Tick-borne Pathogen Detection and Its Association with Alterations in Packed Cell Volume of Dairy Cattle in Thailand
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statements
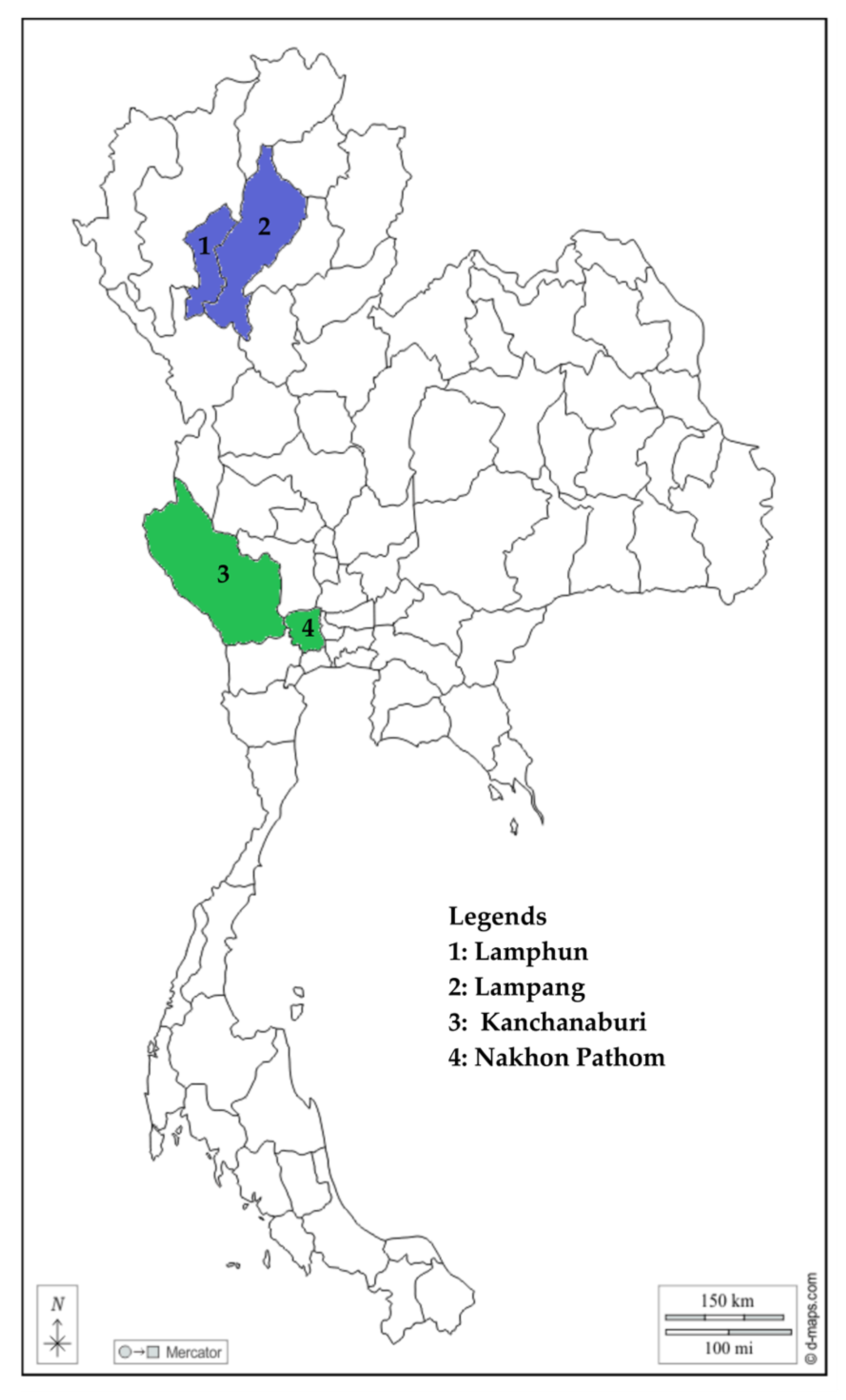
2.2. Background of Farms and Sampled Cattle
2.3. Study Site and Blood Sample Collection
2.4. Hematologic Analysis and Microscopic Examination
2.5. Blood Sample Processing and PCR Tests of DNA Samples
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Tick-borne Pathogen Detection by PCR
3.2. Agreement between PCR and Microscopic Examination Results
3.3. PCV Alterations Associated with Tick-Borne Pathogen Positivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pattamanont, P.; Nutdechanan, J.; Vangtal, A.; Maneetup, C.; Ajariyakhajorn, K. Towards Sustainability of the Dairy Industry in Thailand. FFTC Agricultural Policy Platform. Available online: https://ap.fftc.org.tw/article/3090 (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Lew-Tabor, A.E.; Rodriguez Valle, M. A review of reverse vaccinology approaches for the development of vaccines against ticks and tick borne diseases. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, T.; Lavan, R.P.; Torres, S.; Heaney, K. The economic impact of parasitism from nematodes, trematodes and ticks on beef cattle production. Animals 2023, 13, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiara, H.; Steinaa, L.; Nene, V.; Svitek, N. Theileria in ruminants. In Parasitic Protozoa of Farm Animals and Pets; Florin-Christensen, M., Schnittger, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 187–213. ISBN 978-3-319-70131-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rakwong, P.; Keawchana, N.; Ngasaman, R.; Kamyingkird, K. Theileria infection in bullfighting cattle in Thailand. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirapattharasate, C.; Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Cao, S.; Iguchi, A.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Vudriko, P.; Changbunjong, T.; Sungpradit, S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of bovine Babesia spp. and Theileria orientalis parasites in beef cattle from northern and northeastern Thailand. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udonsom, R.; Mahittikorn, A.; Jirapattharasate, C. Molecular detection and genetic diversity of tick-borne pathogens in goats from the southern part of Thailand. Pathogens 2022, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Ganzinelli, S.; Bhoora, R.; Omondi, D.; Nijhof, A.M.; Florin-Christensen, M. The Piroplasmida Babesia, Cytauxzoon, and Theileria in farm and companion animals: Species compilation, molecular phylogeny, and evolutionary insights. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 1207–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Otgonsuren, D.; Batmagnai, E.; Ahedor, B.; Kothalawala, H.; Vimalakumar, S.C.; Silva, S.S.P.; Yamagishi, J.; Yokoyama, N. Phylogenetic analyses of the mitochondrial, plastid, and nuclear genes of Babesia sp. Mymensingh and its naming as Babesia naoakii n. sp. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Aboge, G.O.; Terkawi, M.A.; Yu, L.; Kamyingkird, K.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Goo, Y.-K.; Yamagishi, J.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Molecular detection and identification of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle in northern Thailand. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simking, P.; Saengow, S.; Bangphoomi, K.; Sarataphan, N.; Wongnarkpet, S.; Inpankaew, T.; Jittapalapong, S.; Munkhjargal, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Yokoyama, N.; et al. The molecular prevalence and MSA-2b gene-based genetic diversity of Babesia bovis in dairy cattle in Thailand. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirapattharasate, C.; Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Cao, S.; Iguchi, A.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Vudriko, P.; Efstratiou, A.; Changbunjong, T.; et al. Molecular detection and genetic diversity of bovine Babesia spp., Theileria orientalis, and Anaplasma marginale in beef cattle in Thailand. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simking, P.; Yatbantoong, N.; Saetiew, N.; Saengow, S.; Yodsri, W.; Chaiyarat, R.; Wongnarkpet, S.; Jittapalapong, S. Prevalence and risk factors of Babesia infections in cattle trespassing natural forest areas in Salakpra Wildlife Sanctuary, Kanchanaburi province. J. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2014, 37, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Aubry, P.; Geale, D.W. A review of bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Coetzee, J.F.; Ewing, S.A. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.K.; Kleinhenz, M.D.; Anantatat, T.; Martin, M.S.; Magnin, G.C.; Coetzee, J.F.; Reif, K.E. Failure to eliminate persistent Anaplasma marginale infection from cattle using labeled doses of chlortetracycline and oxytetracycline antimicrobials. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.K.; Gasser, R.B.; Firestone, S.M.; Anderson, G.A.; Malmo, J.; Davis, G.; Beggs, D.S.; Jabbar, A. Oriental theileriosis in dairy cows causes a significant milk production loss. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, N.N.; Bock, R.E.; Jorgensen, W.K.; Morton, J.M.; Stear, M.J. Is endemic stability of tick-borne disease in cattle a useful concept? Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mans, B.J.; Pienaar, R.; Latif, A.A. A review of Theileria diagnostics and epidemiology. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masatani, T.; Hayashi, K.; Andoh, M.; Tateno, M.; Endo, Y.; Asada, M.; Kusakisako, K.; Tanaka, T.; Gokuden, M.; Hozumi, N.; et al. Detection and molecular characterization of Babesia, Theileria, and Hepatozoon Species in hard ticks collected from Kagoshima, the southern region in Japan. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Huyen, N.X.; Shinuo, C.; Inpankaew, T.; Maklon, K.; Aboulaila, M.; Ueno, A.; Goo, Y.-K.; Yokoyama, N.; Jittapalapong, S.; et al. Molecular and serological prevalence of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in water buffaloes in the northeast region of Thailand. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouLaila, M.; Yokoyama, N.; Igarashi, I. Development and evaluation of a nested PCR based on spherical body protein 2 gene for the diagnosis of Babesia bovis infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, N.; Mizuno, D.; Kuboki, N.; Igarashi, I.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamashina, H.; Hanzaike, T.; Fujii, K.; Onoe, S.; Hata, H.; et al. Epidemiological survey of Theileria orientalis infection in grazing cattle in the eastern part of Hokkaido, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ybañez, A.P.; Sivakumar, T.; Ybañez, R.H.D.; Ratilla, J.C.; Perez, Z.O.; Gabotero, S.R.; Hakimi, H.; Kawazu, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Yokoyama, N.; et al. First molecular characterization of Anaplasma marginale in cattle and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus ticks in Cebu, Philippines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.G.G.; Cockcroft, P.D. Clinical Examination of Farm Animals; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2002; ISBN 978-0-470-75242-5. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, R.; Kristjanson, P. Final Report of Joint ESYS/ILRI/ACIAR Tick Cost Project—Economic Impact of Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases to Livestock in Africa, Asia and Australia; International Livestock Research Institute: Nairobi, Kenya, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koonyosying, P.; Rittipornlertrak, A.; Chomjit, P.; Sangkakam, K.; Muenthaisong, A.; Nambooppha, B.; Srisawat, W.; Apinda, N.; Singhla, T.; Sthitmatee, N. Incidence of hemoparasitic infections in cattle from central and northern Thailand. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, K.; Gedye, K.; McFadden, A.; Pulford, D.; Heath, A.; Pomroy, W. Review of the New Zealand Theileria orientalis Ikeda type epidemic and epidemiological research since 2012. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, J.; Playford, M.; Hickey, K. Theileria orientalis: A review. N. Z. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C. Bovine theileriosis in Australia: A decade of disease. Microbiol. Aust. 2018, 39, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, V.J.; Yabsley, M.J.; Schwartz, D.; LeRoith, T.; Bissett, C.; Broaddus, C.; Schlater, J.L.; Todd, S.M.; Boes, K.M.; Brookhart, M.; et al. Theileria orientalis Ikeda genotype in cattle, Virginia, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, L.; Bitam, I.; Tahri, M.; Bensouilah, M.; De Meeûs, T. Competitive exclusion between piroplasmosis and anaplasmosis agents within cattle. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Meli, M.L.; Dreher, U.M.; Gönczi, E.; Deplazes, P.; Braun, U.; Engels, M.; Schüpbach, J.; Jörger, K.; Thoma, R.; et al. Concurrent infections with vector-borne pathogens associated with fatal hemolytic anemia in a cattle herd in Switzerland. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3775–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.P.; Hamdan, R.H.; Hassan, B.N.H.; Reduan, M.F.H.; Okene, I.A.-A.; Loong, S.K.; Khoo, J.J.; Samsuddin, A.S.; Lee, S.H. Rhipicephalus tick: A contextual review for Southeast Asia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Asada, M.; Battsetseg, B.; Huang, X.; Lan, D.T.B.; Inpankaew, T.; Ybañez, A.P.; Alhassan, A.; Thekisoe, O.M.M.; et al. A PCR based survey of Babesia ovata in cattle from various Asian, African and South American Countries. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittipornlertrak, A.; Nambooppha, B.; Simking, P.; Punyapornwithaya, V.; Tiwananthagorn, S.; Jittapalapong, S.; Chung, Y.-T.; Sthitmatee, N. Low levels of genetic diversity associated with evidence of negative selection on the Babesia bovis apical membrane antigen 1 from parasite populations in Thailand. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancur Hurtado, O.J.; Giraldo-Ríos, C. Economic and health impact of the ticks in production animals. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; Abubakar, M., Perera, P.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78985-765-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, T.; Ikehara, Y.; Igarashi, I.; Inokuma, H.; Yokoyama, N. Dynamics of erythrocyte indices in relation to anemia development in Theileria orientalis-infected cattle. J. Protozool. Res. 2017, 27, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Yadav, A.; Rafiqi, S.I.; Godara, R.; Sudan, V.; Chakraborty, D.; Katoch, R. Epidemiology, haematology and molecular characterization of haemoprotozoon and rickettsial organisms causing infections in cattle of Jammu region, north India. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, O.; Gharbi, M.; Benchikh Elfegoun, M.C. Milk losses due to bovine tropical theileriosis (Theileria annulata infection) in Algeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Rojas, C.; Figueroa, J.V. Diagnostic tools for the identification of Babesia sp. in persistently infected cattle. Pathogens 2019, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Chapter 3.4.2. Bovine babesiosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 12th ed.; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Chapter 3.4.15. Theileriosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 12th ed.; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Chapter 3.4.1. Bovine anaplasmosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 12th ed.; World Organisation for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, K.; Weakley, M.; Do, T.; Mir, S. Current and future molecular diagnostics of tick-borne diseases in cattle. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Province | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lampang | Lamphun | Nakhon Pathom | Kanchanaburi | |
| (N = 10) | (N = 8) | (N = 1) | (N = 1) | |
| Herd size | ||||
| <20 head | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 to 50 head | 6 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| >50 head | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Farm management practices | ||||
| free grazing | 10 | 0 | n.d.a. | n.d.a. |
| stall feeding | 0 | 8 | ||
| Presence of ticks in sampled animals | ||||
| yes | 3 | 0 | n.d.a. | n.d.a. |
| no | 7 | 8 | ||
| Tick control methods | ||||
| yes | 7 | 4 | n.d.a. | n.d.a. |
| no | 3 | 4 | ||
| TBD awareness | ||||
| yes | 10 | 3 | n.d.a. | n.d.a. |
| no | 0 | 5 | ||
| Animal healthcare | ||||
| Livestock technician/veterinarian | 0 | 0 | n.d.a. | n.d.a. |
| farmer–owner | 6 | 6 | ||
| both | 4 | 2 | ||
| Pathogen | Frequency (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lampang | Lamphun | Nakhon Pathom | Kanchanaburi | Total | p Value | |
| Babesia/Theileria/Hepatozoon | 53/84 (63.10) | 9/51 (17.65) | 23/70 (32.86) | 4/60 (6.67) | 89/265 (33.58) | <0.001 *** |
| B. bigemina | 9/84 (10.71) | 2/51 (3.92) | 1/70 (1.43) | n.d. | 12/265 (4.53) | 0.008 ** |
| B. bovis | 7/84 (8.33) | n.d. | 1/70 (1.43) | 1/60 (1.67) | 9/265 (3.40) | 0.024 * |
| T. orientalis | 27/84 (32.14) | 14/51 (27.45) | 17/70 (24.29) | 4/60 (6.67) | 62/265 (23.40) | 0.004 ** |
| A. marginale | 21/84 (25.00) | 1/51 (1.96) | 17/70 (24.29) | 11/60 (18.33) | 50/265 (18.87) | 0.005 ** |
| Single Infections | Dual Infections | Triple Infections | Quadruple Infections | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. bigemina (Bbi) | 4 | Bbi and Bbo | 1 | Bbi, Bbo, and Ama | 1 | Bbi, Bbo, Tor, and Ama | 1 |
| B. bovis (Bbo) | 1 | Bbi and Tor | 1 | Bbi, Tor, and Ama | 2 | ||
| T. orientalis (Tor) | 42 | Bbo and Tor | 1 | Bbo, Tor, and Ama | 2 | ||
| A. marginale (Ama) | 27 | Bbi and Ama | 2 | ||||
| Bbo and Ama | 2 | ||||||
| Tor and Ama | 13 | ||||||
| Microscopy | PCR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTH 18S rRNA | B. bigemina and B. bovis | T. orientalis | A. marginale | |||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Positive | 19 | 17 | 2 | 11 | 14 | 20 | 20 | 30 |
| Negative | 40 | 100 | 9 | 154 | 27 | 115 | 25 | 101 |
| Cohen’s kappa (κ) | 0.20 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.21 | ||||
| SE | 0.075 | 0.108 | 0.084 | 0.079 | ||||
| 95% CI | 0.048–0.343 | −0.105–0.317 | 0.042–0.369 | 0.052–0.363 | ||||
| Pathogen | Positive | Negative | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean PCV ± SD (%) | 95% CI | N | Mean PCV ± SD (%) | 95% CI | ||
| At least 1 TBP | 126 | 27.59 ± 5.21 | 26.67–28.51 | 138 | 30.54 ± 4.52 | 29.78–31.30 | <0.001 *** |
| Babesia/Theileria/Hepatozoon | 88 | 27.18 ± 5.39 | 26.03–28.32 | 176 | 30.11 ± 4.62 | 29.43−30.80 | <0.001 *** |
| T. orientalis | 62 | 26.90 ± 5.44 | 25.52–28.28 | 202 | 29.82 ± 4.76 | 29.16−30.48 | <0.001 *** |
| A. marginale | 49 | 27.84 ± 4.92 | 26.43–29.26 | 215 | 29.43 ± 5.07 | 28.75−30.11 | 0.049 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Galon, E.M.; Tumwebaze, M.A.; Byamukama, B.; Ngasaman, R.; Tiwananthagorn, S.; Kamyingkird, K.; Inpankaew, T.; Xuan, X. Tick-borne Pathogen Detection and Its Association with Alterations in Packed Cell Volume of Dairy Cattle in Thailand. Animals 2023, 13, 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13182844
Adjou Moumouni PF, Galon EM, Tumwebaze MA, Byamukama B, Ngasaman R, Tiwananthagorn S, Kamyingkird K, Inpankaew T, Xuan X. Tick-borne Pathogen Detection and Its Association with Alterations in Packed Cell Volume of Dairy Cattle in Thailand. Animals. 2023; 13(18):2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13182844
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdjou Moumouni, Paul Franck, Eloiza May Galon, Maria Agnes Tumwebaze, Benedicto Byamukama, Ruttayaporn Ngasaman, Saruda Tiwananthagorn, Ketsarin Kamyingkird, Tawin Inpankaew, and Xuenan Xuan. 2023. "Tick-borne Pathogen Detection and Its Association with Alterations in Packed Cell Volume of Dairy Cattle in Thailand" Animals 13, no. 18: 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13182844
APA StyleAdjou Moumouni, P. F., Galon, E. M., Tumwebaze, M. A., Byamukama, B., Ngasaman, R., Tiwananthagorn, S., Kamyingkird, K., Inpankaew, T., & Xuan, X. (2023). Tick-borne Pathogen Detection and Its Association with Alterations in Packed Cell Volume of Dairy Cattle in Thailand. Animals, 13(18), 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13182844










