulin G concentration in Jersey colostrum and the effect of multiple freeze–thaw cycles on evaluating colostrum quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Time | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine Colostrum | ||||||
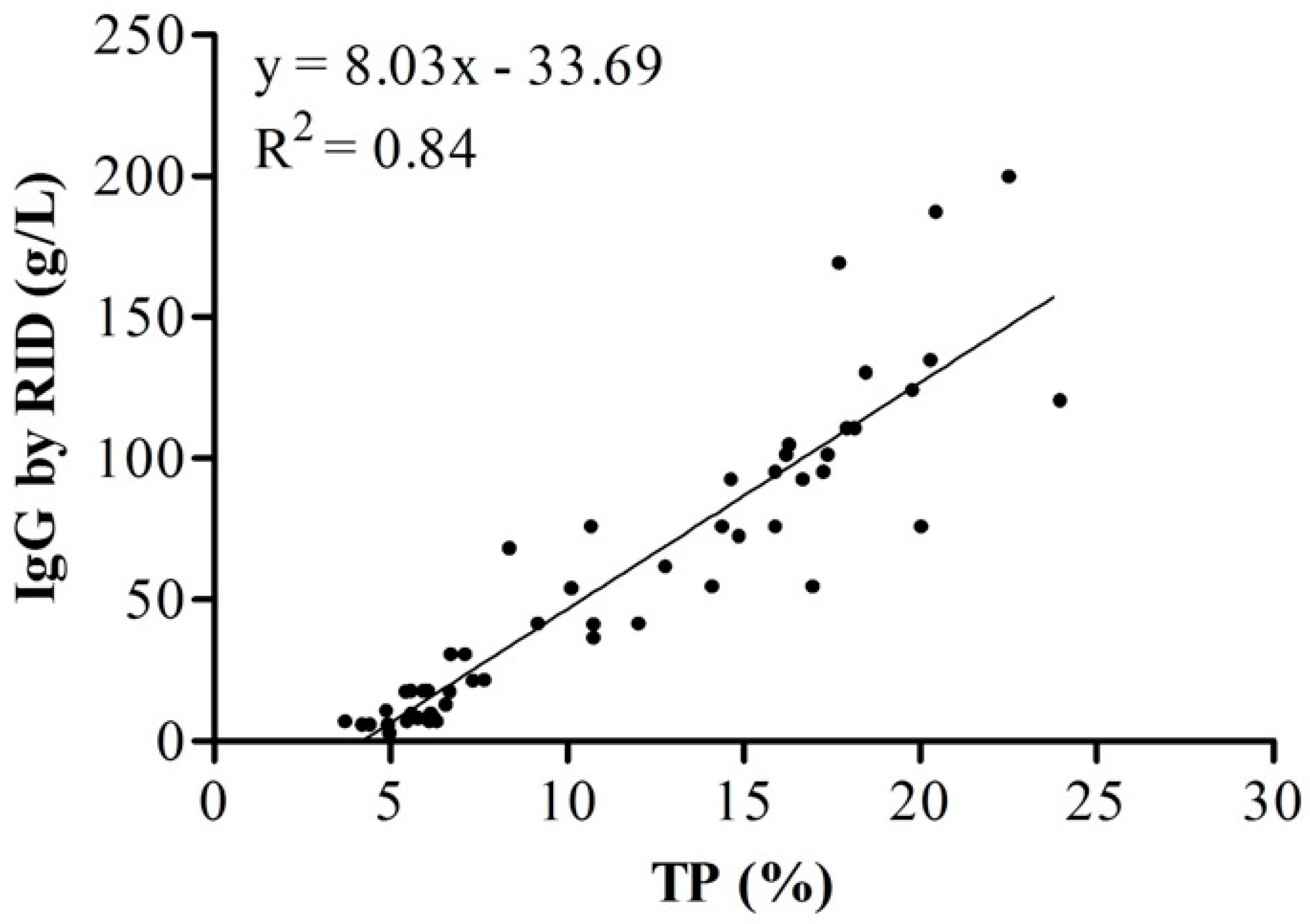
| TP 1 (%) | 0 h | 16.67 a | 3.33 | 15.38–17.96 | 9.18 | 23.96 |
| 24 h | 6.42 b | 1.81 | 5.71–7.14 | 3.7 | 10.74 | |
| IgG 2 (g/L) | 0 h | 99.85 a | 40.84 | 84.31–115.14 | 41.45 | 199.97 |
| 24 h | 19.76 b | 19.01 | 12.24–27.28 | 2.83 | 75.93 | |
| Ovine Colostrum | ||||||
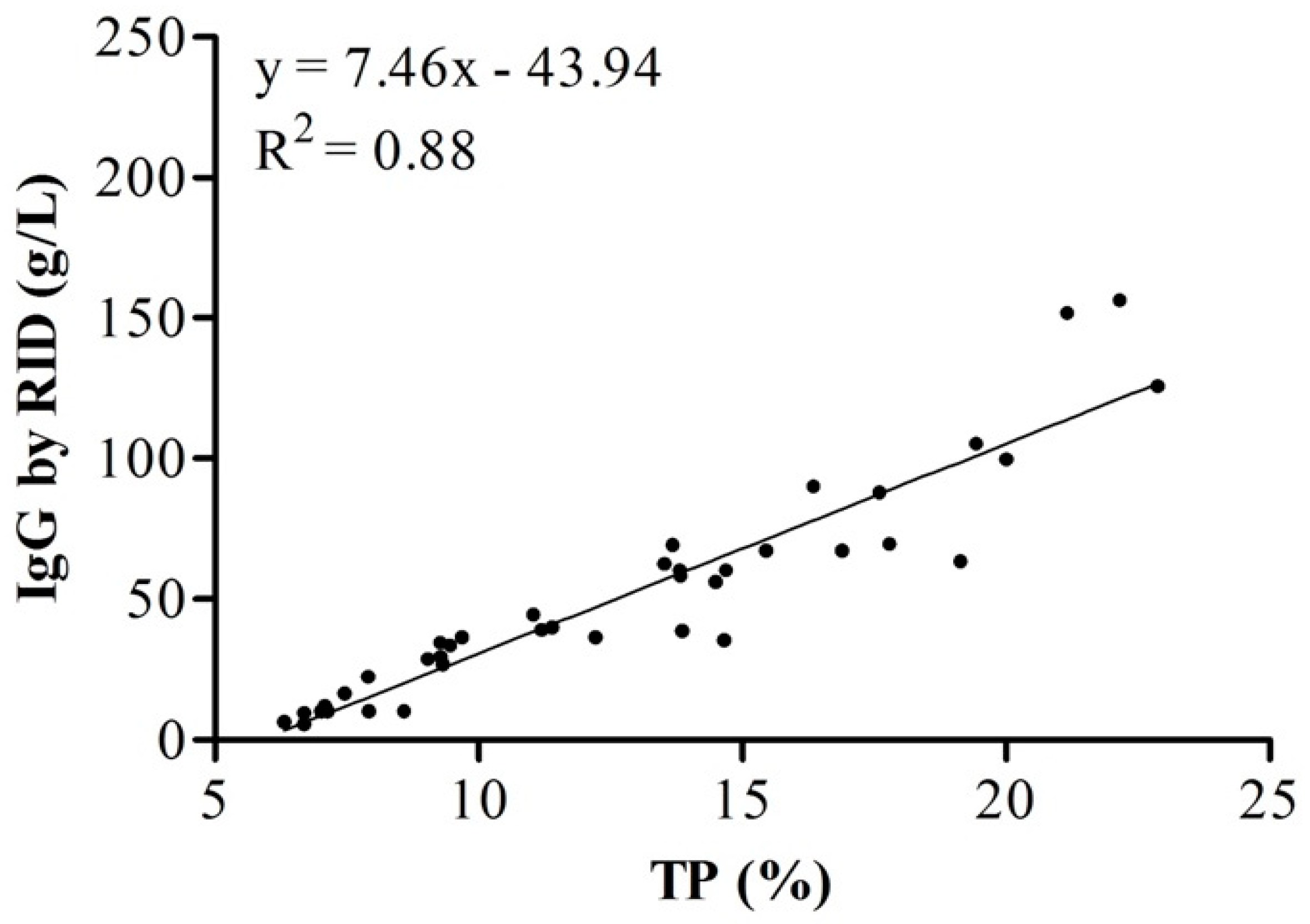
| TP 1 (%) | 0 h | 16.05 a | 4.12 | 14.00–18.01 | 9.27 | 22.88 |
| 24 h | 9.87 b | 3.35 | 8.35–11.39 | 6.32 | 10.79 | |
| IgG 2 (g/L) | 0 h | 77.82 a | 37.58 | 59.14–96.52 | 34.45 | 156.32 |
| 24 h | 27.90 b | 19.81 | 18.88–36.92 | 5.6 | 69.74 |
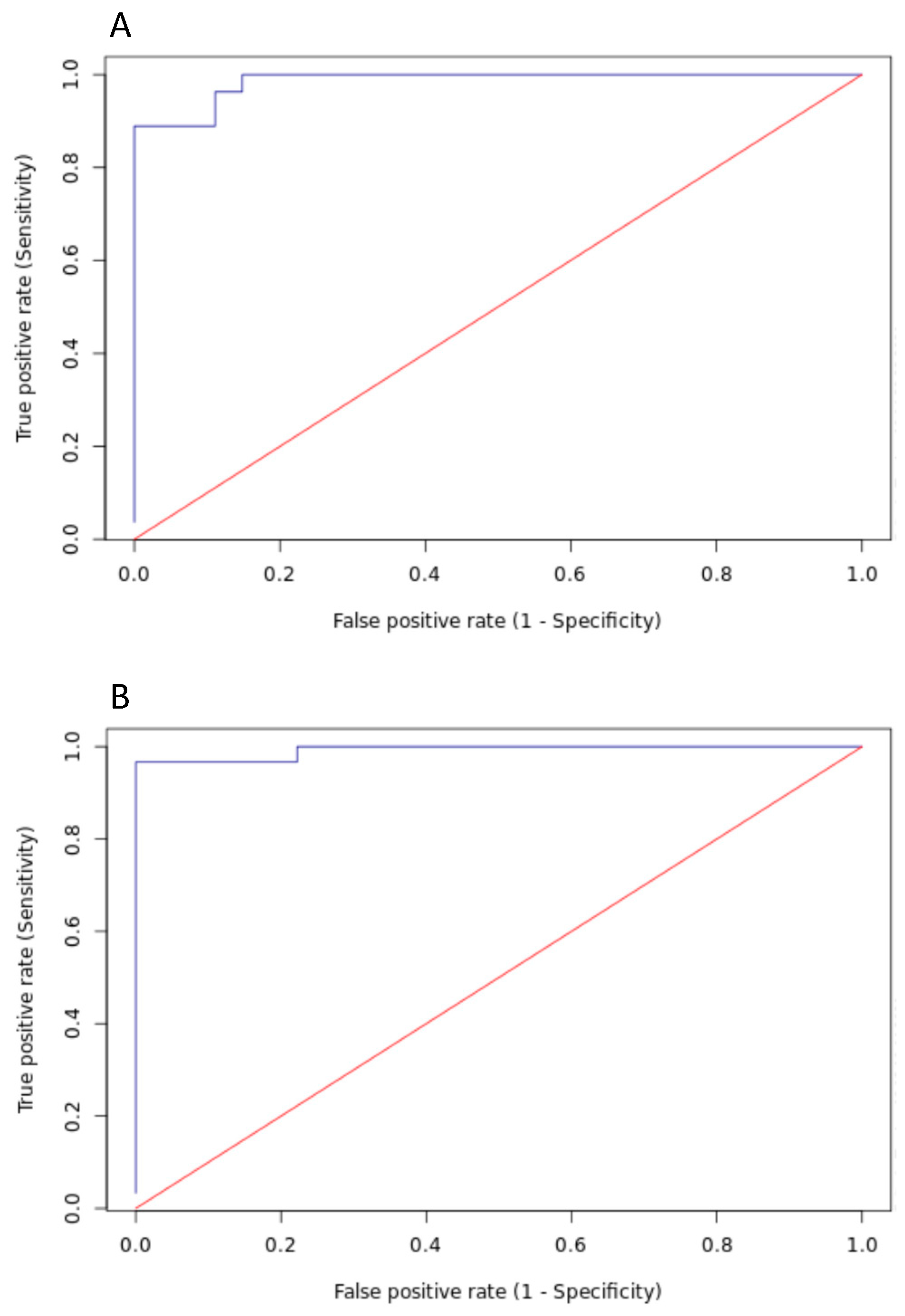
| Species | Cut-Point Value, % Proteins by FT-IR | Se, % (95% CI) | Sp, % (95% CI) | Youden Index 1 | PPV % 2 | NPV % 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine | 8.40% | 100 (87.50–100) | 85.20 (67.50–94.1) | 0.852 | 87.11 | 100 |
| 10.10% | 96.30 (81.70–99.30) | 88.90 (71.90–96.10) | 0.852 | 89.66 | 96.00 | |
| 10.70% | 92.60 (76.60–97.90) | 88.90 (71.90–96.10) | 0.815 | 89.30 | 92.30 | |
| 12.00% | 88.90 (71.90–96.10) | 96.30 (81.70–99.30) | 0.852 | 96.00 | 89.66 | |
| 12.80% | 88.90 (71.90–96.10) | 100 (87.50–100) | 0.889 | 100 | 90.01 | |
| 14.40% | 81.50 (63.30–91.80) | 100 (87.50–100) | 0.815 | 100 | 84.39 | |
| Ovine | 7.90% | 100 (88.60–100) | 77.80 (45.30–93.70) | 0.778 | 65.88 | 100 |
| 8.60% | 96.70 (83.30–99.40) | 88.90 (56.50–98.00) | 0.856 | 98.43 | 78.87 | |
| 9.00% | 96.70 (83.30–99.40) | 100 (70.10–100) | 0.967 | 100 | 98.61 | |
| 9.30% | 90.00 (74.40–96.50) | 100 (70.10–100) | 0.90 | 100 | 95.89 | |
| 9.70% | 80.00 (62.70–90.50) | 100 (70.10–100) | 0.80 | 100 | 92.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spina, A.A.; Ceniti, C.; Trimboli, F.; Britti, D.; Lopreiato, V. Suitability of Protein Content Measured by MilkoScan FT-Plus Milk Analyzer to Evaluate Bovine and Ovine Colostrum Quality. Animals 2021, 11, 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092587
Spina AA, Ceniti C, Trimboli F, Britti D, Lopreiato V. Suitability of Protein Content Measured by MilkoScan FT-Plus Milk Analyzer to Evaluate Bovine and Ovine Colostrum Quality. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092587
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpina, Anna Antonella, Carlotta Ceniti, Francesca Trimboli, Domenico Britti, and Vincenzo Lopreiato. 2021. "Suitability of Protein Content Measured by MilkoScan FT-Plus Milk Analyzer to Evaluate Bovine and Ovine Colostrum Quality" Animals 11, no. 9: 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092587
APA StyleSpina, A. A., Ceniti, C., Trimboli, F., Britti, D., & Lopreiato, V. (2021). Suitability of Protein Content Measured by MilkoScan FT-Plus Milk Analyzer to Evaluate Bovine and Ovine Colostrum Quality. Animals, 11(9), 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092587






