The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the “Weep and Sweep” Response during Gastro—Intestinal Helminth Infections
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Helminths
3. Structure of the Gut Epithelium
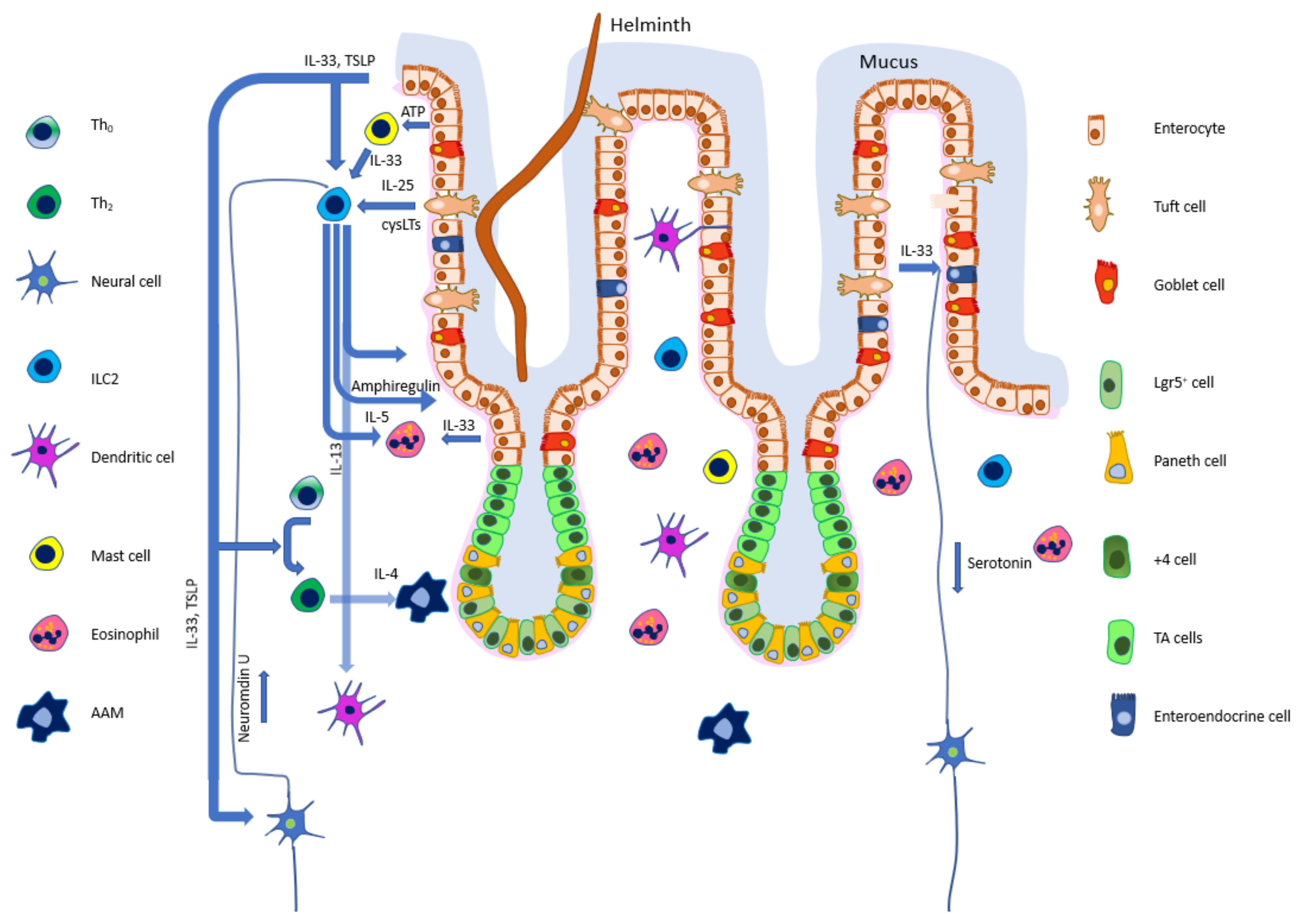
4. Epithelial Cells Modulate the Immune Response
5. Mucus as the First Physical Frontier
6. Epithelium as the Second Physical Frontier
7. Helminth Recognition
8. The First Interplay between the Epithelium and Immune Cells
9. Physical Expulsion of Parasites
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anthony, R.M.; Rutitzky, L.I.; Urban, J.F.; Stadecker, M.J.; Gause, W.C. Protective Immune Mechanisms in Helminth Infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henry, E.K.; Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. Type 2 Cytokine Responses: Regulating Immunity to Helminth Parasites and Allergic Inflammation. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 3, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faniyi, A.A.; Wijanarko, K.J.; Tollitt, J.; Worthington, J.J. Helminth Sensing at the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier—A Taste of Things to Come. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Sharkey, K.A.; McKay, D.M. Modulation of the Immune Response by Helminths: A Role for Serotonin? Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motran, C.C.; Silvane, L.; Chiapello, L.S.; Theumer, M.G.; Ambrosio, L.F.; Volpini, X.; Celias, D.P.; Cervi, L. Helminth Infections: Recognition and Modulation of the Immune Response by Innate Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/sth/index.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Umbrello, G.; Pinzani, R.; Bandera, A.; Formenti, F.; Zavarise, G.; Arghittu, M.; Girelli, D.; Maraschini, A.; Muscatello, A.; Marchisio, P.; et al. Hookworm Infection in Infants: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąska, P.; Norbury, L.J.; Wiśniewski, M.; Januszkiewicz, K.; Wędrychowicz, H. Excretory/Secretory Products of Fasciola Hepatica but Not Recombinant Phosphoglycerate Kinase Induce Death of Human Hepatocyte Cells. Acta Parasitol. 2013, 58, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndibazza, J.; Muhangi, L.; Akishule, D.; Kiggundu, M.; Ameke, C.; Oweka, J.; Kizindo, R.; Duong, T.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Muwanga, M.; et al. Effects of Deworming during Pregnancy on Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes in Entebbe, Uganda: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Fan, H.; Ge, R.L. A Case of Human Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis Accompanied by Lung and Brain Metastases. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaminck, J.; Levecke, B.; Cools, P.; Albonico, M.; Ame, S.; Chanthapaseuth, T.; Viengxay, V.; Do Trung, D.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Asuming-Brempong, E.; et al. Piloting a Surveillance System to Monitor the Global Patterns of Drug Efficacy and the Emergence of Anthelmintic Resistance in Soil-Transmitted Helminth Control Programs: A Starworms Study Protocol. Gates Open Res. 2020, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansur, F.A.F.; Luoga, W.; Behnke, J.M.; Buttle, D.J.; Duce, I.R.; Garnett, M.C. Developing Novel Anthelmintics: The Stability of Cysteine Proteinase Activity in a Supernatant Extract of Papaya Latex. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, M.; Jaros, S.; Baska, P.; Cappello, M.; Długosz, E.; Wedrychowicz, H. Hamsters Vaccinated with Ace-Mep-7 DNA Vaccine Produced Protective Immunity against Ancylostoma Ceylanicum Infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 163, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, M.; Jaros, S.; Bąska, P.; Cappello, M.; Wędrychowicz, H. Ancylostoma Ceylanicum Metalloprotease 6 DNA Vaccination Induces Partial Protection against Hookworm Challenge Infection. Acta Parasitol. 2013, 58, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffoni, L.; Piva, M.M.; Baska, P.; Januszkiewicz, K.; Norbury, L.J.; Prior, K.C.; Dezen, D.; Silva, A.S.; Wedrychowicz, H.; Mendes, R.E. Immunization with the Recombinant Myosin Regulatory Light Chain (FhrMRLC) in Adjuplex® Adjuvant Elicits a Th1-Biased Immune Response and a Reduction of Parasite Burden in Fasciola Hepatica Infected Rats. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 75, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M. Identifying Novel Candidates and Configurations for Human Helminth Vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.J.; Ndao, M. Promising Technologies in the Field of Helminth Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, M.J.; Leung, J.M.; Kashyap, V.; McCune, J.M.; Mahadevan, U.; McKerrow, J.H.; Loke, P. IL-22+ CD4+ T Cells Are Associated with Therapeutic Trichuris Trichiura Infection in an Ulcerative Colitis Patient. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 60ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, J.O. Helminth Therapy and Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.A.; Keikha, M.; Mirmoeeni, S.; Rahimi, M.T.; Jafari, R. Parasite-Based Interventions in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Systematic Review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, P.J.; Chico, M.E.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Ordonez, M.; Strachan, D.; Griffin, G.E.; Nutman, T.B. Reduced Risk of Atopy among School-Age Children Infected with Geohelminth Parasites in a Rural Area of the Tropics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, C.; Tuyen, L.N.; Lewis, S.; Quinnell, R.; Minh, T.T.; Liem, H.T.; Campbell, J.; Pritchard, D.; Hien, T.T.; Farrar, J.; et al. Poor Sanitation and Helminth Infection Protect against Skin Sensitization in Vietnamese Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baska, P.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Zdziarska, A.M.; Wasyl, K.; Wiśniewski, M.; Cywińska, A.; Klockiewicz, M.; Januszkiewicz, K.; Wedrychowicz, H. Fasciola Hepatica—The Pilot Study of in Vitro Assessing Immune Response against Native and Recombinant Antigens of the Fluke. Acta Parasitol. 2013, 58, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maizels, R.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Immune Regulation by Helminth Parasites: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nutman, T.B. Looking beyond the Induction of Th2 Responses to Explain Immunomodulation by Helminths. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Rozo, C.; Bowdridge, S.; Millman, A.; Van Rooijen, N.; Urban, J.F.; Wynn, T.A.; Gause, W.C. An Essential Role for TH2-Type Responses in Limiting Acute Tissue Damage during Experimental Helminth Infection. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Y.; Haq, S.; Banskota, S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Khan, W.I. Trichuris Muris Model: Role in Understanding Intestinal Immune Response, Inflammation and Host Defense. Pathogens 2021, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąska, P.; Norbury, L.J.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Wiśniewski, M.; Januszkiewicz, K. Excretory/Secretory Products from Two Fasciola Hepatica Isolates Induce Different Transcriptional Changes and IL-10 Release in LPS-Activated Bovine “BOMA” Macrophages. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baska, P.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Norbury, L.J.; Wiśniewski, M.; Januszkiewicz, K. Fasciola Hepatica Isolates Induce Different Immune Responses in Unmaturated Bovine Macrophages. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spit, M.; Koo, B.K.; Maurice, M.M. Tales from the Crypt: Intestinal Niche Signals in Tissue Renewal, Plasticity and Cancer. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.G. Intestinal Epithelial Plasticity and Regeneration via Cell Dedifferentiation. Cell Regen. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehart, H.; Clevers, H. Tales from the Crypt: New Insights into Intestinal Stem Cells. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Tan, H.Y.; Kaiko, G.E. Role of the Intestinal Epithelium and Its Interaction With the Microbiota in Food Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 604054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabbott, N.A.; Donaldson, D.S.; Ohno, H.; Williams, I.R.; Mahajan, A. Microfold (M) Cells: Important Immunosurveillance Posts in the Intestinal Epithelium. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Rath, E.; Hölzlwimmer, G.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Loach, D.; Tannock, G.; Haller, D. Lactobacillus Reuteri 100-23 Transiently Activates Intestinal Epithelial Cells of Mice That Have a Complex Microbiota during Early Stages of Colonization. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeuthen, L.H.; Fink, L.N.; Frokiaer, H. Epithelial Cells Prime the Immune Response to an Array of Gut-Derived Commensals towards a Tolerogenic Phenotype through Distinct Actions of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Transforming Growth Factor-β. Immunology 2008, 123, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, M.; Chieppa, M.; Salucci, V.; Avogadri, F.; Sonzogni, A.; Sampietro, G.M.; Nespoli, A.; Viale, G.; Allavena, P.; Rescigno, M. Intestinal Immune Homeostasis Is Regulated by the Crosstalk between Epithelial Cells and Dendritic Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, I.D.; Mileti, E.; Matteoli, G.; Chieppa, M.; Rescigno, M. Intestinal Epithelial Cells Promote Colitis-Protective Regulatory T-Cell Differentiation through Dendritic Cell Conditioning. Mucosal Immunol. 2009, 2, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rate, A.; Bosco, A.; McKenna, K.L.; Holt, P.G.; Upham, J.W. Airway Epithelial Cells Condition Dendritic Cells to Express Multiple Immune Surveillance Genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klementowicz, J.E.; Travis, M.A.; Grencis, R.K. Trichuris Muris: A Model of Gastrointestinal Parasite Infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, C.; Thornton, D.J.; Grencis, R.K. A Sticky End for Gastrointestinal Helminths; the Role of the Mucus Barrier. Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40, e12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M.; Hewitson, J.P.; Murray, J.; Harcus, Y.M.; Dayer, B.; Filbey, K.J.; Grainger, J.R.; McSorley, H.J.; Reynolds, L.A.; Smith, K.A. Immune Modulation and Modulators in Heligmosomoides Polygyrus Infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansemir, A.D.; Sukhdeo, M.V.K. Intestinal Distribution of Worms and Host Ingesta in Nippostrongylus Brasiliensis. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1470–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, M.P.; Vila, C.C.; Cohen, M.; Gentilini, M.V.; Falduto, G.H.; Calcagno, M.A.; Roux, E.; Venturiello, S.M.; Malchiodi, E.L. Cellular and Molecular Changes and Immune Response in the Intestinal Mucosa during Trichinella Spiralis Early Infection in Rats. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roan, F.; Obata-Ninomiya, K.; Ziegler, S.F. Epithelial Cell–Derived Cytokines: More than Just Signaling the Alarm. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, F.; Arasteh, J.M.; Lawley, T.D. Pathogen Resistance Mediated by IL-22 Signaling at the Epithelial-Microbiota Interface. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3676–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herath, M.; Hosie, S.; Bornstein, J.C.; Franks, A.E.; Hill-Yardin, E.L. The Role of the Gastrointestinal Mucus System in Intestinal Homeostasis: Implications for Neurological Disorders. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambort, D.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Nilsson, H.E.; Ermund, A.; Johansson, B.R.; Koeck, P.J.B.; Hebert, H.; Hansson, G.C. Calcium and PH-Dependent Packing and Release of the Gel-Forming MUC2 Mucin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5645–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Evans, C.M.; Roy, M.; Gallagher, A.L.; Kindrachuk, K.N.; Barron, L.; Dickey, B.F.; Wilson, M.S.; Wynn, T.A.; Grencis, R.K.; et al. Muc5ac: A Critical Component Mediating the Rejection of Enteric Nematodes. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.-B.; Ishikawa, N.; Itoh, H.; Ide, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Horii, Y.; Uchiyama, F.; Nawa, Y. Goblet Cell Mucins of Four Genera of the Subfamily Cricetinae with Reference to the Protective Activity against Strongyloides Venezuelensis. Parasite Immunol. 1994, 16, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Dawson, P.A.; Lourie, R.; Hutson, P.; Tong, H.; Grencis, R.K.; McGuckin, M.A.; Thornton, D.J. Immune-Driven Alterations in Mucin Sulphation Is an Important Mediator of Trichuris Muris Helminth Expulsion. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Yu, M. Role of Goblet Cells in Intestinal Barrier and Mucosal Immunity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C. Immunological Aspects of Intestinal Mucus and Mucins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticelli, L.A.; Osborne, L.C.; Noti, M.; Tran, S.V.; Zaiss, D.M.W.; Artis, D. IL-33 Promotes an Innate Immune Pathway of Intestinal Tissue Protection Dependent on Amphiregulin-EGFR Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10762–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaiss, D.M.; Yang, L.; Shah, P.R.; Kobie, J.J.; Urban, J.F.; Mosmann, T.R. Amphiregulin, a TH2 Cytokine Enhancing Resistance to Nematodes. Science 2006, 314, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, N.M.; Ji, Y.; Herbine, K.; Wei, Y.; Park, J.H.; Zullo, K.; Hung, L.Y.; Srivatsa, S.; Young, T.; Oniskey, T.; et al. TFF3 Interacts with LINGO2 to Regulate EGFR Activation for Protection against Colitis and Gastrointestinal Helminths. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Gunduz, M.; Xia, W.; Wei, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Shih, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear Interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the Activation of the INOS/NO Pathway. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, C.Y. Tight Junction in the Intestinal Epithelium: Its Association with Diseases and Regulation by Phytochemicals. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2645465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahner, C.; Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M. Heterogeneity in Expression and Subcellular Localization of Claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the Rat Liver, Pancreas, and Gut. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulluwishewa, D.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Wells, J.M.; Roy, N.C. Regulation of Tight Junction Permeability by Intestinal Bacteria and Dietary Components. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKay, D.M.; Shute, A.; Lopes, F. Helminths and Intestinal Barrier Function. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1283385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.W.; Cao, Y.; Kaplan, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Conroy, M.; Walker, W.A.; Shi, H.N. Duodenal Helminth Infection Alters Barrier Function of the Colonic Epithelium via Adaptive Immune Activation. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, L.P.; Smith, A.; Cheung, L.; Urban, J.F.; Sun, R.; Grinchuk, V.; Desai, N.; Zhao, A.; Raufman, J.P.; Shea-Donohue, T. Type 3 Muscarinic Receptors Contribute to Intestinal Mucosal Homeostasis and Clearance of Nippostrongylus Brasiliensis through Induction of TH2 Cytokines. Am. J. Physiol.—Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G130–G141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDermott, J.R.; Bartram, R.E.; Knight, P.A.; Miller, H.R.P.; Garrod, D.R.; Grencis, R.K. Mast Cells Disrupt Epithelial Barrier Function during Enteric Nematode Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7761–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Kinio, A.; Saleh, M. Functions of NOD-Like Receptors in Human Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuberger, C.; Pott, J.; Maloy, K.J. Why Do Intestinal Epithelial Cells Express MHC Class II? Immunology 2021, 162, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biton, M.; Haber, A.L.; Rogel, N.; Burgin, G.; Beyaz, S.; Schnell, A.; Ashenberg, O.; Su, C.W.; Smillie, C.; Shekhar, K.; et al. T Helper Cell Cytokines Modulate Intestinal Stem Cell Renewal and Differentiation. Cell 2018, 175, 1307–1320.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruickshank, S.M.; Deschoolmeester, M.L.; Svensson, M.; Howell, G.; Bazakou, A.; Logunova, L.; Little, M.C.; English, N.; Mack, M.; Grencis, R.K.; et al. Rapid Dendritic Cell Mobilization to the Large Intestinal Epithelium Is Associated with Resistance to Trichuris Muris Infection. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosen, J.E.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; MacAubas, C.; Mellins, E.D. Epithelial MHC Class II Expression and Its Role in Antigen Presentation in the Gastrointestinal and Respiratory Tracts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Takahashi, D.; Takano, S.; Kimura, S.; Hase, K. The Roles of Peyer’s Patches and Microfold Cells in the Gut Immune System: Relevance to Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kimura, S.; Hase, K. M Cell-Dependent Antigen Uptake on Follicle-Associated Epithelium for Mucosal Immune Surveillance. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Q.; Huang, J.; Ayansola, H.; Masatoshi, H.; Zhang, B. Intestinal Stem Cells and Immune Cell Relationships: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Moltke, J.; Ji, M.; Liang, H.E.; Locksley, R.M. Tuft-Cell-Derived IL-25 Regulates an Intestinal ILC2-Epithelial Response Circuit. Nature 2016, 529, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Xue, J.-B.; Zhao, D.-X.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, S.-M.; Du, Y.-W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Infection by the Parasitic Helminth Trichinella Spiralis Activates a Tas2r-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Intestinal Tuft Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5564–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, L.A.; Filbey, K.J.; Maizels, R.M. Immunity to the Model Intestinal Helminth Parasite Heligmosomoides Polygyrus. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.H.; Klingbeil, O.; He, X.Y.; Wu, X.S.; Arun, G.; Lu, B.; Somerville, T.D.D.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Demerdash, O.E.; et al. POU2F3 Is a Master Regulator of a Tuft Cell-like Variant of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roura, E.; Depoortere, I.; Navarro, M. Review: Chemosensing of Nutrients and Non-Nutrients in the Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Tract. Animal 2019, 13, 2714–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valente, C.; Alvarez, L.; Marques, P.I.; Gusmão, L.; Amorim, A.; Seixas, S.; Prata, M.J. Genes from the TAS1R and TAS2R Families of Taste Receptors: Looking for Signatures of Their Adaptive Role in Human Evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Shanker, Y.G.; Dubauskaite, J.; Zheng, J.Z.; Yan, W. Gγ13 Colocalizes with Gustducin in Taste Receptor Cells and Mediates IP3 Responses to Bitter Denatonium. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 12, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, M.R.; Cao, Y.G.; Gologorsky, M.B.; Li, J.A.; Haber, A.L.; Biton, M.; Lang, J.; Michaud, M.; Regev, A.; Garrett, W.S. The Taste Receptor TAS1R3 Regulates Small Intestinal Tuft Cell Homeostasis. ImmunoHorizons 2020, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadjsombati, M.S.; Mcginty, J.W.; Lyons-Cohen, M.R.; Jaffe, J.B.; Dipeso, L.; Schneider, C.; Miller, C.N.; Pollack, J.L.; Gowda, N.; Fontana, M.F.; et al. Detection of Succinate by Intestinal Tuft Cells Triggers a Type 2 Innate Immune Circuit. Immunity 2018, 49, 33–41.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilic, N.; Gruden-Movsesijan, A.; Cvetkovic, J.; Tomic, S.; Vucevic, D.B.; Aranzamendi, C.; Colic, M.; Pinelli, E.; Sofronic-Milosavljevic, L. Trichinella Spiralis Excretory-Secretory Products Induce Tolerogenic Properties in Human Dendritic Cells via Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latorre, E.; Layunta, E.; Grasa, L.; Pardo, J.; García, S.; Alcalde, A.I.; Mesonero, J.E. Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 Modulate Intestinal IL-10 Differently in Ileum and Colon. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neuper, T.; Frauenlob, T.; Sarajlic, M.; Posselt, G.; Wessler, S.; Horejs-Hoeck, J. TLRr2, TLR4 and TLR10 Shape the Cytokine and Chemokine Release of h. Pylori-Infected Human Dcs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kwon, Y.H.; Dewan, V.; Vahedi, F.; Syed, S.; Fontes, M.E.; Ashkar, A.A.; Surette, M.G.; Khan, W.I. TLR2 Plays a Pivotal Role in Mediating Mucosal Serotonin Production in the Gut. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, M.R.; Lavoie, S.; Michaud, M.; Blum, A.M.; Tran, S.V.; Weinstock, J.V.; Gallini, C.A.; Redding, K.; Margolskee, R.F.; Osborne, L.C.; et al. Tuft Cells, Taste-Chemosensory Cells, Orchestrate Parasite Type 2 Immunity in the Gut. Science 2016, 351, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGinty, J.W.; Ting, H.A.; Billipp, T.E.; Nadjsombati, M.S.; Khan, D.M.; Barrett, N.A.; Liang, H.E.; Matsumoto, I.; von Moltke, J. Tuft-Cell-Derived Leukotrienes Drive Rapid Anti-Helminth Immunity in the Small Intestine but Are Dispensable for Anti-Protist Immunity. Immunity 2020, 52, 528–541.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Moltke, J.; O’Leary, C.E.; Barrett, N.A.; Kanaoka, Y.; Austen, K.F.; Locksley, R.M. Leukotrienes Provide an NFAT-Dependent Signal That Synergizes with IL-33 to Activate ILC2s. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.; Chesné, J.; Ribeiro, H.; Garcia-Cassani, B.; Carvalho, T.; Bouchery, T.; Shah, K.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Harris, N.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuronal Regulation of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells via Neuromedin U. Nature 2017, 549, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, S.; Brestoff, J.R.; Flamar, A.-L.; Moeller, J.B.; Klose, C.S.N.; Rankin, L.C.; Yudanin, N.A.; Monticelli, L.A.; Putzel, G.G.; Rodewald, H.-R.; et al. β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated Negative Regulation of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses. Science 2018, 359, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, D.R.; Douglas, B.; Zullo, K. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILC2): Type 2 Immunity and Helminth Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nausch, N.; Mutapi, F. Group 2 ILCs: A Way of Enhancing Immune Protection against Human Helminths? Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40, e12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cliffe, L.J.; Humphreys, N.E.; Lane, T.E.; Potten, C.S.; Booth, C.; Grencis, R.K. Immunology—Accelerated Intestinal Epithelial Cell Turnover: A New Mechanism of Parasite Expulsion. Science 2005, 308, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, B.; Ruppert, A.L.; Strobel, O.; Lazarus, M.; Urade, Y.; Büchler, M.W.; Weihe, E. Distribution Pattern and Molecular Signature of Cholinergic Tuft Cells in Human Gastro-Intestinal and Pancreatic-Biliary Tract. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Shao, X.; Huang, J. Acetylcholine From Tuft Cells: The Updated Insights Beyond Its Immune and Chemosensory Functions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Sugiura, Y.; Honda, K.; Suematsu, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Deguchi, T.; Fujii, T.; Orihashi, K.; Hippo, Y.; et al. Non-Neuronal Acetylcholine as an Endogenous Regulator of Proliferation and Differentiation of Lgr5-Positive Stem Cells in Mice. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4672–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Shiraishi, A.; Murata, J. The Coordinated Activities of NACHR and Wnt Signaling Regulate Intestinal Stem Cell Function in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birchenough, G.M.H.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Bergström, J.H.; Hansson, G.C. New Developments in Goblet Cell Mucus Secretion and Function. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooke, H.J. “Enteric Tears”: Chloride Secretion and Its Neural Regulation. News Physiol. Sci. 1998, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Kim, G.; Stewart, A.; Urban, J.F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.G.; Chesler, A.; et al. Interleukin-33 Promotes Serotonin Release from Enterochromaffin Cells for Intestinal Homeostasis. Immunity 2021, 54, 151–163.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, K.B.; Yeung, K.A.; Zhao, A.; Gause, W.C.; Finkelman, F.D.; Katona, I.M.; Urban, J.F.; Shea-Donohue, T. Enteric Nematodes Induce Stereotypic STAT6-Dependent Alterations in Intestinal Epithelial Cell Function. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5616–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mckay, D.M.; Fairweather, I.; Halton, D.W.; Johnston, C.F.; Shaw, C. Immunocytochemical and Radioimmunometrical Demonstration of Serotonin- and Neuropeptideimmunoreactivities in the Adult Rat Tapeworm, Hymenolepis Diminuta (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea). Parasitology 1991, 103, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, J.J.; Samuelson, L.C.; Grencis, R.K.; McLaughlin, J.T. Adaptive Immunity Alters Distinct Host Feeding Pathways during Nematode Induced Inflammation, a Novel Mechanism in Parasite Expulsion. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, H.T.M.D.; Lie, K.K.; Giroud-Argoud, J.; Rønnestad, I.; Sæle, O. Effects of Cholecystokinin (Cck) on Gut Motility in the Stomachless Fish Ballan Wrasse (Labrus Bergylta). Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, M.; Balsari, A.; Rossini, A.; Selleri, S.; Calcaterra, C.; Gariboldi, S.; Zanobbio, L.; Arnaboldi, F.; Shirai, Y.F.; Serrao, G.; et al. Activation of Enteroendocrine Cells via TLRs Induces Hormone, Chemokine, and Defensin Secretion. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4296–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daly, K.; Al-Rammahi, M.; Moran, A.; Marcello, M.; Ninomiya, Y.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Sensing of Amino Acids by the Gut-Expressed Taste Receptor T1R1-T1R3 Stimulates CCK Secretion. Am. J. Physiol.—Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bąska, P.; Norbury, L.J. The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the “Weep and Sweep” Response during Gastro—Intestinal Helminth Infections. Animals 2022, 12, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12020175
Bąska P, Norbury LJ. The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the “Weep and Sweep” Response during Gastro—Intestinal Helminth Infections. Animals. 2022; 12(2):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleBąska, Piotr, and Luke James Norbury. 2022. "The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the “Weep and Sweep” Response during Gastro—Intestinal Helminth Infections" Animals 12, no. 2: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12020175
APA StyleBąska, P., & Norbury, L. J. (2022). The Role of the Intestinal Epithelium in the “Weep and Sweep” Response during Gastro—Intestinal Helminth Infections. Animals, 12(2), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12020175





