The Minimal Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Spatial Activities of Leopard Cats in Xinlong, China
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Species Distribution Data
2.2.2. Environment Variables
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Ensemble Species Distribution Models
2.3.2. Assessment of Habitat Landscapes
2.3.3. Two-Species Occupancy Model
3. Results
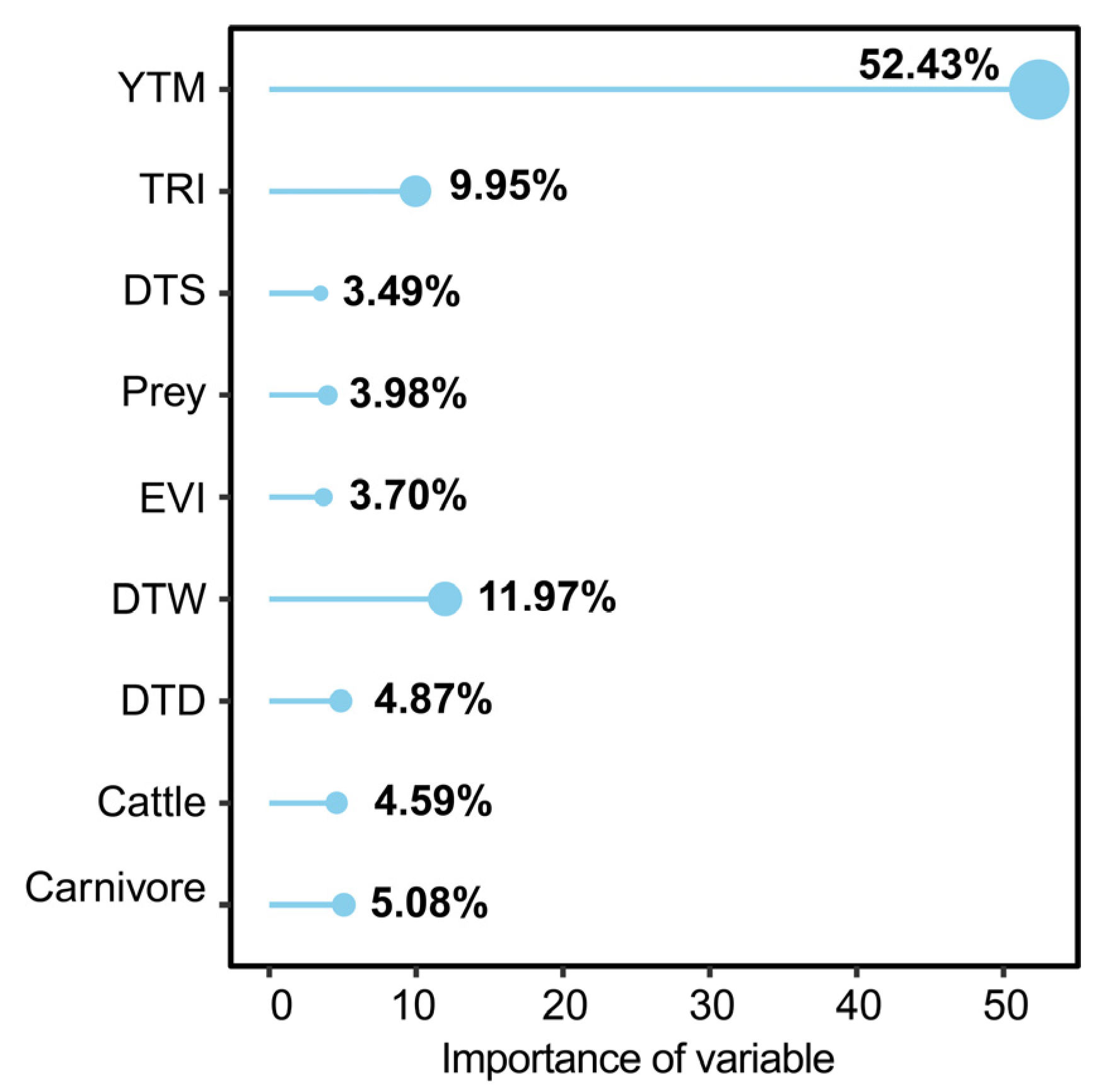
3.1. Habitat Distribution
3.2. Landscape Patterns of Potential Habitats
3.3. Spatial Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimm, S.L.; Jenkins, C.N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T.M.; Gittleman, J.L.; Joppa, L.N.; Raven, P.H.; Roberts, C.M.; Sexton, J.O. The Biodiversity of Species and Their Rates of Extinction, Distribution, and Protection. Science 2014, 344, 6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripple, W.J.; Estes, J.A.; Beschta, R.L.; Wilmers, C.C.; Ritchie, E.G.; Hebblewhite, M.; Berger, J.; Elmhagen, B.; Letnic, M.; Nelson, M.P.; et al. Status and Ecological Effects of the World’s Largest Carnivores. Science 2014, 343, 1241484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, C.; Ripple, W.J. Range Contractions of the World’s Large Carnivores. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marneweck, C.; Butler, A.; Gigliotti, L.; Harris, S.; Jensen, A.; Muthersbaugh, M.; Newman, B.; Saldo, E.; Shute, K.; Titus, K.; et al. Shining the spotlight on small mammalian carnivores: Global status and threats. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 255, 109005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodroffe, R.; Ginsberg, J.R. Edge Effects and the Extinction of Populations Inside Protected Areas. Science 1998, 280, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inskip, C.; Zimmermann, A. Human-felid conflict: A review of patterns and priorities worldwide. Oryx 2009, 43, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveridge, A.J.; Sousa, L.L.; Seymour-Smith, J.; Hunt, J.; Coals, P.; O’Donnell, H.; Lindsey, P.A.; Mandisodza-Chikerema, R.; Macdonald, D.W. Evaluating the Spatial Intensity and Demographic Impacts of Wire-Snare Bush-Meat Poaching on Large Carnivores. Biol. Conservat. 2020, 244, 108504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimirey, Y.; Petersen, W.; Jahed, N.; Akash, M.; Lynam, A.J.; Kun, S.; Din, J.; Nawaz, M.A.; Singh, P.; Dhendup, T.; et al. Prionailurus bengalensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: E.T223138747A78117. 2022. Available online: https://www.mybis.gov.my/sp/20358 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Rasphone, A.; Kamler, J.F.; Tobler, M.; Macdonald, D.W. Density trends of wild felids in northern Laos. Biodivers. Conserv. 2021, 30, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chang, A.-M.; Wada, T.; Chen, M.-T.; Tu, Y.-S. Distribution of Carnivore protoparvovirus 1 in free-living leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis chinensis) and its association with domestic carnivores in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Bu, X.; Xiang, R.; Lu, Q.; Cui, S.; Hao, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Meng, X. Summer habitat selection and impacts of human disturbance on leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis). Ecosyst. Heal. Sustain. 2020, 6, 1856630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Sollmann, R.; Bernard, H.; Ambu, L.N.; Lagan, P.; Mannan, S.; Hofer, H.; Wilting, A. Density and Habitat Use of the Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) in Three Commercial Forest Reserves in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. J. Mammal. 2013, 94, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, A.P.; Naim, M.; Advento, A.D.; Aryawan, A.A.K.; Ps, S.; Caliman, J.-P.; Verwilghen, A.; Veron, G. Diversity and occupancy of small carnivores within oil palm plantations in central Sumatra, Indonesia. Mammal Res. 2015, 60, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, A.S.C.; Aryawan, A.A.K.; Advento, A.D.; Purnomo, D.; Wahyuningsih, R.; Luke, S.H.; Ps, S.; Snaddon, J.L.; Foster, W.A.; Naim, M.; et al. Understory Vegetation in Oil Palm Plantations Promotes Leopard Cat Activity, but Does Not Affect Rats or Rat Damage. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2019, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, E.; Dullemont, H.; Wang, C.-H.; Zhang, J.-W.; Lin, J.-L.; Pei, K.J.-C.; Lai, Y.-C. Fine-Scaled Selection of Resting and Hunting Habitat by Leopard Cats (Prionailurus bengalensis) in a Rural Human-Dominated Landscape in Taiwan. Animals 2023, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Li, H.-D.; Xiao, W.; Xu, K.; Ren, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Fan, M.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Z. Fine-Scale Interactions between Leopard Cats and Their Potential Prey with Contrasting Diel Activities in a Livestock-Dominated Nature Reserve. Animals 2023, 13, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity Hotspots for Conservation Priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.G.; Li, S.X.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Tam, C.; Chen, X.D. Ecological and Socioeconomic Effects of China’s Policies for Ecosystem Services. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Seyler, B.C.; Phuntsok, T.S.; Lu, Y.; Tsomo, L. Traditional beliefs, culture, and local biodiversity protection: An ethnographic study in the Shaluli Mountains Region, Sichuan Province, China. J. Nat. Conserv. 2022, 68, 126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; McShea, W.J.; Garshelis, D.L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Shao, L. Human-wildlife conflicts influence attitudes but not necessarily behaviors: Factors driving the poaching of bears in China. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Chen, X.; Pan, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Song, D.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L. Habitat Selection Differences of Two Sympatric Large Carnivores in the Southwestern Mountains of China. Diversity 2023, 15, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Song, W.; Lee, M.J. Habitat Potential Mapping of Marten (Martes flavigula) and Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) in South Korea Using Artificial Neural Network Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Azlan, J.; Kaicheen, S.S.; Hong, L.L.C.; Yi, M.C.K.; Maiwald, M.J.; Helmy, O.E.; Giordano, A.J.; Brodie, J.F. Ecology, occurrence and distribution of wild felids in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo. Oryx 2023, 57, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Bhattacharya, T.; Poudyal, K.; Sathyakumar, S.; Qureshi, Q. Integrating Aspects of Ecology and Predictive Model-ling: Implications for the Conservation of the Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) in the Eastern Himalaya. Acta Theriol. 2014, 59, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Ndvi and Evi at 30m Spatial Resolution on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau (2013, 2018). In National Tibetan Plateau Data Center. 2022. Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/view/export/exportWordMetadata?metadataId=39b2154d-2164-4c33-b50d-c1c7adb9c738&isChinese=false (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Guisan, A.; Tingley, R.; Baumgartner, J.B.; Naujokaitis-Lewis, I.; Sutcliffe, P.R.; Tulloch, A.I.T.; Regan, T.J.; Brotons, L.; McDonald-Madden, E.; Mantyka-Pringle, C.; et al. Predicting Species Distributions for Conservation Decisions. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Wang, Y. Applying various algorithms for species distribution modelling. Integr. Zoöl. 2013, 8, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Lafourcade, B.; Engler, R.; Araújo, M.B. BIOMOD—A platform for ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Ecography 2009, 32, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qiao, H.; Wang, R.; Wei, H.; Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Li, X. Challenges and Development Trend of Species Dis-tribution Model. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.C.; Crespo, E.G.; Paulo, O.S. Modelling wildlife distributions: Logistic Multiple Regression vs Overlap Analysis. Ecography 1999, 22, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, A.; Gu, J.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, P.; Ma, J.; Jiang, G. Effects of human disturbance on vegetation, prey and Amur tigers in Hunchun Nature Reserve, China. Ecol. Model. 2017, 353, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Additive Logistic Regression: A Statistical View of Boosting. Ann. Stat. 2000, 28, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, B.; Bowen, R.; Griffin, C.; Mcgarigal, K. A Classification-tree Analysis of Nesting Habitat in an Island Population of Northern Harriers. Condor 2008, 110, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Machine Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillotto, L.; Mori, E.; Bosso, L.; Agnelli, P.; Russo, D. The Balkan long-eared bat (Plecotus kolombatovici) occurs in Italy—First confirmed record and potential distribution. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 96, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1998, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, G.; Lewis, J.S.; Gerber, B.D. Recommended survey designs for occupancy modelling using motion-activated cameras: Insights from empirical wildlife data. PeerJ 2014, 2, e532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.H.; Shu, Z.F.; Chen, L.J.; Yao, W.T.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xiao, Z.S. Using Occupancy Models in Wildlife Cam-era-Trapping Monitoring and the Study Case. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, D.I.; Nichols, J.D.; Lachman, G.B.; Droege, S.; Royle, J.A.; Langtimm, C.A. Estimating Site Occupancy Rates When Detection Probabilities Are Less Than One. Ecology 2002, 83, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodal Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, O.M.W.; Hines, J.E.; Beissinger, S.R. Two-species occupancy models: A new parameterization applied to co-occurrence of secretive rails. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraci, J.P.; Clinchy, M.; Zanette, L.Y.; Wilmers, C.C. Fear of humans as apex predators has landscape-scale impacts from mountain lions to mice. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangas, J.G.; Rodríguez-Estival, J. Logging and livestock influence the abundance of common mammal species in Mediterranean forested environments. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; McShea, W.J.; Wang, D.; Li, S. Shared resources between giant panda and sympatric wild and domestic mammals. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 186, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choki, K.; Dhendup, P.; Tenzin, J.; Dorji, D.; Tenzin, K.; Wangmo, T.; Penjor, U. Conservation potential of non-protected area for sympatric carnivores in Bhutan. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 42, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Brown, C.; Dettlaff, M.A.; Batbaatar, A.; Grenke, J.; Bao, T.; Heida, I.P.; Cahill, J.F. The effects of livestock grazing on biodiversity are multi-trophic: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T. Progress in the research and conservation of China’s Felidae species. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 22560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, M.; Doi, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Teranishi, A. Ecology and conservation of two endangered subspecies of the leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) on Japanese islands. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Song, G.; Zhang, D.; Jia, C.; Fan, P.; Hao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Lei, F. Distribution pattern and driving factors of genetic diversity of passerine birds in the Mountains of Southwest China. Avian Res. 2022, 13, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, T.; Pan, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L. Studying the Coexistence Mechanisms of Small Carnivores in an Ideal Research Area of the Mountains of Southwest China. Global Ecol. Conservat. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Vitekere, K.; Wang, J.; Karanja, H.; Consolée, K.T.; Jiang, G.; Hua, Y. Dynamic in Species Estimates of Carnivores (Leopard Cat, Red Fox, and North Chinese Leopard): A Multi-Year Assessment of Occupancy and Coexistence in the Tieqiaoshan Nature Reserve, Shanxi Province, China. Animals 2020, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, W.J.; Savini, T.; Steinmetz, R.; Ngoprasert, D. Periodic resource scarcity and potential for interspecific competition influences distribution of small carnivores in a seasonally dry tropical forest fragment. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 95, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horncastle, V.J.; Chambers, C.L.; Dickson, B.G. Grazing and wildfire effects on small mammals inhabiting montane meadows. J. Wildl. Manag. 2019, 83, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.P.; Sullivan, D.S. Fertilisation, Cattle Grazing and Voles: Collapse of Meadow Vole Populations in Young Forests? Wildlife Res. 2014, 41, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.; Swanson, S.; Tsocanos, S.; Mccue, S. Lentic Meadows and Riparian Functions Impaired After Horse and Cattle Grazing. J. Wildl. Manag. 2021, 85, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Kang, D. Integrating Livestock Grazing and Sympatric Takin to Evaluate the Habitat Suitability of Giant Panda in the Wanglang Nature Reserve. Animals 2021, 11, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prugh, L.R.; Cunningham, C.X.; Windell, R.M.; Kertson, B.N.; Ganz, T.R.; Walker, S.L.; Wirsing, A.J. Fear of Large Carnivores Amplifies Human-Caused Mortality for Mesopredators. Science 2023, 380, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Gu, X.; Song, D.; Yang, B. Camera trapping reveals area of conservation significance for large and medium-sized mammals on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Oryx 2022, 56, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

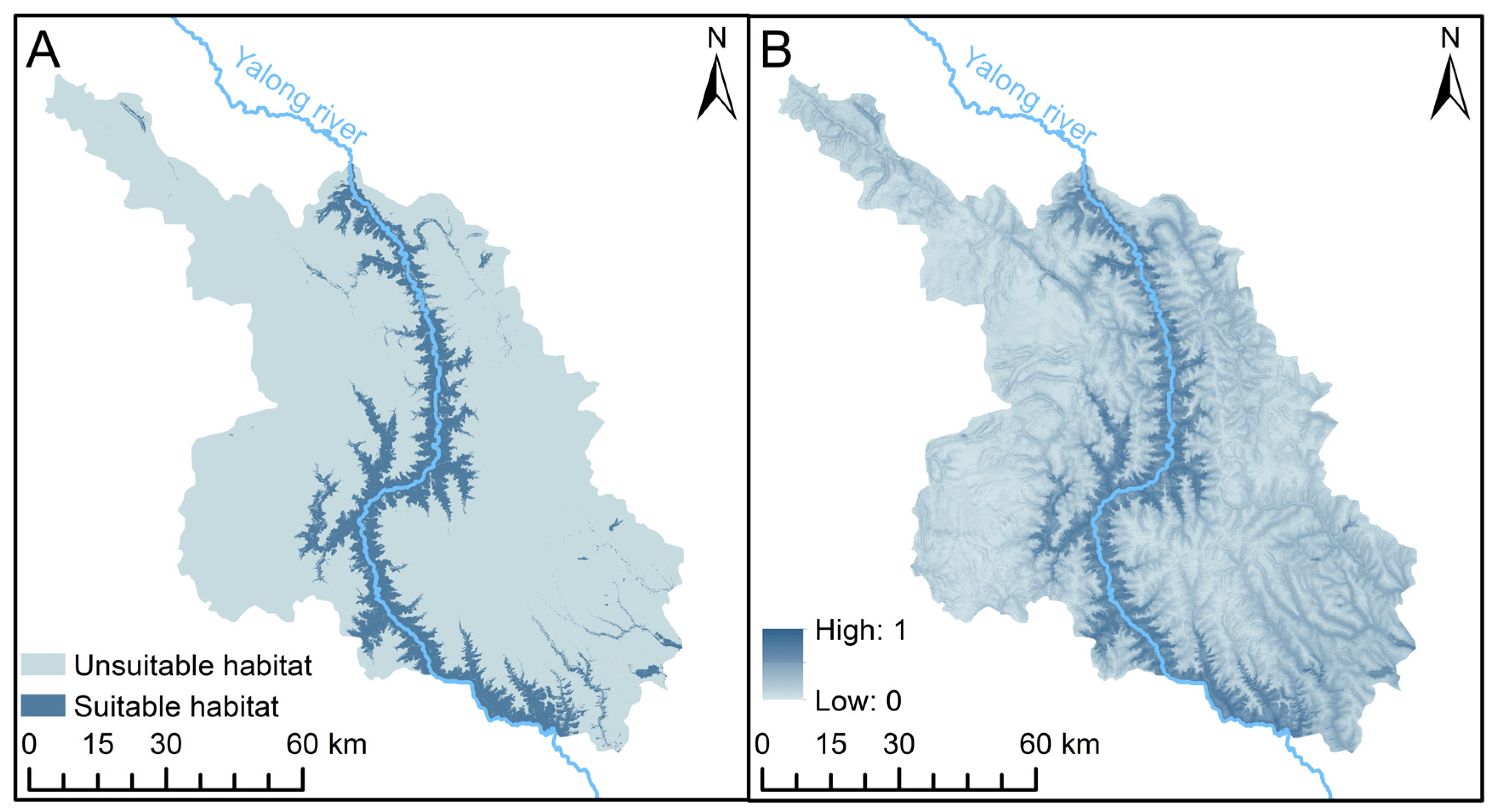

| Landscape Index | Leopard Cats’ Habitat | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable | Unsuitable | ||
| Fragmentation | Number of patches, NP | 6903 | 8782 |
| Patch density, PD (ind./km2) | 0.7426 | 0.9448 | |
| Largest patch index, LPI (%) | 13.1019 | 42.4762 | |
| Mean patch size, MPS (km2) | 19.1935 | 90.7582 | |
| Connectivity | Patch cohesion index, COHESION (%) | 99.8979 | 99.9644 |
| Landscape division index, DIVISION | 0.9828 | 0.644 | |
| Splitting index, SPLIT | 58.2374 | 2.8087 | |
| Human disturbance | Perimeter–area fractal dimension, PAFRAC | 1.4656 | 1.4181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Tian, T.; Pan, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, Q.; Tang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L. The Minimal Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Spatial Activities of Leopard Cats in Xinlong, China. Animals 2023, 13, 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213328
Chen X, Tian T, Pan H, Jin Y, Zhang X, Long Q, Tang L, Yang B, Zhang L. The Minimal Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Spatial Activities of Leopard Cats in Xinlong, China. Animals. 2023; 13(21):3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213328
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xing, Tengteng Tian, Han Pan, Yuyi Jin, Xiaodian Zhang, Qinggang Long, Ling Tang, Biao Yang, and Li Zhang. 2023. "The Minimal Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Spatial Activities of Leopard Cats in Xinlong, China" Animals 13, no. 21: 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213328
APA StyleChen, X., Tian, T., Pan, H., Jin, Y., Zhang, X., Long, Q., Tang, L., Yang, B., & Zhang, L. (2023). The Minimal Impact of Anthropogenic Disturbances on the Spatial Activities of Leopard Cats in Xinlong, China. Animals, 13(21), 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13213328








