Worldwide Research Trends on Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein: A Bibliometric Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
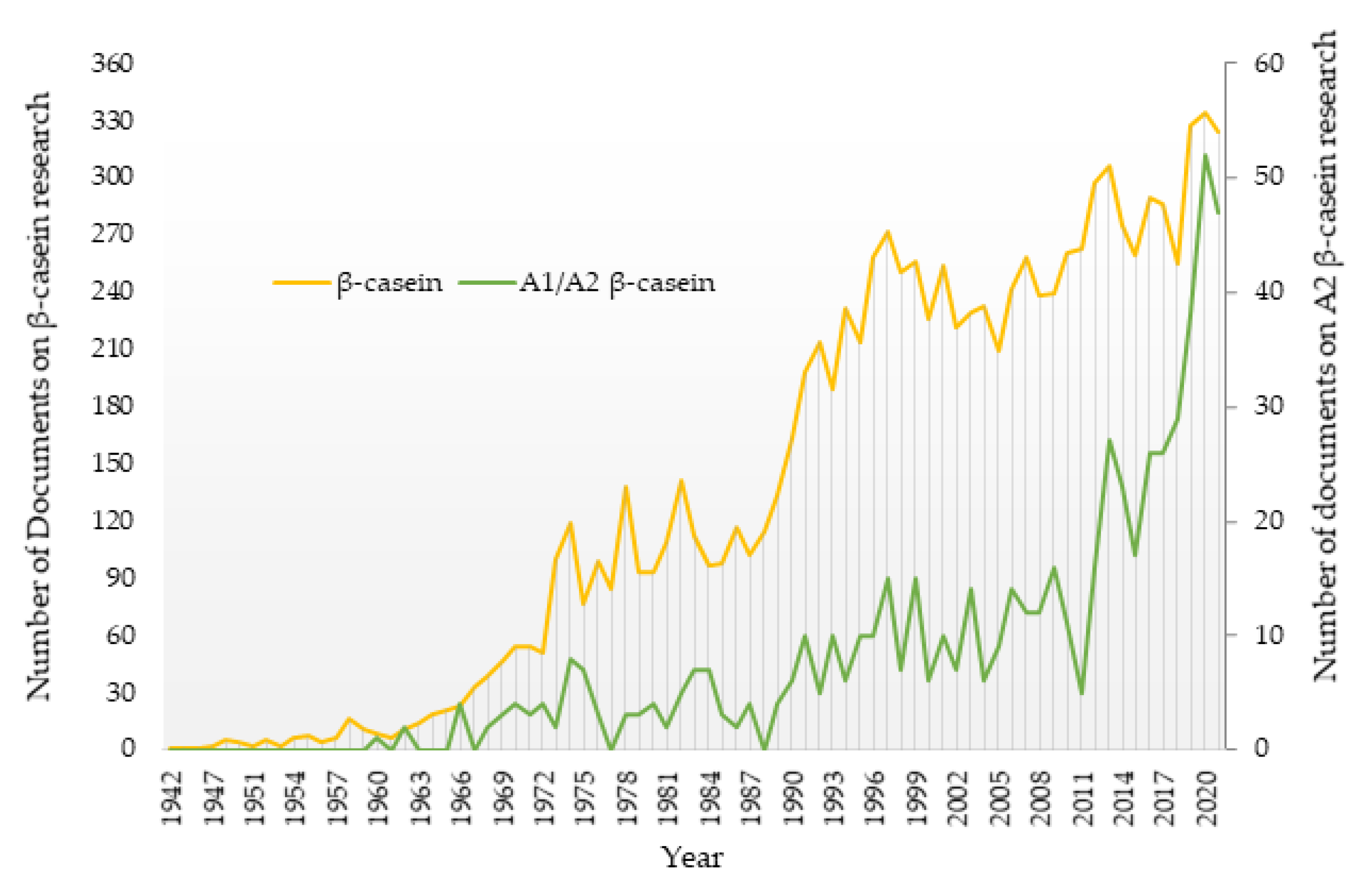
3.1. Evolution of Scientific Output
3.2. Distribution of Scientific Output in Subject Categories
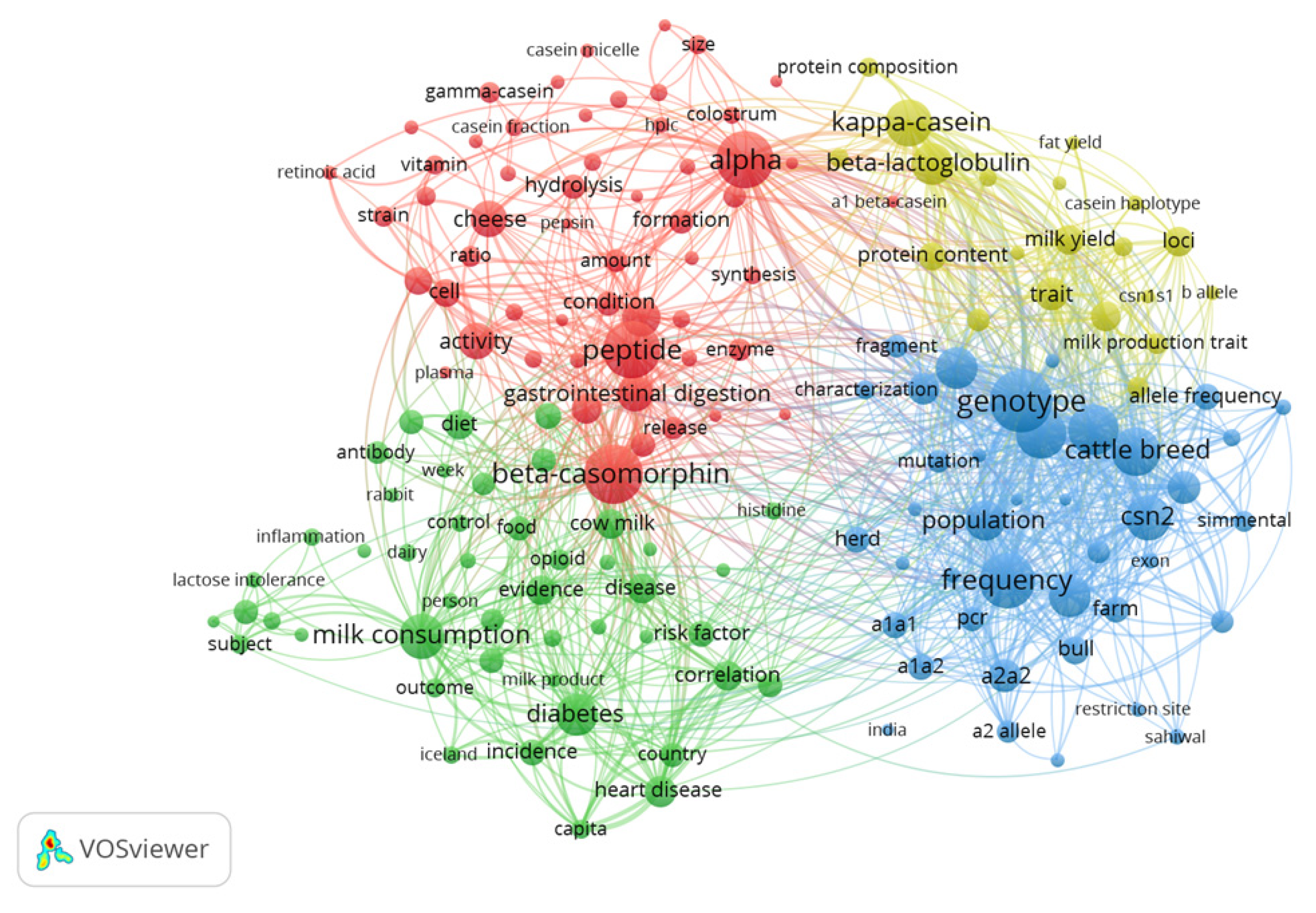
3.3. Analysis of Terms Used in Titles and Abstracts
3.4. Publication Distribution by Country and Institution
3.5. Publication Distribution by Document Type and Source
3.6. The Most Cited Articles Involving A2 and A1 β-Caseins and Health-Related Implications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, J.; Liu, Y. Purification Procedures Meaningfully Influence DNA Quantification in Milk. LWT 2018, 94, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, L.; Worku, M. Recent Perspective on Cow’s Milk Allergy and Dairy Nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, A.; Saini, R.K. A1 Milk and Its Controversy—A Review. Int. J. Bioassays 2015, 4, 4611–4619. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, P.; Mishra, C.; Mishra, B.; Swain, K.; Rout, M.; Mishra, S. Impact of Milk Protein on Human Health: A1 Verses A2. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, A.H.D.N.; Sales, D.C.; Urbano, S.A.; Galvão, J.G.B.; de Andrade Neto, J.C.; Macêdo, C.d.S. Lactose Intolerance and Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Equid Milk for Human Consumption. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 24, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, R.; Sciuto, M.; Marotta, F. Lactose Intolerance: An Update on Its Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Nutr. Res. 2021, 89, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke-Taylor, S.; Dwyer, K.; Woodford, K.; Kost, N. Systematic Review of the Gastrointestinal Effects of A1 Compared with A2 β-Casein. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, L.; Urrutia, O.; Mendizabal, J.A. Conversion to A2 Milk Production with Regard to a Possible Market Demand for Dairy Farms: Possibilities and Implications. ITEA Inf. Tec. Econ. Agrar. 2019, 115, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskous, S. A1- and A2-Milk and Their Effect on Human Health. J. Food Eng. Technol. 2020, 9, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.M.; Chessa, S.; Erhardt, G.J. Invited Review: Milk Protein Polymorphisms in Cattle: Effect on Animal Breeding and Human Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 5335–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaminski, S.; Cieslinska, A.; Elzbieta, K. Polymorphism of Bovine Beta-Casein and Its Potential Effect on Human Health. J. Appl. Genet. 2007, 48, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastiani, C.; Arcangeli, C.; Ciullo, M.; Torricelli, M.; Cinti, G.; Fisichella, S.; Biagetti, M. Frequencies Evaluation of β-Casein Gene Polymorphisms in Dairy Cows Reared in Central Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Venkidasamy, B.; Thirupathi, P.; Chung, I.M.; Subramanian, U. β-Casomorphin: A Complete Health Perspective. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Spencer, G.W.K.; Ong, L.; Gras, S.L. Beta Casein Proteins—A Comparison between Caprine and Bovine Milk. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Sałaga, M.; Storr, M.A.; Fichna, J. Physiology, Signaling, and Pharmacology of Opioid Receptors and Their Ligands in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auestad, N.; Layman, D.K. Dairy Bioactive Proteins and Peptides: A Narrative Review. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianqin, S.; Leiming, X.; Lu, X.; Yelland, G.W.; Ni, J.; Clarke, A.J. Effects of Milk Containing Only A2 Beta Casein versus Milk Containing Both A1 and A2 Beta Casein Proteins on Gastrointestinal Physiology, Symptoms of Discomfort, and Cognitive Behavior of People with Self-Reported Intolerance to Traditional Cows’ Milk. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deth, R.; Clarke, A.; Ni, J.; Trivedi, M. Clinical Evaluation of Glutathione Concentrations after Consumption of Milk Containing Different Subtypes of β-Casein: Results from a Randomized, Cross-over Clinical Trial. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gaudry, D.K.; Lohner, S.; Schmucker, C.; Kapp, P.; Motschall, E.; Horrlein, S.; Roger, C.; Meerpohl, J.J. Milk A1 P-Casein and Health-Related Outcomes in Humans: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 278–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Teixeira, R. Study of the Effects of β-Casein Polymorphism (A2 vs A1) on Acid Coagulation Properties of Milk Official. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2021; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Albarella, S.; Selvaggi, M.; D’anza, E.; Cosenza, G.; Caira, S.; Scaloni, A.; Fontana, A.; Peretti, V.; Ciotola, F. Article Influence of the Casein Composite Genotype on Milk Quality and Coagulation Properties in the Endangered Agerolese Cattle Breed. Animals 2020, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.H.; Schwendel, H.; Harland, D.; Day, L. Differences in the Yoghurt Gel Microstructure and Physicochemical Properties of Bovine Milk Containing A 1 A 1 and A 2 A 2 β-Casein Phenotypes. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cruz-Lovera, C.; Perea-Moreno, A.J.; de la Cruz-Fernández, J.L.; Alvarez-Bermejo, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide Research on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in Public Buildings. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimenez, E.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. DNA Damage Repair System in Plants: A Worldwide Research Update. Genes 2017, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmerón-Manzano, E.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide Scientific Production Indexed by Scopus on Labour Relations. Publications 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archambault, É.; Campbell, D.; Gingras, Y.; Larivière, V. Comparing Bibliometric Statistics Obtained from the Web of Science and Scopus. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimenez, E.; Salinas, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide Research on Plant Defense against Biotic Stresses as Improvement for Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2018, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, J.E.; Buela-Casal, G. The Meaning of the H-Index. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2014, 14, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bornmann, L.; Mutz, R.; Hug, S.E.; Daniel, H.D. A Multilevel Meta-Analysis of Studies Reporting Correlations between the h Index and 37 Different h Index Variants. J. Informetr. 2011, 5, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Montenegro, L.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.; Gimenez, E. Worldwide Research on the Ozone Influence in Plants. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douwe Van Der Ploeg, J. The Food Crisis, Industrialized Farming and the Imperial Regime. J. Agrar. Chang. 2010, 10, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Woodford, K.; Kukuljan, S.; Pal, S. Comparative Effects of A1 versus A2 Beta-Casein on Gastrointestinal Measures: A Blinded Randomised Cross-over Pilot Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasmana, S.; Das, S.; Shrivastava, S. Potential Nutraceuticals from the Casein Fraction of Goat’s Milk. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 46, e13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniloski, D.; Cunha, N.M.D.; McCarthy, N.A.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; McParland, S.; Vasiljevic, T. Health-Related Outcomes of Genetic Polymorphism of Bovine β-Casein Variants: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leischner, C.; Egert, S.; Burkard, M.; Venturelli, S. Potential Protective Protein Components of Cow’s Milk against Certain Tumor Entities. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lee, K.; Chang, M.; Koo, D.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, K.K.; Koo, D.B. Cattle Beta-Casein Gene Targeting Vector Using Homologous Recombination. International Patent Application No. PCT WO 2006/057499, 27 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hye-Min, K.; Hyo Young, P.; Man-Yong, K.; Sanf, M.L. New Porcine Beta-Casein Genomic DNA, Useful for Producing Recombinant Vector for Porcine Specific Gene Expression. Korean Patent PCT KR2008007823, 31 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Bonazza, F.; Palmieri, G.F.; Pucciarelli, S.; Polzonetti, V.; Attarian, L.; Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. A Comparison among β-Caseins Purified from Milk of Different Species: Self-Assembling Behaviour and Immunogenicity Potential. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Sharma, N.; Jawed, B.; Nautiyal, S.; Singh, R. High Resolution Melt Curve Analysis for the Detection of A1, A2 β-Casein Variants in Indian Cows. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 3, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, A.; Rajendran, R.; Ganapathi, P. Detection of A1 and A2 Alleles at Beta-Casein Locus in Bargur and Umblachery (Indian Zebu) Cattle Breeds by Allele-Specific PCR. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2021, B-4273, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglobline, A.N.; Padula, M.P.; Doble, P.A. Quality Control of A1-Free Dairy. Food Control 2022, 135, 108685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Boztepe, S. Assessment of A1 and A2 Variants in the CNS2 Gene of Some Cattle Breeds by Using ACRS-PCR Method. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, A.; Chessa, S.; Bolla, P.; Budelli, E.; Gandini, G.C. Genetic Structure of Milk Protein Polymorphisms and Effects on Milk Production Traits in a Local Dairy Cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2004, 121, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.; Kopuzlu, S.; Topal, M.; Bilgin, O.C. Relationships between Milk Protein Polymorphisms and Production Traits in Cattle: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2018, 61, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, Y.; Vega, S. Péptidos Bioactivos Derivados de Las Proteínas Lácteas: Propiedades y Aplicaciones Principales. Rev. Salud Anim. 2004, 26, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.J. Bioactive Peptides in Milk and Their Biological and Health Implications. Food Rev. Int. 1998, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asledottir, T.; Le, T.T.; Poulsen, N.A.; Devold, T.G.; Larsen, L.B.; Vegarud, G.E. Release of β-Casomorphin-7 from Bovine Milk of Different β-Casein Variants after Ex Vivo Gastrointestinal Digestion. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 81, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Heo, Y.T.; Lee, S.E.; Hwang, K.C.; Lee, H.G.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, N.H. Short Communication: Retinoic Acid plus Prolactin to Synergistically Increase Specific Casein Gene Expression in MAC-T Cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3835–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.J.; Grochoski, G.T.; Clarke, A.J. Health Implications of Milk Containing β-Casein with the A 2 Genetic Variant. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, T.R. Type 1 Diabetes, the A1 Milk Hypothesis and Vitamin D Deficiency. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallén, E.; Wedholm, A.; Andrén, A.; Lundén, A. Effect of β-Casein, κ-Casein and β-Lactoglobulin Genotypes on Concentration of Milk Protein Variants. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2008, 125, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, I.; Gaur, G.K.; Singh, U.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Mann, S. Beta-Casein (CSN2) Polymorphism in Ongole (Indian Zebu) and Frieswal (HF × Sahiwal Crossbred) Cattle. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Chauhan, A. Molecular Characterization of A1/A2 Beta-Casein Alleles in Vrindavani Crossbred and Sahiwal Cattle. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2018, 53, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsen, H.; Olsen, H.G.; Hayes, B.; Sehested, E.; Svendsen, M.; Nome, T.; Meuwissen, T.; Lien, S. Casein Haplotypes and Their Association with Milk Production Traits in Norwegian Red Cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2009, 41, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinc, H.; Ozkan, E.; Koban, E.; Togan, I. Beta-Casein A1/A2, Kappa-Casein and Beta-Lactoglobulin Polymorphisms in Turkish Cattle Breeds. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2013, 56, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gai, N.; Uniacke-lowe, T.; O’regan, J.; Faulkner, H.; Kelly, A.L. Effect of Protein Genotypes on Physicochemical Properties and Protein Functionality of Bovine Milk: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, U. β-Casomorphins: A1 Milk, Milk Peptides and Human Health; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.X. Effects of Cow’s Milk Beta-Casein Variants on Symptoms of Milk Intolerance in Chinese Adults: A Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Study. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sodhi, M.; Mukesh, M.; Sharma, V.; Kataria, R.S.; Sobti, R.C. Harnessing Potential of A2 Milk in India: An Overview. Adv. Anim. Exp. Modeling 2022, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivoglio, D.; Finco, A.; Bucci, G.; Staffolani, G. Is There a Promising Market for the A2 Milk? Analysis of Italian Consumer Preferences. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Poi, R.; de Dominicis, E.; Gritti, E.; Fiorese, F.; Saner, S.; Polverino De Laureto, P. Development of an LC-MS Method for the Identification of β-Casein Genetic Variants in Bovine Milk. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.B.; Harris, D.P.; Hill, J.P.; Bibby, N.J.; Wasmuth, H.E. Type I (Insulin-Dependent) Diabetes Mellitus and Cow Milk: Casein Variant Consumption. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLachlan, C.N.S. β-Casein A1, Ischaemic Heart Disease Mortality, and Other Illnesses. Med. Hypotheses 2001, 56, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tailford, K.A.; Berry, C.L.; Thomas, A.C.; Campbell, J.H. A Casein Variant in Cow’s Milk Is Atherogenic. Atherosclerosis 2003, 170, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noni, I. de Release of β-Casomorphins 5 and 7 during Simulated Gastro-Intestinal Digestion of Bovine β-Casein Variants and Milk-Based Infant Formulas. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truswell, A.S. The A2 Milk Case: A Critical Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Woodford, K.; Kukuljan, S.; Ho, S. Milk Intolerance, Beta-Casein and Lactose. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7285–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.P.G.; Mcnabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C.; Woodford, K.B.; Clarke, A.J. Dietary A1 β-Casein Affects Gastrointestinal Transit Time, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Activity, and Inflammatory Status Relative to A2 β-Casein in Wistar Rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburn, B. Beta Casein A1 and A2 in Milk and Human Health Report to New Zealand Food Safety Authority; New Zealand Food Safety Authority: Melbourne, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- De Noni, I.; FitzGerald, R.; Korhonen, H.; le Roux, Y.; Livesey, C.; Thorsdottir, I.; Tomé, D.; Witkamp, R. Review of the Potential Health Impact of β-casomorphins and Related Peptides. EFSA Sci. Rep. 2009, 231, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kitazawa, H.; Kawai, Y.; Itoh, T. Isolation and Structural Analysis of Antihypertensive Peptides That Exist Naturally in Gouda Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterton, D.E.W.; Nguyen, D.N.; Bering, S.B.; Sangild, P.T. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Bioactive Milk Proteins in the Intestine of Newborns. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1730–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, B.E.; Bylund, D.B.; Huang, T.-S.; Krebs, E.G. Substrate Specificity of the Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinase (Caseins/Protein Sequence). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3448–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mckenzie, H.A.; Brucec Graham, E.R.; Ponzoni, R.W. Effects of Milk Protein Genetic Variants on Milk Yield and Composition. J. Dairy Res. 1984, 51, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Pastewka, J.V.; Peacock, A.C. Differential Staining of Phosphoproteins on Polyacrylamide Gels with a Cationic Carbocyanine Dye. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 56, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F.; Hayes, J.F.; Moxley, J.E.; Monardes, H.G. Association of Genetic Variants of Casein and Milk Serum Proteins with Milk, Fat, and Protein Production by Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 1984, 67, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, J.M.L.; Schennink, A.; van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Bovenhuis, H.; Visker, M.H.P.W.; van Arendonk, J.A.M.; van Hooijdonk, A.C.M. Effects of Milk Protein Variants on the Protein Composition of Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, G.M.; Rosenthal, L.A.; Liu, X.; Hayes, M.P.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Leonard, W.J.; Hennighausen, L.; Finbloom, D.S. STAT5A-Deficient Mice Demonstrate a Defect in Granulocyte-Macrophage-Stimulating Factor—Induced Proliferation and Gene Expression. Blood 1997, 90, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Position | Affiliations | Records | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) | 37 | India |
| 2 | l’Institut National de Recherche pour l’Agriculture, l’Alimentation et l’Environnement (INRAE) | 23 | France |
| 3 | Justus Liebig University Giessen | 29 | Germany |
| 4 | University of Melbourne | 19 | Australia |
| 5 | University of Milan | 18 | Italy |
| 6 | University of Warmia | 17 | Poland |
| 7 | Aarhus University | 15 | Denmark |
| 8 | Université Paris-Saclay | 15 | France |
| 9 | Lincoln University New Zealand | 13 | New Zealand |
| 10 | University of Brescia | 12 | Italy |
| Document Type | Document Type/Total Documents (N°) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Article | 502/618 | 81.2 |
| Review | 31/618 | 5.0 |
| Patent | 27/618 | 4.4 |
| Meeting | 21/618 | 3.4 |
| Other | 19/618 | 3.1 |
| Book | 10/618 | 1.6 |
| Letter | 8/618 | 1.3 |
| Position | Source Titles | Records | % | 5-Years JCR | h-Index | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Dairy Science | 61 | 9.87 | 4.354 | 191 | U.S.A. |
| 2 | International Dairy Journal | 18 | 2.91 | 3.395 | 140 | Netherlands |
| 3 | Journal of Dairy Research | 16 | 2.58 | 2.019 | 77 | U.K. |
| 4 | Animal genetics | 13 | 2.10 | 3.169 | 81 | U.K. |
| 5 | Food Chemistry | 12 | 1.94 | 7.516 | 262 | U.K. |
| 6 | Milchwissenschaft Milk Science International | 11 | 1.78 | 0.247 | 39 | Germany |
| 7 | Nutrients | 9 | 1.45 | 5.719 | 115 | Switzerland |
| 8 | Nutrition Journal | 7 | 1.13 | 3.271 | 90 | U.K. |
| 9 | European Journal of Biochemistry 1 | 6 | 0.97 | - | - | U.K. |
| 10 | Food Hydrocolloids | 6 | 0.97 | 9.147 | 159 | Netherlands |
| Number of Citations 1 | Title (Authors) | Year | Affiliation | Type of Study | +/− A2 -Casein 2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 177 [177] | Polymorphism of bovine beta-casein and its potential effect on human health (Kaminski, S; Cieslinska, A and Kostyra, E) | 2007 | Univ. Warmia (Poland) | Review | + (?) | [12] |
| 136 [136] | Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and cow milk: casein variant consumption (Elliott, RB; Harris, DP; Hill, JP; Bibby, NJ; Wasmuth, HE) | 1999 | Univ. Auckland and New Zealand Dairy Research Institute (New Zealand), and Univ. Düsseldorf (Germany) | Field experiment | + | [64] |
| 116 [116] | Beta-casein A(1), ischaemic heart disease mortality, and other illnesses (McLachlan, CNS) 3 | 2001 | A2 Corp. Ltd. (New Zealand) | Field experiment | + | [65] |
| 83 [83] | A casein variant in cow’s milk is atherogenic (Tailford, KA; Berry, CL; Thomas, AC; Campbell, JH) | 2003 | Univ. Queensland (Australia) | Animal experiment | + | [66] |
| 77 [77] | Release of beta-casomorphins 5 and 7 during simulated gastro-intestinal digestion of bovine beta-casein variants and milk-based infant formula (De Noni, I) | 2008 | Univ. Milan (Italy) | Laboratory experiment | + | [67] |
| 76 [76] | The A2 milk case: a critical review (Truswell, AS) | 2005 | Univ. Sydney (Australia) | Review | − | [68] |
| 73 [73] | Effects of milk containing only A2 beta casein versus milk containing both A1 and A2 beta casein proteins on gastrointestinal physiology, symptoms of discomfort, and cognitive behavior of people with self-reported intolerance to traditional cows’ milk (Sun, JQ; Xu, LM; Lu, X; Yelland, GW, Gregory W; Ni, JY; Clarke, AJ) 3 | 2016 | Fudan Univ., Shanghai Univ., Medical Centers and Consulting Co. (China), Monash Univ. and RMIT Univ (Australia), and A2 Corp. Ltd. (New Zealand) | Clinical human trial | + | [18] |
| 68 [68] | Milk Intolerance, Beta-Casein and Lactose (Pal, S; Woodford, K; Kukuljan, S; Ho, S) 3 | 2015 | Curtin Univ., A2 Corp. Ltd. (Australia) and Lincoln Univ. (New Zealand). | Review | + (?) | [69] |
| 61 [61] | Health implications of milk containing beta-casein with the A(2) genetic variant (Bell, SJ; Grochoski, GT; Clarke, AJ) 3 | 2006 | Ideasphere Inc. (USA), A2 corp LTD (New Zealand) | Review | + (?) | [51] |
| 57 [56] | Comparative effects of A1 versus A2 beta-casein on gastrointestinal measures: a blinded randomised cross-over pilot study (Ho, S; Woodford, K; Kukuljan, S; Pal, S) 3 | 2014 | Curtin Univ., A2 Dairy Products (Australia) and Lincoln Univ. (New Zealand) | Clinical human trial | + | [34] |
| 51 [51] | Effects of cow’s milk beta-casein variants on symptoms of milk intolerance in Chinese adults: a multicentre, randomised controlled study (He, M; Sun, JQ; Jiang, ZQ; Yang, YX) 3 | 2017 | Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou Univ. and Res. Centers, and Chinese Nutrition Society (China) 2 | Clinical human trial | + | [60] |
| 50 [49] | Dietary A1 beta-casein affects gastrointestinal transit time, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity, and inflammatory status relative to A2 beta-casein in Wistar rats (Barnett, MPG; McNabb, WC; Roy, NC; Woodford, KB; Clarke, AJ) 3 | 2014 | AgResearch, Massey Univ., Lincoln Univ. and A2 Corp. Ltd. (New Zealand). | Animal experiment | + | [70] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Montenegro, L.; Alfonso, L.; Mendizabal, J.A.; Urrutia, O. Worldwide Research Trends on Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein: A Bibliometric Study. Animals 2022, 12, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151909
Jiménez-Montenegro L, Alfonso L, Mendizabal JA, Urrutia O. Worldwide Research Trends on Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein: A Bibliometric Study. Animals. 2022; 12(15):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151909
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Montenegro, Lucía, Leopoldo Alfonso, José A. Mendizabal, and Olaia Urrutia. 2022. "Worldwide Research Trends on Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein: A Bibliometric Study" Animals 12, no. 15: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151909
APA StyleJiménez-Montenegro, L., Alfonso, L., Mendizabal, J. A., & Urrutia, O. (2022). Worldwide Research Trends on Milk Containing Only A2 β-Casein: A Bibliometric Study. Animals, 12(15), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151909






