Rumen Fermentation Parameters Prediction Model for Dairy Cows Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Method
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
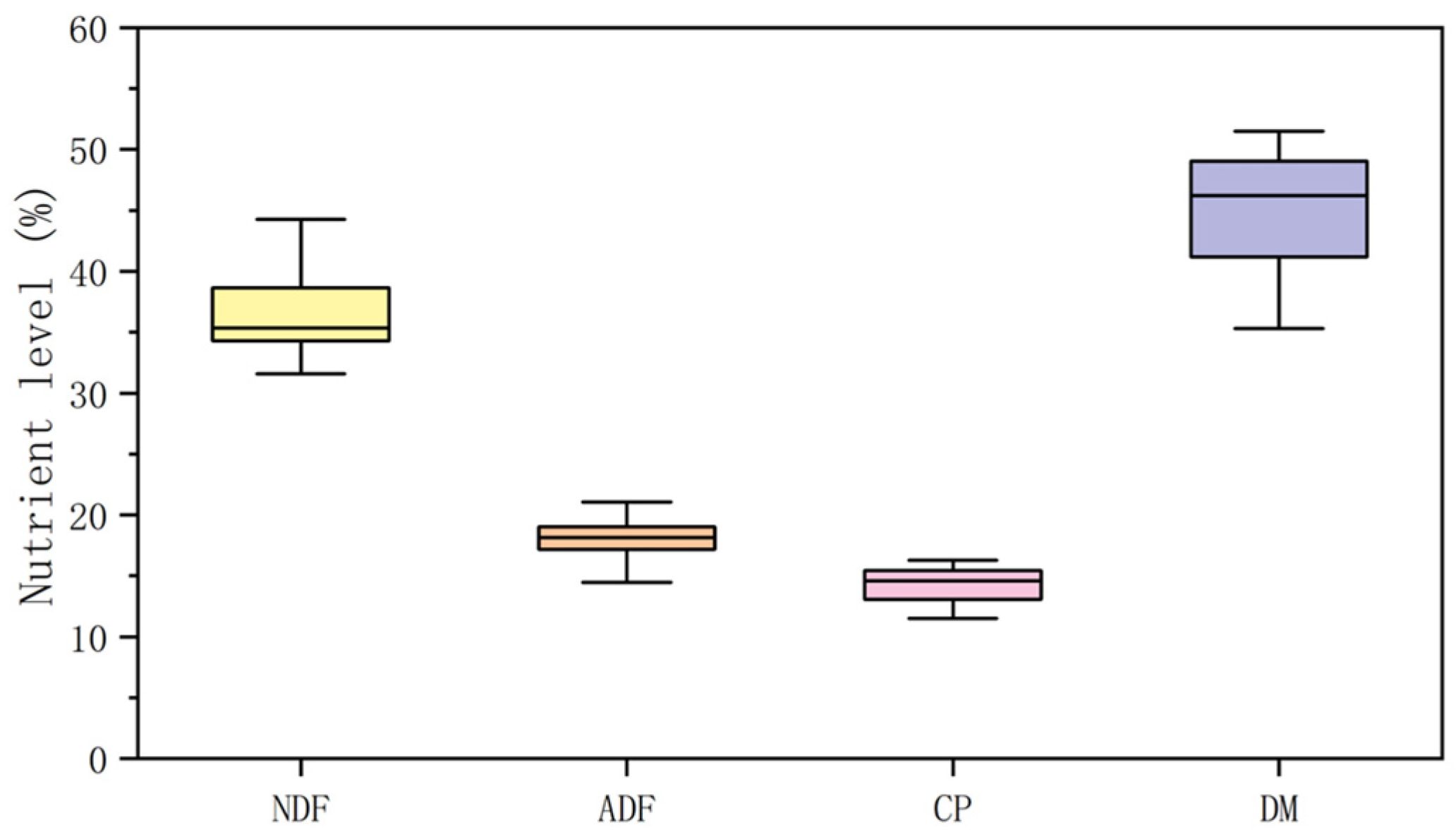
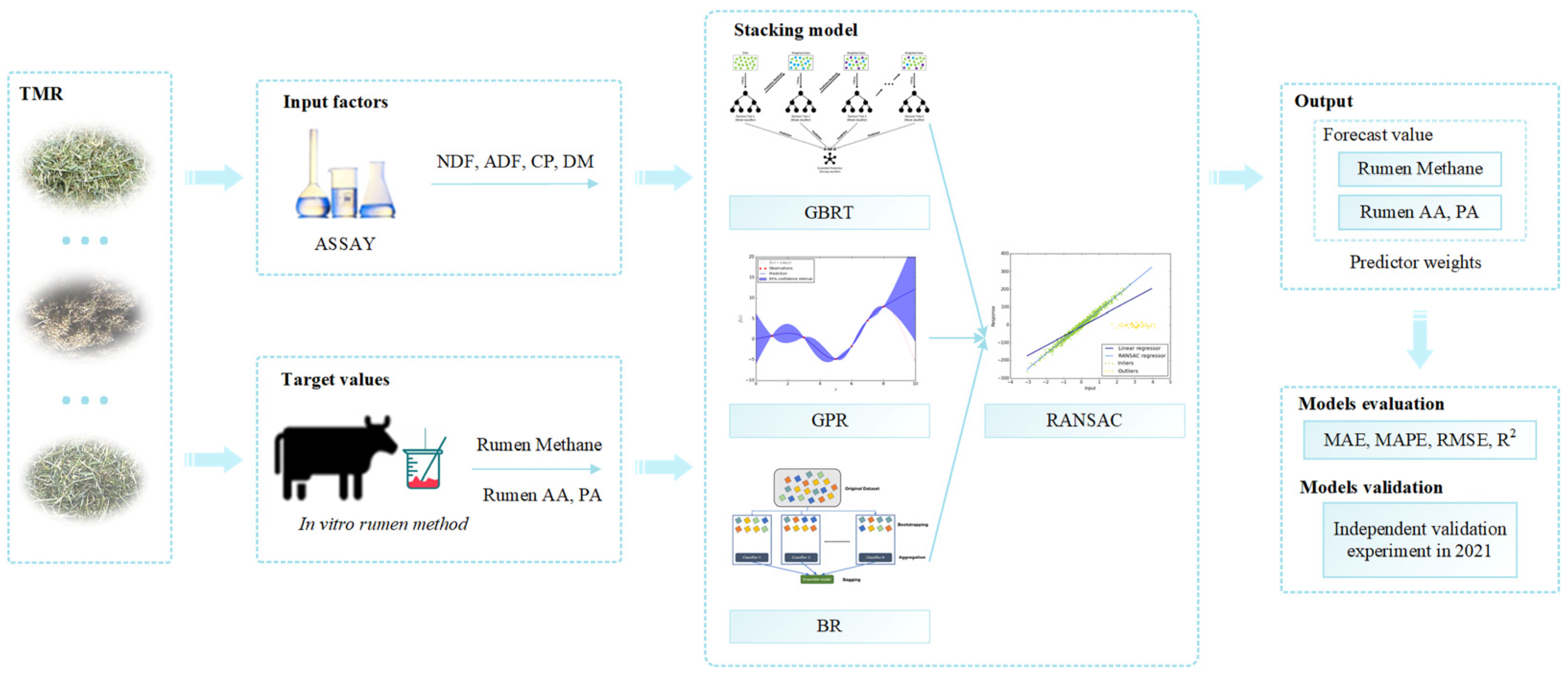
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data for Validation Experiments
2.3. Modeling
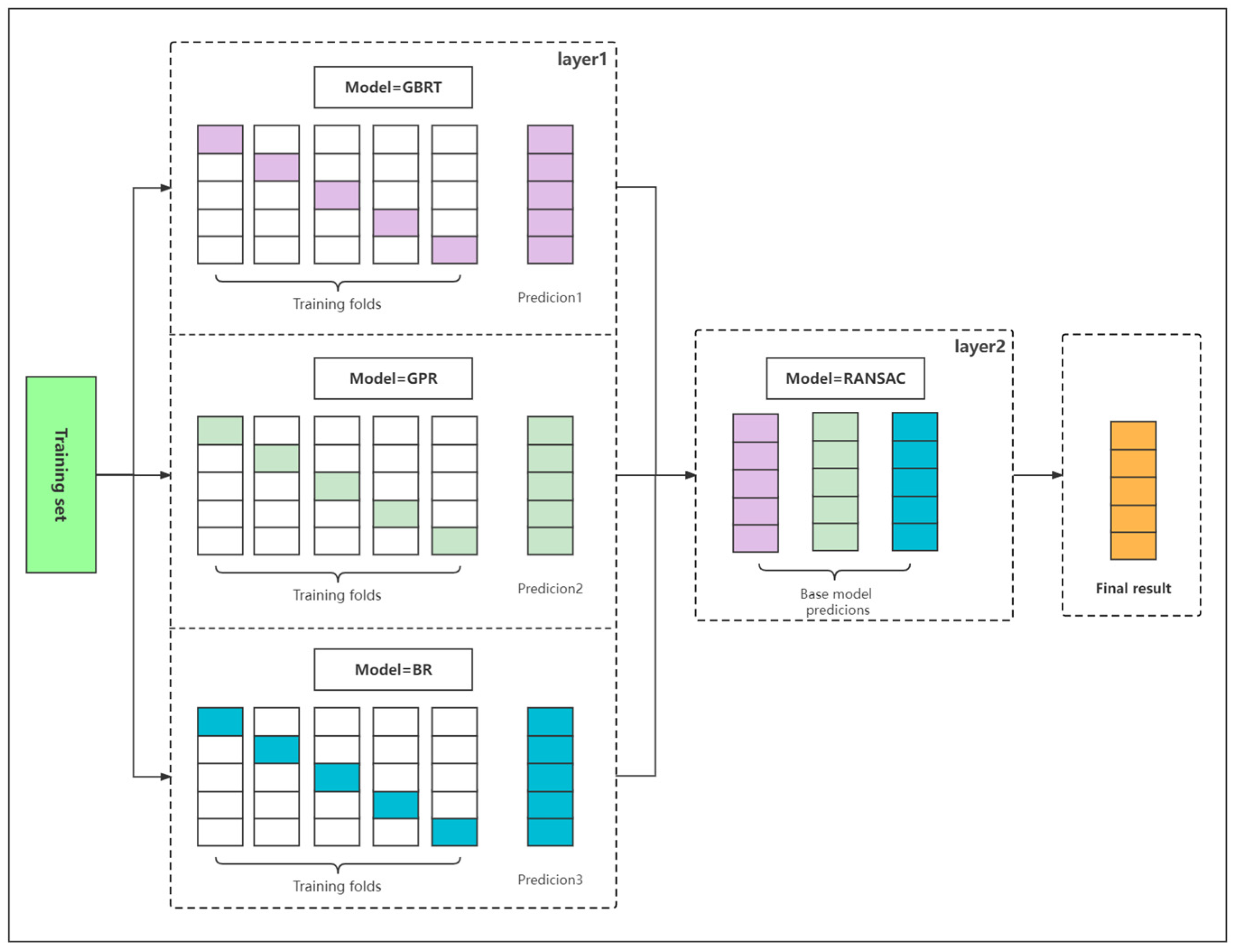
2.3.1. Base-Level Learning Component
2.3.2. Meta-Level Combining Component
2.3.3. Stacking Model
2.4. Model Evaluation Method
3. Results
3.1. Numerical Results
3.2. Results of the Validation Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Comparison of Stacking Models and Base Learners
4.2. Effects of Fiber Content on Rumen Fermentation Parameters
4.3. Effects of C:F Ratio on Rumen Fermentation Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Lv, J.; Lambo, M.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Replacing soybean meal with high-oil pumpkin seed cake in the diet of lactating Holstein dairy cows modulated rumen bacteria and milk fatty acid profile. J. Dairy Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaizier, J.; Krause, D.; Gozho, G.; McBride, B. Subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy cows: The physiological causes, incidence and consequences. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardelli, F.; Ferronato, G.; Gallo, A. Near-infrared calibration models for estimating volatile fatty acids and methane production from in vitro rumen fermentation of different total mixed rations. JDS Commun. 2022, 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, J.; Forbes, J.M.; France, J. Quantitative Aspects of Ruminant Digestion and Metabolism, 2nd ed.; CABI Pub.: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Getachew, G.; DePeters, E.; Robinson, P.; Fadel, J. Use of an in vitro rumen gas production technique to evaluate microbial fermentation of ruminant feeds and its impact on fermentation products. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 123, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, R.M.; Mould, F.L.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Owen, E.; Channa, K.S.; Theodorou, M.K. A semi-automated in vitro gas production technique for ruminant feedstuff evaluation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999, 79, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Ma, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Effects of corn straw treated with CaO on rumen degradation characteristics and fermentation parameters and their correlation with microbial diversity in rumen. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 292, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiby, K.V.; Krizsan, S.J.; Eknæs, M.; Schwarm, A.; Whist, A.C.; Schei, I.; Steinshamn, H.; Lund, P.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Dønnem, I. Associations among nutrient concentration, silage fermentation products, in vivo organic matter digestibility, rumen fermentation and in vitro methane yield in 78 grass silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 285, 115249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhao, G.; James, H.P. Predicting in vitro rumen VFA production using CNCPS carbohydrate fractions with multiple linear models and artificial neural networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Sengupta, S.; Hanigan, M.D. Using artificial neural networks to predict pH, ammonia, and volatile fatty acid concentrations in the rumen. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8850–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Adolphs, J.; Landwehr, N.; Willink, D.; Janke, D.; Amon, T. Supervised machine learning to assess methane emissions of a dairy building with natural ventilation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Kebreab, E.; Niu, M.; Oh, J.; Bannink, A.; Bayat, A.R.; Boland, T.M.; Brito, A.F.; Casper, D.P.; Crompton, L.A. Symposium review: Uncertainties in enteric methane inventories, measurement techniques, and prediction models. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 6655–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poczynek, M.; Toledo, A.F.; Silva, A.P.; Silva, M.D.; Oliveira, G.B.; Coelho, M.G.; Virginio Jr, G.F.; Polizel, D.; Costa, J.H.; Bittar, C.M. Partial corn replacement by soybean hull, or hay supplementation: Effects of increased NDF in diet on performance, metabolism and behavior of pre-weaned calves. Livest. Sci. 2020, 231, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab, U.; Sinclair, L.; Wilkinson, R.; Humphries, D.; Reynolds, C. Milk production, rumen function, and digestion in dairy cows fed diets differing in predominant forage and concentrate type. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 284, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Guo, X.; Xu, L.; Shao, L.; Zhu, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, K. Effect of whole-plant corn silage treated with lignocellulose-degrading bacteria on growth performance, rumen fermentation, and rumen microflora in sheep. Animal 2022, 16, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yue, K.; Liu, X.; Maksimov, N.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of dairy cow production performance by in vitro fermentation technology. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2018, 45, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, X.; Ban, Z.; Yang, H.; Hegarty, R.; Zhao, Y. The effect of cysteamine hydrochloride and nitrate supplementation on in-vitro and in-vivo methane production and productivity of cattle. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 232, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dagar, S.S.; Puniya, A.K.; Upadhyay, R.C. Changes in methane emission, rumen fermentation in response to diet and microbial interactions. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G.; Wei, B.; Sun, Y.; Lan, Y.; Dou, X.; Zhang, Y. Changes in Carbohydrate Composition in Fermented Total Mixed Ration and Its Effects on in vitro Methane Production and Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, O.; Rokach, L. Ensemble learning: A survey. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees, 1st ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, S.A.; Heyns, P. An integrated Gaussian process regression for prediction of remaining useful life of slow speed bearings based on acoustic emission. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 84, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Lennox, B. Model stacking to improve prediction and variable importance robustness for soft sensor development. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, L.; Gleason, C.; Bedford, A.; Liebe, D.; Yohe, T.; Hall, M.; Daniels, K.; White, R. Rumen volatile fatty acid molar proportions, rumen epithelial gene expression, and blood metabolite concentration responses to ruminally degradable starch and fiber supplies. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8857–8869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olijhoek, D.; Hellwing, A.; Noel, S.; Lund, P.; Larsen, M.; Weisbjerg, M.; Børsting, C. Feeding up to 91% concentrate to Holstein and Jersey dairy cows: Effects on enteric methane emission, rumen fermentation and bacterial community, digestibility, production, and feeding behavior. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 9523–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, I.; Wallace, R.J.; Moraïs, S. The rumen microbiome: Balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.N. Dietary manipulation: A sustainable way to mitigate methane emissions from ruminants. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2018, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valadares, R.; Broderick, G.; Valadares Filho, S.; Clayton, M. Effect of replacing alfalfa silage with high moisture corn on ruminal protein synthesis estimated from excretion of total purine derivatives. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2686–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguerre, M.J.; Wattiaux, M.A.; Powell, J.; Broderick, G.A.; Arndt, C. Effect of forage-to-concentrate ratio in dairy cow diets on emission of methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia, lactation performance, and manure excretion. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Lambo, M.T.; Huang, J.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Replacing alfalfa hay with industrial hemp ethanol extraction byproduct and Chinese wildrye hay: Effects on lactation performance, plasma metabolites, and bacterial communities in Holstein cows. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granja-Salcedo, Y.T.; Ribeiro Junior, C.S.; de Jesus, R.B.; Gomez-Insuasti, A.S.; Rivera, A.R.; Messana, J.D.; Canesin, R.C.; Berchielli, T.T. Effect of different levels of concentrate on ruminal microorganisms and rumen fermentation in Nellore steers. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 70, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryan, E.; Ringler, C.; Okoba, B.; Koo, J.; Herrero, M.; Silvestri, S. Can agriculture support climate change adaptation, greenhouse gas mitigation and rural livelihoods? Insights from Kenya. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lana, R.P.; Russell, J.B.; Van Amburgh, M.E. The role of pH in regulating ruminal methane and ammonia production. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Composition | T1 Ingredient, % | T2 Ingredient, % |
|---|---|---|
| Corn silage | 42.76 | 29.31 |
| Steam-flaked corn | 18.32 | 29.87 |
| Alfalfa hay | 17.27 | 10.76 |
| Rapeseed meal | 5.94 | 4.56 |
| Soybean meal | 7.78 | 9.37 |
| Dry corn gluten feed | 2.90 | 6.52 |
| DDGS | 2.92 | 6.52 |
| Premix | 2.11 | 3.09 |
| Nutrient level, % | ||
| NEL(Mcal/kg of DM) | 1.56 | 1.66 |
| CP | 16.39 | 17.62 |
| NDF | 41.24 | 33.61 |
| ADF | 27.52 | 20.03 |
| Ash | 8.12 | 8.05 |
| Starch | 20.26 | 24.86 |
| EE | 3.45 | 4.52 |
| NFC | 30.44 | 36.20 |
| Models | MAE | MAPE | RMSE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| methane (mL/g) | GBRT | 1.018 | 0.108 | 1.129 | 0.903 |
| GPR | 0.855 | 0.087 | 1.12 | 0.904 | |
| BR | 0.764 | 0.066 | 1.081 | 0.911 | |
| Stacking model | 0.525 | 0.042 | 0.968 | 0.928 |
| Models | MAE | MAPE | RMSE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA (mmol/L) | GBRT | 1.579 | 0.03 | 2.499 | 0.821 |
| GPR | 1.532 | 0.03 | 2.174 | 0.864 | |
| BR | 1.441 | 0.027 | 2.579 | 0.809 | |
| Stacking model | 1.015 | 0.019 | 1.975 | 0.888 |
| Models | MAE | MAPE | RMSE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA (mmol/L) | GBRT | 0.883 | 0.028 | 1.112 | 0.829 |
| GPR | 1.159 | 0.037 | 1.367 | 0.742 | |
| BR | 0.959 | 0.03 | 1.114 | 0.828 | |
| Stacking model | 0.584 | 0.019 | 0.74 | 0.924 |
| Models | T1-obs | T1-sim | T2-obs | T2-sim | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| methane (mL/g) | GBRT | 23.11 | 19.44 | 21.94 | 19.43 |
| GPR | 23.11 | 7.26 | 21.94 | 19.6 | |
| BR | 23.11 | 20.84 | 21.94 | 20.86 | |
| Stacking model | 23.11 | 20.8 | 21.94 | 20.44 | |
| AA (mmol/L) | GBRT | 38.16 | 51.94 | 41.55 | 56.72 |
| GPR | 38.16 | 49.23 | 41.55 | 47.83 | |
| BR | 38.16 | 51.9 | 41.55 | 51.07 | |
| Stacking model | 38.16 | 52.54 | 41.55 | 56.4 | |
| PA (mmol/L) | GBRT | 10.74 | 14.58 | 14.02 | 17.25 |
| GPR | 10.74 | 10.8 | 14.02 | 15.09 | |
| BR | 10.74 | 21.45 | 14.02 | 18.87 | |
| Stacking model | 10.74 | 13.87 | 14.02 | 18.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Wei, X. Rumen Fermentation Parameters Prediction Model for Dairy Cows Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Method. Animals 2023, 13, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040678
Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang X, Yu Q, Sun Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Shen W, Wei X. Rumen Fermentation Parameters Prediction Model for Dairy Cows Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Method. Animals. 2023; 13(4):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040678
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuxuan, Jianzhao Zhou, Xinjie Wang, Qingyuan Yu, Yukun Sun, Yang Li, Yonggen Zhang, Weizheng Shen, and Xiaoli Wei. 2023. "Rumen Fermentation Parameters Prediction Model for Dairy Cows Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Method" Animals 13, no. 4: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040678
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, J., Wang, X., Yu, Q., Sun, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Shen, W., & Wei, X. (2023). Rumen Fermentation Parameters Prediction Model for Dairy Cows Using a Stacking Ensemble Learning Method. Animals, 13(4), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040678







