Using Cumulus Cell Biopsy as a Non-Invasive Tool to Access the Quality of Bovine Oocytes: How Informative Are They?
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Experiment 1: Effects of CC Biopsy and Individual Culture System on In Vitro Embryo Production
- Control: The only group wherein in vitro matured (IVM), in vitro fertilized (IVF), and in vitro cultured (IVC) were performed with grouped COCs;
- Individual IVP: Individual COCs were in vitro matured, fertilized, and cultured;
- Biopsy before IVM: Immature COCs were subjected to CC biopsy and then individually maturated, fertilized, and cultured in vitro;
- Biopsy after IVM: Individually matured COCs were subjected to CC biopsy and then fertilized and cultured in vitro;
- Two Biopsies: Individually matured COCs were subjected to CC biopsies before and after IVM and then followed by in vitro fertilization and culture.
2.1.2. Experiment 2: Quantification of mRNA Levels in Biopsies of Immature and Matured Bovine CCs as a Predictor of COC’s Ability to Support Embryo Development
2.2. Oocyte Recovery and IVM
2.3. CC Biopsies
2.4. In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Culture
2.5. Total Cell Number (Hoechst 33342) and Apoptotic Cell Ratio (Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL))
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1: Effect of CC Biopsy and Individual Culture System on In Vitro Embryo Production
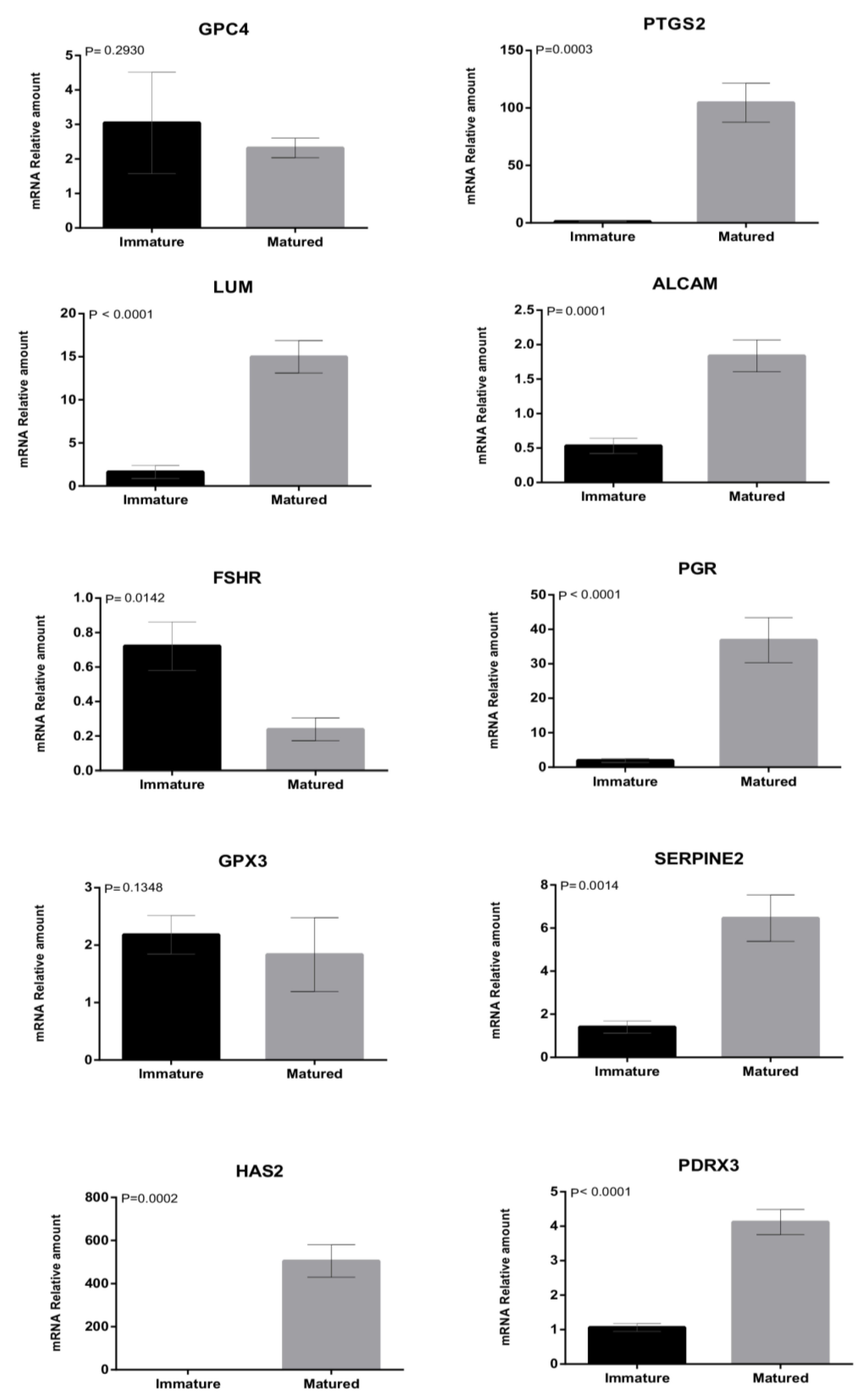
3.2. Experiment 2: Quantification of mRNA Levels in Biopsies of Immature and Matured Bovine CCs as A Predictor of COC Ability to Support Embryo Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizos, D.; Ward, F.; Duffy, P.; Boland, M.P.; Lonergan, P. Consequences of bovine oocyte maturation, fertilization or early embryo development in vitro versus in vivo: Implications for blastocyst yield and blastocyst quality. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2002, 61, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonergan, P.; Faerge, I.; Hyttel, P.M.; Boland, M.; Fair, T. Ultrastructural modifications in bovine oocytes maintained in meiotic arrest in vitro using roscovitine or butyrolactone. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 64, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dode, M.A.N.; Dufort, I.; Massicotte, L.; Sirard, M.-A. Quantitative expression of candidate genes for developmental competence in bovine two-cell embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 73, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kussano, N.; Leme, L.; Guimarães, A.; Franco, M.; Dode, M. Molecular markers for oocyte competence in bovine cumulus cells. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, E.S.; Ripamonte, P.; Franco, M.M.; Junior, J.B.; Dode, M.A.N. Effect of follicle size on mRNA expression in cumulus cells and oocytes of Bos indicus: An approach to identify marker genes for developmental competence. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2009, 21, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, T. Follicular oocyte growth and acquisition of developmental competence. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2003, 78, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirard, M. Resumption of meiosis: Mechanism involved in meiotic progression and its relation with developmental competence. Theriogenology 2001, 55, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhalifa, M.; Madkour, A.; Louanjli, N.; Bouamoud, N.; Saadani, B.; Kaarouch, I.; Chahine, H.; Sefrioui, O.; Merviel, P.; Copin, H.; et al. From global proteome profiling to single targeted molecules of follicular fluid and oocyte: Contribution to embryo development and IVF outcome. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2015, 12, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumesic, D.A.; Meldrum, D.R.; Katz-Jaffe, M.G.; Krisher, R.L.; Schoolcraft, W.B. Oocyte environment: Follicular fluid and cumulus cells are critical for oocyte health. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 103, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, S.; Bender, K.; Fahey, A.G.; Mamo, S.; Brennan, L.; Lonergan, P.; Fair, T. Predictive value of bovine follicular components as markers of oocyte developmental potential. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2014, 26, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivet, A.-L.; Vigneault, C.; Blondin, P.; Sirard, M.-A. Changes in granulosa cells’ gene expression associated with increased oocyte competence in bovine. Reproduction 2013, 145, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulini, F.; Melo, E.O. The Role of Oocyte-Secreted Factors GDF9 and BMP15 in Follicular Development and Oogenesis. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 46, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Luciano, A.M.; Richani, D.; Zeng, H.T.; Wang, X.; De Vos, M.; Sugimura, S.; Smitz, J.; Richard, F.J.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte maturation and quality: Role of cyclic nucleotides. Reproduction 2016, 152, R143–R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luciano, A.M.; Franciosi, F.; Modina, S.C.; Lodde, V. Gap Junction-Mediated Communications Regulate Chromatin Remodeling During Bovine Oocyte Growth and Differentiation Through cAMP-Dependent Mechanism(s)1. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeo, C.X.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Lane, M. Disruption of Bidirectional Oocyte-Cumulus Paracrine Signaling During In Vitro Maturation Reduces Subsequent Mouse Oocyte Developmental Competence1. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, R.; Ritter, L.; Armstrong, D. Oocyte–somatic cell interactions during follicle development in mammals. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2004, 82–83, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assou, S.; Haouzi, D.; Mahmoud, K.; Aouacheria, A.; Guillemin, Y.; Pantesco, V.; Reme, T.; Dechaud, H.; DE Vos, J.; Hamamah, S. A non-invasive test for assessing embryo potential by gene expression profiles of human cumulus cells: A proof of concept study. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 14, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunel, A.; Jorssen, E.; Merckx, E.; Leroy, J.; Bols, P.; Sirard, M. Individual bovine in vitro embryo production and cumulus cell transcriptomic analysis to distinguish cumulus–oocyte complexes with high or low developmental potential. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.J.; Pangas, S.A.; Carson, S.A.; Kovanci, E.; Cisneros, P.; Buster, J.E.; Amato, P.; Matzuk, M.M. Human cumulus granulosa cell gene expression: A predictor of fertilization and embryo selection in women undergoing IVF. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 2869–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamel, M.; Dufort, I.; Robert, C.; Léveillé, M.-C.; Leader, A.; Sirard, M.-A. Identification of follicular marker genes as pregnancy predictors for human IVF: New evidence for the involvement of luteinization process. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 16, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathlet, S.; Adriaenssens, T.; Segers, I.; Verheyen, G.; Van De Velde, H.; Coucke, W.; El, R.R.; Devroey, P.; Smitz, J. Cumulus cell gene expression predicts better cleavage-stage embryo or blastocyst development and pregnancy for ICSI patients. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cillo, F.; Brevini, T.A.; Antonini, S.; Paffoni, A.; Ragni, G.; Gandolfi, F. Association between human oocyte developmental competence and expression levels of some cumulus genes. Reproduction 2007, 134, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.A.; Sciorio, R.; Kinnell, H.; Bayne, R.; Thong, K.J.; De Sousa, P.; Pickering, S. Cumulus gene expression as a predictor of human oocyte fertilisation, embryo development and competence to establish a pregnancy. Reproduction 2009, 138, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, P.; Puard, V.; Chevalier, C.; Teusan, R.; Cadoret, V.; Guérif, F.; Houlgatte, R.; Royere, D. Genomic Assessment of Human Cumulus Cell Marker Genes as Predictors of Oocyte Developmental Competence: Impact of Various Experimental Factors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarica, C.; Cimadomo, D.; Dovere, L.; Giancani, A.; Stoppa, M.; Capalbo, A.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Rienzi, L.; Canipari, R. An integrated investigation of oocyte developmental competence: Expression of key genes in human cumulus cells, morphokinetics of early divisions, blastulation, and euploidy. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2019, 36, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, M.; Dufort, I.; Robert, C.; Léveillé, M.-C.; Leader, A.; Sirard, M.-A. Genomic assessment of follicular marker genes as pregnancy predictors for human IVF. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 16, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demiray, S.B.; Goker, E.N.T.; Tavmergen, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Calimlioglu, N.; Soykam, H.O.; Oktem, G.; Sezerman, U. Differential gene expression analysis of human cumulus cells. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2019, 46, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebhardt, K.M.; Feil, D.K.; Dunning, K.R.; Lane, M.; Russell, D.L. Human cumulus cell gene expression as a biomarker of pregnancy outcome after single embryo transfer. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 47–52.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, A.; Torrealday, S.; Seli, E. Cumulus and granulosa cell markers of oocyte and embryo quality. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 99, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-C.; Shapiro, D.B.; Bernal, D.P.; Wright, G.; Kort, H.I.; Nagy, Z.P. Human oocyte vitrification: In-vivo and in-vitro maturation outcomes. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouandaogo, Z.G.; Frydman, N.A.; Hesters, L.; Assou, S.; Haouzi, D.; Dechaud, H.; Frydman, R.; Hamamah, S. Differences in transcriptomic profiles of human cumulus cells isolated from oocytes at GV, MI and MII stages after in vivo and in vitro oocyte maturation. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raziel, A.; Schachter, M.; Strassburger, D.; Kasterstein, E.; Ron-El, R.; Friedler, S. In vivo maturation of oocytes by extending the interval between human chorionic gonadotropin administration and oocyte retrieval. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 86, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marei, W.F.; Abayasekara, D.R.E.; Wathes, D.C.; Fouladi-Nashta, A.A. Role of PTGS2-generated PGE2 during gonadotrophin-induced bovine oocyte maturation and cumulus cell expansion. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2014, 28, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ocampo, A.; Pedraza, J.; Ortiz, G.; Hernández-Pérez, E.; Porchia, L.; López-Bayghen, E. Assessment of Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 and Versican gene expression profile from the cumulus cells: Association with better in vitro fertilization outcomes. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adriaenssens, T.; Wathlet, S.; Segers, I.; Verheyen, G.; De Vos, A.; Van der Elst, J.; Coucke, W.; Devroey, P.; Smitz, J. Cumulus cell gene expression is associated with oocyte developmental quality and influenced by patient and treatment characteristics. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimada, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Ito, J.; Okazaki, T.; Kawahata, K.; Nishibori, M. Expression of two progesterone receptor isoforms in cumulus cells and their roles during meiotic resumption of porcine oocytes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 33, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamel, M.; Dufort, I.; Robert, C.; Gravel, C.; Leveille, M.-C.; Leader, A.; Sirard, M.-A. Identification of differentially expressed markers in human follicular cells associated with competent oocytes. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 23, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adriaenssens, T.; Segers, I.; Wathlet, S.; Smitz, J. The cumulus cell gene expression profile of oocytes with different nuclear maturity and potential for blastocyst formation. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2010, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Hao, C.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. RUNX2, GPX3 and PTX3 gene expression profiling in cumulus cells are reflective oocyte/embryo competence and potentially reliable predictors of embryo developmental competence in PCOS patients. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cree, L.M.; Hammond, E.R.; Shelling, A.N.; Berg, M.C.; Peek, J.C.; Green, M.P. Maternal age and ovarian stimulation independently affect oocyte mtDNA copy number and cumulus cell gene expression in bovine clones. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallap, T.; Nagy, S.; Jaakma, Ü.; Johannisson, A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H. Usefulness of a triple fluorochrome combination Merocyanine 540/Yo-Pro 1/Hoechst 33342 in assessing membrane stability of viable frozen-thawed spermatozoa from Estonian Holstein AI bulls. Theriogenology 2006, 65, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.; Carvalho, J.; Filho, E.S.; Caixeta, E.; Franco, M.; Rumpf, R.; Dode, M. Effect of Percoll volume, duration and force of centrifugation, on in vitro production and sex ratio of bovine embryos. Theriogenology 2009, 71, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, J.J.; Krogenaes, A.; Susko-Parrish, J.L. Effect of bovine sperm separation by either swim-up or Percoll method on success of in vitro fertilization and early embryonic development. Theriogenology 1995, 44, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, P.; Shukri, N.; Vajta, G.; Booth, P.; Bendixen, C.; Callesen, H. Developmental kinetics of the first cell cycles of bovine in vitro produced embryos in relation to their in vitro viability and sex. Theriogenology 1998, 50, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisher, R.L. In Vivo and In Vitro Environmental Effects on Mammalian Oocyte Quality. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2013, 1, 393–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirard, M.-A.; Richard, F.; Blondin, P.; Robert, C. Contribution of the oocyte to embryo quality. Theriogenology 2006, 65, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.; Khan, M.; Adams, G.; Sirard, M.; Singh, J. Granulosa cell function and oocyte competence: Super-follicles, super-moms and super-stimulation in cattle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 149, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelker, M.; Rings, F.; Lund, Q.; Ghanem, N.; Phatsara, C.; Griese, J.; Schellander, K.; Tesfaye, D. Effect of the microenvironment and embryo density on developmental characteristics and gene expression profile of bovine preimplantative embryos cultured in vitro. Reproduction 2009, 137, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopichandran, N.; Leese, H.J. The effect of paracrine/autocrine interactions on the in vitro culture of bovine preimplantation embryos. Reproduction 2006, 131, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richani, D.; Dunning, K.R.; Thompson, J.G.; Gilchrist, R.B. Metabolic co-dependence of the oocyte and cumulus cells: Essential role in determining oocyte developmental competence. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2020, 27, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, D.K.; Hamilton, R.; McCallie, B.; Schoolcraft, W.B.; Katz-Jaffe, M.G. Human and mouse embryonic development, metabolism and gene expression are altered by an ammonium gradient in vitro. Reproduction 2013, 146, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wydooghe, E.; Heras, S.; Dewulf, J.; Piepers, S.; Van den Abbeel, E.; De Sutter, P.; Vandaele, L.; Van Soom, A. Replacing serum in culture medium with albumin and insulin, transferrin and selenium is the key to successful bovine embryo development in individual culture. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2014, 26, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wydooghe, E.; Vandaele, L.; Heras, S.; De Sutter, P.; Deforce, D.; Peelman, L.; De Schauwer, C.; Van Soom, A. Autocrine embryotropins revisited: How do embryos communicate with each other in vitro when cultured in groups? Biol. Rev. 2015, 92, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, R.; Szpila, M.; Ajduk, A.M. Dynamics of cytoplasm and cleavage divisions correlates with preimplantation embryo development. Reproduction 2018, 155, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y. The effect of Day 3 cell number on pregnancy outcomes in vitrified-thawed single blastocyst transfer cycles. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.C.; Dode, M.A.N.; Rumpf, R. Evaluation of different culture systems on the in vitro production of bovine embryos. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyse, B.A.; Weizman, N.F.; Kadish, S.; Balakier, H.; Sangaralingam, M.; Librach, C.L. Transcriptomics of cumulus cells—A window into oocyte maturation in humans. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, S.; Carter, F.; Lonergan, P.; Leal, C.L.; Al Naib, A.; McGettigan, P.; Mehta, J.P.; Evans, A.C.; Fair, T. Sequential analysis of global gene expression profiles in immature and in vitro matured bovine oocytes: Potential molecular markers of oocyte maturation. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticianelli, J.S.; Emanuelli, I.P.; Satrapa, R.A.; Castilho, A.C.S.; Loureiro, B.; Sudano, M.J.; Fontes, P.K.; Pinto, R.F.P.; Razza, E.M.; Surjus, R.S.; et al. Gene expression profile in heat-shocked Holstein and Nelore oocytes and cumulus cells. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McReynolds, S.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; McCallie, B.R.; Mitchell, S.D.; Stevens, J.; Hansen, K.; Schoolcraft, W.B.; Katz-Jaffe, M.G. Impact of maternal aging on the molecular signature of human cumulus cells. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 98, 1574–1580.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, E.O.; Cordeiro, D.M.; Pellegrino, R.; Wei, Z.; Daye, Z.J.; Nishimura, R.C.; Dode, M.A.N. Identification of molecular markers for oocyte competence in bovine cumulus cells. Anim. Genet. 2016, 48, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzirodos, N.; Hummitzsch, K.; Irving-Rodgers, H.F.; Harland, M.L.; Morris, S.E.; Rodgers, R.J. Transcriptome profiling of granulosa cells from bovine ovarian follicles during atresia. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salhab, M.; Tosca, L.; Cabau, C.; Papillier, P.; Perreau, C.; Dupont, J.; Mermillod, P.; Uzbekova, S. Kinetics of gene expression and signaling in bovine cumulus cells throughout IVM in different mediums in relation to oocyte developmental competence, cumulus apoptosis and progesterone secretion. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assidi, M.; Montag, M.; Sirard, M.-A. Use of Both Cumulus Cells’ Transcriptomic Markers and Zona Pellucida Birefringence to Select Developmentally Competent Oocytes in Human Assisted Reproductive Technologies. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, W.W.-Y.; Funderburgh, J.L.; Xia, Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Conrad, G.W. Focus on Molecules: Lumican. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Assidi, M.; Dieleman, S.J.; Sirard, M.-A. Cumulus cell gene expression following the LH surge in bovine preovulatory follicles: Potential early markers of oocyte competence. Reproduction 2010, 140, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.K.-K.; Fan, C.-C.; Hwu, Y.-M.; Lu, C.-H.; Lin, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Li, S.-H. SERPINE2, an inhibitor of plasminogen activators, is highly expressed in the human endometrium during the secretory phase. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devjak, R.; Tacer, K.F.; Juvan, P.; Klun, I.V.; Rozman, D.; Bokal, E.V. Cumulus Cells Gene Expression Profiling in Terms of Oocyte Maturity in Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation Using GnRH Agonist or GnRH Antagonist. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekart, J.; McNatty, K.; Hutton, J.; Pitman, J. Ranking and selection of MII oocytes in human ICSI cycles using gene expression levels from associated cumulus cells. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2930–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerstein, P.; Cadoret, V.; Dalbies-Tran, R.; Guerif, F.; Bidault, R.; Royere, D. Gene expression in human cumulus cells: One approach to oocyte competence. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | Primer Sequences | Amplicon Size (bp) | Primer Concentration (nM) | GenBank Access Number/Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: GGC GTG AAC CAC GAG AAG TAT AA R: CCC TCC ACG ATG CCA AAG T | 118 | 300 | NM_001034034.2 |
| GPC4 | F: TGG TGA ATC CCA CAA CCC AGT GTA R: TCT CAG CCA CCA TCA GCA TAG CAT | 192 | 300 | NM_001205784.1 |
| LUM | F: GTC TCC CAG TGT CTC TTC TAA R: GAG ATC CAG CTC CAA CAA AG | 179 | 300 | NM_173934.1 |
| PTGS2 | F: GAG GAA CTT ACA GGA GAG AAG R: CGG GAG AGC ATA TAG GAT TAC | 193 | 250 | NM_174445.2 |
| ALCAM | F: GGA CAG CCT GAA GGA ATT AG R: CCA ATC TGC TTA GTC ACC TC | 182 | 300 | NM_174238.1 |
| FSHR | F: GGA TGC CAT CAT CGA CTC TG R: TGA CTC GAA GCT TGG TGA GAA C | 133 | 300 | NM_174061 |
| GPX3 | F: GCT AGA CCC TTT ACT GTT ACA C R: GTT CCT CTC TGG CAT TCT TC | 189 | 300 | NM_174077.4 |
| PGR | F: TCAGGCTGGCATGGTTCTTGG R: CTTAGGGCTTGGCTTTCGTTTGG | 126 | 300 | NM_001205356.1 |
| SERPINE2 | F: GAC TCC TTT CCT ACA TCT TTC C R: CAG TAC AGT GTT CCA CCA TC | 158 | 300 | NM_174669.2 |
| HAS2 | F: GGG TTC TTC CCT TTC TTT CT R: CCA CCC AGC TTT GTT TAT TG | 240 | 250 | NM_174079.2 |
| PDRX3 | F: GGC AGG AAC TTT GAT GAG AT R: GTG TGT AGC GGA GGT ATT TC | 205 | 300 | NM_174643.1 |
| Treatment | Oocytes n | Cleavage at D2 n (% ± S.D.) | Blastocyst at D7 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi n (%) | Bl n (%) | Bx n (%) | Total n (% ± SD) | |||
| Control | 177 | 135 (76.2 ± 5.0) a | 19 (28.0%) | 25 (37.0%) | 24 (35.0%) | 68 (38.4 ± 7.8) a |
| Individual IVP | 112 | 76 (68.0 ± 17.4) a,b | 12 (32.4%) | 16 (43.2%) | 9 (24.4%) | 37(33.0 ± 5.1) a,b |
| Immature Biopsy | 112 | 63 (56.2 ± 8.5) b | 9 (29.0%) | 16 (52.0%) | 6 (19.0%) | 31 (27.6 ± 4.2) b |
| Matured Biopsy | 112 | 70 (62.5 ± 4.5) b | 6 (21.6%) | 15 (53.5%) | 7 (25.0%) | 28 (25.0 ± 4.3) b |
| Two Biopsies | 112 | 67(60.0 ± 4.0) b | 13 (45.0%) | 9 (31.0%) | 7 (24.0%) | 29 (25.8 ± 3.5) b |
| Treatments | Total Number of Cells Mean ± SD | Apoptotic Cells Ratio % |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 134.0 ± 24.8 a | 3.73 a |
| Individual IVP | 118.0 ± 18.1 b | 3.81 a |
| Immature Biopsy | 113.0 ± 20.2 b | 6.72 b |
| Matured Biopsy | 119.2 ± 19.3 b | 5.62 b |
| Two Biopsies | 115.5 ± 19.0 b | 7.53 b |
| Treatment | Oocytes n | Cleavage at D2 n (% ± S.D.) | Blastocyst at D7 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi n (%) | Bl n (%) | Bx n (%) | Be n (%) | Total n (% ± SD) | |||
| Control | 160 | 100 (62.5 ± 14.4) | 14 (28.5%) | 12 (24.5%) | 19 (38.7%) | 4 (8.1%) | 49 (30.6 ± 7.5) |
| Two Biopsies | 160 | 98 (61.2 ± 21.9) | 13 (28.2%) | 15 (32.6%) | 18 (39.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 46 (28.7 ± 9.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sprícigo, J.F.W.; Guimarães, A.L.S.; Cunha, A.T.M.; Leme, L.d.O.; Carneiro, M.C.; Franco, M.M.; Dode, M.A.N. Using Cumulus Cell Biopsy as a Non-Invasive Tool to Access the Quality of Bovine Oocytes: How Informative Are They? Animals 2022, 12, 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223113
Sprícigo JFW, Guimarães ALS, Cunha ATM, Leme LdO, Carneiro MC, Franco MM, Dode MAN. Using Cumulus Cell Biopsy as a Non-Invasive Tool to Access the Quality of Bovine Oocytes: How Informative Are They? Animals. 2022; 12(22):3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223113
Chicago/Turabian StyleSprícigo, José Felipe Warmling, Ana Luiza Silva Guimarães, Andrielle Thainar Mendes Cunha, Ligiane de Oliveira Leme, Marcos Coura Carneiro, Maurício Machaim Franco, and Margot Alves Nunes Dode. 2022. "Using Cumulus Cell Biopsy as a Non-Invasive Tool to Access the Quality of Bovine Oocytes: How Informative Are They?" Animals 12, no. 22: 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223113
APA StyleSprícigo, J. F. W., Guimarães, A. L. S., Cunha, A. T. M., Leme, L. d. O., Carneiro, M. C., Franco, M. M., & Dode, M. A. N. (2022). Using Cumulus Cell Biopsy as a Non-Invasive Tool to Access the Quality of Bovine Oocytes: How Informative Are They? Animals, 12(22), 3113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223113





