The Improvement of Porcine In Vitro Embryo Development through Regulating Autophagy by miRNA-143 Inhibition
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collecting and Preparing the Oocytes
2.2. Outline of the Experiment
2.3. Parthenogenetic Activation of Porcine Oocytes
2.4. Microinjection
2.5. Assessment of Embryo Development
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining of Embryo
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis via qRT-PCR
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Embryo Growth after miR-143 Microinjection
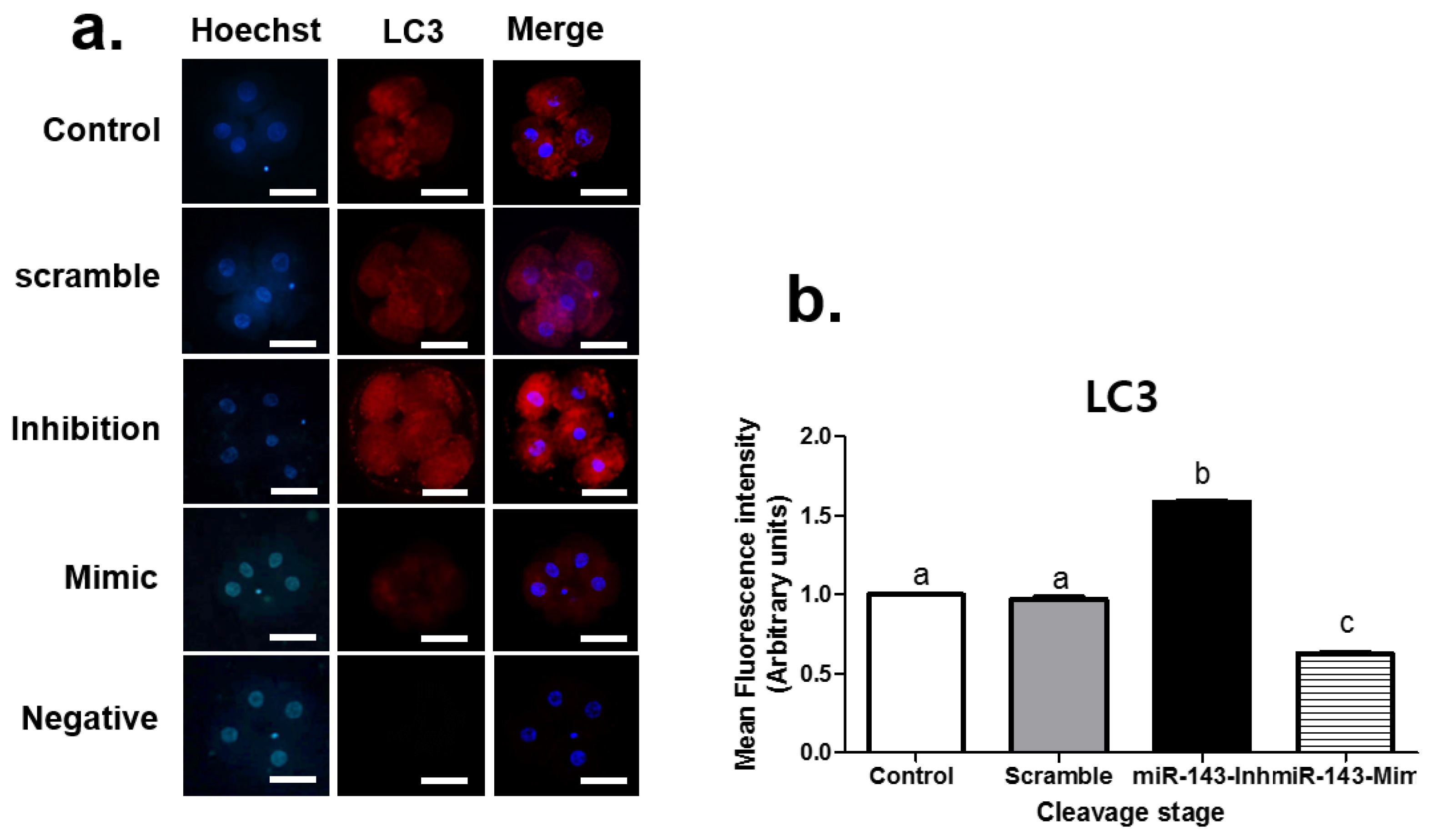
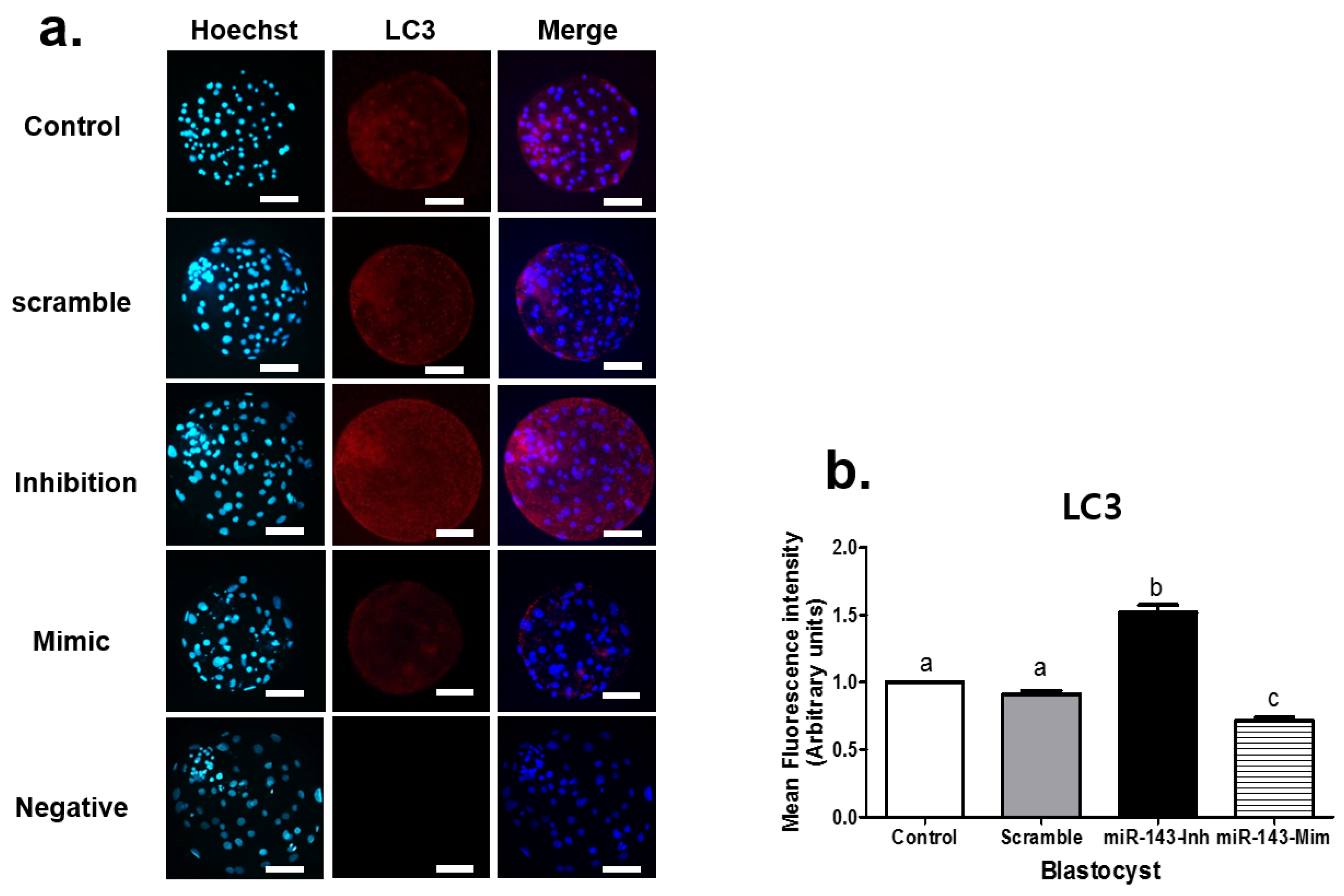
3.2. Effect of miR-143 Microinjection on Autophagy in Porcine Embryos
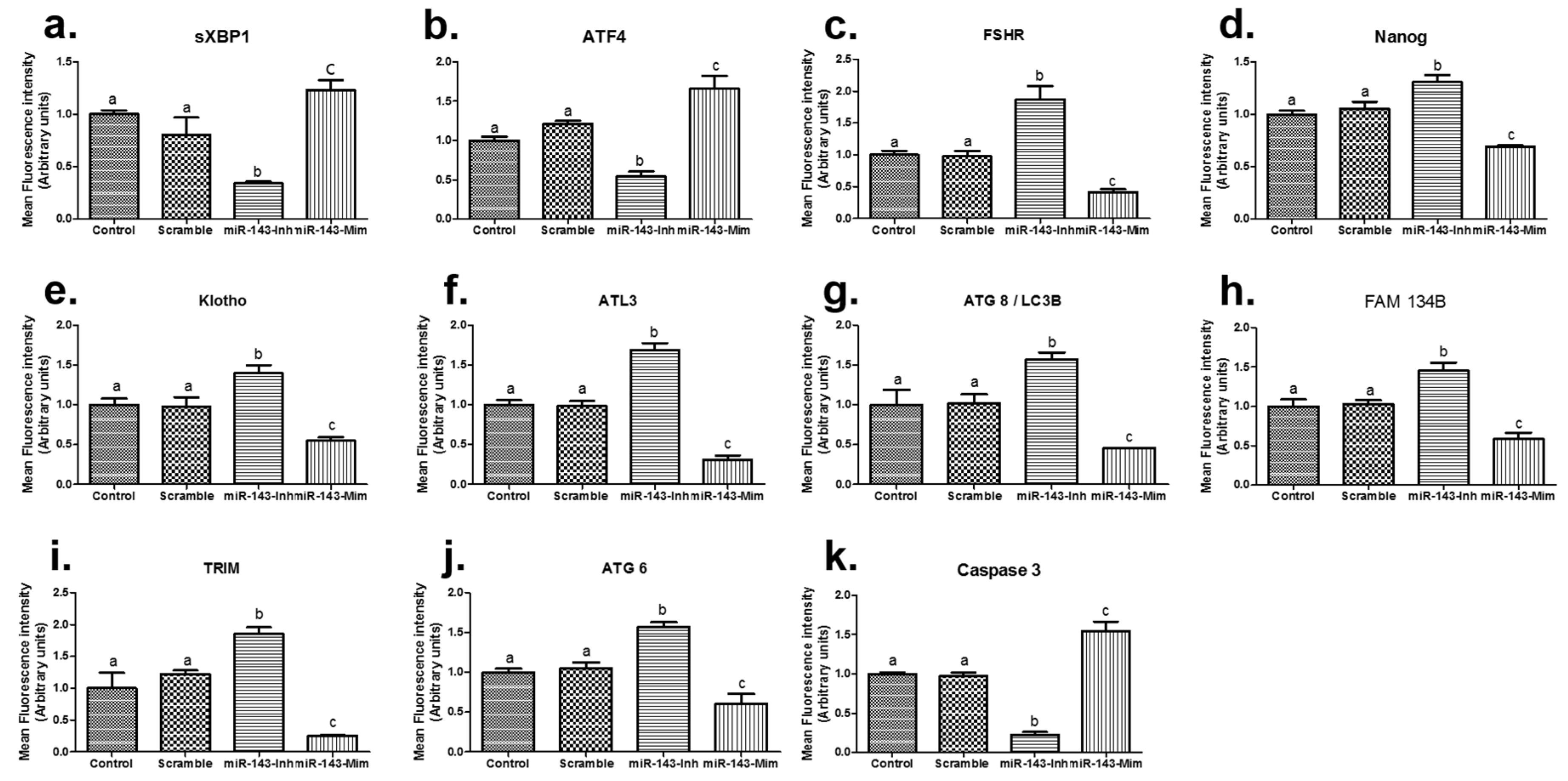
3.3. Gene Expression Analysis of Embryos Microinjected with miR-143
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, T.-Y. MicroRNAs in Human Diseases: From Lung, Liver and Kidney Diseases to Infectious Disease, Sickle Cell Disease and Endometrium Disease. Immune Netw. 2011, 11, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Kaneda, M.; O’Carroll, D.; Hajkova, P.; Barton, S.C.; Sun, Y.A.; Lee, C.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Lao, K.; Surani, M.A. Maternal microRNAs are essential for mouse zygotic development. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausser, J.; Syed, A.P.; Bilen, B.; Zavolan, M. Analysis of CDS-located miRNA target sites suggests that they can effectively inhibit translation. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagga, S.; Bracht, J.; Hunter, S.; Massirer, K.; Holtz, J.; Eachus, R.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs Results in Target mRNA Degradation. Cell 2005, 122, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, N.; Kropp, J.; Khatib, H. MicroRNA Signaling in Embryo Development. Biology 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Q. TGF-β signaling controls FSHR signaling-reduced ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis through the SMAD4/miR-143 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawke, D.C.; Ahmed, D.B.; Watson, A.J.; Betts, D.H. Murine Blastocysts Release Mature MicroRNAs Into Culture Media That Reflect Developmental Status. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 655882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yao, J.; Cao, C.; Liang, X.; Huang, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, G.; Tao, C.; Li, C.; et al. PPARγ is regulated by miR-27b-3p negatively and plays an important role in porcine oocyte maturation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, J.T.; Flöter, V.L.; Robinson, M.D.; Bauersachs, S.; Ulbrich, S.E. Small RNA-seq analysis of single porcine blastocysts revealed that maternal estradiol-17beta exposure does not affect miRNA isoform (isomiR) expression. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, H.M.; Curry, E.; Calcatera, S.M.; Krisher, R.L.; Paczkowski, M.; Pratt, S.L. Cloning and expression of porcine Dicer and the impact of developmental stage and culture conditions on MicroRNA expression in porcine embryos. Gene 2012, 501, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. Exosomal miR-143-3p derived from follicular fluid promotes granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting BMPR1A in polycystic ovary syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.-T.; Zheng, X.-B.; Fan, D.-J.; Yao, Q.-Q.; Hu, J.-C.; Lian, L.; Wu, X.-J.; Lan, P.; He, X.-S. MicroRNA-143 Targets ATG2B to Inhibit Autophagy and Increase Inflammatory Responses in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hu, T.; Hu, P.; Qi, C.; Qian, L. miR-143-3p inhibits endometriotic stromal cell proliferation and invasion by inactivating autophagy in endometriosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Jin, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, G.; Lee, B. The effects of canthaxanthin on porcine oocyte maturation and embryo development in vitro after parthenogenetic activation and somatic cell nuclear transfer. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2016, 51, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlo, M.R.; Kim, G.A.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, B.C. Zinc supplementation alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress during porcine oocyte in vitro maturation by upregulating zinc transporters. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 236, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Ma, X.; An, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. MicroRNA-29b regulates DNA methylation by targeting Dnmt3a/3b and Tet1/2/3 in porcine early embryo development. Dev. Growth Differ. 2018, 60, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Kosuke, M.; Koriyama, M.; Inada, E.; Saitoh, I.; Ohtsuka, M.; Nakamura, S.; Sakurai, T.; Watanabe, S.; Miyoshi, K. Timing of CRISPR/Cas9-related mRNA microinjection after activation as an important factor affecting genome editing efficiency in porcine oocytes. Theriogenology 2017, 108, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridlo, M.; Kim, E.; Kim, G. MicroRNA-210 Regulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Porcine Embryos. Animals 2021, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Kim, G.A.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Ridlo, M.R.; Lee, S.H.; Ra, K.; Ahn, C.; Lee, B.C. Phytanic acid-derived peroxisomal lipid metabolism in porcine oocytes. Theriogenology 2020, 157, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lee, S.; Setyawan, E.M.N.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, G.A.; Han, H.J.; Ahn, C.; Lee, B.C. A potential role of knockout serum replacement as a porcine follicular fluid substitute for in vitro maturation: Lipid metabolism approach. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6984–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Jin, J.-X.; Lee, S.; A Kim, G.; Suh, Y.H.; Ahn, M.S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, B.Y. Improved early development of porcine cloned embryos by treatment with quisinostat, a potent histone deacetylase inhibitor. J. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 65, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, J.C.; A Jones, P. Epigenetics and MicroRNAs. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 61, 24R–29R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.-X.; Lee, S.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, G.A.; Lee, B.C. The HDAC Inhibitor LAQ824 Enhances Epigenetic Reprogramming and In Vitro Development of Porcine SCNT Embryos. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taweechaipaisankul, A.; A Kim, G.; Jin, J.; Lee, S.; Qasim, M.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, B.C. Enhancement of epigenetic reprogramming status of porcine cloned embryos with zebularine, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-M.; Pang, R.T.K.; Chiu, P.C.N.; Wong, B.P.C.; Lao, K.; Lee, K.-F.; Yeung, W.S.B. Sperm-borne microRNA-34c is required for the first cleavage division in mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 109, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-X.; Du, Z.-Q.; Wright, E.C.; Rothschild, M.F.; Prather, R.S.; Ross, J.W. Small RNA Profile of the Cumulus-Oocyte Complex and Early Embryos in the Pig1. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Syed, T.W.; Liu, R.; Yu, J. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Fang, L.; Xuan, J.; Li, H.; Khorshidi, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Li, X.; Yang, B.B. miR-17 extends mouse lifespan by inhibiting senescence signaling mediated by MKP7. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, Y.; Shu, Y.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Lu, G.; Zhang, S. miR-124 regulates cell apoptosis and autophagy in dopaminergic neurons and protects them by regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Shen, J.; Li, D.; Ning, B.; Guo, L.; Bing, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Overexpression of microRNA-9 inhibits 3T3-L1 cell adipogenesis by targeting PNPLA3 via activation of AMPK. Gene 2019, 730, 144260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Guan, G.; Wu, X.; Shi, F.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, W. Circular RNA FOXP1 relieves trophoblastic cell dysfunction in recurrent pregnancy loss via the miR-143-3p/S100A11 cascade. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9081–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgisdottir, A.B.; Lamark, T.; Johansen, T. The LIR motif—Crucial for selective autophagy. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3237–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaffagnini, G.; Martens, S. Mechanisms of Selective Autophagy. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Product Number | Micro-RNA | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm | Base Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rna-double-Customorder | miR-143 mimic | UGAGAUGAAGCACUGUAGCUC | 73.8 | 21 |
| GAGCUACAGUGCUUCAUCUCA | ||||
| rna-single-Customorder | miR-143 inhibitor | GAGCUACAGUGCUUCAUCUCA | 73.8 | 21 |
| rna-double-Customorder | Scramble | CGAACAGAUAAAGCCGCUGUAAGUA | - | 25 |
| UACUUACAGCGGCUUUAUCUGUUCG |
| Genes | Primer Sequences | Accession Number | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| sXBP1 | F: GGAGTTAAGACAGCGCTTGG R: GAGATGTTCTGGAGGGGTGA | NM_001271738.1 | 142 |
| ATF4 | F: AGTCCTTTTCTGCGAGTGGG R: CTGCTGCCTCTAATACGCCA | NM_001123078.1 | 80 |
| FSHR | F: TTCACAGTCGCCCTCTTTCC R: ACGTACAGCTGTGACAAGGG | NM_214386.3 | 101 |
| Nanog | F: GGTTTATGGGCCTGAAGAAA R: GATCCATGGAGGAAGGAAGA | NM_01119971 | 98 |
| Klotho | F: GCTACAGC ATCAGA CGTGGA R: TCCCTT CTAGGGG CTGATTT | XM_021065566.1 | 147 |
| ATL3 | F: TCGAGGAAGTACAGGTCGGT R: TGGCATCCCTACCACTCT GA | XM_021082904.1 | 127 |
| ATG8/LC3 | F: GGGCGTAGGAGACACAAGAG R: AAGGTTTTCTCGGACGGCAT | NM_001190290.1 | 134 |
| FAM134B | F: TTGCCCACTGAGCTCAAGAG R: CACTGCTCAGAGGAAGGGTG | XM_003483804.4 | 103 |
| TRIM | F: AAAACCCGATTGCTTTGCCC R: CTTCCAGCAGCTCCATCACA | XM_021065576.1 | 91 |
| ATG6 | F: AGGGAGCTGGCATTAGAGGA R: AGCCTGGACCTTCTCGAGAT | NM_001044530.1 | 99 |
| Caspase3 | F: GCCATGGTGAAGAAGGAAAA R: GGCAGGCCTGAATTATGAAA | NM_214131.1 | 132 |
| GAPDH | F: GTCGGTTGTGGATCTGACCT R: TTGACGAAGTGGTCGTTGAG | NM_001206359 | 207 |
| Group | Number of Embryos | Number of Embryos Developed (Mean ± SEM, %) | Total Blastocyst Cell Number (Mean ± SEM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≧2 Cells | Blastocyst | |||
| Control | 192 | 151 (78.65 ± 0.56) a | 38 (20.03 ± 0.9) a | 63.13 ± 0.65 a |
| Scramble | 189 | 147 (77.74 ± 0.74) a | 36 (19.15 ± 0.63) a | 61.33 ± 0.64 a |
| miR-143-inhibition | 191 | 167 (87.54 ± 0.35) b | 60 (31.58 ± 1.50) b | 76.21 ± 0.71 b |
| miR-143-mimic | 189 | 126 (66.31 ± 1.76) c | 24 (13.04 ± 1.43) c | 46.08 ± 0.44 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ridlo, M.R.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, E.P.; Kim, G.A. The Improvement of Porcine In Vitro Embryo Development through Regulating Autophagy by miRNA-143 Inhibition. Animals 2022, 12, 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192651
Ridlo MR, Kim EH, Kim EP, Kim GA. The Improvement of Porcine In Vitro Embryo Development through Regulating Autophagy by miRNA-143 Inhibition. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192651
Chicago/Turabian StyleRidlo, Muhammad Rosyid, Eui Hyun Kim, Eun Pyo Kim, and Geon A. Kim. 2022. "The Improvement of Porcine In Vitro Embryo Development through Regulating Autophagy by miRNA-143 Inhibition" Animals 12, no. 19: 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192651
APA StyleRidlo, M. R., Kim, E. H., Kim, E. P., & Kim, G. A. (2022). The Improvement of Porcine In Vitro Embryo Development through Regulating Autophagy by miRNA-143 Inhibition. Animals, 12(19), 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192651





