The Characteristics of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification
2.2. MLST Analysis
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.4. Virulence Gene Detection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
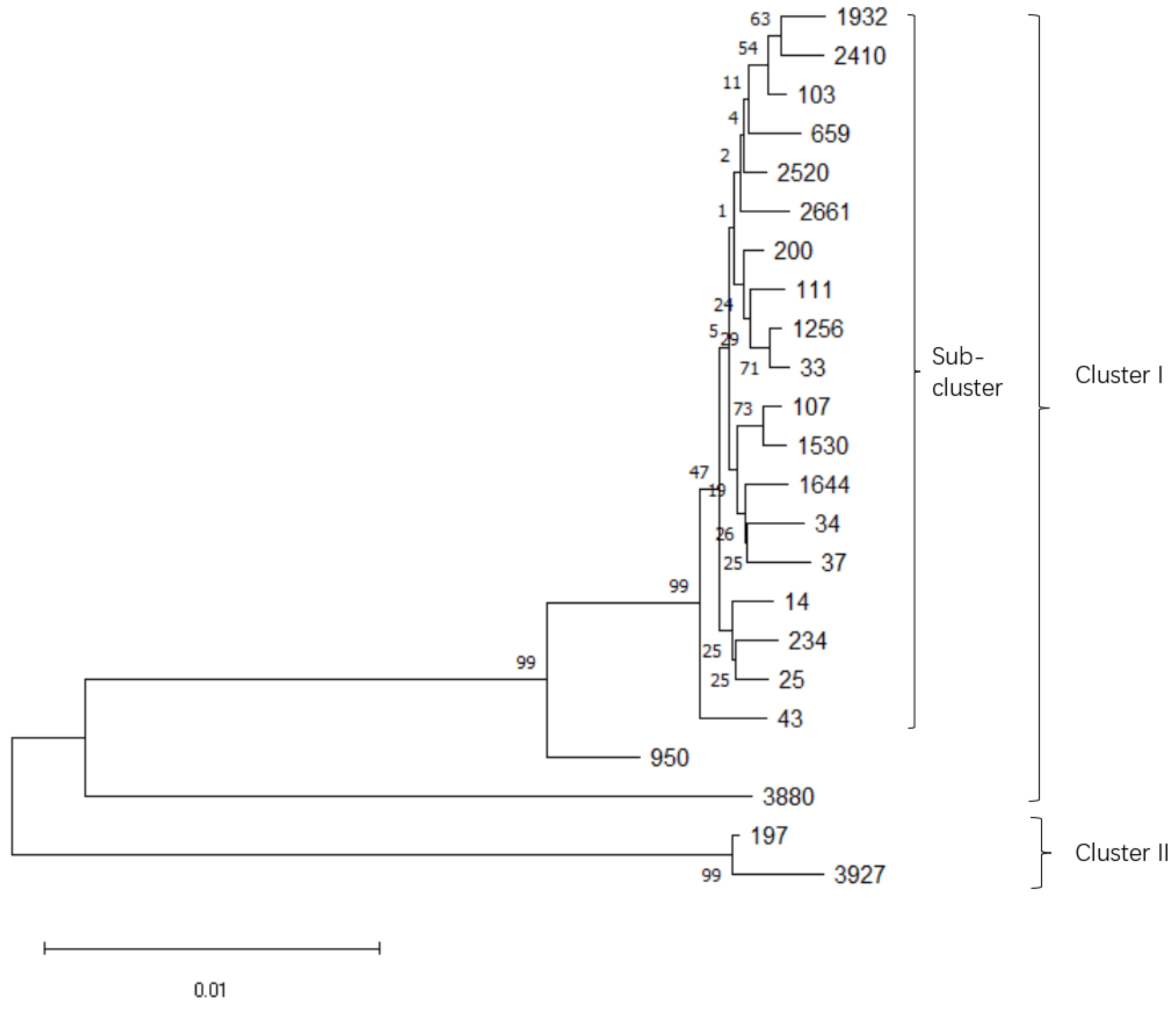
3.1. Microbiological Characterization and Sequence Types of K. pneumoniae Isolates
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination
3.3. Virulence Gene Detection
3.4. Correlations between Virulence Gene Frequency and Antimicrobial Susceptibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bar, D.; Tauer, L.W.; Bennett, G.; González, R.; Hertl, J.A.; Schukken, Y.H.; Schulte, H.F.; Welcome, F.L.; Gröhn, Y.T. The cost of generic clinical mastitis in dairy cows as estimated by using dynamic programming. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertl, J.A.; Groehn, Y.T.; Leach, J.; Bar, D.; Bennett, G.J.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Rauch, B.J.; Welcome, F.L.; Tauer, L.W.; Schukken, Y.H. Effects of clinical mastitis caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and other organisms on the probability of conception in New York State Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Deng, Z.; Cai, L.; Shan, R.; Zhang, S.; Zou, J.; Kastelic, J.P. Incidence of clinical mastitis and distribution of pathogens on large Chinese dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4797–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Ma, S.; Lei, L.; He, J.; Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence, etiology, and economic impact of clinical mastitis on large dairy farms in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 242, 108570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, L.K.; Fung, C.P.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, N.; Yeh, K.M.; Koh, T.H.; Ip, M. Molecular typing and virulence analysis of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from liver abscess patients and stool samples from noninfectious subjects in Hong Kong, Singapore, and Taiwan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3761–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.G.; Zhao, S.; Simjee, S.; Wagner, D.D.; McDermott, P.F. Antimicrobial resistance of foodborne pathogens. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virto, M.; Santamarina-García, G.; Amores, G.; Hernández, I. Antibiotics in Dairy Production: Where Is the Problem? Dairy 2022, 3, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Shang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Characteristics of quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from bovine mastitis in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6244–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, J. Molecular Characterization and Antimicrobial Sensitivity of Pathogens from Sub-Clinical and Clinical Mastitis in Eastern China. Pak. Vet. J. 2013, 33, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gong, Z.; Shang, S. Isolation and characterization of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from raw cow milk in Jiangsu and Shandong provinces, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Yang, S.J.; Shin, S.; Seo, K.S.; Park, Y.H.; Park, K.T. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bovine Mastitic Milk in Korea. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, P.A.; Shanthi, M.; Sekar, U. Characterisation of virulence genes associated with pathogenicity in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candan, E.D.; Aksöz, N. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Characteristics of carbapenem resistance and virulence factors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuursted, K.; Schler, L.; Hansen, F.; Dam, K.; Struve, C. Virulence of a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain carrying the New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1 (NDM-1). Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennequin, C.; Robin, F. Correlation between antimicrobial resistance and virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champs, C.D.; Rich, C.; Chandezon, P.; Chanal, C.; Sirot, D.; Forestier, C. Factors associated with antimicrobial resistance among clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: 1-year survey in a French university hospital. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 23, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.S.; Gonzalez, R.N.; Harmon, R.J.; Nickerson, S.C.; Smith, K.L. Laboratory Handbook on Bovine Mastitis; National Mastitis Council: Madison, WI, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, S.; Heller, E.D.; Krifucks, O.; Sela, S.; Hammer-Muntz, O.; Leitner, G. Identification of a bovine mastitis Escherichia coli subset. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.; Brisse, S. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae Nosocomial Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Li, Z.; Lan, S.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Song, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Shan, W. Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with cattle infections in southwest China using multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), antibiotic resistance and virulence-associated gene profile analysis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49 (Suppl. 1), 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M100-S21; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 21st ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2011.
- M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 31st ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021.
- Turton, J.F.; Perry, C.; Elgohari, S.; Hampton, C.V. PCR characterization and typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae using capsular type-specific, variable number tandem repeat and virulence gene targets. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.L.; Ko, W.C.; Cheng, K.C.; Lee, C.C.; Lai, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C. Comparison of prevalence of virulence factors for Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses between isolates with capsular K1/K2 and non-K1/K2 serotypes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, J.; Dufour, S.; Archambault, M. Characterization of Klebsiella isolates obtained from dairy cattle clinical mastitis cases. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3392–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Bamberg, W.; Beldavs, Z.G.; Dumyati, G.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Maloney, M.; McAllister-Hollod, L.; Nadle, J.; et al. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Choi, H.I.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; Gho, Y.S.; Jeon, S.G. Vaccination with Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived extracellular vesicles protects against bacteria-induced lethality via both humoral and cellular immunity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Virulence evolution, molecular mechanisms of resistance and prevalence of ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A review over the last 10 years. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Min, W.; Li, X.; Hu, F.; Tang, A. ST37 Klebsiella pneumoniae: Development of carbapenem resistance in vivo during antimicrobial therapy in neonates. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Fang, L.X.; Cheng, K.; Xu, G.H.; Wang, X.R.; Liao, X.P.; Liu, Y.H.; Jian, S. Clonal Spread of 16S rRNA Methyltransferase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST37 with High Prevalence of ESBLs from Companion Animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura-Silva, R.; Cerdeira, L.; Oliveira-Silva, M.; da Costa, K.R.C.; Sano, E.; Fuga, B.; Moura, Q.; Esposito, F.; Lincopan, N.; Wyres, K.; et al. Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A retrospective study in Manaus, Brazil. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, S.G.; Tchesnokova, V.; Struve, C.; Weissman, S.J.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Yakovenko, O.; Aprikian, P.; Sokurenko, E.V.; Krogfelt, K.A. Comparative structure-function analysis of mannose-specific FimH adhesins from Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6592–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regué, M.; Hita, B.; Piqué, N.; Izquierdo, L.; Merino, S.; Fresno, S.; Benedí, V.J.; Tomás, J.M. A gene, uge, is essential for Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Wang, C.K.; Peng, H.L.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Hong, Y.M.; Lin, C.T. Role of the small RNA RyhB in the Fur regulon in mediating the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and iron acquisition systems in Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, Y. Integron carrier of Klebsiella pneumoniae and its correlation with virulence genes and drug resistance in Chinese. Chin. J. Nosocomiol. 2021, 31, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Gu, G.; Han, Q.; Zhao, L.; Qian, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Xu, J. Distribution of drug resistance and virulence genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates and their relationship. Chongqing Med. 2016, 45, 2820–2823. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q. Distribution of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a hospital and the relationship between its drug resistance and the number of virulence genes carried. Lab. Med. Clin. 2021, 18, 3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, S.; Ze, N.; He, C. Relationship between virulence of clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates and drug resistance phenotypes. Chin. J. Nosocomiol. 2022, 32, 496–500. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidullina, E.; Shelenkov, A.; Yanushevich, Y.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Edelstein, M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of OXA-48- and CTX-M-15-Co-Producing Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 Recovered from Nosocomial Outbreak. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.; Davies, F.; Turton, J.; Perry, C.; Payne, Z.; Pike, R. Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids in “High-Risk” Clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Including Those Carrying blaNDM-5. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkova, P.; Lazareva, I.; Avdeeva, A.; Sulian, O.; Likholetova, D.; Ageevets, V.; Lebedeva, M.; Gostev, V.; Sopova, J.; Sidorenko, S. Emergence of Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids Harboring New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae in Russia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ST | MLST Allele | Isolates (No.) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST14 | 1-6-1-1-1-1-1 | 4 | 5.9 |
| ST25 | 2-1-1-1-10-4-13 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST33 | 2-3-5-1-12-4-9 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST34 | 2-3-6-1-9-7-4 | 2 | 2.9 |
| ST37 | 2-9-2-1-13-1-16 | 2 | 2.9 |
| ST43 | 2-6-1-5-11-1-15 | 7 | 10.3 |
| ST103 | 4-1-1-1-9-1-6 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST107 | 2-1-2-17-27-1-39 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST111 | 2-1-5-1-17-4-42 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST197 | 16-28-21-27-47-22-67 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST200 | 2-1-2-1-12-1-68 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST234 | 2-1-2-1-7-1-24 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST659 | 66-1-65-1-9-11-8 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST950 | 2-1-1-20-56-4-31 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST1256 | 2-1-58-1-12-4-220 | 4 | 5.9 |
| ST1530 | 1-1-1-3-27-1-39 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST1644 | 2-95-2-3-1-4-274 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST1932 | 10-7-1-26-10-4-127 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST2410 | 4-1-13-2-10-44-6 | 6 | 8.8 |
| ST2520 | 2-1-2-1-9-1-42 | 3 | 4.4 |
| ST2661 | 4-7-2-1-9-4-25 | 13 | 19.1 |
| ST3880 | 18-22-26-22-154-13-165 | 1 | 1.5 |
| ST3927 | 16-24-21-138-153-40-67 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Types | Virulence Genes | Isolates (No.) | Positive Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capsular polysaccharides | rmpA | 3 | 4.4 |
| wcaG | 8 | 11.8 | |
| Allantoins | allS | 0 | 0.0 |
| Siderophores | kfuBC | 34 | 50.0 |
| ybtA | 16 | 23.5 | |
| iucB | 36 | 52.9 | |
| iroNB | 3 | 4.4 | |
| Pilis | fimH | 68 | 100.0 |
| Lipopolysaccharides | ureA | 68 | 100.0 |
| uge | 68 | 100.0 | |
| wabG | 68 | 100.0 |
| Antimicrobial | Virulence Genes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | rmpA | wcaG | kfuBC | ybtA | iucB | iroNB | |
| R (no.) | 0.015 | 0.176 | −0.143 | −0.348 ** | 0.110 | 0.231 | 0.176 |
| TE | - | 0.276 * | −0.049 | −0.463 ** | −0.075 | 0.359 ** | 0.276 * |
| S | - | 0.257 * | −0.213 | −0.299 * | 0.099 | 0.370 ** | 0.257 * |
| GM | - | −0.054 | −0.091 | −0.125 | −0.139 | −0.015 | −0.054 |
| AZM | - | −0.054 | −0.091 | 0.025 * | −0.139 | −0.265 * | −0.054 |
| CEF | - | −0.078 | 0.008 | −0.183 | 0.120 | −0.113 | −0.078 |
| P | - | 0.089 | 0.023 | 0.000 | 0.132 | 0.191 | 0.089 |
| AMX | - | 0.149 | −0.040 | −0.189 | 0.161 | 0.167 | 0.149 |
| PIP | - | −0.073 | −0.124 | −0.242 * | 0.154 | −0.068 | −0.073 |
| βL | - | 0.046 | 0.078 | −0.072 | 0.119 | 0.228 | 0.046 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Wu, X.; Cao, H.; Pei, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. The Characteristics of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China. Animals 2022, 12, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192627
Xu T, Wu X, Cao H, Pei T, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Yang Z. The Characteristics of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192627
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tianle, Xinyue Wu, Hainan Cao, Tianxu Pei, Yu Zhou, Yi Yang, and Zhangping Yang. 2022. "The Characteristics of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China" Animals 12, no. 19: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192627
APA StyleXu, T., Wu, X., Cao, H., Pei, T., Zhou, Y., Yang, Y., & Yang, Z. (2022). The Characteristics of Multilocus Sequence Typing, Virulence Genes and Drug Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China. Animals, 12(19), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192627






