Electroencephalogram and Physiological Responses as Affected by Slaughter Empathy in Goats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Animals
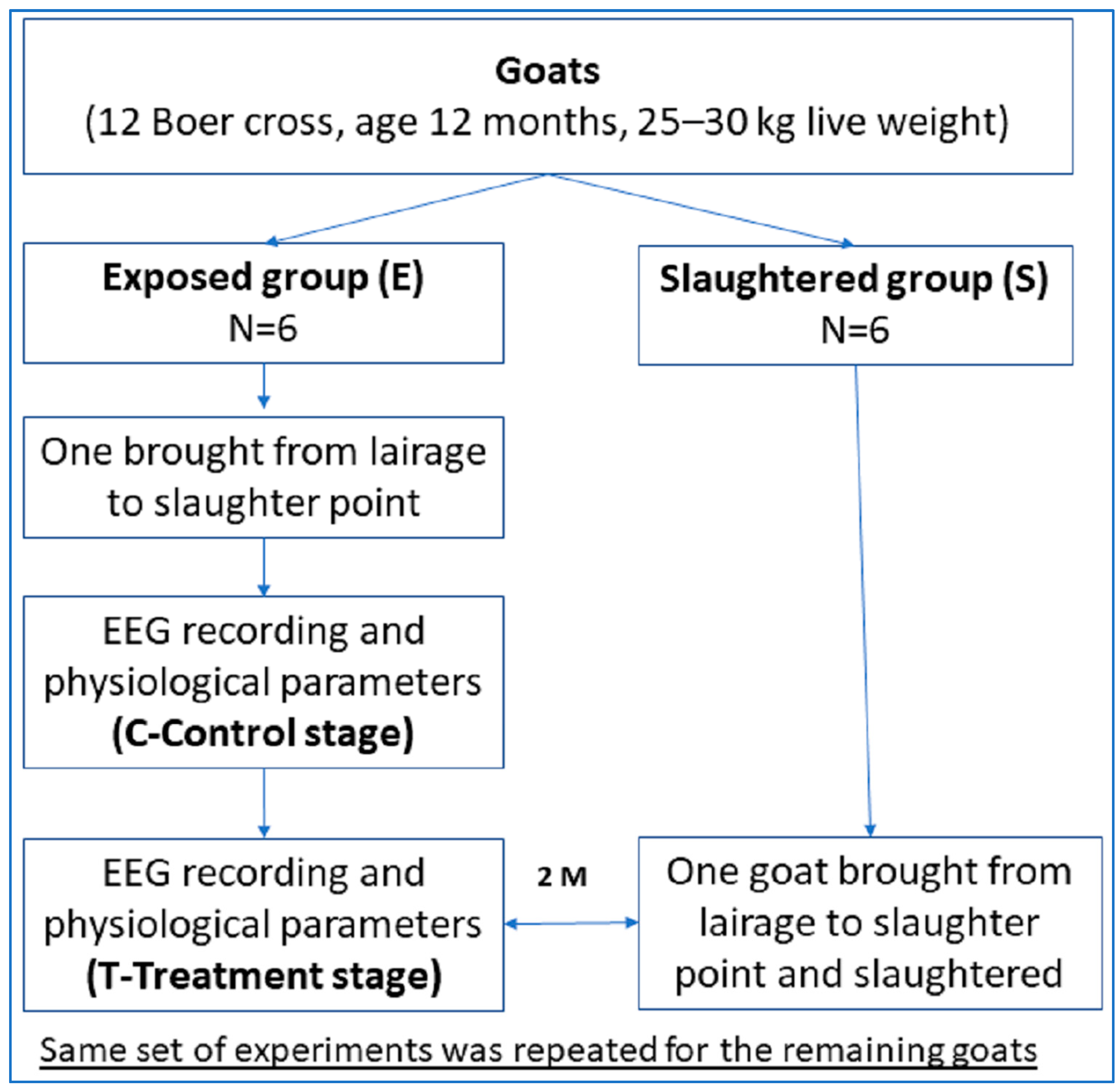
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Design
2.4. Electroencephalogram Recording
2.5. Physiological Responses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. EEG Variable
3.1.1. Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Theta Waves Pattern
3.1.2. Ptot and F50
3.2. Physiological Responses
4. Conclusions
5. Limitation and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panksepp, J. Emotional Causes and Consequences of Social-Affective Vocalization. In Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Lezama-García, K.; Orihuela, A.; Olmos-Hernández, A.; Reyes-Long, S.; Mota-Rojas, D. Facial Expressions and Emotions in Domestic Animals. CABI Rev. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, T. Making Slaughterhouses More Humane for Cattle, Pigs, and Sheep. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2013, 1, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendl, M.; Burman, O.H.P.; Paul, E.S. An Integrative and Functional Framework for the Study of Animal Emotion and Mood. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briefer, E.F.; Maigrot, A.-L.; Mandel, R.; Freymond, S.B.; Bachmann, I.; Hillmann, E. Segregation of Information about Emotional Arousal and Valence in Horse Whinnies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briefer, E.F.; Tettamanti, F.; McElligott, A.G. Emotions in Goats: Mapping Physiological, Behavioural and Vocal Profiles. Anim. Behav. 2015, 99, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintze, S.; Smith, S.; Patt, A.; Bachmann, I.; Würbel, H. Are Eyes a Mirror of the Soul? What Eye Wrinkles Reveal about a Horse’s Emotional State. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Marcet-Rius, M.; Ogi, A.; Hernández-Ávalos, I.; Mariti, C.; Martínez-Burnes, J.; Mora-Medina, P.; Casas, A.; Domínguez, A.; Reyes, B.; et al. Current Advances in Assessment of Dog’s Emotions, Facial Expressions, and Their Use for Clinical Recognition of Pain. Animals 2021, 11, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.J.; Paul, E.S.; Mendl, M. Cognitive Bias and Affective State. Nature 2004, 427, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briefer, E.F. Vocal Contagion of Emotions in Non-Human Animals. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal, F.B.M. Putting the Altruism Back into Altruism: The Evolution of Empathy. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špinka, M. Social Dimension of Emotions and Its Implication for Animal Welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 138, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panksepp, J.; Panksepp, J.B. Toward a Cross-Species Understanding of Empathy. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, J.L.; Nicol, C.J.; Clark, C.C.A.; Paul, E.S. Measuring Empathic Responses in Animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 138, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Abubakar, A.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hayat, M.N.; Kaka, U.; Pateiro, M.; Sazili, A.Q.; Hoffman, L.C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Pre-Slaughter Stress Mitigation in Goats: Prospects and Challenges. Meat Sci. 2023, 195, 109010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebli, Y.; Otmani, S.E.; Chentouf, M.; Hornick, J.-L.; Bindelle, J.; Cabaraux, J.-F. Foraging Behavior of Goats Browsing in Southern Mediterranean Forest Rangeland. Animals 2020, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaraw, P.; Verma, A.K.; Kumar, P. Barbari Goats: Current Status. In Sustainable Goat Production in Adverse Environments: Volume II; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Baciadonna, L. Assessing Emotions to Improve Animal Welfare: The Use of a Multimodal Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baciadonna, L.; Duepjan, S.; Briefer, E.F.; Padilla de la Torre, M.; Nawroth, C. Looking on the Bright Side of Livestock Emotions—The Potential of Their Transmission to Promote Positive Welfare. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, M.; Hasan, B.; Algotsson, M.; Sarenbo, S. Handling and Welfare of Bovine Livestock at Local Abattoirs in Bangladesh. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2014, 17, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, T. Animal Welfare and Society Concerns Finding the Missing Link. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, C.; Tarumán, J.; Larrondo, C. Main Factors Affecting Animal Welfare and Meat Quality in Lambs for Slaughter in Chile. Animals 2018, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GREGORY, N.G.; BENSON, T.; SMITH, N.; MASON, C.W. Sheep Handling and Welfare Standards in Livestock Markets in the UK. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 147, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, S.; Gebresenbet, G.; Bobobee, E.; Aklaku, E.; Hamdu, I. Effect of Transportation and Pre-Slaughter Handling on Welfare and Meat Quality of Cattle: Case Study of Kumasi Abattoir, Ghana. Vet. Sci. 2014, 1, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.R.; Islam, M.J.; Amin, A.; Shaikat, A.H.; Pasha, M.R.; Doyle, R.E. Animal-Based Welfare Assessment of Cattle and Water Buffalo in Bangladeshi Slaughterhouses. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2020, 23, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Manrique, A.; Gomila, A. Emotional Contagion in Nonhuman Animals: A Review. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2022, 13, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Abubakar, A.A.; Sazili, A.Q.; Kaka, U.; Goh, Y.-M. Application of Electroencephalography in Preslaughter Management: A Review. Animals 2022, 12, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabow, A.B.; Goh, Y.M.; Zulkifli, I.; Sazili, A.Q.; Kaka, U.; Kadi, M.Z.A.A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Nakyinsige, K.; Adeyemi, K.D. Blood Parameters and Electroencephalographic Responses of Goats to Slaughter without Stunning. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaka, U.; Cheng, C.H.; Meng, G.Y.; Fakurazi, S.; Kaka, A.; Behan, A.A.; Ebrahimi, M. Electroencephalographic Changes Associated with Antinociceptive Actions of Lidocaine, Ketamine, Meloxicam, and Morphine Administration in Minimally Anaesthetized Dogs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 305367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabow, A.B.; Goh, Y.M.; Zulkifli, I.; Sazili, A.Q.; Kadir, M.Z.A.A.; Kaka, U.; Khadijah, N.; Adeyemi, K.D.; Ebrahimi, M. Electroencephalographic Responses to Neck Cut and Exsanguination in Minimally Anaesthetized Goats. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghazli, R.; Othman, A.H.; Kaka, U.; Abubakar, A.A.; Imlan, J.C.; Hamzah, H.; Sazili, A.Q.; Goh, Y.M. Physiological and Electroencephalogram Responses in Goats Subjected to Pre-and during Slaughter Stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6396–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Goh, Y.M.; Mohamed Mustapha, N.; Raghazli, R.; Kaka, U.; Imlan, J.C.; Abubakar, A.A.; Abdullah, R. Physiological and Electroencephalographic Changes in Goats Subjected to Transportation, Lairage, and Slaughter. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabow, A.B.; Goh, Y.M.; Zulkifli, I.; Kadir, M.Z.A.; Kaka, U.; Adeyemi, K.D.; Abubakar, A.A.; Imlan, J.C.; Ebrahimi, M.; Sazili, A.Q. Electroencephalographic and Blood Parameters Changes in Anaesthetised Goats Subjected to Slaughter without Stunning and Slaughter Following Different Electrical Stunning Methods. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Gibson, T.; Stafford, K.; Mellor, D. Pain Perception at Slaughter. Anim. Welf. 2012, 21, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.C.; Johnson, C.B. Neurophysiological Techniques to Assess Pain in Animals. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, I.; Abubakar, A.A.; Sazili, A.Q.; Goh, Y.M.; Imlan, J.C.; Kaka, U.; Sabow, A.B.; Awad, E.A.; Othman, A.H.; Raghazali, R.; et al. The Effects of Sea and Road Transport on Physiological and Electroencephalographic Responses in Brahman Crossbred Heifers. Animals 2019, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Johnson, C.; Murrell, J.; Hulls, C.; Mitchinson, S.; Stafford, K.; Johnstone, A.; Mellor, D. Electroencephalographic Responses of Halothane-Anaesthetised Calves to Slaughter by Ventral-Neck Incision without Prior Stunning. N. Z. Vet. J. 2009, 57, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, E.; Başar-Eroglu, C.; Karakaş, S.; Schürmann, M. Gamma, Alpha, Delta, and Theta Oscillations Govern Cognitive Processes. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 39, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llonch, P.; Rodríguez, P.; Casal, N.; Carreras, R.; Muñoz, I.; Dalmau, A.; Velarde, A. Electrical Stunning Effectiveness with Current Levels Lower than 1 A in Lambs and Kid Goats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 98, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, W.J.; Quiroga, R.Q. Imaging Brain Function with EEG; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-4983-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, C.S.; Anilkumar, A.C. EEG Normal Sleep; Europe PMC: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.-H.; Lee, J.-T. Stress and EEG. Converg. Hybrid Inf. Technol. 2010, 27, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerwijk, E.L.; Ford, J.M.; Weiss, S.J. Resting-State EEG Delta Power Is Associated with Psychological Pain in Adults with a History of Depression. Biol. Psychol. 2015, 105, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomp, M.; d’Ingeo, S.; Henry, S.; Cousillas, H.; Hausberger, M. Brain Activity Reflects (Chronic) Welfare State: Evidence from Individual Electroencephalography Profiles in an Animal Model. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 236, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Jeong, D.-K.; Kim, J.-Y. Emotional Stress Recognition Using Electroencephalogram Signals Based on a Three-Dimensional Convolutional Gated Self-Attention Deep Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.Y.; Bani, N.A.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Aris, S.A.M. Electroencephalogram (EEG) Human Stress Level Classification Based on Theta/Beta Ratio. Int. J. Integr. Eng 2020, 12, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, I.; Goh, Y.M.; Norbaiyah, B.; Sazili, A.Q.; Lotfi, M.; Soleimani, A.F.; Small, A.H. Changes in Blood Parameters and Electroencephalogram of Cattle as Affected by Different Stunning and Slaughter Methods in Cattle. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.; White, P.J.; Mohler, V.L.; Lomax, S. Electroencephalography Can Distinguish between Pain and Anaesthetic Intervention in Conscious Lambs Undergoing Castration. Animals 2020, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, J.C.; Johnson, C.B.; White, K.L.; Taylor, P.M.; Haberham, Z.L.; Waterman–Pearson, A.E. Changes in the EEG during Castration in Horses and Ponies Anaesthetized with Halothane. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2003, 30, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlan, J.C.; Kaka, U.; Goh, Y.-M.; Idrus, Z.; Awad, E.A.; Abubakar, A.A.; Ahmad, T.; Nizamuddin, H.N.Q.; Sazili, A.Q. Effects of Slaughter Knife Sharpness on Blood Biochemical and Electroencephalogram Changes in Cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlan, J.C.; Kaka, U.; Goh, Y.-M.; Idrus, Z.; Awad, E.A.; Abubakar, A.A.; Ahmad, T.; Quaza Nizamuddin, H.N.; Sazili, A.Q. Effects of Slaughter Positions on Catecholamine, Blood Biochemical and Electroencephalogram Changes in Cattle Restrained Using a Modified Mark IV Box. Animals 2021, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.A.; Zulkifli, I.; Goh, Y.M.; Kaka, U.; Sabow, A.B.; Imlan, J.C.; Awad, E.A.; Othman, A.H.; Raghazli, R.; Mitin, H.; et al. Effects of Stocking and Transport Conditions on Physicochemical Properties of Meat and Acute-Phase Proteins in Cattle. Foods 2021, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, S.R.; Chambers, P.; Johnson, C.B.; Singh, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Kongara, K. Effect of Combinations of Morphine, Dexmedetomidine and Maropitant on the Electroencephalogram in Response to Acute Electrical Stimulation in Anaesthetized Dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Johnson, C.; Murrell, J.; Mitchinson, S.; Stafford, K.; Mellor, D. Electroencephalographic Responses to Concussive Non-Penetrative Captive-Bolt Stunning in Halothane-Anaesthetised Calves. N. Z. Vet. J. 2009, 57, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Johnson, C.; Murrell, J.; Chambers, J.; Stafford, K.; Mellor, D. Components of Electroencephalographic Responses to Slaughter in Halothane-Anaesthetised Calves: Effects of Cutting Neck Tissues Compared with Major Blood Vessels. N. Z. Vet. J. 2009, 57, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.; Johnson, C.; Murrell, J.; Chambers, J.; Stafford, K.; Mellor, D. Amelioration of Electroencephalographic Responses to Slaughter by Non-Penetrative Captive-Bolt Stunning after Ventral-Neck Incision in Halothane-Anaesthetised Calves. N. Z. Vet. J. 2009, 57, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkman, B.; Boissy, A.; Meunier-Salaün, M.-C.; Canali, E.; Jones, R.B. A Critical Review of Fear Tests Used on Cattle, Pigs, Sheep, Poultry and Horses. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 340–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Jiang, D.M.; Zhang, Y.N. A Hierarchical Bidirectional GRU Model With Attention for EEG-Based Emotion Classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 118530–118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, L.; Chai, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Spatial-Frequency Convolutional Self-Attention Network for EEG Emotion Recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; Yin, Z.; Song, Y. Transformers for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition: A Hierarchical Spatial Information Learning Model. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 4359–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, J.S.; Keltner, D. Fear, Anger, and Risk. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2001, 81, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Reimert, I.; Kemp, B. Measuring Farm Animal Emotions—Sensor-Based Approaches. Sensors 2021, 21, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Ley, M.; Hanke, S. Emotion Recognition from Physiological Signal Analysis: A Review. Electron Notes Comput. Sci 2019, 343, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshin, J.C.; Lindquist, K.A. Chapter 14 Neuroimaging of Emotion Dysregulation. In The Oxford Handbook of Emotion Dysregulation; Beauchaine, T.P., Crowell, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- De Ridder, N. Sensory Stimuli and the Effect on Pig Welfare. Agri. Food Life Sci. 2021. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/547046 (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Vogel, K.D.; Grandin, T. 2009 Restaurant Animal Welfare and Humane Slaughter Audits in US Federally Inspected Beef and Pork Slaughter Plants. Available online: https://www.grandin.com/survey/2009.restaurant.audits.html (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Kumar, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abubakar, A.A.; Hayat, M.N.; Kaka, U.; Ajat, M.; Meng, G.Y.; Sazili, A.Q. Improving Animal Welfare Status and Meat Quality through Assessment of Stress Biomarkers: A Critical Review. Meat Sci. 2022, 197, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Abubakar, A.A.; Verma, A.K.; Umaraw, P.; Nizam, M.H.; Mehta, N.; Ahmed, M.A.; Kaka, U.; Sazili, A.Q. New Insights in Improving Sustainability in Meat Production: Opportunities and Challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiz, E.E.; Yalcintan, H. Comparison of Certain Haematological and Biochemical Parameters Regarding Pre-Slaughter Stress in Saanen, Maltese, Gokceada and Hair Goat Kids. Istanb. Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2013, 39, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.M.; Warner, R.D. Have We Underestimated the Impact of Pre-Slaughter Stress on Meat Quality in Ruminants? Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.C.; Littlejohn, R.P.; Asher, G.W.; Pearse, A.J.T.; Stevenson-Barry, J.M.; McGregor, S.K.; Manley, T.R.; Duncan, S.J.; Sutton, C.M.; Pollock, K.L.; et al. A Comparison of Biochemical and Meat Quality Variables in Red Deer (Cervus Elaphus) Following Either Slaughter at Pasture or Killing at a Deer Slaughter Plant. Meat Sci. 2002, 60, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, Y.-B.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-M.; Lee, J.-K.; Jung, J.-S.; Suh, H.-W. The Regulation of Blood Glucose Level in Physical and Emotional Stress Models: Possible Involvement of Adrenergic and Glucocorticoid Systems. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakyinsige, K.; Che Man, Y.B.; Aghwan, Z.A.; Zulkifli, I.; Goh, Y.M.; Abu Bakar, F.; Al-Kahtani, H.A.; Sazili, A.Q. Stunning and Animal Welfare from Islamic and Scientific Perspectives. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, D.L.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; van de Ven, R.J.; Warner, R.D.; Ferguson, D.M.; Shaw, F.D.; Stark, J.L.; Gardner, G.E.; McIntyre, B.L.; Tudor, G.D.; et al. Hormones, Stress and the Welfare of Animals. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 54, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, K.A.; Gerich, T. Comparison of Simultaneous Changes in Electroencephalographic and Haemodynamic Variables in Sheep Anaesthetised with Halothane. Vet. Rec. 2001, 149, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Control Stage | Treatment Stage | t Value | p-Value | Cohen’s d Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha (µv) | 0.999 ± 0.062 | 1.152 ± 0.088 | −1.490 | 0.144 | −0.32 |
| Beta (µv) | 1.402 ± 0.049 | 1.832 ± 0.098 | −3.818 | 0.000 * | −0.89 |
| Delta (µv) | 9.050 ± 0.814 | 9.693 ± 0.812 | −0.521 | 0.605 | −0.13 |
| Theta (µv) | 1.741 ± 0.114 | 2.266 ± 0.215 | −2.508 | 0.017 | −0.49 |
| Parameters | Control Stage | Treatment Stage | t Value | p-Value | Cohen’s d Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 79.33 ± 9.03 | 88.17 ± 12.96 | −1.385 | 0.225 | −0.91 |
| Temperature (rectal, °C) | 37.23 ± 0.26 | 37.33 ± 0.16 | −0.278 | 0.790 | −0.18 |
| Temp (auditory, °C) | 38.83 ± 0.17 | 38.99 ± 0.24 | −0.855 | 0.425 | −0.29 |
| Glucose (mMol/L) | 4.12 ± 0.16 | 4.88 ± 0.23 | −2.969 | 0.031 | −1.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, P.; Abubakar, A.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Hayat, M.N.; Ajat, M.; Kaka, U.; Goh, Y.M.; Sazili, A.Q. Electroencephalogram and Physiological Responses as Affected by Slaughter Empathy in Goats. Animals 2023, 13, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061100
Kumar P, Abubakar AA, Ahmed MA, Hayat MN, Ajat M, Kaka U, Goh YM, Sazili AQ. Electroencephalogram and Physiological Responses as Affected by Slaughter Empathy in Goats. Animals. 2023; 13(6):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Pavan, Ahmed Abubakar Abubakar, Muideen Adewale Ahmed, Muhammad Nizam Hayat, Mokrish Ajat, Ubedullah Kaka, Yong Meng Goh, and Awis Qurni Sazili. 2023. "Electroencephalogram and Physiological Responses as Affected by Slaughter Empathy in Goats" Animals 13, no. 6: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061100
APA StyleKumar, P., Abubakar, A. A., Ahmed, M. A., Hayat, M. N., Ajat, M., Kaka, U., Goh, Y. M., & Sazili, A. Q. (2023). Electroencephalogram and Physiological Responses as Affected by Slaughter Empathy in Goats. Animals, 13(6), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061100









