Histopathological Study on Collagen in Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. Histological Process
2.3. Trichrome Staining
2.4. Herovici’s Staining
2.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
3. Results
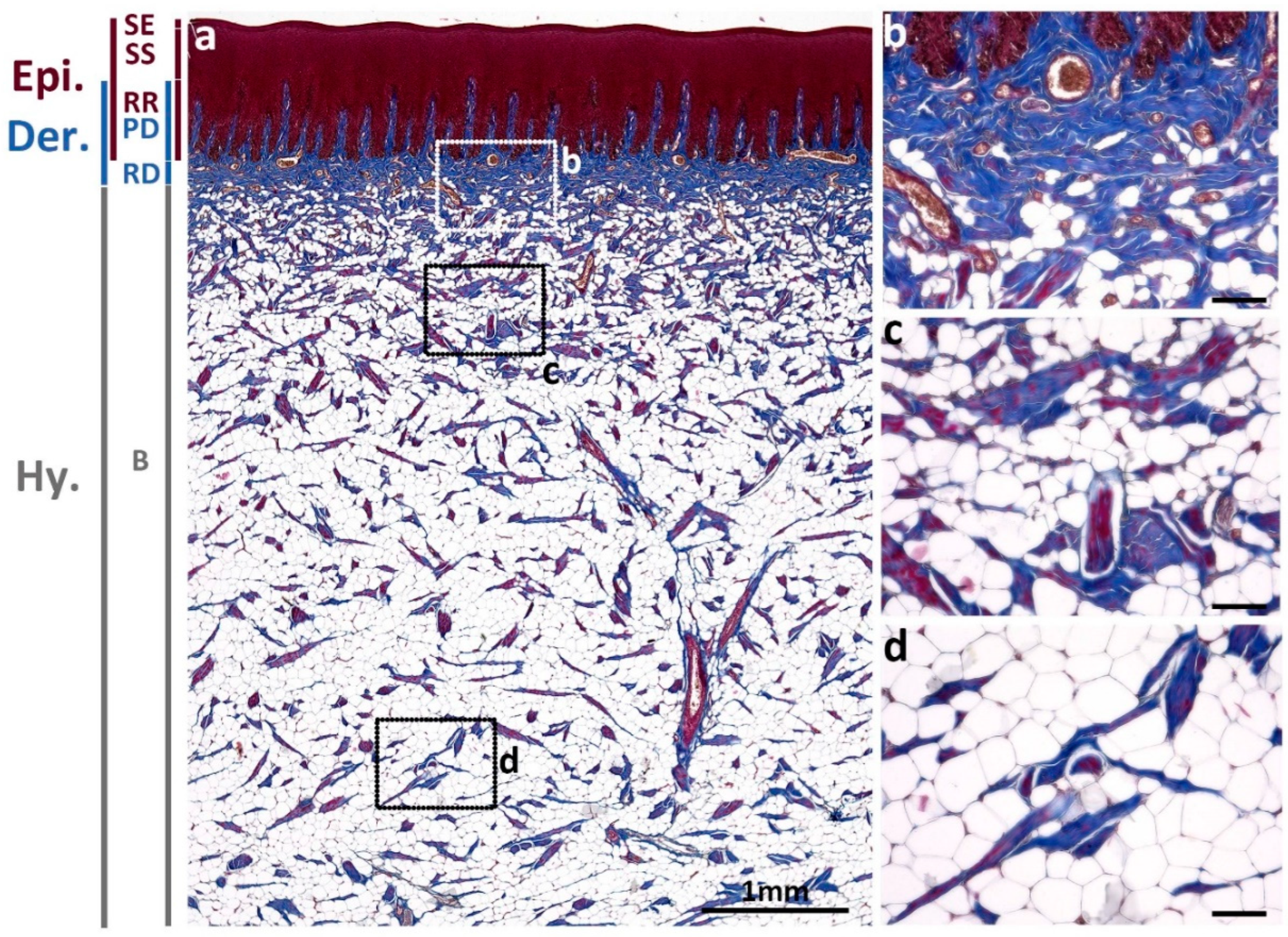
3.1. Normal Skin
3.1.1. Collagens Distribution in Normal Skin
3.1.2. Type I and Type III Collagen Distribution in Normal Skin
3.2. Wounded Skin
3.2.1. Collagen Distribution during Wound Healing in Trichrome Staining
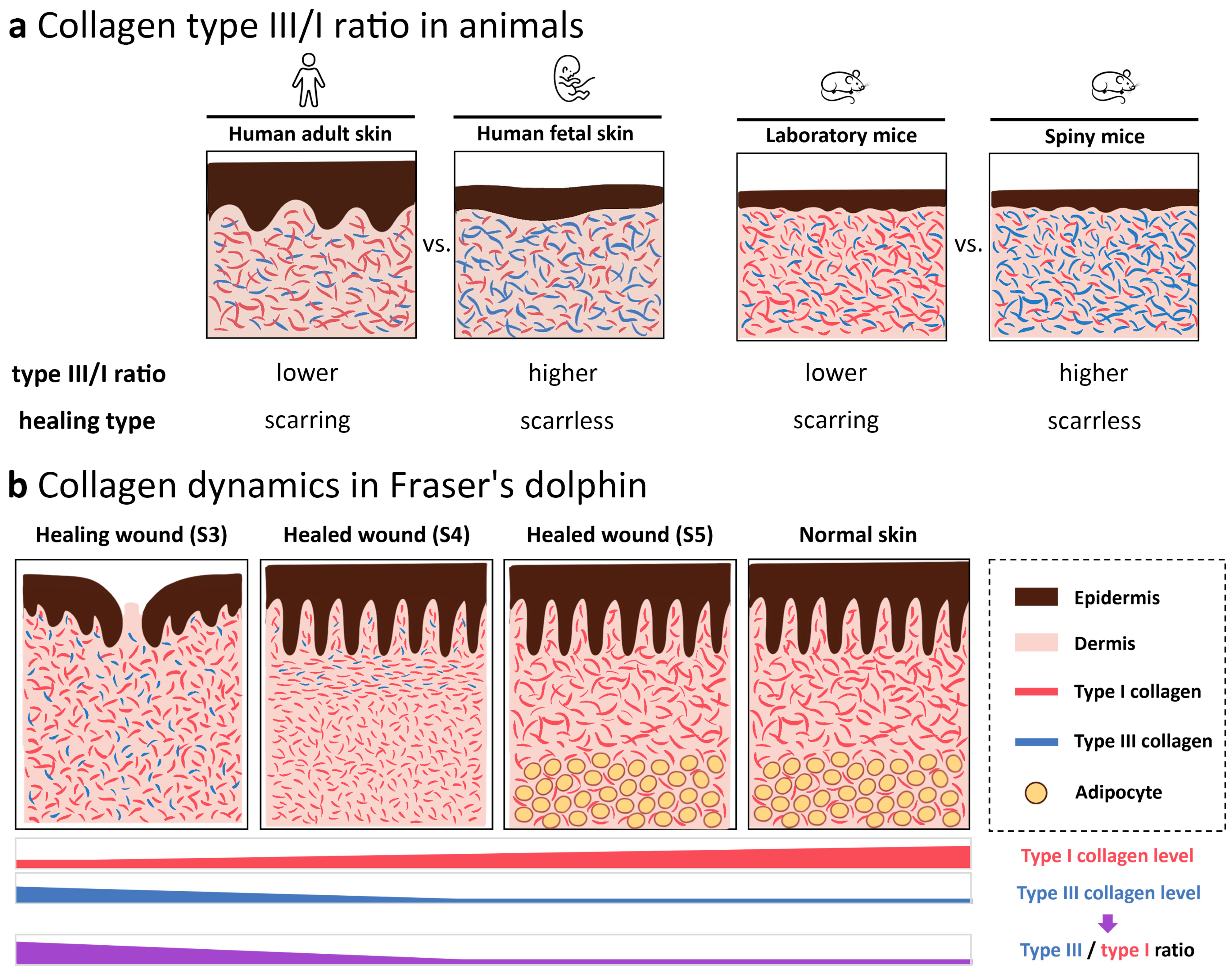
3.2.2. Type I and Type III Collagen Composition Changes during Wound Healing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the Extracellular Matrix in Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Jackson, C.J. Extracellular Matrix Reorganization During Wound Healing and Its Impact on Abnormal Scarring. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.T.; Holbrook, K.A.; Madri, J.A. Collagen Types I, III, and V in Human Embryonic and Fetal Skin. Am. J. Anat. 1986, 175, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, C.R.; Smolenski, K.A.; Duance, V.C.; Light, N.D.; Young, S.; Dyson, M. Type I and III Collagen Content and Fibre Distribution in Normal Human Skin during Ageing. Br. J. Dermatol. 1987, 117, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.R.; Melman, L.; Jenkins, E.; Deeken, C.; Frisella, M.M.; Brunt, L.M.; Eagon, J.C.; Matthews, B.D. Collagen Type I:III Ratio of the Gastroesophageal Junction in Patients with Paraesophageal Hernias. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Suzumura, T.; Nakamura, A.; Tsukiji, S.; Ujihara, Y.; Nakamura, M. Second Harmonic Generation Light Quantifies the Ratio of Type III to Total (I + III) Collagen in a Bundle of Collagen Fiber. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, K.; Shaw, L.E.; Symmank, D.; Weninger, W. The Extracellular Matrix in Skin Inflammation and Infection. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 682414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, V.W. Collagen, Stiffness, and Adhesion: The Evolutionary Basis of Vertebrate Mechanobiology. MBoC 2020, 31, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Byrne, M.; Krane, S.; Jaenisch, R. Type III Collagen Is Crucial for Collagen I Fibrillogenesis and for Normal Cardiovascular Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’hondt, S.; Guillemyn, B.; Syx, D.; Symoens, S.; De Rycke, R.; Vanhoutte, L.; Toussaint, W.; Lambrecht, B.N.; De Paepe, A.; Keene, D.R.; et al. Type III Collagen Affects Dermal and Vascular Collagen Fibrillogenesis and Tissue Integrity in a Mutant Col3a1 Transgenic Mouse Model. Matrix Biol. 2018, 70, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoret, C.L. The Pathophysiology of Wound Repair. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2005, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Rai, V.; K Agrawal, D. Regulation of Collagen I and Collagen III in Tissue Injury and Regeneration. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 7, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, G.; Janis, J.E.; Attinger, C.E. The Basic Science of Wound Healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 12S–34S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew-Steiner, S.S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Collagen in Wound Healing. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H.; Cozzi, B. Regional Anatomy, Development, and Hydrodynamics Including Skin Anatomy. In Atlas of the Anatomy of Dolphins and Whales; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 5–135. ISBN 978-0-12-802446-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lingham-Soliar, T. The Dinosaurian Origin of Feathers: Perspectives from Dolphin (Cetacea) Collagen Fibers. Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, B.; Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H. General Appearance and Hydrodynamics (Including Skin Anatomy). In Anatomy of Dolphins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 21–31. ISBN 978-0-12-407229-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, V.E.; Sokolov, V.E. Mammal Skin; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1982; ISBN 978-0-520-03198-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Dillaman, R.M.; McLellan, W.A.; Pabst, D.A. Structural Fiber Reinforcement of Keel Blubber in Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J. Morphol. 2004, 261, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, D.A. To Bend a Dolphin: Convergence of Force Transmission Designs in Cetaceans and Scombrid Fishes. Am. Zool. 2000, 40, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-Y.; Hughes, M.W.; Liu, T.-Y.; Chuong, C.-M.; Wang, H.-V.; Yang, W.-C. Defining Wound Healing Progression in Cetacean Skin: Characteristics of Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei). Animals 2022, 12, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, A.W.; Kiama, S.G.; Seifert, M.G.; Goheen, J.R.; Palmer, T.M.; Maden, M. Skin Shedding and Tissue Regeneration in African Spiny Mice (Acomys). Nature 2012, 489, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, J.; Varholick, J.A.; Rana, S.; Sunshine, M.D.; Doré, S.; Barbazuk, W.B.; Fuller, D.D.; Maden, M.; Simmons, C.S. Spiny Mouse (Acomys): An Emerging Research Organism for Regenerative Medicine with Applications beyond the Skin. NPJ Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harn, H.I.-C.; Wang, S.-P.; Lai, Y.-C.; Van Handel, B.; Liang, Y.-C.; Tsai, S.; Schiessl, I.M.; Sarkar, A.; Xi, H.; Hughes, M.; et al. Symmetry Breaking of Tissue Mechanics in Wound Induced Hair Follicle Regeneration of Laboratory and Spiny Mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedon, D. Disorders of Collagen. In Weedon’s Skin Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 303–329.e27. ISBN 978-0-7020-3485-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, M.M.W. Fetal Wound Healing. In Textbook on Scar Management; Téot, L., Mustoe, T.A., Middelkoop, E., Gauglitz, G.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–9. ISBN 978-3-030-44765-6. [Google Scholar]
- Teare, J.P.; Greenfield, S.M.; Thompson, R.P.H.; Simpson, J.; Sherman, D.; Bray, G.; Williams, R.; Peters, T.J.; Catterall, A.P.; Murray-Lyon, J.M. Comparison of Serum Procollagen III Peptide Concentrations and PGA Index for Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis. Lancet 1993, 342, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.J.; Karsdal, M.A. Type III Collagen. In Biochemistry of Collagens, Laminins and Elastin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 21–30. ISBN 978-0-12-809847-9. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, W.G. A Polychrome Stainfor Differentiating Precollagen from Collagen. Stain. Technol. 1963, 38, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levame, M.; Meyer, F. Herovici’s picropolychromium. Application to the identification of type I and III collagens. Pathol. Biol. 1987, 35, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watt, F.M.; Fujiwara, H. Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions in Normal and Diseased Skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.J.; Pezzone, M.A.; Brown, B.N.; Badylak, S.F. Quantitative Multispectral Imaging of Herovici’s Polychrome for the Assessment of Collagen Content and Tissue Remodelling. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosset, E.M.; Trombetta-eSilva, J.; Hepfer, G.; Yao, H.; Bradshaw, A.D. SPARC and the N-Propeptide of Collagen I Influence Fibroblast Proliferation and Collagen Assembly in the Periodontal Ligament. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Tang, H.; Hu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tao, R.; Wu, Z. Controlled Release of Chitosan/Heparin Nanoparticle-Delivered VEGF Enhances Regeneration of Decellularized Tissue-Engineered Scaffolds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carwardine, M.; Camm, M.; Robinson, R.; Llobet, T. Handbook of Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises of the World; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-691-20210-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sidgwick, G.P.; Bayat, A. Extracellular Matrix Molecules Implicated in Hypertrophic and Keloid Scarring: Extracellular Matrix Molecules in Raised Scarring. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Observations on the Remarkable (and Mysterious) Wound-Healing Process of the Bottlenose Dolphin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2503–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Animal ID | Sex | Age | Body Length | Carcass Condition | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD20181128 | M | Adult | 250 cm | Freshly dead | Stage 5 wound: 1 |
| TP20190115 | M | Adult | 247 cm | Freshly dead | Stage 3 wound: 1 Stage 4 wound: 8 Stage 5 wound: 5 |
| TT20190326 | M | Sub-adult | 200 cm | Freshly dead | Normal skin: 2 Stage 4 wound: 1 |
| IL20191105 | M | Sub-adult | 221 cm | Freshly dead | Normal skin: 2 Stage 4 wound: 4 Stage 5 wound: 3 |
| PT20201109 | M | Sub-adult | 189 cm | Freshly dead | Normal skin: 2 Stage 3 wound: 1 |
| HL20201112 | F | Calf | 122 cm | Freshly dead | Stage 3 wound: 1 |
| Staining on Normal Skin | Type I Collagen | Type III Collagen |
|---|---|---|
| Herovici’s staining | +high amount (fuchsia to red) | −low amount (no blue) |
| IHC staining | +(in the whole dermis) | −(barely seen) |
| Wounded Skin Tissue | Granulation Tissue | Reticular Dermis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 3 Wound | Upper/Middle Layer | Bottom Layer | Adjacent Area |
| Herovici’s staining | purple + blue | purple/fuchsia | fuchsia to red |
| IHC staining type I | + | ++ | +++ |
| IHC staining type III | + | + | + |
| Healed Wound | Immature Healed (Stage 4) | Mature Healed (Stage 5) | Unwounded Skin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Herovici’s staining | purple/fuchsia | fuchsia to red | fuchsia to red |
| Collagen type | type I+ type III | mainly type I | type I |
| Collagen bundle | thin | thin + thick (main) | thick |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.-Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Wang, H.-V.; Yang, W.-C. Histopathological Study on Collagen in Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei). Animals 2023, 13, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101681
Su C-Y, Liu T-Y, Wang H-V, Yang W-C. Histopathological Study on Collagen in Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei). Animals. 2023; 13(10):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101681
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chen-Yi, Tzu-Yu Liu, Hao-Ven Wang, and Wei-Cheng Yang. 2023. "Histopathological Study on Collagen in Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei)" Animals 13, no. 10: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101681
APA StyleSu, C.-Y., Liu, T.-Y., Wang, H.-V., & Yang, W.-C. (2023). Histopathological Study on Collagen in Full-Thickness Wound Healing in Fraser’s Dolphins (Lagenodelphis hosei). Animals, 13(10), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101681





