SV40T/E6E7-Induced Proliferation Is Involved in the Activity of E2F3 in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Proliferation Assays
2.3. Senescence-Associated β-Galactosidase Assay
2.4. Illumina HiSeq mRNA Sequencing
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
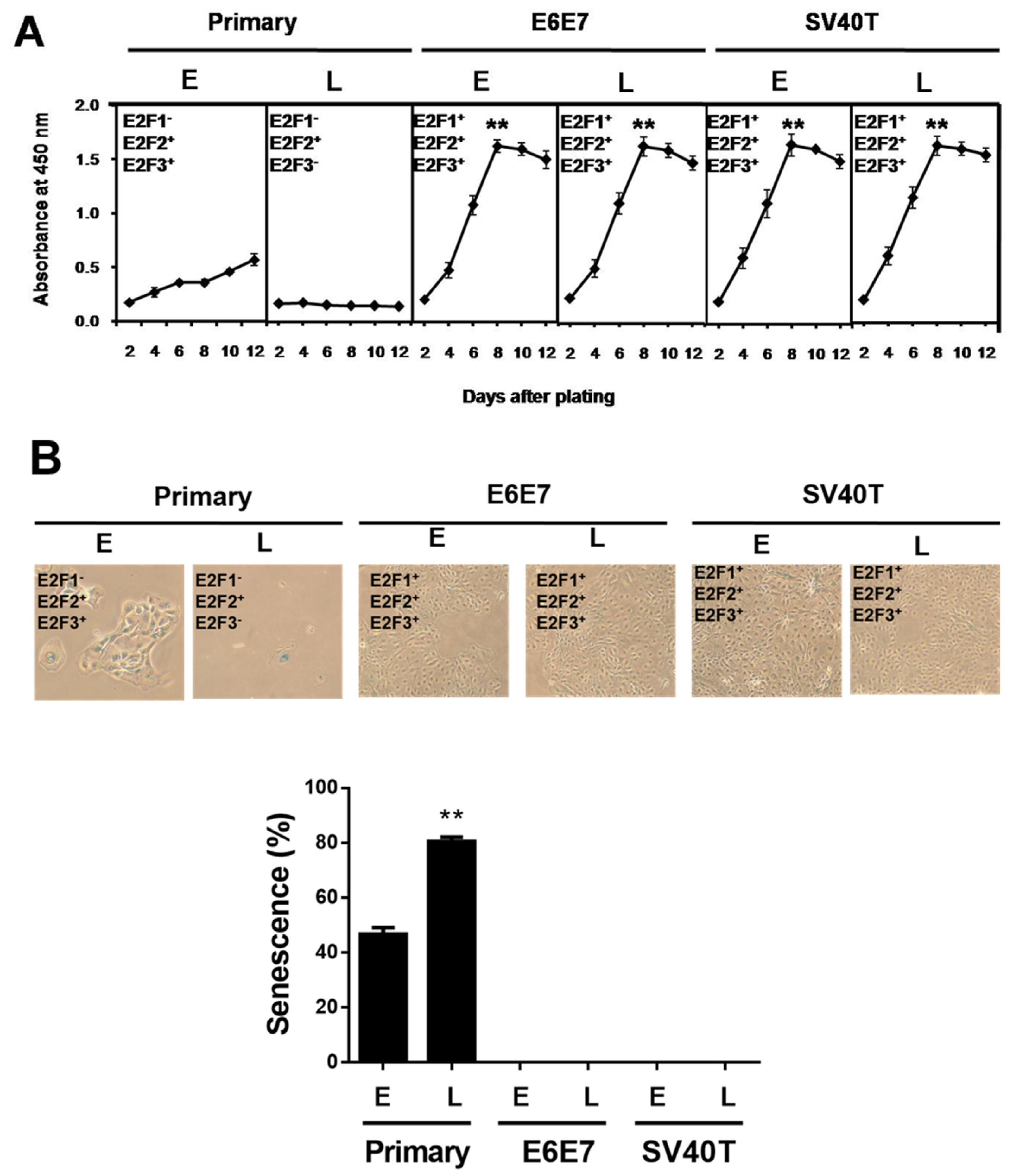
3.1. SV40T- and E6E7-Induced Proliferation of BMECs
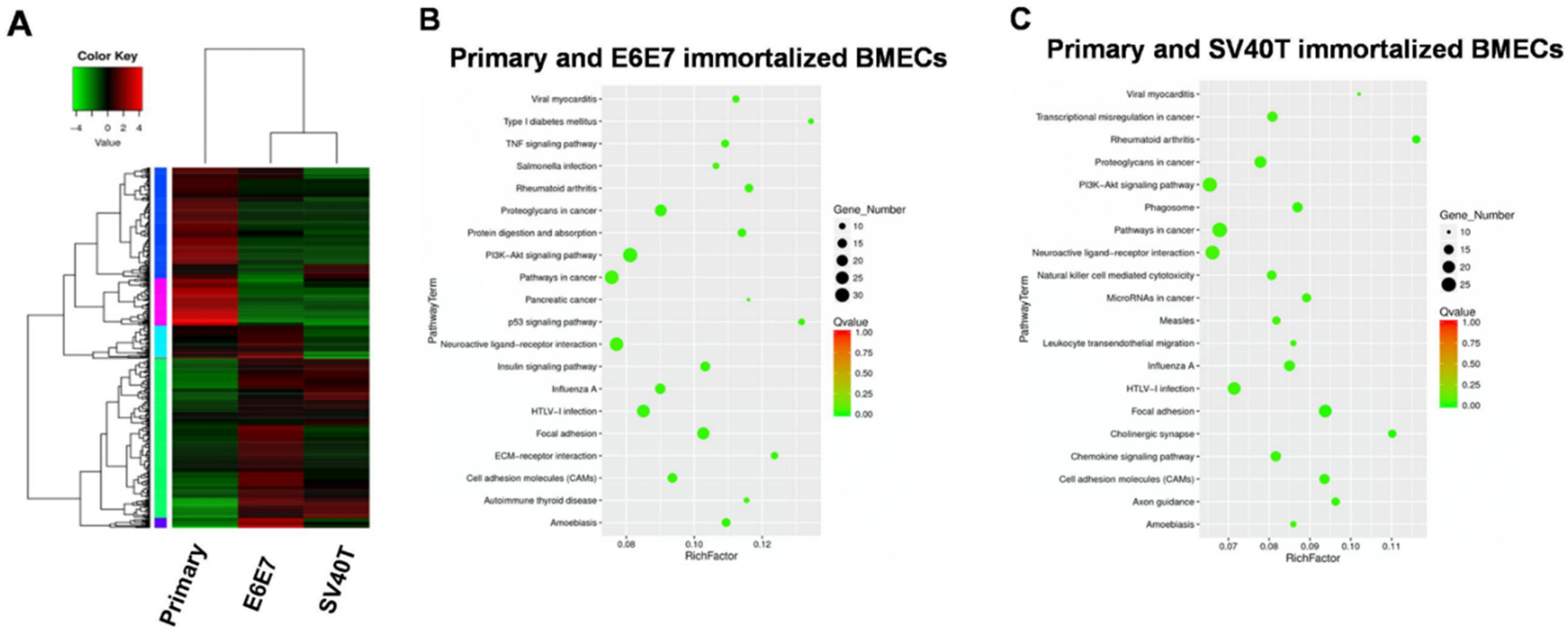
3.2. Identification of Signaling Pathways Responsible for BMECs’ Immortalization by Transcriptome Analysis
3.3. Involvement of E2F Signaling Pathway in the Proliferation of the Immortalized BMECs
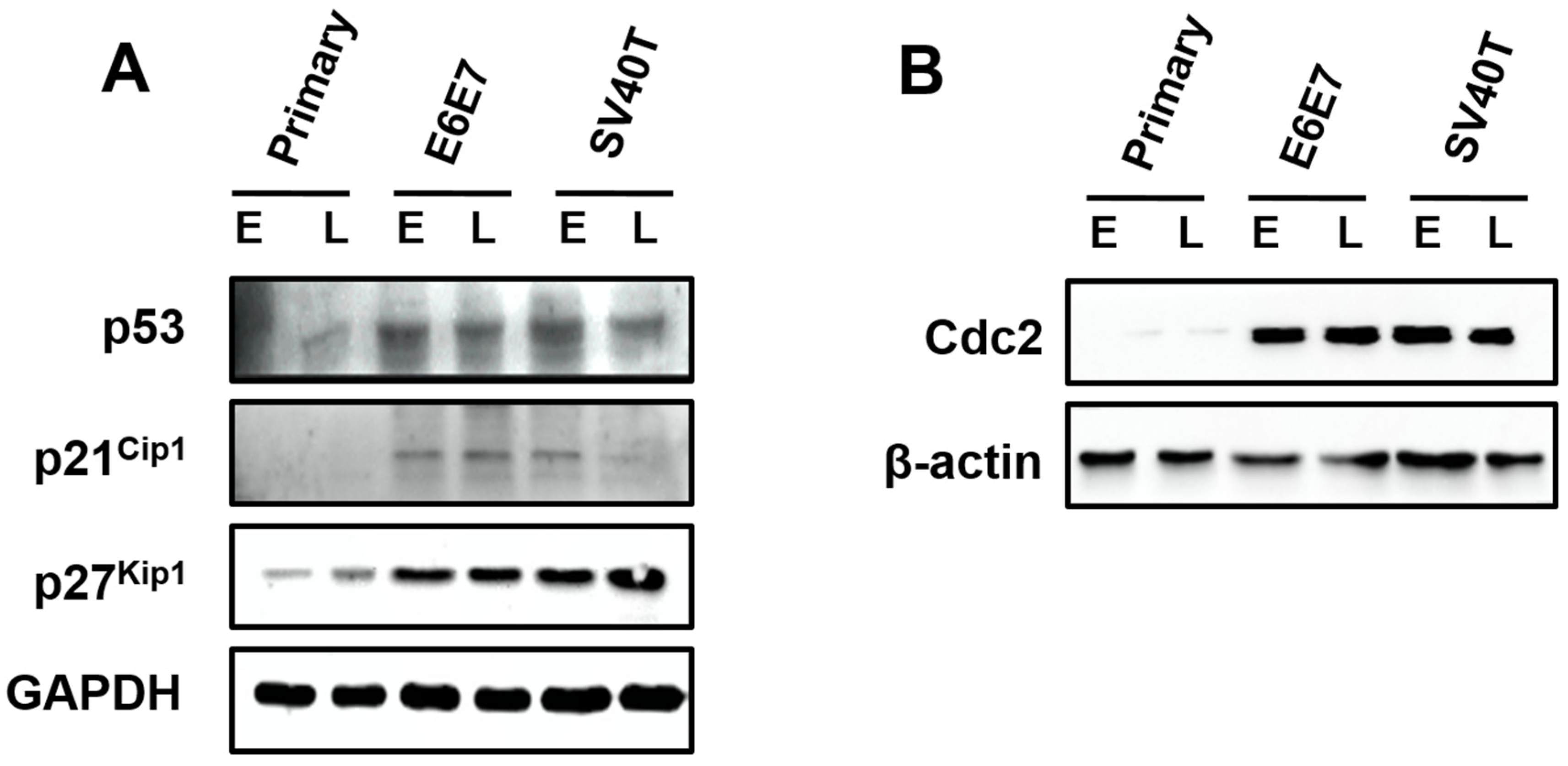
3.4. Involvement of p53 Signaling Pathways in the Proliferation of the Immortalized BMECs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sherr, C.; DePinho, R. Cellular senescence: Mitotic clock or culture shock? Cell 2000, 102, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.Y.; Opavsky, R.; Sharma, N.; Wu, L.; Naidu, S.; Nolan, E.; Feria-Arias, E.; Timmers, C.; Opavska, J.; de Bruin, A.; et al. Mouse development with a single E2F activator. Nature 2018, 454, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, A.; Tainsky, M. Critical pathways in cellular senescence and immortalization revealed by gene expression profiling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5975–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Pacal, M.; Wenzel, P.; Knoepfler, P.; Leone, G.; Bremner, R. Division and apoptosis of E2f-deficient retinal progenitors. Nature 2009, 462, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawado, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nishimoto, Y.; Ohno, K.; Sakaguchi, K.; Matsukage, A. dE2F2, a novel E2F-family transcription factor in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, B.; Denissov, S.; Douma, S.; Stunnenberg, H.; Bernards, R.; Peeper, D. E2F transcriptional repressor complexes are critical downstream targets of p19(ARF)/p53-induced proliferative arrest. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyson, N.; Howley, P.; Munger, K.; Harlow, E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science 1989, 243, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Saenz Robles, M.; Pipas, J. Cellular transformation of mouse embryo fibroblasts in the absence of activator E2Fs. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5124–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Timmers, C.; Maiti, B.; Saavedra, H.; Sang, L.; Chong, G.; Nuckolls, F.; Giangrande, P.; Wright, F.; Field, S.; et al. The E2F1-3 transcription factors are essential for cellular proliferation. Nature 2001, 414, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wenzel, P.; Saenz-Robles, M.; Nair, V.; Ferrey, A.; Hagan, J.; Gomez, Y.; Sharma, N.; Chen, H.; Ouseph, M.; et al. E2f1-3 switch from activators in progenitor cells to repressors in differentiating cells. Nature 2009, 462, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Tsai, S.; Leone, G. Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: An exit from cell cycle control. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, P.; Chong, J.; Saenz-Robles, M.; Ferrey, A.; Hagan, J.; Gomez, Y.; Rajmohan, R.; Sharma, N.; Chen, H.; Pipas, J.; et al. Cell proliferation in the absence of E2F1-3. Dev Biol. 2001, 351, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiyono, T.; Foster, S.; Koop, J.; Mcdougall, J.; Galloway, D.; Klingelhutz, A. Both Rb/p16INK4a inactivation and telomerase activity are required to immortalize human epithelial cells. Nature 1998, 396, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellappan, S.; Kraus, V.; Kroger, B.; Munger, K.; Howley, P.; Phelps, W.; Nevins, J. Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen, and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4549–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nevins, J. E2F: A link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science 1992, 258, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, D.; Saenz-Robles, M.; Pipas, J. SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit cellular transformation. Oncogene 2015, 24, 7729–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, K.; Lin, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, G. Biological characterization of bovine mammary epithelial cell lines immortalized by HPV16 E6/E7 and SV40T. In Vitro Cell. Dev.-Anim. 2016, 52, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudjonsson, T.; Villadsen, R.; Ronnov-Jessen, L.; Petersen, O. Immortalization protocols used in cell culture models of human breast morphogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khleif, S.; DeGregori, J.; Yee, C.; Otterson, G.; Kaye, F.; Nevins, J.; Howley, P. Inhibition of cyclin D-CDK4/CDK6 activity is associated with an E2F-mediated induction of cyclin kinase inhibitor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, L.; Leone, G. The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Bartkova, J.; Bartek, J. Convergence of mitogenic signalling cascades from diverse classes of receptors at the cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase-pRb-controlled G1 checkpoint. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 6917–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabrielli, B.; Sarcevic, B.; Sinnamon, l.; Walker, G.; Castellano, M.; Wang, X.; Ellem, K. A cyclin D-Cdk4 activity required for G2 phase cell cycle progression is inhibited in ultraviolet radiation-induced G2 phase delay. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13961–13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- VanArsdale, T.; Boshoff, C.; Arndt, K.; Abraham, R. Molecular Pathways: Targeting the Cyclin D-CDK4/6 Axis for Cancer Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Leone, G.; Wang, H. Cyclin D-CDK4/6 functions in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2020, 148, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D. Cyclin-dependent kinases: Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1997, 13, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, S.; Sage, J.; Skotheim, J. Integrating Old and New Paradigms of G1/S Control. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhan, K.; Ning, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, G. Short-chain fatty acids inhibit bovine rumen epithelial cells proliferation via upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors 1A, but not mediated by G protein-coupled receptor 41. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2020, 104, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhen, H.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Y. MicroRNA-200b Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Ovine Preadipocytes by Targeting p27 and KLF9. Animals 2021, 11, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Jiang, M.; Yang, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, G. Butyrate inhibits the bovine rumen epithelial cell proliferation via downregulation of positive regulators at G0/G1 phase checkpoint. Biocell. 2022, 46, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestell, R.; Albanese, C.; Reutens, A.; Segall, J.; Lee, R.; Arnold, A. The cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in hormonal regulation of proliferation and differentiation. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 501–534. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhan, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, G. SV40T/E6E7-Induced Proliferation Is Involved in the Activity of E2F3 in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals 2022, 12, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12141790
Zhang Y, Zhan K, Hu Z, Zhao G. SV40T/E6E7-Induced Proliferation Is Involved in the Activity of E2F3 in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals. 2022; 12(14):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12141790
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yihui, Kang Zhan, Zixuan Hu, and Guoqi Zhao. 2022. "SV40T/E6E7-Induced Proliferation Is Involved in the Activity of E2F3 in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells" Animals 12, no. 14: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12141790
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhan, K., Hu, Z., & Zhao, G. (2022). SV40T/E6E7-Induced Proliferation Is Involved in the Activity of E2F3 in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals, 12(14), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12141790



