Housing Conditions Affect Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior but Not Their Physiological Status
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
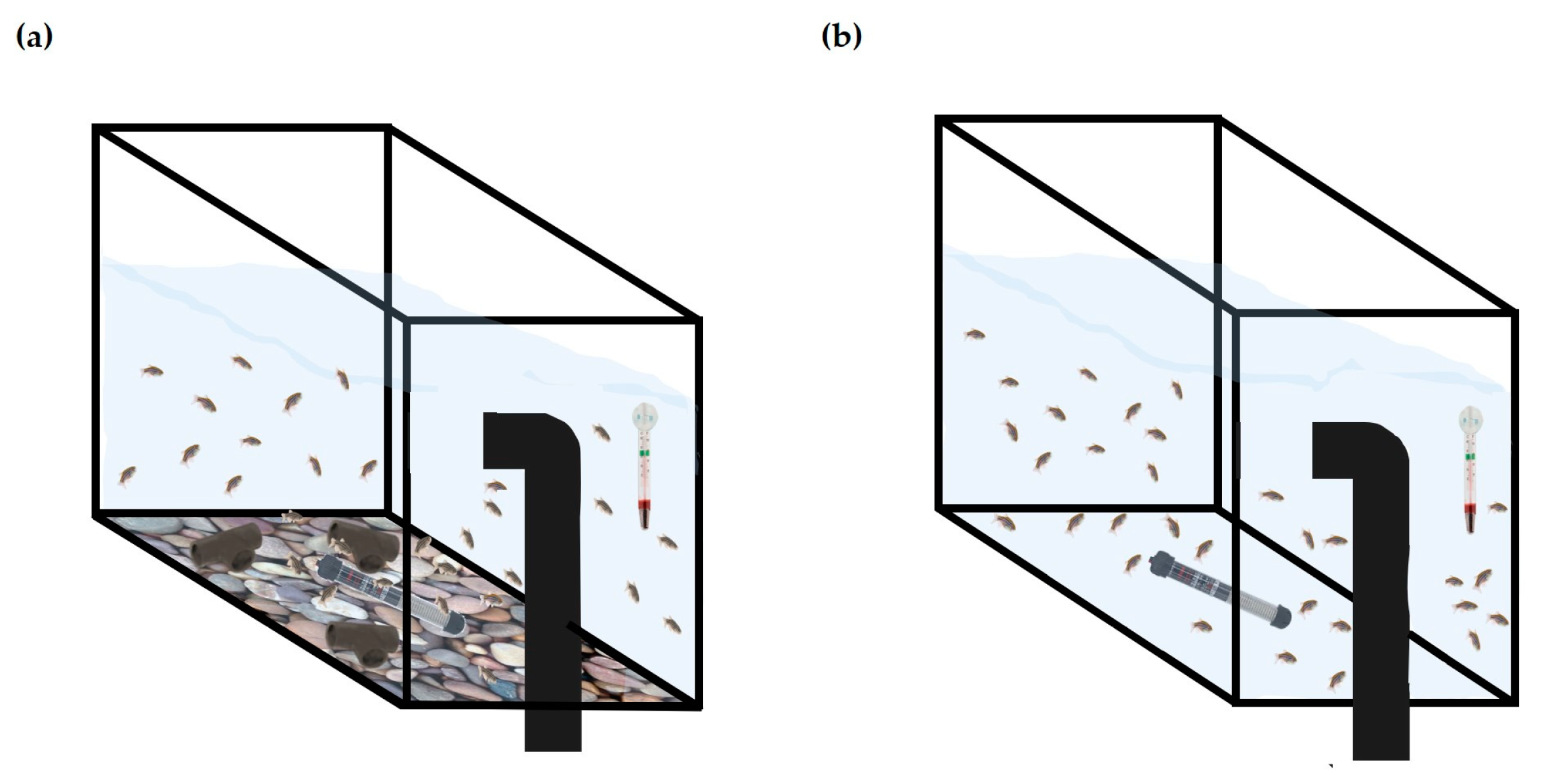
2.2. Animals and Housing
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioral Testing
2.4.1. Shoaling Test
2.4.2. White/Black Tank Test
2.4.3. Novel Tank Test
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Cortisol Extraction and Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Shoaling
3.2. White/Black Tank
3.3. Novel Tank
3.4. Biochemical Analysis
3.5. Cortisol Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.J.; Paull, G.C.; Tyler, C.R. Improving zebrafish laboratory welfare and scientific research through understanding their natural history. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1038–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.D.; Readman, G.D.; Owen, S.F. Key issues concerning environmental enrichment for laboratory-held fish species. Lab. Anim. 2009, 43, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Braubach, O.; Spitsbergen, J.; Gerlai, R.; Kalueff, A.V. Zebrafish models for translational neuroscience research: From tank to bedside. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcon, M.; Mocelin, R.; Benvenutti, R.; Costa, T.; Herrmann, A.P.; De Oliveira, D.L.; Koakoski, G.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Piato, A. Environmental enrichment modulates the response to chronic stress in zebrafish. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb176735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newberry, R.C. Environmental enrichment: Increasing the biological relevance of captive environments. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1995, 44, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, J.; Morgan, R.; Finnøen, M.H.; Dey, A.; Sarkar, K.; Jutfelt, F. On the observation of wild zebrafish (Danio rerio) in India. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engeszer, R.E.; Patterson, L.B.; Rao, A.A.; Parichy, D.M. Zebrafish in the wild: A review of natural history and new notes from the field. Zebrafish 2007, 4, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, P.; Jones, S.; Young, I.S.; Sneddon, L.U. What do zebrafish want? Impact of social grouping, dominance and gender on preference for enrichment. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kistler, C.; Hegglin, D.; Würbel, H.; König, B. Preference for structured environment in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and checker barbs (Puntius oligolepis). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 135, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerber, B.; Stamer, A.; Stadtlander, T. Environmental Enrichment and Its Effects on Welfare in Fish, 1st ed.; FiBL: Frick, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.A.; Spence, R.; Jones, F.A.; Spence-Jones, H.C. Shade as enrichment: Testing preferences for shelter in two model fish species. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, J.; Johnsson, J.I. Environmental enrichment for fish in captive environments: Effects of physical structures and substrates. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.A.; Winder, L.A.; Watt, P.J. Enrichment increases aggression in zebrafish. Fishes 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carfagnini, A.G.; Rodd, F.H.; Jeffers, K.B.; Bruce, A.E.E. The effects of habitat complexity on aggression and fecundity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2009, 86, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basquill, S.P.; Grant, J.W. An increase in habitat complexity reduces aggression and monopolization of food by zebra fish (Danio rerio). Can. J. Zoöl. 1998, 76, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleström, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Schorderet, D.F.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Sohm, F.; Warner, S. Zebrafish: Housing and husbandry recommendations. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, C.H.; Reed, B.T.; Hawkins, P. Enrichment for laboratory zebrafish—A review of the evidence and the challenges. Animals 2021, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, N.; Paull, G.; Grierson, A.; Dunford, K.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M.; Sneddon, L.U.; Wren, N.; Higgins, J.; Hawkins, P. Report of a meeting on contemporary topics in zebrafish husbandry and care. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson, M.; Kettunen, P. Effects of Holding Density on the Welfare of Zebrafish: A Systematic Review. Zebrafish 2021, 18, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midttun, H.L.E.; Øverli, Ø.; Tudorache, C.; Mayer, I.; Johansen, I.B. Non-invasive sampling of water-borne hormones demonstrates individual consistency of the cortisol response to stress in laboratory zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal, A.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Tallo-Parra, O.; Lopez-Bejar, M.; Tort, L. Comparative assessment of cortisol in plasma, skin mucus and scales as a measure of the hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal axis activity in fish. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Alacid, L.; Sanahuja, I.; Ordóñez-Grande, B.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Herrera, M.; Ibarz, A. Skin mucus metabolites and cortisol in meagre fed acute stress-attenuating diets: Correlations between plasma and mucus. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.Á. Using skin mucus to evaluate stress in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellf. Immunol. 2016, 59, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Martinez, L.; Brandts, I.; Reyes-López, F.; Tort, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Teles, M. Skin Mucus as a Relevant Low-Invasive Biological Matrix for the Measurement of an Acute Stress Response in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Water 2022, 14, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.R.; Ruhl, N.; Winberg, S.; Oliveira, R.F. Social phenotypes in zebrafish. In The Rights and Wrongs of Zebrafish: Behavioral Phenotyping of Zebrafish; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 95–130. [Google Scholar]
- Buske, C.; Gerlai, R. Diving deeper into Zebrafish development of social behavior: Analyzing high resolution data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, R.E.; Chadwick, L.; McGinnis, G.C. Behavioral measures of anxiety in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, S.; Karia, M.; Cheng, R.-K.; Mathuru, A.S. An automated assay system to study novel tank induced anxiety. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorge, S.; Ferreira, J.M.; Olsson, I.A.S.; Valentim, A.M. Adult Zebrafish Anesthesia: A Study of Efficacy and Behavioral Recovery of Different Anesthetics. Zebrafish 2021, 18, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friard, O.; Gamba, M. BORIS: A free, versatile open-source event-logging software for video/audio coding and live observations. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Khan, A.; Gerlai, R. Early social deprivation does not affect cortisol response to acute and chronic stress in zebrafish. Stress 2021, 24, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Shi, X.; Yeung, L.W.; Lam, P.K.; Wu, R.S.; Zhou, B. Hexabromocyclododecane-induced developmental toxicity and apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 93, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriello, T.; Felix, L.M.; Monteiro, S.M.; Santos, D.; Cofone, R.; Ferrandino, I. Exposure to aluminium causes behavioural alterations and oxidative stress in the brain of adult zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 85, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durak, I.; Yurtarslanl, Z.; Canbolat, O.; Akyol, O.A. A Methodological Approach to Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Assay Based on Inhibition of Nitroblue Tetrazolium (NBT) Reduction. Clin. Chim. Acta 1993, 214, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claiborne, A. Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Glutathione and zebrafish: Old assays to address a current issue. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gartaganis, S.P.; Patsoukis, N.E.; Nikolopoulos, D.K.; Georgiou, C.D. Evidence for oxidative stress in lens epithelial cells in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Eye 2007, 21, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesquita, C.S.; Oliveira, R.; Bento, F.; Geraldo, D.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Marcos, J.C. Simplified 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fuentes, G.; Rubio-Escalante, F.J.; Noreña-Barroso, E.; Escalante-Herrera, K.S.; Schlenk, D. Impacts of oxidative stress on acetylcholinesterase transcription, and activity in embryos of zebrafish (Danio rerio) following Chlorpyrifos exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, I.; Oliveira, R.; Lourenço, J.; Grisolia, C.K.; Mendo, S.; Soares, A. Biomarkers as a tool to assess effects of chromium (VI): Comparison of responses in zebrafish early life stages and adults. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankani, K.C.; Pearce, J.M. Open source laboratory sample rotator mixer and shaker. HardwareX 2017, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onarheim, T.; Janczak, A.M.; Nordgreen, J. The Effects of Social vs. Individual Housing of Zebrafish on Whole-Body Cortisol and Behavior in Two Tests of Anxiety. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 859848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Paull, G.C.; Tyler, C.R. Effects of environmental enrichment on survivorship, growth, sex ratio and behaviour in laboratory maintained zebrafish Danio rerio. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilkes, L.; Owen, S.F.; Readman, G.D.; Sloman, K.A.; Wilson, R.W. Does structural enrichment for toxicology studies improve zebrafish welfare? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 139, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, A.D.; Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish models of anxiety-like behaviors. In The Rights and Wrongs of Zebrafish: Behavioral Phenotyping of Zebrafish; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, C.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.; Franks, B. Free-choice exploration increases affiliative behaviour in zebrafish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 203, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Social behavior of zebrafish: From synthetic images to biological mechanisms of shoaling. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.M.; Volpato, G.L.; Braithwaite, V.A. A Psychological Aversive Condition Does Not Change Individual Zebrafish Preference for Background Color or Artificial Plant Enrichments. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2021, 25, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, B.R.; dos Santos, R.C.; Dias, C.A.G.M.; Maximino, C.; Gouveia, A., Jr. White environment can be used as an aversive stimulus in zebrafish inhibitory avoidance learning. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, R.; Gorissen, M.; Stokkermans, M.; Zethof, J.; Ebbesson, L.O.; Van De Vis, H.; Flik, G.; Bos, R.V.D. The effects of environmental enrichment and age-related differences on inhibitory avoidance in zebrafish (Danio rerio Hamilton). Zebrafish 2015, 12, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Strungaru, S.A.; Huang, J.C.; Hsiao, C.D. Which zebrafish strains are more suitable to perform behavioral studies? A comprehensive comparison by phenomic approach. Biology 2020, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciol, A.; Iqbal, M.; Eada, A.; Tran, S.; Gerlai, R. The light-dark task in zebrafish confuses two distinct factors: Interaction between background shade and illumination level preference. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 179, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R.; Lahav, M.; Guo, S.; Rosenthal, A. Drinks like a fish: Zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, R.E.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral phenotyping in zebrafish: Comparison of three behavioral quantification methods. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, J.M. Investigating the Effects of Highly Preferred Environmental Enrichment on the Behaviour and Welfare of Laboratory Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, B.D.; Gibbon, A.J.; Cleal, M.; Norton, W.H.J.; Parker, M.O. Chronic unpredictable early-life stress (CUELS) protocol: Early-life stress changes anxiety levels of adult zebrafish. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 108, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, B.D.; Gibbon, A.J.; Cleal, M.; Sudwarts, A.; Pritchett, D.; Miletto Petrazzini, M.E.; Brennan, C.H.; Parker, M.O. Moderate early life stress improves adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) working memory but does not affect social and anxiety-like responses. Dev. Psychobiol. 2021, 63, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Fatema, M.K.; Reichard, M.; Huq, K.A.; Wahab, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.F.; Smith, C. The distribution and habitat preferences of the zebrafish in Bangladesh. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 69, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, A.C.V.V.; Abreu, M.S.; Zanandrea, R.; Saibt, N.; Friedrich, M.T.; Koakoski, G.; Gusso, D.; Piato, A.L.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Environmental and pharmacological manipulations blunt the stress response of zebrafish in a similar manner. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcon, M.; Mocelin, R.; Sachett, A.; Siebel, A.M.; Herrmann, A.P.; Piato, A. Enriched environment prevents oxidative stress in zebrafish submitted to unpredictable chronic stress. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Wagle, M.; Guo, S. Identification of environmental stressors and validation of light preference as a measure of anxiety in larval zebrafish. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Facciol, A.; Tran, S.; Gerlai, R. Re-examining the factors affecting choice in the light–dark preference test in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 327, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, A.; Furné, M.; Trenzado, C.E.; de Haro, C.; Sánchez-Muros, M. Study of the oxidative state, as a marker of welfare, on Gilthead Sea Bream, Sparus aurata, subjected to handling stress. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2012, 43, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, D.; Marasco, V.; Møller, A.P. A meta-analysis of glucocorticoids as modulators of oxidative stress in vertebrates. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2011, 181, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jorge, S.; Félix, L.; Costas, B.; Valentim, A.M. Housing Conditions Affect Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior but Not Their Physiological Status. Animals 2023, 13, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061120
Jorge S, Félix L, Costas B, Valentim AM. Housing Conditions Affect Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior but Not Their Physiological Status. Animals. 2023; 13(6):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061120
Chicago/Turabian StyleJorge, Sara, Luís Félix, Benjamín Costas, and Ana M. Valentim. 2023. "Housing Conditions Affect Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior but Not Their Physiological Status" Animals 13, no. 6: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061120
APA StyleJorge, S., Félix, L., Costas, B., & Valentim, A. M. (2023). Housing Conditions Affect Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior but Not Their Physiological Status. Animals, 13(6), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13061120







