Simple Summary
In this work, we identified that the miR-183/96/182 cluster was highly expressed in bovine embryonic muscle; meanwhile, it widely existed in other organizations. Functional assays indicated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster targets the FoxO1 gene to regulate the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts.
Abstract
Muscle development is an important factor affecting meat yield and quality and is coordinated by a variety of the myogenic genes and signaling pathways. Recent studies reported that miRNA, a class of highly conserved small noncoding RNA, is actively involved in regulating muscle development, but many miRNAs still need to be further explored. Here, we identified that the miR-183/96/182 cluster exhibited higher expression in bovine embryonic muscle; meanwhile, it widely existed in other organizations. Functionally, the results of the RT-qPCR, EdU, CCK8 and immunofluorescence assays demonstrated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster promoted proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblast. Next, we found that the miR-183/96/182 cluster targeted FoxO1 and restrained its expression. Meanwhile, the expression of FoxO1 had a negative correlation with the expression of the miR-183/96/182 cluster during myoblast differentiation. In a word, our findings indicated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster serves as a positive regulator in the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts through suppressing the expression of FoxO1.
1. Introduction
Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue accounting for most of the body weight and participates in movement and metabolism [1]. For livestock, skeletal muscle development is an important factor affecting meat yield and quality. Skeletal muscle originates from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in the embryonic mesoderm, which could change to myogenic progenitor cells. The myogenic progenitor cells differentiate into mononuclear myoblasts; then, the myoblasts further experience proliferation, differentiation and fusion into multinuclear myotubes, which ultimately form muscle fibers [2]. Once the mature muscle has formed, myogenic progenitor cells will enter quiescence and exist as muscle satellite cells, which could participates in the repair of muscle fibers [3]. It is now generally accepted that this complex and long-term process is precisely coordinated by the myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), containing Myogenic differentiation 1 (MyoD1), Myogenic regulatory factor 4 (Mrf4), Myogenin (MyoG) and Myogenic factor 5 (Myf5) [4]. Tuning these genes’ expression in muscle development is realized through a transcriptional and post-transcriptional network. Increasing evidence has suggested that noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) involving post-transcriptional regulation is a vital factor in muscle development, including long noncoding RNA [5], circular RNA and small RNA [6,7]. Although the genetic and molecular pathways of regulating muscle development have been well-established in the past decades, numerous unknown regulatory molecules and mechanisms involved in this process remain unidentified.
MicroRNAs (miRNA), a class of ~22 nucleotide small noncoding RNAs, are highly conserved and do not possess potential coding. The seed region of miRNA located in 2~8 nucleotides at the 5′ end normally conjugates with the 3′-untranslated region (3′ UTR) of the target mRNA. By this means, miRNAs are capable of decaying or impeding protein translations of the target mRNAs [8]. Numerous studies have underlined the key roles of miRNAs in regulating skeletal muscle development through their inhibiting effects on several myogenic regulatory factors and important signaling pathways. The MyomiR family, a class of miRNA specifically expressed in muscles, includes miR-133, miR-1, miR-208a/b, miR-206, miR-486 and miR-499 [9]. For instance, miR-206, which is highly and exclusively expressed in muscles, was positively regulated by MyoD and targeted Pax7 to promote terminal differentiation [10], while some non-muscle-specific miRNAs also participated in regulating muscle development, such as miR-24, miR-27a, miR-125b, miR-29, miR-486, miR-221/222 and miR-214 [11]. Moreover, the indispensable functions of miRNAs in muscle development have verified that the deficiency of Dicer in skeletal muscle reduced the production of muscle miRNAs and led to embryonic death during embryogenesis [12].
The conserved miR-183/96/182 cluster is one of the most studied miRNA clusters, which is situated at a 5-kb genomic region in humans and mice and possesses similar seed sequences [13]. Many upstream regulators, including Wnt/beta-Catenin, the p21-ZEB1 complex, GSK3β, MyoD and so on, were certified to regulate the expression of the miR-183/96/182 cluster [14,15,16,17]. Increasing studies have shown that the miR-183/96/182 cluster plays an important role in tumorigenesis, cancer progression, tumor invasion and metastasis. Notably, an inconsistency has arisen with respect to the functions of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in various tumor cells [18], which prompted that its versatility in different biological processes. Nevertheless, there are research gaps in the regulatory role of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in muscle development, especially in livestock animals. Therefore, we attempted to explore the function and mechanism of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in bovine skeletal muscle development. In this study, we found that the miR-183/96/182 cluster accelerated the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts by targeting the FoxO1 gene, which enriched the network of miRNAs regulating bovine muscle development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Muscle samples in Qinchuan cattle were collected at the adult stage (24 months) and embryonic stage (90 days) from a local livestock farm in Xi’an (Shannxi, China). Other tissue samples included a liver, kidney, heart, lung and spleen that were obtained at the embryonic stage (90 days), and each sample was collected from three cattle about the same age. After surgical removal, all samples were placed in liquid nitrogen to snap-freeze and then kept at −80 °C until RNA isolation. Our study protocols were approved by the Animal the Ethics Committee of Northwest A&F University.
2.2. Cell Culture
As previously described, the primary myoblasts of bovines were obtained from the longissimus muscle at the fetal stage (90 days) [19]. Briefly, the stripped muscle tissues were cut into pieces, then digested with collagenase I in 37 °C for 2 h, whereafter the digested muscles were filtered using a 200-mesh filter, and the filtrate was washed with PBS and centrifuged at 1500 rpm three times. Finally, the collected cells were cultured in DMEM (BI, ISR) supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (BI, ISR) and 2% penicillin–streptomycin (Biosharp, Anhui, China). When 90% confluence was reached, the medium was changed to DMEM with 2% horse serum and 2% penicillin–streptomycin to induce cell differentiation. The HEK-293T cells were cultured in DMEM with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. All cells were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
2.3. Vector Construction and Transfection
The fragment of bovine FoxO1 3′UTR containing the miR-183/96/182 cluster wild binding site or mutant sites was cloned into the psiCHECK2 vector. These vectors were verified by sequencing. The mimics and inhibitors of the miR-183/96/182 cluster were synthesized by General Biol (Chuzhou, China) to the overexpression or knockdown of the miR-183/96/182 cluster, respectively. All vectors and mimics or inhibitors were transfected into myoblasts using Troubfect (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
The total RNA from tissues and cells was extracted using the Trizol reagent (AG, Beijing, China) and was reverse transcribed using the RT reagent kit (AG, Beijing, China). For mRNA, random and oligo (dT) primers were used to synthesize cDNA, and for miRNA, random and stem-loop primers were used to synthesize cDNA. The RT-qPCR assay was performed using the SYBR Green Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) on the CFX96 System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). We applied β-actin and U6 as an internal control for the mRNA and miRNA. The quantitation data was analyzed by the 2−ΔΔCt method, and each sample was replicated three times. All primers are listed in Table S1.
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
The myoblasts were cultured in 96-well plates and then transfected after the cell density reached 70–80%. For the CCK-8 assay, each well was treated with 10 μL of CCK-8 (UE, Suzhou, China) and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C in the dark. The absorbance of each sample was detected using a microplate reader at 450 nm, and each sample was replicated eight times. The EdU Cell Proliferation Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) was used to measure the capacity of cell proliferation, and Hoechst 33342 was used to stain the nuclei. Each sample was replicated three times. Finally, the images were observed by fluorescence microscopy (AMG EVOS, SEA, USA).
2.6. Immunofluorescence Assay
After transfection, bovine myoblast differentiation was induced for 4 d. Then, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min. After washing, the cells were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 15 min and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 min, following incubation at 4 °C overnight with antibody-MyHC diluted 1:250 (GeneTex, Irvine, CA, USA). Next, we used the homologous fluorescent secondary antibody (Immunoway, Plano, TX, USA) diluted 1:500 to incubate cells for 2 h at room temperature. Hoechst 33342 was used to stain the nuclei. Finally, the images were observed under a fluorescent microscope.
2.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
The psiCHECK2-FoxO1-WT or psiCHECK2-FoxO1-Mut and miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics were co-transfected into HEK293T cells using Troubfect (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). After transfection for 24 h, the cells were lysed, and next, we used the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay Kit (Promega, MDN, USA) to detect luciferase activities according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, the ratios of renilla and firefly activity were calculated, and each sample was replicated eight times.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
We used GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA) and SPSS 22.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) to analyze the data. Significance analyses between two groups were performed by an independent sample t-test, and for three or more groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare any discrepancies. All data were presented as the mean ± SEM. A statistical significance was indicated as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 or **** p < 0.0001.
3. Results
3.1. The Expression Characteristics of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster in Cattle Tissues
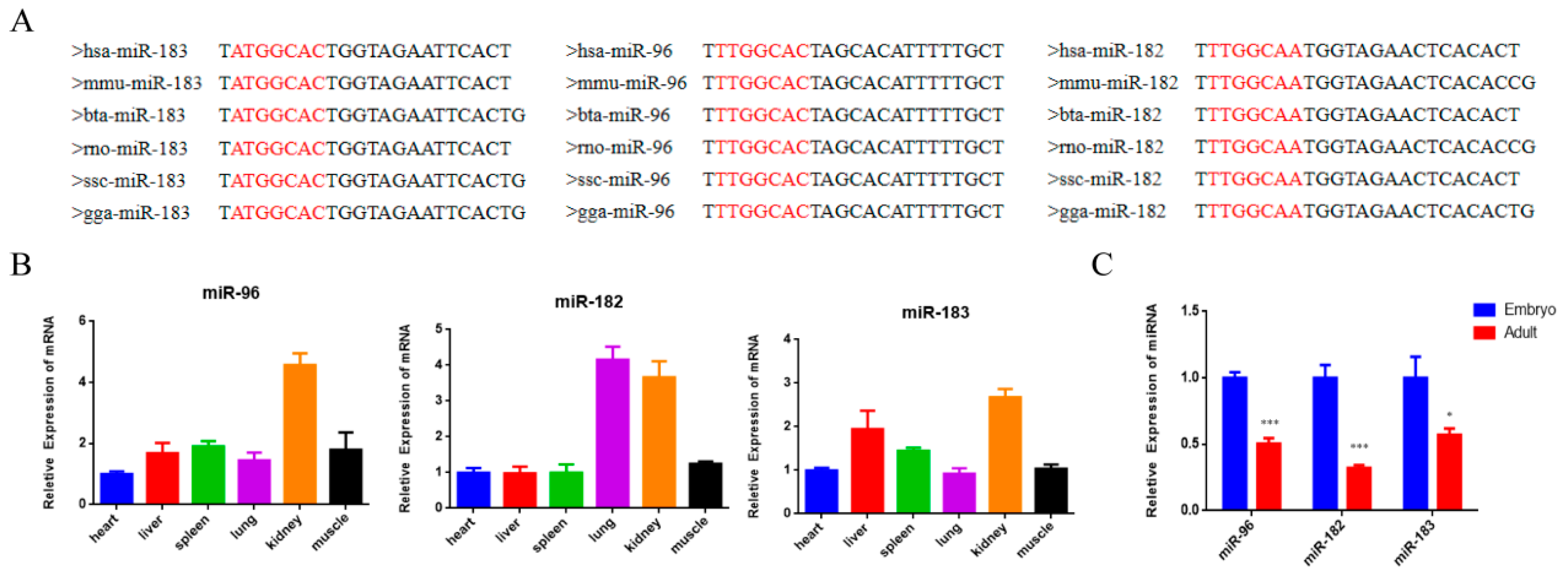
There have been numerous studies that have proven the important roles of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in various cancer cells [18]. In this study, we aimed to explore whether the miR-183/96/182 cluster also has regulatory functions in bovine myoblasts. Firstly, we downloaded the mature sequences of miR-183, miR-96 and miR-182 to examine their conservatism in different species. The results demonstrated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster is highly conserved among species (Figure 1A). Through quantifying the expression features of the miR-183/96/182 cluster, we found that it exhibits varying expression patterns in various tissues in bovines (Figure 1B). In addition, the miR-183/96/182 cluster had a significantly higher presence in embryonic muscle (Figure 1C), which suggested that it may be a positive regulator in embryonic muscle development.
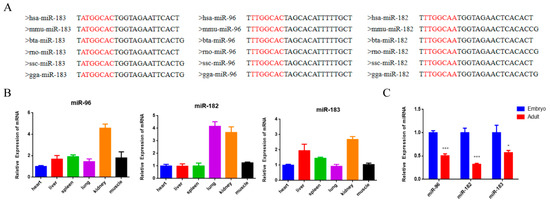
Figure 1.
The expression characteristics of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in cattle. (A) Conservative analysis of the mature sequence of the miR-183/96/182cluster among different species. The red letters show the miRNA seed sequence. (B) The expression feature of the miR-183-96-182 cluster in different tissues of fetal cattle. (C) The expression level of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in fetal and adult bovine muscle tissues. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.
3.2. miR-183/96/182 Cluster Promoted Bovine Myoblast Proliferation
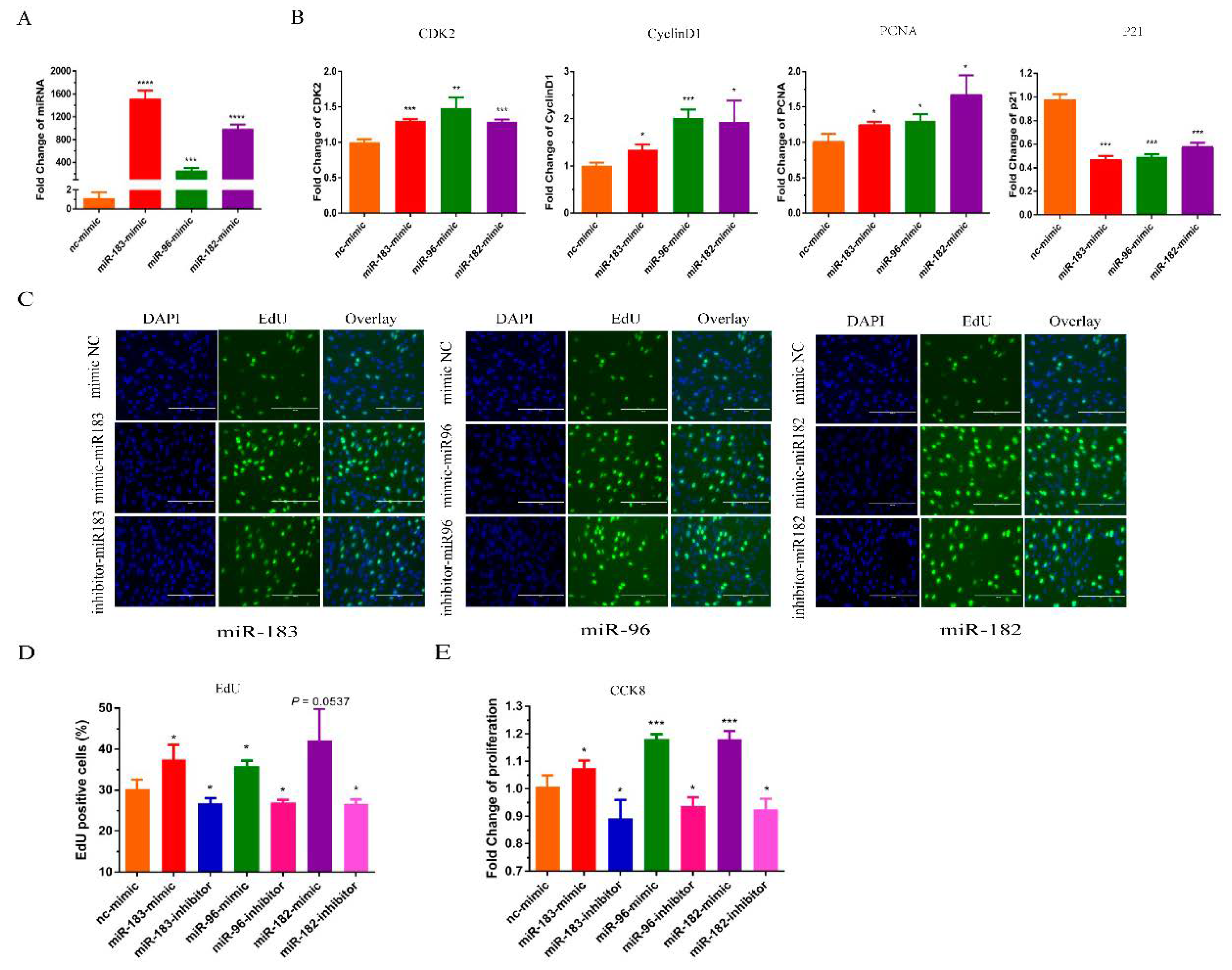
The miR-183/96/182 cluster has been shown to promote most cancer cell proliferation [18]. To verify whether the miR-183/96/182 cluster influences bovine myoblast proliferation, we transfected bovine myoblasts with miR-183/96/182 mimics to increase its expression. The expression level of miR-183/96/182 was significantly higher than the control group (Figure 2A). A RT-qPCR assay was used to detect the expression of marker genes of proliferation. Our results demonstrated that the overexpression of the miR-183/96/182 cluster remarkably enhanced the expression of PCNA, CDK2 and cyclin D; meanwhile, the level of P21 was significantly reduced (Figure 2B). The EdU proliferation assays revealed that the overexpression of miR-183/96/182 significantly increased the number of EdU-positive cells, and silencing miR-183/96/182 reduced the positive cells (Figure 2C,D). In addition, the results of the CCK8 assays showed that overexpressing miR-183/96/182 could increase the vitality of myoblasts, and silencing miR-183/96/182 could inhibit the vitality of the myoblasts (Figure 2E). Thus, our results showed that the miR-183/96/182 cluster can facilitate the proliferation of bovine myoblasts.
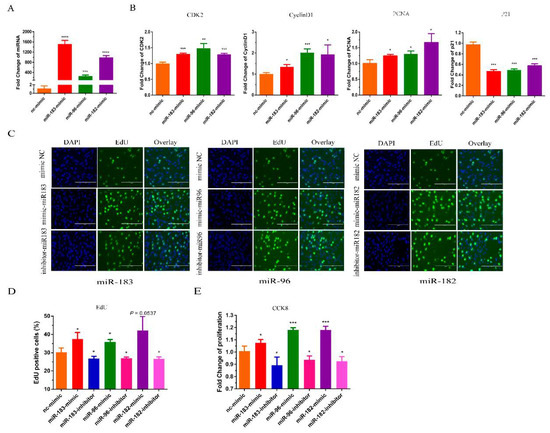
Figure 2.
The miR-183/96/182 cluster promotes bovine myoblast proliferation. (A) The detection of expression efficiency after the transfection of miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics. (B) The expression levels of the cell proliferation genes CyclinD1, PCNA, CDK2 and P21 mRNA were detected by RT-qPCR. (C,D) EdU-positive cells were detected after transfection of the miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics and inhibitors. (E) Proliferation in bovine myoblasts was performed by the CCK-8 assay. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.
3.3. miR-183/96/182 Cluster Promotedpromote Bovine Myoblast Differentiation
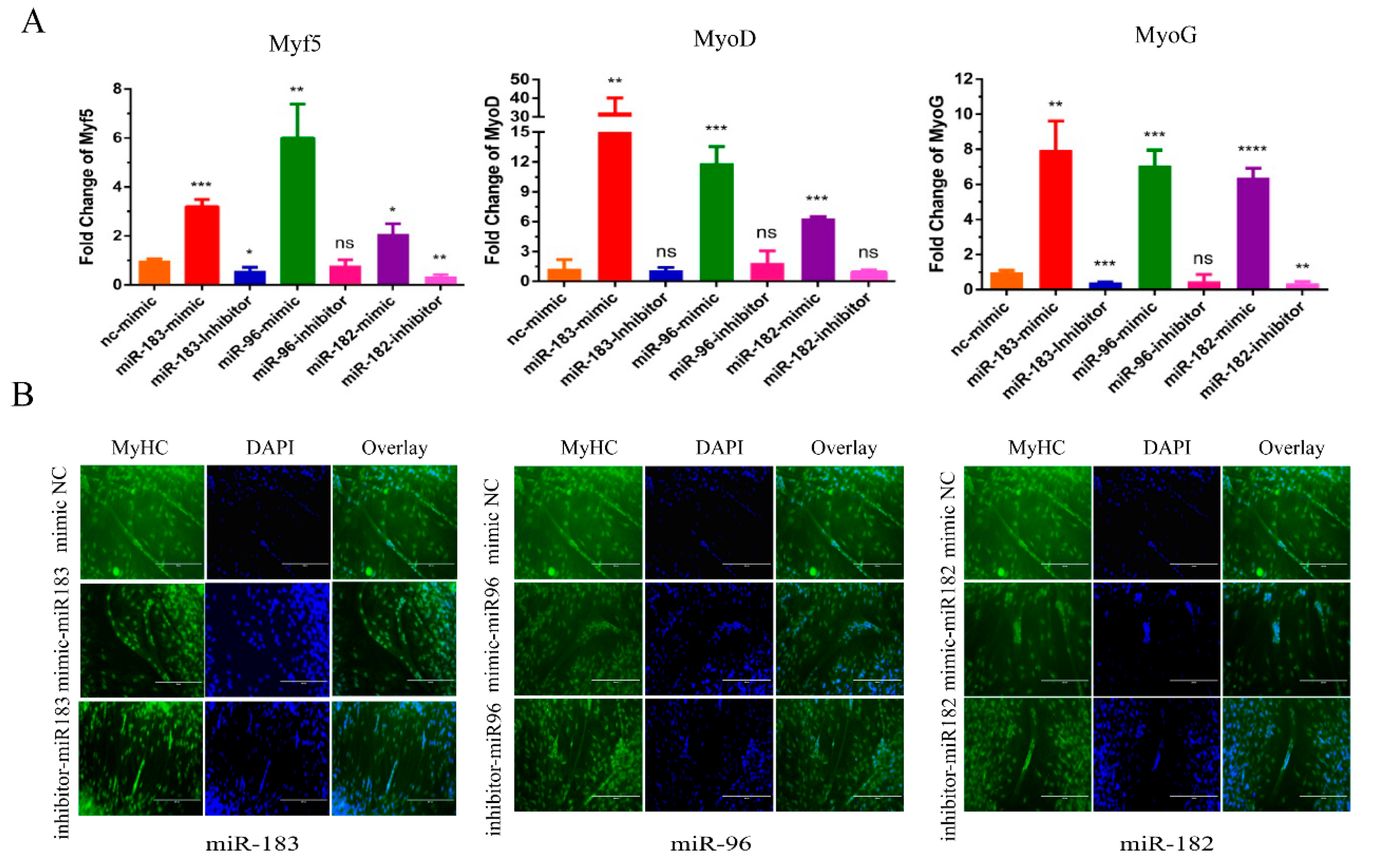
Next, we verified the potential functions of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in myoblast differentiation. After the transfection of miR-183/96/182 mimics for 24 h, we used 2% horse serum medium to induce myoblast differentiation until day 3. Subsequently, we detected the expression level of the differentiation marker genes by RT-qPCR. As shown in Figure 3A, there is a significant rise in the expression level of the differentiation marker genes, including MyoG, MyoD and Myf5. However, silencing the miR-183/96/182 cluster reduced the expression of differentiation marker genes at the mRNA level. Additionally, the immunofluorescence assay also demonstrated that overexpressing the miR-183/96/182 cluster could prompt the myotube to become bigger (Figure 3B). Inversely, the myotube became lesser after silencing the miR-183/96/182 cluster (Figure 3B). Consequently, all the results suggested that the miR-183/96/182 cluster promoted bovine myoblast differentiation.
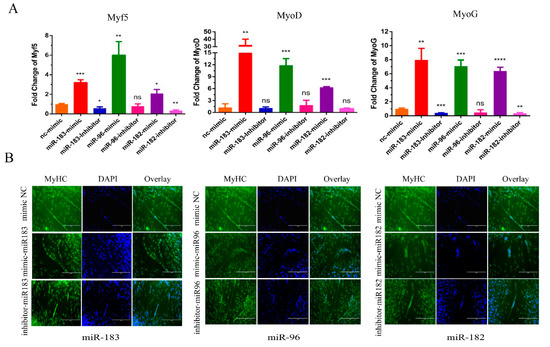
Figure 3.
The miR-183/96/182 cluster promotes bovine myoblast differentiation. (A) The expression levels of cell differentiation genes MyoG, MyoD and Myf5 were detected by RT-qPCR. (B) Immunofluorescence (MyHC) was performed to evaluate the cell differentiation. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. NS represented no difference. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.
3.4. FoxO1 as a Target Gene of the miR-183-96-182 Cluster
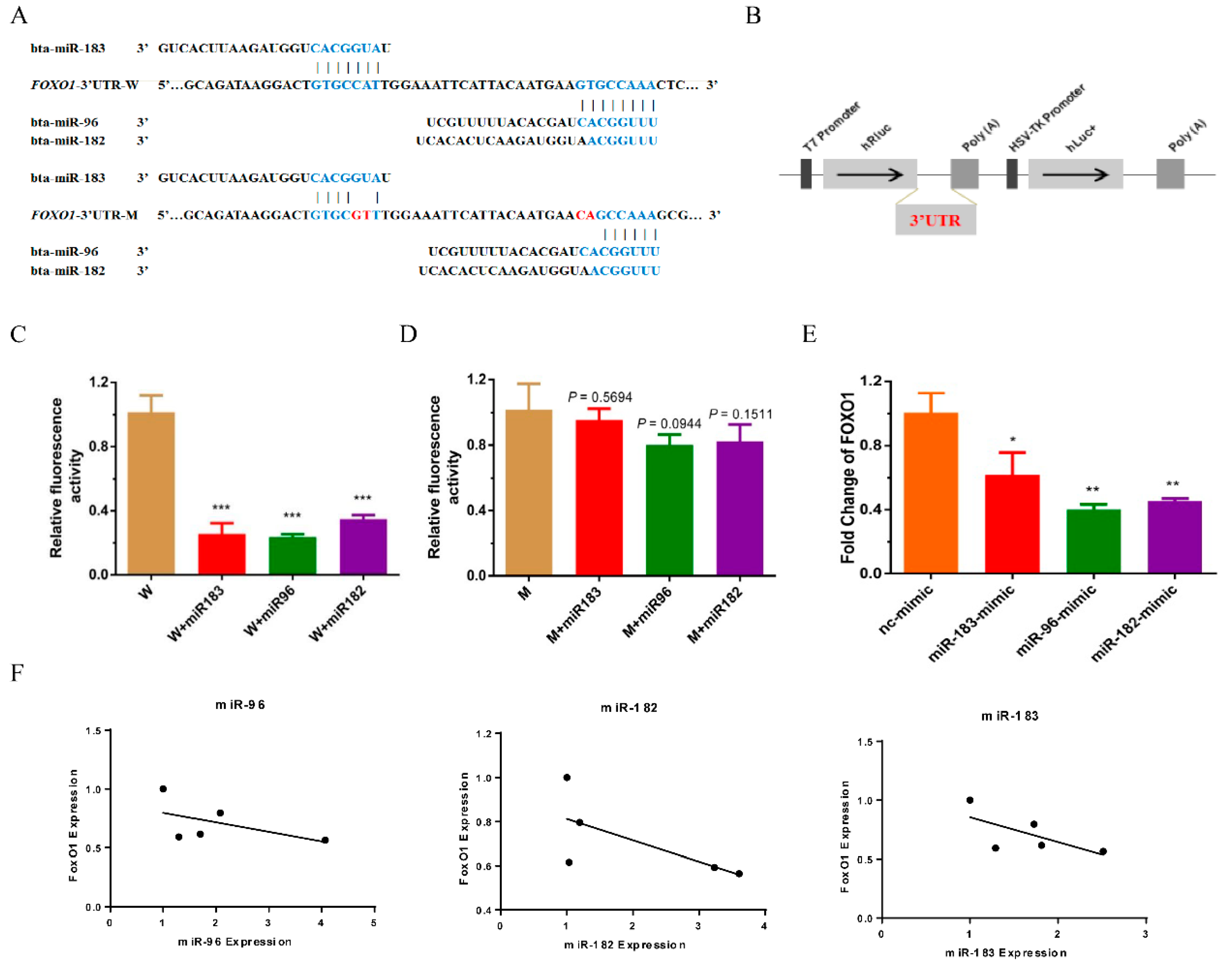
FoxO1, a well-known direct target of the miR-183/96/182 cluster, has been confirmed in various types of cancers, such as prostate [20], liver [16], breast [21], lymphoma [22] and so on. In addition, FoxO1 has also been proven to participate in muscle differentiation and glucose and lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle [23,24,25]. However, whether the miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates FoxO1 in bovine muscle is still unclear. As expected, we found that FoxO1 was potentially targeted by the miR-183/96/182 cluster, and the distribution of potential binding sites is demonstrated in Figure 4A. To investigating the binding of the miR-183/96/182 cluster and FoxO1, we constructed a dual-luciferase reporter system of FoxO1 3′UTR (wild type) (Figure 4B). The results indicated that the luciferase activity of pCK-FoxO1-WT was notably suppressed in HEK293T cells after co-transfection with the miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics (Figure 4C). Analogously, we further used the vector of pCK-FoxO1-MUT to verify this interaction (Figure 4A,D). There was no longer a response in the pCK-FoxO1-MUT system when the miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics were transfected (Figure 4D). The RT-qPCR assay indicated that the expression of FoxO1 was markedly decreased after overexpressing the miR-183/96/182 cluster in bovine myoblasts (Figure 4E). Additionally, we found that the expression of FoxO1 had a negative correlation with the expression of the miR-183/96/182 cluster during myoblast differentiation (Figure 4F). Taken together, these results demonstrated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts by targeting FoxO1.
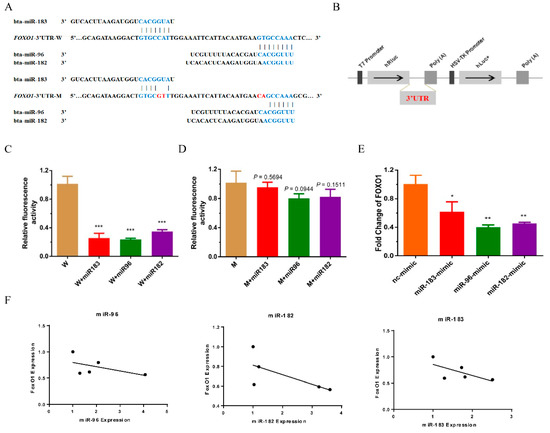
Figure 4.
FoxO1 was the target of the miR-183/96/182 cluster. (A) The distribution of potential binding sites of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in the 3′UTR of FoxO1. The red letters indicate the certain mutated bases. (B) The illustration shows the construct of a dual-luciferase reporter system. (C,D) The luciferase activity of the FoxO1 (wild or mutant) psi-check2 reporter vector was detected after co-transfection of the miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics in HEK293T cells. (E) The mRNA of FoxO1 were detected by RT-qPCR after transfection of the miR-183/96/182 cluster mimics and inhibitors. (F) The correlation analysis on the expression of FoxO1 and the miR-183/96/182 cluster during myoblast differentiation. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
Muscle development is precisely coordinated by members of the myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) family and myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) [26,27]. In recent years, miRNA have been certified to mediate the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by RNA interference [13]. To date, numerous studies have established a powerful role of miRNAs in cell differentiation, growth, apoptosis and development, as we all know that myoblast proliferation and differentiation are the key factors affecting muscle development. Therefore, the potential effects of miRNAs in myoblast proliferation and differentiation cannot be ignored. As we all know, the conserved miR-183/96/182 cluster is one of the most studied miRNA clusters, which possesses similar seed sequences to target identical genes; meanwhile, it plays a crucial role by coordinating the key genes in various cellular processes [13]. Consistent with our analysis, the mature fragment of the miR-183/96/182 cluster is highly conserved in different species (human, mouse, bovine, rat, pig and chicken). However, it is still unclear whether the miR-183/96/182 cluster has a regulatory function in bovine myoblasts. In this study, we indicated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster serves as a positive regulator in the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts through suppressing the expression of FoxO1.
Previous studies have demonstrated that the miR-183/96/182 cluster possessed an accelerated role in cell proliferation in most types of cancer. A classic example is that miR-182 and miR-183 facilitate cell proliferation and tumor invasion by inhibiting PDCD4 in various cancer cells, which is a typical tumor suppressor gene [28,29]. Interestingly, miR-96 was found to weaken pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, and miR-183 suppressed gastric cancer proliferation in the past few years [30,31]. These discrepant results may be caused by different types of cancer cells or competition between target genes or the involvement of different signaling pathways. Therefore, it is necessary for us to continue to explore the regulatory functions of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in various cellular environments and different life processes. Recent studies have reported the modulating capability of miR-96 and miR-183 in muscle oxidative, and the results showed that miR-96 and miR-183 can inhibit glucose utilization and fat catabolism [32].
Here, we further exhibited that the miR-183/96/182 cluster plays a vital role in promoting skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. The miR-183/96/182 cluster exhibited widely different expression patterns across bovine tissues, which is also consistent with its extensive functions in various tissues and cell development. Specifically, we observed a higher level of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in embryonic muscle tissue than adult muscle. The embryonic period is a critical stage for muscle growth and development; in addition, the miR-183/96/182 cluster can accelerate the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts, suggesting that miR-183/96/182 plays a crucial part in myogenesis. Notably, several studies in mice have confirmed that miR-96-5p and miR-183-5p, via suppressing FHL1, impede the differentiation and fusion of myoblasts [33,34]. Contrary to their results, we found that the miR-183/96/182 cluster promoted the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts through using RT-qPCR, EdU, CCK8 and immunofluorescence assays. This positive regulatory effect of the miR-183/96/182 cluster for bovine myoblasts is essential for skeletal muscle development. To be noted, the differences between species are likely mainly responsible for the function differences. Additionally, there may be competition between target genes in a specific context.
Mechanism studies have shown that FoxO1 acts as a target gene of the miR-183/96/182 cluster to mediate bovine myoblast development. It is known that FoxO1, a member of the “O” subclass of the (FOX) family, has a considerable effect on various cellular physiological process. FoxO1 is found in most muscle types and plays a vital regulation in myoblast proliferation and differentiation, muscle growth and metabolism [35]. The function of FoxO1 in muscle differentiation has been widely reported. Some researchers have demonstrated that FoxO1 facilitates myotube fusion in mouse primary myoblasts [36]. However, other studies have revealed that FoxO1 is an inhibitor for muscle differentiation. At an early myogenesis stage, FoxO1 has been reported to impinge on the nutrient-sensing mTOR pathway, the Notch pathway and myostatin to repress myoblast differentiation [37,38,39]. The study in vivo showed that FoxO1 transgenic mice exhibited a remarkable reduction in muscle mass and the decreased expression of type I fiber genes and impaired skeletal muscle production [25]. Generally, most studies support FoxO1 as an inhibitor in myogenesis. Furthermore, increasing studies have verified that FoxO1 is a direct target gene to the miR-183-96-182 cluster. In bovine ovaries, the miR-183-96-182 cluster promotes granulosa cell proliferation, cycle progression and restrains apoptosis through targeting FoxO1 [40,41]. In the present study, we also confirmed that FoxO1 was the target gene of the miR-183-96-182 cluster using the dual-luciferase reporter assay, and overexpressing miR-183/96/182 cluster led to decreasing levels of FoxO1 mRNA in bovine myoblasts. Importantly, we observed that the expression of FoxO1 was negatively correlated with the expression of the miR-183/96/182 cluster during myoblast differentiation. Thus, our results established a pattern that the miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts by targeting FoxO1. It is worth noting that we just uncovered a potential mechanism that the miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates muscle development, but there are other target genes of the miR-183/96/182 cluster that unceasingly need to be elucidated.
5. Conclusions
Overall, we characterized the miR-183/96/182 cluster in bovine muscle and identified the miR-183/96/182 cluster as a positive regulator in the differentiation and proliferation of bovine myoblasts. Mechanistically, we found that the miR-183/96/182 cluster targets the FoxO1 gene to regulate the proliferation and differentiation of bovine myoblasts. Our findings not only confirmed the universality of the regulatory functions of the miR-183/96/182 cluster in various biochemical processes but also provided a theoretical basis to clarify skeletal muscle development in bovines from a layer of noncoding RNAs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani12202799/s1, Table S1: Primer Information in our work.
Author Contributions
W.R., K.L., H.C. and B.H. conceived the ideas and designed the work. W.R. and K.L. performed the experiments, and W.R. drafted the manuscript. J.Y. helped perform the experiments. X.Q. and J.L. provided some samples. H.C. and B.H. revised the manuscript critically. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agricultural Improved Seed Project of Shandong Province (2020LZGC014-03), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-37), the Program of Yunnan Provincial Major S&T Project (2019ZG007 and 2019ZG011), the Doctoral Startup Project of Chuxiong Normal University (no. BSQD2101) and the Yunling Scholar and the Young and Middleaged Academic Technology Leader Backup Talent Cultivation Program in Yunnan Province, China (2018HB045). The Program of National Beef Cattle and Yak Industrial Technology System (CARS-37).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal the Ethics Committee of Northwest A&F University, Approval Code: NWAFU-DK2022066.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the members of their laboratory for their helpful and constructive advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
References
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chal, J.; Pourquié, O.A.-O. Making muscle: Skeletal myogenesis In Vivo and In Vitro. Development 2017, 144, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chargé, S.B.; Rudnicki, M.A. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzinger, C.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Rudnicki, M.A. Building muscle: Molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, H. Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of skeletal myogenesis and muscle diseases. Cancer Lett. 2018, 417, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, G.F.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Münsterberg, A. microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, B.; Wang, J.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; Cao, X.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Huang, B.; Chen, H. Biogenesis and ceRNA role of circular RNAs in skeletal muscle myogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 117, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, K. MiR-206, a key modulator of skeletal muscle development and disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.J.G.; Dutta, A. miR-206 and -486 induce myoblast differentiation by downregulating Pax7. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Gong, J.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, C.L.; Chen, H.; Fang, X.T. Effects of microRNAs on skeletal muscle development. Gene 2018, 668, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, J.R.; Georges, S.A.; Seay, H.R.; Tapscott, S.J.; McManus, M.T.; Goldhamer, D.J.; Swanson, M.S.; Harfe, B.D. Essential role for Dicer during skeletal muscle development. Dev. Biol. 2007, 311, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambal, S.; Shah, M.; Mihelich, B.; Nonn, L. The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays together. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zheng, D.; Hu, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, M.; Tucker, L.; Monahan, R.; Resnick, M.B.; Liu, M.; Ramratnam, B. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta inhibits microRNA-183-96-182 cluster via the β-Catenin/TCF/LEF-1 pathway in gastric cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 2988–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Hara, T.; Choi, Y.; Subramanian, M.; Francis, P.; Bilke, S.; Walker, R.L.; Pineda, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A p21-ZEB1 complex inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the microRNA 183-96-182 cluster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, W.K.; He, M.; Chan, A.W.; Law, P.T.; Wong, N. Wnt/β-Catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2015, 362, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, R.D.; Sachdeva, M.; Mito, J.K.; Eward, W.C.; Brigman, B.E.; Ma, Y.; Dodd, L.; Kim, Y.; Lev, D.; Kirsch, D.G. Myogenic transcription factors regulate pro-metastatic miR-182. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liang, A.J.; Fan, Y.P.; Huang, Y.R.; Zhao, X.M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.F. Dysregulation and functional roles of miR-183-96-182 cluster in cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42805–42825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kitagawa, E.; Watanabe, H.; Sakurada, T.; Aso, H.; Yamaguchi, T. AMPK activation by AICAR inhibits myogenic differentiation and myostatin expression in cattle. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 349, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, A.; Jung, M.; Stephan, C.; Erbersdobler, A.; Jung, K.; Yousef, G.M. The antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in prostate cancer by inhibition of FOXO1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttilla, I.K.; White, B.A. Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23204–23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ushmorov, A.; Leithäuser, F.; Guan, H.; Steidl, C.; Färbinger, J.; Pelzer, C.; Vogel, M.J.; Maier, H.J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. FOXO1 is a tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2012, 119, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accili, D.; Arden, K.C. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 2004, 117, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribal, M.L.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Shutter, J.R.; Accili, D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-dependent myoblast differentiation by Foxo forkhead transcription factors. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Miura, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kai, Y.; Mizukami, J.; Taniguchi, T.; Mochida, K.; Hata, T.; Matsuda, J.; Aburatani, H.; et al. Skeletal muscle FOXO1 (FKHR) transgenic mice have less skeletal muscle mass, down-regulated Type I (slow twitch/red muscle) fiber genes, and impaired glycemic control. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41114–41123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassar-Duchossoy, L.; Gayraud-Morel, B.; Gomès, D.; Rocancourt, D.; Buckingham, M.; Shinin, V.; Tajbakhsh, S. Mrf4 determines skeletal muscle identity in Myf5:Myod double-mutant mice. Nature 2004, 431, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, A.; Tsikitis, M.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Sharan, R.; Kluger, Y.; Dynlacht, B.D. An initial blueprint for myogenic differentiation. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.L.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, Y. miR-183 induces cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating PDCD4 expression in the SW1990 pancreatic cancer cell line. Biomed. Pharm. 2015, 70, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.L.; Wang, F.; Li, M.L.; Yu, Z.S.; Hao, Y.Z.; Chen, S.S. MicroRNA-182 modulates chemosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Du, X.; Tai, S.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Kang, P.; Ji, D.; Jiang, X.; et al. GPC1 regulated by miR-96-5p, rather than miR-182-5p, in inhibition of pancreatic carcinoma cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6314–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; He, J.; Liu, D. MicroRNA-183 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and invasion via directly targeting Bmi-1. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Y.; Tang, Z.; Shen, S.; et al. miR-183 and miR-96 orchestrate both glucose and fat utilization in skeletal muscle. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Min, K.H.; Lee, W. MiR-96-5p Induced by Palmitic Acid Suppresses the Myogenic Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts by Targeting FHL1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Min, K.H.; Lee, W. MiR-183-5p induced by saturated fatty acids regulates the myogenic differentiation by directly targeting FHL1 in C2C12 myoblasts. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z. FoxO1: A novel insight into its molecular mechanisms in the regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation and fiber type specification. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10662–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bois, P.R.; Grosveld, G.C. FKHR (FOXO1a) is required for myotube fusion of primary mouse myoblasts. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.L.; Unterman, T.G. Regulation of myostatin expression and myoblast differentiation by FoxO and SMAD transcription factors. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C188–C199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.L.; Kim, J.-H.; Zhang, C.; Unterman, T.G.; Chen, J. Forkhead box protein O1 negatively regulates skeletal myocyte differentiation through degradation of mammalian target of rapamycin pathway components. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.I.; Funahashi, Y.; Shawber, C.J.; Castrillon, D.H.; Kollipara, R.; DePinho, R.A.; Kitajewski, J.; Accili, D. A Foxo/Notch pathway controls myogenic differentiation and fiber type specification. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, S.; Salilew-Wondim, D.; Hoelker, M.; Rings, F.; Neuhoff, C.; Tholen, E.; Schellander, K.; Tesfaye, D. MicroRNA-183-96-182 Cluster Regulates Bovine Granulosa Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Transition by Coordinately Targeting FOXO1. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, S.; Du, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, Q. SMAD4 Inhibits Granulosa Cell Apoptosis via the miR-183-96-182 Cluster and FoxO1 Axis. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).