Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Anatomic Evaluation
2.3. MRI Technique
3. Results
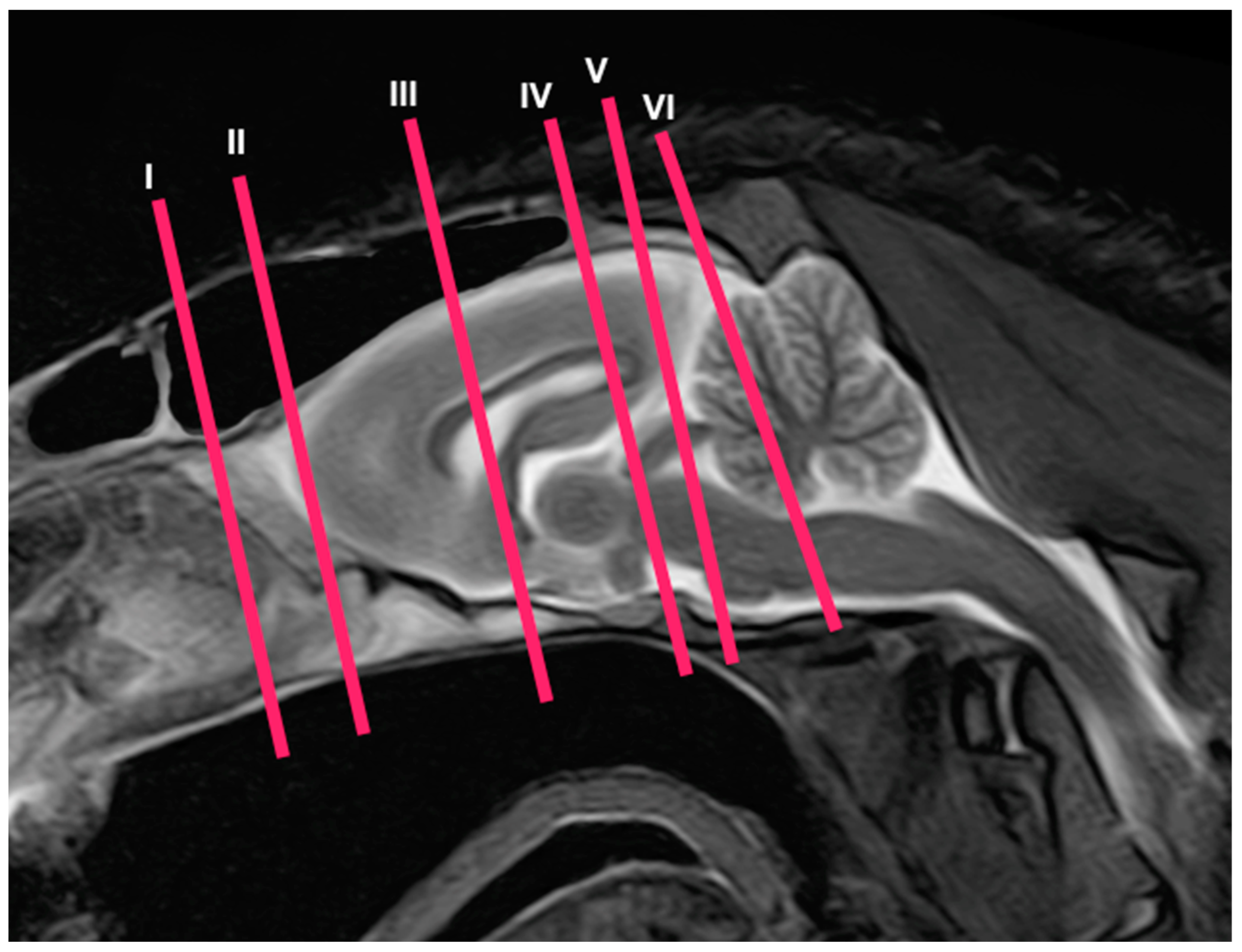
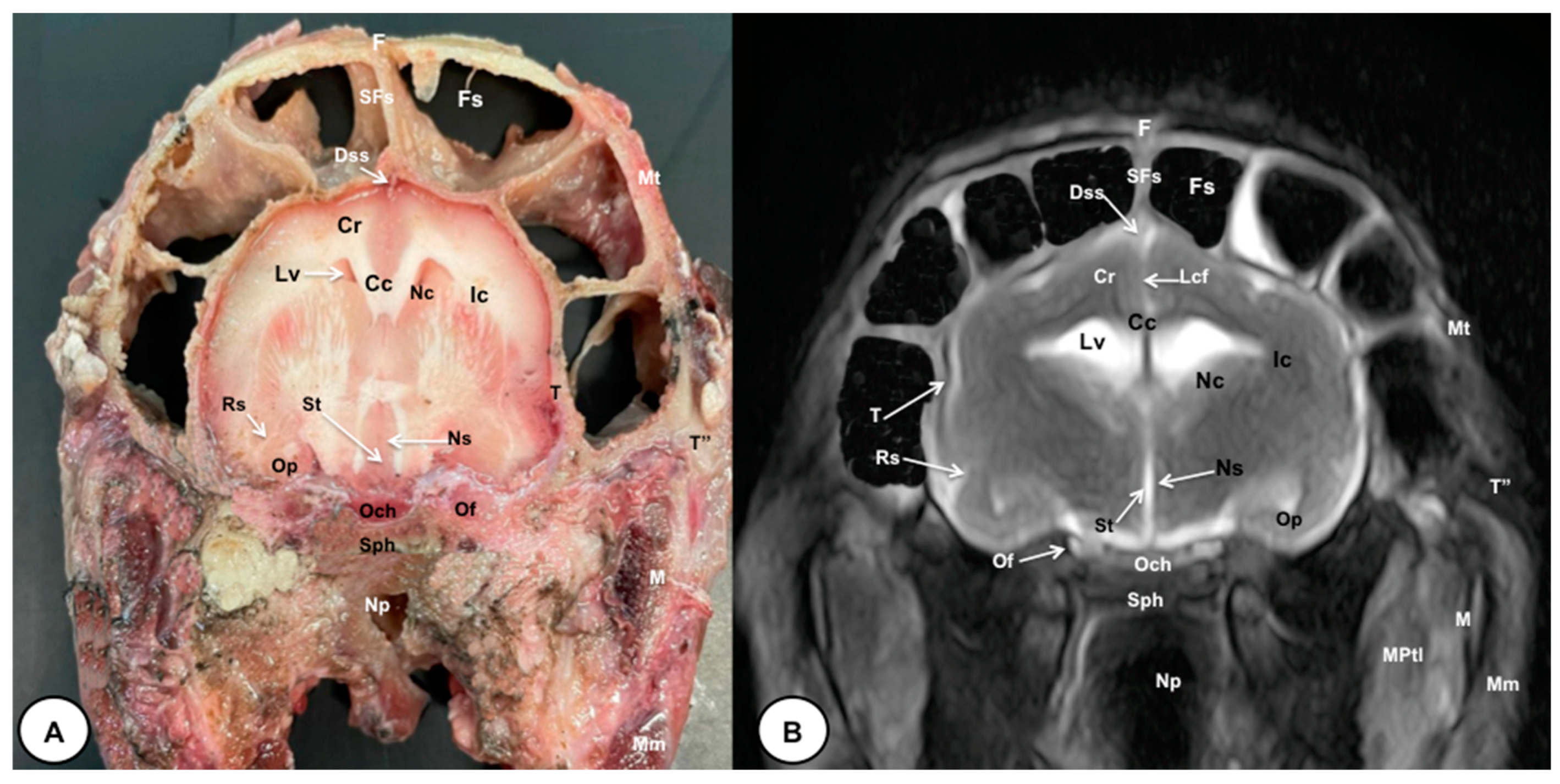
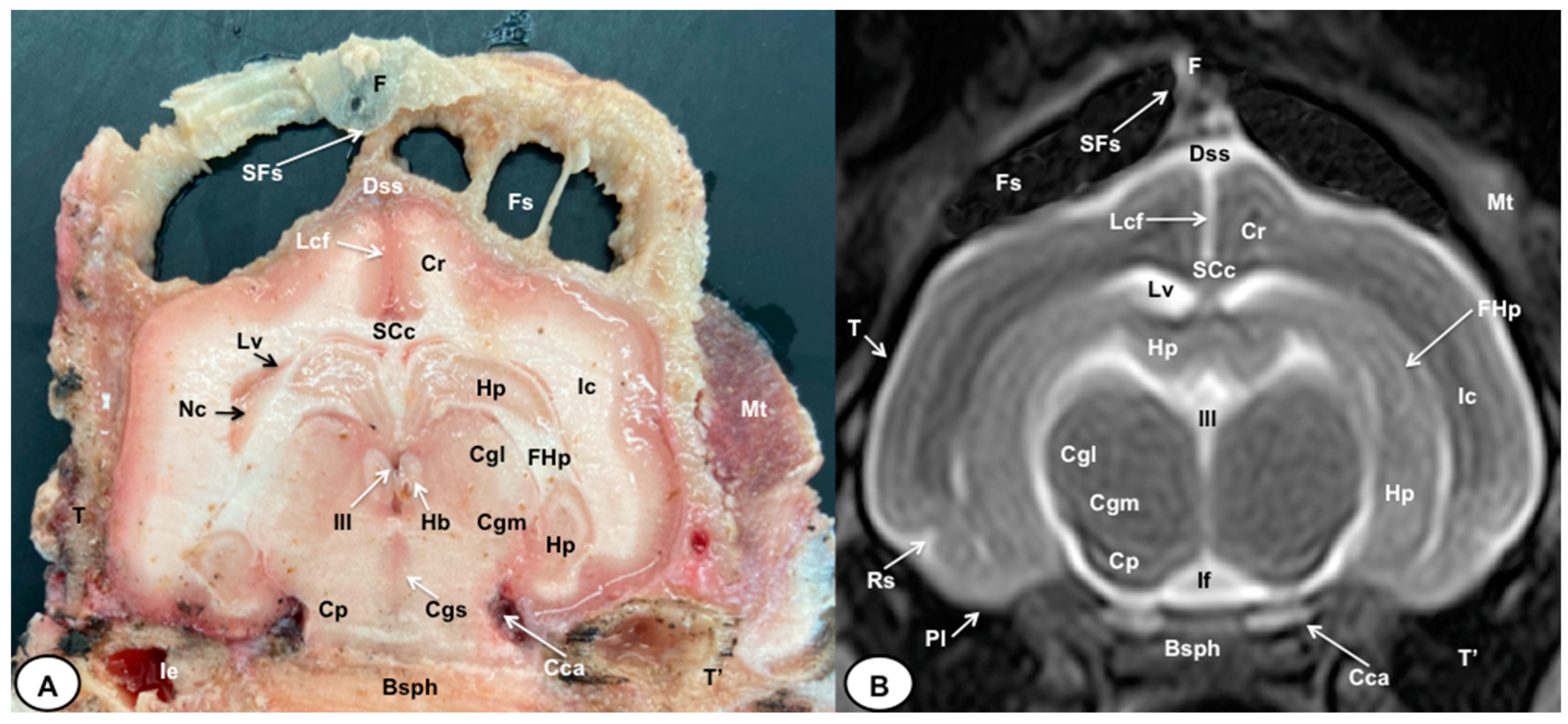
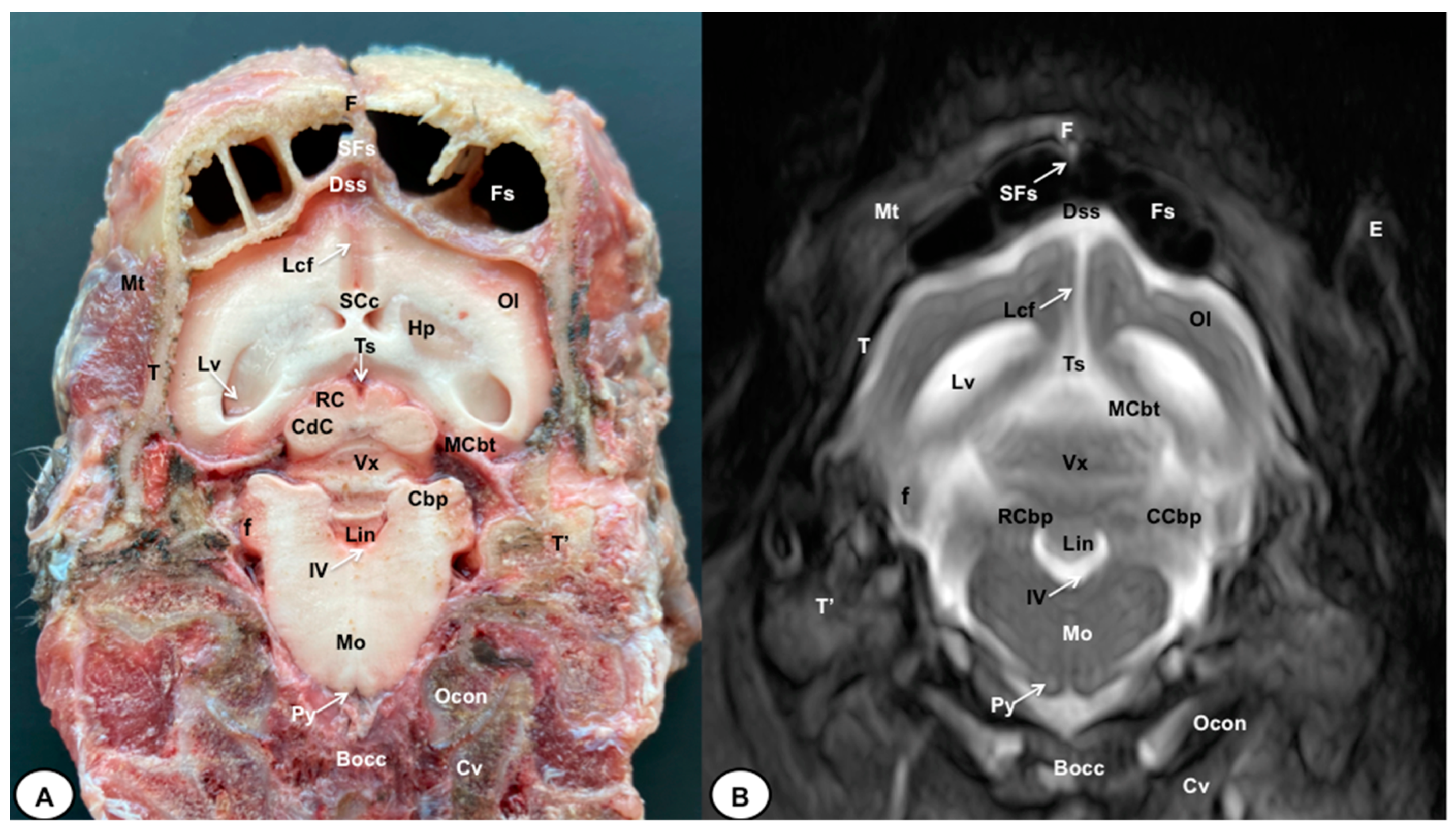
3.1. Anatomical Cross-Sections
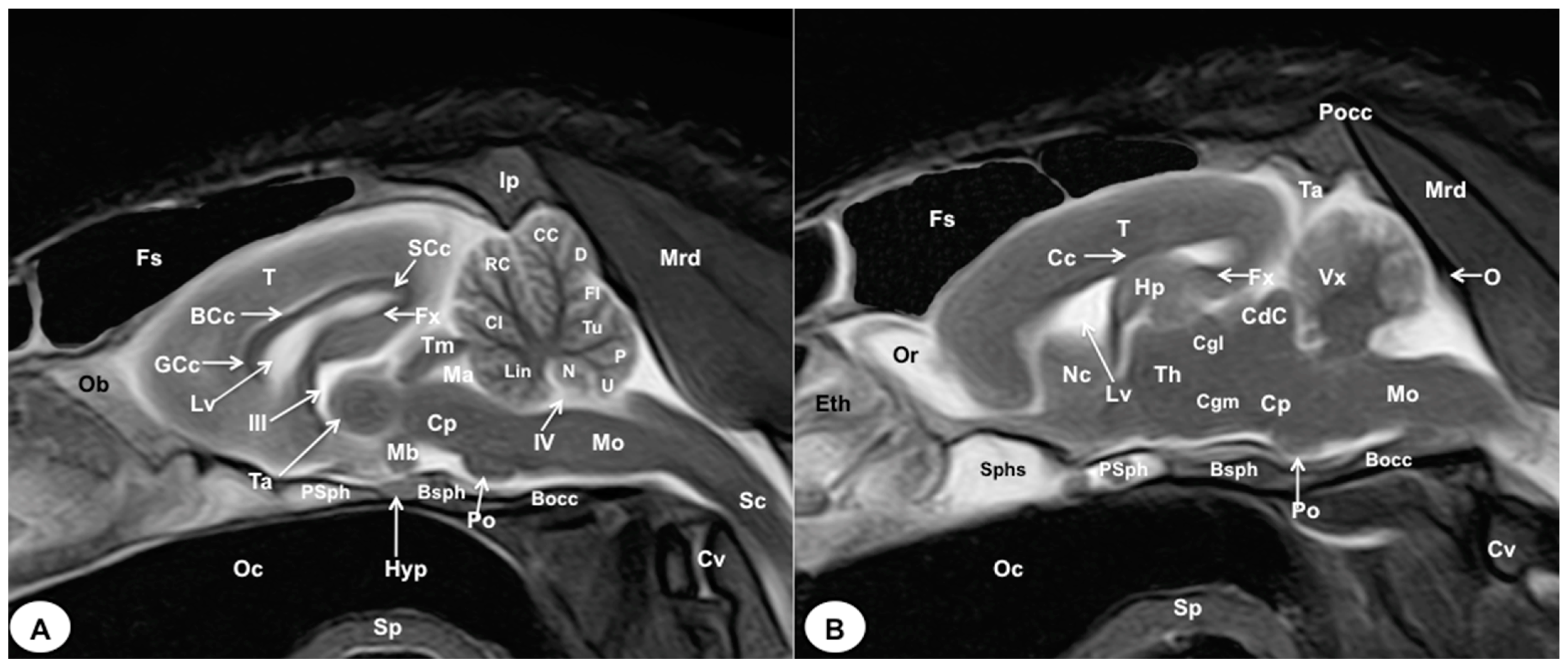
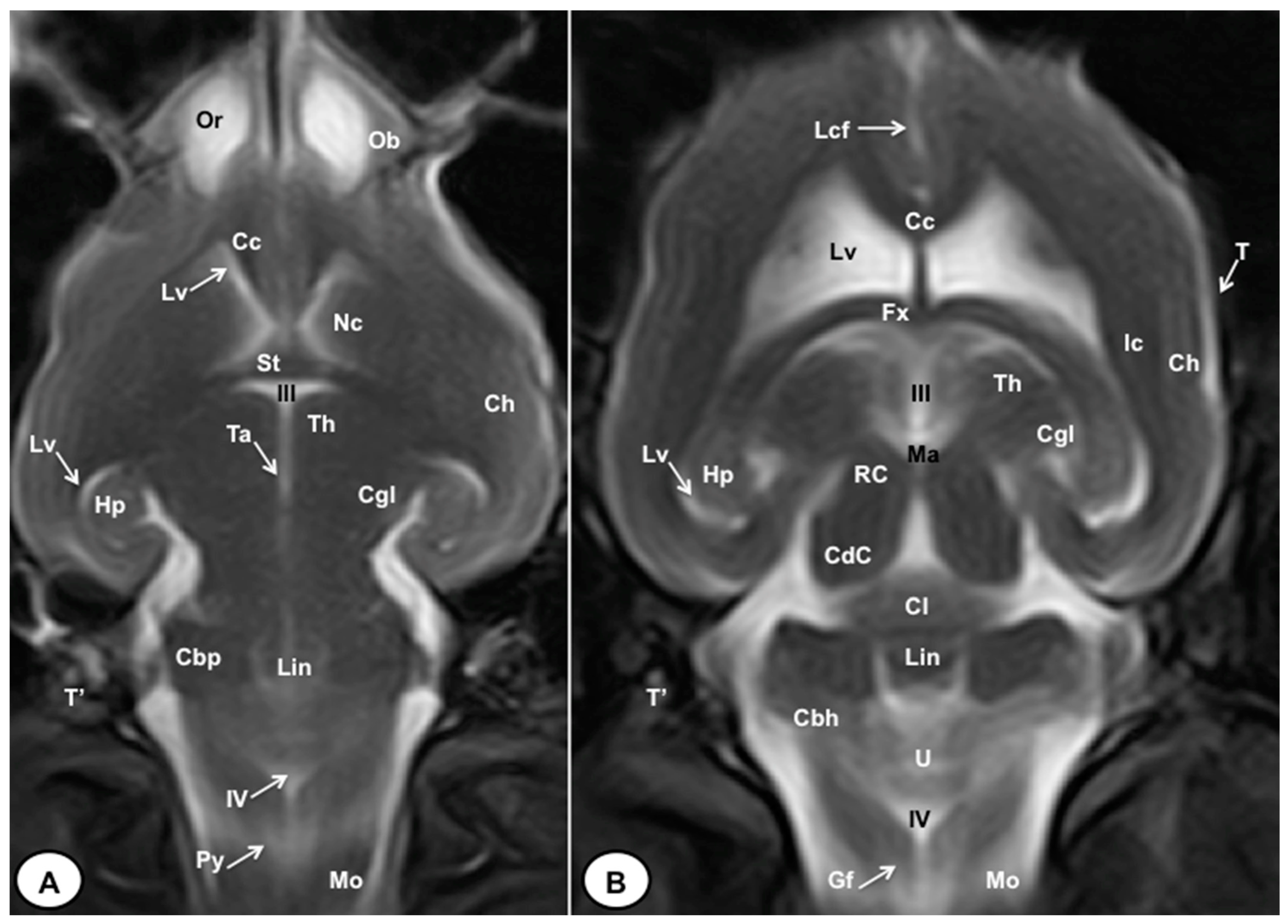
3.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banzato, T.; Russo, E.; Di Toma, A.; Palmisano, G.; Zotti, A. Anatomic imaging of the Boa constrictor head: A comparison between radiography, computed tomography and cadaver anatomy. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Caelenberg, A.I.; De Rycke, L.M.; Hermans, K.; Verhaert, L.; Van Bree, H.J.; Gielen, I.M. Comparison of radiography and CT to identify changes in the skulls of four rabbits with dental disease. J. Vet. Dent. 2011, 28, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Rodríguez, E.; Encinoso Quintana, M.; Morales Bordon, D.; Garcés, J.G.; Artiles Nuez, H.; Jaber, J.R. Anatomical Description of Rhinoceros Iguana (Cyclura cornuta cornuta) Head by Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Gross-Sections. Animals 2023, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arencibia, A.; Corbera, J.A.; Ramírez, G.; Díaz-Bertrana, M.L.; Pitti, L.; Morales, M.; Jaber, J.R. Anatomical Assessment of the Thorax in the Neonatal Foal Using Computed Tomography Angiography, Sectional Anatomy, and Gross Dissections. Animals 2020, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, R.; Carrascosa, C.; Rivero, M.; Peña, S.; Fernández, T.; Suarez-Bonnet, A.; Jaber, J.R. Analysis of equine cervical spine using three-dimensional computed tomographic reconstruction. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2012, 40, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amori, G.; De Smet, K. Hystrix cristata. In IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016, p. e.T10746A22232484. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/especies/10746/22232484 (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. (Eds.) Species Hystrix (Hystrix) cristata. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2005; p. 1543. [Google Scholar]
- Angelici, F.M.; Colangelo, P.; Gippoliti, S. Out of Europe: Investigating Hystrix cristata (Rodentia: Hystricidae) skull morphometric geographic variability in Africa. Biogeographia 2021, 36, a001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, G. Porcupines. In Grzimek1s Encyclopedia of Mammals; Grzimek, B., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Capello, V.; Cauduro, A. Comparison of Diagnostic Consistency and Diagnostic Accuracy Between Survey Radiography and Computed Tomography of the Skull in 30 Rabbits with Dental Disease. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2016, 25, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, V. Diagnostic Imaging of Dental Disease in Pet Rabbits and Rodents. Veter Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2016, 19, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głodek, J.; Adamiak, Z.; Przeworski, A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Reptiles, Rodents, and Lagomorphs for Clinical Diagnosis and Animal Research. Comp. Med. 2016, 66, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Fornazari, F.; Guimaraes, F.F.; Teixeira, C.R.; Langoni, H. Isolation of Staphylococcus epidermidis from inflamed upper respiratory tract of an orange-spined hairy dwarf porcupine (Sphiggurus villosus). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 18, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Caelenberg, A.I.; De Rycke, L.M.; Hermans, K.; Verhaert, L.; van Bree, H.J.; Gielen, I.M. Low-field magnetic resonance imaging and cross-sectional anatomy of the rabbit head. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllhaupt, D.; Augsburger, H.; Schwarz, A.; Fischer, G.; Kircher, P.; Hatt, J.M.; Ohlerth, S. Magnetic resonance imaging anatomy of the rabbit brain at 3 T. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capello, V.; Lennox, A. Advanced diagnostic imaging and surgical treatment of an odontogenic retromasseteric abscess in a guinea pig. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 56, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Moreno, E.; Arbat-Plana, A.; Batalle, D.; Soria, G.; Illa, M.; Prats-Galino, A.; Eixarch, E.; Gratacos, E. A Magnetic Resonance Image Based Atlas of the Rabbit Brain for Automatic Parcellation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, J.W.; Wen, G.Y.; Wisniewski, H.M. Atlas of the Rabbit Brain and Spinal Cord; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Popesko, P.; Rajtova, V.; Horak, J. Anatomy of Small Laboratory Animals; Wolfe Publishing Ltd.: London, UK, 1990; pp. 14–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gray-Edwards, H.L.; Salibi, N.; Josephson, E.M.; Hudson, J.A.; Cox, N.R.; Randle, A.N.; McCurdy, V.J.; Bradbury, A.M.; Wilson, D.U.; Beyers, R.J.; et al. High resolution MRI anatomy of the cat brain at 3Tesla. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 227, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature. Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria; Ithaca: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arencibia, A.; Encinoso, M.; Jaber, J.R.; Morales, D.; Blanco, D.; Artiles, A.; Vázquez, J.M. Magnetic resonance imaging study in a normal Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris) stifle joint. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaber, J.R.; Encinoso, M.; Morales, D.; Artiles, A.; Santana, M.; Blanco, D.; Arencibia, A. Anatomic study of the normal Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris) brain and associated structures using low field magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Anat. 2016, 20, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Khalifa, A.; Belkhiria, J.; Hamdi, H.; Chandoul, W.; Mattoussi, A. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and associated structures of the one humped camel (Camelus dromedarius): A comparative study. J. New Sci. 2019, 68, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar]
- Arencibia, A.; Hidalgo, M.; Vázquez, J.M.; Contreras, S.; Ramírez, G.; Oros, J. Sectional anatomic and magnetic resonante imaging features of the head of juvenile loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta careta). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, A.L.; Cuenca, R.; Zamora, M.A.; Parga, M.L.; Lavin, S.; Alegre, F.; Marco, I. Sectional anatomic and magnetic resonance imaging of coelomic structures of loggerhead sea turtles. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdy, M.A.A. Correlation between computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and cross-sectional anatomy of the head of the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus, Linnaeus 1758). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2022, 51, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arencibia, A.; Matos, J.; Encinoso, M.; Gil, F.; Artiles, A.; Martínez-Gomariz, F.; Vázquez, J.M. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging study of a normal tarsal joint in a Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, T.M.; Litster, A.L.; Gregory, R.J. Big cat scan: Magnetic resonance imaging of the tiger. Australas. Radiol. 2004, 48, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinoso, M.; Oros, J.; Ramírez, G.; Jaber, J.R.; Artiles, A.; Arencibia, A. Anatomic Study of the Elbow Joint in a Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris) Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging andGross Dissections. Animals 2019, 9, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Encinoso, M.; Morales, D.; Déniz, S.; Guerra, J.V.; Jaber, J.R. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of a Rhinosinusitis Secondary to a Dental Abscess in a Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata). Slov. Vet. Res. 2023, 60, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, N.; Mori, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Jiang, H.; Ye, X.; Xu, X.; Richards, L.J.; Nathans, J.; Miller, M.I.; Toga, A.W.; et al. An MRI-based atlas and database of the developing mouse brain. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Bordon, D.; Encinoso, M.; Arencibia, A.; Jaber, J.R. Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Animals 2023, 13, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162551
Morales-Bordon D, Encinoso M, Arencibia A, Jaber JR. Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Animals. 2023; 13(16):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162551
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Bordon, Daniel, Mario Encinoso, Alberto Arencibia, and José Raduan Jaber. 2023. "Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Animals 13, no. 16: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162551
APA StyleMorales-Bordon, D., Encinoso, M., Arencibia, A., & Jaber, J. R. (2023). Cranial Investigations of Crested Porcupine (Hystrix cristata) by Anatomical Cross-Sections and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Animals, 13(16), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162551






