Wind Speed and Landscape Context Mediate Campylobacter Risk among Poultry Reared in Open Environments
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
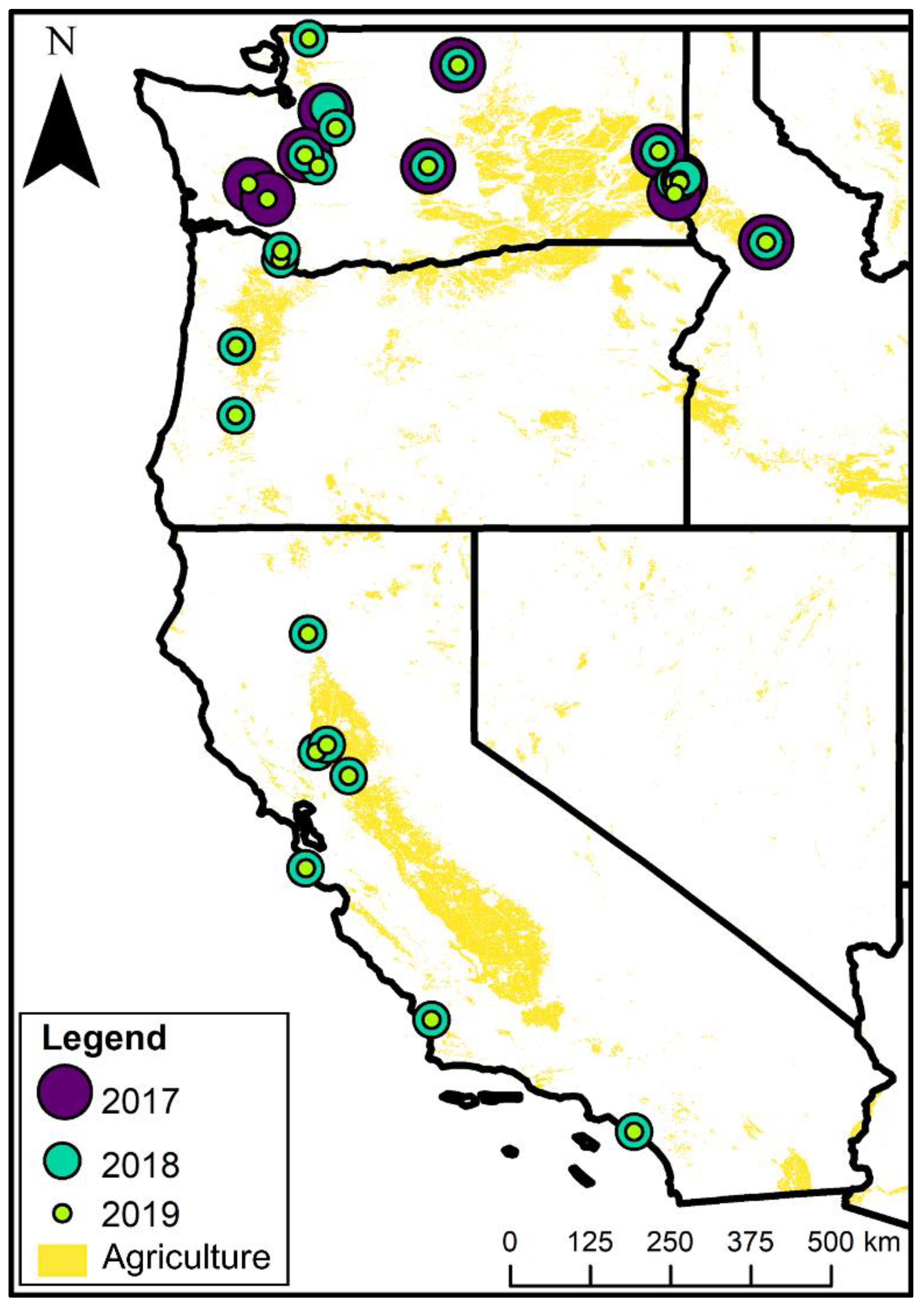
2.1. Farm Surveys
2.2. Bacterial Testing
2.3. Landscape Characteristics
2.4. Wild Bird Surveys
2.5. Weather Variables
2.6. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.7. Flock Management
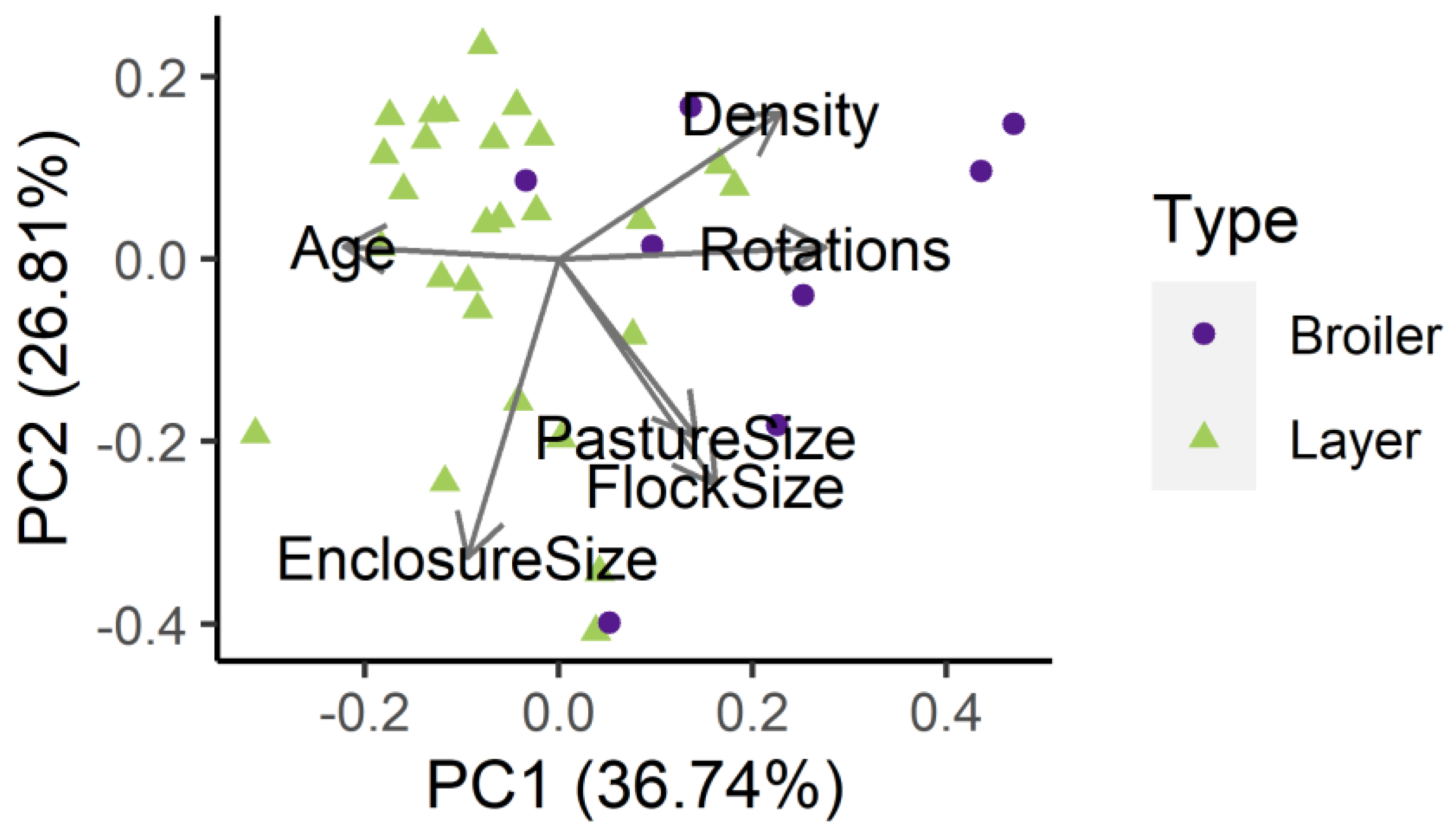
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Farm Characteristics
3.2. Bacteria Detection
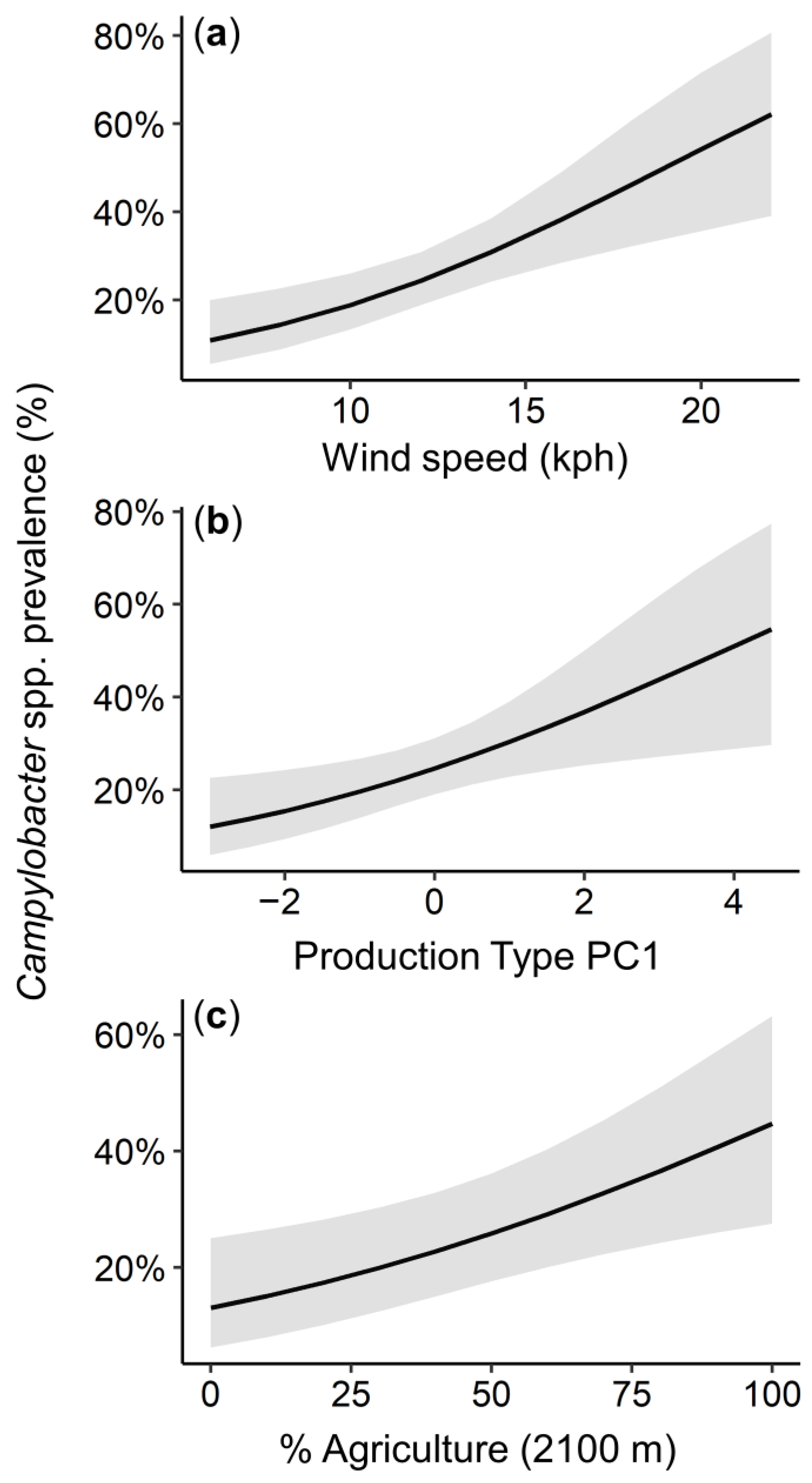
3.3. Mediators of Campylobacter spp. Prevalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batz, M.B.; Hoffmann, S.; Morris, J.G. Ranking the Disease Burden of 14 Pathogens in Food Sources in the United States Using Attribution Data from Outbreak Investigations and Expert Elicitation. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rukambile, E.; Sintchenko, V.; Muscatello, G.; Kock, R.; Alders, R. Infection, Colonization and Shedding of Campylobacter and Salmonella in Animals and Their Contribution to Human Disease: A Review. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, S.; Busani, L. The Use of Vaccination in Poultry Production. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2007, 26, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Meirhaeghe, H.; Schwarz, A.; Dewulf, J.; Immerseel, V.; Vanbeselaere, B.; De Gussem, M. Transmission of Poultry Disease and Biosecurity in Poultry Production. In Biosecurity in Animal Production and Veterinary Medicine, 1st ed.; Dewulf, J., Van Immerseel, F., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019; pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, D.A. Biosecurity and Infectious Animal Disease; Oxford University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rothrock, M.J.; Gibson, K.E.; Micciche, A.C.; Ricke, S.C. Pastured Poultry Production in the United States: Strategies to Balance System Sustainability and Environmental Impact. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erian, I.; Phillips, C.J.C. Public Understanding and Attitudes towards Meat Chicken Production and Relations to Consumption. Animals 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.S.; Davies, R.H.; Dewulf, J.; Gast, R.K.; Huwe, J.K.; Jones, D.R.; Waltman, D.; Willian, K.R. The Impact of Different Housing Systems on Egg Safety and Quality 1. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.; Feber, R.; Hemery, G.; Cook, P.; James, K.; Lamberth, C.; Dawkins, M. Welfare and Environmental Benefits of Integrating Commercially Viable Free-Range Broiler Chickens into Newly Planted Woodland: A UK Case Study. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, P.G.; Seideman, S.; Ricke, S.C.; O’Bryan, C.A.; Fanatico, A.F.; Rainey, R. Organic Poultry: Consumer Perceptions, Opportunities, and Regulatory Issues. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2009, 18, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, D.A.; Gow, H.; Hayes, D.; Matthews, W.; Norwood, B.; Rosen-molina, J.T.; Thurmanl, W. Economic and Market Issues on the Sustainability of Egg Production in the United States: Analysis of Alternative Production Systems. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.A.; Adalja, A.; Beaulieu, E.; Key, N.; Martinez, S.; Melton, A.; Perez, A.; Ralston, K.; Stewart, H.; Suttles, S.; et al. Trends in U.S. Local and Regional Food Systems. Local and Regional Food Systems: Trends, Resources and Federal Initiatives; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 87–195. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, K.A.; Smith, O.M.; Crespo, R.; Jones, M.S.; Crossley, M.S.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Prevalence Patterns for Enteric Parasites of Chickens Managed in Open Environments of the Western United States. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altekruse, S.F.; Stern, N.J.; Fields, P.I.; Swerdlow, D.L. Campylobacter Jejuni: An Emerging Foodborne Pathogen of Global Significance. J. Exp. Food Chem. 1999, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shehata, A.M.; Arif, M.; Paswan, V.K.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elbestawy, A.R. Approaches to Prevent and Control Campylobacter Spp. Colonization in Broiler Chickens: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 4989–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossler, E.; Signorini, M.L.; Romero-Scharpen, A.; Soto, L.P.; Berisvil, A.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Fusari, M.L.; Olivero, C.; Zbrun, M.V.; Frizzo, L.S. Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Thermotolerant Campylobacter in Food-Producing Animals Worldwide. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.D.; Greenwood, M.H.; Feltham, R.K.A.; Healing, T.D.; Donaldson, J.; Jones, D.M.; Colwell, R.R. Microbial Ecology of Campylobacter Jejuni in a United Kingdom Chicken Supply Chain: Intermittent Common Source, Vertical Transmission, and Amplification by Flock Propagation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4614–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, D.; Rothrock, M.J.; Pang, H.; Guo, M.; Mishra, A. Predicting Salmonella Prevalence Associated with Meteorological Factors in Pastured Poultry Farms in Southeastern United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, D.S.; Gennet, S.; Kilonzo, C.; Partyka, M.; Chaumont, N.; Atwill, E.R.; Kremen, C. Comanaging Fresh Produce for Nature Conservation and Food Safety. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11126–11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, L.; Atwill, E.R.; Jay-Russell, M.; Cooley, M.; Carychao, D.; Gorski, L.; Mandrell, R.E. Occurrence of Generic Escherichia Coli, E. Coli O157 and Salmonella Spp. in Water and Sediment from Leafy Green Produce Farms and Streams on the Central California Coast. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Edworthy, A.E.; Taylor, J.M.; Jones, M.S.; Tormanen, A.; Kennedy, C.M.; Fu, Z.; Latimer, C.E.; Michelotti, L.; Sato, C.; et al. Agricultural Intensification Heightens Food Safety Risk Associated with Wild Birds. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Are We Overestimating Risk of Enteric Pathogen Spillover from Wild Birds to Humans? Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 652–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, O.M.; Kennedy, C.M.; Owen, J.P.; Northfield, T.D.; Latimer, C.E.; Snyder, W.E. Highly Diversified Crop–Livestock Farming Systems Reshape Wild Bird Communities. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, A.S.E.; Stern, N.J.; Line, E.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Craven, S.E.; Stern, N.J.; Line, E.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A. Determination of the Incidence of Salmonella Spp., Campylobacter jejuni, and Clostridium perfringens in Wild Birds near Broiler Chicken Houses by Sampling Intestinal Droppings. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gerwe, T.J.W.M.; Bouma, A.; Van Den Broek, J.; Klinkenberg, D.; Stegeman, J.A.; Heesterbeek, J.A.P. Quantifying Transmission of Campylobacter Spp. among Broilers. Aplied Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5765–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berndtson, E.; Emanuelson, U.; Engvall, A.; Danielsson-Tham, M.L. A 1-Year Epidemiological Study of Campylobacters in 18 Swedish Chicken Farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 1996, 26, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoraibi, C.; Pitesky, M.; Dailey, N.; Niemeier, D. Operational Challenges and Opportunities in Pastured Poultry Operations in the United States. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1648–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, P.I.P.; Rosado, C.M.C.; Crespo, J.P.; Crespo, D.G.; Mourão, J.L.; Chaveiro-Soares, M.A.; Brás, J.L.A.; Mendes, I.; Gama, L.T.; Prates, J.A.M.; et al. Pasture Intake Improves the Performance and Meat Sensory Attributes of Free-Range Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, S.; Pratt, C.; Bliefield, N.; Mayer, D.G.; Redding, M.R.; McGahan, E. Establishing Soil Nutrient Distribution Zones across Free Range Egg Farms to Guide Practical Nutrient Management Strategies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, C.; Nagarajan, V.; Biswas, D. Proper Farm Management Strategies for Safer Organic Animal Farming Practice. In Safety and Practice for Organic Food; Biswas, D., Micallef, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 181–192. ISBN 9780128120606. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, N.J.; Marion, G.; Davidson, R.S.; White, P.C.L.; Hutchings, M.R. Modelling Parasite Transmission in a Grazing System: The Importance of Host Behaviour and Immunity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.S.; Fu, Z.; Reganold, J.P.; Karp, D.S.; Besser, T.E.; Tylianakis, J.M.; Snyder, W.E. Organic Farming Promotes Biotic Resistance to Foodborne Human Pathogens. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour-Zavala, L. A Laboratory Manual for the Isolation, Identification and Characterization of Avian Pathogens, 6th ed.; American Association of Avian Pathologists: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2016; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, J.; Stehman, S.V.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.A.; Sorenson, D.G.; Granneman, B.J.; Poss, R.V.; Baer, L.A. Thematic Accuracy Assessment of the 2011 National Land Cover Database (NLCD). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jay, M.T.; Cooley, M.; Carychao, D.; Wiscomb, G.W.; Sweitzer, R.A.; Crawford-miksza, L.; Farrar, J.A.; Lau, D.K.; Connell, J.O.; Millington, A.; et al. Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Feral Swine near Spinach Fields and Cattle, Central California Coast. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, C.E.; Rothrock, M.J.; Mishra, A. Comparison between Random Forest and Gradient Boosting Machine Methods for Predicting Listeria Spp. Prevalence in the Environment of Pastured Poultry Farms. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoogsteen, M.J.J.; Lantinga, E.A.; Bakker, E.J.; Groot, J.C.J.; Tittonell, P.A. Estimating Soil Organic Carbon through Loss on Ignition: Effects of Ignition Conditions and Structural Water Loss. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.M. GlmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility among Packages for Zero-Inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolker, B. Bbmle: Tools for General Maximum Likelihood Estimation; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=bbmle (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Ludecke, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.S.; Patil, I.; Waggoner, P.; Makowski, D. Performance: An R package for assessment, comparison, and testing of statisitcal models. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-387-95364-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ricke, S.C.; Rothrock, M.J. Gastrointestinal Microbiomes of Broilers and Layer Hens in Alternative Production Systems. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robino, P.; Tomassone, L.; Tramuta, C.; Rodo, M.; Giammarino, M.; Vaschetti, G.; Nebbia, P. Prevalence of Campylobacter Jejuni, Campylobacter coli and Enteric Helicobacter in Domestic and Free Living Birds in North-Western Italy. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2010, 152, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Bryant, J.E.; Cuong, N.V.; Hoang, N.V.M.; Campbell, J.; Hoang, N.V.; Dung, T.T.N.; Duy, D.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Thompson, C.; et al. An Epidemiological Investigation of Campylobacter in Pig and Poultry Farms in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayala, A.J.; Yabsley, M.J.; Hernandez, S.M. A Review of Pathogen Transmission at the Backyard Chicken–Wild Bird Interface. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 539925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.J.; Haas, L.K.; Williams, B.M.; Fink, S.S.; Yabsley, M.J.; Hernandez, S.M. Risky Business in Georgia’s Wild Birds: Contact Rates between Wild Birds and Backyard Chickens Is Influenced by Supplemental Feed. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Olimpi, E.M.; Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Cornell, K.A.; Frishkoff, L.O.; Northfield, T.D.; Bowles, T.M.; Edworthy, M.; Eilers, J.; Fu, Z.; et al. A Trait-Based Framework for Predicting Foodborne Pathogen Risk from Wild Birds. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, C.M.; Nasr, M.A.F.; Gale, E.; Petek, M.; Stafford, K.; Turp, M.; Coles, G.C. Prevalence of Nematode Infection and Faecal Egg Counts in Free-Range Laying Hens: Relations to Housing and Husbandry. Br. Poult. Sci. 2013, 54, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, O.; Kassem, I.I.; Shen, Z.; Lin, J.; Rajashekara, G.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter in Poultry: Ecology and Potential Interventions. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bacteria | Years | Positive/Tested (Prevalence) | C. jejuni | C. coli | Unknown Campylobacter spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campylobacter spp. | 2017–2019 | 250/962 (26.0%) | 121/606 (20.0%) | 10/606 (1.7%) | 119/962 (12.4%) |
| 2017 | 54/126 (42.9%) | 24/126 (19.0%) | 0/126 (0%) | 30/126 (23.8%) | |
| 2018 | 80/356 (22.5%) | N/A | N/A | 80/356 (22.5%) | |
| 2019 | 116/480 (24.2%) | 97/480 (20.2%) | 10/480 (2.1%) | 9/480 (1.9%) | |
| Salmonella spp. | 2017–2018 | 8/482 (1.7%) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | 0/126 (0%) | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 2018 | 8/359 (2.2%) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, O.M.; Cornell, K.A.; Crossley, M.S.; Crespo, R.; Jones, M.S.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Wind Speed and Landscape Context Mediate Campylobacter Risk among Poultry Reared in Open Environments. Animals 2023, 13, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030492
Smith OM, Cornell KA, Crossley MS, Crespo R, Jones MS, Snyder WE, Owen JP. Wind Speed and Landscape Context Mediate Campylobacter Risk among Poultry Reared in Open Environments. Animals. 2023; 13(3):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Olivia M., Kevin A. Cornell, Michael S. Crossley, Rocio Crespo, Matthew S. Jones, William E. Snyder, and Jeb P. Owen. 2023. "Wind Speed and Landscape Context Mediate Campylobacter Risk among Poultry Reared in Open Environments" Animals 13, no. 3: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030492
APA StyleSmith, O. M., Cornell, K. A., Crossley, M. S., Crespo, R., Jones, M. S., Snyder, W. E., & Owen, J. P. (2023). Wind Speed and Landscape Context Mediate Campylobacter Risk among Poultry Reared in Open Environments. Animals, 13(3), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030492






