Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Exotic Pets: The Situation in the Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database Source and Management
2.2. Study Design and Animal Samples
2.3. Microbiological Diagnosis Techniques and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
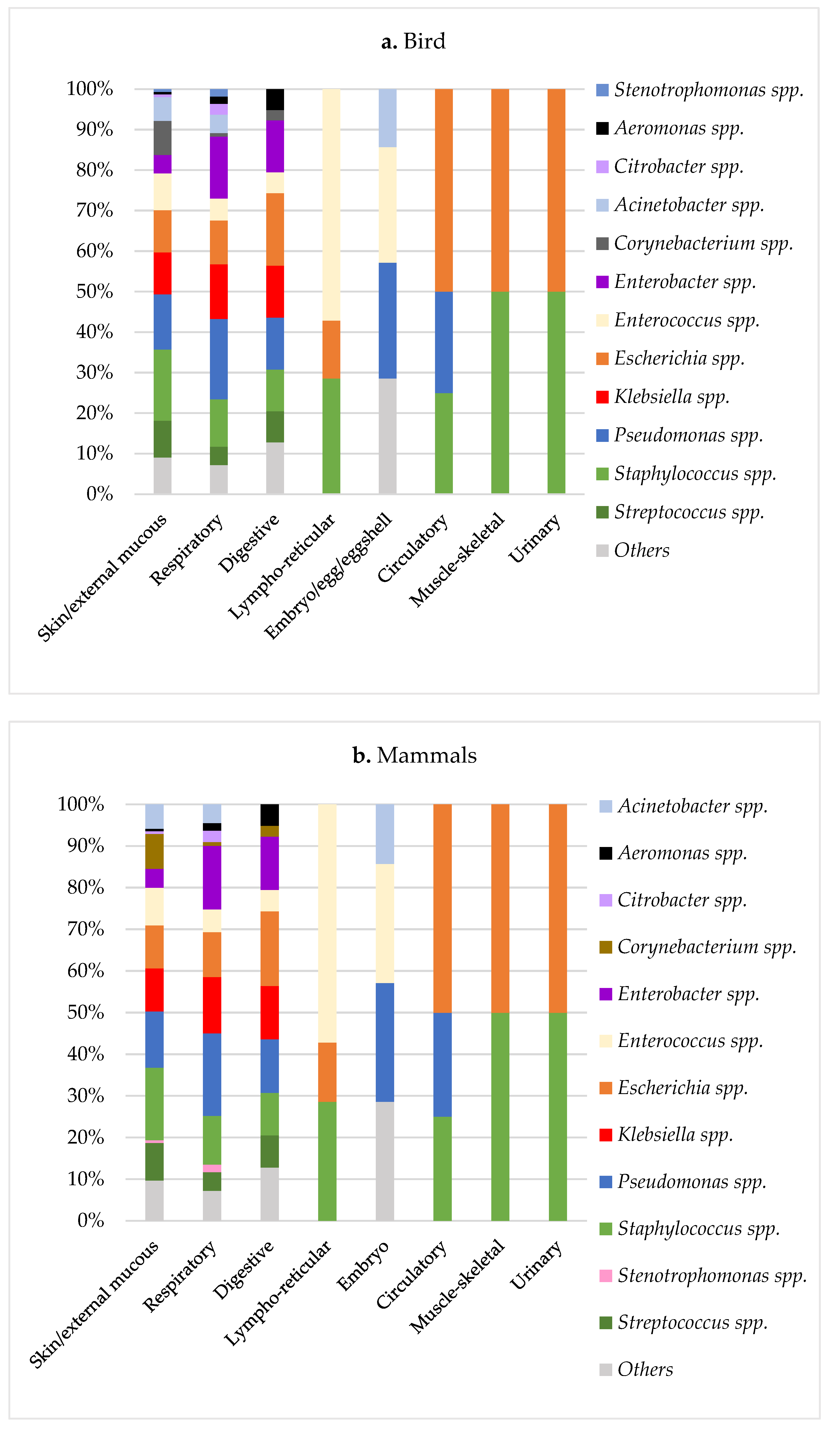
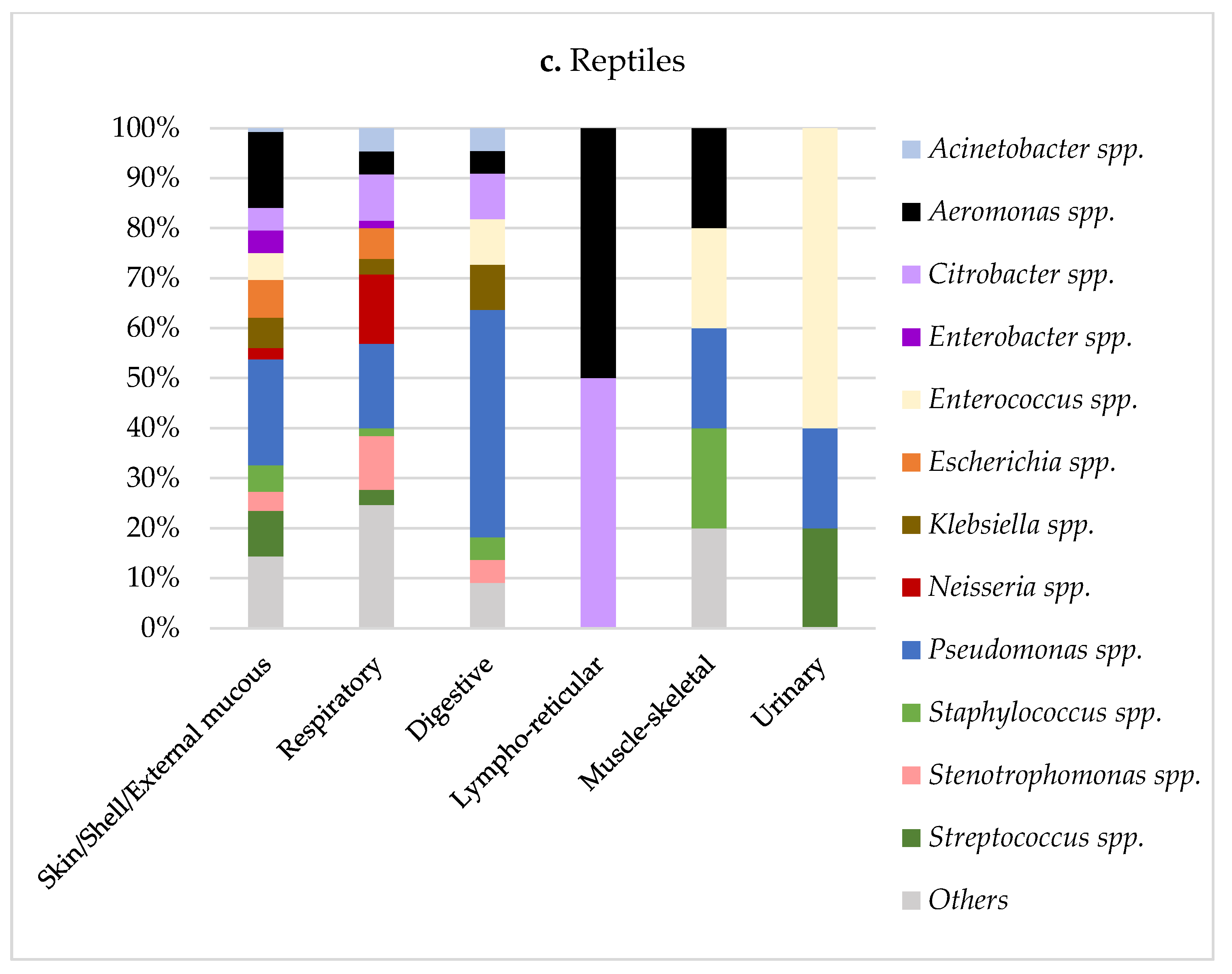
3.1. Microbiological Results in Exotic Pets
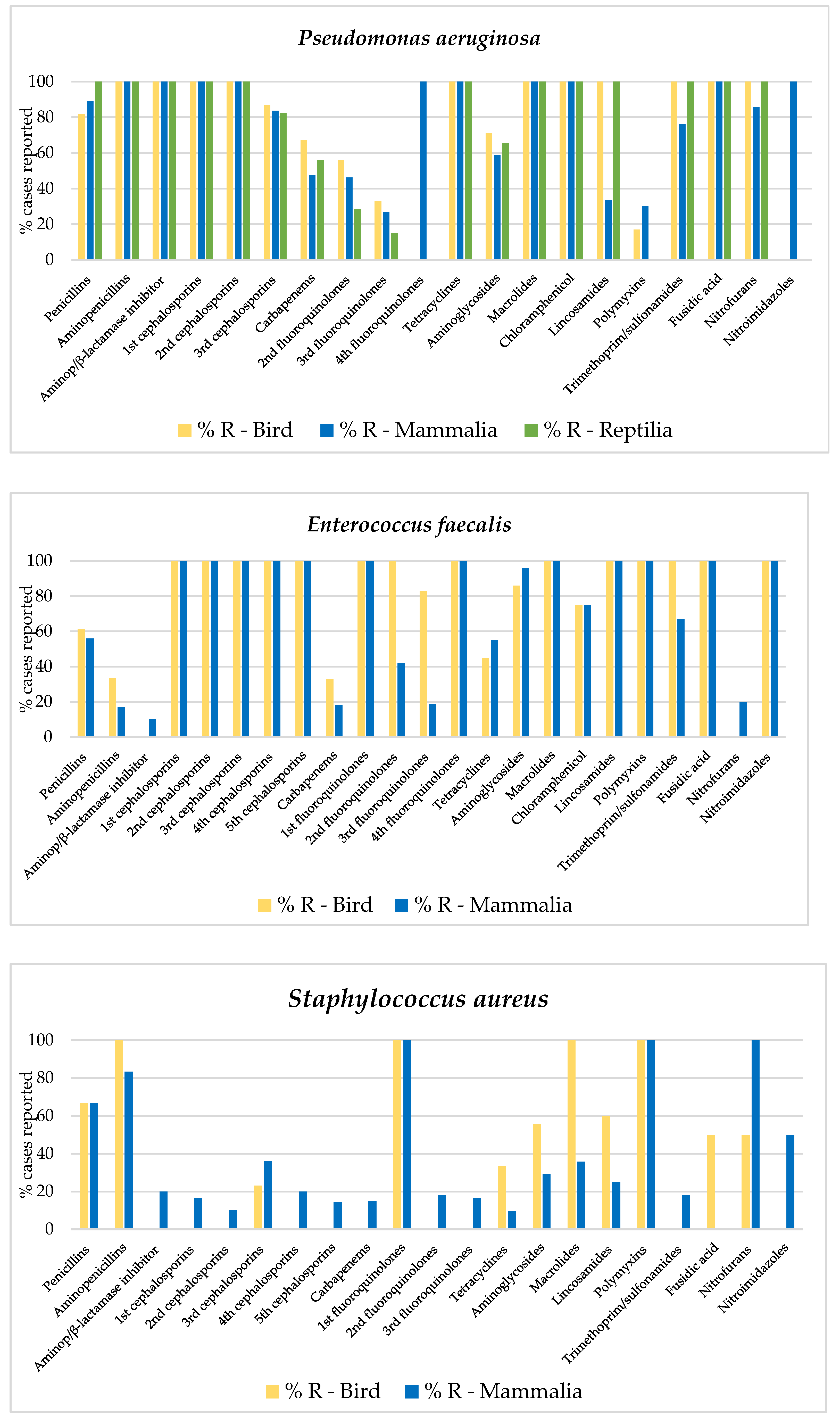
3.2. Prevalence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria
3.3. Frequency of Multidrug Resistance Profiles
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


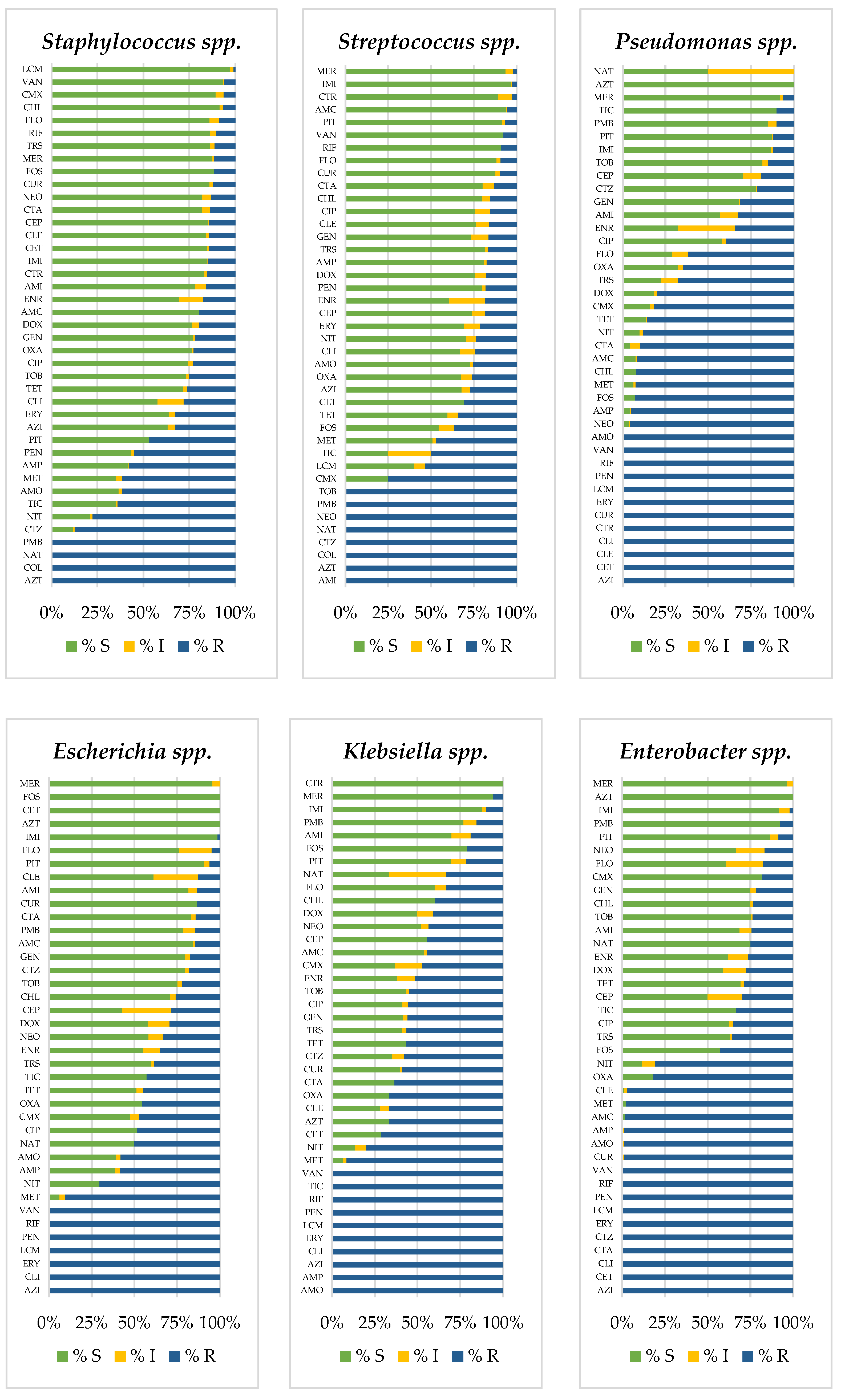
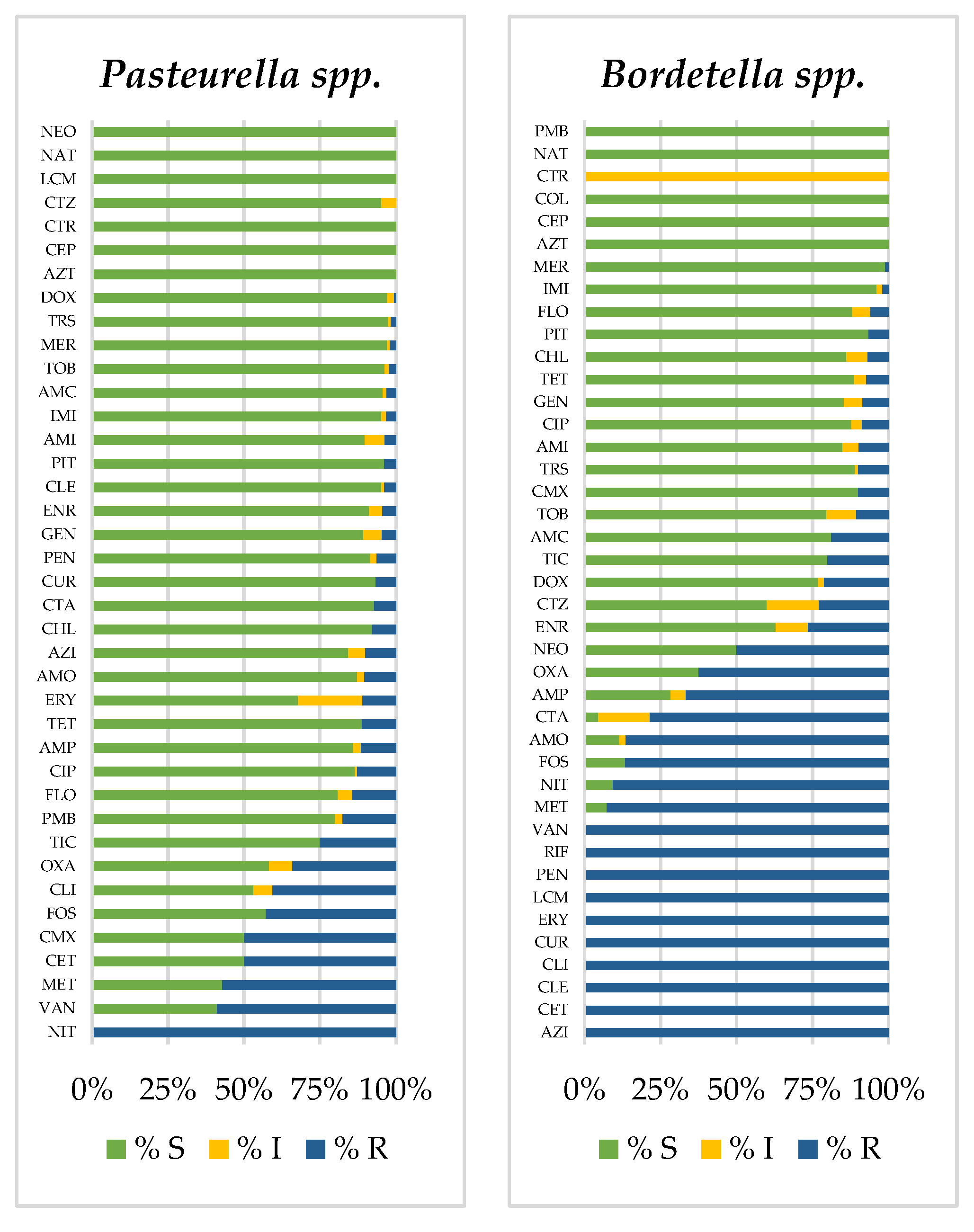

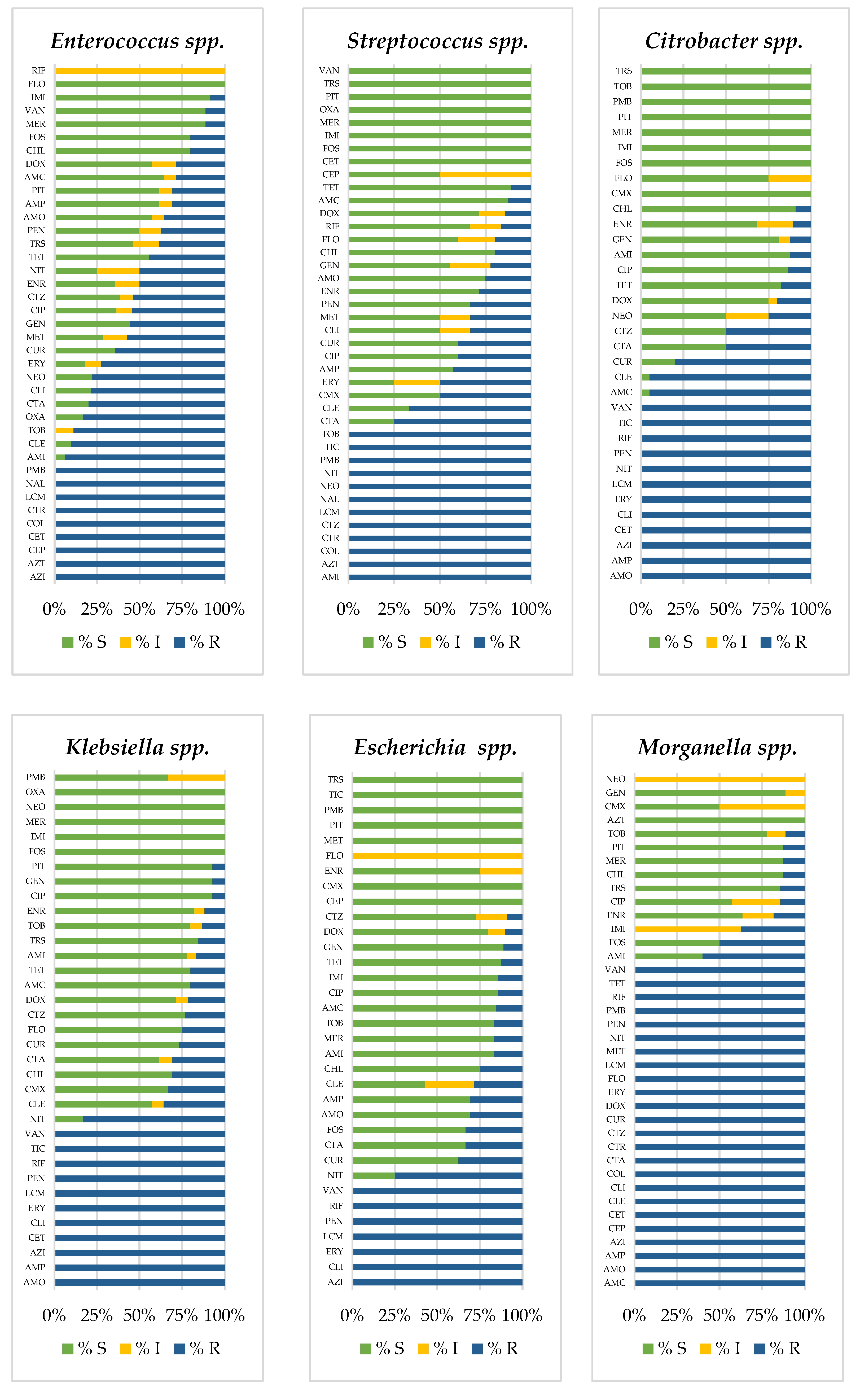
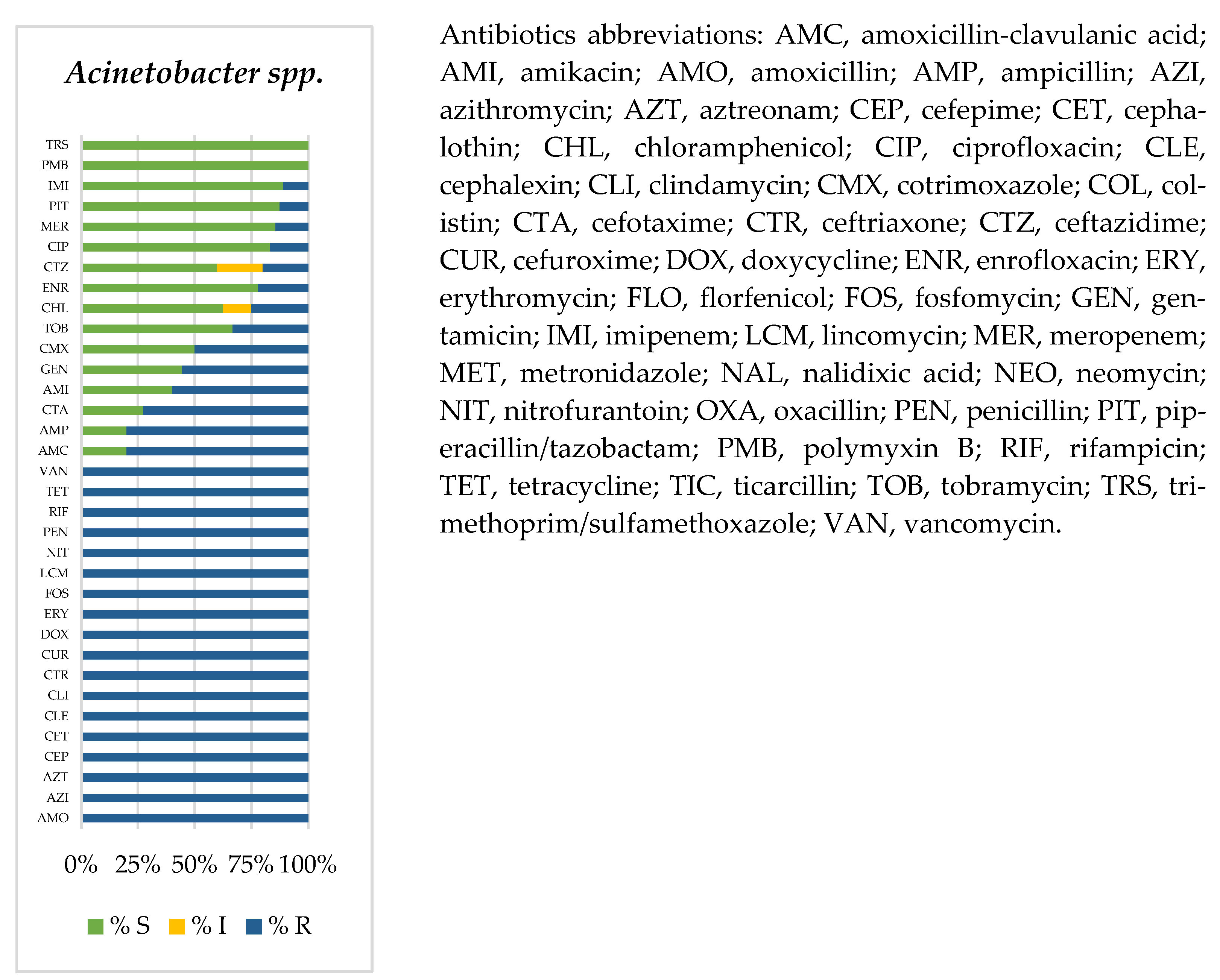
| a. Birds | ||||||
| E. cloacae | E. faecalis | E. coli | K. pneumoniae | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | |
| CFR | CFR | CLE | CLE | CFR | AMI | |
| CLE | CLE | AMI | AMO | CLE | GEN | |
| CET | CET | AMP-S | AMP | CET | AMO | |
| CFZ | CFZ | AMO | CLI | CFZ | AMP | |
| AMI | AMI | AMP | AMC | AMI | CLI | |
| AMP-S | GEN | CHL | DOX | GEN | DOX | |
| AMO | AMO | CLI | TET | AMP-S | TET | |
| AMP | AMP | AMC | CUR | AMO | CTZ | |
| CLI | CHL | DOX | CTA | AMP | NEO | |
| AMC | CLI | TET | CTZ | CHL | TOB | |
| OXA | AMC | FOX | TOB | CLI | FA | |
| DOX | OXA | CUR | FA | AMC | AZI | |
| TRS | DOX | CTA | LMC | DOX | CLR | |
| TET | TET | CTZ | AZI | TET | ERY | |
| FOX | FOX | TOB | CLR | FOX | PIT | |
| CUR | CUR | FA | ERY | CUR | TIC | |
| CTZ | CDN | LMC | JO | CFM | COL | |
| TOB | CFM | AZI | PIT | CEF | PMB | |
| FA | CTA | CLR | TIC | CTA | MIN | |
| LMC | CPD | ERY | CPD | |||
| AZI | CTZ | JO | CTR | |||
| CLR | CTR | PIT | KAN | |||
| ERY | KAN | MIN | NEO | |||
| JO | NEO | TOB | ||||
| SPT | ETP | |||||
| IMI | IMI | |||||
| FA | MER | |||||
| AZI | FA | |||||
| CLR | LMC | |||||
| ERY | AZI | |||||
| JO | CLR | |||||
| PIT | ERY | |||||
| COL | JO | |||||
| PIT | ||||||
| PMB | ||||||
| MIN | ||||||
| TGC | ||||||
| b. Mammals | ||||||
| B. bronchis | E. cloacae | E. coli | K. pneumoniae | P. multocida | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus |
| CFR | CFR | CET | CET | AMI | CFR | CFR |
| CLE | CLE | GEN | AMI | GEN | CLE | CLE |
| CET | CFZ | AMP-S | GEN | AMO | CET | CET |
| CFZ | AMI | AMO | AMP-S | AMP | CFZ | CFZ |
| AMI | GEN | AMP | AMO | CHL | AMI | AMI |
| GEN | AMP-S | CHL | AMP | CLI | GEN | GEN |
| AMP-S | AMO | CLI | CHL | NIT | AMP-S | AMP-S |
| AMO | AMP | AMC | CLI | CDN | AMO | AMO |
| AMP | CLI | OXA | AMC | LMC | AMP | AMP |
| CLI | AMC | MET | OXA | ERY | CHL | CLI |
| AMC | OXA | NIT | MET | JO | CLI | AMC |
| OXA | MET | DOX | DOX | PMB | AMC | OXA |
| MET | NIT | TRS | TRS | OXA | MET | |
| DOX | DOX | TET | TET | MET | NIT | |
| TRS | TRS | CUR | FOX | DOX | DOX | |
| FOX | TET | CDN | CUR | TRS | TRS | |
| CUR | FOX | CFM | CDN | TET | TET | |
| CPD | CUR | CEF | CFM | FOX | FOX | |
| CTR | CDN | CTR | CEF | CUR | CUR | |
| KAN | CFM | KAN | CPD | CDN | CDN | |
| CIP | CEF | TOB | CTR | CTA | CEF | |
| MER | CTA | MER | KAN | CEP | CTA | |
| AZI | CPD | LMC | SPT | CPD | CEP | |
| CLR | CTR | AZI | CIP | CTR | CPD | |
| ERY | KAN | CLR | MER | KAN | CTR | |
| LVX | SPT | ERY | LMC | NEO | KAN | |
| JO | TOB | LVX | MXF | TOB | NEO | |
| PIT | CIP | JO | AZI | ETP | SPT | |
| TIC | MER | PIT | CLR | CIP | MER | |
| MIN | LMC | TIC | ERY | MER | FA | |
| AZI | MIN | LVX | FA | LMC | ||
| CLR | JO | AZI | MXF | |||
| ERY | PIT | CLR | ERY | |||
| LVX | TIC | ERY | LVX | |||
| JO | NOR | LVX | JO | |||
| PIT | PMB | JO | TIC | |||
| TIC | MIN | PIT | NOR | |||
| MIN | TIC | COL | ||||
| PMB | PMB | |||||
| MIN | MIN | |||||
| TGC | ||||||
| c. Reptiles | ||||||
| A. hydrophyla | C. freundii | E. cloacae | E. coli | M. morganii | P. aeruginosa | S. maltophilia |
| CLE | CFR | CFR | GEN | CFR | CFR | CFR |
| GEN | CLE | CLE | AMC | CLE | CLE | CLE |
| AMP-S | CFZ | CFZ | OXA | CFZ | CFZ | CFZ |
| AMO | AMI | AMI | CEF | AMI | AMI | AMI |
| AMP | AMO | GEN | CEP | GEN | GEN | GEN |
| CHL | AMP | AMP-S | NEO | AMO | AMP-S | AMP-S |
| DOX | CHL | AMO | LMC | AMP | AMO | AMO |
| FOX | AMC | AMP | MXF | CHL | AMP | AMP |
| CUR | OXA | CHL | AZI | AMC | CHL | CHL |
| CEP | FOX | AMC | CLR | OXA | CLI | AMC |
| MER | CUR | OXA | ERY | DOX | AMC | OXA |
| AZI | CEF | NIT | JO | TRS | OXA | TRS |
| LMC | DOX | CUR | DOX | TET | ||
| MXF | FOX | CEF | TRS | FOX | ||
| AZI | CUR | KAN | TET | CUR | ||
| CLR | CFM | NEO | FOX | CDN | ||
| ERY | LMC | CIP | CDN | CFM | ||
| JO | MXF | MER | CFM | CEF | ||
| MIN | AZI | LMC | CEF | CEP | ||
| CLR | MXF | CEP | CTR | |||
| ERY | AZI | CTR | SPT | |||
| JO | CLR | SPT | TOB | |||
| TIC | ERY | TOB | ETP | |||
| PMB | JO | CIP | CIP | |||
| TGC | COL | IMI | IMI | |||
| PMB | LMC | MER | ||||
| MIN | MXF | FA | ||||
| TGC | AZI | LMC | ||||
| CLR | MXF | |||||
| ERY | AZI | |||||
| JO | CLR | |||||
| MIN | ERY | |||||
| TGC | JO | |||||
| PIT | ||||||
| TIC | ||||||
References
- Darwich, L.; Seminati, C.; Burballa, A.; Nieto, A.; Durán, I.; Tarradas, N.; Molina-López, R.A. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacterial Isolates from Urinary Tract Infections in Companion Animals in Spain. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, R.; Montrose, V.; Wills, A. ExNOTic: Should We Be Keeping Exotic Pets? Animals 2017, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, T.Z. Update: Reptiles and Salmonella. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2011, 20, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L. Pet Animals as Reservoirs of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria: Review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larry, K.; Joseph, A.; Frederick, J. Exposure to Nontraditional Pets at Home and to Animals in Public Settings: Risks to Children. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Fernández, R.; Durán, I.; Molina-López, R.A.; Darwich, L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Cats and Dogs From the Iberian Peninsula. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 621597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.M.; Smith, K.F.; D’Auria, J.P. Exotic Pets: Health and Safety Issues for Children and Parents. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2012, 26, e2–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, C.; Arena, P.C.; Steedman, C.; Jessop, M. A Review of Captive Exotic Animal-Linked Zoonoses. J. Environ. Health Res. 2012, 12, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Day, M.J. Pet-Related Infections. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 94, 794–802. [Google Scholar]
- Broens, E.M.; van Geijlswijk, I.M. Prudent Use of Antimicrobials in Exotic Animal Medicine. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2018, 21, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Vila, J.; Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Pérez-Santigosa, N.; de Frutos-Escobar, C.; Herrero-Herrero, A. Salmonella in Free-Living Exotic and Native Turtles and in Pet Exotic Turtles from SW Spain. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 85, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, C.; Ingresa-Capaccioni, S.; González-Bodi, S.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Vega, S. Free-Living Turtles Are a Reservoir for Salmonella but Not for Campylobacter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ardiaca García, M.; Montesinos Barceló, A.; Bonvehí Nadeu, C.; Jekl, V. Respiratory Diseases in Guinea Pigs, Chinchillas and Degus. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2021, 24, 419–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Found. Stat. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Berends, M.S.; Luz, C.F.; Friedrich, A.W.; Sinha, B.N.M.; Albers, C.J.; Glasner, C. AMR—An R Package for Working with Antimicrobial Resistance Data. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EMA/CVMP/CHMP. Categorisation of Antibiotics in the European Union; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cantas, L.; Suer, K. Review: The Important Bacterial Zoonoses in “One Health” Concept. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lightfoot, N. Bacteria of Potential Health Concern. In Heterotrophic Plate Counts and Drinking-Water Safety: The Significance of HPCs for Water Quality and Human Health; Bartram, J., Cotruvo, J., Exner, M., Fricker, C., Glasmacher, A., Eds.; IWA Publishing; World Health Organization: London, UK, 2003; p. 61. ISBN 1-84339-025-6. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, D.L.; Khakhria, R.; Johnson, W.M. Human Salmonellosis Associated with Exotic Pets. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2786–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th Revision; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ciofu, O.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Tolerance and Resistance of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms to Antimicrobial Agents—How P. Aeruginosa Can Escape Antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanderi, T.; Shrimanker, I.; Mansoora, Q.; Shah, K.; Yumen, A.; Komanduri, S. Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia: An Emerging Pathogen of the Respiratory Tract. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e921466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Q.; Rao, X. Morganella Morganii, a Non-Negligent Opportunistic Pathogen. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 50, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The Animal-Foods-Environment Interface of Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Germany: An Observational Study on Pathogenicity, Resistance Development and the Current Situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, J.; Falgenhauer, L.; Domann, E.; Bauerfeind, R.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T. Multiresistant Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from Humans, Companion Animals and Horses in Central Hesse, Germany. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ewers, C.; Stamm, I.; Pfeifer, Y.; Wieler, L.H.; Kopp, P.A.; Schønning, K.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Scheufen, S.; Stolle, I.; Günther, S.; et al. Clonal Spread of Highly Successful ST15-CTX-M-15 Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Companion Animals and Horses. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2676–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danko, D.; Bezdan, D.; Afshin, E.E.; Ahsanuddin, S.; Bhattacharya, C.; Butler, D.J.; Chng, K.R.; Donnellan, D.; Hecht, J.; Jackson, K.; et al. A global metagenomic map of urban microbiomes and antimicrobial resistance. Cell 2021, 184, 3376–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Access, Watch, Reserve (AWaRe) Classification of Antibiotics for Evaluation and Monitoring of Use, 2021; (WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.04). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]



| Class | % Negatives (N) | % Positives (N) | Sum * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birds | 26.6 | (149) | 73.4 | (412) | 561 |
| Mammals | 18.3 | (539) | 81.7 | (2399) | 2938 |
| Reptiles | 7.8 | (29) | 92.2 | (345) | 374 |
| Total | 18.5 | (717) | 81.5 | (3156) | 3873 |
| Class | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birds | 53 | 73 | 62 | 121 | 103 | 412 (13) |
| Columbiformes | 3 | 1 | 4 (1) | |||
| Galliformes | 5 | 7 | 10 | 15 | 16 | 53 (12.8) |
| Passeriformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 (1) | |
| Psittaciformes | 47 | 65 | 52 | 102 | 85 | 351 (85.2) |
| Mammals | 265 | 342 | 434 | 602 | 756 | 2399 (76) |
| Carnivora | 20 | 22 | 20 | 22 | 16 | 100 (4.1) |
| Eulipotyphla | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 7(0.3) | |
| Lagomorpha | 200 | 235 | 297 | 454 | 571 | 1757 (73.2) |
| Rodentia | 43 | 85 | 116 | 125 | 166 | 535 (22.3) |
| Reptiles | 60 | 44 | 55 | 96 | 90 | 345 (11) |
| Squamata | 27 | 14 | 22 | 41 | 34 | 138 (40) |
| Testudines | 33 | 30 | 33 | 55 | 56 | 207 (60) |
| Total | 378 | 459 | 551 | 819 | 949 | 3156 (100) |
| Isolations Per Animal Class (% 1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbiological Results | Birds | Mammals | Reptiles | Total Population |
| Acinetobacter spp. 2 | 16 (3.9) | 96 (4) | 12 (3.5) | 124 (3.9) |
| A. baumannii | 3 (0.7) | 12 (0.5) | 4 (1.1) | |
| A. Iwoffii | 5 (1.2) | 17 (0.7) | 1 (0.3) | |
| Aeromonas spp. 2 | 5 (1.2) | 18 (0.7) | 34 (9.8) | 57 (1.8) |
| A. hydrophila | 2 (0.4) | 14 (0.6) | 17 (4.9) | |
| A. veronii | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 6 (1.7) | |
| Bordetella spp. 2 | 1 (0.2) | 164 (6.8) | 7 (2) | 172 (5.4) |
| B. bronchiseptica | 1 (0.2) | 155 (6.5) | 5 (1.4) | |
| Citrobacter spp. 2 | 5 (1.2) | 20 (0.8) | 20 (5.8) | 45 (1.4) |
| C. freundii | 4 (1) | 10 (0.4) | 14 (4) | |
| Enterobacter spp. 2 | 35 (8.5) | 152 (6.3) | 14 (4) | 201 (6.4) |
| E. cloacae | 27 (6.5) | 120 (5) | 11 (3.2) | |
| Enterococcus spp. 2 | 33 (8) | 103 (4.3) | 18 (5.2) | 154 (4.9) |
| E. faecalis | 14 (3.4) | 56 (2.3) | 8 (2.3) | |
| Escherichia spp. 2 | 55 (13.3) | 128 (5.3) | 15 (4.3) | 198 (6.3) |
| E. coli | 54 (13.1) | 118 (4.9) | 15 (4.3) | |
| Klebsiella spp. 2 | 46 (11.1) | 146 (6.1) | 16 (4.6) | 208 (6.6) |
| K. pneumoniae | 30 (7.3) | 98 (4.1) | 3 (0.9) | |
| K. oxytoca | 12 (2.9) | 37 (1.5) | 12 (3.5) | |
| Morganella spp. 2 | 0 | 6 (0.2) | 14 (4) | 20 (0.6) |
| M. morganii | 0 | 5 (0.2) | 14 (4) | |
| Pasteurella spp. 2 | 2 (0.4) | 198 (8.3) | 1 (0.3) | 201 (6.4) |
| P. multocida | 2 (0.4) | 144 (6) | 1 (0.3) | |
| Pseudomonas spp. 2 | 57 (13.8) | 315 (13.1) | 80 (23.2) | 452 (14.3) |
| P. aeruginosa | 44 (10.7) | 217 (9) | 62 (18) | |
| P. fluorescens | 0 | 16 (0.7) | 0 | |
| Staphylococcus spp. 2 | 69 (16.7) | 389 (16.2) | 11 (3.2) | 469 (14.9) |
| S. aureus | 11 (2.7) | 122 (5.1) | 1 (0.3) | |
| S. epidermidis | 8 (1.9) | 25 (1) | 0 | |
| S. pseudintermedius | 0 | 20 (0.8) | 0 | |
| S. sciuri | 7 (1.7) | 9 (0.4) | 1 (0.3) | |
| S. xylosus | 2 (0.4) | 37 (1.5) | 2 (0.6) | |
| Stenotrophomonas spp. 2 | 4 (1) | 18 (0.8) | 16 (4.6) | 38 (1.2) |
| S. maltophilia | 4 (1) | 18 (0.8) | 16 (4.6) | |
| Streptococcus spp. 2 | 30 (7.3) | 236 (9.8) | 17 (4.9) | 283 (9) |
| S. intermedius | 0 | 26 (1.1) | 0 | |
| Other spp. | 54 (13.1) | 410 (17.1) | 70 (20.3) | 534 (16.9) |
| Total | 412 (100) | 2399 (100) | 345 (100) | 3156 (100) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Ibarra, E.; Molina-López, R.A.; Durán, I.; Garcias, B.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Exotic Pets: The Situation in the Iberian Peninsula. Animals 2022, 12, 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151912
Muñoz-Ibarra E, Molina-López RA, Durán I, Garcias B, Martín M, Darwich L. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Exotic Pets: The Situation in the Iberian Peninsula. Animals. 2022; 12(15):1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151912
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Ibarra, Eleonora, Rafael A. Molina-López, Inma Durán, Biel Garcias, Marga Martín, and Laila Darwich. 2022. "Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Exotic Pets: The Situation in the Iberian Peninsula" Animals 12, no. 15: 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151912
APA StyleMuñoz-Ibarra, E., Molina-López, R. A., Durán, I., Garcias, B., Martín, M., & Darwich, L. (2022). Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Exotic Pets: The Situation in the Iberian Peninsula. Animals, 12(15), 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12151912






