Mother–Young Bonding: Neurobiological Aspects and Maternal Biochemical Signaling in Altricial Domesticated Mammals
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of Altricials, Precocials and Semialtricials
3. Sensitive Period
4. Factors That Influence the Bonding Process
4.1. Maternal Care
4.2. Importance of Nest-Building in Altricial Species
5. Neural Pathways Involved in the Bonding Process of Altricial Species
5.1. Licking and Tactile Sensitivity of the Brain
5.2. Olfactory Stimuli
5.3. Auditory Stimuli
5.4. Visual Stimuli
6. The Role of Neurobiological Systems for Mother–Young Recognition and Bonding
6.1. Neurotransmitters and Neurohormones
6.2. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) and Hypothalamic –Pituitary–Thyroid (HPT) Axes
6.3. Brain–Gut–Microbiome Axis
7. Factors That Affect Maternal Recognition and Performance
8. Future Directions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraser, A.F. Comportamiento de Los Animales de Granja; Acribia: Zaragoza, España, 1980; p. 292. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, R. La Evolución Del Aprendizaje. In Comportamiento Animal. Un Enfoque Evolutivo y Ecológico; Maier, R., Ed.; McGrawHill Interamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2001; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Marcet-Rius, M.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Mora-Medina, P.; Lezama-García, K.; Orihuela, A. Mother-Young Bond in Non-Human Mammals: Neonatal Communication Pathways and Neurobiological Basis. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1064444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sèbe, F.; Aubin, T.; Boué, A.; Poindron, P. Mother–young vocal communication and acoustic recognition promote preferential nursing in sheep. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clutton-Brock, T.H. The Evolution of Parental Care; Princenton University Press: Princenton, NJ, USA, 1991; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Keverne, E.B. Neurobiological and molecular approaches to attachment and bonding. In Attachment and Bonding. A New Synthesis; Grossmann, K.E., Hrdy, S.B., Lamb, M.E., Porges, S.W., Sachser, N., Eds.; Dahlem Workshop: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 101–117. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts, E.A.; Dale, J. Individual recognition: It is good to be different. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, D.D.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal care and the development of stress responses. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1999, 9, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévy, F.; Keller, M.; Poindron, P. Olfactory regulation of maternal behavior in mammals. Horm. Behav. 2004, 46, 284–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, J.L.; Champagne, D.L.; Meaney, M.J.P. Variations of maternal care differentially influence ‘fear’ reactivity and regional patterns of cfos immunoreactivity in response to the shock-probe burying test. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, F.R.; Zanettini, C.; Sgobio, C.; Sarli, C.; Carone, V.; Moles, A.; Ammassari-Teule, M. Intensification of maternal care by double-mothering boosts cognitive function and hippocampal morphology in the adult offspring. Hippocampus 2011, 21, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeyer, C.M.; Meaney, M.J.; Reader, S.M. Early maternal care predicts reliance on social learning about food in adult rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2013, 55, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardini, G.; Bowen, J.; Mariti, C.; Fatjó, J.; Sighieri, C.; Gazzano, A. Influence of maternal care on behavioural development of domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) living in a home environment. Animals 2017, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezama-García, K.; Mariti, C.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Martínez-Burnes, J.; Barrios-García, H.; Gazzano, A. Maternal behaviour in domestic dogs. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2019, 7, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad, K.; Curley, J.; Keverne, E. Mother–infant bonding and the evolution of mammalian social relationships. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damián, J.P.; Hötzel, M.J.; Banchero, G.; Ungerfeld, R. Growing without a mother during rearing affects the response to stressors in rams. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 209, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toinon, C.; Waiblinger, S.; Rault, J. Maternal Deprivation Affects Goat Kids’ Social Behavior before and after Weaning. Dev. Psychobiol. 2022, 64, e22269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusui, T.; Isaka, Y.; Mori, Y. Early Weaning Deprives Mouse Pups of Maternal Care and Decreases Their Maternal Behavior in Adulthood. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 162, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Diorio, J.; Tannenbaum, B.; Caldji, C.; Francis, D.; Freedman, A.; Sharma, S.; Pearson, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care, Hippocampal Glucocorticoid Receptors, and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Responses to Stress. Science 1997, 277, 1659–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, C.P.; Thiels, E.; Alberts, J.R. Weaning in rats: I. maternal behavior. Dev. Psychobiol. 1990, 23, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriceau, S.; Shionoya, K.; Jakubs, K.; Sullivan, R.M. Early-Life Stress Disrupts Attachment Learning: The Role of Amygdala Corticosterone, Locus Ceruleus Corticotropin Releasing Hormone, and Olfactory Bulb Norepinephrine. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15745–15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohki-Hamazaki, H. Neurobiology of Imprinting. Brain Nerve 2012, 64, 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Curley, J.P.; Keverne, E.B. Genes, brains and mammalian social bonds. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazábal, D.E.; Pereira, M.; Agrati, D.; Ferreira, A.; Fleming, A.S.; González-Mariscal, G.; Lévy, F.; Lucion, A.B.; Morrell, J.I.; Numan, M.; et al. Flexibility and adaptation of the neural substrate that supports maternal behavior in mammals. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1875–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiber, I.B.R.; Weiß, B.M.; Kingma, S.A.; Komdeur, J. The importance of the altricial—precocial spectrum for social complexity in mammals and birds—A review. Front. Zool. 2017, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czerwinski, V.H.; Smith, B.P.; Hynd, P.I.; Hazel, S.J. The influence of maternal care on stress-related behaviors in domestic dogs: What can we learn from the rodent literature? J. Vet. Behav. 2016, 14, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Keller, M.; Lévy, F. Mother-young relationships in sheep: A model for a multidisciplinary approach of the study of attachment in mammals. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, A.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Strappini, A.; Serrapica, F.; Braghieri, A.; Mora-Medina, P.; Napolitano, F. Neurophysiological mechanisms of cow–calf bonding in buffalo and other farm animals. Animals 2021, 11, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numan, M. Hypothalamic neural circuits regulating maternal responsiveness toward infants. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev. 2006, 5, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, G.; Poindron, P. Parental care in mammals. In Hormones, Brain and Behavior. Pfaff, D.W., Arnold, A.P., Fahrbach, S.E., Etgen, A.M., Rubin, R.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 215–298. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert, P.H.; Dean, K.F.; Reiter, L.W. Development of locomotor activity of rat pups in figure-eight mazes. Dev. Psychobiol. 1985, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patin, V.; Vincent, A.; Lordi, B.; Caston, J. Does prenatal stress affect the motoric development of rat pups? Dev. Brain Res. 2004, 149, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.A.; Francis, D.D.; Mar, A.; Meaney, M.J. Variations in maternal care in the rat as a mediating influence for the effects of environment on development. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 79, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavely, J.A. Pediatric neurology of the dog and cat. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 36, 475–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimble, D.P. Didelphid behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, C. Behavioural development in the neonatal lamb: Effect of maternal and birth-related factors. Theriogenology 2003, 59, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévy, F.; Keller, M. Neurobiology of maternal behavior in sheep. In Advances in the Study of Behavior; Brockmann, J.H., Roper, T., Naguib, M., Edwards., W., Barnard, C., Mitani, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 38, pp. 399–437. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, G.D. Early ontogeny of locomotor behaviour: A comparison between altricial and precocial animals. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatzle, M.; Hoops, M.; Kauffold, J.; Seeger, J.; Fietz, S.A. Development of deep and upper neuronal layers in the domestic cat, sheep and pig neocortex. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2017, 46, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.O.; Blomberg, S.P.; Owens, I.P.F. Convergent maternal care strategies in ungulates and macropods. Evolution 2002, 56, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P. Parental Behavior. In Social Behavior in Farm Animals; Keeling, L.J., Gonyou, H.W., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; p. 406. ISBN 9780851993973. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamichi, M.; Yamada, K. Distribution of dorsal carriage among simians. Primates 2009, 50, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algers, B.; Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Maternal Behavior in pigs. Horm. Behav. 2007, 52, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, K. Energetic trade-offs between brain size and offspring production: Marsupials confirm a general mammalian pattern. BioEssays 2011, 33, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, P.M.; Harvey, P.H. Brain size, development and metabolism in birds and mammals. J. Zool. 1985, 207, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, A.C. Brain at Birth. In Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science; Shackelford, T., Weekes-Shackelford, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich, P.D.; Ul-Haq, M.; von Koenigswald, W.; Sanders, W.J.; Smith, B.H.; Zalmout, I.S. New protocetid whale from the middle eocene of pakistan: Birth on land, precocial development, and sexual dimorphism. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.A.; Murie, J.O. Inheritance of nest sites in female columbian ground squirrels. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1984, 15, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, F.; Wen, J.; Sukhchuluun, G.; Chi, Q.-S.; Wang, D.-H. Precocious Torpor in an Altricial Mammal and the Functional Implications of Heterothermy During Development. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canals, M.; Figueroa, D.P.; Miranda, J.P.; Sabat, P. Effect of gestational and postnatal environmental temperature on metabolic rate in the altricial rodent, Phyllotis darwini. J. Therm. Biol. 2009, 34, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.R. A Comparative Study of Prenatal Behavioral Otogeny in Altricial and Precocial Murid Rodents; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ferner, K.; Schultz, J.A.; Zeller, U. Comparative anatomy of neonates of the three major mammalian groups (monotremes, marsupials, placentals) and implications for the ancestral mammalian neonate morphotype. J. Anat. 2017, 231, 798–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, T.I. Altricial and precocial mammals: A model of neural and muscular development. Zoo Biol. 1992, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, E.; Vallortigara, G. Origins of Knowledge: Insights from Precocial Species. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroobants, S.; Creemers, J.; Bosmans, G.; D’Hooge, R. Post-weaning infant-to-mother bonding in nutritionally independent female mice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Aoki, N.; Kitajima, T.; Iikubo, E.; Katagiri, S.; Matsushima, T.; Homma, K.J. Thyroid Hormone Determines the Start of the Sensitive Period of Imprinting and Primes Later Learning. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemche, E. Research Evidence from Studies on Filial Imprinting, Attachment, and Early Life Stress: A New Route for Scientific Integration. Acta Ethol. 2020, 23, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhuis, J.J. Early Learning and the Development of Filial Preferences in the Chick. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 98, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poindron, P.; Orgeur, P.; Le Neindre, P.; Kann, G.; Raksanyi, I. Influence of the Blood Concentration of Prolactin on the Length of the Sensitive Period for Establishing Maternal Behavior in Sheep at Parturition. Horm. Behav. 1980, 14, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, S.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; Van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Moran, G.; Pederson, D.R.; Benoit, D. Unresolved States of Mind, Anomalous Parental Behavior, and Disorganized Attachment: A Review and Meta-Analysis of a Transmission Gap. Attach. Hum. Dev. 2006, 8, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, K.J.; Sullivan, R.M. Defining Age Limits of the Sensitive Period for Attachment Learning in Rat Pups. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongrácz, P.; Altbäcker, V.; Fenes, D. Human Handling Might Interfere with Conspecific Recognition in the European Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus ). Dev. Psychobiol. 2001, 39, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, L.; Arnold, A.-M.K.; Goerlich-Jansson, V.C.; Vinke, C.M. The Importance of Early Life Experiences for the Development of Behavioural Disorders in Domestic Dogs. Behaviour 2018, 155, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, J.S. Learning in Newborn Kittens. Sci. Am. 1972, 227, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, X. Etologia Veterinaria, 1st ed.; Multimédica: Madrid, España, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, E.I. Sensitive Periods in the Development of the Brain and Behavior. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keverne, E.B.; Kendrick, K.M. Oxytocin Facilitation of Maternal Behavior in Sheepa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 652, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kamboj, M.; Chandra, S.; Singh, R.K. Effect of Calf Suckling Dummy Calf Used and Weaning on Milk Ejection Stimuli and Milk Yield of Murrah Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Hübener, M.; Bonhoeffer, T. Neuronal Plasticity: Beyond the Critical Period. Cell 2014, 159, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, M.; Deputte, B.L.; Heyman, Y.; Delatouche, L.; Richard, C.; Baudoin, C. Visual Discrimination by Heifers (Bos taurus) of Their Own Species. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 121, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, M.; Deputte, B.L.; Heyman, Y.; Baudoin, C. Individual Recognition in Domestic Cattle (Bos taurus): Evidence from 2D-Images of Heads from Different Breeds. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G. Odour, and the Recognition of Lambs by Merino Ewes. Appl. Anim. Ethol. 1978, 4, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, K.K.; Katz, L.S. Role of the Vomeronasal Organ in Neonatal Offspring Recognition in Sheep. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.; Shillito, E.E. The importance of odour, appearance and voice in maternal recognition of the young in merino sheep (Ovis aries). Appl. Anim. Ethol. 1977, 3, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, R.S. Neuroendocrine regulation of maternal behavior. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 36, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, J.; Orihuela, A.; Galina, C.S.; Aguirre, V. A Note on Behavioral Responses to Brief Cow-Calf Separation and Reunion in Cattle (Bos indicus). J. Vet. Behav. 2007, 2, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustritz, M.V.R. Reproductive behavior of small animals. Theriogenology 2005, 64, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pageat, P.; Gaultier, E. Current research in canine and feline pheromones. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2003, 33, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.M.; Young, L.J. neuropeptidergic regulation of affiliative behavior and social bonding in animals. Horm. Behav. 2006, 50, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Macbeth, A.H.; Pagani, J.; Young, W.S. Oxytocin: The great facilitator of life. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 88, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielsky, I.F.; Young, L.J. Oxytocin, Vasopressin, and Social Recognition in Mammals. Peptides 2004, 25, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, M.E.; DeCárdenas, E.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Caldwell, H.K. Impairments in the Initiation of Maternal Behavior in Oxytocin Receptor Knockout Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitman, D.C.; Albers, H.E. Role of Oxytocin in the Hypothalamic Regulation of Sexual Receptivity in Hamsters. Brain Res. 1995, 680, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P.O.; Suderman, M.; Sasaki, A.; Huang, T.C.T.; Hallett, M.; Meaney, M.J.; Szyf, M. Broad Epigenetic Signature of Maternal Care in the Brain of Adult Rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkeybile, A.M.; Carter, C.S.; Wroblewski, K.L.; Puglia, M.H.; Kenkel, W.M.; Lillard, T.S.; Karaoli, T.; Gregory, S.G.; Mohammadi, N.; Epstein, L.; et al. Early Nurture Epigenetically Tunes the Oxytocin Receptor. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 99, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danoff, J.S.; Wroblewski, K.L.; Graves, A.J.; Quinn, G.C.; Perkeybile, A.M.; Kenkel, W.M.; Lillard, T.S.; Parikh, H.I.; Golino, H.F.; Gregory, S.G.; et al. Genetic, Epigenetic, and Environmental Factors Controlling Oxytocin Receptor Gene Expression. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.; Diorio, J.; Sharma, S.; Meaney, M.J. Naturally occurring variations in maternal behavior in the rat are associated with differences in estrogen-inducible central oxytocin receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12736–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, M.; Okabe, S.; Mogi, K.; Kikusui, T. Oxytocin and mutual communication in mother-infant bonding. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poindron, P. Mechanisms of Activation of Maternal Behaviour in Mammals. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, S.L.; Panesar, S.; Steiner, M.; Fleming, A.S. The Effects of Adrenalectomy and Corticosterone Replacement on Induction of Maternal Behavior in the Virgin Female Rat. Horm. Behav. 2006, 49, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Bridges, R.S. Effects of Maternal Behavior Induction and Pup Exposure on Neurogenesis in Adult, Virgin Female Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakov, M.; Fleming, A. The Effects of Early Rearing Environment on the Hormonal Induction of Maternal Behavior in Virgin Rats. Horm. Behav. 2005, 48, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischner, D.; Kemper, N.; Krieter, J. Nest-Building Behaviour in Sows and Consequences for Pig Husbandry. Livest. Sci. 2009, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechard, A.; Mason, G. Leaving Home: A Study of Laboratory Mouse Pup Independence. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2010, 125, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.; García-Torres, E.; Prager, G.; Hudson, R.; Rödel, H.G. Development of Behavior in the Litter Huddle in Rat Pups: Within- and between-Litter Differences. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P. Burrowing and Nest Building Behavior as Indicators of Well-Being in Mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Storm, D.R. Maternal Behavior Is Impaired in Female Mice Lacking Type 3 Adenylyl Cyclase. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellini, C.; Dal Bosco, A.; Arias-Álvarez, M.; Lorenzo, P.L.; Cardinali, R.; Rebollar, P.G. The Main Factors Affecting the Reproductive Performance of Rabbit Does: A Review. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 122, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P.; Oester, H.; Stauffacher, M. The Influence of Pup Odour on the Nest Related Behaviour of Rabbit Does (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 93, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, J.A.; Briscoe, N.J.; Handasyde, K.A. Comparing the Thermal Suitability of Nest-Boxes and Tree-Hollows for the Conservation-Management of Arboreal Marsupials. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 209, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Swan, K.-M.; Vienola, K.; Farmer, C.; Oliviero, C.; Peltoniemi, O.; Valros, A. Nest-Building in Sows: Effects of Farrowing Housing on Hormonal Modulation of Maternal Characteristics. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2013, 148, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, B.I.; Lisborg, L.; Vestergaard, K.S.; Vanicek, J. Nest-Building, Behavioural Disturbances and Heart Rate in Farrowing Sows Kept in Crates and Schmid Pens. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2003, 80, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, M.; Wechsler, B.; Gygax, L.; Weber, R. Influence of Straw Length, Sow Behaviour and Room Temperature on the Incidence of Dangerous Situations for Piglets in a Loose Farrowing System. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 117, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Medina, P.; Napolitano, F.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Berdugo-Gutiérrez, J.; Ruiz-Buitrago, J.; Guerrero-Legarreta, I. Imprinting, Sucking and Allosucking Behaviors in Buffalo Calves. J. Buffalo Sci. 2018, 7, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insel, T.R.; Young, L.J. The Neurobiology of Attachment. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, J.; Sullivan, R.M. The Neurobiology of Safety and Threat Learning in Infancy. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 143, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Morrell, J.I. Functional Mapping of the Neural Circuitry of Rat Maternal Motivation: Effects of Site-Specific Transient Neural Inactivation. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldji, C.; Tannenbaum, B.; Sharma, S.; Francis, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care during Infancy Regulates the Development of Neural Systems Mediating the Expression of Fearfulness in the Rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5335–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr-Phillips, E.J.; Beery, A.K. Natural Variation in Maternal Care Shapes Adult Social Behavior in Rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.A.; Weaver, I.C.G.; Diorio, J.; Sharma, S.; Meaney, M.J. Natural Variations in Maternal Care Are Associated with Estrogen Receptor Alpha Expression and Estrogen Sensitivity in the Medial Preoptic Area. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4720–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, T.L.; Picetti, R.; Contarino, A.; Koob, G.F.; Vale, W.W.; Lee, K.-F. Mice Deficient for Both Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRFR1) and CRFR2 Have an Impaired Stress Response and Display Sexually Dichotomous Anxiety-Like Behavior. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, T.L.; Vale, W.W. CRF and CRF Receptors: Role in Stress Responsivity and Other Behaviors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, R.; Cruz, Y.; Lucio, R.A.; Ninomiya, J.; Martínez–Gómez, M. Temporal and Behavioral Patterning of Parturition in Rabbits and Rats. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.; Distel, H. Nipple Location By Newborn Rabbits: Behavioural Evidence for Pheromonal Guidance. Behaviour 1983, 85, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val-Laillet, D.; Nowak, R. Early Discrimination of the Mother by Rabbit Pups. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 111, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.M.; Wilson, D.A. Molecular Biology Of Early Olfactory Memory. Learn. Mem. 2003, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, R.; Meurisse, M.; Cornilleau, F.; Moussu, C.; Keller, M.; Lévy, F. Disruption of Adult Olfactory Neurogenesis Induces Deficits in Maternal Behavior in Sheep. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 347, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.A.; Kendrick, K.M. Mammalian Social Odours: Attraction and Individual Recognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 2061–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, M.L.; Ward, S.J.; Temple-Smith, P.D. Olfactory Cues, Genetic Relatedness and Female Mate Choice in the Agile Antechinus (Antechinus agilis). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2007, 61, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsley, C.H.; Bridges, R.S. Morphine Treatment and Reproductive Condition Alter Olfactory Preferences for Pup and Adult Male Odors in Female Rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 1990, 23, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Velarde, A.; Huertas, S.; Cajiao, M. (Eds.) Animal welfare, A Global Vision in Ibero-America, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; pp. 1–516. [Google Scholar]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Orihuela, A.; Napolitano, F.; Mora-Medina, P.; Alonso-Spilsbury, M. Olfaction in Animal Behaviour and Welfare. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Guerrerro-Legarreta, I.; de Rosa, G.; Mora-Medina, P.; Braghieri, A.; Fabio, N. Dairy Buffalo Behaviour and Welfare from Calving to Milking. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2019, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Dahlöf, L.-G.; Hansen, S. Olfactory Mechanisms in the Control of Maternal Aggression, Appetite, and Fearfulness: Effects of Lesions to Olfactory Receptors, Mediodorsal Thalamic Nucleus, and Insular Prefrontal Cortex. Behav. Neurosci. 1987, 101, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, S.; Masaoka, M.; Rai, D.; Kondo, Y.; Sakuma, Y. Both Olfactory Epithelial and Vomeronasal Inputs Are Essential for Activation of the Medial Amygdala and Preoptic Neurons of Male Rats. Neuroscience 2011, 199, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillet, A.C.; Moussu, C.; Poissenot, K.; Keller, M.; Birnbaumer, L.; Leinders-Zufall, T.; Zufall, F.; Chamero, P. Sensory Detection by the Vomeronasal Organ Modulates Experience-Dependent Social Behaviors in Female Mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.D.; Fleming, A.S.; Stern, J.M. Somatosensory Control of the Onset and Retention of Maternal Responsiveness in Primiparous Sprague-Dawley Rats. Physiol. Behav. 1992, 51, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouette-Lahlou, I.; Godinot, F.; Vernet-Maury, E. The Mother Rat’s Vomeronasal Organ Is Involved in Detection of Dodecyl Propionate, the Pup’s Preputial Gland Pheromone. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 66, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelman, R.; Zarrow, M.X.; Denenberg, V.H.; Myers, M. Olfactory Bulb Removal Eliminates Maternal Behavior in the Mouse. Science 1971, 171, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. The Role of Olfactory Cues in Mother-Pup, Groupmate, and Sex Recognition of Lesser Flat-Headed Bats, Tylonycteris Pachypus. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 15792–15799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R. Do Newborn Rabbits Learn the Odor Stimuli Releasing Nipple-Search Behavior? Dev. Psychobiol. 1985, 18, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouventin, P.; Aubin, T.; Lengagne, T. Finding a Parent in a King Penguin Colony: The Acoustic System of Individual Recognition. Anim. Behav. 1999, 57, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin, T.; Jouventin, P. How to Vocally Identify Kin in a Crowd: The Penguin Model. Adv. Study Behav. 2002, 31, 243–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, I.; Mathevon, N.; Jouventin, P. Mother’s Voice Recognition by Seal Pups. Nature 2001, 412, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, M.D.; Beecher, I.M.; Hahn, S. Parent-Offspring Recognition in Bank Swallows (Riparia riparia): II. Development and Acoustic Basis. Anim. Behav. 1981, 29, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, R. Effect of Kitten Vocalizations on Maternal Behavior. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1977, 91, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branchi, I.; Santucci, D.; Alleva, E. Ultrasonic Vocalisation Emitted by Infant Rodents: A Tool for Assessment of Neurobehavioural Development. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, R.A.; Harker, A.; Salamanca, S.; Pellis, S.M.; Li, F.; Gibb, R.L. Development of Ultrasonic Calls in Rat Pups Follows Similar Patterns Regardless of Isolation Distress. Dev. Psychobiol. 2020, 62, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, F.R.; Scalera, E.; Sarli, C.; Moles, A. Pups Call, Mothers Rush: Does Maternal Responsiveness Affect the Amount of Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Mouse Pups? Behav. Genet. 2005, 35, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Saito, T.R.; Furudate, S.; Takahashi, K.W. Prolactin Levels and Maternal Behavior Induced by Ultrasonic Vocalizations of the Rat Pup. Exp. Anim. 2001, 50, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidbey, J.H.; Ranger, M.; Myers, M.M.; Anwar, M.; Ludwig, R.J.; Schulz, A.M.; Barone, J.L.; Kolacz, J.; Welch, M.G. Early Life Maternal Separation and Maternal Behaviour Modulate Acoustic Characteristics of Rat Pup Ultrasonic Vocalizations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P. A Light and Electron Microscopic Study of the Development of Two Regions of the Chick Forebrain. Dev. Brain Res. 1985, 20, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, E.F.; Jacqmot, O.; Espinheira Gomes, F.N.C.M.; Sha, M.F.; Niogi, S.N.; Johnson, P.J. Characterizing the Canine and Feline Optic Pathways in Vivo with Diffusion MRI. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2022, 25, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sabrout, K. Does the Blindness Affect the Behavioural Activities of Rabbit? J. Anim. Behav. Biometeorol. 2018, 6, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.D.; Kulczycki, J.; Shanks, N.; Meaney, M.J.; Anisman, H. The Effects of Early Postnatal Stimulation on Morris Water-Maze Acquisition in Adult Mice: Genetic and Maternal Factors. Psychopharmacology 1996, 128, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturman-Hulbe, M.; Stone, C.P. Maternal Behavior in the Albino Rat. J. Comp. Psychol. 1929, 9, 203–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenkel, W.M.; Yee, J.R.; Carter, C.S. Is Oxytocin a Maternal–Foetal Signalling Molecule at Birth? Implications for Development. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 26, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, T.M. Oxytocin, Motivation and the Role of Dopamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 119, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpey-Schafer, E. Experimental Physiology. Br. Med. J. 1933, 2, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsucci, F.; Paoloni, G.; Conti, C.; Reda, M.; Fulcheri, M. The Role of Oxytocin in Plasticity, Memory and Attachment Dynamics. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost Agents 2013, 27, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Strathearn, L. Maternal Neglect: Oxytocin, Dopamine and the Neurobiology of Attachment. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.L.; Goursaud, A.-P.S.; Bachevalier, J.; Anderson, K.D.; Pedersen, C.A. Peripherally Administered Non-Peptide Oxytocin Antagonist, L368,899®, Accumulates in Limbic Brain Areas: A New Pharmacological Tool for the Study of Social Motivation in Non-Human Primates. Horm. Behav. 2007, 52, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.A.; Caldwell, J.D.; Walker, C.; Ayers, G.; Mason, G.A. Oxytocin Activates the Postpartum Onset of Rat Maternal Behavior in the Ventral Tegmental and Medial Preoptic Areas. Behav. Neurosci. 1994, 108, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.A.; Prange, A.J. Induction of maternal behavior in virgin rats after intracerebroventricular administration of oxytocin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 6661–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, C.A.; Vadlamudi, S.V.; Boccia, M.L.; Amico, J.A. Maternal Behavior Deficits in Nulliparous Oxytocin Knockout Mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, O.J. Brain Oxytocin Correlates with Maternal Aggression: Link to Anxiety. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6807–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthschilling, C.A.; Albiero, G.; Lazzari, V.M.; Becker, R.O.; de Moura, A.C.; Lucion, A.B.; Almeida, S.; da Veiga, A.B.G.; Giovenardi, M. Analysis of Transcriptional Levels of the Oxytocin Receptor in Different Areas of the Central Nervous System and Behaviors in High and Low Licking Rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby, S.C.; Ashbrook, D.G.; Malik, H.R.; Chatterjee, D.; Pan, P.; Fleming, A.S.; McGowan, P.O. The Role of Interindividual Licking Received and Dopamine Genotype on Later--life Licking Provisioning in Female Rat Offspring. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, A.; Naef, V.; Santorelli, F.M.; Mariti, C.; Gazzano, A. Oxytocin Receptor Gene Polymorphism in Lactating Dogs. Animals 2021, 11, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, H.K. Neurobiology of Sociability. Sens. Nat. 2012, 1, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohlström, A.; Carlsson, C.; Uvnäs-Moberg, K. Effects of Oxytocin Treatment in Early Life on Body Weight and Corticosterone in Adult Offspring from Ad Libitum-Fed and Food-Restricted Rats. Neonatology 2000, 78, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Brito, A.; Gonçalves, I.; Santos, C.A. The Brain as a Source and a Target of Prolactin in Mammals. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, R.S.; Numan, M.; Ronsheim, P.M.; Mann, P.E.; Lupini, C.E. Central Prolactin Infusions Stimulate Maternal Behavior in Steroid-Treated, Nulliparous Female Rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8003–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Limón-Morales, O.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin Function and Putative Expression in the Brain. Endocrine 2017, 57, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, R.S.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin-Induced Neurogenesis in the Maternal Brain. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemian, F.; Shafigh, F.; Roohi, E. Regulatory Role of Prolactin in Paternal Behavior in Male Parents: A Narrative Review. J. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 62, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Sierra, E.; Chico Ponce de León, F.; Portugal Rivera, A. Neurotransmisores Del Sistema Límbico. Salud Ment. 2005, 28, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Angoa-Pérez, M.; Kuhn, D.M. Neuronal Serotonin in the Regulation of Maternal Behavior in Rodents. Neurotransmitter 2015, 2, e615. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, G.; Derrickson, B. Principios de Anatomía y Fisiología, 13th ed.; Tortora, G., Derrickson, B., Eds.; Editorial Médica Panamericana: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2018; ISBN 9786078546114. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, K.; Zsiros, V.; Jiang, Z.; Nakao, K.; Kolata, S.; Zhang, S.; Belforte, J.E. GABAergic Interneuron Origin of Schizophrenia Pathophysiology. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrati, P.; Carmona, C.; Dominguez, G.; Beyer, C.; Rosenblatt, J. GABA Receptor Agonists in the Medial Preoptic Area and Maternal Behavior in Lactating Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 87, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, S.V.; Dmitrieva, L.E.; Sizonov, V.A. Cardiac, Respiratory, and Motor Activity in Norm and after Activation of Catecholaminergic Systems in Newborn Rat Pups. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 48, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, V.M.; Grella, S.L.; Chatterjee, D.; Fleming, A.S. Previous Maternal Experience Affects Accumbal Dopaminergic Responses to Pup-Stimuli. Brain Res. 2008, 1198, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angoa-Pérez, M.; Kane, M.J.; Sykes, C.E.; Perrine, S.A.; Church, M.W.; Kuhn, D.M. Brain Serotonin Determines Maternal Behavior and Offspring Survival. Genes Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavegatto, S.; Nelson, R.J. Interaction of Nitric Oxide and Serotonin in Aggressive Behavior. Horm. Behav. 2003, 44, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Gammie, S.C. GABA enhancement of maternal defense in mice: Possible neural correlates. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 86, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, E.; Morita, S.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Tsukahara, S. The glutamatergic system in the preoptic area is involved in the retention of maternal behavior in maternally experienced female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 120, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.J. Baby Love? Oxytocin-Dopamine Interactions in Mother-Infant Bonding. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, T.; Swart, J.M.; Grattan, D.R.; Brown, R.S.E. The Prolactin Family of Hormones as Regulators of Maternal Mood and Behavior. Front. Glob. Women’s Health 2021, 2, 767467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.S.E.; Aoki, M.; Ladyman, S.R.; Phillipps, H.R.; Wyatt, A.; Boehm, U.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin action in the medial preoptic area is necessary for postpartum maternal nursing behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10779–10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, L.; Li, M. 5-HT2A receptors modulate dopamine D2-mediated maternal effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 180, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzerelle, A.; Soiza-Reilly, M.; Hainer, C.; Ruet, P.-L.; Lesch, K.-P.; Bader, M.; Alenina, N.; Scotto-Lomassese, S.; Gaspar, P. Dorsal raphe serotonin neurotransmission is required for the expression of nursing behavior and for pup survival. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoicas, I.; Kornhuber, J. The Role of the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors in Social Behavior in Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, D.D.; Young, L.J.; Meaney, M.J.; Insel, T.R. Naturally Occurring Differences in Maternal Care are Associated with the Expression of Oxytocin and Vasopressin (V1a) Receptors: Gender Differences. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curley, J.P.; Jensen, C.L.; Franks, B.; Champagne, F.A. Variation in maternal and anxiety-like behavior associated with discrete patterns of oxytocin and vasopressin 1a receptor density in the lateral septum. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.; Gabler, N.; Ross, J.; Escobar, J.; Patience, J.; Rhoads, R.; Baumgard, L. The effects of heat stress and plane of nutrition on metabolism in growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, A.; McCabe, P.M.; Nation, D.A.; Tabak, B.A.; Rossetti, M.A.; McCullough, M.E.; Schneiderman, N.; Mendez, A.J. Evaluation of Enzyme Immunoassay and Radioimmunoassay Methods for the Measurement of Plasma Oxytocin. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandtzaeg, O.K.; Johnsen, E.; Roberg-Larsen, H.; Seip, K.F.; MacLean, E.L.; Gesquiere, L.R.; Leknes, S.; Lundanes, E.; Wilson, S.R. Proteomics tools reveal startlingly high amounts of oxytocin in plasma and serum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Chabaud, C.; Cozzi, A.; Codecasa, E.; Pageat, P. Validation of a Commercially Available Enzyme ImmunoAssay for the Determination of Oxytocin in Plasma Samples from Seven Domestic Animal Species. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Han, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, M.; He, M.; Rainer, G.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X. Measurement of ultra-trace level of intact oxytocin in plasma using SALLE combined with nano-LC–MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 173, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.A.; Li, X.; Menden, A.; Lee, M.R.; Lai, J.F. Oxytocin analysis from human serum, urine, and saliva by orbitrap liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, E.L.; Wilson, S.R.; Martin, W.L.; Davis, J.M.; Nazarloo, H.P.; Carter, C.S. Challenges for measuring oxytocin: The blind men and the elephant? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 107, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, B.A.; Leng, G.; Szeto, A.; Parker, K.J.; Verbalis, J.G.; Ziegler, T.E.; Lee, M.R.; Neumann, I.D.; Mendez, A.J. Advances in human oxytocin measurement: Challenges and proposed solutions. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uvnäs Moberg, K.; Handlin, L.; Kendall-Tackett, K.; Petersson, M. Oxytocin is a principal hormone that exerts part of its effects by active fragments. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 133, 109394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanadesikan, G.E.; Hammock, E.A.D.; Tecot, S.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Hart, R.; Carter, C.S.; MacLean, E.L. What are oxytocin assays measuring? Epitope mapping, metabolites, and comparisons of wildtype & knockout mouse urine. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 143, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplan, J.D.; Karim, A.; Chandra, P., St.; Germain, G.; Abdallah, C.G.; Altemus, M. Neurobiology of Maternal Stress: Role of Social Rank and Central Oxytocin in Hypothalamic–Pituitary Adrenal Axis Modulation. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rault, J.-L. Effects of positive and negative human contacts and intranasal oxytocin on cerebrospinal fluid oxytocin. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 69, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.M.; Samineni, S.; Allen, P.C.; Stockinger, D.; Bales, K.L.; Hwa, G.G.C.; Roberts, J.A. Plasma and CSF oxytocin levels after intranasal and intravenous oxytocin in awake macaques. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 66, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza-Sepulveda, M.L.; Fleming, A.S.; Jonas, W. Mothering revisited: A role for cortisol? Horm. Behav. 2020, 121, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.A.; Cardoso, C.; Ellenbogen, M.A. A meta-analytic review of the correlation between peripheral oxytocin and cortisol concentrations. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2016, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C. Biological perspectives on social attachment and bonding. In Attachment and Bonding: A New Synthesis; Carter, C., Ahnert, L., Grossmann, K., Hrday, S., Lamb, M., Porges, S., Sachser, N., Eds.; The Dahlemn Workshops: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gatta, E.; Mairesse, J.; Deruyter, L.; Marrocco, J.; Van Camp, G.; Bouwalerh, H.; Lo Guidice, J.-M.; Morley-Fletcher, S.; Nicoletti, F.; Maccari, S. Reduced maternal behavior caused by gestational stress is predictive of life span changes in risk-taking behavior and gene expression due to altering of the stress/anti-stress balance. Neurotoxicology 2018, 66, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohn, J.P.; Martinez, M.E.; Zafer, M.; López-Espíndola, D.; Keyes, L.M.; Hernandez, A. Increased aggression and lack of maternal behavior in Dio3-deficient mice are associated with abnormalities in oxytocin and vasopressin systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, R.A.; Cox, J.J.; van Kats, J.P.; Burbach, J.P. Thyroid hormone regulates the oxytocin gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 3771–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, N.; Davidkova, G.; Zhu, Y.-S.; Koibuchi, N.; Chin, W.W.; Pfaff, D. Differential Interaction of Estrogen Receptor and Thyroid Hormone Receptor Isoforms on the Rat Oxytocin Receptor Promoter Leads to Differences in Transcriptional Regulation. Neuroendocrinology 2001, 74, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, J.; Drobnik, J. Vasopressin and oxytocin release and the thyroid function. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 55, 423–441. [Google Scholar]
- Desouza, L.A.; Ladiwala, U.; Daniel, S.M.; Agashe, S.; Vaidya, R.A.; Vaidya, V.A. Thyroid hormone regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult rat brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 29, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorjahan, N.; Cattini, P.A. Neurogenesis in the Maternal Rodent Brain: Impacts of Gestation-Related Hormonal Regulation, Stress, and Obesity. Neuroendocrinology 2022, 112, 702–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M.; Verdu, E.F. Microbes and the gut-brain axis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, N. Role of gut microbiota in brain function and stress-related pathology. Biosci. Microbiota Food Heal. 2019, 38, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, N.; Larauche, M.; Biraud, M.; Molet, J.; Million, M.; Mayer, E.; Taché, Y. Limited Nesting Stress Alters Maternal Behavior and In Vivo Intestinal Permeability in Male Wistar Pup Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshim, P.; Walton, G.; Chakrabarti, B.; Givens, I.; Saddy, D.; Kitchen, I.; Swann, J.R.; Bailey, A. Maternal Weaning Modulates Emotional Behavior and Regulates the Gut-Brain Axis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.T.; Coe, C.L. Maternal separation disrupts the integrity of the intestinal microflora in infant rhesus monkeys. Dev. Psychobiol. 1999, 35, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Marchesi, J.R.; Scully, P.; Codling, C.; Ceolho, A.-M.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Early Life Stress Alters Behavior, Immunity, and Microbiota in Rats: Implications for Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Psychiatric Illnesses. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackers, H.S.; Thomas, S.; Williamson, K.; Posey, R.; Kimmel, M.C. Emerging literature in the Microbiota-Brain Axis and Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 95, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabé, B.P.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Rackers, H.S.; Welke, L.; Mantha, A.; Kimmel, M.C. Improving Mental Health for the Mother-Infant Dyad by Nutrition and the Maternal Gut Microbiome. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Velarde, A.; Marcet-Rius, M.; Orihuela, A.; Bragaglio, A.; Hernández-Ávalos, I.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Whittaker, A.L. Analgesia during Parturition in Domestic Animals: Perspectives and Controversies on Its Use. Animals 2022, 12, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Burnes, J.; Muns, R.; Barrios-García, H.; Villanueva-García, D.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Mota-Rojas, D. Parturition in Mammals: Animal Models, Pain and Distress. Animals 2021, 11, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Martínez-Burnes, J.; Napolitano, F.; Domínguez-Muñoz, M.; Guerrero-Legarreta, I.; Mora-Medina, P.; Ramírez-Necoechea, R.; Lezama-García, K.; González-Lozano, M. Dystocia: Factors Affecting Parturition in Domestic Animals. CABI Rev. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuller, W.; Sietsma, S.; Hendriksen, S.; Sperling, D. Use of Paracetamol in Sows around Farrowing: Effect on Health and Condition of the Sow, Piglet Mortality, Piglet Weight and Piglet Weight Gain. Porc. Heal. Manag. 2021, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, S.H.; Jarvis, S.; Hall, S.A.; Ashworth, C.J.; Rutherford, K.M.D. Periparturient Behavior and Physiology: Further Insight into the Farrowing Process for Primiparous and Multiparous Sows. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummaruk, P.; Sang-Gassanee, K. Effect of Farrowing Duration, Parity Number and the Type of Anti-Inflammatory Drug on Postparturient Disorders in Sows: A Clinical Study. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2013, 45, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, A.C.; Philipp, H.; Kleemann, R. Investigation on the Efficacy of Meloxicam in Sows with Mastitis-Metritis-Agalactia Syndrome. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 26, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzenberg, D.S.; Mayer, H.S. Experience-Dependent Mechanisms in the Regulation of Parental Care. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 54, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, A.S.; Luebke, C. Timidity Prevents the Virgin Female Rat from Being a Good Mother: Emotionality Differences between Nulliparous and Parturient Females. Physiol. Behav. 1981, 27, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, A.; Valera-Marín, G.; Hernández-Martínez, A.; Lanuza, E.; Martínez-García, F.; Agustín-Pavón, C. Wired for Motherhood: Induction of Maternal Care but Not Maternal Aggression in Virgin Female CD1 Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seip, K.M.; Morrell, J.I. Exposure to Pups Influences the Strength of Maternal Motivation in Virgin Female Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolzenberg, D.S.; Rissman, E.F. Oestrogen-Independent, Experience-Induced Maternal Behaviour in Female Mice. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, T.M.; Duhr, M.; Flint, B. Pathology of House Mouse (Mus musculus) Predation on Laysan Albatross (Phoebastria aimutabilis) on Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhr, M.; Flint, E.N.; Hunter, S.A.; Taylor, R.V.; Flanders, B.; Howald, G.; Norwood, D. Control of House Mice Preying on Adult Albatrossess at Midwy Atoll National Wildlife Refuge. In Island Invasives: Scaling up to Meet the Challenge; Veitch, C.R., Ciout, M.N., Russell, J.C., West, C.J., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 62, pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, N.R.; Beck, A.; Fontbonne, A. The View of the French Dog Breeders in Relation to Female Reproduction, Maternal Care and Stress during the Peripartum Period. Animals 2020, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, N.; Kockaya, M.; Kapancik, S.; Bakir, D. Determination of Serum Adenosine Deaminase and Xanthine Oxidase Activity in Kangal Dogs with Maternal Cannibalism. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kockaya, M.; Ercan, N.; Demirbas, Y.S.; Da Graça Pereira, G. Serum Oxytocin and Lipid Levels of Dogs with Maternal Cannibalism. J. Vet. Behav. 2018, 27, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, P.D.; Brown, S.C. It’s a Dog Eat Dog World: Observations of Dingo (Canis familiaris) Cannibalism. Aust. Mammal. 2017, 39, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, P.; Waterhouse, T.; Dwyer, C.; Stott, A. The Perception of the Welfare of Sheep in Extensive Systems. Small Rumin. Res. 2006, 62, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, C.M. Genetic and physiological determinants of maternal behavior and lamb survival: Implications for low-input sheep management. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, E246–E258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, L.J.; Campbell, C.S. Maternal Behavior in the Primiparous and Multiparous Golden Hamster1. Z. Tierpsychol. 2010, 50, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemps, A.; Timmermans, P. Effects of Social Rearing Conditions and Partus Experience on Periparturitional Behaviour in Java-Macaques (Macaca fascicularis). Behaviour 1984, 88, 200–214. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, B.S.; Moss, H.A. Birth Order and Sex of Sibling as Determinants of Mother-Infant Interaction. Child Dev. 1976, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardini, G.; Bowen, J.; Raviglione, S.; Farina, R.; Gazzano, A. Maternal Behaviour in Domestic Dogs: A Comparison between Primiparous and Multiparous Dogs. Behaviour 2015, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oczak, M.; Maschat, K.; Berckmans, D.; Vranken, E.; Baumgartner, J. Classification of Nest-Building Behaviour in Non-Crated Farrowing Sows on the Basis of Accelerometer Data. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 140, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçkaya, M.; Demirbas, Y.S. The Use of Carbetocin in the Treatment of Maternal Cannibalism in Dogs. J. Vet. Behav. 2020, 40, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
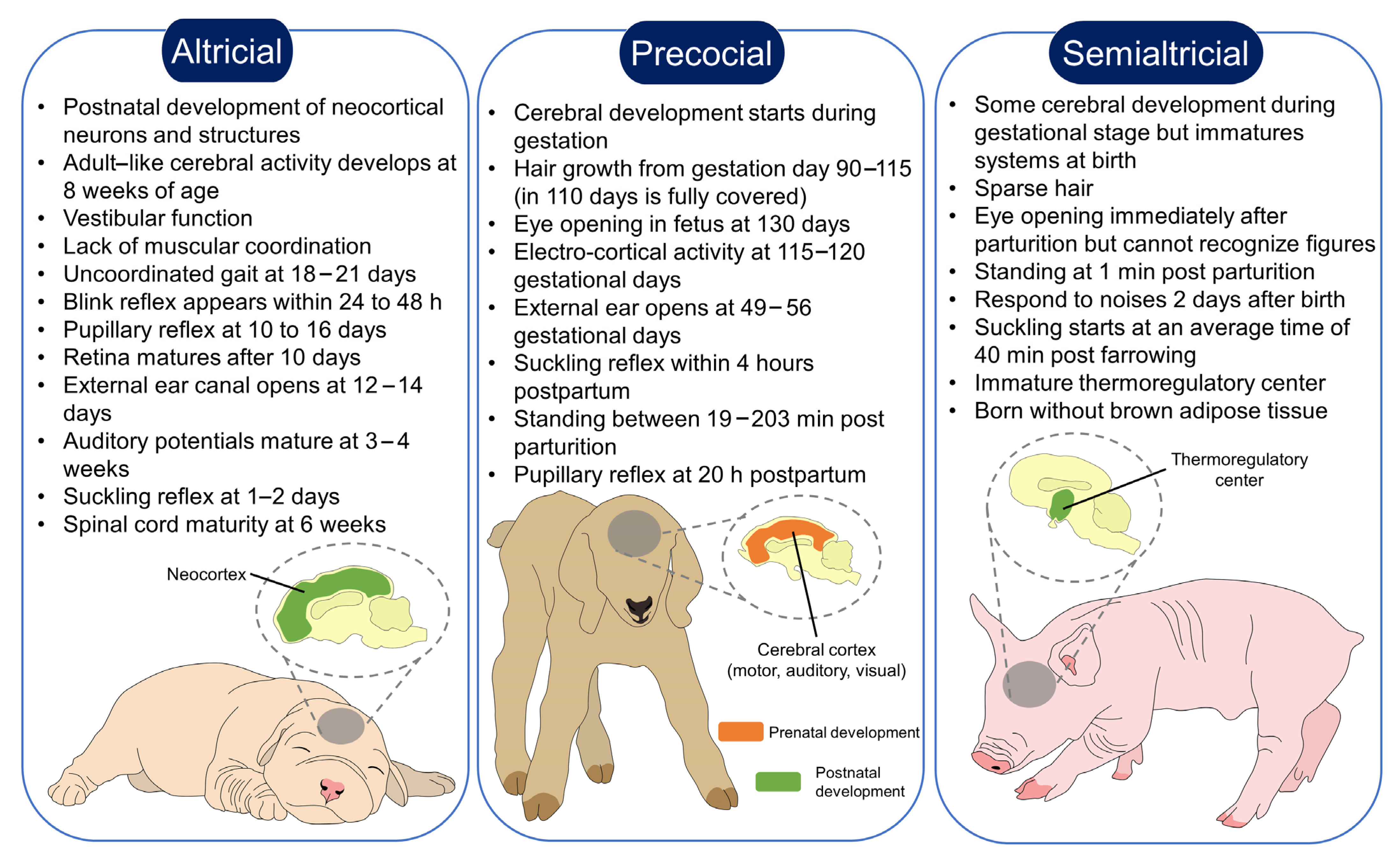
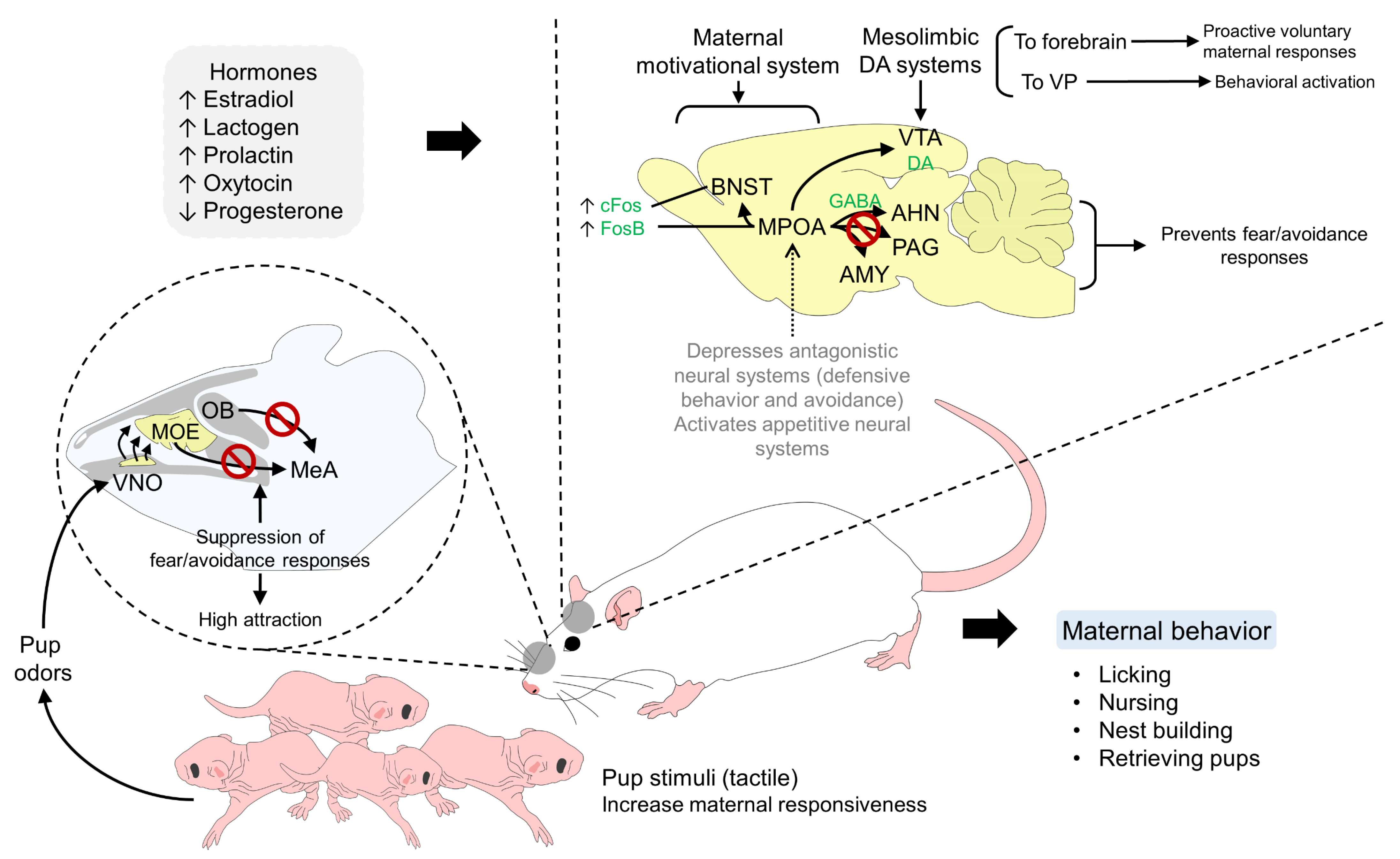
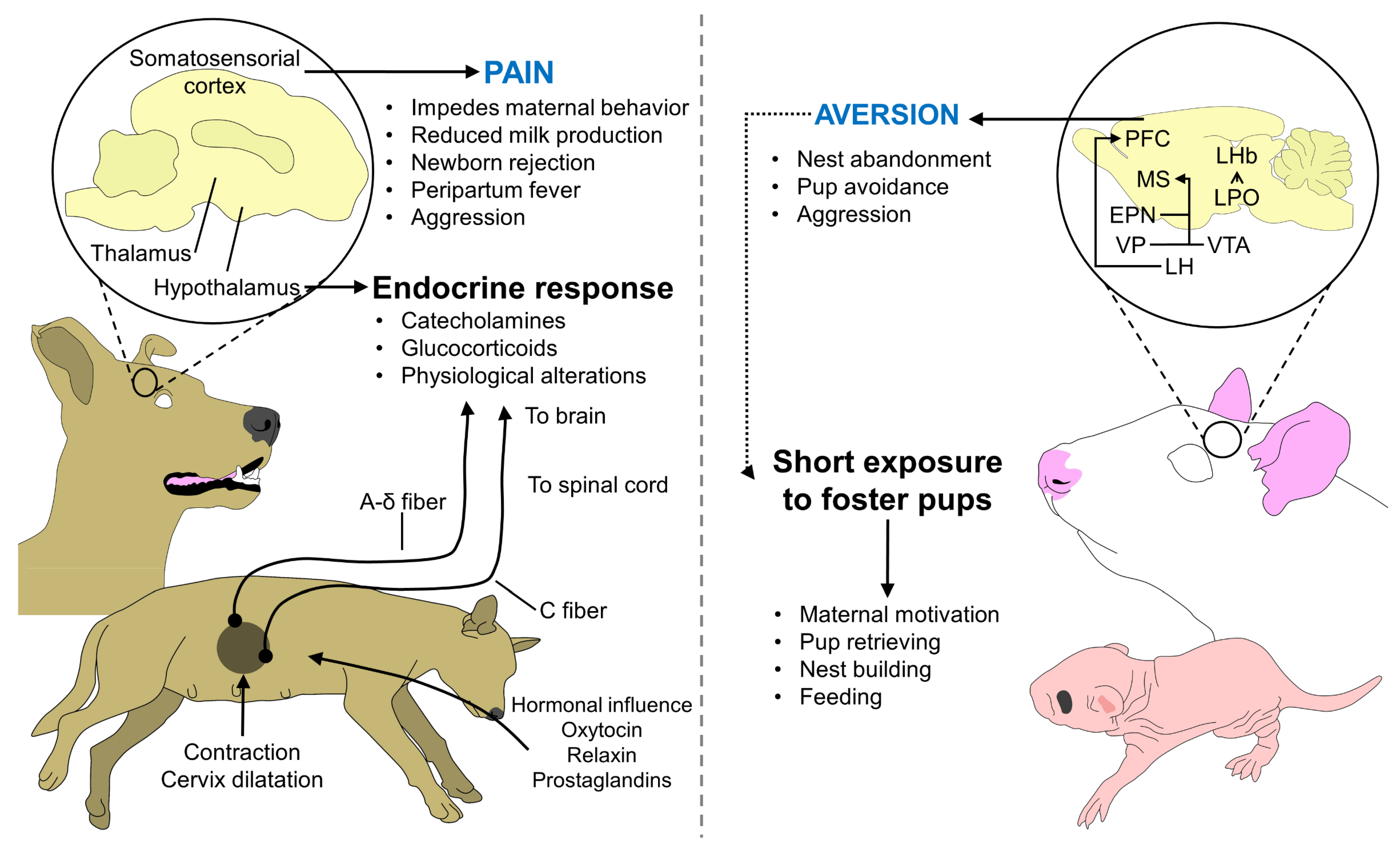
| Species | Pre-Natal Development | PostNatal Development | Functional Senses Immediately after Birth | Maternal Care | Bonding | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altricial |
|
|
|
|
| [49,50,51] |
| Precocial |
|
|
|
|
| [52,53,54,55] |
| Neurotransmitter | Synthesis | Status | Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXT | PVN, SOP | ↑ | Maternal behavior | [153] |
| ↓ | Lack of newborn retrieving and licking. | [155] | ||
| GABA | Presynaptic neuron | ↑ | Maternal defense | [176] |
| GLU | Presynaptic neuron | ↑ | Long-term maternal experience. | [177] |
| DA | Dopaminergic neurons | ↑ | Maternal care, bonding, reward system. | [178] |
| ↓ | Impaired maternal recognition. | |||
| PRL | Lactotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland | ↑ | Maternal care. | [179] |
| ↓ | Litter abandonment. | [180] | ||
| 5-HT | Enteric nervous system, CNS, Merkel and pulmonary cells | ↑ | Modulates DA maternal effects. | [181] |
| ↓ | Reduces pup survival and nursing behavior. | [182] | ||
| NMDA | Ionotropic neurons | ↓ | Impaired retrieval. | [183] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bienboire-Frosini, C.; Marcet-Rius, M.; Orihuela, A.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Mora-Medina, P.; Olmos-Hernández, A.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Mota-Rojas, D. Mother–Young Bonding: Neurobiological Aspects and Maternal Biochemical Signaling in Altricial Domesticated Mammals. Animals 2023, 13, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030532
Bienboire-Frosini C, Marcet-Rius M, Orihuela A, Domínguez-Oliva A, Mora-Medina P, Olmos-Hernández A, Casas-Alvarado A, Mota-Rojas D. Mother–Young Bonding: Neurobiological Aspects and Maternal Biochemical Signaling in Altricial Domesticated Mammals. Animals. 2023; 13(3):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030532
Chicago/Turabian StyleBienboire-Frosini, Cécile, Míriam Marcet-Rius, Agustín Orihuela, Adriana Domínguez-Oliva, Patricia Mora-Medina, Adriana Olmos-Hernández, Alejandro Casas-Alvarado, and Daniel Mota-Rojas. 2023. "Mother–Young Bonding: Neurobiological Aspects and Maternal Biochemical Signaling in Altricial Domesticated Mammals" Animals 13, no. 3: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030532
APA StyleBienboire-Frosini, C., Marcet-Rius, M., Orihuela, A., Domínguez-Oliva, A., Mora-Medina, P., Olmos-Hernández, A., Casas-Alvarado, A., & Mota-Rojas, D. (2023). Mother–Young Bonding: Neurobiological Aspects and Maternal Biochemical Signaling in Altricial Domesticated Mammals. Animals, 13(3), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13030532









