Impact of Season on Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Pathogenic Diversity in Two Captive Duck Species
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Potentially Pathogenic Bacterial Identification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis and Keystone Taxa
3. Results
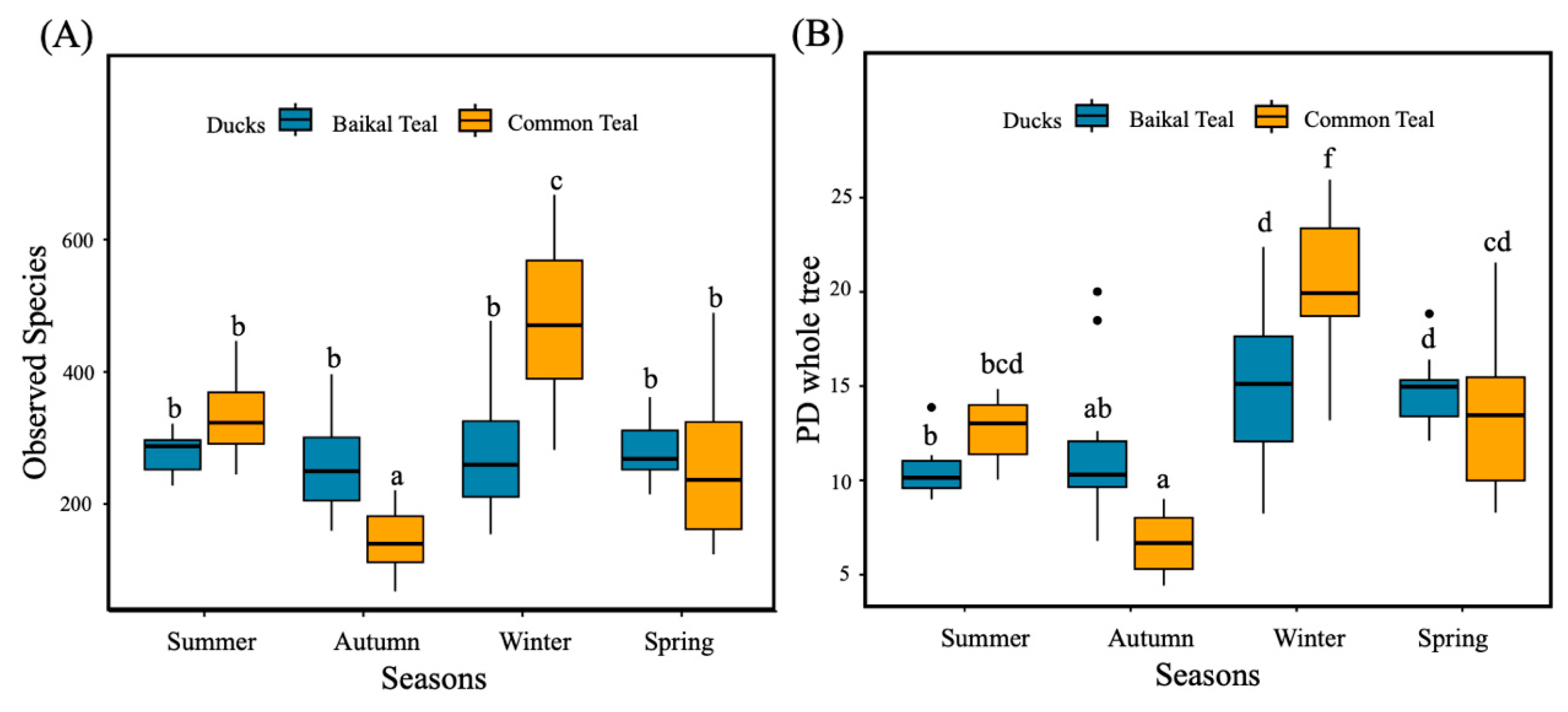
3.1. Intestinal Bacterial Alpha Diversity
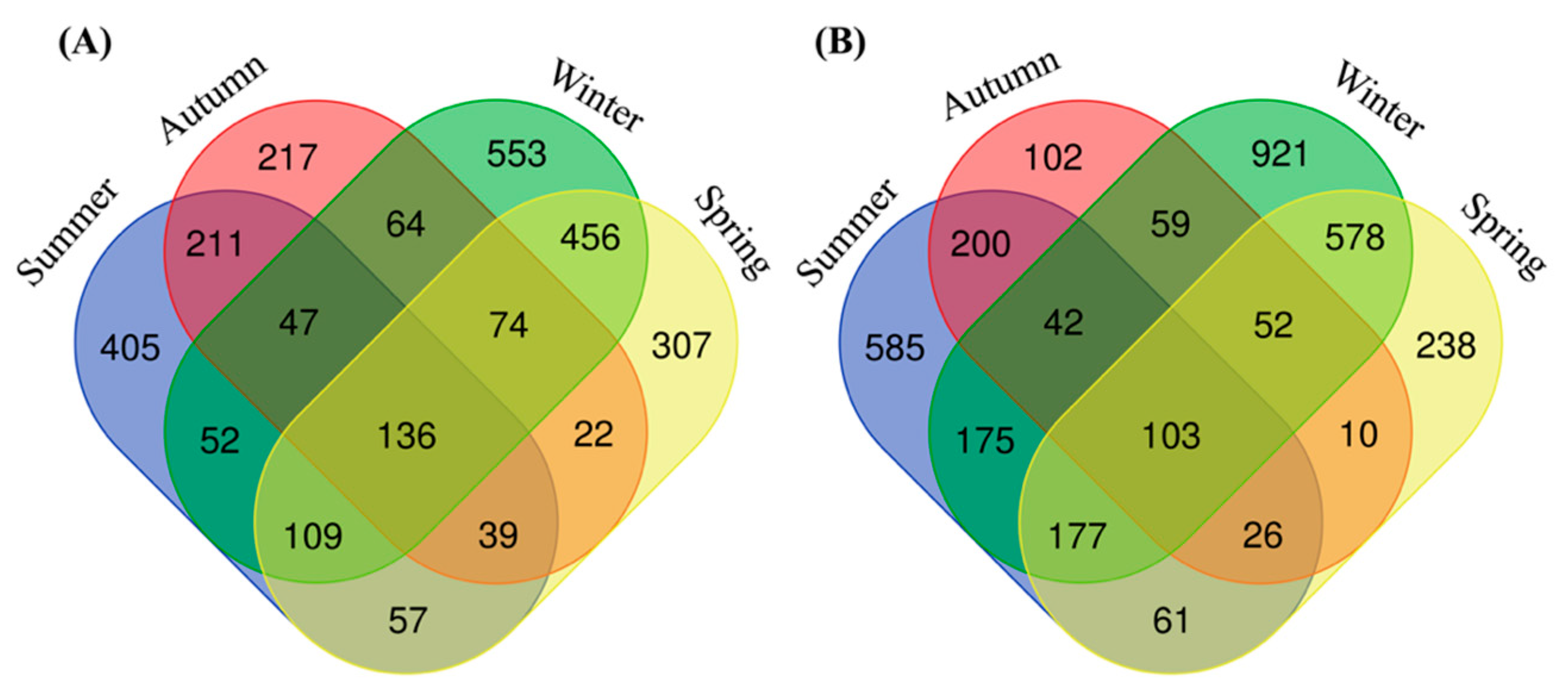
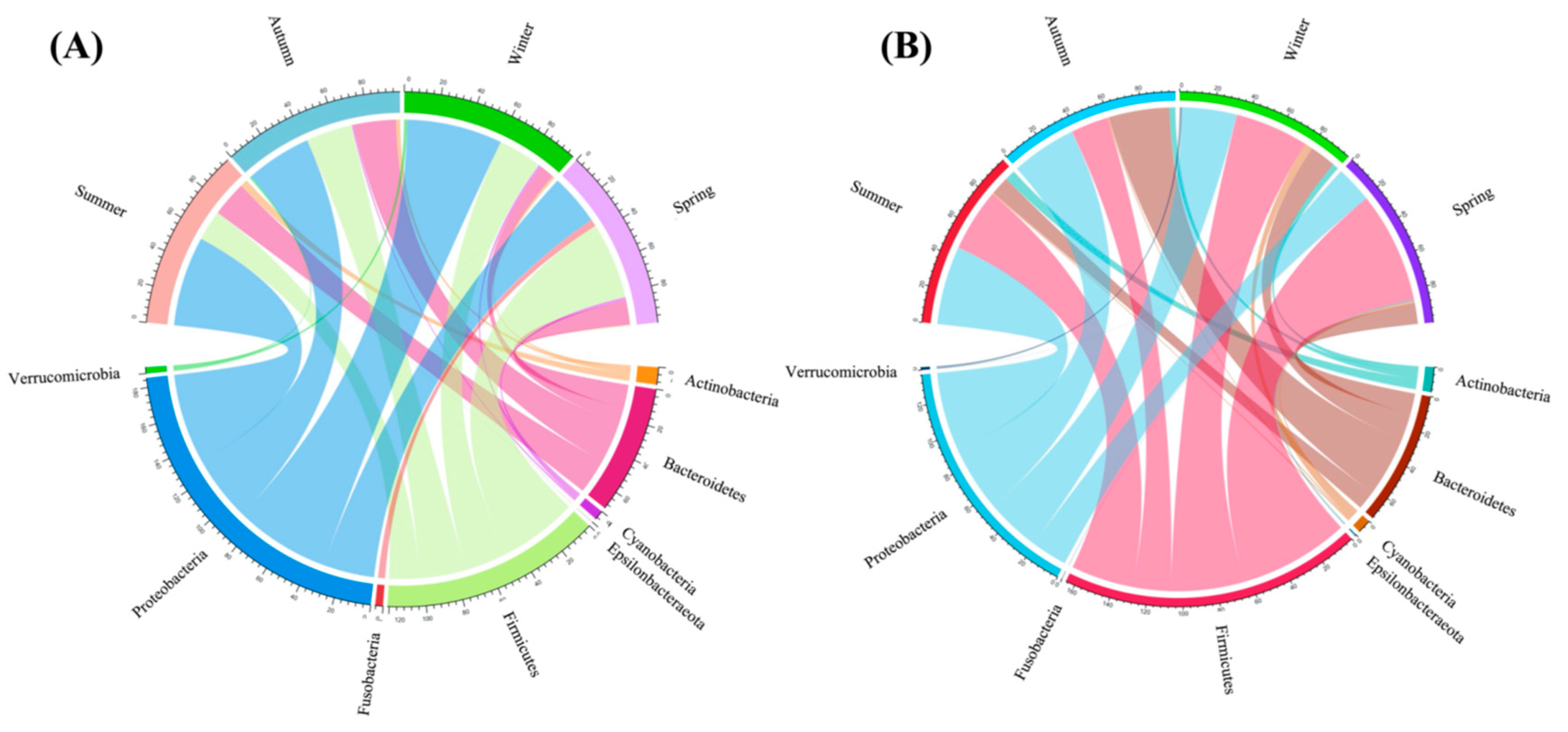
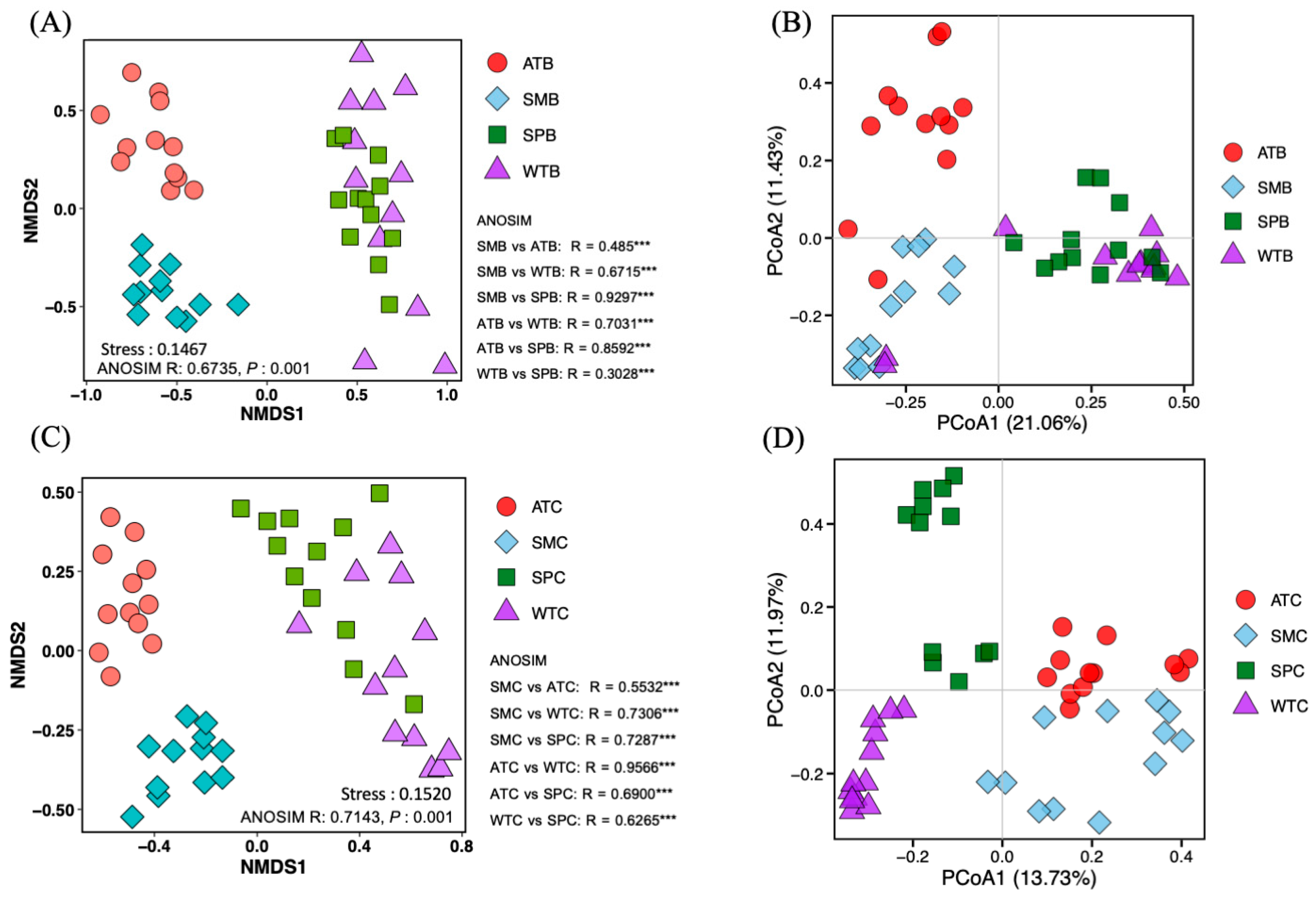
3.2. Intestinal Bacterial Community Structure
3.3. Co-Occurrence Pattern and Keystone Taxa of Intestinal Microbial Communities
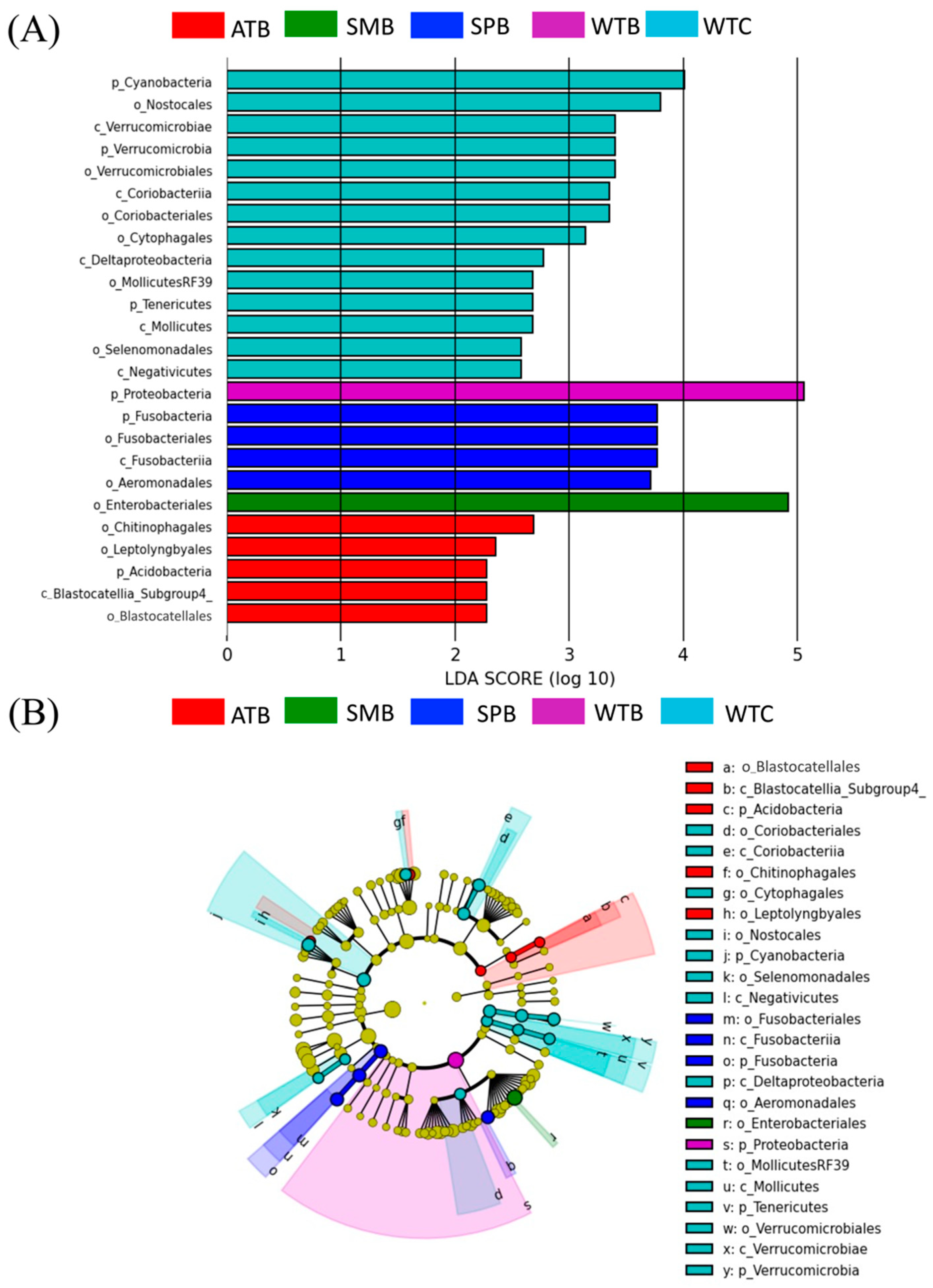
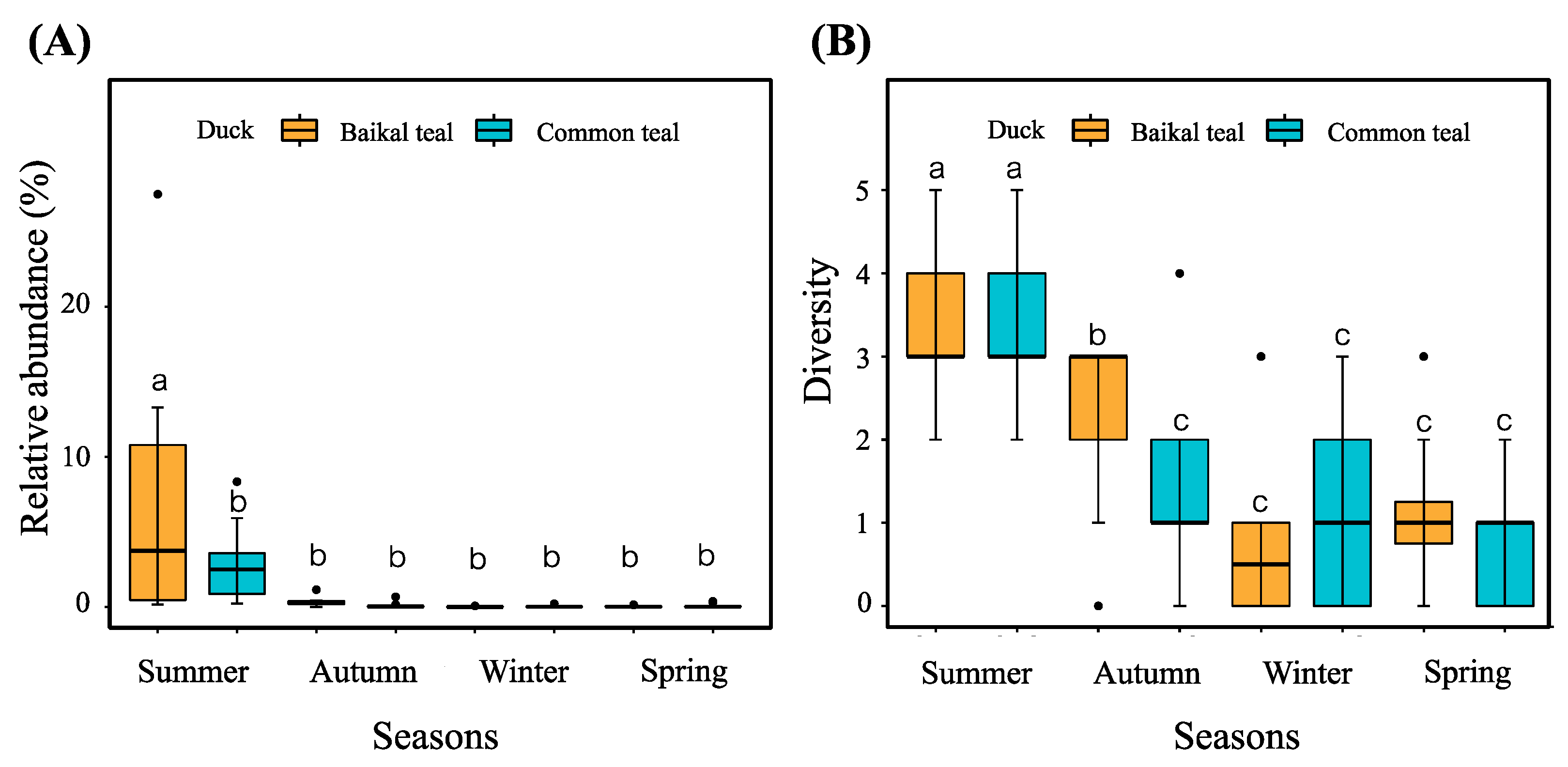
3.4. Potential Pathogenic Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. The Intestinal Bacterial Composition
4.2. Seasonal Variation Effect
4.3. Co-Occurrence Network and Key Taxa
4.4. Pathogenic Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barko, P.C.; McMichael, M.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Williams, D.A. The gastrointestinal microbiome: A review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schretter, C.E. Links between the gut microbiota, metabolism, and host behavior. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Yun, C.; Pang, Y.; Qiao, J. The impact of the gut microbiota on the reproductive and metabolic endocrine system. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1894070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya-Ciriaco, N.; Gómez-Acata, S.; Muñoz-Arenas, L.C.; Dendooven, L.; Estrada-Torres, A.; Vega-Pérez, A.H.D.; Navarro-Noya, Y.E. Dietary effects on gut microbiota of the mesquite lizard Sceloporus grammicus (Wiegmann, 1828) across different altitudes. Microbiome 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ding, H. Effects of diet shift on the gut microbiota of the critically endangered Siberian Crane. Avian Res. 2023, 14, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, M.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xu, H. Seasonal dynamics of gut microbiota in a cohort of wild Tibetan macaques (Macaca thibetana) in western China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 25, e01409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, J.; Moeller, A.H. The effects of temperature on animal gut microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.H.; Ivey, K.; Cornwall, M.B.; Herr, K.; Rede, J.; Taylor, E.N.; Gunderson, A.R. The lizard gut microbiome changes with temperature and is associated with heat tolerance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01181-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Wong, M.K.S.; Hyodo, S.; Goto, S.; Hamasaki, K. Temperature modulation alters the gut and skin microbial profiles of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1027621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, M.W.; Matson, K.D.; Versteegh, M.A.; van der Velde, M.; Parmentier, H.K.; Arts, J.; Salles, J.F.; Tieleman, B.I. Gut microbiota of homing pigeons shows summer–winter variation under constant diet indicating a substantial effect of temperature. Anim. Microbiome 2022, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Maltecca, C.; Tiezzi, F. Potential use of gut microbiota composition as a biomarker of heat stress in monogastric species: A review. Animals 2021, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Wijmenga, C.; Fu, J.; Zhernakova, A. Host genetics and gut microbiome: Challenges and perspectives. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Zhang, F.; Fu, R.; Yan, S.; Zhou, L. Significant differences in bacterial and potentially pathogenic communities between sympatric hooded crane and greater white-fronted goose. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrop, A.H.; McGowan, R.Y. Britain’s first Baikal teal. British Birds 2009, 102, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Tajiri, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Tagome, K.; Nakano, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yamamura, Y.; Ohkawara, K. Satellite telemetry of the annual migration of Baikal Teal Anas formosa wintering at Katano-kamoike, Ishikawa, Japan. Ornithol. Sci. 2015, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.P.; Han, S.W.; Paik, I.H.; Jin, S.D.; Paek, W.K. Status of wintering populations of the Baikal teal (Anas formosa) in Geumgang River, Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2014, 7, e213–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, R.R.; Khan, A.; Noor-un-Nisa, R.A.; Hadi, R. Hymenolepis jonesae n.sp. (Cestode) in common teal (Anas Crecca Linn.) from Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 13, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Youssefi, M.R.; Hosseini, S.H.; Tabarestani, A.H.A.; Ardeshir, H.A.; Jafarzade, F.; Rahimi, M.T. Gastrointestinal helminthes of green–winged teal (Anas crecca) from North Iran. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S143–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W. Diversity of wintering waterbirds enhanced by restoring aquatic vegetation at Shengjin Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D.; Gallagher, K.; Youngblut, N.; Buckley, D.; Zinder, S. Millimeter-scale patterns of phylogenetic and trait diversity in a salt marsh microbial mat. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Huang, M.; Qian, L.; Yan, X.; Lv, Q.; Ye, H.; Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, W.Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. The depletion of carbohydrate metabolic genes in the gut microbiome contributes to the transition from central obesity to type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 747646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Lin, Q.; Qu, J. Gut microbiota in Tibetan herdsmen reflects the degree of urbanization. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Raoul, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Pulcini, G.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. Food components and dietary habits: Keys for a healthy gut microbiota composition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.; Sandercock, B.K.; Jumpponen, A.; Zeglin, L.H. The avian gut microbiota: Community, physiology and function in wild birds. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhao, G.; Song, Y.; Zhou, L. Variations in gut bacterial communities of hooded crane (Grus monacha) over spatial-temporal scales. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, P.R.; Tamrakar, N.; Singh, L.; Tandon, A.; Sharma, D. Rice nutritional and medicinal properties: A review article. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, R.; Dharumadurai, D.; Manogaran, G.P. An Introduction to Actinobacteria. In Actinobacteria-Basics and Biotechnological Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Cao, L. Characterising the interspecific variations and convergence of gut microbiota in Anseriformes herbivores at wintering areas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Song, Y. The gut microbiome of hooded cranes (Grus monacha) wintering at Shengjin Lake, China. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 6, e00447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, L. Comparing the intestinal bacterial communities of sympatric wintering hooded crane (Grus monacha) and domestic goose (Anser anser domesticus). Avian Res. 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Y.; Yan, S.; Song, Y.; Zhou, L. Significant differences in the gut bacterial communities of hooded crane (Grus monacha) in different seasons at a stopover site on the flyway. Animals 2020, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, L. Is intestinal bacterial diversity enhanced by trans-species spread in the mixed-species flock of hooded crane (Grus monacha) and bean goose (Anser fabalis) wintering in the lower and middle Yangtze River floodplain? Animals 2021, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, N.; Xu, W. Effects of variation in food resources on foraging habitat use by wintering hooded cranes (Grus monacha). Avian Res. 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.; Ryu, H.; Baker, A.J.; Santo Domingo, J.W.; Buehler, D.M. Gastro-intestinal microbiota of two migratory shorebird species during spring migration staging in Delaware Bay, USA. J. Ornithol. 2014, 155, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Duan, L.; Wei, C.; Wang, M.; Jin, J.; Liu, S.; Mehmood, K.; Shahzad, M. Comparison of the intestinal microbial community in ducks reared differently through high-throughput sequencing. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9015054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Song, S.J.; Delsuc, F.; Prest, T.L.; Oliverio, A.M.; Korpita, T.M.; Alexiev, A.; Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Kowalewski, M.; et al. The effects of captivity on the mammalian gut microbiome. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedová, L.; Kreisinger, J.; Kubovčiak, J.; Těšický, M.; Martin, J.F.; Tomášek, O.; Kauzálová, T.; Sedláček, O.; Albrecht, T. Gut microbiota variation between climatic zones and due to migration strategy in passerine birds. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1080017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeen, H.R.; Willard, D.E.; Jones, A.W.; Winger, B.M.; Gyllenhaal, E.F.; Tsuru, B.R.; Hackett, S.J.; Novembre, J. Intestinal microbiota of Nearctic-Neotropical migratory birds vary more over seasons and years than between host species. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 3290–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Tao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Y. Temporal variations in the gut microbiota of the globally endangered Sichuan partridge (Arborophila rufipectus): Implications for adaptation to seasonal dietary change and conservation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00747-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestion, E.; Jacob, S.; Zinger, L.; Di Gesu, L.; Richard, M.; White, J.; Cote, J. Climate warming reduces gut microbiota diversity in a vertebrate ectotherm. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Suarez-Zamorano, N.; Tarallo, V.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rigo, D.; Fabbiano, S.; Stevanović, A.; Hagemann, S.; et al. Gut microbiota orchestrates energy homeostasis during cold. Cell 2015, 163, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Nonaka, I.; Higuchi, K.; Takusari, N.; Kurihara, M.; Takenaka, A.; Mitsumori, M.; Kajikawa, H.; Aminov, R.I. Influence of high temperature and humidity on rumen bacterial diversity in Holstein heifers. Anaerobe 2007, 13, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, R.; Wu, N.; Zhu, G.; Yang, C. Heat stress mediates changes in fecal microbiome and functional pathways of laying hens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Lear, G.; Lewis, G.D. Time after time: Detecting annual patterns in stream bacterial biofilm communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2502–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, M.; Stenuit, B.; Ho, J.; Wang, A.; Parke, C.; Knight, M.; Alvarez-Cohen, L.; Shapira, M. Assembly of the Caenorhabditis elegans gut microbiota from diverse soil microbial environments. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.H.; Qu, Y.F. Comparative study on gut microbiota in three Anura frogs from a mountain stream. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, G.; Leunert, F.; Cirés, S.; Jöhnk, K.D.; Rücker, J.; Nixdorf, B.; Wiedner, C. Competitiveness of invasive and native cyanobacteria from temperate freshwaters under various light and temperature conditions. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.A.; Bolte, L.A.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo-Cravo, A.P.; Schmeller, D.S.; Chatzinotas, A.; Vredenburg, V.T.; Loyau, A. Environmental factors and host microbiomes shape host–pathogen dynamics. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchado, M.S.; Lauber, M.; Reitmeier, S.; Kacprowski, T.; Baumbach, J.; Haller, D.; List, M. Network analysis methods for studying microbial communities: A mini-review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2687–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial community structure and its functional implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Baah-Acheamfour, M.; Carlyle, C.N.; Bissett, A.; Richardson, A.E.; Siddique, T.; Bork, E.W.; Chang, S.X. Determinants of bacterial communities in Canadian agroforestry systems. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Elser, J.J.; Gsell, A.S.; Huszar, V.L.; Ibelings, B.W.; Jeppesen, E.; Kosten, S.; Mooij, W.M.; Roland, F.; Sommer, U.; et al. Plankton dynamics under different climatic conditions in space and time. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Teng, J.H.; Song, J.X.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, Q. The seasonal variation of microbial communities in drinking water sources in Shanghai. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.B.; Vasconcelos, E.J.; Diniz, P.P.; Calloway, K.N.; Richardson, E.; Meinersmann, R.J.; Cox, N.A.; Berrang, M.E. The cecal microbiome of commercial broiler chickens varies significantly by season. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, L.D.; Hernández, A.M.; Peimbert, M. Exploring the cockatiel (Nymphicus hollandicus) fecal microbiome, bacterial inhabitants of a worldwide pet. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Sharshov, K.; Cao, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Distinctive gut microbial community structure in both the wild and farmed Swan goose (Anser cygnoides). J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberán, A.; Ramirez, K.S.; Leff, J.W.; Bradford, M.A.; Wall, D.H.; Fierer, N. Why are some microbes more ubiquitous than others? Predicting the habitat breadth of soil bacteria. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulreesh, H.H.; Paget, T.A.; Goulder, R. Campylobacter in waterfowl and aquatic environments: Incidence and methods of detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7122–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Matabang, M.A.; Miller, D.; Aggarwal, R.; LaFortune, A. First case report on Empedobacter falsenii Bacteremia. IDCases 2023, 33, e01814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Dong, N.; Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Lu, J.; Shu, L.; Cheng, Q.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. Emergence of an Empedobacter falsenii strain harbouring a tet (X)-variant-bearing novel plasmid conferring resistance to tigecycline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, D.D.; Pacheco, A.; Lindner, A.S. Detecting potential pathogens on hospital surfaces: An assessment of carpet tile flooring in the hospital patient environment. Indoor Built Environ. 2010, 19, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Oshaghi, M.A.; Afshar, D.; Arandian, M.H.; Hajikhani, S.; Akhavan, A.A.; Yakhchali, B.; Shirazi, M.H.; Rassi, Y.; Jafari, R.; et al. Aerobic bacterial flora of biotic and abiotic compartments of a hyperendemic zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis (ZCL) focus. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Yoon, J.H.; Takeuchi, M.; Pyun, Y.R.; Park, Y.H. Sphingomonas aquatilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas koreensis sp. nov., and Sphingomonas taejonensis sp. nov., yellow-pigmented bacteria isolated from natural mineral water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbjerg, L.H.; Gaini, S.; Justesen, U.S. First report of Sphingomonas koreensis as a human pathogen in a patient with meningitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, J.; Frei, R.; Burkhalter, F. A rare case of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis with Sphingomonas koreensis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2016, 36, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidoux, O.; Argenson, J.N.; Jacomo, V.; Drancourt, M. Molecular identification of a Dietzia maris hip prosthesis infection isolate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2634–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azcona, J.M.; Arponen, S.; Sarriá, C.; Sáez-Nieto, J.A.; López-Brea, M.; de las Cuevas, M.C. Isolation of Dietzia maris from bone marrow in an immunocompetent patient. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2011, 33, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, J.; Velkers, F.C.; Bouwstra, R.J.; Beerens, N.; Stegeman, J.A.; de Boer, W.F.; van Hooft, P.; Elbers, A.R.W.; Bossers, A.; Jurburg, A.D. An observational field study of the cloacal microbiota in adult laying hens with and without access to an outdoor range. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Human campylobacteriosis: A public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, G.D.; Hoar, B.M.; Whiteside, D.P.; Morck, D.W. Campylobacter canadensis sp. nov., from captive whooping cranes in Canada. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Gulhan, T. Campylobacter in wild birds: Is it an animal and public health concern? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 812591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, J.; Eddington, H.; Christman, N.D.; Pryor, W.; Chaston, J.M.; Erickson, D.L.; Wilson, E. Increased microbial diversity and decreased prevalence of common pathogens in the gut microbiomes of wild turkeys compared to domestic turkeys. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01423-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, H.C.; Hald, T.; Wong, L.F.; Madsen, M.; Korsgaard, H.; Bager, F.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Mølbak, K. Salmonella control programs in Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Hong, M.; Wang, Y.; Dong, P.; Cheng, H.; Yan, H.; Yao, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. Assessing the risks of potential bacterial pathogens attaching to different microplastics during the summer–autumn period in a mariculture cage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhai, S.; Li, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Q.; Shan, H.; Liu, S. Identification of Vibrio alginolyticus as a causative pathogen associated with mass summer mortality of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) in China. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, J.; Khattak, R.H.; Li, Z.; Teng, L.; Liu, Z. Insights into the composition of gut microbiota in response to environmental temperature: The case of the Mongolia racerunner (Eremias argus). Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 36, e02125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.P.; Welsh, M.E.; Dekkers, M.G.; Abercrombie, S.T.; Mitchell, C.E. Host physiological phenotype explains pathogen reservoir potential. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, S.A.; Genersch, E.; McMahon, D.P.; Rafaluk-Mohr, C.; Rolff, J. Tripartite interactions: How immunity, microbiota and pathogens interact and affect pathogen virulence evolution. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 50, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Luangtongkum, T. The worldwide trend of Campylobacter spp., infection from duck-related isolates and associated phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance, since 1985: Identifying opportunities and challenges for prevention and control. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeli, S.; Thomann, A.; Wyss, F.; Kuehni-Boghenbor, K.; Brodard, I.; Perreten, V. Arsenicicoccus dermatophilus sp. nov., a hypha-forming bacterium isolated from the skin of greater flamingos (Phoenicopterus roseus) with pododermatitis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 4046–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.; Shaaban, H.; Sensakovic, J.W.; Perez, G. An interesting case of Empedobacter brevis bacteremia after right knee cellulitis. J. Glob. Infect. 2012, 4, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, A.I.; Fernandez, A.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Sierra, E.; Mendez, M.; Arbelo, M.; Ventosa, A.; Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F. Flavobacterium ceti sp. nov., isolated from beaked whales (Ziphius cavirostris). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2604–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Ryoo, N. A case of Flavobacterium ceti meningitis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyburgh, C.M.; Bragg, R.R.; Boucher, C.E. Lactococcus garvieae: An emerging bacterial pathogen of fish. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 123, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, R.; Szuplewska, M.; Mitura, M.; Decewicz, P.; Chmielowska, C.; Pawłot, A.; Sebtkowska, D.; Czarnecki, J.; Bartosik, D. Genome structure of the opportunistic pathogen Paracoccus yeei (Alphaproteobacteria) and identification of putative virulence factors. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herp, S.; Durai Raj, A.C.; Salvado Silva, M.; Woelfel, S.; Stecher, B. The human symbiont Mucispirillum schaedleri: Causality in health and disease. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 210, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakda, P.; Xiang, X.; Song, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L. Impact of Season on Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Pathogenic Diversity in Two Captive Duck Species. Animals 2023, 13, 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243879
Sakda P, Xiang X, Song Z, Wu Y, Zhou L. Impact of Season on Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Pathogenic Diversity in Two Captive Duck Species. Animals. 2023; 13(24):3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakda, Patthanan, Xingjia Xiang, Zhongqiao Song, Yuannuo Wu, and Lizhi Zhou. 2023. "Impact of Season on Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Pathogenic Diversity in Two Captive Duck Species" Animals 13, no. 24: 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243879
APA StyleSakda, P., Xiang, X., Song, Z., Wu, Y., & Zhou, L. (2023). Impact of Season on Intestinal Bacterial Communities and Pathogenic Diversity in Two Captive Duck Species. Animals, 13(24), 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243879







