A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp.
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Campylobacter-Associated Pathogenesis in Humans
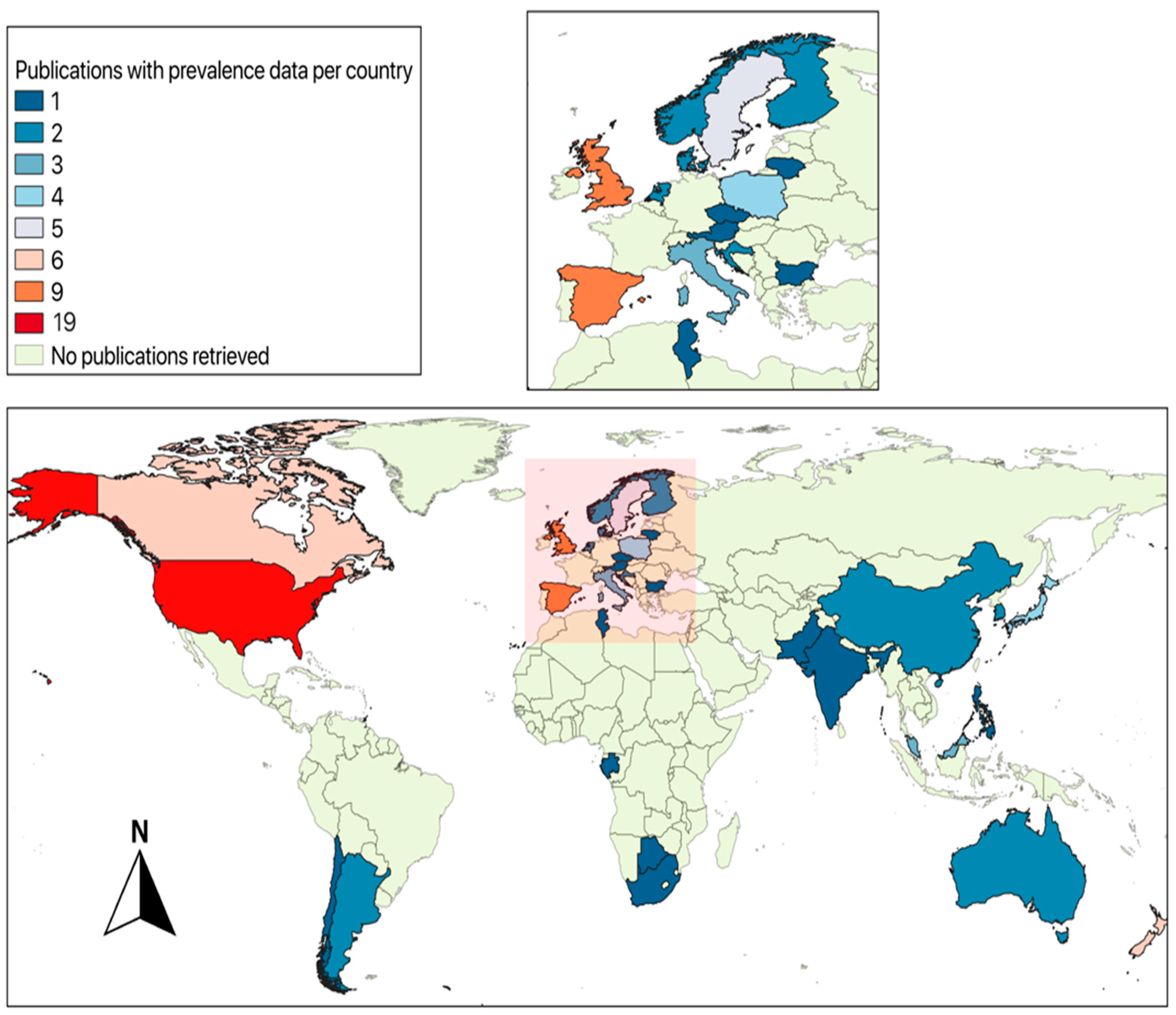
3. Literature on Wildlife Carriers of Campylobacter spp.
4. Wildlife Sources of Campylobacter Species
5. Wildlife Carriers of Campylobacter Species
5.1. Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles
5.2. Birds
Potential Role of Birds in Spreading Antibiotic Resistance via Campylobacter spp.
5.3. Mammals
6. Summary/Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahin, O.; Fitzgerald, C.; Stroika, S.; Zhao, S.; Sippy, R.J.; Kwan, P.; Plummer, P.J.; Han, J.; Yaeger, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Molecular evidence for zoonotic transmission of an emergent, highly pathogenic Campylobacter jejuni clone in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Campylobacter. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Keithlin, J.; Sargeant, J.; Thomas, M.K.; Fazil, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the proportion of Campylobacter cases that develop chronic sequelae. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Man, S.M. The clinical importance of emerging Campylobacter species. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Human campylobacteriosis: A public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Dallas, J.F.; Strachan, N.J.; MacRae, M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Wilson, D.J.; Gormley, F.J.; Falush, D.; Ogden, I.D.; Maiden, M.C.; et al. Campylobacter genotyping to determine the source of human infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2009, 48, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, E.A.; Jean, S.M.; Machiah, D.K.; Breding, E.; Sharma, P. Extraintestinal campylobacteriosis in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comp. Med. 2014, 64, 496–500. [Google Scholar]
- Macartney, L.; Al-Mashat, R.R.; Taylor, D.J.; McCandlish, I.A. Experimental infection of dogs with Campylobacter jejuni. Vet. Rec. 1988, 122, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, S.L.; Rankin, S.C.; Byrne, B.A.; Weese, J.S. Enteropathogenic bacteria in dogs and cats: Diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment, and control. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemelka, K.W.; Brown, A.W.; Wallace, S.M.; Jones, E.; Asher, L.V.; Pattarini, D.; Applebee, L.; Gilliland, T.C., Jr.; Guerry, P.; Baqar, S. Immune response to and histopathology of Campylobacter jejuni infection in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo). Comp. Med. 2009, 59, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Kaminjolo, J.; Loregnard, R.; Kitson-Piggott, W. Campylobacter infections in calves, piglets, lambs and kids in Trinidad. Br. Vet. J. 1992, 148, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turowski, E.E.; Shen, Z.; Ducore, R.M.; Parry, N.M.; Kirega, A.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Fox, J.G. Isolation of a Campylobacter lanienae-like bacterium from laboratory chinchillas (Chinchilla laniger). Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández, H.; Neto, U.F.; Fernandes, F.; de Almeida Pedra, M.; Trabulsi, L.R. Culture supernatants of Campylobacter jejuni induce a secretory response in jejunal segments of adult rats. Infect. Immun. 1983, 40, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stahl, M.; Ries, J.; Vermeulen, J.; Yang, H.; Sham, H.P.; Crowley, S.M.; Badayeva, Y.; Turvey, S.E.; Gaynor, E.C.; Li, X.; et al. A novel mouse model of Campylobacter jejuni gastroenteritis reveals key pro-inflammatory and tissue protective roles for Toll-like receptor signaling during infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colles, F.M.; Dingle, K.E.; Cody, A.J.; Maiden, M.C. Comparison of Campylobacter populations in wild geese with those in starlings and free-range poultry on the same farm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, V. Faeco-prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in urban wild birds and pets in New Zealand. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanley, K.; Jones, K. Cattle and sheep farms as reservoirs of Campylobacter. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 104s–113s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, S.A.; Allen, V.M.; Domingue, G.; Jørgensen, F.; Frost, J.A.; Ure, R.; Whyte, R.; Tinker, D.; Corry, J.E.; Gillard-King, J.; et al. Sources of Campylobacter spp. colonizing housed broiler flocks during rearing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemos, M.-L.; Nunes, A.; Ancora, M.; Cammà, C.; Costa, P.M.D.; Oleastro, M. Campylobacter jejuni in different canine populations: Characteristics and zoonotic potential. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manser, P.A.; Dalziel, R.W. A survey of Campylobacter in animals. J. Hyg. 1985, 95, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oporto, B.; Juste, R.; López-Portolés, J.; Hurtado, A. Genetic diversity among Campylobacter jejuni isolates from healthy livestock and their links to human isolates in Spain. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, D.; Pasmans, F.; Messens, W.; Martel, A.; Van Immerseel, F.; Rasschaert, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Deun, K.; Haesebrouck, F. Poultry as a host for the zoonotic pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesley, I.; Wells, S.; Harmon, K.; Green, A.; Schroeder-Tucker, L.; Glover, M.; Siddique, I. Fecal shedding of Campylobacter and Arcobacter spp. in dairy cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, D.J.; Streicker, D.G.; Altizer, S. Linking anthropogenic resources to wildlife–pathogen dynamics: A review and meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a Foodborne Pathogen: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butzler, J.P. Campylobacter, from obscurity to celebrity. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debruyne, L.; Gevers, D.; Vandamme, P. Taxonomy of the Family Campylobacteraceae. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme, P.; Dewhirst, F.; Paster, B.; Stephen, L. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol 2, Part C (The Proteobacteria); Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.; Iraola, G. Pathogenomics of emerging Campylobacter species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00072-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, A.M.; Storey, D.B.; Taff, C.C.; Townsend, A.K.; Huang, B.C.; Kong, N.T.; Clothier, K.A.; Spinner, A.; Byrne, B.A.; Weimer, B.C. Genomic comparison of Campylobacter spp. and their potential for zoonotic transmission between birds, primates, and livestock. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 7165–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endtz, H.P. Campylobacter infections. In Hunter’s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Altekruse, S.F.; Stern, N.J.; Fields, P.I.; Swerdlow, D.L. Campylobacter jejuni—An emerging foodborne pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.S.L.; Birtles, A.; Bolton, F.J.; French, N.P.; Robinson, S.E.; Newbold, L.S.; Upton, M.; Fox, A.J. Longitudinal study of the molecular epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni in cattle on dairy farms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3626–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, A.; Gaull, F.; Kasimir, S.; Gürtler, M.; Mielke, H.; Linnebur, M.; Fehlhaber, K. Prevalences and transmission routes of Campylobacter spp. strains within multiple pig farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 108, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Kürekci, C.; Sakin, F.; Epping, L.; Knüver, M.T.; Semmler, T.; Stingl, K. Characterization of Campylobacter spp. strains isolated from wild birds in Turkey. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 712106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, S.C.; Miller, M.A.; Byrne, B.A.; Chouicha, N.; Hardin, D.; Jessup, D.; Dominik, C.; Roug, A.; Schriewer, A.; Jang, S.S.; et al. Epidemiology and potential land-sea transfer of enteric bacteria from terrestrial to marine species in the Monterey Bay Region of California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.S.L.; Xavier, C.; Santovenia, M.; Pruckler, J.; Stroika, S.; Joyce, K.; Gardner, T.; Fields, P.I.; McLaughlin, J.; Tauxe, R.V.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing confirms wild birds as the source of a Campylobacter outbreak associated with the consumption of raw peas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4540–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, M.K.; Ojima, S.; Sano, H.; Shindo, J.; Shirafuji, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanabe, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Hu, D.L. Differential Distribution of Salmonella Serovars and Campylobacter spp. isolates in free-living crows and broiler chickens in Aomori, Japan. Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogden, I.D.; Dallas, J.F.; MacRae, M.; Rotariu, O.; Reay, K.W.; Leitch, M.; Thomson, A.P.; Sheppard, S.K.; Maiden, M.; Forbes, K.J.; et al. Campylobacter excreted into the environment by animal sources: Prevalence, concentration shed, and host association. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, R.D.; Midwinter, A.C.; Marshall, J.C.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; Pleydell, E.J.; French, N.P. Campylobacter jejuni strains associated with wild birds and those causing human disease in six high-use recreational waterways in New Zealand. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01228-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, A.M.; Miller, W.A.; Byrne, B.A.; Chouicha, N.; Boyce, W.M.; Townsend, A.K. Prevalence and pathogenic potential of Campylobacter isolates from free-living, human-commensal American crows. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shyaka, A.A.; Chaisowwong, W.; Okouchi, Y.; Fukumoto, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Kawamoto, K. Virulence characterization of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from resident wild birds in Tokachi area, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, K.; Lu, J.; Mukherjee, P.; Berglund, T.; Varughese, E.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Campylobacter jejuni Colonization in the crow gut involves many deletions within the cytolethal distending toxin gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01893-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Etterijck, R.; Breynaert, J.; Revets, H.; Devreker, T.; Vandenplas, Y.; Vandamme, P.; Lauwers, S. Isolation of Campylobacter concisus from feces of children with and without diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2304–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolton, F.; Hutchinson, D.; Coates, D. Blood-free selective medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from feces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 19, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whelan, C.D.M.; Girdwood, R.W.; Fricker, C.R. The significance of wild birds (Larus sp.) in the epidemiology of Campylobacter infections in humans. Epidemiol. Infect. 1988, 101, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dediste, A.; Vandenberg, O.; Vlaes, L.; Ebraert, A.; Douat, N.; Bahwere, P.; Butzler, J.P. Evaluation of the ProSpecT microplate assay for detection of Campylobacter: A routine laboratory perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levesque, S.F.; Carrier, N.; Frost, E.; Arbeit, R.D.; Michaud, S. Campylobacteriosis in urban versus rural areas: A case-case study integrated with molecular typing to validate risk factors and to attribute sources of infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iglesias-Torrens, Y.M.; Guirado, P.; Llovet, T.; Munoz, C.; Cerda-Cuellar, M.; Madrid, C.; Balsalobre, C.; Navarro, F. Population structure, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence-associated genes in Campylobacter jejuni isolated from three ecological niches: Gastroenteritis patients, broilers, and wild birds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nohra, A.G.; Marshall, J.C.; Midwinter, A.C.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; French, N.P. Shifts in the molecular epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections in a sentinel region of New Zealand following implementation of food safety interventions by the poultry industry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01753-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärenlampi, R.; Rautelin, H.; Hänninen, M.L. Evaluation of genetic markers and molecular typing methods for prediction of sources of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli infections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1683–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champion, O.L.; Gaunt, M.W.; Gundogdu, O.; Elmi, A.; Witney, A.A.; Hinds, J.; Dorrell, N.; Wren, B.W. Comparative phylogenomics of the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni reveals genetic markers predictive of infection source. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16043–16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denis, M.; Soumet, C.; Rivoal, K.; Ermel, G.; Blivet, D.; Salvat, G.; Colin, P. Development of a m-PCR assay for simultaneous identification of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 29, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhans, A.; Jacobson, M.; Hansson, I.; Lebbad, M.; Lambertz, S.T.; Gammelgård, E.; Saager, M.; Akande, O.; Fellström, C. Occurrence of pathogens in wild rodents caught on Swedish pig and chicken farms. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sails, A.D.; Swaminathan, B.; Fields, P.I. Utility of multilocus sequence typing as an epidemiological tool for investigation of outbreaks of gastroenteritis caused by Campylobacter jejuni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4733–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kärenlampi, R.; Rautelin, H.; Schönberg-Norio, D.; Paulin, L.; Hänninen, M.-L. Longitudinal Study of Finnish Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolates from humans, using Multilocus Sequence Typing, including comparison with epidemiological data and isolates from poultry and cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, W.O.D.; Masters, N.; Kuballa, A.; Marinoni, O.; Katouli, M. Marker genes of fecal indicator bacteria and potential pathogens in animal feces in subtropical catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.N.D.; Baggesen, D.L.; Nielsen, E.M. The occurrence and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli in organic pigs and their outdoor environment. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 116, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardner, T.J.F.; Xavier, C.; Klein, R.; Pruckler, J.; Stroika, S.; McLaughlin, J.B. Outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw peas. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2011, 53, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis-Iversen, J.R.; Morris, V.; Sowa, A.; Harris, J.; Atterbury, R.; Sparks, N.; Allen, V. Persistent environmental reservoirs on farms as risk factors for Campylobacter in commercial poultry. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lydekaitiene, V.L.K.E. Prevalence and genetic diversity of C. jejuni isolated from broilers and their environment using flaa-rflp typing and mlst analysis. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2020, 20, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, R.S.H.; Börjesson, S.; Sannö, A.; Jernberg, T.; Aspán, A.; Ågren, E.O.; Hansson, I. Prevalence and genomic characteristics of zoonotic gastro-intestinal pathogens and ESBL/pAmpC producing Enterobacteriaceae among Swedish corvid birds. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2019, 9, 1701399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldenstrom, J.B.T.; Carlsson, I.; Hasselquist, D.; Achterberg, R.P.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Olsen, B. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter lari, and Campylobacter coli in different ecological guilds and taxa of migrating birds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5911–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sensale, M.C.A.; Dipineto, L.; Santaniello, A.; Calabria, M.; Menna, L.F.; Fioretti, A. Survey of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in different taxa and ecological guilds of migratory birds. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 5, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, A.C.F.E.; de Rijk, S.; Versluis, M.A.J.; Coipan, C.; Buij, R.; Muskens, G.; Koene, M.; Pijnacker, R.; Duim, B.; van der Graaf-van Bloois, L.; et al. Tracing the animal sources of surface water contamination with Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medley, S.P.M.; Alexander, K.A. Anthropogenic landscapes increase Campylobacter jejuni infections in urbanizing banded mongoose (Mungos mungo): A one health approach. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e007888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, M.Y.I.A.J.; Aziz, S.A.; Zakaria, Z.; Khan, A.R.; Habib, I. Occurrence of antibiotic resistant C. jejuni and E. coli in wild birds, chickens, humans, and the environment in Malay villages, Kedah, Malaysia. Vet. Med. 2022, 67, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.P.R.; Coipan, C.; Mulder, A.C.; Fernandes Veludo, A.; de Rijk, S.; van Hoek, A.; Buij, R.; Muskens, G.; Koene, M.; Veldman, K.; et al. Sources and transmission routes of campylobacteriosis: A combined analysis of genome and exposure data. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, C.M.R.J.; Van, T.T.H. Campylobacter hepaticus, the cause of Spotty Liver Disease in chickens, can enter a viable but nonculturable state. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 266, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, D.R.C.; Hea, S.Y.; Brightwell, G. Importance of the farm environment and wildlife for transmission of Campylobacter jejuni in a pasture-based dairy herd. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossler, E.O.C.; Soto, L.P.; Frizzo, L.S.; Zimmermann, J.; Rosmini, M.R.; Sequeira, G.J.; Signorini, M.L.; Zbrun, M.V. Prevalence, genotypic diversity and detection of virulence genes in thermotolerant Campylobacter at different stages of the poultry meat supply chain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 326, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbrun, M.V.R.E.; Olivero, C.R.; Soto, L.P.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Frizzo, L.S.; Signorini, M.L. Possible reservoirs of thermotolerant Campylobacter at the farm between rearing periods and after the use of enrofloxacin as a therapeutic treatment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 340, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesiyun, A.A.S.-J.A.; Thompson, N.N. Isolation of enteric pathogens from bats in Trinidad. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachand, N.R.A.; Onanga, R.; Arsenault, J.; Gonzalez, J.P. public health significance of zoonotic bacterial pathogens from bushmeat sold in urban markets of Gabon, Central Africa. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baily, J.L.M.G.; Bayliss, S.; Foster, G.; Moss, S.E.; Watson, E.; Pascoe, B.; Mikhail, J.; Pizzi, R.; Goldstone, R.J.; Smith, D.G.; et al. Evidence of land-sea transfer of the zoonotic pathogen Campylobacter to a wildlife marine sentinel species. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondo, K.J.P.D.L.; Janecko, N.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Parmley, E.J.; Weese, J.S.; Rousseau, J.; Taboada, E.; Mutschall, S.; Jardine, C.M. Salmonella, Campylobacter, Clostridium difficile, and anti-microbial resistant Escherichia coli in the faeces of sympatric meso-mammals in southern Ontario, Canada. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.E.B.K.A.; Beckmen, K.B.; Oaks, J.L.; Davis, M.A.; Baker, K.N.K.; Mazet, J.A.K. Aerobic oral and rectal bacteria of free-ranging steller sea lion pups and juveniles (Eumetopias jubatus) in alaska. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greig, D.J.G.; Smith, W.A.; Conrad, P.A.; Field, C.L.; Fleetwood, M.; Harvey, J.T.; Ip, H.S.; Jang, S.; Packham, A.; Wheeler, E.; et al. Surveillance for zoonotic and selected pathogens in harbor seals Phoca vitulina from central California. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 111, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatta, Y.O.T.; Tsuchiaka, S.; Katayama, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Masangkay, J.S.; Puentespina, R., Jr.; Eres, E.; Cosico, E.; Une, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; et al. Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in rectal swab samples from Rousettus amplexicaudatus in the Philippines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaing, C.T.J.B.; Gardner, S.; McLoughlin, K.; Slezak, T.; Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.A. Pathogen surveillance in wild bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.G.J.H.; Mun, S.H.; An, J.U.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Song, H.; Seong, J.K.; Suh, J.G.; Cho, S. The wild mouse (Micromys minutus): Reservoir of a novel Campylobacter jejuni strain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.I.T.; Nakadai, A.; Kato, T.; Hayama, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Hayashidani, H. Prevalence of Salmonella, Yersinia and Campylobacter spp. in Feral Raccoons (Procyon lotor) and Masked Palm Civets (Paguma larvata) in Japan. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschall, S.K.H.; Bondo, K.J.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Jardine, C.M.; Taboada, E.N. Campylobacter jejuni strain dynamics in a raccoon (Procyon lotor) population in southern Ontario, Canada: High prevalence and rapid subtype turnover. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkola, S.; Rossi, M.; Jaakkonen, A.; Simola, M.; Tikkanen, J.; Hakkinen, M.; Tuominen, P.; Huitu, O.; Niemimaa, J.; Henttonen, H.; et al. Host-dependent clustering of Campylobacter strains from small mammals in Finland. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 621490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhynd, K.J.R.L.; Elcock, D.A.; Whitehall, P.J.; Rycroft, A.; Macgregor, S.K. Prevalence of Salmonella spp. and thermophilic Campylobacter spp. In the small Asian mongoose (Herpestes javanicus) in barbados, west indies. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2014, 45, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, M.P.D.L.; Taboada, E.N.; Parmley, E.J.; Mutschall, S.; Jardine, C.M. Molecular and statistical analysis of Campylobacter spp. and antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter carriage in wildlife and livestock from Ontario farms. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahpour, N.Z.B.; Alipour, A.; Khayatzadeh, J. Wild-bird feces as a source of Campylobacter jejuni infection in children’s playgrounds in Iran. Food Control 2015, 50, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilles, N.G.-B.I.; Alba-Casals, A.; López-Soria, S.; Pérez-Méndez, N.; Saco, M.; González-Solís, J.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance of zoonotic enteropathogens in gulls from southern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilles, N.S.A.; Cerda-Cuellar, M. Free-living waterfowl as a source of zoonotic bacteria in a dense wild bird population area in Northeastern Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benskin, C.M.H.R.G.; Pickup, R.W.; Mainwaring, M.C.; Wilson, K.; Hartley, I.R. Life history correlates of fecal bacterial species richness in a wild population of the blue tit Cyanistes caeruleus. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broman, T.P.H.; Bergström, S.; Sellin, M.; Waldenström, J.; Danielsson-Tham, M.L.; Olsen, B. Campylobacter jejuni in black-headed gulls (Larus ridibundus): Prevalence, genotypes, and influence on C. jejuni epidemiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4594–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colles, F.M.M.; Howe, J.C.; Devereux, C.L.; Gosler, A.G.; Maiden, M.C.J. Dynamics of Campylobacter colonization of a natural host, Sturnus vulgaris (European Starling). Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craft, J.E.H.; Christman, N.D.; Pryor, W.; Chaston, J.M.; Erickson, D.L.; Wilson, E. Increased microbial diversity and decreased prevalence of common pathogens in the gut microbiomes of wild turkeys compared to domestic turkeys. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0142321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, S.E.S.; Line, E.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P. Determination of the incidence of Salmonella spp., Campylobacter jejuni, and Clostridium perfringens in wild birds near broiler chicken houses by sampling intestinal droppings. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, L.B.T.; Bergström, S.; Olsen, B.; On, S.L.W.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter subantarcticus sp. nov., isolated from birds in the sub-Antarctic region. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Sanchez, S.M.; Casas, F.; Hofle, U. Prevalence of Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp and Campylobacter sp in the intestinal flora of farm-reared, restocked and wild red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa): Is restocking using farm-reared birds a risk? Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L.; Huang, J.J.; Wang, C.M.; Li, M.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, B.; Chang, H.; Ji, J.W.; Sen, K.Y.; He, H.X. Emergence of Genetic Diversity and Multi-Drug Resistant Campylobacter jejuni From Wild Birds in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzic, A.U.-C.R.; Stepien-Pysniak, D.; Dec, M.; Puchalski, A.; Wernicki, A. Isolation, identification and antibiotic resistance of Campylobacter strains isolated from domestic and free-living pigeons. Br. Poult. Sci. 2016, 57, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, D.M.M.; Morishita, T.Y.; Wack, R.F. Fecal shedding and antimicrobial susceptibility of selected bacterial pathogens and a survey of intestinal parasites in free-living waterfowl. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, H.G.W.; Montefusco, A.; Schlatter, R. Wild birds as reservoir of thermophilic enteropathogenic Campylobacter species in Southern Chile. Mem. Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1996, 91, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- French, N.P.M.A.; Holland, B.; Collins-Emerson, J.; Pattison, R.; Colles, F.; Carter, P. Molecular epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from wild-bird fecal material in children’s playgrounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabriele-Rivet, V.F.J.H.; Tremblay, D.; Harel, J.; Cote, N.; Arsenault, J. Prevalence and risk factors for Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Coxiella burnetii, and Newcastle disease virus in feral pigeons (Columba livia) in public areas of Montreal, Canada. Can. J. Vet. Res. Rev. Can. De Rech. Vet. 2016, 80, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, K.S.A.A.; Jaganathan, M.; Tan, C.G.; Chong, C.T.; Tang, S.C.; Ideris, A.; Dare, C.M.; Bradbury, J.M. Survey of Campylobacter, Salmonella and Mycoplasmas in house crows (Corvus splendens) in Malaysia. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pena, F.J.L.; Serrano, T.; Ruano, M.J.; Belliure, J.; Benzal, J.; Herrera-Leon, S.; Vidal, V.; D’Amico, V.; Perez-Boto, D.; Barbosa, A. Isolation of Campylobacter spp. from three species of antarctic penguins in different geographic locations. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.R.H.; Baker, A.J.; Domingo, J.W.S.; Buehler, D.M. Gastro-intestinal microbiota of two migratory shorebird species during spring migration staging in Delaware Bay, USA. J. Ornithol. 2014, 155, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, B.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Rahbek, C.; Madsen, J.J.; Waino, M.; Chriel, M.; Nordentoft, S.; Baggesen, D.L.; Madsen, M. Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in wild birds on Danish livestock farms. Acta Vet. Scand. 2016, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, L.A.B.M.; Coffey, P.; Elliott, J.; Jones, T.R.; Jones, R.C.; Lahuerta-Marin, A.; Leatherbarrow, A.H.; McNiffe, K.; Norman, D.; Williams, N.J.; et al. molecular epidemiology and characterization of Campylobacter spp. isolated from wild bird populations in Northern England. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Indykiewicz, P.A.M.; Minias, P.; Spica, D.; Kowalski, J. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of Campylobacter spp. in urban and rural black-headed gulls Chroicocephalus ridibundus. Ecohealth 2021, 18, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinovic, L.D.S.; Kompes, G.; Goprek, S.; Simpraga, B.; Krstulovic, F.; Mikulic, M.; Humski, A. Occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in gulls feeding on zagreb rubbish tip, Croatia; their diversity and antimicrobial susceptibility in perspective with human and broiler isolates. Pathogens 2020, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapperud, G.R.O. Avian wildlife reservoir of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, Yersinia spp., and Salmonella spp. in Norway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, J.I.S.; Waldenström, J.; Griekspoor, P.; Olsen, B. Prevalence of Campylobacter in wild birds of the mid-Atlantic region, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.I.S. Prevalence of three Campylobacter species, C. jejuni, C. coli, and C. lari, using multilocus sequence typing in wild birds of the Mid-Atlantic region, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzelman, J.M.; Amick, A.; Preedit, J.; Scopel, C.O.; Olapade, O.; Gradus, S.; Singh, A.; Sedmak, G. Identification of human enteric pathogens in gull feces at Southwestern Lake Michigan bathing beaches. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klomp, J.E.M.; Smith, S.B.; McKay, J.E.; Ferrera, I.; Reysenbach, A.L. Cloacal microbial communities of female spotted towhees Pipilo maculatus: Microgeographic variation and individual sources of variability. J. Avian Biol. 2008, 39, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanen, S.R.M.; Pohja-Mykra, M.; Nieminen, T.; Raunio-Saarnisto, M.; Sauvala, M.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Hanninen, M.L.; Kivisto, R. Population genetics and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from western jackdaws and game birds in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02365-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krawiec, M.W.-B.A.; Bednarski, M.; Wieliczko, A. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Genotypic Characteristic of Campylobacter spp. Isolates from Free-Living Birds in Poland. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutkowska, J.T.-S.A.; Kucharczyk, M.; Kucharczyk, H.; Zalewska, J.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and glycopeptide-resistant enterococci in fecal samples of birds from South-Eastern Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, S.J.W.; Byrne, B.A.; Fritz, H.; Taff, C.C.; Townsend, A.K.; Weimer, B.C.; Mete, A.; Wheeler, S.; Boyce, W.M. Comparative analysis of Campylobacter isolates from wild birds and chickens using MALDI-TOF MS, biochemical testing, and DNA sequencing. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, F.G.; Li, D.; Liang, J.R.; Fu, X.Q.; Xu, W.; Duan, R.; Wang, X.; Jing, H.Q.; Dai, J.J. Characteristics of microbial communities and intestinal pathogenic bacteria for migrated Larus ridibundus in southwest China. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lillehaug, A.J.; Bergsjo, B.; Hofshagen, A.; Tharaldsen, J.; Nesse, L.L.; Handeland, K. Screening of feral pigeon (Colomba livia), mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) and graylag goose (Anser anser) populations for Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., avian influenza virus and avian paramyxovirus. Acta Vet. Scand. 2005, 46, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, M.P.T.; Cichewicz, R.; Henshaw, M.; Millard, C.; Steen, C.; Zeller, T.K. Communities of cloacal bacteria in Tree Swallow families. Condor 1996, 98, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malekian, M.S.J.; Hosseinpour, Z. Pathogen Presence in Wild Birds Inhabiting Landfills in Central Iran. Ecohealth 2021, 18, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenzoni, M.L.M.G.; Moretta, I.; Crotti, S.; Agnetti, F.; Moretti, A.; Pitzurra, L.; Casagrande Proietti, P.; Sechi, P.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Franciosini, M.P. Microbiological and parasitological survey of zoonotic agents in apparently healthy feral pigeons. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, C.P.M.D.; Marco-Jimenez, F.; Vega, S. Wild Griffon Vultures (Gyps fulvus) as a source of Salmonella and Campylobacter in Eastern Spain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, F.J.A.; Di Marcantonio, L.; Ercole, C.; Di Donato, G.; Garofolo, G.; Di Giannatale, E. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of C. jejuni isolates from italian wild bird populations. Pathogens 2020, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Maldonado, B.M.-D.L.; Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Jorda, J.; Vega, S.; Marco-Jimenez, F.; Marin, C. Wild Bonelli’s eagles (Aquila fasciata) as carrier of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella and Campylobacter in Eastern Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 101372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.M.-M.B.; Pastor-Tiburón, N.; Moraleda, V.; González, F.; García-Peña, F.J.; Pérez-Cobo, I.; Revuelta, L.; Marín, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter from wild birds of prey in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migura-Garcia, L.R.R.; Cerda-Cuellar, M. Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella Serovars and Campylobacter spp. Isolated from an opportunistic gull species, yellow-legged gull (Larus michahellis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Yousif, I.M.A.-A.S.; Abu, J.; Khairani-Bejo, S.; Puan, C.L.; Bitrus, A.A.; Aliyu, A.B.; Awad, E.A. Occurrence of antibiotic resistant Campylobacter in wild birds and poultry. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2019, 15, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.S.M.; Marshall, J.; Fearnhead, P.; Holland, B.R.; Hotter, G.; French, N.P. Campylobacter jejuni colonization and population structure in urban populations of ducks and starlings in New Zealand. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Lopez, R.A.V.N.; Martin, M.; Mateu, E.; Obon, E.; Cerda-Cuellar, M.; Darwich, L. Wild raptors as carriers of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella and Campylobacter strains. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.E.G.D.; Crothers, E.; Canney, A.; Kaneko, A.; Matsuda, M. Occurrence of Campylobacter spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. in seagulls (Larus spp.). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2002, 2, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, E.A.T.; Ryan, P.G.; Naicker, P.R.; Keddy, K.H.; Gaglio, D.; Witteveen, M.; Cerda-Cuellar, M. Seabirds (Laridae) as a source of Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp. and antimicrobial resistance in South Africa. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4164–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, Y.L.; Koons, N.R.; Linthicum, A.R.; Ramachandran, A. Survey of zoonotic parasites and bacteria in faeces of Canada geese (Branta canadensis) in North-Central Oklahoma. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najdenski, H.D.T.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Nikolov, B.; Petrova-Dinkova, G.; Dalakchieva, S.; Popov, K.; Hristova-Nikolova, I.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Peev, S.; Trifonova-Hristova, A.; et al. Migratory birds along the Mediterranean—Black Sea Flyway as carriers of zoonotic pathogens. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Catedral, L.I.; Baird, K.; Ewen, J.G.; Hauber, M.E.; Brunton, D.H. No evidence of Campylobacter, Salmonella and Yersinia in free-living populations of the red-crowned parakeet (Cyanoramphus novaezelandiae). N. Z. J. Zool. 2009, 36, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmgren, H.B.T.; Waldenström, J.; Lindberg, P.; Aspán, A.; Olsen, B. Salmonella Amager, Campylobacter jejuni, and urease-positive thermophilic Campylobacter found in free-flying peregrine falcons (Falco peregrinus) in Sweden. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pao, S.H.; Kim, C.; Wildeus, S.; Ettinger, M.R.; Wilson, M.D.; Watts, B.D.; Whitley, N.C.; Porto-Fett, A.C.S.; Schwarz, J.G.; Kaseloo, R.; et al. Prevalence and molecular analyses of Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella spp. in co-grazing small ruminants and wild-living birds. Livest. Sci. 2014, 160, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmgren, H.S.M.; Bergstrom, S.; Olsen, B. Enteropathogenic bacteria in migrating birds arriving in Sweden. Scand. J. Infect. Diss. 1997, 29, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucemilo, M.V.K.; Dovc, A.; Muzinic, J.; Pavlak, M.; Jercic, J.; Zupancic, Z. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella typhimurium, and avian Paramyxovirus type 1 (PMV-1) in pigeons from different regions in Croatia. Z. Fur Jagdwiss. 2003, 49, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.G.K.; Verheijen, B.; Elk, M.; Buehler, D.M.; Domingo, J.W.S. Intestinal microbiota and species diversity of Campylobacter and Helicobacter spp. in migrating shorebirds in Delaware Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanwal, S.N.Z.; Aalam, V.; Akhtar, J.; Masood, F.; Javed, S.; Bokhari, H. Variation in antibiotic susceptibility and presence of type VI secretion system (T6SS) in Campylobacter jejuni isolates from various sources. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konicek, C.V.P.; Bartak, P.; Knotek, Z.; Hess, C.; Racka, K.; Hess, M.; Troxler, S. Detection of zoonotic pathogens in wild birds in the cross-border region Austria—Czech Republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.K.D.; MacRae, M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Sproston, E.L.; Gormley, F.J.; Strachan, N.J.; Ogden, I.D.; Maiden, M.C.; Forbes, K.J. Campylobacter genotypes from food animals, environmental sources and clinical disease in Scotland 2005/6. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dyke, M.I.M.; McLellan, N.L.; Huck, P.M. The occurrence of Campylobacter in river water and waterfowl within a watershed in southern Ontario, Canada. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.K.M.; Jang, H.K. Genetic characterization and epidemiological implications of Campylobacter isolates from wild birds in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.E.C.; Clough, H.E.; Diggle, P.J.; Hart, C.A.; Hazel, S.; Kemp, R.; Leatherbarrow, A.J.; Moore, A.; Sutherst, J.; Turner, J.; et al. Frequency and spatial distribution of environmental Campylobacter spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6501–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.K.Y.; Kaneko, K.; Totake, Y.; Ogawa, M. Occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in free-living wild birds from Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 1988, 24, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. 2023. Available online: https://www.qgis.org/en/site/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Masila, N.M.; Ross, K.E.; Gardner, M.G.; Whiley, H. Zoonotic and public health implications of Campylobacter species and squamates (lizards, snakes and amphisbaenians). Pathogens 2020, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Shia, W.Y.; Jhou, Y.J.; Shyu, C.L. Occurrence and molecular characterization of reptilian Campylobacter fetus strains isolated in Taiwan. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Kik, M.; Timmerman, A.J.; Severs, T.T.; Kusters, J.G.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A. Occurrence, diversity, and host association of intestinal Campylobacter, Arcobacter, and Helicobacter in reptiles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiley, H.; McLean, R.; Ross, K. Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in lizard faeces from central Australia using quantitative PCR. Pathogens 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrick, M.E.; Gilbert, M.J.; Blaser, M.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Fitzgerald, C. Human infections with new subspecies of Campylobacter fetus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1678–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Duim, B.; Zomer, A.L.; Wagenaar, J.A. Living in cold blood: Arcobacter, Campylobacter, and Helicobacter in Reptiles. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.I.-C.S.; Gonzalez-Bodi, S.; Marco-Jimenez, F.; Vega, S. Free-living turtles are a reservoir for Salmonella but not for Campylobacter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S.; Gultepe, N.; Yildiz, H. Natural and experimental infections of Campylobacter cryaerophila in rainbow trout: Gross pathology, bacteriology, clinical pathology and chemotherapy. Fish Pathol. 2000, 35, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, H.; Elmali, M.; Ulukanli, Z.; Atabay, H.; Tekinsen, K.K. Presence of Campylobacter (C. jejuni) in recreational, lake and stream water and fresh fish in Turkey. Archiv. Fur Lebensm. 2005, 56, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Loewenherz-Lüning, K.; Heitmann, M.; Hildebrandt, G. Survey about the occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in food of animal origin. 1. Fleischwirtschaft 1996, 76, 956–991. [Google Scholar]
- Gossling, J.; Loesche, W.J.; Nace, G.W. Large intestine bacterial flora of nonhibernating and hibernating leopard frogs (Rana pipiens). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 44, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martel, A.; Adriaensen, C.; Sharifian-Fard, M.; Spitzen-van der Sluijs, A.; Louette, G.; Baert, K.; Crombaghs, B.; Dewulf, J.; Pasmans, F. The absence of zoonotic agents in invasive bullfrogs (Lithobates catesbeianus) in Belgium and The Netherlands. Ecohealth 2013, 10, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysok, B.; Sołtysiuk, M.; Stenzel, T. Wildlife waterfowl as a source of pathogenic Campylobacter strains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormohamed, A.; Fakhr, M.K. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter spp. in Oklahoma conventional and organic retail poultry. Open. Microbiol. J. 2014, 8, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, Y.K.; Oh, J.Y.; Jeong, O.M.; Moon, O.K.; Kang, M.S.; Jung, B.Y.; An, B.K.; Youn, S.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Jang, I.; et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in wild birds of South Korea. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, K.D.; Meece, J.K.; Henkel, J.S.; Shukla, S.K. Birds, migration and emerging zoonoses: West Nile virus, Lyme disease, Influenza A and enteropathogens. Clin. Med. Res. 2003, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Seepersadsingh, N.; Inder, L.; Caesar, K. Some bacterial enteropathogens in wildlife and racing pigeons from Trinidad. J. Wildl. Dis. 1998, 34, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanassova, V.; Ring, C. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. in poultry and poultry meat in Germany. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 51, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, N.J.; Bannov, V.A.; Svetoch, E.A.; Mitsevich, E.V.; Mitsevich, I.P.; Volozhantsev, N.V.; Gusev, V.V.; Perelygin, V.V. Distribution and Characterization of Campylobacter spp. from Russian poultry. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebola, M.; Borilova, G.; Steinhauserova, I. Prevalence of Campylobacter subtypes in pheasants (Phasianus colchicus spp. torquatus) in the Czech Republic. Vet. Med. 2007, 52, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seguino, A.; Chintoan-Uta, C.; Smith, S.H.; Shaw, D.J. Public health significance of Campylobacter spp. colonisation of wild game pheasants (Phasianus colchicus) in Scotland. Food. Microbiol. 2018, 74, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waldenström, J.M.D.; Veldman, K.; Broman, T.; Hasselquist, D.; Olsen, B. Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from wild birds in Sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2438–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, P.A.; Moraes, T.P.; Wilsmann, D.E.; Ferrasso, M.M.; Marinheiro, M.F.; Heinen, J.G.; Calabuig, C.I.P.; Timm, C.D. Ocorrência de Campylobacter e Enterobacteriaceae em aves silvestres e frangos de corte. Arq. Bras. De Med. Veterinária E Zootec. 2019, 71, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skovgård, H.; Kristensen, K.; Hald, B. Retention of Campylobacter (Campylobacterales: Campylobacteraceae) in the House Fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grange, Z.L.; Gartrell, B.D.; Biggs, P.J.; Nelson, N.J.; Marshall, J.C.; Howe, L.; Bahn, M.G.M.; French, N.P. Using a common commensal bacterium in endangered Takahe as a model to explore pathogen dynamics in isolated wildlife populations. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanska, B.K.P.; Andrzejewska, M.; Spica, D.; Kartanas, E.; Ulrich, W.; Jerzak, L.; Kasprzak, M.; Bochenski, M.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in White Stork Ciconia ciconia in Poland. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippy, R.; Sandoval-Green, C.M.; Sahin, O.; Plummer, P.; Fairbanks, W.S.; Zhang, Q.; Blanchong, J.A. Occurrence and molecular analysis of Campylobacter in wildlife on livestock farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thépault, A.; Rose, V.; Queguiner, M.; Chemaly, M.; Rivoal, K. Dogs and cats: Reservoirs for highly diverse Campylobacter jejuni and a potential source of human exposure. Animals 2020, 10, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkan, S.; Vazirian, B.; Khamesipour, F.; Dida, G.O. Prevalence of thermotolerant Campylobacter species in dogs and cats in Iran. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewska, M.S.B.; Klawe, J.J.; Spica, D.; Chudzinska, M. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli species in cats and dogs from Bydgoszcz (Poland) region. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, B.; Pedersen, K.; Wainø, M.; Jørgensen, J.C.; Madsen, M. Longitudinal study of the excretion patterns of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. in young pet dogs in Denmark. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, J.; Barton, M.D.; Lanser, J. Campylobacter species in cats and dogs in South Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 1999, 77, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, C.; Lemmens, C.; Flahou, B.; De Laender, P.; Bouts, T.; Vercammen, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Smet, A.; Haesebrouck, F. Presence of Helicobacter and Campylobacter species in faecal samples from zoo mammals. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Holmes, B.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Lawson, P.A.; Thorne, P.; Byrer, D.E.; Ross, H.M.; Xerry, J.; Thompson, P.M.; Collins, M.D. Campylobacter insulaenigrae sp. nov., isolated from marine mammals. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2369–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, R.A.; Gulland, M.D.F.; Atwill, E.R.; Lawrence, J.; Jang, S.; Conrad, P.A. Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. in northern elephant seals, California. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1967–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, R.A.; Miller, W.G.; Foley, J.E.; Lawrence, J.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Conrad, P.A.; Byrne, B.A. Campylobacter insulaenigrae isolates from northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) in California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.A.K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; Naumann, S.; et al. Wildlife as sentinels of antimicrobial resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; McEwan, N.R.; Stanley, K.; Nava-Diaz, R.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp. Animals 2023, 13, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081334
Olvera-Ramírez AM, McEwan NR, Stanley K, Nava-Diaz R, Aguilar-Tipacamú G. A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp. Animals. 2023; 13(8):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081334
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlvera-Ramírez, Andrea Margarita, Neil Ross McEwan, Karen Stanley, Remedios Nava-Diaz, and Gabriela Aguilar-Tipacamú. 2023. "A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp." Animals 13, no. 8: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081334
APA StyleOlvera-Ramírez, A. M., McEwan, N. R., Stanley, K., Nava-Diaz, R., & Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. (2023). A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp. Animals, 13(8), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081334





