Metabolic Fate Is Defined by Amino Acid Nature in Gilthead Seabream Fed Different Diet Formulations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets
2.2. Fish Husbandry
2.3. Metabolic Flux Assays
Metabolic Budget Determination
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
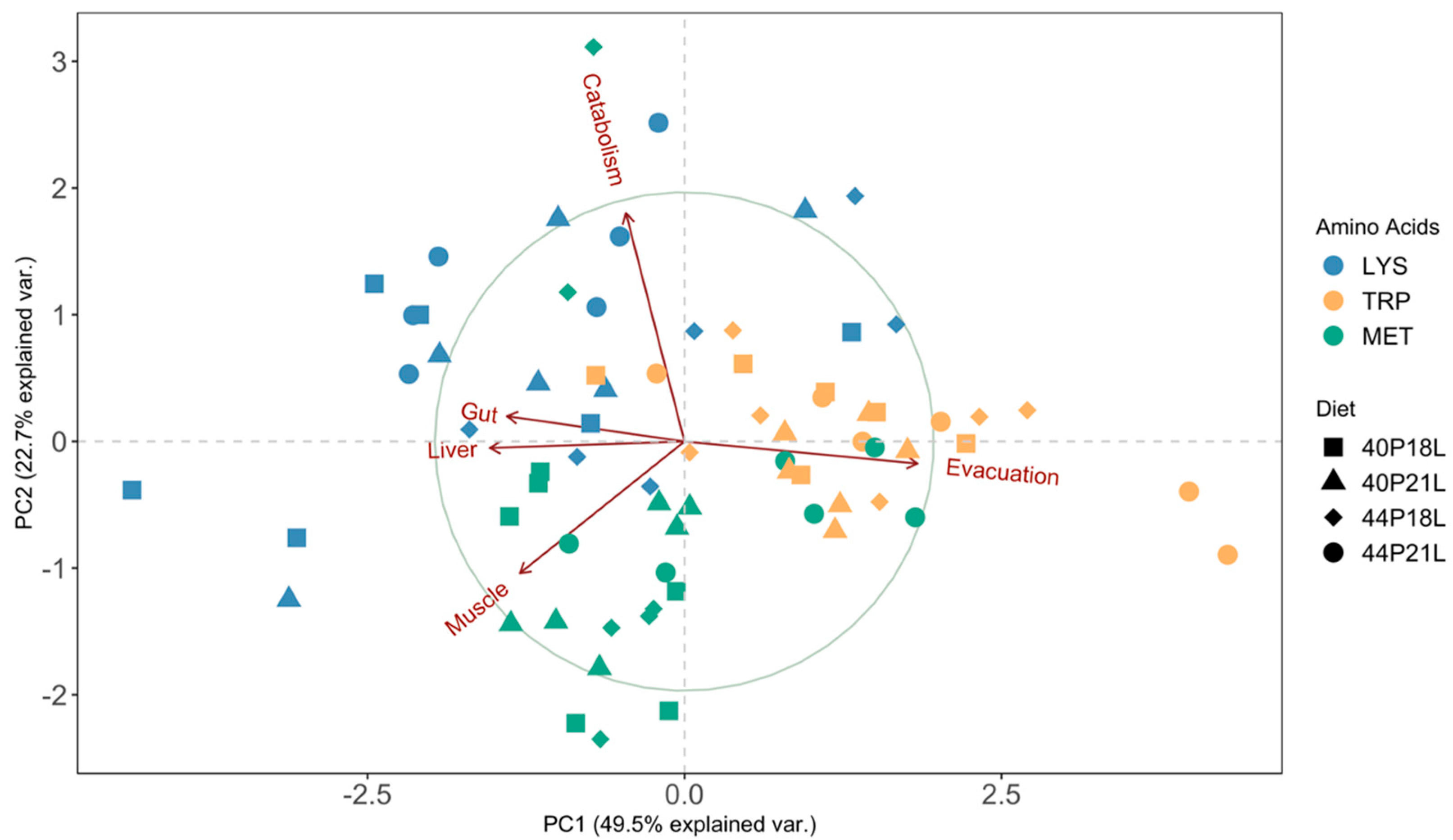
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carter, C.G.; Houlihan, D.F. Protein synthesis. Fish Physiol. 2001, 20, 31–75. [Google Scholar]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Ozório, R.O.A.; Suurd, E.A.; Verreth, J.A.J. Amino acid profiles and amino acid utilization in larval african catfish (Clarias gariepinus): Effects of ontogeny and temperature. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1998, 19, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Grasdalen, H.; Rønnestad, I. Amino acid requirements of fish larvae and post-larvae: New tools and recent findings. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Yúfera, M.; Ueberschär, B.; Ribeiro, L.; Saele, Ø.; Boglione, C. Feeding behaviour and digestive physiology in larval fish: Current knowledge, and gaps and bottlenecks in research. Rev. Aquac. 2013, 5, S59–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Grasdalen, H.; Dinis, M.T. A new method to estimate the relative bioavailability of individual amino acids in fish larvae using 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 134, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Aragão, C.; Rønnestad, I. Proteins. In Larval Fish Nutrition; Holt, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, S.J.; Seiliez, I. Protein and amino acid nutrition and metabolism in fish: Current knowledge and future needs. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Wu, G. Nutrition and functions of amino acids in fish. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1285, 133–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. Amino Acids: Biochemistry and Nutrition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hoglund, E.; Overli, O.; Winberg, S. Tryptophan metabolic pathways and brain serotonergic activity: A comparative review. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; Costas, B.; Azeredo, R.; Gesto, M. Physiological roles of tryptophan in teleosts: Current knowledge and perspectives for future studies. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardy, R.W. Utilization of plant proteins in fish diets: Effects of global demand and supplies of fishmeal. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Peres, H. Replacing fishmeal and fish oil in industrial aquafeeds for carnivorous fish. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Davies, D.A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 203–233. [Google Scholar]
- Turchini, G.M.; Trushenski, J.T.; Glencross, B.D. Thoughts for the future of aquaculture nutrition: Realigning perspectives to reflect contemporary issues related to judicious use of marine resources in aquafeeds. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2019, 81, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.J.; Schrama, J.W. Bioenergetics. In Fish Nutrition; Hardy, R.W., Kaushik, S.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 17–55. [Google Scholar]
- Teodósio, R.; Engrola, S.; Cabano, M.; Colen, R.; Masagounder, K.; Aragão, C. Metabolic and nutritional responses of nile tilapia juveniles to dietary methionine sources. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodósio, R.; Engrola, S.; Colen, R.; Masagounder, K.; Aragão, C. Optimizing diets to decrease environmental impact of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) production. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodósio, R.; Aragão, C.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Engrola, S. Amino acid metabolism in gilthead seabream is affected by the dietary protein to energy ratios. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 8230704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas, B. Stress Mitigation in Sole (Solea senegalensis) through Improved Nitrogen Nutrition: Amino Acid Utilization, Disease Resistance and Immune Status. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rønnestad, I.; Rojas-García, C.R.; Tonheim, S.K.; Conceição, L.E.C. In vivo studies of digestion and nutrient assimilation in marine fish larvae. Aquaculture 2001, 201, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.B.; Hardy, R.W.; Stickney, R.R. A new method for force-feeding larval fish. Aquaculture 1993, 116, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, L.E.C.; Morais, S.; Rønnestad, I. Tracers in fish larvae nutrition: A review of methods and applications. Aquaculture 2007, 267, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Teodósio, R.; Aragão, C.; Colen, R.; Carrilho, R.; Dias, J.; Engrola, S. A nutritional strategy to promote gilthead seabream performance under low temperatures. Aquaculture 2021, 537, 736494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennos, A.R. Statistical and Data Handling Skills in Biology, 3rd ed.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, S. A purified test diet for coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, fry. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1981, 47, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, S.J. Whole body amino acid composition of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and turbot (Psetta maxima) with an estimation of their IAA requirement profiles. Aquat. Living Resour. 1998, 11, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saavedra, M.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Dinis, M.T. Metabolism of tryptophan, methionine and arginine in Diplodus sargus larvae fed rotifers: Effect of amino acid supplementation. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, K.; Dabrowska, H. Digestion of protein by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Rich.) and absorption of amino acids within the alimentary tract. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1981, 69, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Kamisaka, Y.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Morais, S.; Tonheim, S.K. Digestive physiology of marine fish larvae: Hormonal control and processing capacity for proteins, peptides and amino acids. Aquaculture 2007, 268, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Nordrum, S.; Krogdahl, Å.; Buddington, R.K. Absorption of glucose, amino acids, and dipeptides by the intestines of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 22, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, S.; Palacin, M. The role of amino acid transporters in inherited and acquired diseases. Biochem. J. 2011, 436, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyde, R.; Taylor, P.M.; Hundal, H.S. Amino acid transporters: Roles in amino acid sensing and signalling in animal cells. Biochem. J. 2003, 373, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gershon, M.D. Serotonin receptors and transporters—Roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, K.; Hu, F. Effect of dietary tryptophan on growth, intestinal microbiota, and intestinal gene expression in an improved triploid crucian carp. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 676035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.; Figueira, L.; Santos, A.; Barr, Y.; Helland, S.; Dinis, M.T.; Aragão, C. Is dietary taurine supplementation beneficial for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae? Aquaculture 2013, 384–387, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Conceicão, L.E.C.; Aragão, C.; Dinis, M.T. Free amino acids are absorbed faster and assimilated more efficiently than protein in postlarval senegal sole (Solea senegalensis). J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2809–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belghit, I.; Skiba-Cassy, S.; Geurden, I.; Dias, K.; Surget, A.; Kaushik, S.J.; Panserat, S.; Seiliez, I. Dietary methionine availability affects the main factors involved in muscle protein turnover in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueiredo-Silva, C.; Lemme, A.; Sangsue, D.; Kiriratnikom, S. Effect of DL-methionine supplementation on the success of almost total replacement of fish meal with soybean meal in diets for hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis mossambicus). Aquac. Nutr. 2015, 21, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami-Durante, H.; Bazin, D.; Cluzeaud, M.; Fontagné-Dicharry, S.; Kaushik, S.J.; Geurden, I. Effect of dietary methionine level on muscle growth mechanisms in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 483, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mai, K.; Trushenski, J.; Wu, G. New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: Towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Amino Acids: Metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, J.S. Amino acid metabolism. Fish Physiol. 2001, 20, 77–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, F.; Dias, J.; Geurden, I.; Dinis, M.T.; Panserat, S.; Engrola, S. High-glucose feeding of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae: Effects on molecular and metabolic pathways. Aquaculture 2016, 451, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, F.; Dias, J.; Geurden, I.; Dinis, M.T.; Panserat, S.; Engrola, S. Dietary glucose stimulus at larval stage modifies the carbohydrate metabolic pathway in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles: An in vivo approach using 14C-starch. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 201, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Guillén, C.; Yúfera, M.; Engrola, S. Ghrelin in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) post-larvae: Paracrine effects on food intake. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 204, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, C.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Martins, D.; Rønnestad, I.; Gomes, E.; Dinis, M.T. A balanced dietary amino acid profile improves amino acid retention in post-larval Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquaculture 2004, 233, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.; Figueira, L.; Dinis, M.T.; Aragão, C. How does fish metamorphosis affect aromatic amino acid metabolism? Amino Acids 2009, 36, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, M.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Helland, S.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Dinis, M.T. Effect of lysine and tyrosine supplementation in the amino acid metabolism of Diplodus sargus larvae fed rotifers. Aquaculture 2008, 284, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ingredients (%) | 44P21L | 44P18L | 40P21L | 40P18L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal SP a | 22.00 | 22.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 |
| Fishmeal b | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Soy protein concentrate c | 6.40 | 6.00 | 6.90 | 6.40 |
| Wheat gluten d | 7.00 | 6.40 | 6.00 | 6.00 |
| Corn gluten e | 11.00 | 11.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Soybean meal f | 12.00 | 12.00 | 12.00 | 12.00 |
| Rapeseed meal g | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Sunflower meal h | 4.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Wheat meal i | 2.90 | 4.90 | 7.00 | 10.50 |
| Whole peas j | 3.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Fish oil k | 10.60 | 8.52 | 10.85 | 9.00 |
| Rapeseed oil l | 6.60 | 5.68 | 6.85 | 5.70 |
| Vitamin and Mineral Premix m | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Vitamin E n | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Choline chloride o | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Betaine HCl p | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Soy lecithin q | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Guar gum r | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Antioxidant powder s | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Mono-calcium phosphate t | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.40 | 1.40 |
| L-Lysine u | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| L-Threonine v | 0.20 | 0.20 | - | - |
| Proximate composition (% as fed) | ||||
| Dry matter | 94.17 | 93.73 | 94.69 | 94.05 |
| Ash | 8.53 | 9.22 | 8.10 | 8.20 |
| Crude protein | 44.72 | 43.88 | 40.40 | 40.43 |
| Crude lipids | 20.32 | 17.65 | 21.38 | 18.40 |
| Total phosphorus | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.20 | 1.19 |
| Gross energy (MJ kg−1) | 22.33 | 21.71 | 22.11 | 21.66 |
| Amino Acids (mg AA g−1 as fed) | 44P21L | 44P18L | 40P21L | 40P18L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arginine | 45.1 | 42.9 | 31.4 | 29.8 |
| Histidine | 12.8 | 12.1 | 9.8 | 10.0 |
| Lysine | 43.0 | 40.8 | 23.8 | 22.4 |
| Threonine | 21.7 | 19.6 | 15.3 | 16.3 |
| Isoleucine | 24.1 | 23.3 | 16.9 | 18.0 |
| Leucine | 41.4 | 39.6 | 32.9 | 33.8 |
| Valine | 24.2 | 23.2 | 20.2 | 20.6 |
| Tryptophan | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Methionine | 13.0 | 12.2 | 10.0 | 10.1 |
| Phenylalanine | 27.7 | 26.7 | 20.2 | 19.9 |
| Cystine | 3.1 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.3 |
| Tyrosine | 23.1 | 21.9 | 15.9 | 14.5 |
| Aspartic acid + Asparagine | 54.6 | 51.5 | 33.1 | 31.3 |
| Glutamic acid + Glutamine | 104.5 | 99.4 | 65.4 | 64.3 |
| Alanine | 26.3 | 24.9 | 21.0 | 20.6 |
| Glycine | 29.0 | 27.6 | 24.1 | 24.2 |
| Proline | 32.2 | 30.4 | 26.1 | 26.2 |
| Serine | 26.4 | 25.1 | 19.7 | 20.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teodósio, R.; Aragão, C.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Dias, J.; Engrola, S. Metabolic Fate Is Defined by Amino Acid Nature in Gilthead Seabream Fed Different Diet Formulations. Animals 2022, 12, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131713
Teodósio R, Aragão C, Conceição LEC, Dias J, Engrola S. Metabolic Fate Is Defined by Amino Acid Nature in Gilthead Seabream Fed Different Diet Formulations. Animals. 2022; 12(13):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131713
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeodósio, Rita, Claúdia Aragão, Luís E. C. Conceição, Jorge Dias, and Sofia Engrola. 2022. "Metabolic Fate Is Defined by Amino Acid Nature in Gilthead Seabream Fed Different Diet Formulations" Animals 12, no. 13: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131713
APA StyleTeodósio, R., Aragão, C., Conceição, L. E. C., Dias, J., & Engrola, S. (2022). Metabolic Fate Is Defined by Amino Acid Nature in Gilthead Seabream Fed Different Diet Formulations. Animals, 12(13), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131713









