Detection the eDNA of Batrachuperus taibaiensis from the Zhouzhi Heihe River Using a Nested PCR Method and DNA Barcoding
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Field Sampling and Collection
2.2. Batrachuperus Genus Specific Primers for Nested PCR
2.3. Environmental DNA Extraction and Detection
2.4. Measures for Avoiding Contamination in eDNA
2.5. DNA Barcoding
3. Results
3.1. Total eDNA Yield in Different Seasons
3.2. Species-Specific Nested PCR
3.3. Detection of Batrachuperus taibaiensis DNA in Water Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Q.T.; Gong, D.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Zuo, J.H.; Nan, X.M. Distribution and conservation of Batrachuperus Stream Salamanders in China. Chin. J. Wildl. 2017, 38, 682–688. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.Z.; Zeng, X.M. How many species are in the genus Batrachuperus? A phylogeographical analysis of the stream salamanders (family Hynobiidae) from southwestern China. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1469–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.T.; Zeng, X.M.; Wu, G.F.; Liu, Z.J.; Fu, J.Z. A new species of Batrachuperus from northwestern China. Asiat. Herpetol. Res. 2001, 9, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.N.; Xiao, B. Study on the development and protection of biodiversity in Heihe river wetland. Shaanxi For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 2, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Liu, X.L.; Sun, C.M. Shaanxi Aquatic Wildlife; Xi’an Map Publishing House: Xi’ an, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.C. Surface Water and Groundwater Coupling Simulation Research in Heihe Basin of Shaanxi; Chang’an University: Xi’ an, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.X. Based on Cytb and D-Loop Region Sequence Analysis of the Pedigree Geography of Batrachuperus Taibaienses; Shaanxi Normal University: Xi’ an, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deiner, K.; Altermatt, F. Transport distance of invertebrate environmental DNA in a natural river. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88786. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson, M.S.; Collins, P.C.; Finarelli, J.A.; Egan, D.; Conchuir, R.Q.; Wightman, G.D.; King, J.J.; Gauthier, D.T.; Whelan, K.; Carlsson, J.E.L.; et al. An eDNA assay for Irish Petromyzon marinus and Salmo trutta and field validation in running water. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 87, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Pilliod, D.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Molecular detection of vertebrates in stream water: A demonstration using Rocky Mountain Tailed Frogs and Idaho Giant Salamanders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichmiller, J.J.; Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. The Relationship between the distribution of common carp and their environmental DNA in a small lake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Secondi, J.; Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Miaud, C.; Audebaud, B. Detection of a global aquatic invasive amphibian, Xenopus laevis, using environmental DNA. Amphib-Reptil. 2016, 37, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Duparc, A.; Pellier-Cuit, S.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C. Persistence of environmental DNA in freshwater ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biggs, J.; Ewald, N.; Valentini, A.; Gaboriaud, C.; Dejean, T.; Griffiths, R.A.; Foster, J.; Wilkinson, J.W.; Arnell, A.; Brotherton, P.; et al. Using eDNA to develop a national citizen science-based monitoring programme for the great crested newt (Trituruscristatus). Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Sepulveda, A.; Ray, A.; Baumgardt, J.; Waits, L.P. Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T.; Doi, H. Using environmental DNA to estimate the distribution of an invasive fish species in ponds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geerts, A.N.; Boets, P.; Heede, S.V.D.; Goethals, P.; Heyden, C.V.D. A search for standardized protocols to detect alien invasive crayfish based on environmental DNA (eDNA): A lab and field evaluation. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 84, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusa, L.; García-Vázquez, E. A simple, rapid method for detecting seven common invasive fish species in Europe from environmental DNA. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Moller, P.R. Detection of a diverse marine fish fauna using environmental DNA from seawater samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. The use of environmental DNA of fishes as an efficient method of determining habitat connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Doi, H.; Kawabata, Z. Estimation of fish biomass using environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinlo, R.; Gleeson, D.; Lintermans, M.; Furlan, E. Methods to maximise recovery of environmental DNA from water samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Walser, J.C.; Mchler, E.; Altermatt, F. Choice of capture and extraction methods affect detection of freshwater biodiversity from environmental DNA. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. Effects of water pH and proteinase K treatment on the yield of environmental DNA from water samples. Limnology 2016, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clusa, L.; Ardura, A.; Fernández, S.; Roca, A.A.; García-Vázquez, E. An extremely sensitive nested PCR-RFLP mitochondrial marker for detection and identification of salmonids in eDNA from water samples. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clusa, L.; Ardura, A.; Gower, F.; Miralles, L.; Tsartsianidou, V.; Zaiko, A.; Garcia-Vazques, E. An easy phylogenetically informative method to trace the globally invasive potamopyrgus mud snail from river’s eDNA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, R.S.; Tang, F.S.; He, H.B.; Wang, J.; Li, J.T.; Li, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lin, L.; Zhang, K. DNA barcoding and molecular phylogenetic relationships of Epinephelus species from western Pacific coastal areas. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 851–860. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.E.; Zhang, X.J.; Kong, L.F.; Li, Q.J. Molecular identification of dried shellfish products sold on the market using DNA barcoding. Ocean Univ. China Ocean. Coast. Sea Res. 2021, 20, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.M.; Tong, D. Introduction of water diversion project in Xi’an Heihe river. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1992, 2, 42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.J.; Jiang, W.; Deng, J.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.X. Analysis of variation in water temperature of rare aquatic wildlife natrue reserve of Heihe river. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2017, 36, 1505–1510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Zhao, H.; Kong, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Q.J. Establishment of analysis method for environment DNA of Batrachuperus from water samples. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2021, 48, 784–789. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModel Test 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minamoto, T.; Naka, T.; Moji, K.; Maruyama, A. Techniques for the practical collection of environmental DNA: Filter selection, preservation, and extraction. Limnology 2016, 17, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.J.; Jiang, W.; Deng, J.; Kong, F.; Zhang, H.X. Measurement and analysis of morphological features of the Batrachuperus taibaiensis. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2017, 36, 622–629. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Strickler, K.M.; Fremier, A.K.; Goldberg, C.S. Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Ye, C.Y.; Jiang, J.P. Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians; Sichuan Publishing House of Science & Technology: Chengdu, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Factors influencing detection of eDNA from a stream-dwelling amphibian. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, S.F.; Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Schwartz, M.K.; Lowe, W.H.; Letcher, B.H.; Whiteley, A.R. Distance, flow and PCR inhibition: eDNA dynamics in two headwater streams. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
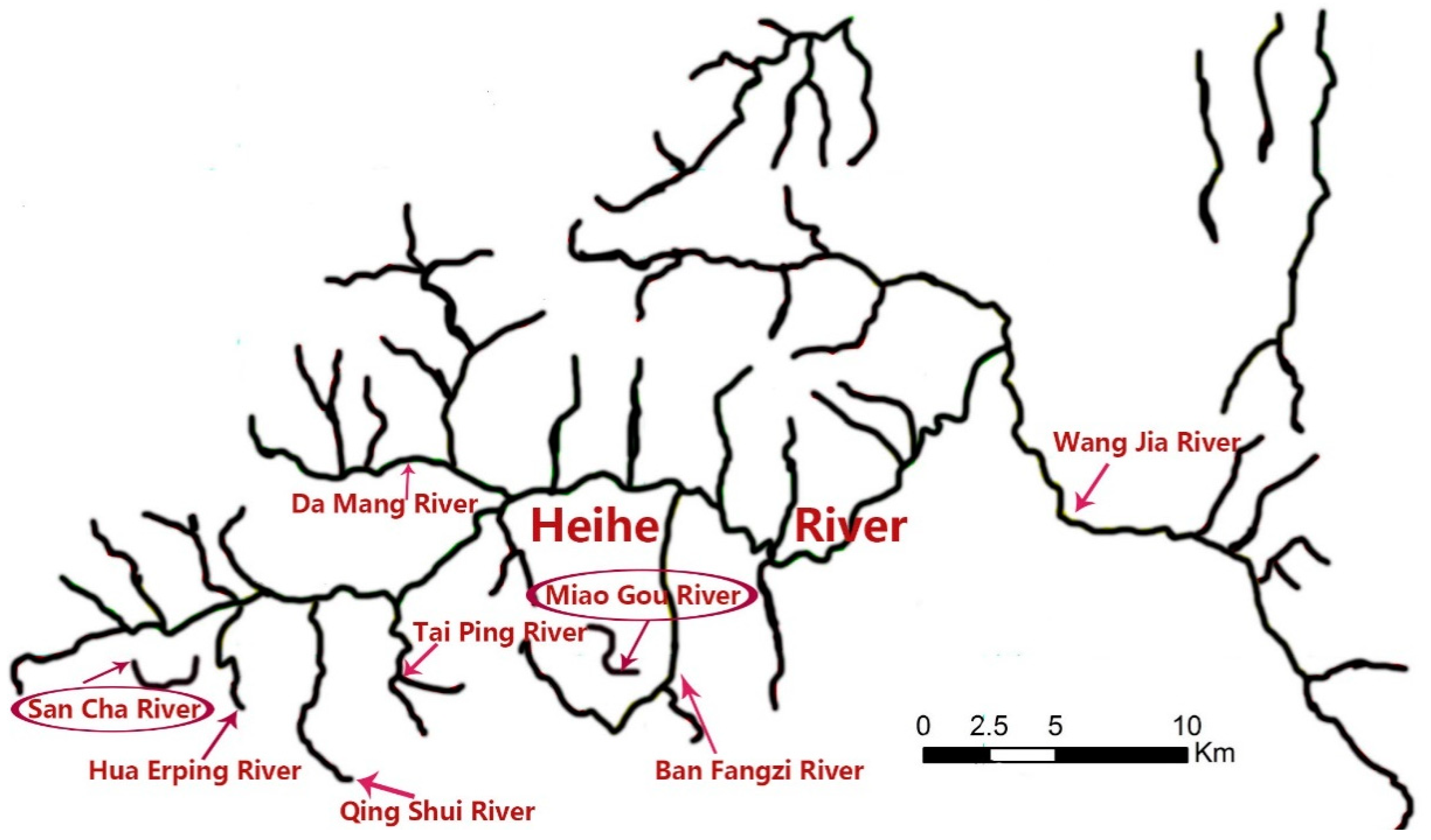




| Collection Time | Location | Site Name | Coordinates | Distance between the Most Upstream Site and the Other Site (m) | Batrachuperus Species Appeared or Not |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 April | San Cha river | 4-1-4 | 33.82884 N, 107.81094 W | 0 | + |
| 4-1-3 | 33.82897 N, 107.80912 W | 50 | + | ||
| 4-1-2 | 33.82917 N, 107.81048 W | 80 | + | ||
| 4-1-1 | 33.82938 N, 107.81062 W | 90 | + | ||
| 4-1-5 | 33.82890 N, 107.81094 W | 140 | − | ||
| 4-1-6 | 33.82918 N, 107.81126 W | 240 | − | ||
| Miao Gou river | 4-2-4 | 33.82928 N, 107.95356 W | 0 | + | |
| 4-2-3 | 33.82919 N, 107.95385 W | 40 | + | ||
| 4-2-2 | 33.82918 N, 107.95362 W | 65 | + | ||
| 4-2-1 | 33.82920 N, 107.95325 W | 80 | + | ||
| 4-2-5 | 33.82859 N, 107.95459 W | 140 | − | ||
| 4-2-6 | 33.82858 N, 107.95496 W | 240 | − | ||
| 1 August | San Cha river | 8-1-3 | 33.82899 N, 107.80912 W | 0 | + |
| 8-1-2 | 33.82837 N, 107.80970 W | 150 | + | ||
| 8-1-1 | 33.82951 N, 107.81059 W | 250 | + | ||
| 8-1-4 | 33.82928 N, 107.81107 W | 300 | − | ||
| 8-1-5 | 33.82932 N, 107.81181 W | 400 | − | ||
| Miao Gou river | 8-2-3 | 33.82969 N, 107.95307 W | 0 | + | |
| 8-2-2 | 33.82942 N, 107.95377 W | 200 | + | ||
| 8-2-1 | 33.82925 N, 107.95342 W | 300 | + | ||
| 8-2-4 | 33.82875 N, 107.95449 W | 360 | − | ||
| 8-2-5 | 33.82852 N, 107.95499 W | 460 | − |
| Primer | Primer Sequence | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size (bp) | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | F:5′-GTAGATAAGGCTACTCTTACTC-3′ R:5′-ATGGGTGGAATGGAACT-3′ | 46 | 160 | This study |
| P2 | F:5′-TTGAGGTGGGTTCTCTGTAGATAAG-3′ R:5′-GGTTGGCGGGTGTAAAA-3′ | 52 | 290 | [33] |
| B. pinchonii | B. tibetanus | B. taibaiensis | Species in Our Study | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. pinchonii | / | 0.0677 ± 0.0204 | 0.0963 ± 0.0266 | 0.1077 ± 0.0313 |
| B. tibetanus | / | / | 0.0928 ± 0.0257 | 0.0947 ± 0.0282 |
| B. taibaiensis | / | / | / | 0.0532 ± 0.0195 |
| B. pinchonii | B. tibetanus | B. taibaiensis | Species in Our Study | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| intraspecific genetic distances | 0.0253 ± 0.009 | 0.0310 ± 0.0109 | 0.0322 ± 0.0113 | 0.0019 ± 0.0018 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Zhao, H.; Kong, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Wang, Q. Detection the eDNA of Batrachuperus taibaiensis from the Zhouzhi Heihe River Using a Nested PCR Method and DNA Barcoding. Animals 2022, 12, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091105
Ma H, Zhang H, Deng J, Zhao H, Kong F, Jiang W, Zhang H, Dong X, Wang Q. Detection the eDNA of Batrachuperus taibaiensis from the Zhouzhi Heihe River Using a Nested PCR Method and DNA Barcoding. Animals. 2022; 12(9):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091105
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hongying, Han Zhang, Jie Deng, Hu Zhao, Fei Kong, Wei Jiang, Hongxing Zhang, Xianggui Dong, and Qijun Wang. 2022. "Detection the eDNA of Batrachuperus taibaiensis from the Zhouzhi Heihe River Using a Nested PCR Method and DNA Barcoding" Animals 12, no. 9: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091105
APA StyleMa, H., Zhang, H., Deng, J., Zhao, H., Kong, F., Jiang, W., Zhang, H., Dong, X., & Wang, Q. (2022). Detection the eDNA of Batrachuperus taibaiensis from the Zhouzhi Heihe River Using a Nested PCR Method and DNA Barcoding. Animals, 12(9), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091105






