Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Note
2.2. Husbandry
2.3. Problem Solving Tests
2.3.1. Problem Solving in the Home Cage
2.3.2. Problem Solving in an Open Field
2.3.3. Problem Solving in the Light/Dark Box
2.4. Faecal Sample Collection and Extraction
2.5. Faecal Corticosterone Metabolite Quantification
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
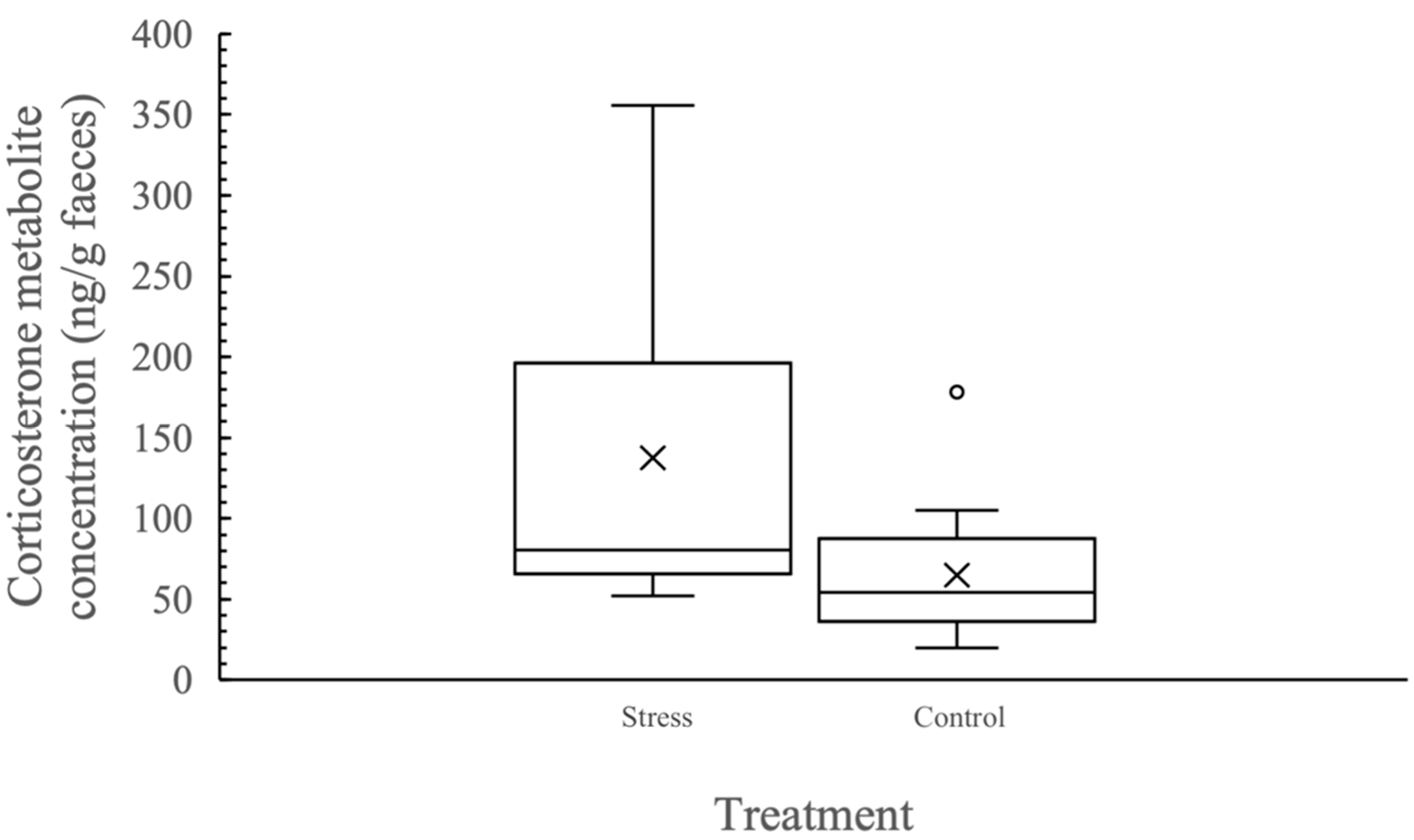
3.1. Biological Validation of the Assay to Measure Faecal Corticosterone Metabolites
3.2. Individual Variation in Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration
3.3. Latency to Solve Problems
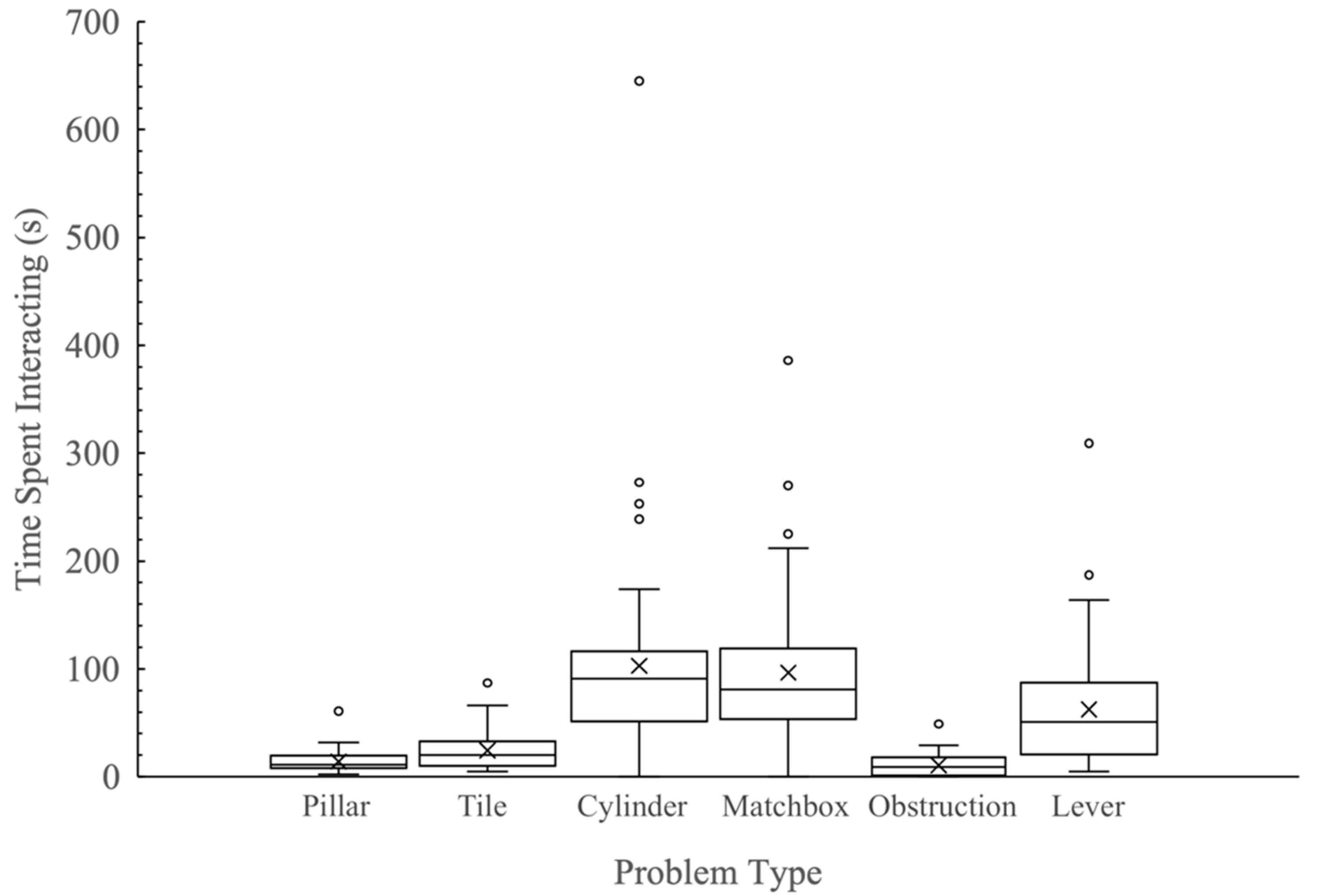
3.4. Time Spent Interacting with Problems
3.5. Overall Solving Performance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malishev, M.; Kramer-Schadt, S. Movement, Models, and Metabolism: Individual-Based Energy Budget Models as next-Generation Extensions for Predicting Animal Movement Outcomes across Scales. Ecol. Model. 2021, 441, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, V.; Guenther, A.; Øverli, Ø.; Seltmann, M.W.; Altschul, D. Future Directions for Personality Research: Contributing New Insights to the Understanding of Animal Behavior. Animals 2019, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palme, R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Glucocorticoids: Advances and Problems. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 199, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, K.A. Energy Costs of Growth in Neonate Reptiles. Herpetol. Monogr. 2000, 14, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, J.C. The Comparative Biology of Environmental Stress: Behavioural Endocrinology and Variation in Ability to Cope with Novel, Changing Environments. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöwe, M.; Rosivall, B.; Drent, P.J.; Möstl, E. Selection for Fast and Slow Exploration Affects Baseline and Stress-Induced Corticosterone Excretion in Great Tit Nestlings, Parus Major. Horm. Behav. 2010, 58, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of Stress throughout the Lifespan on the Brain, Behaviour and Cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, J.C.; Maney, D.L.; Breuner, C.W.; Jacobs, J.D.; Lynn, S.; Ramenofsky, M.; Richardson, R.D. Ecological Bases of Hormone—Behavior Interactions: The Emergency Life History Stage. Am. Zool. 1998, 38, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schommer, N.C.; Hellhammer, D.H.; Kirschbaum, C. Dissociation between Reactivity of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis and the Sympathetic-Adrenal-Medullary System to Repeated Psychosocial Stress. Psychosom. Med. 2003, 65, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, C.; Rose, S.P. Corticosterone Enhances Long-Term Retention in One-Day-Old Chicks Trained in a Weak Passive Avoidance Learning Paradigm. Brain Res. 1994, 647, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis, Neuroendocrine Factors and Stress. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 53, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bókony, V.; Lendvai, A.Z.; Vagasi, C.I.; Patras, L.; Pap, P.L.; Nemeth, J.; Vincze, E.; Papp, S.; Preiszner, B.; Seress, G.; et al. Necessity or Capacity? Physiological State Predicts Problem-Solving Performance in House Sparrows. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.K.Y.; Lea, S.E.G.; Hempel de Ibarra, N.; Robert, T. How to Stay Perfect: The Role of Memory and Behavioural Traits in an Experienced Problem and a Similar Problem. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reader, S.M.; Laland, K.N. Animal Innovation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, A.; Samson, J. Innovative Problem Solving in Wild Meerkats. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, C.M. Imitation, Culture and Cognition. Anim. Behav. 1993, 46, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowell, M.K.; Pillay, N.; Rymer, T.L. Problem Solving in Animals: Proposal for an Ontogenetic Perspective. Animals 2021, 11, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laland, K.N.; Reader, S.M. Foraging Innovation in the Guppy. Anim. Behav. 1999, 57, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Horik, J.O.; Madden, J.R. A Problem with Problem Solving: Motivational Traits, but Not Cognition, Predict Success on Novel Operant Foraging Tasks. Anim. Behav. 2016, 114, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wise, R.A. Role of Brain Dopamine in Food Reward and Reinforcement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esch, L.; Wöhr, C.; Erhard, M.; Krüger, K. Horses’ (Equus Caballus) Laterality, Stress Hormones, and Task Related Behavior in Innovative Problem-Solving. Animals 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochais, C.; Schradin, C.; Pillay, N. Seasonal Changes in Problem-Solving in Wild African Striped Mice. Anim. Cogn. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, W.A.; Turner, A.A.; Croshaw, O.B.; Ferguson, J.A.; Julson, Z.J.-N.; Volp, T.M.; Kerr, S.E.; Rymer, T.L. Melomys Cervinipes (Rodentia: Muridae). Mamm. Species 2018, 50, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, M.K.; Rymer, T.L. Innovation in a Native Australian Rodent, the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat (Melomys Cervinipes). Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, M.K.; Rymer, T.L. Exploration Influences Problem Solving in the Fawn-footed Mosaic-tailed Rat (Melomys Cervinipes). Ethology 2021, 127, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.A. Do Melomys Cervinipes Have Personalities? Variations in Behaviour and Hormones in a Tropical Rainforest Rodent. Bachelor’s Thesis, James Cook University, Queensland, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Careau, V.; Thomas, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Réale, D. Energy Metabolism and Animal Personality. Oikos 2008, 117, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S.; Lannert, H. Long-Term Effects of Corticosterone on Behavior, Oxidative and Energy Metabolism of Parietotemporal Cerebral Cortex and Hippocampus of Rats: Comparison to Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bee, M.; Bernal, X.; Calisi, R.; Carere, C.; Carter, T.; Fuertbauer, L.; Ha, J.C.; Hubrecht, R.; Jennings, D.; Metcalfe, N.; et al. Guidelines for the Treatment of Animals in Behavioural Research and Teaching. Anim. Behav. 2020, 159, i–xi. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC). Australian Code for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes; National Health and Medical Research Council: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Pfeffer, K.; Fritz, J.; Kotrschal, K. Hormonal Correlates of Being an Innovative Greylag Goose, Anser. Anim. Behav. 2002, 63, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rader, R.; Krockenberger, A. Three-Dimensional Use of Space by a Tropical Rainforest Rodent, Melomys Cervinipes, and Its Implications for Foraging and Home-Range Size. Wildl. Res. 2006, 33, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.H. The Ecology of Rattus Fuscipes and Melomys Cervinipes (Rodentia: Muridaae) in a South-East Queensland Rain Forest. Aust. J. Zool. 1971, 19, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulling, K.; Wilson, D.; Rymer, T.L. Olfactory Recognition of Snake Cues by Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rats Melomys Cervinipes. Behaviour 2019, 156, 1235–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friard, O.; Gamba, M. BORIS: A Free, Versatile Open-Source Event-Logging Software for Video/Audio Coding and Live Observations. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.M.; Heintz, M.R.; Lonsdorf, E.V.; Parr, L.A.; Santymire, R.M. Validation of a Field Technique and Characterization of Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolite Analysis in Wild Chimpanzees (P and Troglodytes). Am. J. Primatol. 2013, 75, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, E.D.; Kent, M.; Thompson, B.; Bardi, M.; Lambert, K. Maternal-Induced Shifts in Allostatic Demands: Reproductive Experience Alters Emotional and Cognitive Biobehavioral Responses in Rats (Rattus Norvegicus). Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 701, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Dutang, C. Fitdistrplus: An R Package for Fitting Distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Diagnostic Checking in Regression Relationships. R News 2002, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R.; Singmann, H.; Love, J.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M. Package Emmeans. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/index.html (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Stoffel, M.A.; Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. RptR: Repeatability Estimation and Variance Decomposition by Generalized Linear Mixed-effects Models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Therneau, T.M.; Lumley, T. Package Survival. Surviv. Anal. Publ. CRAN 2014, 2, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P.; Fabian, S. Package Survminer. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survminer/index.html (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Liker, A.; Bókony, V. Larger Groups Are More Successful in Innovative Problem-Solving in-House Sparrows. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7893–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, R.A. Finding Optimal Normalizing Transformations via Best Normalize. R J. 2021, 13, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Sarkar, D.; Bates, M.D.; Matrix, L. The Lme4 Package. R Package Version 2007, 2, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 2020, 3, 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, C.; Zeileis, A.; Zeileis, M.A. Package Aer. R Package Version 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, L.M.; Cyr, N.E.; Romero, R.C. Corticosterone Responses Change Seasonally in Free-Living House Sparrows (Passer Domesticus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 149, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeling, S.K.; Nockels, C.F. Effects of Age, Sex, and Ascorbic Acid Ingestion on Chicken Plasma Corticosterone Levels. Poult. Sci. 1978, 57, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.C.; Waddell, B.J. Circadian Variation in Basal Plasma Corticosterone and Adrenocorticotropin in the Rat: Sexual Dimorphism and Changes across the Estrous Cycle. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 3842–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepschy, M.; Touma, C.; Hruby, R.; Palme, R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Adrenocortical Activity in Male and Female Rats. Lab. Anim. 2007, 41, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, A.S.; Guez, D. Innovation and Problem Solving: A Review of Common Mechanisms. Behav. Processes 2014, 109, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszy, J.; Laszlovszky, I.; Gyertyán, I. Dopamine D3 Receptor Antagonists Improve the Learning Performance in Memory-Impaired Rats. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall-Shackleton, S.A.; Bonier, F.; Romero, L.M.; Moore, I.T. Glucocorticoids and Stress Are Not Synonymous. Integr. Org. Biol. 2019, 1, obz017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, C.P.; Lill, A.; Reina, R.D. Does Habitat Fragmentation Cause Stress in the Agile Antechinus? A Haematological Approach. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2012, 182, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.L.; Nicol, C.J.; Clark, C.C.A.; Paul, E.S. Measuring Empathic Responses in Animals. Spec. Issue Living Large Groups 2012, 138, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.; Jenkins, M.A.; Ruehrdanz, A.; Gilmer, M.J.; Olson, J.; Pawar, A.; Holley, L.; Sierra-Rivera, S.; Linder, D.E.; Pichette, D.; et al. Physiological and Behavioral Effects of Animal-Assisted Interventions on Therapy Dogs in Pediatric Oncology Settings. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 200, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boissy, A.; Manteuffel, G.; Jensen, M.B.; Moe, R.O.; Spruijt, B.; Keeling, L.J.; Winckler, C.; Forkman, B.; Dimitrov, I.; Langbein, J.; et al. Assessment of Positive Emotions in Animals to Improve Their Welfare. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Orchard, S.M.; Sanford, L.D. Home Cage Activity and Behavioral Performance in Inbred and Hybrid Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abdallah, N.M.-B.; Fuss, J.; Trusel, M.; Galsworthy, M.J.; Bobsin, K.; Colacicco, G.; Deacon, R.M.J.; Riva, M.A.; Kellendonk, C.; Sprengel, R.; et al. The Puzzle Box as a Simple and Efficient Behavioral Test for Exploring Impairments of General Cognition and Executive Functions in Mouse Models of Schizophrenia. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rowell, M.K.; Santymire, R.M.; Rymer, T.L. Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes. Animals 2022, 12, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010082
Rowell MK, Santymire RM, Rymer TL. Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes. Animals. 2022; 12(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleRowell, Misha K., Rachel M. Santymire, and Tasmin L. Rymer. 2022. "Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes" Animals 12, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010082
APA StyleRowell, M. K., Santymire, R. M., & Rymer, T. L. (2022). Corticosterone Metabolite Concentration Is Not Related to Problem Solving in the Fawn-Footed Mosaic-Tailed Rat Melomys Cervinipes. Animals, 12(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010082





