Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Mutational Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the Sox Gene Family in Buffalo
2.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of Buffalo Sox Genes
2.3. Gene Structure, Motif Pattern, and Conserved Domain Analysis
2.4. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Comparative Amino Acid Analysis
2.6. Synteny Analysis and Chromosome Localization
2.7. Selection Analysis of the Sox Gene Family
2.8. Analysis of Recombination Breakpoints in the Sox Gene Family
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of Buffalo Sox Genes
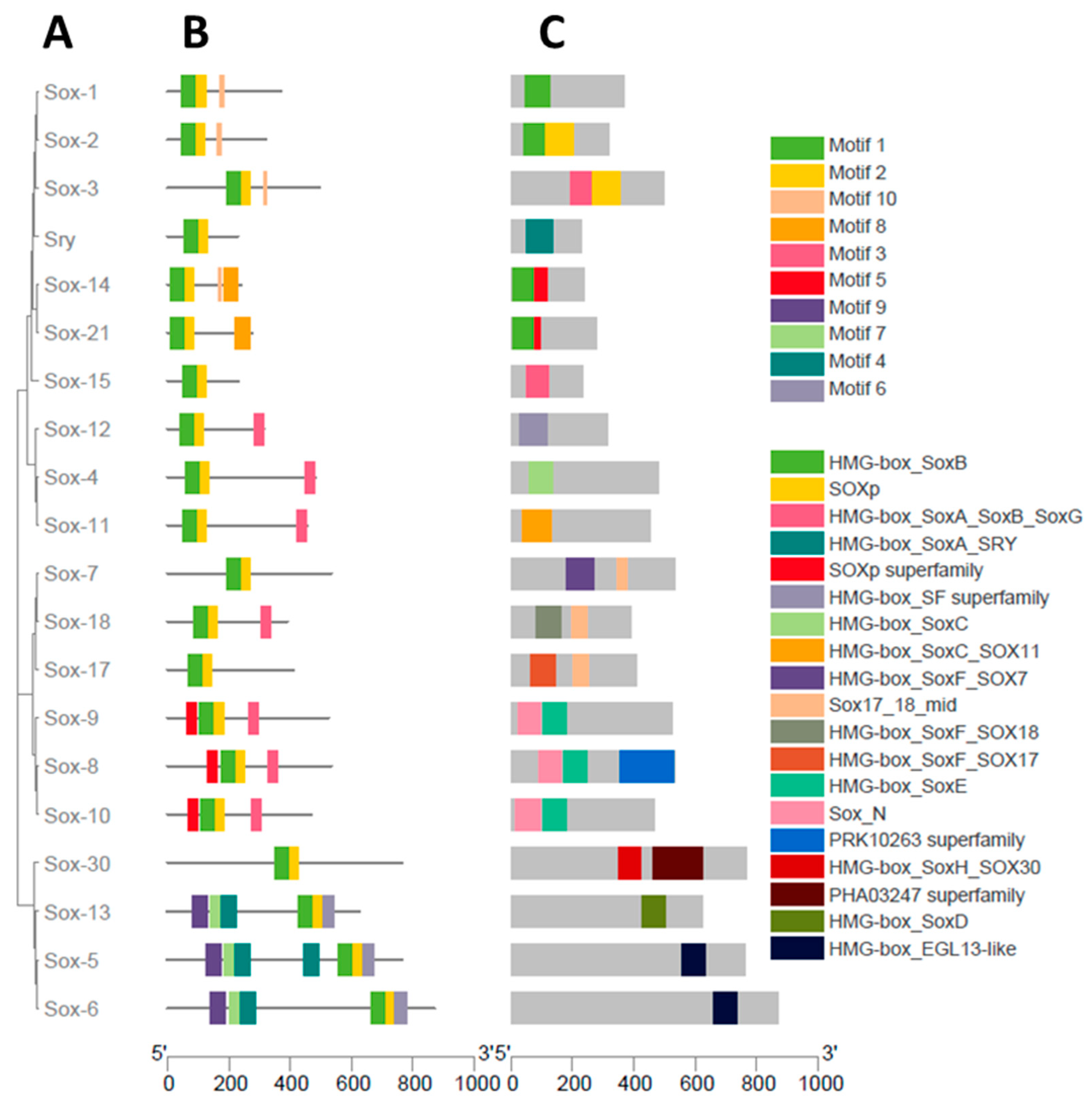
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Sox Gene Family
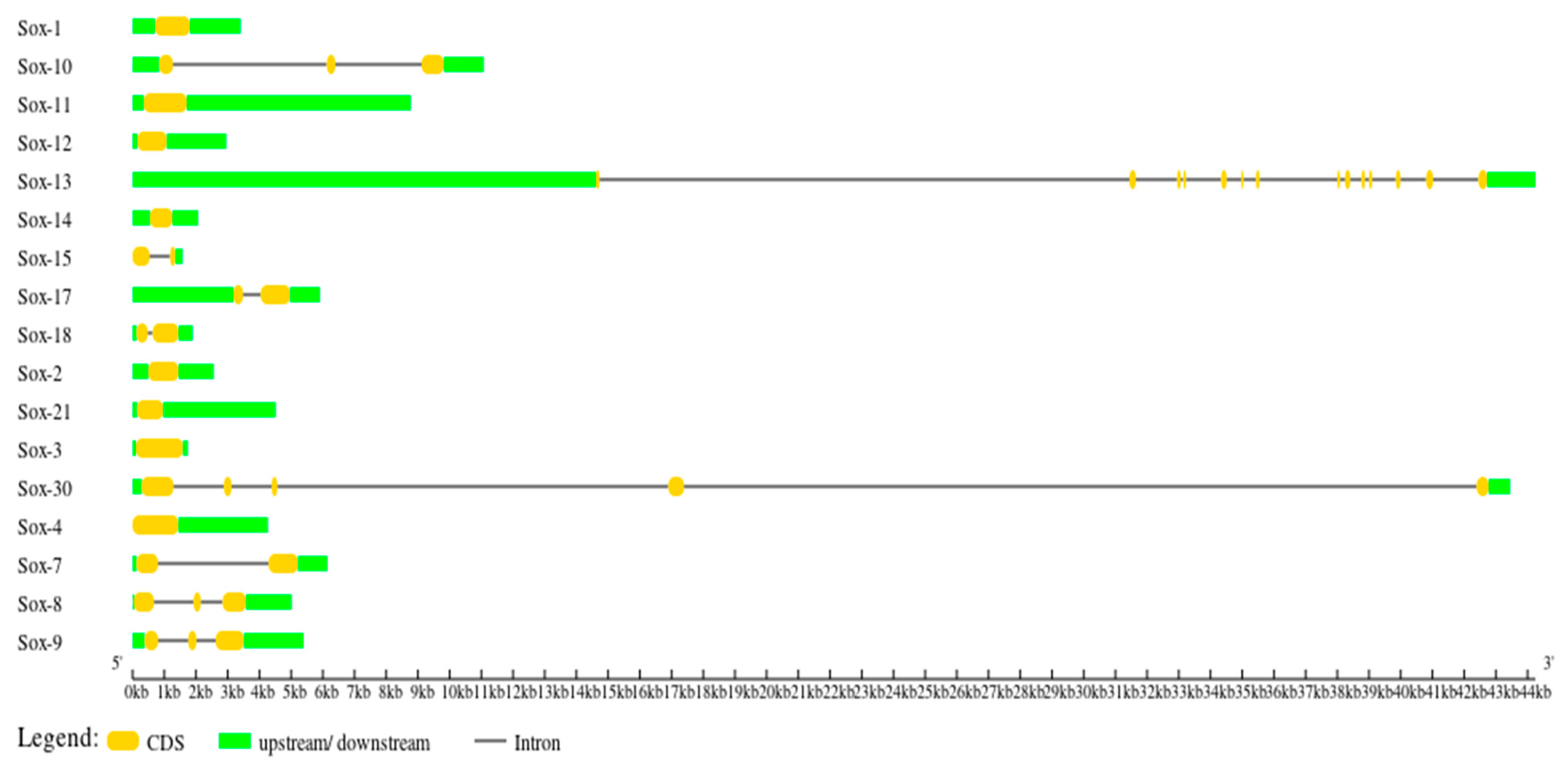
3.3. Gene Structure Characterization of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family
3.4. Physiochemical Attributes of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family
3.5. Comparative Amino Acid Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family
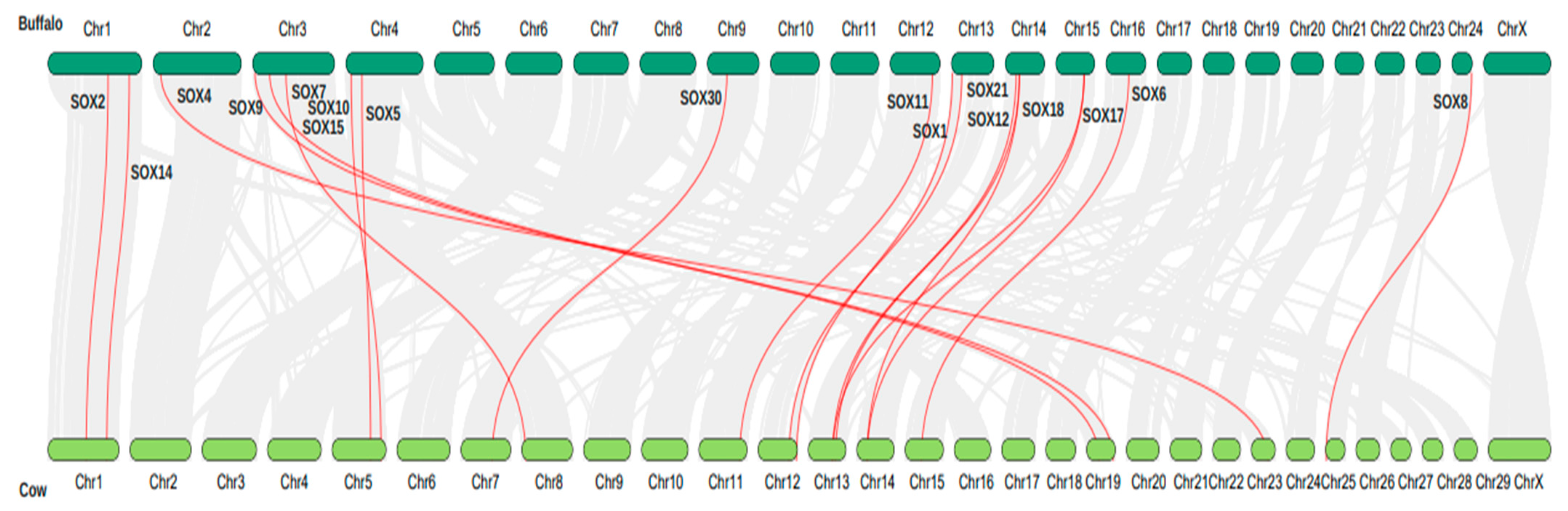
3.6. Synteny Analysis and Chromosome Localization of the Sox Gene Family in Buffalo
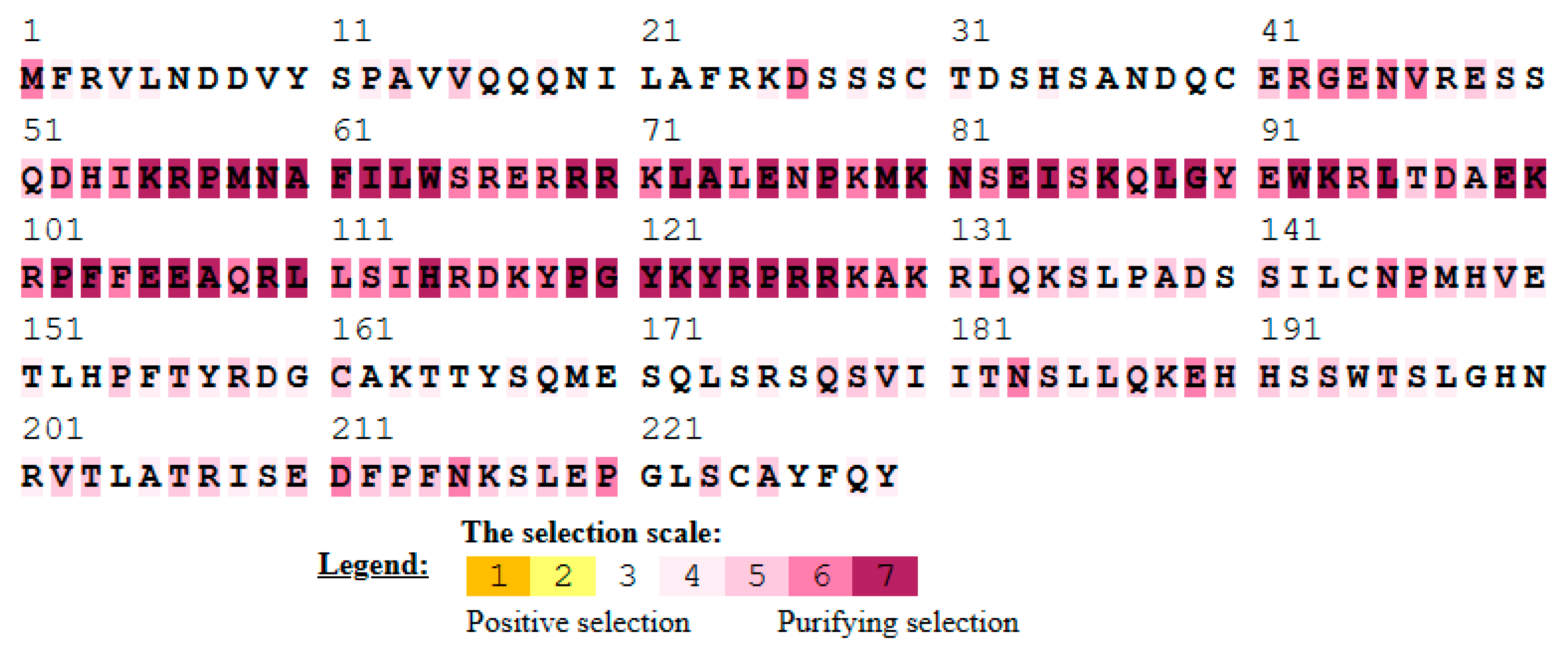
3.7. Single Amino Acid Site Evolution
3.8. Recombination Analysis Using Genetic Algorithm Recombination Detection (GARD)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanghuayphrai, N.; Nakavisut, S.; Dongpaletum, C.; Phothikanit, G.; Supanun, S. Genetic Parameters and Trends for Weaning Weight and Calving Interval of Department of Livestock Development Swamp Buffalo. Editor. Board 2013, 32, 717. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Duan, A.; Liang, S.; Ma, X.; Deng, T. Genomic Identification, Evolution, and Expression Analysis of Collagen Genes Family in Water Buffalo during Lactation. Genes 2020, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rexroad, C.; Vallet, J.; Matukumalli, L.K.; Reecy, J.; Bickhart, D.; Blackburn, H.; Boggess, M.; Cheng, H.; Clutter, A.; Cockett, N. Genome to Phenome: Improving Animal Health, Production, and Well-Being–a New USDA Blueprint for Animal Genome Research 2018–2027. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, C.S.; Palanisamy, A.; Satheshkumar, S.; Gomathy, V.S.; Raj, G.D.; Thangavel, A. Sox-2 Gene Expression Pattern in Stem Cells Derived from Different Stages of in Vitro Produced Buffalo (Bubalus Bubalis) Embryos. Buffalo Bull. 2013, 32, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Hou, C.-C.; She, Z.-Y.; Yang, W.-X. The SOX Gene Family: Function and Regulation in Testis Determination and Male Fertility Maintenance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Adamski, M.; Bergum, B.; Guder, C.; Jordal, S.; Leininger, S.; Zwafink, C.; Rapp, H.T.; Adamska, M. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Sox Family in the Calcareous Sponge Sycon Ciliatum: Multiple Genes with Unique Expression Patterns. Evodevo 2012, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Bao, Z. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of the SOX Gene Family in a Bivalve Mollusc Patinopecten Yessoensis. Gene 2017, 627, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wetering, M.; Oosterwegel, M.; van Norren, K.; Clevers, H. Sox-4, an Sry-like HMG Box Protein, Is a Transcriptional Activator in Lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3847–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, M.H.; Burley, S.K. Architectural Transcription Factors: Proteins That-Remodel DNA. Cell 1997, 88, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gubbay, J.; Collignon, J.; Koopman, P.; Capel, B.; Economou, A.; Münsterberg, A.; Vivian, N.; Goodfellow, P.; Lovell-Badge, R. A Gene Mapping to the Sex-Determining Region of the Mouse Y Chromosome Is a Member of a Novel Family of Embryonically Expressed Genes. Nature 1990, 346, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, P.; Schepers, G.; Brenner, S.; Venkatesh, B. Origin and Diversity of the SOX Transcription Factor Gene Family: Genome-Wide Analysis in Fugu Rubripes. Gene 2004, 328, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Pan, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhong, L.; Shao, J.; Sun, M.; Jiang, H. Genome-Wide Identification, Phylogeny and Expressional Profile of the Sox Gene Family in Channel Catfish (Ictalurus Punctatus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2018, 28, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Wan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile of the Sox Gene Family in Different Tissues and during Embryogenesis in the Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei). Gene 2020, 763, 144956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Mano, H.; Koopman, P. Regulation of Amh during Sex Determination in Chickens: Sox Gene Expression in Male and Female Gonads. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. C 2005, 62, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Cheng, D.; Li, D.; Meng, M.; Peng, L.; Tang, L.; Pan, M.; Xiang, Z.; Xia, Q.; Lu, C. Identification and Characterization of Sox Genes in the Silkworm, Bombyx Mori. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, G.E.; Teasdale, R.D.; Koopman, P. Twenty Pairs of Sox: Extent, Homology, and Nomenclature of the Mouse and Human Sox Transcription Factor Gene Families. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crémazy, F.; Berta, P.; Girard, F. Genome-Wide Analysis of Sox Genes in Drosophila Melanogaster. Mech. Dev. 2001, 109, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magie, C.R.; Pang, K.; Martindale, M.Q. Genomic Inventory and Expression of Sox and Fox Genes in the Cnidarian Nematostella Vectensis. Dev. Genes Evol. 2005, 215, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Ashby, M.; Materna, S.C.; Brown, C.T.; Chen, L.; Cameron, R.A.; Davidson, E.H. Gene Families Encoding Transcription Factors Expressed in Early Development of Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Dev. Biol. 2006, 300, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Yang, C.; Tao, W.; Wang, D. Genome-Wide Identification and Transcriptome-Based Expression Profiling of the Sox Gene Family in the Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafar, I.; Iftikhar, R.; Ahmad, S.U.; Rather, M.A. Genome Wide Identification, Phylogeny, and Synteny Analysis of Sox Gene Family in Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio). Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 30, e00607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.; Wheatley, S.C.; Andrews, J.E.; Sinclair, A.H.; Koopman, P. A Male-Specific Role for SOX9 in Vertebrate Sex Determination. Development 1996, 122, 2813–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhukhar, V.G. SRY and SOX9: The Main Genetic Factors of Mammalian Sex Determination. Tsitologiia 2012, 54, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, M.; Källström, M.; Muhr, J. Sox21 Promotes the Progression of Vertebrate Neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.; Hargrave, M.R.; Christiansen, J.; Cooper, L.; Kun, J.; Evans, T.; Gangadharan, U.; Greenfield, A.; Koopman, P. The Sry-Related Gene Sox9 Is Expressed during Chondrogenesis in Mouse Embryos. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, R.; Andersson, E.; Betnér, E.; Bijl, S.; Fowler, W.; Höök, L.; Leyhr, J.; Mannelqvist, A.; Panara, V.; Smith, K. Embryonic Expression Patterns and Phylogenetic Analysis of Panarthropod Sox Genes: Insight into Nervous System Development, Segmentation and Gonadogenesis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Sakai, D.; Osumi, N.; Wada, H.; Wakamatsu, Y. Sox Genes Regulate Type 2 Collagen Expression in Avian Neural Crest Cells. Dev. Growth Differ. 2006, 48, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Goodyer, C.G.; Wang, R. The Emerging Role of SOX Transcription Factors in Pancreatic Endocrine Cell Development and Function. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A. The Pfam Protein Families Database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple Sequence Alignment Using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2003, 1, 2.3.1–2.3.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for Motif Discovery and Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Anderson, J.B.; DeWeese-Scott, C.; Fedorova, N.D.; Geer, L.Y.; He, S.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Lanczycki, C.J. CDD: A Curated Entrez Database of Conserved Domain Alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; De Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E. ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. Proteom. Protoc. Handb. 2005, 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, T.; Frishman, D. PROMPT: A Protein Mapping and Comparison Tool. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, N.-L.; Kumar, P.; Hu, J.; Henikoff, S.; Schneider, G.; Ng, P.C. SIFT Web Server: Predicting Effects of Amino Acid Substitutions on Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W452–W457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN Web Server: A Tool to Predict the Functional Effect of Amino Acid Substitutions and Indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doss, C.G.P.; Rajith, B.; Garwasis, N.; Mathew, P.R.; Raju, A.S.; Apoorva, K.; William, D.; Sadhana, N.R.; Himani, T.; Dike, I.P. Screening of Mutations Affecting Protein Stability and Dynamics of FGFR1—A Simulation Analysis. Appl. Transl. Genom. 2012, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P. PhD-SNPg: A Webserver and Lightweight Tool for Scoring Single Nucleotide Variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W247–W252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Vihinen, M. Performance of Protein Stability Predictors. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. SNAP: Predict Effect of Non-Synonymous Polymorphisms on Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bendl, J.; Musil, M.; Štourač, J.; Zendulka, J.; Damborský, J.; Brezovský, J. PredictSNP2: A Unified Platform for Accurately Evaluating SNP Effects by Exploiting the Different Characteristics of Variants in Distinct Genomic Regions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capriotti, E.; Altman, R.B.; Bromberg, Y. Collective Judgment Predicts Disease-Associated Single Nucleotide Variants. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A Toolkit for Detection and Evolutionary Analysis of Gene Synteny and Collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Stern, A.; Mayrose, I.; Bacharach, E.; Pupko, T. Selecton: A Server for Detecting Evolutionary Forces at a Single Amino-Acid Site. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2101–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Posada, D.; Gravenor, M.B.; Woelk, C.H.; Frost, S.D.W. Automated Phylogenetic Detection of Recombination Using a Genetic Algorithm. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugiura, N. Further Analysts of the Data by Akaike’s Information Criterion and the Finite Corrections: Further Analysts of the Data by Akaike’s. Commun. Stat. Methods 1978, 7, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, S.; Nadeem, A.; Javed, M.; Hassan, F.; Luo, X.; Khalid, R.B.; Liu, Q. Genomic Identification, Evolution and Sequence Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene Family in Buffalo. Genes 2020, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hassan, F.; Luo, Y.; Fatima, I.; Ahmed, I.; Ihsan, A.; Safdar, W.; Liu, Q.; ur Rehman, S. Comparative Genomic Characterization of Buffalo Fibronectin Type III Domain Proteins: Exploring the Novel Role of FNDC5/Irisin as a Ligand of Gonadal Receptors. Biology 2021, 10, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Hassan, F.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Characterization of Buffalo Genetic Resources: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Animals 2021, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Feng, T.; Wu, S.; Luo, X.; Lei, A.; Luobu, B.; Hassan, F.; Liu, Q. Comparative Genomics, Evolutionary and Gene Regulatory Regions Analysis of Casein Gene Family in Bubalus bubalis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 662609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Shafique, L.; Yousuf, M.R.; Liu, Q.; Ahmed, J.Z.; Riaz, H. Spectrophotometric Calibration and Comparison of Different Semen Evaluation Methods in Nili-Ravi Buffalo Bulls. Pak. Vet. J 2019, 39, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Nadeem, A.; Li, Z.; Javed, M.; Liu, Q.; Azhar, J.; Rehman, M.S.; Cui, K.; ur Rehman, S. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Energy Homeostasis of Dairy Animals: Exploiting Their Modulation through Nutrigenomic Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiggia, A.; Whitfield, S.; Goodfellow, P.N.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Bianchi, M.E. Evolutionary Conservation in the DNA-Binding and -Bending Properties of HMG-Boxes from SRY Proteins of Primates. Gene 1995, 154, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Han, J.; Xiao, K.; Liu, X.; Tan, C.; Zeng, Q.; Du, H. Genome-wide Analysis of the Chinese Sturgeon Sox Gene Family: Identification, Characterisation and Expression Profiles of Different Tissues. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 96, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.V.B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between Stability of a Protein and Its Dipeptide Composition: A Novel Approach for Predicting in Vivo Stability of a Protein from Its Primary Sequence. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsushi, I. Thermostability and Aliphatic Index of Globular Proteins. J. Biochem. 1980, 88, 1895–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.K.; Sen, M.K. An In-Silico Characterization of Sry-Related HMG Box C (SOXC) in Humans and Mouse. Meta Gene 2019, 19, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A Simple Method for Displaying the Hydropathic Character of a Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magadum, S.; Banerjee, U.; Murugan, P.; Gangapur, D.; Ravikesavan, R. Gene Duplication as a Major Force in Evolution. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, K.J.; Farslow, J.C.; Fitzpatrick, K.A.; Lynch, M.; Katju, V.; Bergthorsson, U. High Spontaneous Rate of Gene Duplication in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurst, L.D. The Ka/Ks Ratio: Diagnosing the Form of Sequence Evolution. Trends Genet. TIG 2002, 18, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, H.; Xiang, Y. Comparative Genomic Analysis of the WRKY III Gene Family in Populus, Grape, Arabidopsis and Rice. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consortium, M.G.S.; Waterston, R.H.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Birney, E.; Rogers, J.; Abril, J.F. Initial Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of the Mouse Genome. Nature 2002, 420, 520–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Posada, D.; Gravenor, M.B.; Woelk, C.H.; Frost, S.D.W. GARD: A Genetic Algorithm for Recombination Detection. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 3096–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z. Inference of Selection from Multiple Species Alignments. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, M.; Sánchez-Villagra, M.R.; Salzburger, W.; Matschiner, M. Bayesian Divergence-Time Estimation with Genome-Wide Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Data of Sea Catfishes (Ariidae) Supports Miocene Closure of the Panamanian Isthmus. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carruthers, T.; Sun, M.; Baker, W.J.; Smith, S.A.; de Vos, J.M.; Eiserhardt, W.L. The Implications of Incongruence between Gene Tree and Species Tree Topologies for Divergence Time Estimation. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 1124–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Dubchak, I.; Shon, J.; Park, J. Comparative Genomics Approaches to Study Organism Similarities and Differences. J. Biomed. Inform. 2002, 35, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Koonin, E.V. Comparative Genome Analysis. Methods Biochem. Anal. 2001, 43, 359–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sivashankari, S.; Shanmughavel, P. Comparative Genomics-a Perspective. Bioinformation 2007, 1, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Bickhart, D.M.; Ramunno, L.; Iamartino, D.; Williams, J.L.; Liu, G.E. Genomic Structural Differences between Cattle and River Buffalo Identified through Comparative Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis. Data Br. 2018, 19, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Talenti, A.; Young, R.; Jayaraman, S.; Callaby, R.; Jadhav, S.K.; Dhanikachalam, V.; Manikandan, M.; Biswa, B.B.; Low, W.Y. Whole Genome Analysis of Water Buffalo and Global Cattle Breeds Highlights Convergent Signatures of Domestication. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu Santos, D.J.; Ferreira de Camargo, G.M.; Cardoso, D.F.; Buzanskas, M.E.; Aspilcueta-Borquis, R.R.; Hurtado-Lugo, N.A.; de Araújo Neto, F.R.; Galvão de Albuquerque, L.; Ma, L.; Tonhati, H. Linkage Disequilibrium-Based Inference of Genome Homology and Chromosomal Rearrangements between Species. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 2327–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, R.A.; Dessailly, B.H.; Orengo, C.A. Residue Mutations and Their Impact on Protein Structure and Function: Detecting Beneficial and Pathogenic Changes. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, L. Genetic Mutation. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Hartatik, T.; Bintara, S.; Ismaya, I.; Panjono, P.; Widyobroto, B.P.; Agus, A.; Budisatria, I.G.S.; Leroy, P. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of Sex Determining Region-Y Gene Coding Sequences in Belgian Blue Bull and Wagyu Bull Crossbred Cattle. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 478, p. 12020. [Google Scholar]
- Berta, P.; Hawkins, J.B.; Sinclair, A.H.; Taylor, A.; Griffiths, B.L.; Goodfellow, P.N.; Fellous, M. Genetic Evidence Equating SRY and the Testis-Determining Factor. Nature 1990, 348, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, E.J.; Cotinot, C.Y. Comparative HMG-Box Sequences of the SRY Gene between Sheep, Cattle and Goats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Shi, H.; Zhou, R.; Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Kudo, T.; Sutou, S. Characterization of Bovidae Sex-Determining Gene SRY. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2001, 33, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, C.A.I.; ZHANG, T.D.M. Unique Variations of SRY Gene Result in Distinct Patrilineal Phylogeny of Capra Hircus and Other Domestic Bovidae. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2013, 30, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Parma, P.; Feligini, M.; Greppi, G.; Enne, G. The Complete Coding Region Sequence of River Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) SRY Gene. DNA Seq. 2004, 15, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Hanif, Q.; Chen, H.; Lei, C.; Dang, R. Copy Number Variations of Four Y-Linked Genes in Swamp Buffaloes. Animals 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, L.B.; Scarciolla, O.; Vanni, G.F.; Nardone, A.M.; Frajese, G.; Novelli, G.; Stuppia, L. Identification of a Novel Mutation in the SRY Gene in a 46, XY Female Patient. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 49, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Yu, C.; Lanzano, P.; Heller, D.; Thomas, L.; Warburton, D.; Kitajewski, J.; Stadtmauer, L. A de Novo Mutation (Gln2Stop) at the 5’ End of the SRY Gene Leads to Sex Reversal with Partial Ovarian Function. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.T.; Ren, Z.R.; Zhang, M.L.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, F.Y.; Huang, S.Z. A New de Novo Mutation (A113T) in HMG Box of the SRY Gene Leads to XY Gonadal Dysgenesis. J. Med. Genet. 1993, 30, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domenice, S.; Yumie Nishi, M.; Correia Billerbeck, A.E.; Latronico, A.C.; Aparecida Medeiros, M.; Russell, A.J.; Vass, K.; Marino Carvalho, F.; Costa Frade, E.M.; Prado Arnhold, I.J. A Novel Missense Mutation (S18N) in the 5′ Non-HMG Box Region of the SRY Gene in a Patient with Partial Gonadal Dysgenesis and His Normal Male Relatives. Hum. Genet. 1998, 102, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonova, S.; Robeva, R.; Sirakov, M.; Mainhard, K.; Tomova, A.; Ledig, S.; Kumanov, P.; Savov, A. A Novel SRY Gene Mutation p. F109L in a 46, XY Female with Complete Gonadal Dysgenesis. Sex. Dev. 2015, 9, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xue, M.; Zhao, M.; He, F.; Li, C.; Li, X. Identification of a Novel Mutation (Ala66Thr) of SRY Gene Causes XY Pure Gonadal Dysgenesis by Affecting DNA Binding Activity and Nuclear Import. Gene 2018, 651, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, J.L.; Soardi, F.C.; Bernardi, R.D.; Oliveira, L.E.C.; Benedetti, C.E.; Guerra-Junior, G.; Maciel-Guerra, A.T.; de Mello, M.P. The Novel p. E89K Mutation in the SRY Gene Inhibits DNA Binding and Causes the 46, XY Disorder of Sex Development. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2011, 44, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filges, I.; Kunz, C.; Miny, P.; Boesch, N.; Szinnai, G.; Wenzel, F.; Tschudin, S.; Zumsteg, U.; Heinimann, K. A Novel Missense Mutation in the High Mobility Group Domain of SRY Drastically Reduces Its DNA-Binding Capacity and Causes Paternally Transmitted 46,XY Complete Gonadal Dysgenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 851–855.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helszer, Z.; Dmochowska, A.; Szemraj, J.; Słowikowska-Hilczer, J.; Wieczorek, M.; Jędrzejczyk, S.; Kałużewski, B. A Novel Mutation (c. 341A>G) in the SRY Gene in a 46,XY Female Patient with Gonadal Dysgenesis. Gene 2013, 526, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, J.R.; Taylor, A.; Berta, P.; Levilliers, J.; Van der Auwera, B.; Goodfellow, P.N. Mutational Analysis of SRY: Nonsense and Missense Mutations in XY Sex Reversal. Hum. Genet. 1992, 88, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnoi, M.-F.; Dumargne, M.-C.; Rojo, S.; Witchel, S.F.; Duncan, A.J.; Eozenou, C.; Bignon-Topalovic, J.; Yatsenko, S.A.; Rajkovic, A.; Reyes-Mugica, M. Mutations Involving the SRY-Related Gene SOX8 Are Associated with a Spectrum of Human Reproductive Anomalies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamb, A.N.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Neill, N.J.; Talkowski, M.E.; Blumenthal, I.; Girirajan, S.; Keelean-Fuller, D.; Fan, Z.; Pouncey, J.; Stevens, C. Haploinsufficiency of SOX5 at 12p12. 1 Is Associated with Developmental Delays with Prominent Language Delay, Behavior Problems, and Mild Dysmorphic Features. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Hooli, B.; Mullin, K.; Tate, R.E.; Bubnys, A.; Kirchner, R.; Chapman, B.; Hofmann, O.; Hide, W.; Tanzi, R.E. Silencing of the Drosophila Ortholog of SOX5 Leads to Abnormal Neuronal Development and Behavioral Impairment. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daoud, H.; Valdmanis, P.N.; Gros-Louis, F.; Belzil, V.; Spiegelman, D.; Henrion, E.; Diallo, O.; Desjarlais, A.; Gauthier, J.; Camu, W. Resequencing of 29 Candidate Genes in Patients with Familial and Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Y-Linked SNP in SRY Gene Differentiates Chinese Indigenous Swamp Buffalo and Introduced River Buffalo. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 1240–1244. [Google Scholar]



| Motif | Protein Sequence | Length (No. of Amino Acids) | Pfam Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEME-1 | IKRPMNAFMVWAKDZRRKLAQZNPDMHNAEISKRLGKEWKLLSESEKRPF | 50 | HMG |
| MEME-2 | IEEAERLRAQHMKDYPDYKYRPRRKKKTL | 29 | - |
| MEME-3 | HFDFPDYDTPELSEEIAGBWETFDVAELDFYL | 32 | - |
| MEME-4 | QKKLAASQIEKQRQQMELARQQQEQIARQQQQLLQQQHKINLLQQQIQQV | 50 | - |
| MEME-5 | DDKFPVCIREAVSQVLKGYDWTLVPMPVRVNG | 32 | SoxN |
| MEME-6 | VDGKKLRIGEYKALMRSRRQEMRQYFTVGQQPQIPIAT | 38 | - |
| MEME-7 | EIKGTPESLAEKERQLLVMINQLTSLREQLLAAHDE | 36 | - |
| MEME-8 | HTHSHPSPGNPGYMIPCNCSAWPAPGLQPPLAYILFPGMGKPGJDPY | 47 | - |
| MEME-9 | VTFGTPERRKGSLADVVDTLKQKKLEELIKNEPEESPCIEKLLSKDWKEK | 50 | - |
| MEME-10 | HWEQPVYTTLTR | 12 | - |
| Sr. No. | Gene | Chr | Exon | AA | MW | pI | II | AI | (GRAVY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sox1 | 13 | 1 | 370 | 37,471.04 | 9.7 | 51.56 | 56.51 | −0.462 |
| 2 | Sox2 | 1 | 1 | 321 | 34,538.03 | 9.74 | 59.66 | 48.1 | −0.738 |
| 3 | Sox3 | X | 1 | 497 | 49,942.45 | 9.9 | 71.26 | 60.42 | −0.371 |
| 4 | Sox4 | 2 | 2 | 482 | 47,842.16 | 7.2 | 58.7 | 54.32 | −0.473 |
| 5 | Sox5 | 4 | 27 | 764 | 84,193.73 | 6.15 | 63.43 | 67.98 | −0.758 |
| 6 | Sox6 | 16 | 27 | 870 | 96,885.84 | 7.08 | 62.81 | 63.4 | −0.839 |
| 7 | Sox7 | 3 | 2 | 534 | 57,021.97 | 9.53 | 62.66 | 55.47 | −0.822 |
| 8 | Sox8 | 24 | 3 | 534 | 56,084.84 | 7.42 | 59.58 | 52.62 | −0.687 |
| 9 | Sox9 | 3 | 3 | 525 | 57,358.68 | 6.31 | 81.38 | 46.7 | −0.999 |
| 10 | Sox10 | 4 | 4 | 469 | 50,020.2 | 6.19 | 58.52 | 53.3 | −0.822 |
| 11 | Sox11 | 12 | 1 | 455 | 47,465.32 | 4.95 | 66.32 | 57.65 | −0.653 |
| 12 | Sox12 | 14 | 1 | 314 | 33,997.76 | 5.14 | 67.74 | 49.87 | −0.982 |
| 13 | Sox13 | 5 | 17 | 666 | 73,923.77 | 6.35 | 70.28 | 71.37 | −0.729 |
| 14 | Sox14 | 1 | 1 | 240 | 26,485.39 | 9.68 | 53.51 | 63.17 | −0.585 |
| 15 | Sox15 | 3 | 2 | 233 | 25,180.29 | 9.85 | 71.44 | 50.73 | −0.855 |
| 16 | Sox17 | 15 | 2 | 410 | 43,036.69 | 5.91 | 65.3 | 60.39 | −0.512 |
| 17 | Sox18 | 14 | 2 | 391 | 41,533.25 | 8.42 | 75.69 | 63.12 | −0.569 |
| 18 | Sox21 | 13 | 1 | 277 | 28,696.95 | 9.74 | 57.93 | 68.77 | −0.217 |
| 19 | Sox30 | 9 | 5 | 766 | 83,895.1 | 8.92 | 67.12 | 70.08 | −0.61 |
| 20 | SRY | Y | 1 | 229 | 26,425.82 | 9.47 | 63.01 | 63.49 | −0.884 |
| Gene | Indel | Position | Amino Acid/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sox1 | Insertion | 39 | G |
| Sox2 | Insertion | 27 | G |
| Sox3 | Insertion | 1–45 | MIGQGASLQACQSPGLRVARGGPSPNPEGSEQVYKRPGERPTRLR |
| Sox3 | Insertion | 188 | G |
| Sox4 | Insertion | 400 | S |
| Sox6 | Insertion | 287 | Q |
| Sox7 | Insertion | 1–147 | MRGWSPAPAPGPRDHRRLPPPGRRHLRCELAGRGAAPGLRGTDPREPPGRRRGGPGAGARWGSGPPPASPPGRSERGRCGPGRRGARAVKEGGAAPPSRVIGGRSLSKLINKGPGRGCRPSWTPQPVRGPGQRRPDDAKRGDPRAAM |
| Sox9 | Insertion | 388 | Q |
| Sox18 | Insertion | 298–299 | GP |
| Gene Pairs | Chromosome | Duplication | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Time (MYA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sox17/Sox18 | 15/14 | SD | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.56 | 9.65 |
| Sox8/Sox9 | 24/3 | SD | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.58 | 12.66 |
| Sox30/Sox13 | 9/5 | SD | 0.40 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 21.41 |
| Sox5/Sox6 | 16/4 | SD | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 21.07 |
| Sox21/Sox7 | 13/3 | SD | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.81 | 10.17 |
| Sox11/Sox4 | 12/2 | SD | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.56 | 9.65 |
| Sox3/Sox1 | X/13 | SD | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 10.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, M.; Rehman, M.S.-u.; Rehman, M.S.N.-u.; AlKahtane, A.A.; Al-Hazani, T.M.; Hassan, F.-u.; Rehman, S.u. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Mutational Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family. Animals 2023, 13, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142246
Abdullah M, Rehman MS-u, Rehman MSN-u, AlKahtane AA, Al-Hazani TM, Hassan F-u, Rehman Su. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Mutational Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family. Animals. 2023; 13(14):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142246
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Muhammad, Muhammad Saif-ur Rehman, Muhammad Shah Nawaz-ul Rehman, Abdullah A. AlKahtane, Tahani Mohamed Al-Hazani, Faiz-ul Hassan, and Saif ur Rehman. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Mutational Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family" Animals 13, no. 14: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142246
APA StyleAbdullah, M., Rehman, M. S.-u., Rehman, M. S. N.-u., AlKahtane, A. A., Al-Hazani, T. M., Hassan, F.-u., & Rehman, S. u. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Mutational Analysis of the Buffalo Sox Gene Family. Animals, 13(14), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13142246








