Giant Multinucleated Cells Are Associated with Mastocytic Inflammatory Signature Equine Asthma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Procedure and Processing
2.3. Cytology
- (1)
- Differential cell counts were performed at 40× magnification on a minimum of 500 cells and 5 high power fields (HPF) [23]. Epithelial cells were excluded, when present and GMC were counted as macrophages (i.e., a GMC with two nuclei accounted for two macrophages).
- (2)
- Counts of GMC were performed at 40× magnification over 15 HPF and expressed as GMC:single macrophages (GMC:M) ratio. They were obtained from:
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Horses
3.2. Giant Multinucleated Cell Counts
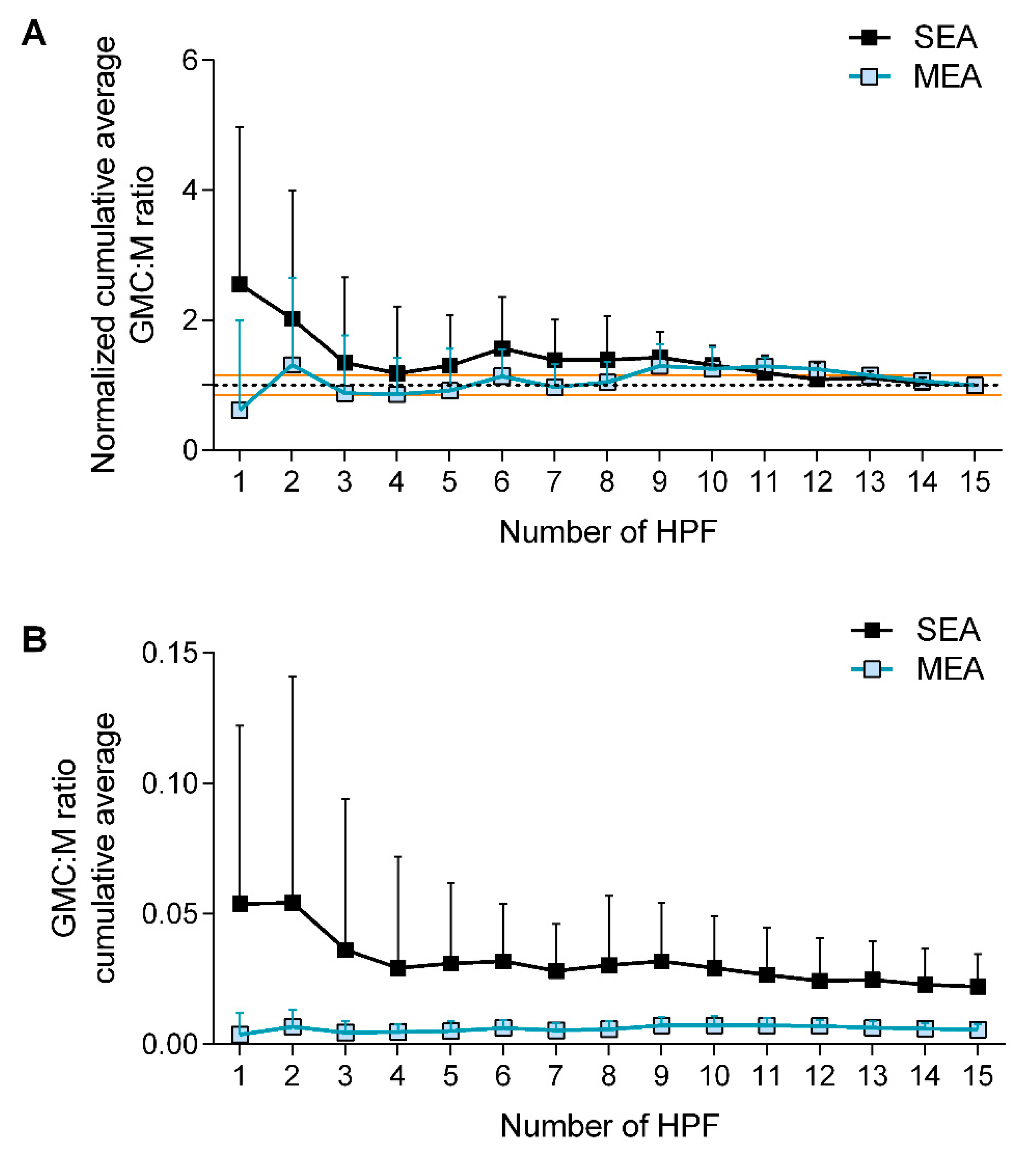
3.2.1. Counting Method
3.2.2. Disease Effect and External Validity of the Study
3.3. Giant Multinucleated Cell Counts Relationship with Clinical Parameters and Inflammatory Signatures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couetil, L.L.; Cardwell, J.M.; Gerber, V.; Lavoie, J.P.; Leguillette, R.; Richard, E.A. Inflammatory airway disease of horses-revised consensus statement. J. Vet. Intern. Med./Am. Coll. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, D.; Vrins, A.; Beauchamp, G.; Lavoie, J.P. Evaluation of variations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in horses with recurrent airway obstruction. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.P.; Maghni, K.; Desnoyers, M.; Taha, R.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q.A. Neutrophilic airway inflammation in horses with heaves is characterized by a th2-type cytokine profile. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klukowska-Rotzler, J.; Swinburne, J.E.; Drogemuller, C.; Dolf, G.; Janda, J.; Leeb, T.; Gerber, V. The interleukin 4 receptor gene and its role in recurrent airway obstruction in swiss warmblood horses. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclere, M.; Lavoie-Lamoureux, A.; Lavoie, J.P. Heaves, an asthma-like disease of horses. Respirology 2011, 16, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, U.; Klukowska-Rotzler, J.; Dolf, G.; Swinburne, J.E.; Ramseyer, A.; Bugno, M.; Burger, D.; Blott, S.; Gerber, V. A region on equine chromosome 13 is linked to recurrent airway obstruction in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2007, 39, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, R.S.; Collie, D.D.; Dixon, P.M.; McGorum, B.C. Evaluation of nebulised hay dust suspensions (hds) for the diagnosis and investigation of heaves. 2: Effects of inhaled hds on control and heaves horses. Equine Vet. J. 2002, 34, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, R.S.; Collie, D.D.; Dixon, P.M.; McGorum, B.C. Inhaled endotoxin and organic dust particulates have synergistic proinflammatory effects in equine heaves (organic dust-induced asthma). Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 33, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, R.S.; Dixon, P.M.; Collie, D.D.; McGorum, B.C. Pulmonary and systemic effects of inhaled endotoxin in control and heaves horses. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirie, R.S.; Dixon, P.M.; McGorum, B.C. Endotoxin contamination contributes to the pulmonary inflammatory and functional response to aspergillus fumigatus extract inhalation in heaves horses. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Baur, M.E.; Beadle, R.E. Temporal clinical exacerbation of summer pasture-associated recurrent airway obstruction and relationship with climate and aeroallergens in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullone, M.; Murcia, R.Y.; Lavoie, J.P. Environmental heat and airborne pollen concentration are associated with increased asthma severity in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2016, 48, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorum, B.C.; Dixon, P.M.; Halliwell, R.E. Phenotypic analysis of peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lymphocytes in control and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affected horses, before and after ‘natural (hay and straw) challenges’. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1993, 36, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmallenbach, K.H.; Rahman, I.; Sasse, H.H.; Dixon, P.M.; Halliwell, R.E.; McGorum, B.C.; Crameri, R.; Miller, H.R. Studies on pulmonary and systemic aspergillus fumigatus-specific ige and igg antibodies in horses affected with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 66, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, U.; Buechner-Maxwell, V.A.; Witonsky, S.G.; Hite, R.D. Role of lung surfactant in respiratory disease: Current knowledge in large animal medicine. J. Vet. Intern. Med./Am. Coll. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, V.; Robinson, N.E.; Luethi, S.; Marti, E.; Wampfler, B.; Straub, R. Airway inflammation and mucus in two age groups of asymptomatic well-performing sport horses. Equine Vet. J. 2003, 35, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, P.J.; Glogauer, M.; McCulloch, C.A. An overview of the derivation and function of multinucleated giant cells and their role in pathologic processes. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordeau, M.E.; Joubert, P.; Dewachi, O.; Hamid, Q.; Lavoie, J.P. Il-4, il-5 and ifn-gamma mrna expression in pulmonary lymphocytes in equine heaves. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 97, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie-Lamoureux, A.; Moran, K.; Beauchamp, G.; Mauel, S.; Steinbach, F.; Lefebvre-Lavoie, J.; Martin, J.G.; Lavoie, J.P. Il-4 activates equine neutrophils and induces a mixed inflammatory cytokine expression profile with enhanced neutrophil chemotactic mediator release ex vivo. Am. J. Physiology. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L472–L482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.L.; Mikhailenko, I.; Tondravi, M.M.; Keegan, A.D. Il-4 promotes the formation of multinucleated giant cells from macrophage precursors by a stat6-dependent, homotypic mechanism: Contribution of e-cadherin. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 1542–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caslin, H.L.; Kiwanuka, K.N.; Haque, T.T.; Taruselli, M.T.; MacKnight, H.P.; Paranjape, A.; Ryan, J.J. Controlling mast cell activation and homeostasis: Work influenced by bill paul that continues today. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.M. Bronchoalveolar lavage: Sampling technique and guidelines for cytologic preparation and interpretation. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2008, 24, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, N.J.; Hecker, K.G.; Gilroy, C.V.; Warren, A.L.; Leguillette, R. Reliability of 400-cell and 5-field leukocyte differential counts for equine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Vet. Clin. Pathol./Am. Soc. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 42, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagianni, A.E.; Lisowski, Z.M.; Hume, D.A.; Scott Pirie, R. The equine mononuclear phagocyte system: The relevance of the horse as a model for understanding human innate immunity. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, I.; Kecelj, P.; Kosnik, M.; Mermolja, M. Multinucleated giant cells in bronchoalveolar lavage. Acta Cytol. 2003, 47, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, I.; Yang, H.; Lauzon, W.; Gendron, N. M-csf and gm-csf promote alveolar macrophage differentiation into multinucleated giant cells with distinct phenotypes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 60, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.E.; McCandless, E.E.; Olszewski, M.A.; Robinson, N.E. Alveolar macrophage phenotypes in severe equine asthma. Vet. J. 2020, 256, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullone, M.; Joubert, P.; Gagne, A.; Lavoie, J.P.; Helie, P. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid neutrophilia is associated with the severity of pulmonary lesions during equine asthma exacerbations. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.E.; Vitari, C.A.; Shende, M.; Strollo, D.C.; Larkin, A.; Yousem, S.A. Asthmatic granulomatosis: A novel disease with asthmatic and granulomatous features. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, H.; Naito, Y.; Ogasawara, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Kasamatsu, N.; Hashizume, I. Idiopathic bronchocentric granulomatosis in an asthmatic adolescent. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclere, M.; Lavoie-Lamoureux, A.; Gelinas-Lymburner, E.; David, F.; Martin, J.G.; Lavoie, J.P. Effect of antigenic exposure on airway smooth muscle remodeling in an equine model of chronic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Bienzle, D.; Lee, G.K.C.; Piche, E.; Viel, L.; Odemuyiwa, S.O.; Beeler-Marfisi, J. Flow cytometric analysis of equine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells in horses with and without severe equine asthma. Vet. Pathol. 2022, 59, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullone, M.; Lavoie, J.P. Asthma “of horses and men”-how can equine heaves help us better understand human asthma immunopathology and its functional consequences? Mol. Immunol. 2015, 66, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclere, M.; Desnoyers, M.; Beauchamp, G.; Lavoie, J.P. Comparison of four staining methods for detection of mast cells in equine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Vet. Intern. Med./Am. Coll. Vet. Intern. Med. 2006, 20, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, K.L.; Holian, A. Macrophage fusion caused by particle instillation. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 1, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, J.J.; Baker, B.; Ryan, J.J. Mast cell production and response to il-4 and il-13. Cytokine 2015, 75, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, S.; Baptiste, K.E.; Fjeldborg, J.; Horohov, D.W. A review of the equine age-related changes in the immune system: Comparisons between human and equine aging, with focus on lung-specific immune-aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 20, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zissel, G.; Schlaak, M.; Muller-Quernheim, J. Age-related decrease in accessory cell function of human alveolar macrophages. J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res. 1999, 47, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, S.V.; Liao, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Giant cell arteritis: Immune and vascular aging as disease risk factors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couetil, L.L.; Ward, M.P. Analysis of risk factors for recurrent airway obstruction in north american horses: 1,444 cases (1990–1999). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Turin Cohort | Montreal Cohort | |
|---|---|---|
| (N = 22) | (N = 20) | |
| Controls | ||
| N | 0 | 10 |
| Sex (M:F) | - | 5:5 |
| Age (years) | - | 10.4 ± 3.6 |
| Mild to moderate equine asthma (MEA) | ||
| N | 14 | 5 |
| Sex (M:F) | 8:6 | 3:2 |
| Age (years) | 7.4 ± 5.7 | 8.2 ± 1.6 |
| Severe equine asthma (SEA) | ||
| N | 8 | 5 |
| Sex (M:F) | 6:2 | 3:2 |
| Age (years) | 15.6 ± 5.4 | 16.0 ± 4.5 |
| Mastocytic asthma (M-MEA) | ||
| N | 7 | 1 |
| Sex (M:F) | 6:1 | M |
| Age (years) | 6.5 ± 7.5 | 8 |
| Paucigranulocytic | Neutrophilic 1 | Mastocytic 2 | Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| MEA | 1 | 5 | 8 | 5 |
| SEA | 1 | 8 | 1 | 3 |
| β Coefficient | 95% CI | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BALF Neutrophil % | 0.0002534 | −0.0001471 | 0.0006538 | 0.20 |
| BALF Mast cell % | −0.0037398 | −0.0065036 | −0.0009760 | 0.01 |
| BALF Macrophage % | −0.0000191 | −0.0004785 | 0.0004402 | 0.93 |
| BALF Lymphocyte % | −0.0001442 | −0.0005176 | 0.0002291 | 0.43 |
| BALF Eosinophil % | −0.0003903 | −0.0072857 | 0.0065051 | 0.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basano, I.; Romolo, A.; Iamone, G.; Memoli, G.; Riccio, B.; Lavoie, J.-P.; Miniscalco, B.; Bullone, M. Giant Multinucleated Cells Are Associated with Mastocytic Inflammatory Signature Equine Asthma. Animals 2022, 12, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091070
Basano I, Romolo A, Iamone G, Memoli G, Riccio B, Lavoie J-P, Miniscalco B, Bullone M. Giant Multinucleated Cells Are Associated with Mastocytic Inflammatory Signature Equine Asthma. Animals. 2022; 12(9):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091070
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasano, Ilaria, Alessandra Romolo, Giulia Iamone, Giulia Memoli, Barbara Riccio, Jean-Pierre Lavoie, Barbara Miniscalco, and Michela Bullone. 2022. "Giant Multinucleated Cells Are Associated with Mastocytic Inflammatory Signature Equine Asthma" Animals 12, no. 9: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091070
APA StyleBasano, I., Romolo, A., Iamone, G., Memoli, G., Riccio, B., Lavoie, J.-P., Miniscalco, B., & Bullone, M. (2022). Giant Multinucleated Cells Are Associated with Mastocytic Inflammatory Signature Equine Asthma. Animals, 12(9), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091070





