Understanding the Pathogenesis of Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) through an Integrated Morphological and Molecular Approach
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outbreaks and Fish Tissue Sampling
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) of MLO DNA
2.5. MLO DNA Absolute Quantification
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
| Gene | Primers Sequence, 5′ to 3′ | Amplicon Length (bp) | Accession Number (NCBI; GenBank) | Efficiency (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β 1 | F: ACATTGCCAACCTCATCATCG R: TTGAGCAGGTCCTTGTCCTTG | 91 | AJ223954 | 101.5 | 0.999 |
| IL-6 2 | F: ACTCCCCTCTGTCACACACC R: GGCAGACAGGTCCTCCACTA | 91 | DQ866150 | 101.8 | 0.984 |
| IL-8 3 | F: AGAATGTCAGCCAGCCTTGT R: TCTCAGACTCATCCCCTCAGT | 69 | AJ279069 | 103.0 | 0.994 |
| IL-10 4 | F: CGACTTTAAATCTCCCATCGAC R: GCATTGGACGATCTCTTTCTTC | 70 | AB118099 | 100.0 | 0.991 |
| TNF-α 5 | F: GGGGACAAACTGTGGACTGA R: GAAGTTCTTGCCCTGCTCTG | 66 | AJ277604 | 104.0 | 0.997 |
| TLR5 6 | F: GGCATCAGCCTGTTGAATTT R: ATGAAGAGCGAGAGCCTCAG | 89 | AB091105 | 101.0 | 0.987 |
| TCR-β 7 | F: CTCCGCTAAGGAGTGTGAAGATAG R: CAGGCCATAGAAGGTACTCTTAGC | 412 | AF329700 | 102.2 | 0.995 |
| MHC-I 8 | F: TCCCTCCCTCAGTGTCT R: GGGTAGAAACCTGTAGCGTG | 73 | AY523661 | 102.5 | 0.998 |
| MHC-II 9 | F: TGCCATGCTGATGTGCAG R: GTCCCTCAGCCAGGTCACT | 67 | AF115533 | 100.9 | 0.999 |
| IgM 10 | F: CTTGGCTTGTTGACGATGAG R: GGCTAGTGGTGTTGAATTGG | 72 | S63348 | 97.9 | 1.000 |
| IgT 11 | F: AGCACCAGGGTGAAACCA R: GCGGTGGGTTCAGAGTCA | 72 | AY870265 | 101.2 | 0.998 |
| B-act 12 | F: ACAGACTGTACCCATCCCAAAC R: AAAAAGCGCCAAAATAACAGAA | 167 | AJ438158 | 99.8 | 0.999 |
| EF1 13 | F: ACCCTCCTCTTGGTCGTTTC R: TGATGACACCAACAGCAACA | 63 | AF498320 | 100.0 | 0.999 |
| 60S 14 | F: AGCCACCAGTATGCTAACCAGT R: TGTGATTGCACATTGACAAAAA | 147 | NM001165047 | 104.1 | 0.998 |
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
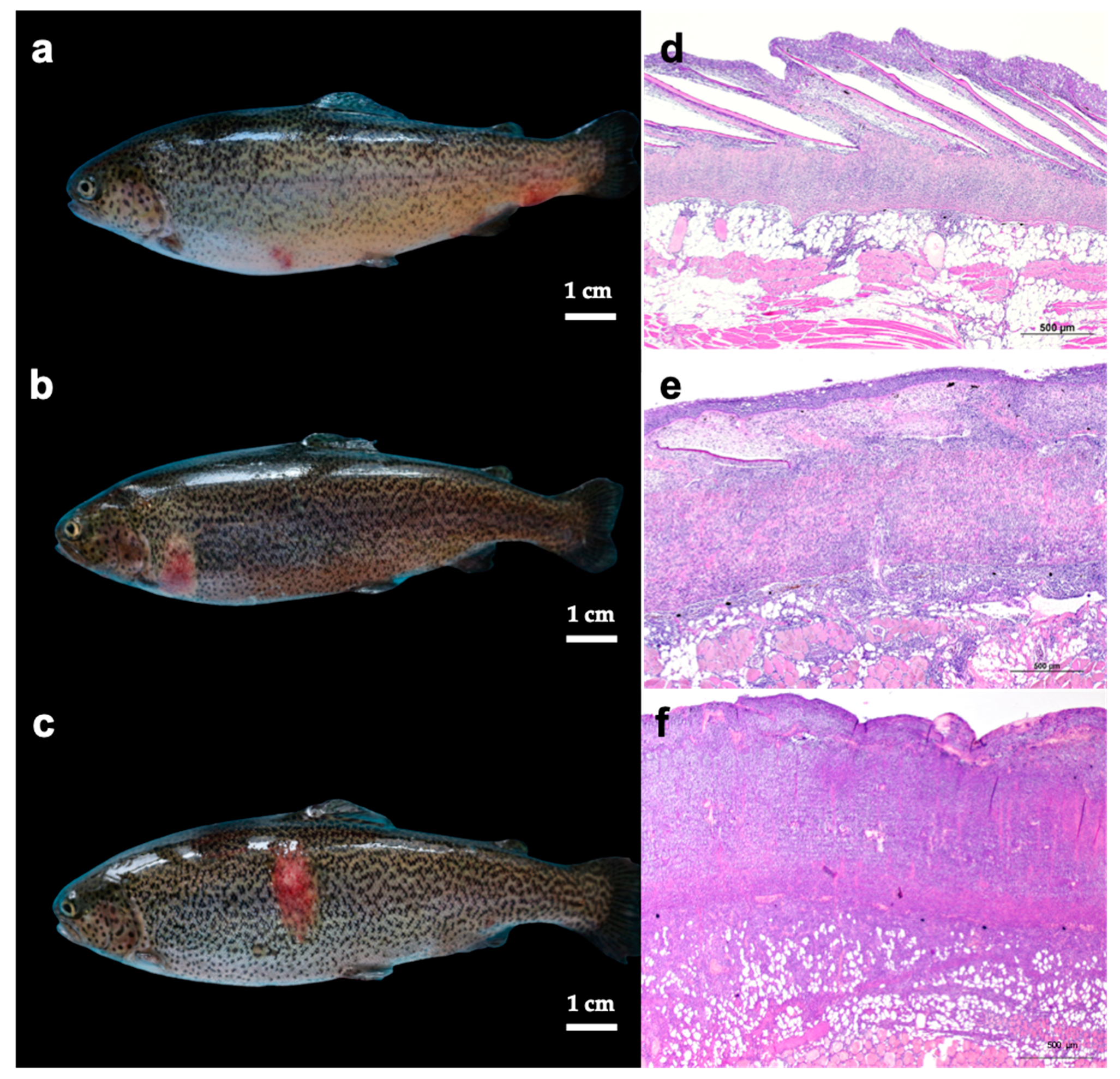
3.1. Gross Lesions and Histology of Skin, Spleen, and Head Kidney
3.2. Amplification of MLO DNA by PCR
3.3. Absolute Quantification of MLO Using qPCR
3.4. Immune Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metselaar, M.; Orioles, M.; Galeotti, M.; Adams, A.; Thompson, K.D. Red mark syndrome—Current state of knowledge. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Pond, M.J.; Peeler, E.J.; Rimmer, G.S.E.; Oidtmann, B.; Way, K.; Feist, S.W. Emergence of cold water strawberry disease of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in England and Wales: Outbreak investigations and transmission studies. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 79, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orioles, M.; Galeotti, M.; Saccà, E.; Bulfoni, M.; Corazzin, M.; Bianchi, S.; Torge, D.; Macchiarelli, G.; Magi, G.E.; Schmidt, J.G. Effect of temperature on transfer of Midichloria-like organism and development of red mark syndrome in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.P.; Beleau, M.H.; Busch, R.A.; Roberts, S.; Krieger, R.I. Strawberry disease in rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. Fish Dis. 1985, 8, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, H.; Vuillaume, A.; Sochon, E. Isolation of an adeno-like virus from two cases of strawberry disease in rainbow trout. Ann. de l'Institut Pasteur/Virol. 1985, 136, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, E.; Ortega, C.; Muzquiz, J.L.; Docando, J.; Alonso, J.L.; Sanz, F.; Arnal, M.C. Descripcion de un Caso de Enfermedad de la Fresa en ESPANA: Estudio Etiologico, Clinico y Epidemiologico; Centro de Investigaciones Marinas: Pontevedra, Spain, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kfoury, J.R.; Okamoto, N.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshimizu, M.; Lapatra, S.E.; Maita, M. “Rash” Skin Disease of Rainbow Trout. Fish Pathol. 1996, 31, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, H.W.; Girons, A.; Rizgalla, G.; LaPatra, S.; Branson, E.J.; MacKenzie, K.; Davies, M.; Collins, R.O.; Diab, A.; Crumlish, M. Strawberry disease in rainbow trout in Scotland: Pathology and association with Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Veter Rec. 2006, 158, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Algoet, M.; Feist, S.W.; Bateman, K.; Peeler, E.J.; Branson, E.J. Studies on red mark syndrome. Finfish News 2006, 1, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, D.; Crumlish, M.; LaPatra, S.E.; Noguera, P.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W. Workshop on Salmonid Skin Disease. In Proceedings of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 13th International Conference on Fish and Shellfish Diseases, Grado, Italy, 17–21 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Noguera, P. Red mark syndrome. Fish Farmer 2008, 31, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Bergmann, W.; Knüsel, R.; Heistinger, H.; Licek, E. Appearance of red mark syndrome/cold water strawberry disease in Switzerland and Austria. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 88, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galeotti, M.; Giavenni, R.; Volpatti, D.; Beraldo, P.; Feist, S.W. Red mark syndrome/cold water strawberry disease: Emergence in Italy and histopathological investigations. In Proceedings of the O-073 15th International Conference on Diseases of Fish and Shellfish, Split, Croatia, 12–16 September 2011; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Kubilay, A.; Ciftci, S.; Yıldırım, P.; Didinen, B.I.; Metin, S.; Demirkan, T.; Ozen, M.R.; Oidtman, B. First observation of Red Mark Syndrome (RMS) in cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792) in Turkey. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2014, 34, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sasani, F.; Shokrpoor, S.; Rahmati-Holasoo, H.; Zargar, A. Appearance of Red Mark Syndrome (RMS) in cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1972) in Iran. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2016, 36, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Galeotti, M.; Ronza, P.; Beraldo, P.; Bulfon, C.; Magi, G.E.; Manzano, M.; Volpatti, D. First report of Red Mark Syndrome (RMS) in farmed rainbow trout in Slovenia. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, W.T.; Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, J.W.; Han, S.J.; Kwon, J.; Jun, J.W.; Park, S.C. Emergence of Rickettsial Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fry Displaying the Appearance of Red Mark Syndrome in Korea. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galeotti, M.; Volpatti, D.; Byadgi, O.; Beraldo, P.; Orioles, M.; Sarti, M.; Magi, G.E. Red mark syndrome (RMS) in farmed rainbow trout: First report of outbreaks in Bosnia and Herzegovina. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.J.; LaPatra, S.E.; Snekvik, K.R.; St-Hilaire, S.; Cain, K.D.; Call, D.R. Strawberry disease lesions in rainbow trout from southern Idaho are associated with DNA from a Rickettsia-like organism. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 82, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.J.; LaPatra, S.E.; Snekvik, K.R.; Cain, K.D.; Call, D.R. Quantitative PCR demonstrates a positive correlation between a Rickettsia-like organism and severity of strawberry disease lesions in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Schmidt, J.G.; Chen, D.; Kania, P.W.; Buchmann, K.; Olesen, N.J. Skin immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) experimentally exposed to the disease Red Mark Syndrome. Veter Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 211, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, M.; Thompson, K.; Paley, R.; Green, D.M.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.; Feist, S.; Adams, A. Investigating the involvement of a Midichloria -like organism (MLO) in red mark syndrome in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, A.; Sassera, D.; Serra, V.; Bandi, C.; McCarthy, U.; Bazzocchi, C. Molecular evidence for a bacterium of the family Midichloriaceae (order Rickettsiales) in skin and organs of the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) affected by red mark syndrome. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, M.; Manzano, M.; Beraldo, P.; Bulfon, C.; Rossi, G.; Volpatti, D.; Magi, G.E. Ultrastructural and biomolecular detection of Rickettsiales-like organisms in tissues of rainbow trout with Red Mark Syndrome. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, M.; Volpatti, D.; Beraldo, P.; Brunetti, B.; Galletti, E.; Feist, S. Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Farmed in Italy: Anatomohistopathological Investigations. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 148, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeotti, M.; Sarli, G.; Sirri, R.; Mandrioli, L.; Beraldo, P.; Bronzatti, P.; Giavenni, R.; Orioles, M.; Magi, G.; Volpatti, D. Red mark syndrome of trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss ; Walbaum, 1792): Histopathological scoring and correlation with gross lesions. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, U.; Casadei, E.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. Red mark syndrome in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: Investigation of immune responses in lesions using histology, immunohistochemistry and analysis of immune gene expression. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oidtmann, B.; LaPatra, S.E.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.; Pond, M.; Peeler, E.J.; Noguera, P.A.; Bruno, D.W.; St-Hilaire, S.; Schubiger, C.B.; Snekvik, K.; et al. Differential characterization of emerging skin diseases of rainbow trout—A standardized approach to capturing disease characteristics and development of case definitions. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in realtime RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2002–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Sigh, J.; Kania, P.W.; Holten-Andersen, L.; Buchmann, K.; Clark, T.; Rasmussen, J.S.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Lorenzen, N. Approaches towards DNA Vaccination against a Skin Ciliate Parasite in Fish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, C.; Blanco, M.; Martin, S.; Jouneau, L.; Bernardet, J.-F.; Houel, A.; Lunazzi, A.; Duchaud, E.; Michel, C.; Quillet, E.; et al. Transcriptional Responses of Resistant and Susceptible Fish Clones to the Bacterial Pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Balcázar, J.L.; Merrifield, D.L.; Carnevali, O.; Gioacchini, G.; de Blas Ignacio Ruiz-Zarzuela, I. Expression of immune-related genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) induced by probiotic bacteria during Lactococcus garvieae infection. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 31, 196e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahi, A.; Casadei, E.; Tacchi, L.; Muñoz, P.; LaPatra, S.E.; Salinas, I. Tissue Microenvironments in the Nasal Epithelium of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Define Two Distinct CD8α+ Cell Populations and Establish Regional Immunity. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4453–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Spelman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔddCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orioles, M.; Schmidt, J.; Tomè, P.; Vendramin, N.; Galeotti, M. A questionnaire-based survey on the presence of red mark syndrome in Italian rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orioles, M.; Bulfoni, M.; Saccà, E.; Cesselli, D.; Schmidt, J.; Galeotti, M. Development and application of a sensitive droplet digital PCR for the detection of red mark syndrome infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orioles, M.; Saccà, E.; Metselaar, M.; Bulfoni, M.; Cesselli, D.; Galeotti, M. Observations on Red Mark Syndrome in juvenile rainbow trout farmed in RAS system. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1889–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinok, I.; Capkin, E.; Kayis, S. Development of multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of five bacterial fish pathogens. Veter Microbiol. 2008, 131, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Cerro, A.; Soto, S.; Landeras, E.; Heviab, M.; Guijarro, J.; Mendoza, M. PCR-based procedures in detection and DNA-fingerprinting of Salmonella from samples of animal origin. Food Microbiol. 2002, 19, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, M.; Thompson, K.D.; Gratacap, R.M.L.; Kik, M.J.L.; LaPatra, S.E.; Lloyd, S.J.; Call, D.R.; Smith, P.D.; Adams, A. Association of red-mark syndrome with a Rickettsia-like organism and its connection with strawberry disease in the USA. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secombes, C.; Zou, J.; Daniels, G.; Cunningham, C.; Koussounadis, A.; Kemp, G. Rainbow trout cytokine and cytokine receptor genes. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-H.; Lin, H.-T.; Foung, Y.-F.; Lin, J.H.-Y. The bioactivity of teleost IL-6: IL-6 protein in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) induces Th2 cell differentiation pathway and antibody production. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, M.; Odaka, T.; Suetake, H.; Tahara, D.; Miyadai, T. Teleost IL-6 promotes antibody production through STAT3 signaling via IL-6R and gp130. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Yin, X.; Zhong, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ye, J. Interleukin-6 gets involved in response to bacterial infection and promotes antibody production in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 89, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.M.; Maehr, T.; Diaz-Rosales, P.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Bioactivity studies of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) interleukin-6: Effects on macrophage growth and antimicrobial peptide gene expression. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Wentzel, A.S.; Tijhaar, E.J.; Rakus, K.; Vanderplasschen, A.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Forlenza, M. Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Il10 Inhibits Inflammatory Activities of Carp Macrophages and Promotes Proliferation of Igm+ B Cells and Memory T Cells in a Manner Similar to Carp Il10. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3694–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimholt, U. MHC and Evolution in Teleosts. Biology 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Su, B.; Fu, Q.; Shang, M.; Gao, C.; Tan, F.; Li, C. Identification, characterization and expression analysis of TLR5 in the mucosal tissues of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) following bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 68, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Becerril, M.; Alamillo, E.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Ascencio, F.; Esteban, M.A.; Angulo, C. Molecular characterization and expression analyses of toll like receptor-5 induced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus antigens in Pacific red snapper. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 68, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariconti, M.; Epis, S.; Sacchi, L.; Biggiogera, M.; Sassera, D.; Genchi, M.; Alberti, E.; Montagna, M.; Bandi, C.; Bazzocchi, C. A study on the presence of flagella in the order Rickettsiales: The case of ‘Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii’. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.-M.; Whitworth, T.; Popov, V.; Walker, D.H. Effect of Antibody on the Rickettsia-Host Cell Interaction. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3524–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.-M.; Whitworth, T.; Olano, J.P.; Popov, V.L.; Walker, D.H. Fc-Dependent Polyclonal Antibodies and Antibodies to Outer Membrane Proteins A and B, but Not to Lipopolysaccharide, Protect SCID Mice against Fatal Rickettsia conorii Infection. Infect. Immun. 2003, 72, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Morvan, C.; Troutaud, D.; Deschaux, P. Differential effects of temperature on specific and nonspecific immune defences in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 165e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| FARM—A | FARM—B | Control | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | Skin | Spleen | Head KIDNEY | Sample No. | Skin | Spleen | Head Kidney | Sample No. | Skin | Spleen | Head Kidney |
| 1-12911 | + | + | - | 1-12931 | + | + | + | C19-12929 | - | - | - |
| 3-12913 | + | + | + | 2-12932 | + | + | + | C20-12930 | - | - | - |
| 4-12914 | + | + | + | 3-12933 | + | - | - | C21-12949 | - | - | - |
| 5-12915 | - | - | + | 4-12934 | + | + | + | C22-12950 | - | - | - |
| 6-12916 | + | + | + | 5-12935 | + | + | + | C23-12951 | - | - | - |
| 7-12917 | + | + | + | 6-12936 | - | + | + | ||||
| 8-12918 | + | + | - | 7-12937 | + | + | + | ||||
| 9-12919 | - | + | + | 8-12938 | + | + | + | ||||
| 10-12920 | - | - | + | 9-12939 | - | + | + | ||||
| 11-12921 | + | - | + | 10-12940 | + | - | - | ||||
| 12-12922 | + | + | + | 11-12941 | + | - | + | ||||
| 13-12923 | + | + | + | 12-12942 | + | - | + | ||||
| 14-12924 | - | - | - | 13-12943 | + | + | + | ||||
| 15-12925 | + | + | - | 14-12944 | + | + | + | ||||
| 16-12926 | + | - | - | 15-12945 | + | - | - | ||||
| 17-12927 | - | + | + | 16-12946 | + | + | + | ||||
| 18-12928 | - | + | + | 17-12947 | + | + | + | ||||
| 18-12948 | + | + | + | ||||||||
| Farm -A | Farm -B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | Skin | Spleen | Head-Kidney | Sample No. | Skin | Spleen | Head-Kidney |
| 1-12911 | 8.87 × 10−3 | 1.15 × 10−4 | 5.36 × 10−4 | 1-12931 | 1.74 × 10−3 | 1.59 × 10−4 | 8.99 × 10−4 |
| 3-12913 | 1.57 × 10−3 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 8.58 × 10−4 | 2-12932 | 4.27 × 10−3 | 3.94 × 10−4 | 2.93 × 10−4 |
| 4-12914 | 1.55 × 10−2 | 3.32 × 10−3 | 9.97 × 10−4 | 3-12933 | 5.06 × 10−3 | 6.59 × 10−5 | 2.64 × 10−4 |
| 5-12915 | 6.75 × 10−4 | 1.76 × 10−3 | 3.87 × 10−4 | 4-12934 | 1.42 × 10−2 | 5.28 × 10−3 | 1.63 × 10−2 |
| 6-12916 | 5.73 × 10−3 | 4.00 × 10−5 | 9.17 × 10−4 | 5-12935 | 1.05 × 10−2 | - | 1.05 × 10−3 |
| 7-12917 | 4.57 × 10−3 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 2.82 × 10−4 | 6-12936 | 3.71 × 10−3 | 4.22 × 10−5 | 2.57 × 10−4 |
| 8-12918 | 6.88 × 10−4 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 3.28 × 10−4 | 7-12937 | 9.11 × 10−3 | 5.59 × 10−4 | 1.42 × 10−5 |
| 9-12919 | 1.23 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 3.35 × 10−4 | 8-12938 | 8.37 × 10−3 | 5.73 × 10−5 | 2.23 × 10−3 |
| 10-12920 | 7.38 × 10−3 | 5.81 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−3 | 9-12939 | 5.14 × 10−4 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 2.07 × 10−4 |
| 11-12921 | 2.13 × 10−4 | 2.18 × 10−5 | 4.19 × 10−5 | 10-12940 | 3.19 × 10−3 | 6.16 × 10−6 | 1.32 × 10−4 |
| 12-12922 | 1.82 × 10−3 | 9.45 × 10−4 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 11-12941 | 2.85 × 10−3 | 3.83 × 10−5 | 5.38 × 10−4 |
| 13-12923 | 3.33 × 10−3 | 3.62 × 10−5 | 1.72 × 10−4 | 12-12942 | 8.90 × 10−2 | 3.32 × 10−4 | 1.35 × 10−3 |
| 14-12924 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 3.48 × 10−6 | 1.05 × 10−5 | 13-12943 | 6.40 × 10−3 | 9.38 × 10−6 | 8.99 × 10−5 |
| 15-12925 | 7.39 × 10−3 | 2.39 × 10−3 | 6.73 × 10−4 | 14-12944 | 1.14 × 10−2 | 7.06 × 10−3 | - |
| 16-12926 | 5.72 × 10−4 | 3.93 × 10−5 | 3.57 × 10−4 | 15-12945 | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.06 × 10−4 | 3.25 × 10−4 |
| 17-12927 | 2.01 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−4 | 1.04 × 10−4 | 16-12946 | 1.51 × 10−1 | 3.72 × 10−3 | 3.96 × 10−5 |
| 18-12928 | 1.07 × 10−4 | 5.34 × 10−6 | 7.01 × 10−4 | 17-12947 | 2.69 × 10−2 | 1.65 × 10−2 | 1.94 × 10−4 |
| 18-12948 | 2.14 × 10−2 | 2.30 × 10−4 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galeotti, M.; Orioles, M.; Saccà, E.; Byadgi, O.; Pesaro, S.; Di Cerbo, A.; Magi, G.E. Understanding the Pathogenesis of Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) through an Integrated Morphological and Molecular Approach. Animals 2023, 13, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061103
Galeotti M, Orioles M, Saccà E, Byadgi O, Pesaro S, Di Cerbo A, Magi GE. Understanding the Pathogenesis of Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) through an Integrated Morphological and Molecular Approach. Animals. 2023; 13(6):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061103
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaleotti, Marco, Massimo Orioles, Elena Saccà, Omkar Byadgi, Stefano Pesaro, Alessandro Di Cerbo, and Gian Enrico Magi. 2023. "Understanding the Pathogenesis of Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) through an Integrated Morphological and Molecular Approach" Animals 13, no. 6: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061103
APA StyleGaleotti, M., Orioles, M., Saccà, E., Byadgi, O., Pesaro, S., Di Cerbo, A., & Magi, G. E. (2023). Understanding the Pathogenesis of Red Mark Syndrome in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) through an Integrated Morphological and Molecular Approach. Animals, 13(6), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061103







