A New Parasitic Archamoeba Causing Systemic Granulomatous Disease in Goldfish Extends the Diversity of Pathogenic Endolimax spp.
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
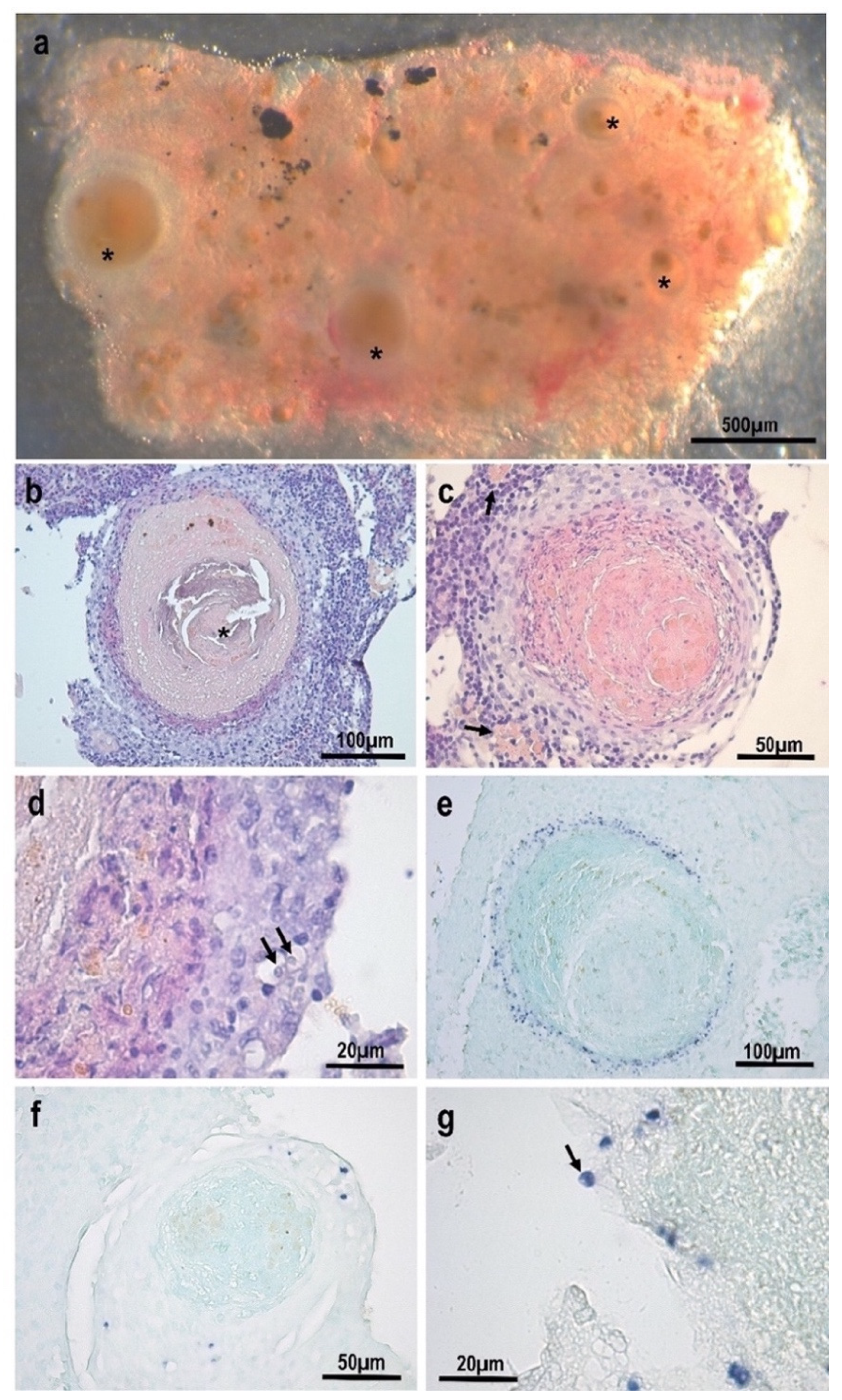
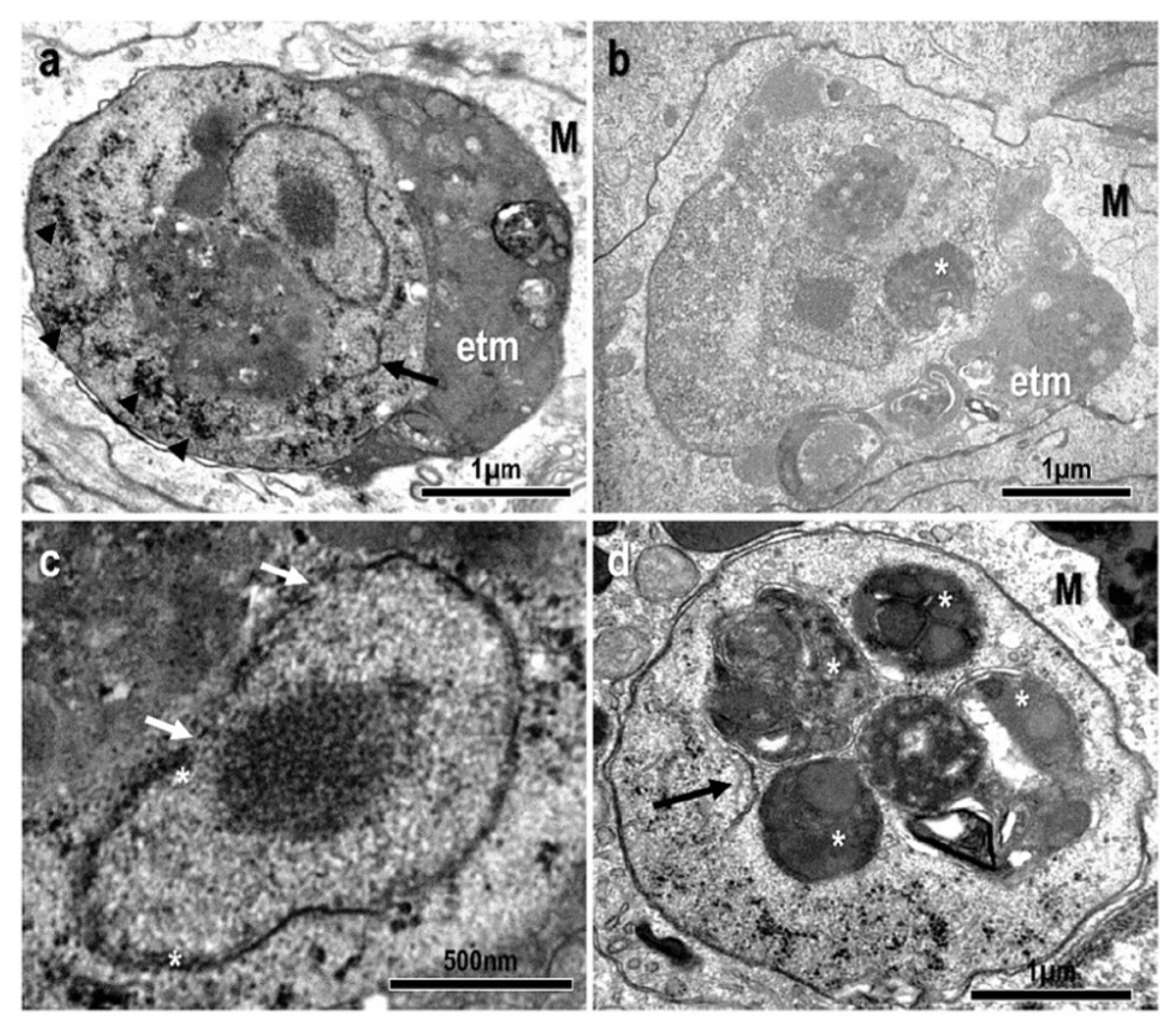
3.1. Morphological and Histopathological Observations
3.2. SSU rDNA Characterization and Phylogenetic Inference
3.3. Description of the Species: Endolimax carassius n. sp.
- Type host: Carassius auratus
- Locality: The parasite was detected in Carassius auratus from commercial ornamental fish suppliers in Barcelona, Spain. Previous reports in North America, Central Europe and Israel. Presumed to be distributed worldwide
- Location in the host: Systemic: mostly found within the inflammatory layer at the periphery of granulomatous lesions in the kidney. Detected via qPCR in samples from asymptomatic fish with a high prevalence (83%);
- Material deposited: A partial SSU rDNA (2934 bps) comprising the coding region between helixes 1–48 was deposited in GenBank with Accession no. ON646298;
- Taxonomic remarks: High morphological and pathogenic resemblance with Endolimax piscium but with distinct SSU rDNA genotype (87.5% pairwise identity). Phylogenetic clustering with terrestrial Endolimax sp. genotypes and with genotypes of the genus Iodamoeba as the closest sister group.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Constenla, M.; Padros, F.; Palenzuela, O. Endolimax piscium sp. nov. (Amoebozoa), causative agent of systemic granulomatous disease of cultured sole, Solea senegalensis Kaup. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, C.S.; Stensvold, C.R. Systematic review on Endolimax nana: A less well studied intestinal ameba. Trop. Parasitol. 2016, 6, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silberman, J.D.; Clark, C.G.; Diamond, L.S.; Sogin, M.S. Phylogeny of the genera Entamoeba and Endolimax as deduced from small-subunit ribosomal RNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chihi, A.; Stensvold, C.R.; Ben-Abda, I.; Ben-Romdhane, R.; Aoun, K.; Siala, E.; Bouratbine, A. Development and evaluation of molecular tools for detecting and differentiating intestinal amoebae in healthy individuals. Parasitology 2019, 146, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Suzuki, J.; Azuma, Y.; Kobayashi-Ogata, N.; Kartikasari, D.P.; Yanagawa, Y.; Iwata, S. Growth-promoting effects of the hydrogen-sulfide compounds produced by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans subsp. desulfuricans co-cultured with Escherichia coli (DH5α) on the growth of Entamoeba and Endolimax species isolates from swine. Biosci. Trends 2019, 13, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Lebbad, M.; Hansen, A.; Beser, J.; Belkessa, S.; O’Brien Andersen, L.; Clark, C.G. Differentiation of Blastocystis and parasitic archamoebids encountered in untreated wastewater samples by amplicon-based next-generation sequencing. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 9, e00131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, E.F.; Jamy, M.; Burki, F.; Clark, C.G.; Stensvold, C.R. Unravelling the phylogeny of a common intestinal protist: Intrageneric diversity of Endolimax. Protist 2022, 173, 125908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Lebbad, M.; Clark, C.G. Last of the human protists: The phylogeny and genetic diversity of Iodamoeba. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constenla, M.; Padrós, F. Histopathological and ultrastructural studies on a novel pathological condition in Solea senegalensis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 90, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constenla, M.; Padros, F.; del Pozo, R.; Palenzuela, O. Development of different diagnostic techniques for Endolimax piscium (archamoebae) and their applicability in Solea senegalensis clinical samples. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constenla, M.; Padros, F.; Villanueva-González, A.; del Pozo, R.; Palenzuela, O. Horizontal transmission of Endolimax piscium, causative agent of systemic amoebiasis in Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 130, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrós, F.; Constenla, M. Diseases caused by amoebae in fish: An overview. Animals 2021, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelker, F.A.; Anver, M.R.; McKee, A.E.; Casey, H.W.; Brenniman, G.R. Amebiasis in goldfish. Vet. Pathol. 1977, 14, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dykova, I.; Lom, J.; Machackova, B.; Sawyer, T.K. Amoebic infections in goldfishes and granulomatous lesions. Folia Parasitol. 1996, 43, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.A.; Wolf, J.C.; Duncan, R.B.; Cardinale, J.L. Systemic Granulomatous Amebiasis in Goldfish (Carassius auratus). Proceedings of the International Association for Aquatic Animal Medicine (IAAAM) Conference, San Diego, California, USA, 1998. Available online: https://www.vin.com/doc/?id=3864320 (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Palenzuela, O.; Redondo, M.J.; Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Description of Enteromyxum scophthalmi gen. nov., sp. nov. (Myxozoa), an intestinal parasite of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) using morphological and ribosomal RNA sequence data. Parasitology 2002, 124, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, W.; Strunk, O.; Westram, R.; Richter, L.; Meier, H.; Yadhukumar; Buchner, A.; Lai, T.; Steppi, S.; Jobb, G.; et al. ARB: A software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwight, Z.; Palais, R.; Wittwer, C.T. uMELT: Prediction of high-resolution melting curves and dynamic melting profiles of PCR products in a rich web application. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1019–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landsberg, J.H.; Paperna, I. Systemic granuloma in goldfish caused by a Dermocystidium-like aetiological agent. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1992, 13, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lom, J.; Dykova, I. Protozoan Parasites of Fish; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhagen, D.; Jendrysek, S.; Körting, W. Amöbiasis bei goldfishen. Kleintierpraxis 1993, 38, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, I.G.; Prior, H.C.; Rodwell, B.J.; Harris, G.O. Iridovirus-like virions in imported dwarf gourami (Colisa lalia) with systemic amoebiasis. Aust. Vet. J. 1993, 70, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, G.; Nash, M.; Schlotfeldt, H.-J. Systemic amoebiasis in cultured European catfish, Silurus glanis L. J. Fish Dis. 1988, 11, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palíková, M.; Navrátil, S.; Dyková, I.; Pavlík, I.; Slany, M.; Tichy, F.; Novotny, L.; Zendulkova, D.; Kriz, P.; Laichmanova, M. Archamoeba infection manifested by granulomatous inflammatory lesions in European tench, Tinca tinca (L.). Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish Pathol. 2012, 32, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Zadrobílková, E.; Walker, G.; Čepička, I. Morphological and molecular evidence support a close relationship between the free-living archamoebae Mastigella and Pelomyxa. Protist 2015, 166, 14–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.J. Characterizing regions of ambiguous alignment caused by the expansion and contraction of hairpin-stem loops in ribosomal RNA molecules. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kück, P.; Meusemann, K.; Dambach, J.; Thormann, B.; von Reumont, B.M.; Wägele, J.W.; Misof, B. Parametric and non-parametric masking of randomness in sequence alignments can be improved and leads to better resolved trees. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, K.M.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Alignment uncertainty and genomic analysis. Science 2008, 319, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Cantellano, M.; Martínez-Palomo, A. Pathogenesis of intestinal amebiasis: From molecules to disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Constenla, M.; Palenzuela, O. A New Parasitic Archamoeba Causing Systemic Granulomatous Disease in Goldfish Extends the Diversity of Pathogenic Endolimax spp. Animals 2023, 13, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050935
Constenla M, Palenzuela O. A New Parasitic Archamoeba Causing Systemic Granulomatous Disease in Goldfish Extends the Diversity of Pathogenic Endolimax spp. Animals. 2023; 13(5):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050935
Chicago/Turabian StyleConstenla, Maria, and Oswaldo Palenzuela. 2023. "A New Parasitic Archamoeba Causing Systemic Granulomatous Disease in Goldfish Extends the Diversity of Pathogenic Endolimax spp." Animals 13, no. 5: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050935
APA StyleConstenla, M., & Palenzuela, O. (2023). A New Parasitic Archamoeba Causing Systemic Granulomatous Disease in Goldfish Extends the Diversity of Pathogenic Endolimax spp. Animals, 13(5), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13050935





