The Distinctive Forehead Cleft of the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) Hardly Affects Biosonar Beam Formation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
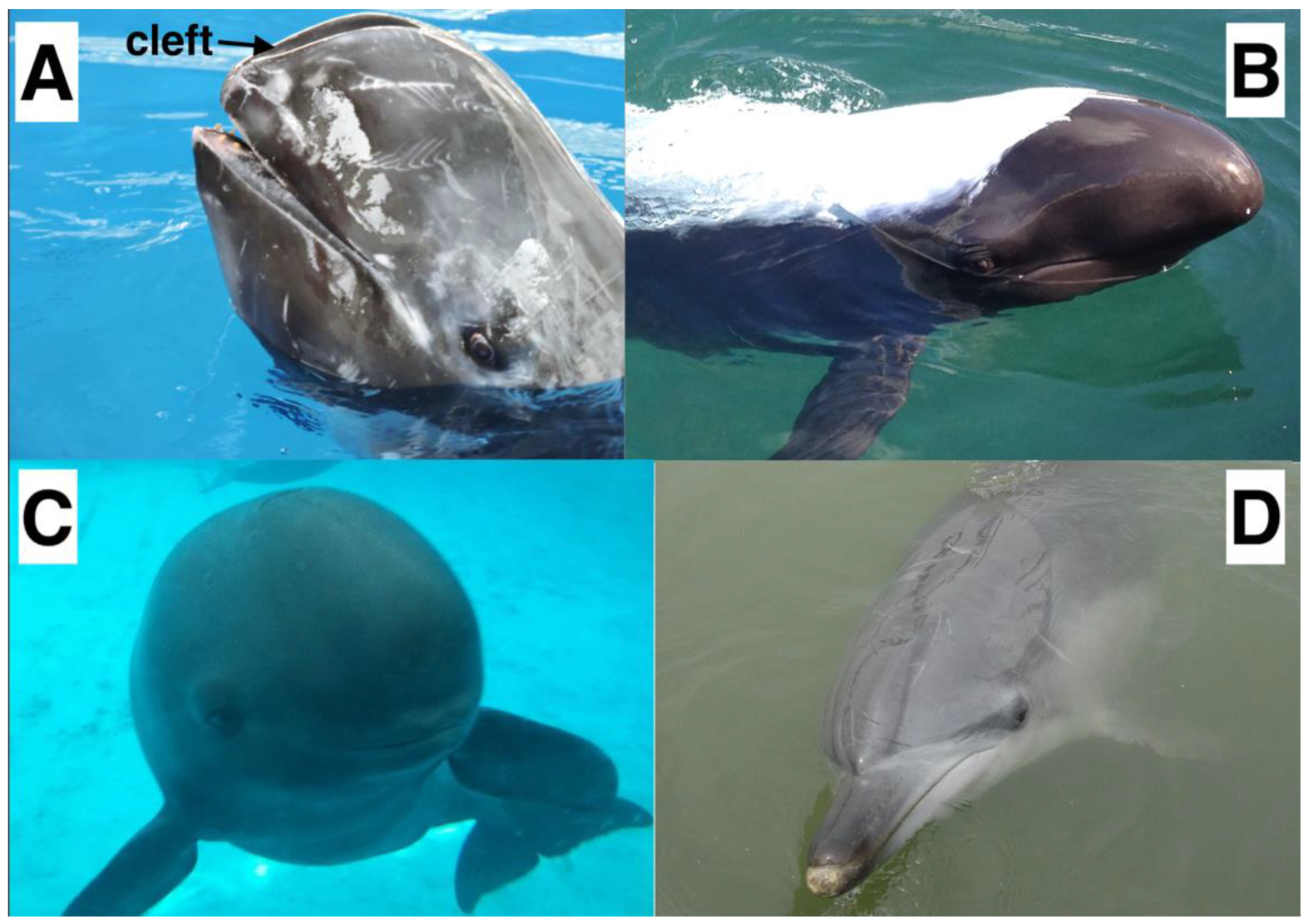
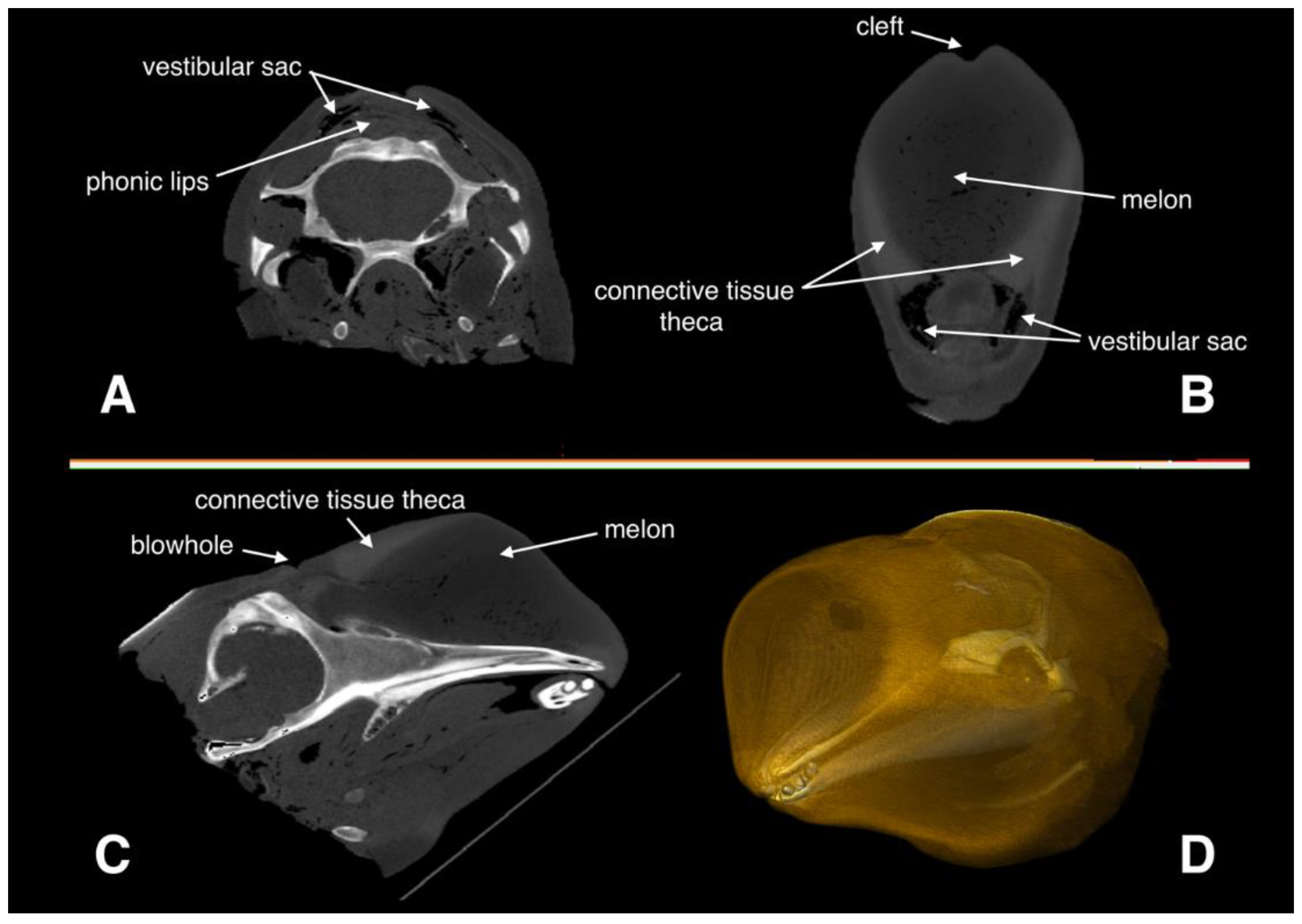
2.1. Medical CT Scan and Image Analysis
2.2. Reconstruction of Acoustic Properties
2.3. FE Model Construction
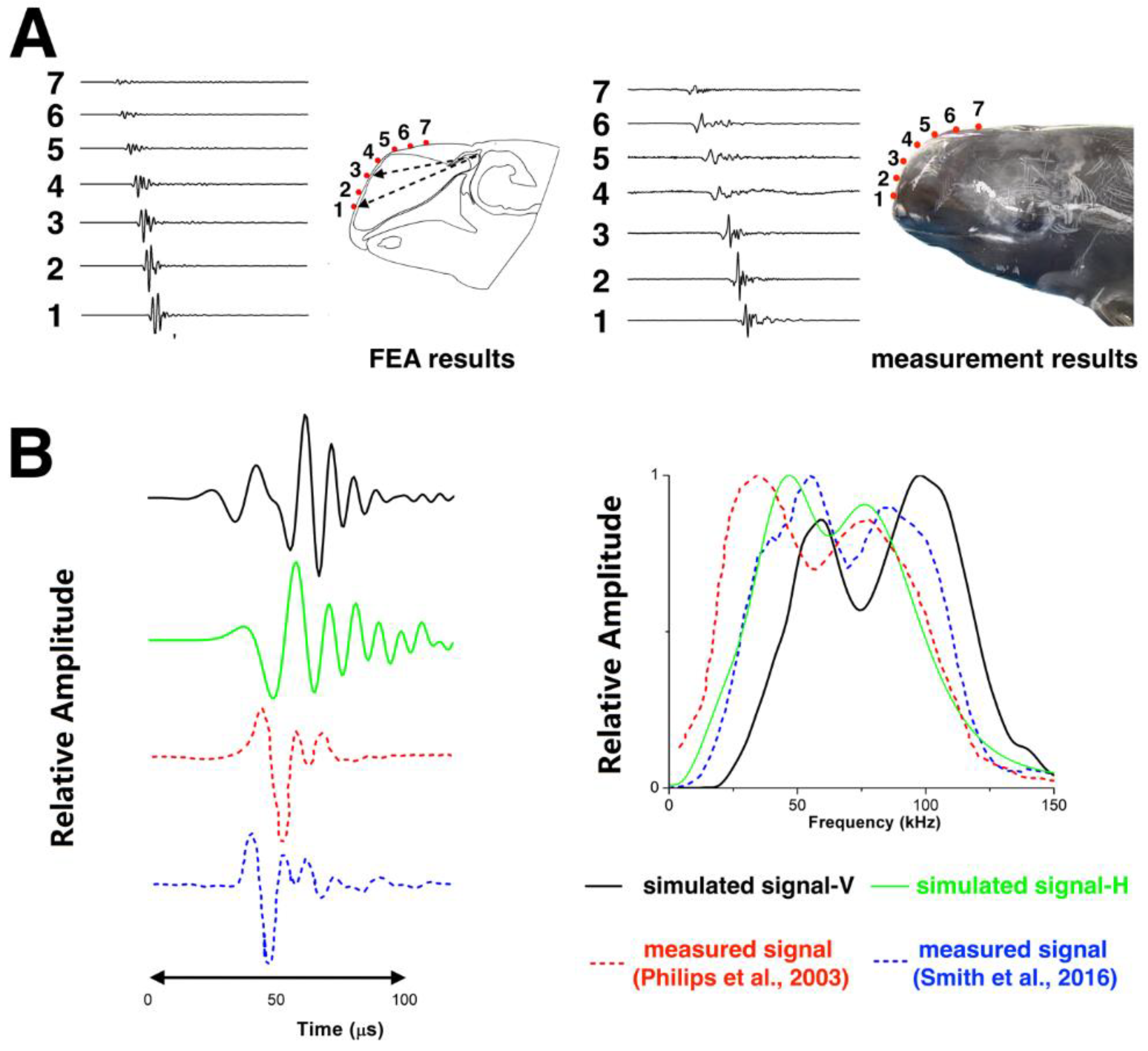
2.4. Model Validation
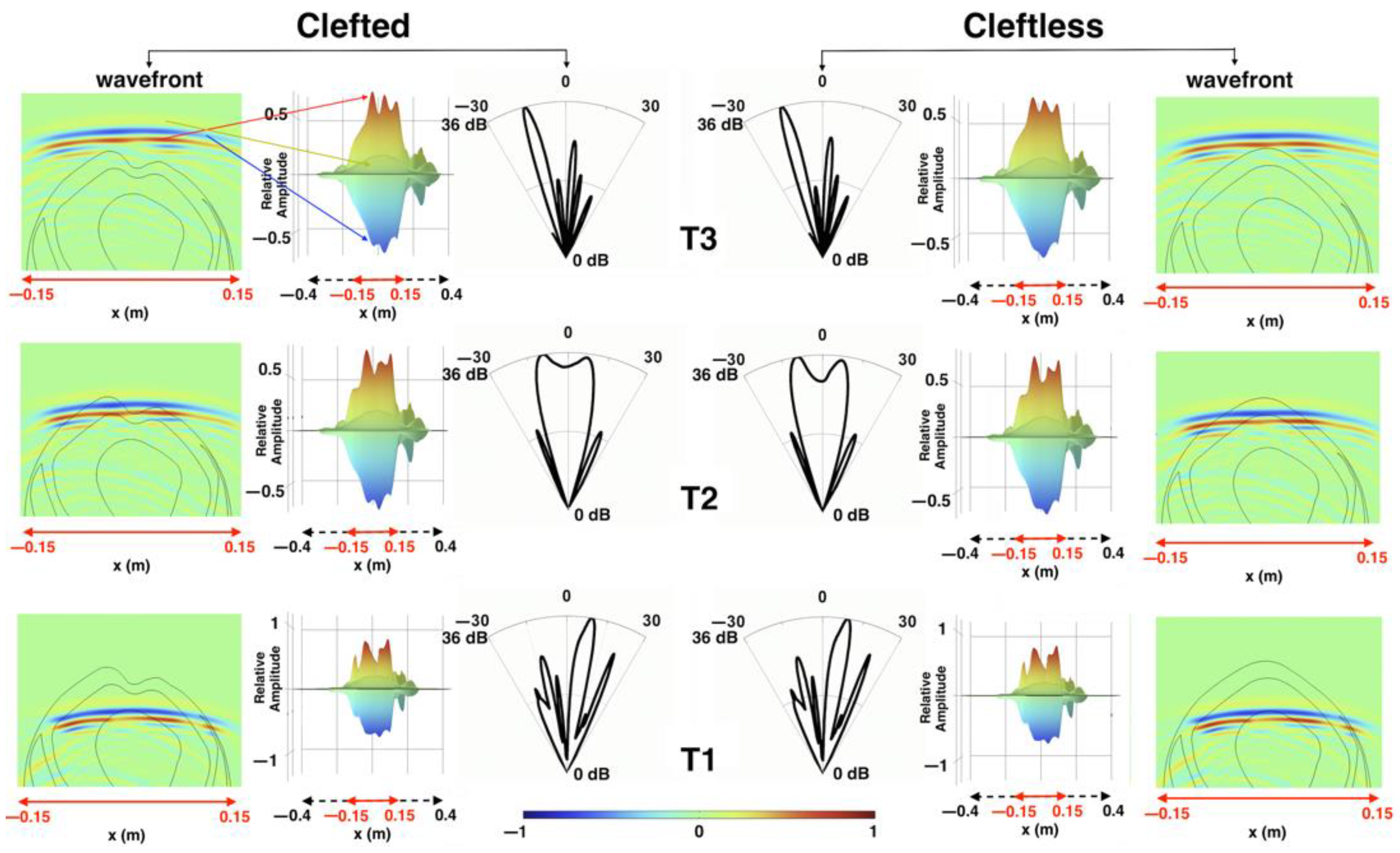
3. Results
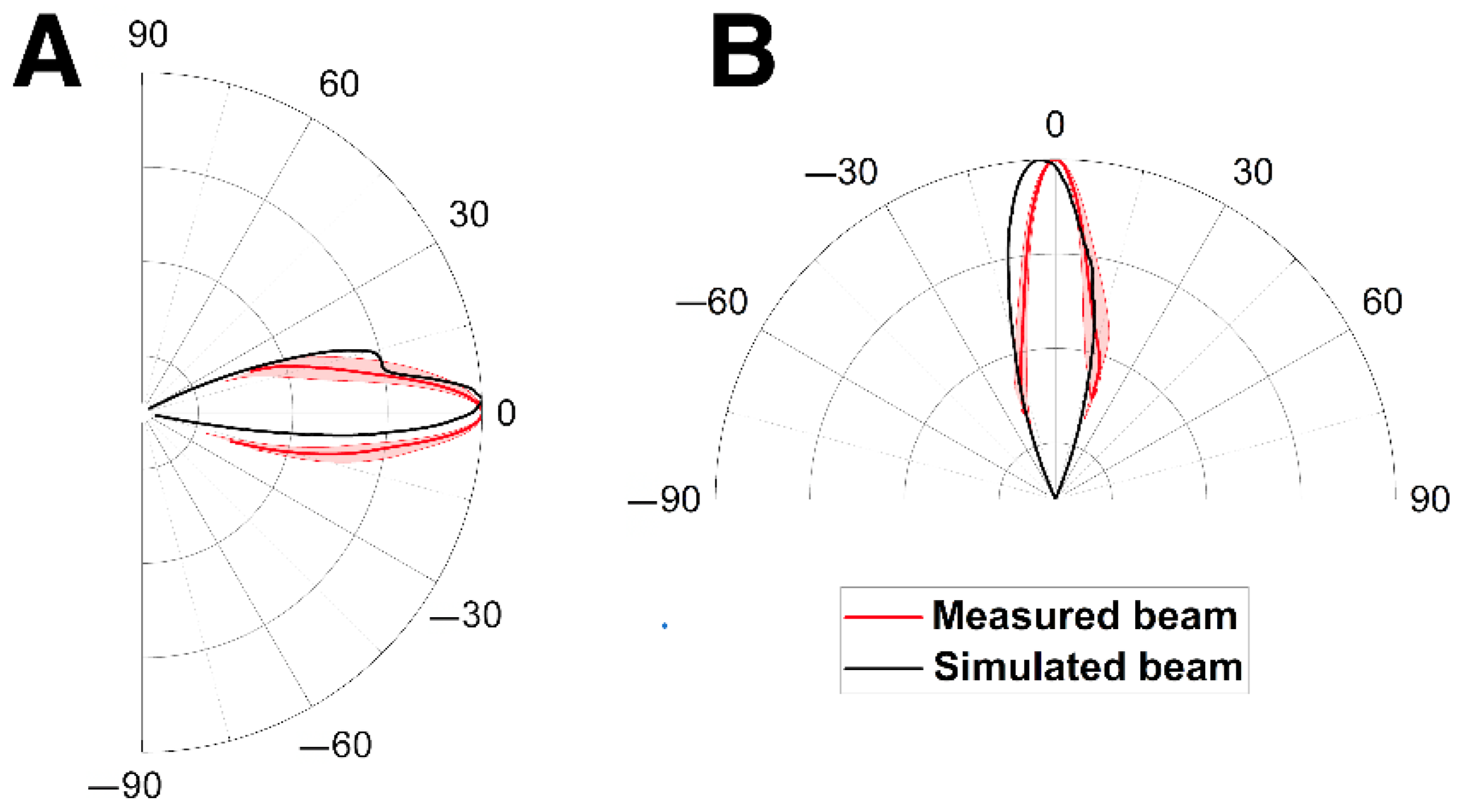
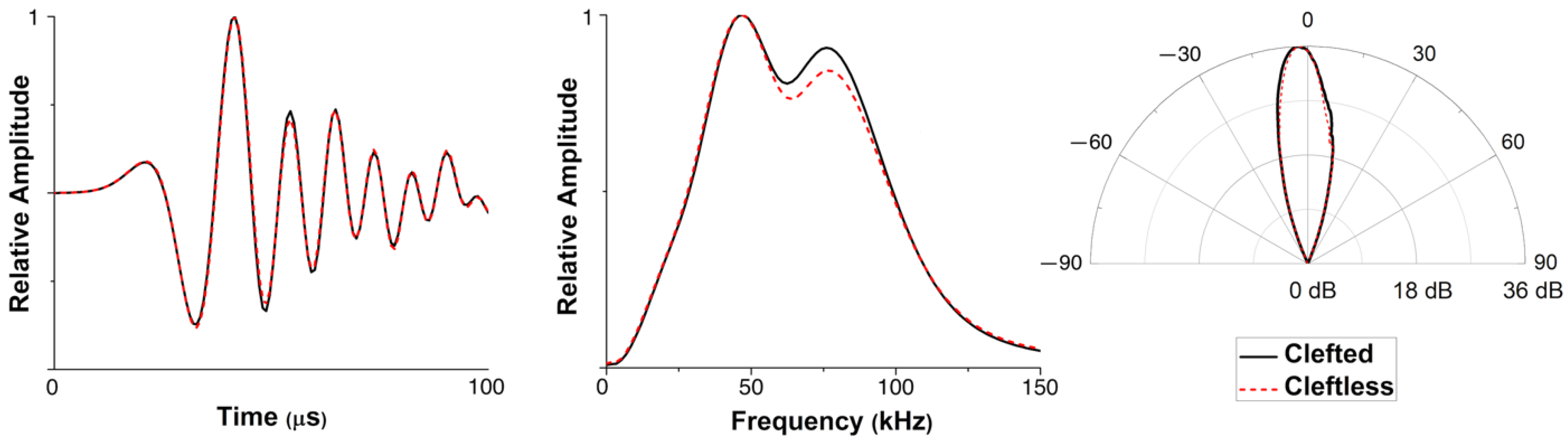
3.1. Model Validation
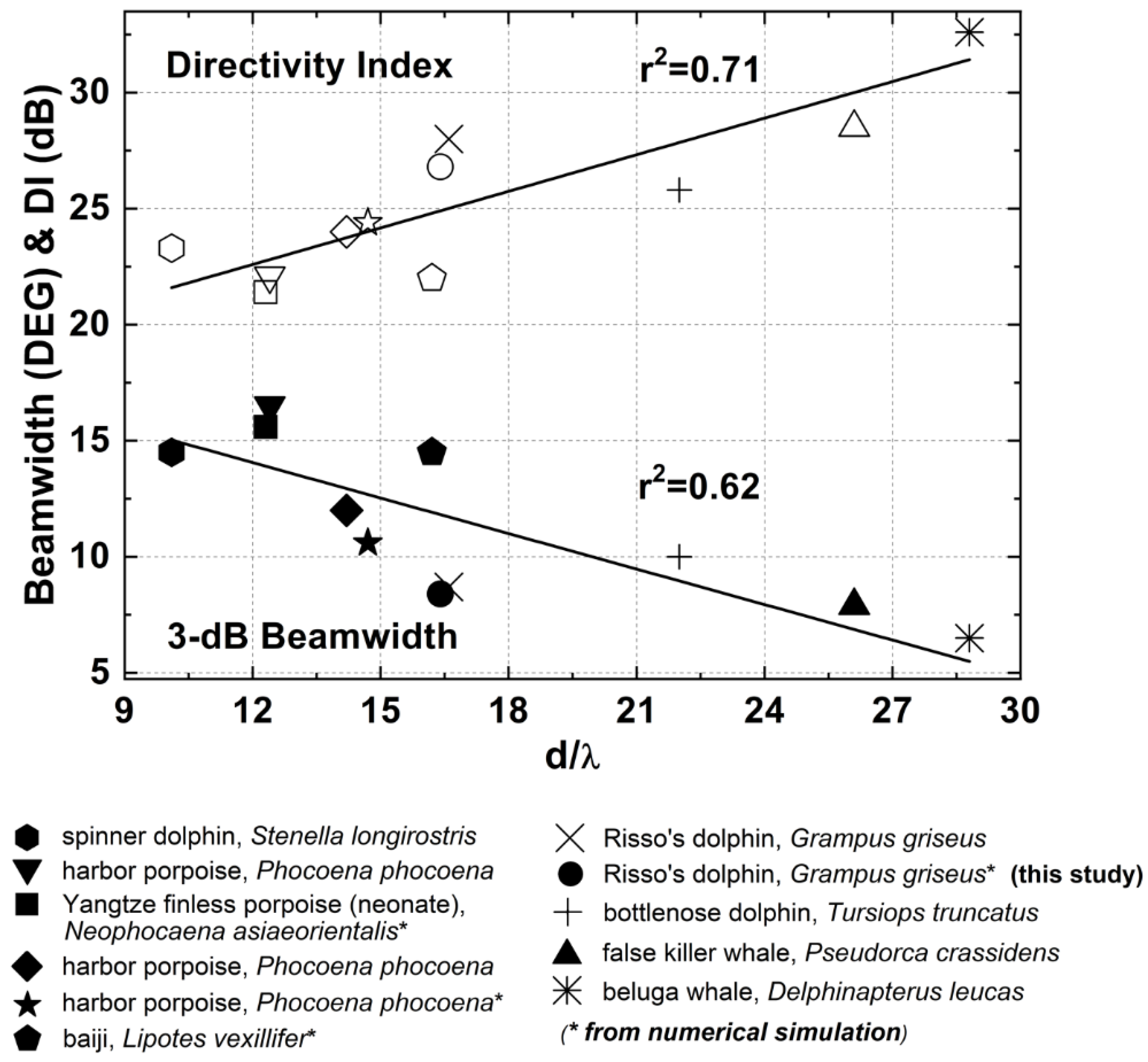
3.2. Sound Propagation through the Cleft
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leatherwood, S.; Perrin, W.F.; Kirby, V.L.; Hubbs, C.L.; Dahleim, M. Distribution and movements of Risso’s dolphin. Grampus griseus, in the Eastern North Pacific. Fish. Bull. 1980, 77, 951–963. [Google Scholar]
- Philips, J.D.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Au, W.W.; Pawloski, J.L.; Roitblat, H.L. Echolocation in the Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Kerr, I.; Payne, R. Echolocation clicks of two free-ranging, oceanic delphinids with different food preferences: False killer whales Pseudorca crassidens and Risso’s dolphins Grampus griseus. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.B.; Kloepper, L.N.; Yang, W.-C.; Huang, W.-H.; Jen, I.-F.; Rideout, B.P.; Nachtigall, P.E. Transmission beam characteristics of a Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leatherwood, S.; Reeves, R.R.; Foster, L. The Sierra Club Handbook of Whales and Dolphins; Tien Wah Press: Singapore, 1983; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L. The Sonar of Dolphins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993; 277p. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L.; Kastelein, R.A.; Benoit-Bird, K.J. Acoustic radiation from the head of echolocating harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, W.W.L.; Houser, D.S.; Finneran, J.J.; Lee, W.; Talmadge, L.A.; Moore, P.W. The acoustic field on the forehead of echolocating Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cranford, T.W.; Amundin, M.; Norris, K.S. Functional morphology and homology in the odontocete nasal complex: Implications for sound Generation. J. Morphol. 1996, 228, 223–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroyan, J.L.; Cranford, T.W.; Kent, J.; Norris, K.S. Computer modeling of acoustic beam formation in Delphinus delphis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 92, 2539–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cranford, T.W.; Trijoulet, V.; Smith, C.R.; Krysl, P. Validation of a vibroacoustic finite element model using bottlenose dolphin simulations: The dolphin biosonar beam is focused in stages. Bioacoustics 2014, 23, 161–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Wei, C. A review of new understanding of the role of individual structure within the head of dolphins in formation of biosonar signal and beam. Oceanogr. Fish. Open Access J. 2017, 2, 555579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Au, W.W.L.; Ketten, D.R.; Zhang, Y. Finite element simulation of broadband biosonar signal propagation in the near- and far-field of an echolocating Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Au, W.W.L.; Ketten, D.R.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y. Biosonar signal propagation in the harbor porpoise’s (Phocoena phocoena) head: The role of various structures in the formation of the vertical beam. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 4179–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Yu, Z.; Au, W.W.L. Simulation of ultrasound beam formation of baiji (Lipotes vexillifer) with a finite element model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, K.S.; Harvey, G.W. Sound transmission in the porpoise head. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1974, 56, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroyan, J.L. Three-dimensional modeling of hearing in Delphinus delphis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 3305–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tubelli, A.; Zosuls, A.; Ketten, D.; Mountain, D.C. Prediction of a mysticete audiogram via finite element analysis of the middle ear. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 730, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Song, Z.; Au, W.W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. A numerical evidence of biosonar beam formation of a neonate Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis). J. Theor. Comput. Acoust. 2018, 26, 1850009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Au, W.W.L.; Ketten, D.R. Modeling of the near to far acoustic fields of an echolocating bottlenose dolphin and harbor porpoise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 1790–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumont, E.R.; Piccirillo, J.; Grosse, I.R. Finite-element analysis of biting behavior and bone stress in the facial skeletons of bats. Anat. Rec. 2005, 283, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.K.; Wilson, P.S.; Fuiman, L.A. Predicting pressure sensitivity through ontogeny in larval red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus). Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2019, 37, 010006. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, A.K.; Wilson, P.S.; Fuiman, L.A. Ontogenetic change in predicted acoustic pressure sensitivity in larval red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus). J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb201962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krysl, P.; Hawkins, A.D.; Schilt, C.; Cranford, T.W. Angular oscillation of solid scatterers in response to progressive planar acoustic waves: Do fish otoliths rock? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldevilla, M.S.; McKenna, M.F.; Wiggins, S.M.; Shadwick, R.E.; Cranford, T.W.; Hildebrand, J.A. Cuvier’s beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris) head tissues: Physical properties and CT imaging. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 209, 2319–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, D.; Au, W.W.L.; Yu, Z. Acoustic property reconstruction of a neonate Yangtze finless porpoise’s (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis) head based on CT Imaging. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos-Francisco, D.; García-Carrillo, N.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M. Radiological characterization of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fat by X-ray micro-computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Sánchez, J.; García-Carrillo, N.; Guardiola, F.A.; Ceballos-Francisco, D.; Esteban, M. Ultrasonography and X-ray micro-computed tomography characterization of the effects caused by carrageenin in the muscle of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérenger, J.P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 114, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Lammers, M.; Wisniewska, D.; Beedholm, K. Nasal sound production in echolocating delphinids (Tursiops truncatus and Pseudorca crassidens) is dynamic, but unilateral: Clicking on the right side and whistling on the left side. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 4091–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, W.W.L.; Kastelein, R.A.; Rippe, T.; Schooneman, N.M. Transmission beam pattern and echolocation signals of a harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 3699–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Hastings, M. Principles of Marine Bioacoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Au, W.W.L.; Song, Z.; Yu, Z. The role of various structures in the head on the formation of the biosonar beam of the baiji (Lipotes vexillifer). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C. Sound production and propagation in cetaceans. In Neuroendocrine Regulation of Animal Vocalization; Rosenfeld, C.S., Hoffmann, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Pawloski, J.L.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Blonz, M.; Gisner, R.C. Echolocation signals and transmission beam pattern of a false killer whale (Pseudorca crassidens). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblitz, J.C.; Wahlberg, M.; Stilz, P.; Madsen, P.T.; Beedholm, K.; Schnitzler, H. Asymmetry and dynamics of a narrow sonar beam in an echolocating harbor porpoise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, W.W.L.; Moore, P.W.B.; Pawloski, D.A. Echolocation transmitting beam of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.; Penner, R.H.; Turl, C.W. Propagation of beluga echolocation signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Pacini, A.F.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Laule, G.E.; Aragones, L.V.; Magno, C.; Suarez, J.A. Transmission beam pattern and dynamics of a spinner dolphin (Stenella longirostris). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, D.M.; Johnson, M.; Beedholm, K.; Wahlberg, M.; Madsen, P.T. Acoustic gaze adjustments during active target selection in echolocating porpoises. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 4358–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisniewska, D.M.; Ratcliffe, J.M.; Beedholm, K.; Christensen, C.B.; Johnson, M.; Koblitz, J.C.; Wahlberg, M.; Madsen, P.T. Range-dependent flexibility in the acoustic field of view of echolocating porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). eLife 2015, 4, e05651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloepper, L.N.; Nachtigall, P.E.; Quintos, C.; Vlachos, S. Single-lobed frequency dependent beam shape in an echolocating false killer whale (Pseudorca crassidens). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Structures and Seawater | Sound Speed (m/s) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Melon | 1378–1466 | 948–986 |
| Connective tissues | 1548–1581 | 1021–1035 |
| Muscle | 1496–1533 | 998–1014 |
| Mandibular fat | 1428 | 970 |
| Brain | 1485 | 994 |
| Bony structures | 3800 | 2000 |
| Seawater | 1483 | 998 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Gill, L.G.; Erbe, C.; Smith, A.B.; Yang, W.-C. The Distinctive Forehead Cleft of the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) Hardly Affects Biosonar Beam Formation. Animals 2022, 12, 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243472
Wei C, Gill LG, Erbe C, Smith AB, Yang W-C. The Distinctive Forehead Cleft of the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) Hardly Affects Biosonar Beam Formation. Animals. 2022; 12(24):3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243472
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chong, Lachlan G. Gill, Christine Erbe, Adam B. Smith, and Wei-Cheng Yang. 2022. "The Distinctive Forehead Cleft of the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) Hardly Affects Biosonar Beam Formation" Animals 12, no. 24: 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243472
APA StyleWei, C., Gill, L. G., Erbe, C., Smith, A. B., & Yang, W.-C. (2022). The Distinctive Forehead Cleft of the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) Hardly Affects Biosonar Beam Formation. Animals, 12(24), 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243472







