The Adrenal Gland of Squamata (Reptilia): A Comparative Overview
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. The Adrenal Gland
2. Paracrine Relationships in the Adrenal Gland
3. The Morphology of the Chromaffin and the Steroidogenic Tissues
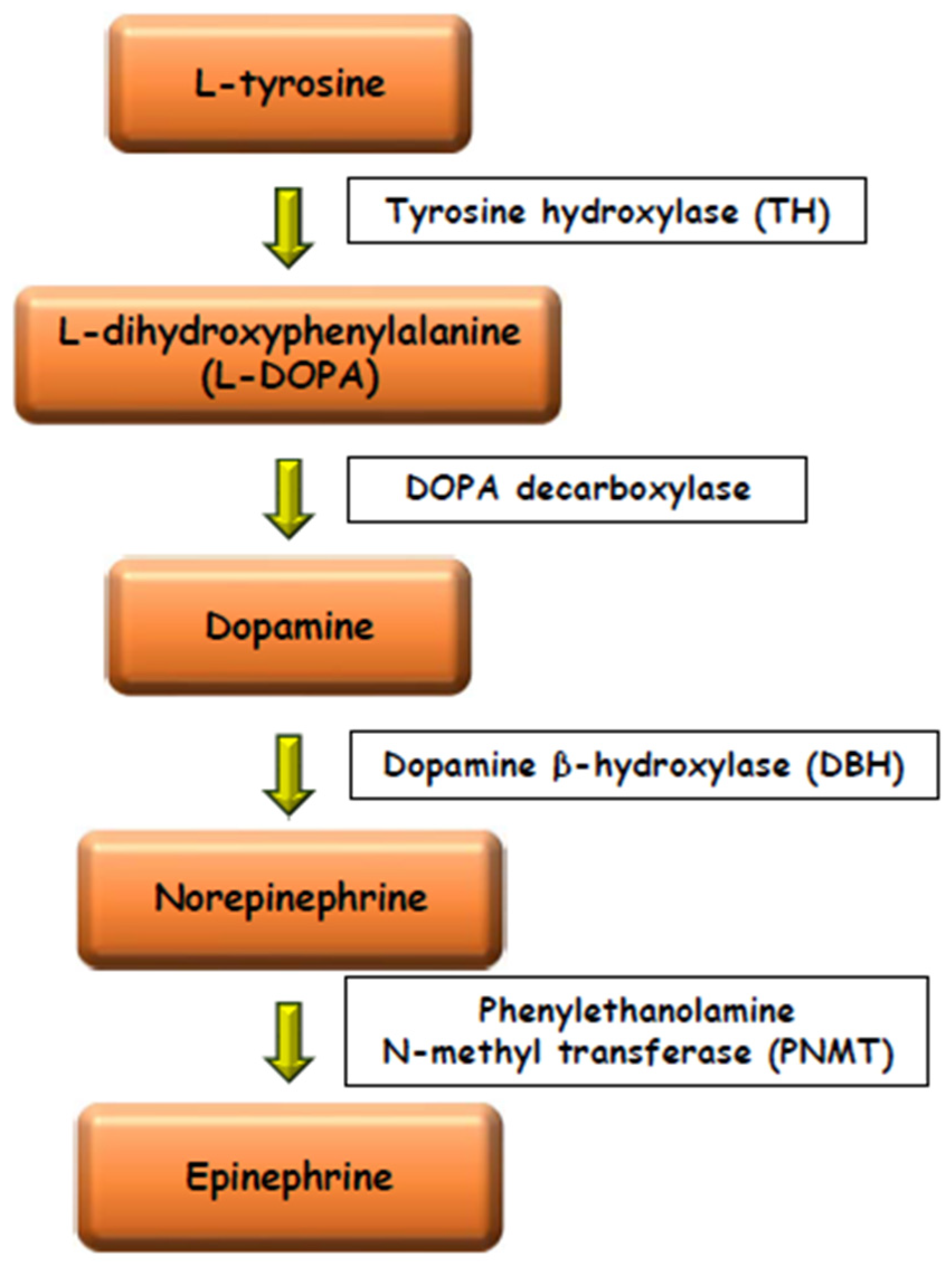
4. The NE/E Cell Ratio
5. The Adrenal Gland of Reptiles
6. The Adrenal Gland of Squamata
6.1. Lacertidae
6.2. Scincidae
6.3. Superfamily Cordyliformes
7. The NE/E Cell Ratio and the Distribution of the Chromaffin Cells in Squamata
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perry, F.S.; Capaldo, A. The autonomic nervous system and chromaffin tissue: Neuroendocrine regulation of catecholamine secretion in non-mammalian vertebrates. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2011, 165, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varano, L.; Laforgia, V. Evolutionary trends in the adrenal gland of reptiles. In Symposium on the Evolution of Terrestrial Vertebrates; Ghiara, G., Angelini, F., Olmo, E., Varano, L., Eds.; Mucchi: Modena, Italy, 1991; Volume 4, pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, D.O. Vertebrate Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Accordi, F. The chromaffin cells of urodele amphibians. J. Anat. 1991, 179, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grassi Milano, E.; Accordi, F. Evolutionary trends in adrenal gland of anurans and urodeles. J. Morphol. 1986, 189, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi Milano, E. Development of the adrenal gland in amniotes: A comparison between chelonians and birds. Boll. Zool. 1991, 58, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Barra, T.; Rosati, L.; Valiante, S.; Capaldo, A.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V. Adrenal gland response to endocrine disrupting chemicals in fishes, amphibians and reptiles: A comparative overview. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 297, 113550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsia, R.V.; McIlroy, P.J.; John-Alder, H.B. Adrenocortical function in avian and non-avian reptiles: Insights from dispersed adrenocortical cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2023, 281, 111424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, S.W.; Winkler, H. The adrenal chromaffin cell. Sci. Am. 1985, 253, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H. Immunohistochemical analysis of the localization of neuropeptides in the adrenal gland. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1985, 48, 453–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupland, R.E. The natural history of the chromaffin cell. Twenty-five years on the beginning. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1989, 52, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goumon, Y.; Muller, A.; Glattard, E.; Marban, C.; Gasnier, C.; Strub, J.M.; Chasserot-Golaz, S.; Rohr, O.; Stefano, G.B.; Welters, I.D.; et al. Identification of morphine-6-glucuronide in chromaffin cell secretory granules. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8082–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden, L.E.; Jiang, S.Z. What’s new in endocrinology: The chromaffin cell. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrart-Bornstein, M.; Hinson, J.P.; Bornstein, S.R.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Vinson, G.P. Intraadrenal interactions in the regulation of adrenocortical steroidogenesis. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 101–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, F.; Zhang, L.; Wessel, J.; Zhang, K.; Wen, G.; Kennedy, B.P.; Rana, B.K.; Das, M.; Rodriguez-Flores, J.L.; Smith, D.W.; et al. Tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine biosynthesis: Discovery of common human genetic variants governing transcription, autonomic activity, and blood pressure in vivo. Circulation 2007, 116, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.A.; Thoenen, H. Selective induction by glucocorticoids of tyrosine hydroxylase in organ cultures of rat pheochromocytoma. Neuroscience 1977, 2, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelner, K.L.; Pollard, H.B. Glucocorticoid receptors and regulation of phenylethanolamine-N- methyltransferase activity in cultured chromaffin cells. J. Neurosci. 1985, 5, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evinger, M.J.; Towle, A.C.; Park, D.H.; Lee, P.; Joh, T.H. Glucocorticoids stimulate transcription of the rat phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) gene in vivo and in vitro. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1992, 12, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Carmichael, S.W.; Mukherjee, M. Avian adrenal medulla: Cytomorphology and function. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2001, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hodel, A. Effects of glucocorticoids on adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Neuroendocr. 2001, 13, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman, R.J. Control of epinephrine synthesis in the adrenal medulla by the adrenal cortex: Hormonal specificity and dose-response characteristics. Endocrinology 1966, 79, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsicker, K.; Huber, K.; Schober, A.; Kalcheim, C. Resolved and open issues in chromaffin cell development. Mech. Dev. 2013, 130, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariasen, R.D.; Newcomer, W.S. Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activity in the avian adrenal following immobilization or adrenocorticotropin. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1974, 23, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforgia, V.; Varano, L. The influence of the interrenal steroidogenic tissue on the chromaffin cells of the adrenal gland of Lacerta s. sicula Raf.: Effects of ACTH administration during the winter. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1978, 23, 379–390. [Google Scholar]
- Capaldo, A.; Laforgia, V.; Sciarrillo, R.; De Falco, M.; Valiante, S.; Gay, F.; Virgilio, F.; Varano, L. Effects of dopamine on the adrenal gland of Podarcis sicula (Reptilia, Lacertidae). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 135, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capaldo, A.; Sciarrillo, R.; Valiante, S.; Gay, F.; Virgilio, F.; Varlese, M.G.; Laforgia, V.; Varano, L. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) modulates pituitary-adrenal axis activity in the lizard, Podarcis sicula. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 137, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.G.; Vijayan, M.M.; Perry, S.F. Modulation of catecholamine storage and release by the pituitary-interrenal axis in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus Mykiss. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1996, 165, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Gay, F.; De Falco, M.; Virgilio, F.; Laforgia, V.; Varano, L. The adrenal gland of newt Triturus carnifex (Amphibia, Urodela) following in vivo betamethasone administration. Anat. Embriol. 2006, 211, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; Bornstein, S.R. Cross-talk between adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex in stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, W. Changes of the biology of the adrenal cortex in the Vertebrate evolution. Nova Acta Leopold. NF 1984, 56, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Annual cycle of the chromaffin cells of Triturus cristatus. J. Morphol. 1991, 208, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Valiante, S.; Sciarrillo, R.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Annual and daily serum aldosterone and catecholamine patterns in males of the Italian crested newt, Triturus carnifex (Amphibia, Urodela). Ital. J. Zool. 2010, 77, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, F.; Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A. Human follicle-stimulating hormone modulation of adrenal gland activity in the Italian crested newt, Triturus carnifex (Amphibia, Urodela). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A-Mol. Int. Physiol. 2008, 151, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano-Lanza, G. Sulla istofisiologia degli elementi cellulari della parte midollare del surrene. Quad. Anat. Prat. S 1961, 17, 251–284. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, W.J.; Barajas, L.; Latta, H. The ultrastructure of the human adrenal medulla with comparative studies of white rat. Anat. Rec. 1971, 169, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Lee, B.R.; Kamitani, T. A simple and sensitive method for the demonstration of norepinephrine-storing adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 138, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.G. Identification of and observations on epinephrine and norepinephrine containing cells in the adrenal medulla. Am. J. Anat. 1963, 112, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, A.G.E. Histochemistry Theoretical and Applied; Little, Brown & Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Tramezzani, J.H.; Chiocchio, S.; Wasserman, G.F. A technique for light and electron microscopic identification of adrenaline and noradrenaline storing cells. Cytochemistry 1964, 12, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Laforgia, V.; Sciarrillo, R.; Valiante, S.; Gay, F.; Varano, L. Localization and role of serotonin in the adrenal gland of Podarcis sicula (Reptilia, Lacertidae). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 132, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; De Falco, M.; Rosati, L.; Laforgia, V. Transmission electron microscopy: A method for studying the adrenal chromaffin cells. In Chromaffin Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology; Borges, R., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2565, pp. 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzàlez-Santana, A.; Castañeira, L.; Baz-Dàvila, R.; Estévez-Herrera, J.; Domìnguez, N.; Méndez-Lòpez, I.; Padìn, J.F.; Castañeira, A.; Machado, J.D.; Ebert, S.N.; et al. Adrenergic chromaffin cells are adrenergic even in the absence of epinephrine. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, U.K.; Soliman, S.M.M.; Mazher, K.M.; Hassan, R.M.; Nabil, T.M. Histological, histochemical, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical identification and characterization of the neurosecretory cells of the adult rabbit’s adrenal medulla. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2022, 51, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneu, V.; Borges, R.; Gandìa, L.; Garcìa, A.G. Forty years of the adrenal chromaffin cell through ISCCB meetings around the world. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2023, 475, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idelman, S. The structure of the mammalian adrenal cortex. In General, Comparative and Clinical Endocrinology of the Adrenal Cortex; Chester Jones, I., Henderson, I.W., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA, 1978; pp. 1–199. [Google Scholar]
- Klingbeil, C.K.; Holmes, W.N.; Pearce, R.B.; Cronshaw, J. Functional significance of interrenal cell zonation in the adrenal gland of the duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Cell Tissue Res. 1979, 201, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, W.N.; Cronshaw, J. Adrenal gland: Some evidence for the structural and functional zonation of the steroidogenic tissues. J. Exper. Zool. 1984, 232, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofts, B.; Phillips, J.G. Some aspects of the structure of the adrenal gland in snakes. J. Endocrinol. 1965, 33, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitani, F. Functional zonation of the rat adrenal cortex: The development and maintenance. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2016, 90, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinson, G.P. Functional Zonation of the Adult Mammalian Adrenal Cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. Cytophysiology of the avian adrenal medulla. In International Review of Cytology; Bourne, G., Danielli, J.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 253–284. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, E.L.; Kimball, R.T. Data types and the phylogeny of Neoaves. Birds 2021, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, E.N. Relationships of the paleartctic lizards assigned to the genera Lacerta, Algyroides and Psammodromus (Reptilia: Lacertidae). Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) Zool. 1973, 25, 291–366. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, B.; Cei, J.M. Immunological data on the taxonomy of some Italian lizards (Reptilia, Lacertidae). Mon. Zool. Ital. 1977, 11, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, B.; Cei, J.M.; Crespo, E.G. Immunological investigations on the taxonomic status of some Mediterranean lizards (Reptilia, Lacertidae). Mon. Zool. Ital. 1977, 11, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, D.; Mayer, W. Albumin evolution and its phylogenetic and taxonomic implications in several lacertid lizards. Amphibia-Reptilia 1985, 6, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.L. Phylogeny and systematics of Squamata (Reptilia) based on morphology. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2008, 310, 1–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, D.G.; Noonan, B.P.; Moss, T.; Townsend, T.M.; Reeder, T.W.; Sites, J.W., Jr.; Wiens, J.J. Estimating divergence times and evaluating dating methods using phylogenomic and mitochondrial data in squamate reptiles. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2012, 65, 974–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, T.M.; Larson, A.; Louis, E.; Macey, J.R. Molecular phylogenetics of Squamata: The position of snakes, amphisbaeninans, and dibamids, and the root of the squamate tree. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 735–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, N.; Hedges, S.B. The phylogeny of squamate reptiles (lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians) inferred from nine nuclear protein-coding genes. CR Biol. 2005, 328, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.J.; Hutter, C.R.; Mulcahy, D.G.; Noonan, B.P.; Townsend, T.M.; Sites, J.W.; Reeder, T.W. Resolving the phylogeny of lizard and snakes (Squamata) with extensive sampling of genes and species. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyron, R.A.; Burbrink, F.T.; Wiens, J.J. A phylogeny and revised classification of Squamata, including 4161 species of lizards and snakes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, S.P.; Anderson, J.S. The phylogenetic definition of Reptilia. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The NCBI Taxonomy Database. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Gabe, M.; Martoja, M. Contribution à l’histologie de la glande surrénale des Squamata. Archs Anat. Microsc. 1961, 50, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gabe, M.; Rancurel, P. Contribution à l’histologie de la glande surrénale de Crocodylus niloticus Laur. Archs Anat. Microsc. 1964, 53, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Gabe, M.; Saint Girons, H. Particularités histologiques de la glande surrénale chez Sphenodon punctatus Gray. C. R. Hebd. SÉAnc Acad. Sci. Paris 1964, 258, 3559–3562. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, G.F.; Tramezzani, J.H. Separate distribution of adrenaline and noradrenaline secreting cells in the adrenal of snakes. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1963, 3, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varano, L.; Della Corte, F.; Galgano, M. Brevi note sulla ultrastruttura delle cellule a catecolamine di Lacerta s. sicula Raf. Atti Soc. Pel. Sci. Fis. Mat. Nat. 1969, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, W.; Pavlicev, M. The phylogeny of the family Lacertidae (Reptilia) based on nuclear DNA sequences: Convergent adaptations to arid habitats within the subfamily Eremiainae. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2007, 44, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforgia, V.; Varano, L.; Capaldo, A.; Cavagnuolo, A.; Putti, R. Comparative morphology of the adrenal gland in some species belonging to the family Lacertidae. Amphib. Reptil. 1990, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, A.; Laforgia, V.; Varano, L.; Putti, R.; Cavagnuolo, A. Distributive patterns of chromaffin cells in the adrenal gland of reptiles belonging to family Lacertidae. In Symposium on the Evolution of Terrestrial Vertebrates; Ghiara, G., Angelini, F., Olmo, E., Varano, L., Eds.; Mucchi: Modena, Italy, 1991; Volume 4, pp. 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Laforgia, V.; Varano, L.; Capaldo, A.; Putti, R.; Cavagnuolo, A. Comparative morphology of the adrenal gland in selected species of the genus Podarcis. Amphib. Reptil. 1991, 12, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A.; Varano, L.; Putti, R.; Cavagnuolo, A. Comparative morphology of the adrenal gland in some Mediterranean species of the family Lacertidae. In Lacertids of the Mediterranean Region; Valakos, E.D., Böhme, W., Pérez-Mellado, V., Maragou, P., Eds.; Hellenic Zoological Society: Athens, Greece; Bonn, Germany; Alicante, Spain, 1993; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Capaldo, A.; Laforgia, V.; Varano, L.; Cavagnuolo, A. The adrenal gland of some lizards living in xeric habitats: Morphology and NA/A cell ratio. Boll. Soc. Nat. Napoli 1994, 102, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lovern, M.B. Hormones and reproductive cycles in lizards. In Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates: Reptiles; Norris, D.O., Lopez, K.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 321–353. [Google Scholar]
- Laforgia, V.; Capaldo, A.; Sciarrillo, R.; Cavagnuolo, A.; Putti, R. The structure of the adrenal gland in eight species of the family Scincidae. Electron microscopic studies. In Scientia Herpetologica; Llorente, G.A., Montori, A., Santos, X., Carretero, M.A., Eds.; Asociaciòn Herpetològica Española: Barcelona, Spain, 1995; pp. 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, M. Generic relationships within Cordyliformes (Reptilia: Squamata). Bull. Inst. R. Sci. Nat. Belg. (Biol.) 1991, 61, 121–188. [Google Scholar]
- Laforgia, V.; Varano, L. Morphology and distribution of chromaffin cells in the adrenal gland of Cordylidae (Reptilia, Sauria): A comparative study. J. Morphol. 1982, 171, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varano, L.; Laforgia, V.; Putti, R.; Cavagnuolo, A.; Capaldo, A. La morfologia dell’interrenale di Podarcis s. sicula Raf. dopo somministrazione di corteccia surrenale. Ric. Sci. Educ. Perman. 1984, 38, 531–532. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, E.N.; Arribas, O.; Carranza, S. Systematics of the Palearctic and Oriental lizard tribe Lacertini (Squamata: Lacertidae: Lacertinae), with descriptions of eight new genera. Zootaxa 2007, 1430, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Borja, M.; Bohòrquez-Alonso, M.L. Morphology, behaviour and evolution of Gallotia lizards from the Canary Islands. Animals 2023, 13, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtler, J.F. The taxonomic history of the Linnean genus Lacerta (Squamata: Sauria: Lacertidae) in the mirror of book-illustration. Bonn. Zool. Bull. 2010, 57, 307–328. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.J.; Arnold, E.N. Relationships of wall lizards, Podarcis (Reptilia: Lacertidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Copeia 1999, 3, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulakakis, N.; Lymberakis, P.; Valakos, E.; Zouros, E.; Mylonas, M. Phylogenetic relationships and biogeography of Podarcis species from the Balkan Peninsula, by Bayesian and maximum likelihood analyses of mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogen Evol. 2005, 37, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliverio, M.; Bologna, M.A.; Mariottini, P. Molecular biogeography of the Mediterranean lizards Podarcis Wagler, 1830, and Teira Gray, 1838 (Reptilia, Lacertidae). J. Biogeogr. 2000, 27, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psonis, N.; Antoniou, A.; Kukushkin, O.; Jablonski, D.; Petrov, B.; Crnobrnia-Isailovic, J.; Sotiropoulos, K.; Gherghel, I.; Lymberakis, P.; Poulakakis, N. Hidden diversity in the Podarcis tauricus (Sauria, Lacertidae) species subgroup in the light of multilocus phylogeny and species delimitation. Mol. Phylogen Evol. 2017, 106, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbs, R.; Gray, C.L.; Böhm, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Grenyer, R.; Jetz, W.; Meiri, S.; Roll, U.; Owen, N.R.; Rosindell, J. Global priorities for conservation of reptilian phylogenetic diversity in the face of human impact. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, D.-A.; Guillette, L.J., Jr. Reptiles as models of contaminant induced endocrine disruption. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 1998, 53, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, M.; Sciarrillo, R.; Capaldo, A.; Russo, T.; Gay, F.; Valiante, S.; Varano, L.; Laforgia, V. The effects of the fungicide methyl thiophanate on adrenal gland morphophysiology of the lizard, Podarcis sicula. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 53, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Henry, P.F.P. Assessing effects of pesticides on amphibians and reptiles: Status and needs. Herpetol. J. 1992, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capaldo, A. The Adrenal Gland of Squamata (Reptilia): A Comparative Overview. Animals 2023, 13, 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172686
Capaldo A. The Adrenal Gland of Squamata (Reptilia): A Comparative Overview. Animals. 2023; 13(17):2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172686
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapaldo, Anna. 2023. "The Adrenal Gland of Squamata (Reptilia): A Comparative Overview" Animals 13, no. 17: 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172686
APA StyleCapaldo, A. (2023). The Adrenal Gland of Squamata (Reptilia): A Comparative Overview. Animals, 13(17), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13172686





