Fishermen Interviews: A Cost-Effective Tool for Evaluating the Impact of Fisheries on Vulnerable Sea Turtles in Tunisia and Identifying Levers of Mitigation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
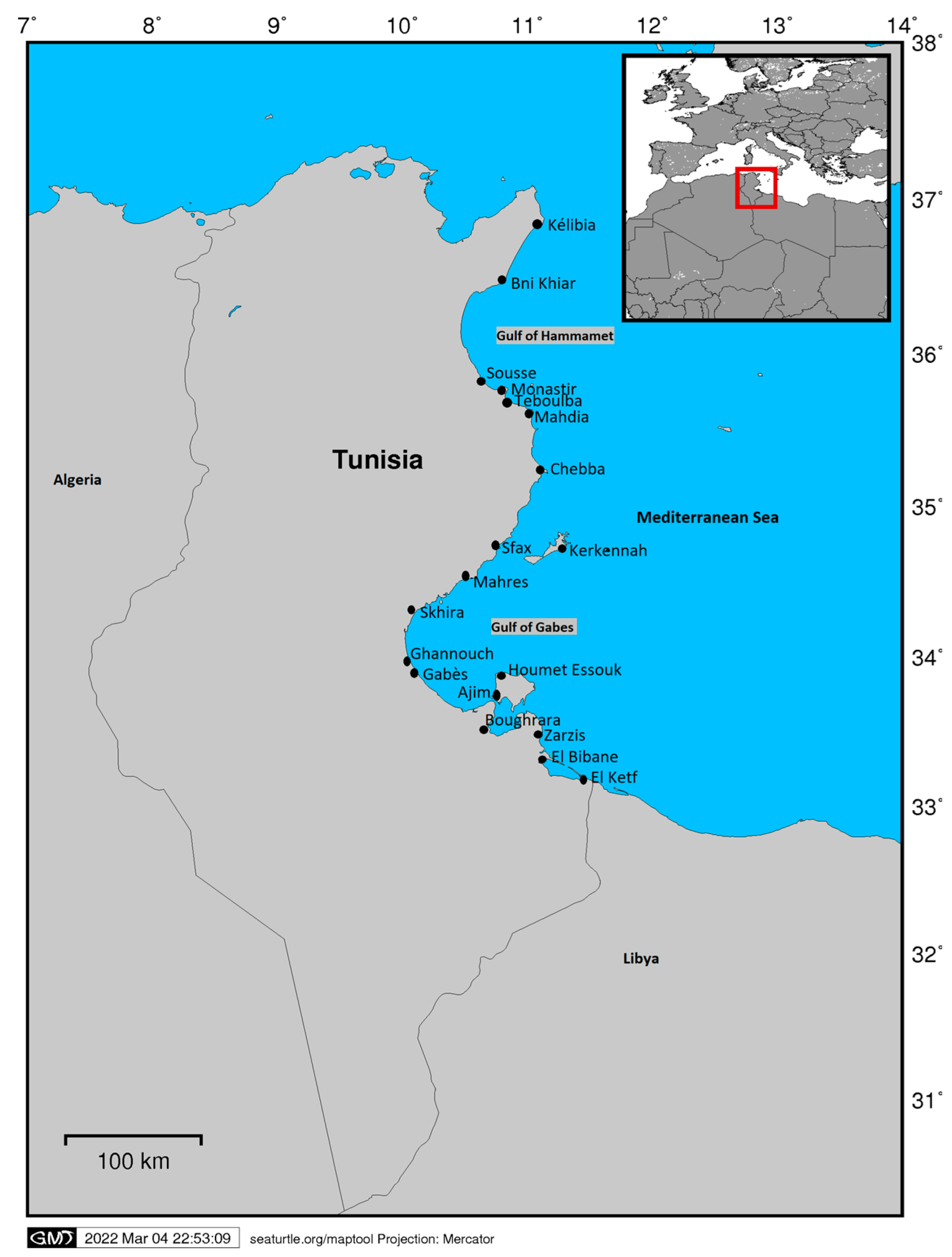
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Interviews—Questionnaires
- Characteristics of vessels involved: length, tonnage, number of fishermen, and engine power.
- Fishing gear used, including information about the seasons and gear characteristics (for nets: type of nets [correlated to mesh size], depth, distance between floats, and distance between sinkers; for longlines: longline type (benthic vs. pelagic), number of floats/km, number of sinkers/km, number of buoys/km, hook size, diameter and length of the mainline, and bait types; for trawls: otter board length, arm length, size of the cul-de-sac meshes, size of the vertical opening, length of the head rope, and length of the foot rope).
- For every gear type, the fishing effort was expressed in terms of the number of days per month at sea and the number of fishing operations per fishing trip for the last twelve months.
- For every gear type, information was given about the monthly frequency of the sea turtle bycatch and the mortality rate over the last twelve months; additional information was given about the bycatch of other animals in the same period, such as elasmobranchs, cetaceans, and birds.
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
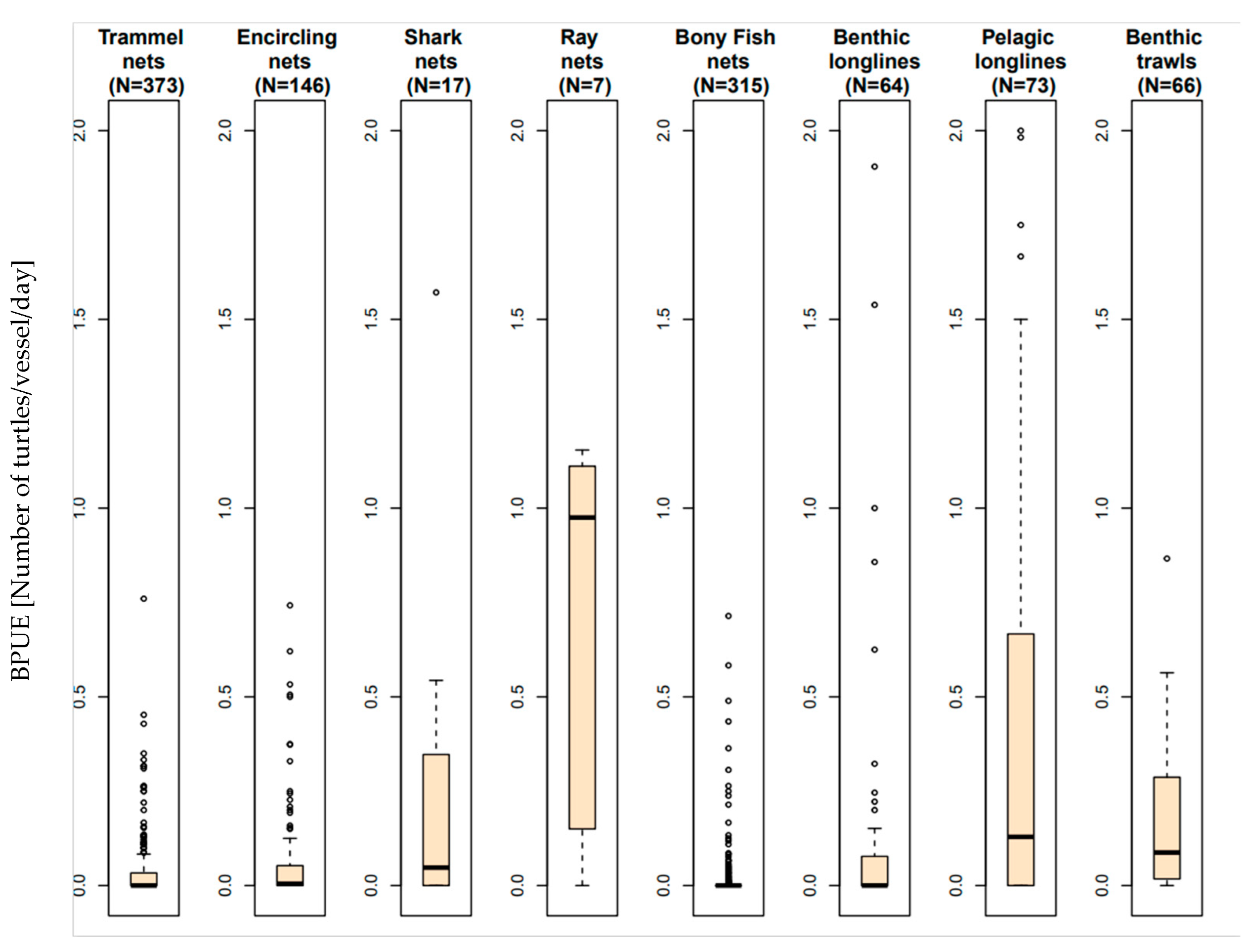
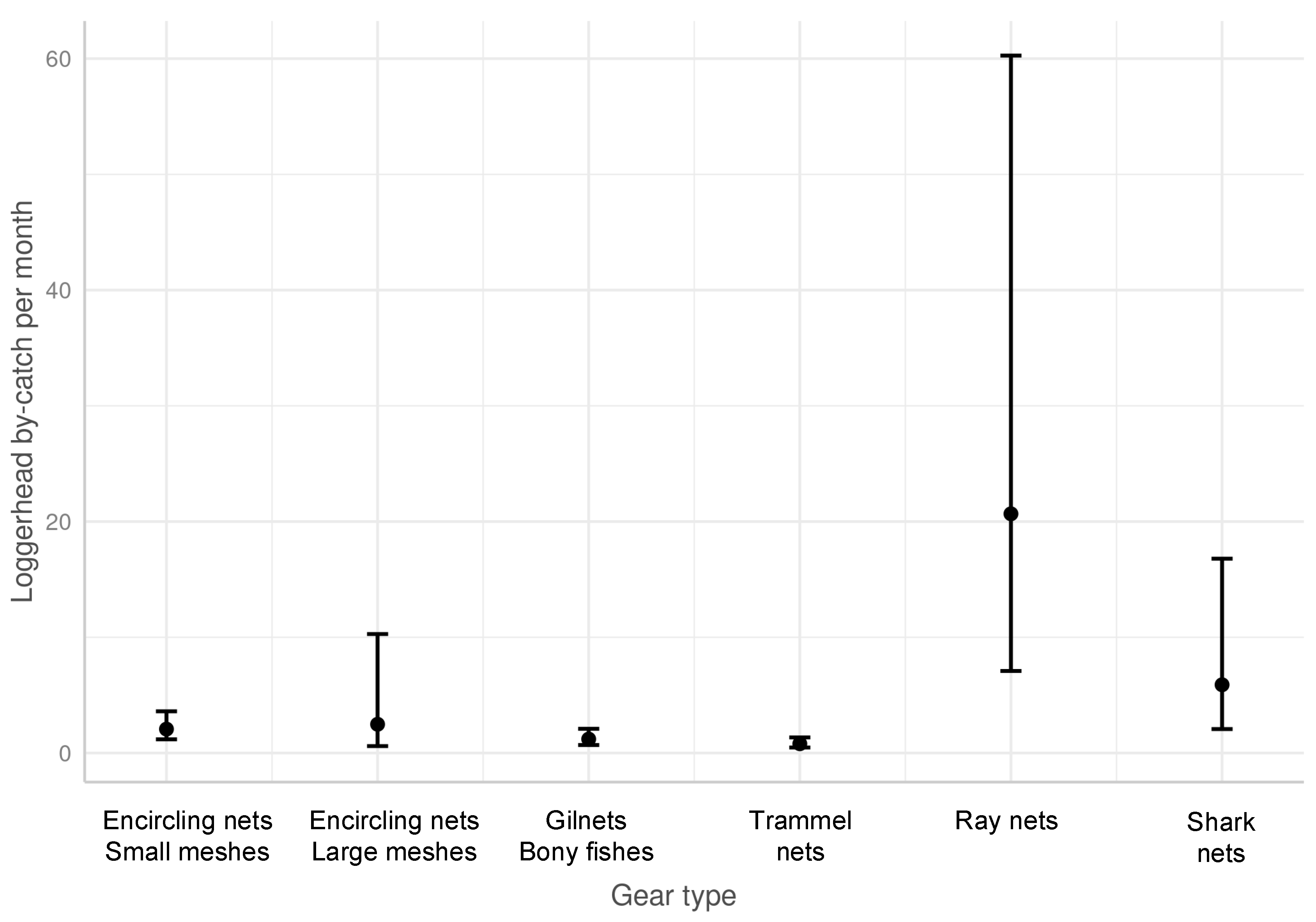
3.1. Relative Impact on Sea Turtles and BPUE According to the Fishing Gear
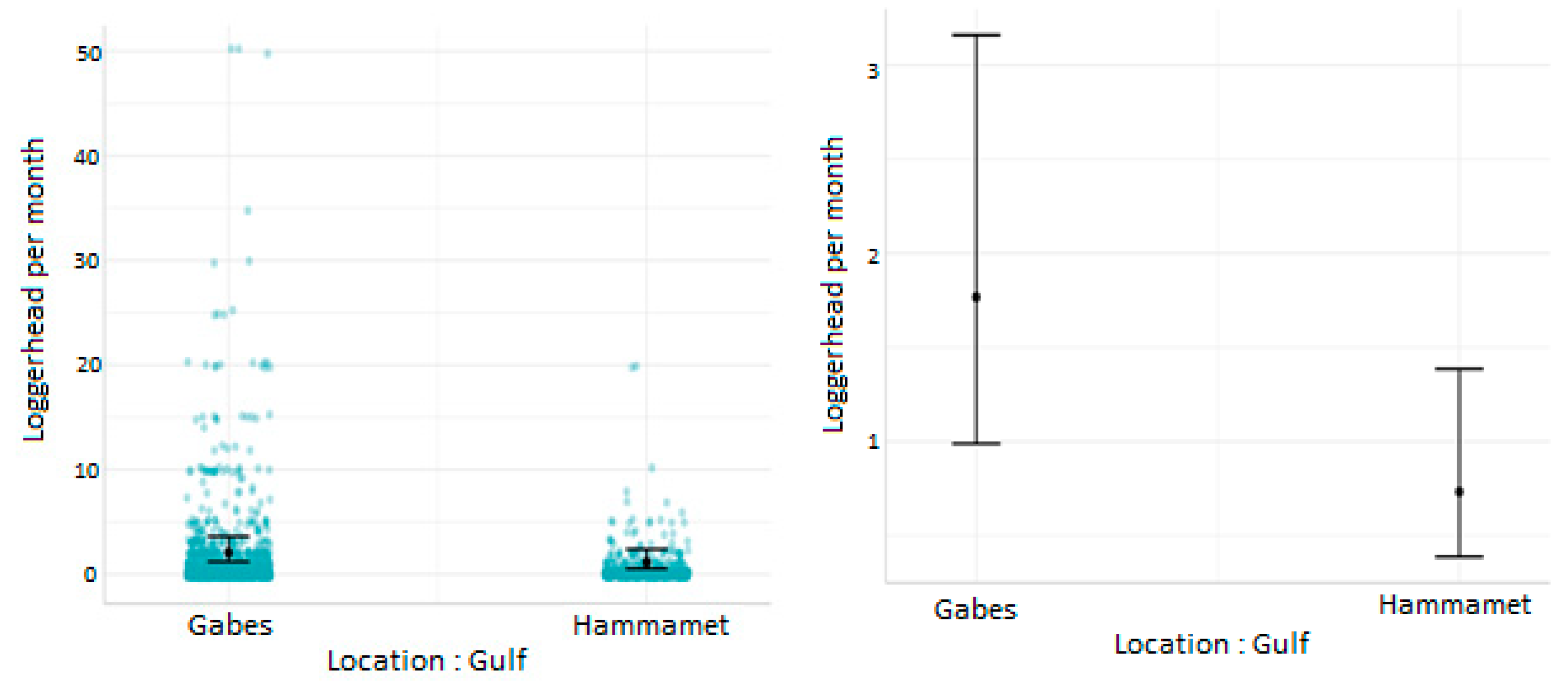
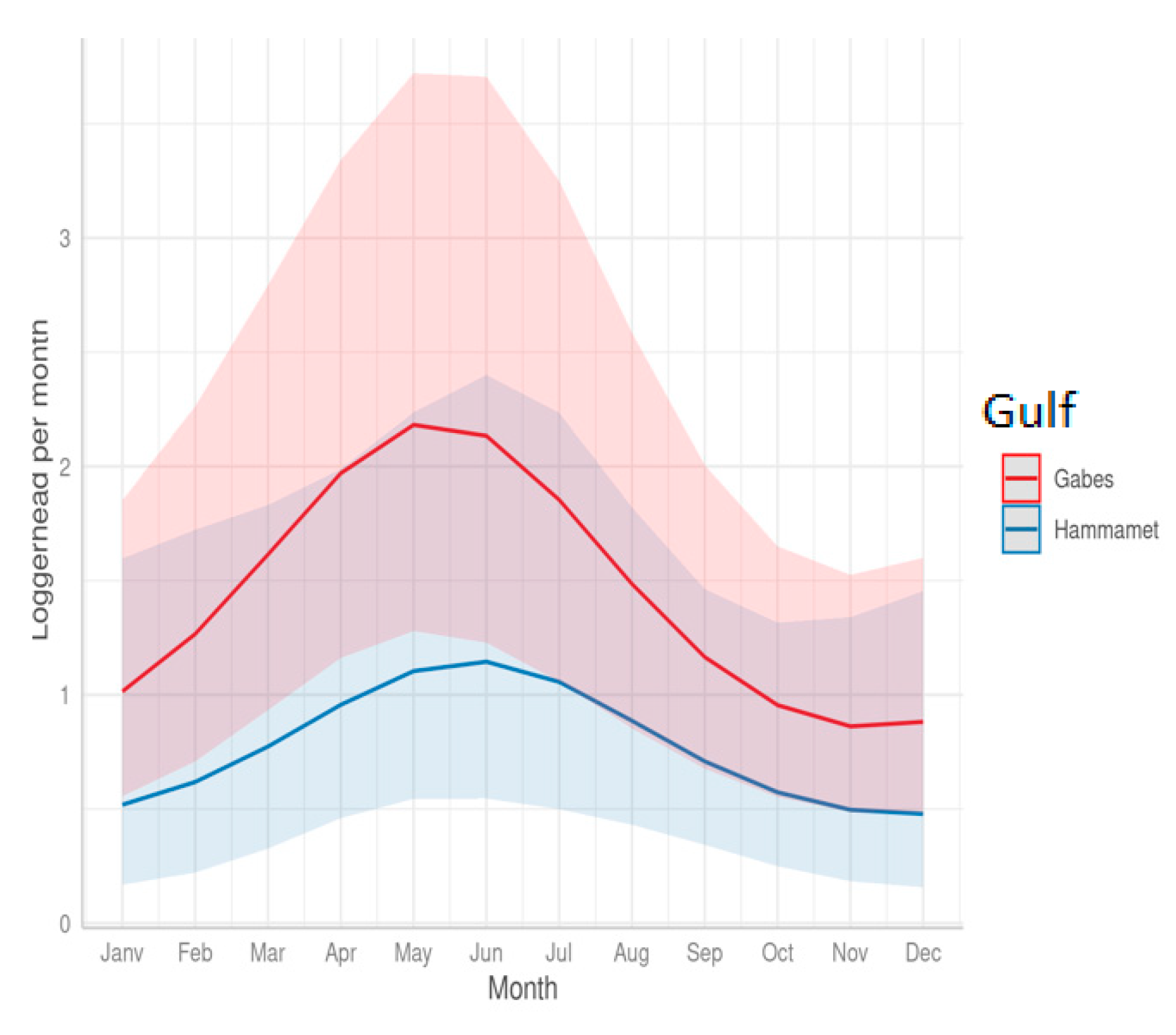
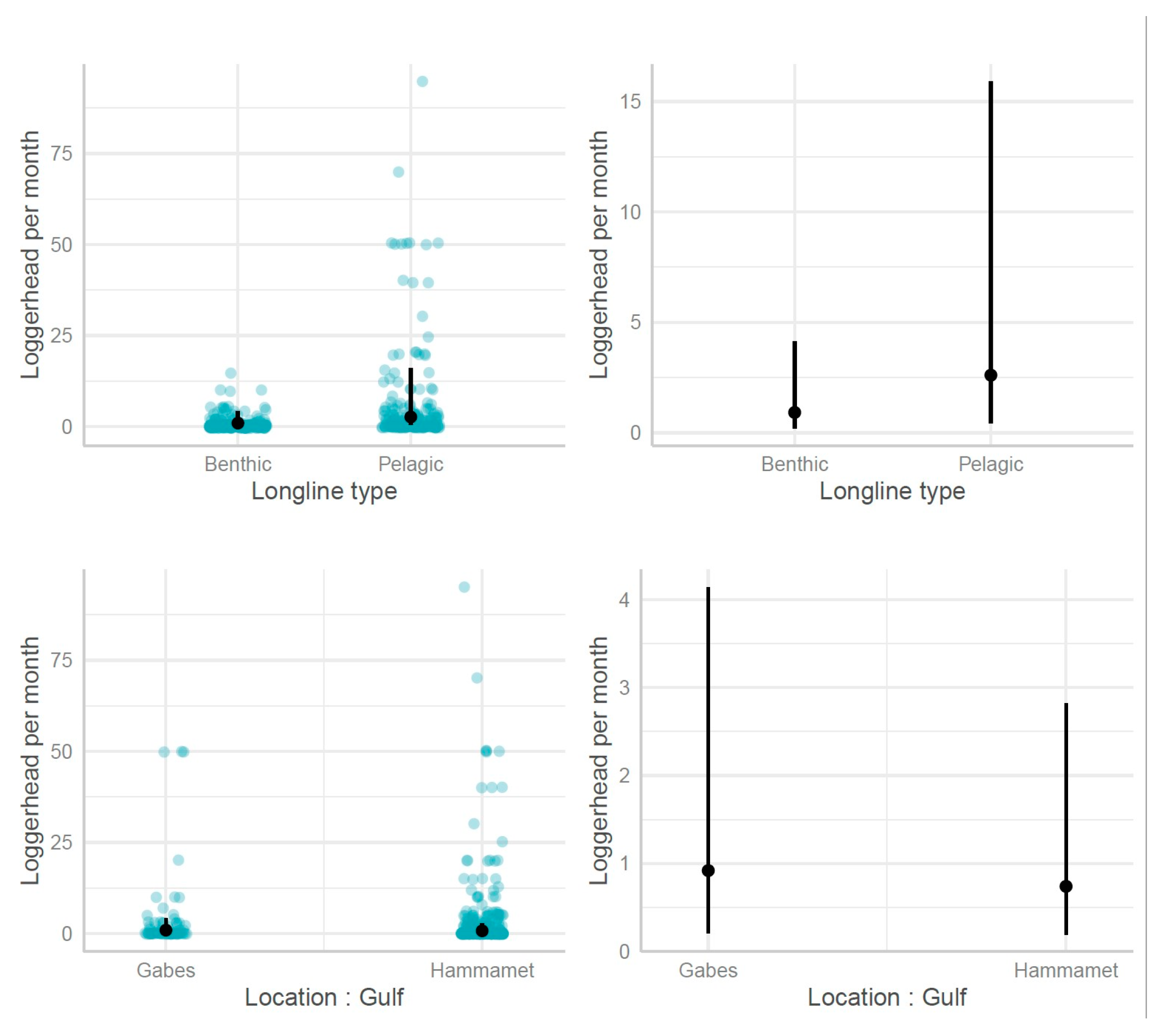
3.2. Effect of Cofactors on the Level of Sea Turtle Bycatch Risk for Each Gear Type
3.2.1. Fishing Nets
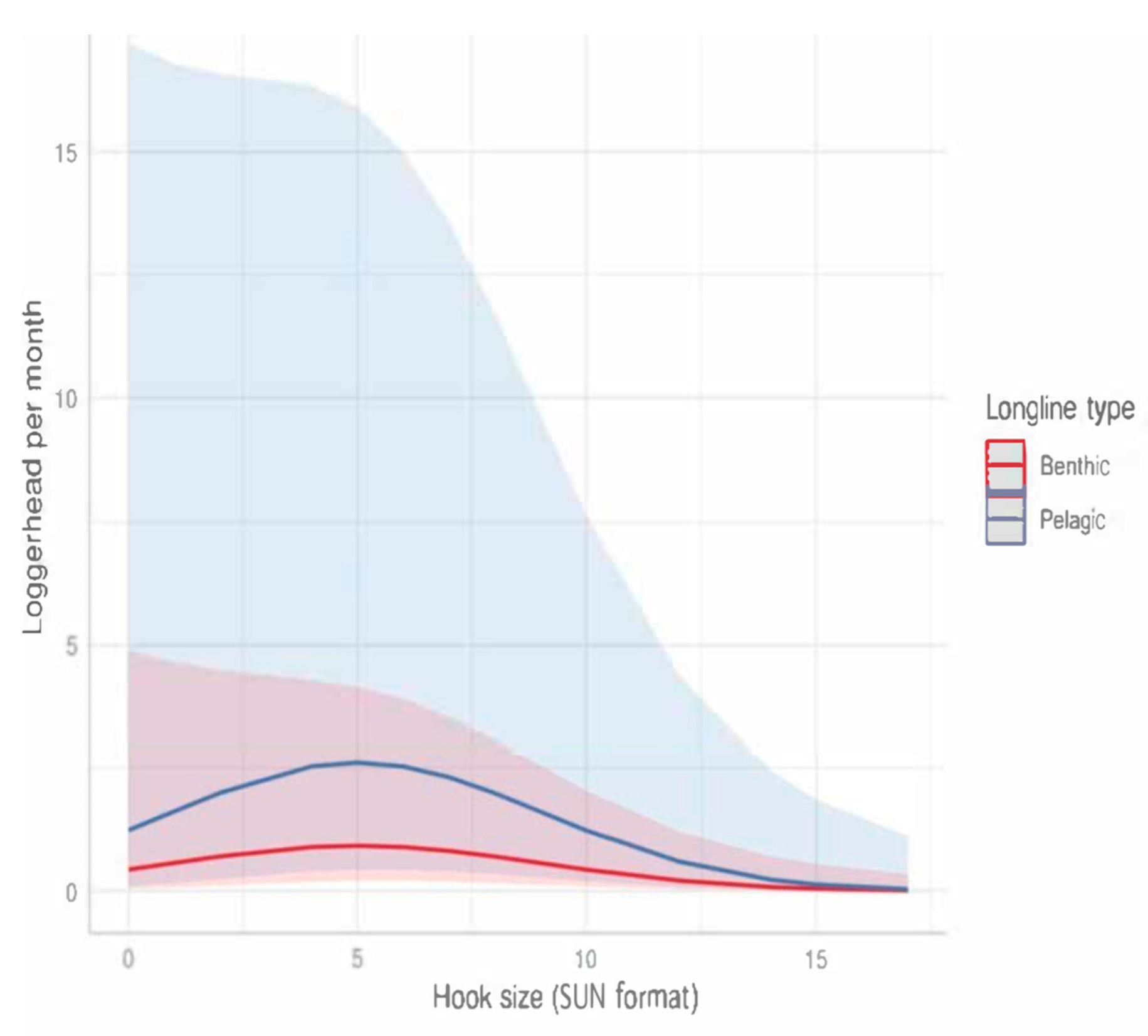
3.2.2. Longlines
3.2.3. Trawls
4. Discussion
- Interest in the interview approach for assessing fisheries bycatch
- Impact of Tunisian fisheries on sea turtles
- Mortality concurrent with bycatch
- Turtle species and size classes interacting with fisheries
- Factors influencing the bycatch risk
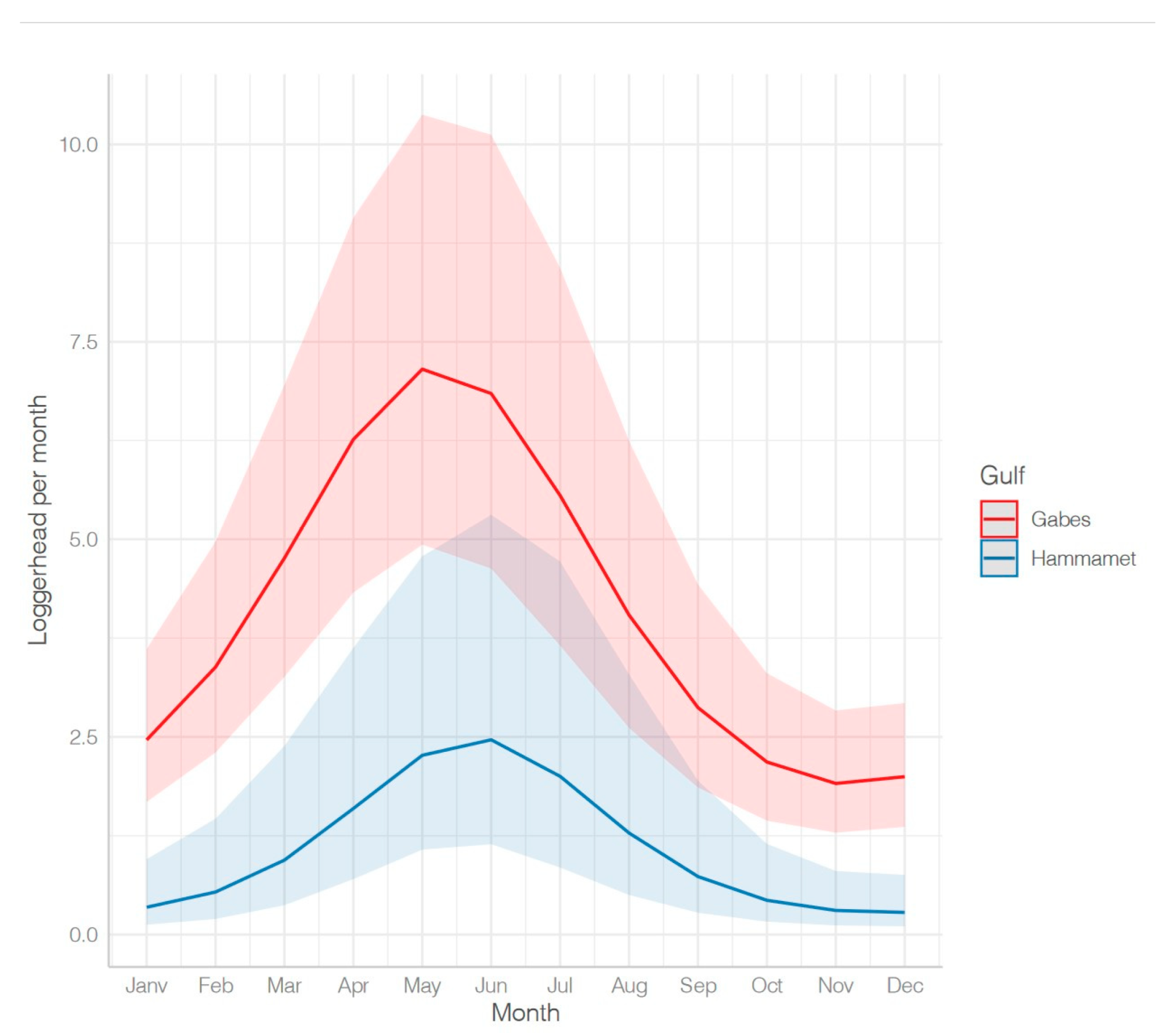
- Influence of fishing location
- Seasonal variations
- Gear characteristics influencing the sea turtle bycatch rate
- Levers of mitigation
- -
- Testing modification of the trawl vertical opening and turtle excluder devices designed for fish trawls;
- -
- Testing deterrent devices, such as green LED lights on large mesh gillnets and trammel nets.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colloca, F.; Scarcella, G.; Libralato, S. Recent Trends and Impacts of Fisheries Exploitation on Mediterranean Stocks and Ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormerod, S.J. Current issues with fish and fisheries: Editor’s overview and introduction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewison, R.L.; Crowder, L.B.; Read, A.J.; Freeman, S.A. Understanding Impacts of Fisheries Bycatch on Marine Megafauna. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.P.; Lewison, R.L.; McDonald, S.L.; McDonald, R.K.; Kot, C.Y.; Kelez, S.; Bjorkland, R.K.; Finkbeiner, E.M.; Helmbrecht, S.; Crowder, L.B. Global Patterns of Marine Turtle Bycatch. Conserv. Lett. 2010, 3, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P. Incidental Catch OfMarine Turtles in the Mediterranean Sea: Captures, Mortality, Priorities; WWF Mediterranean Marine Turtle Programme: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Casale, P.; Margaritoulis, D. Sea Turtles in the Mediterranean: Distribution, Threats and Conservation Priorities; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shoop, C.R.; Dodd, C.K. Synopsis of the Biological Data on the Loggerhead Sea Turtle Caretta caretta (Linnaeus 1758). Copeia 1989, 1989, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P.; Heppell, S. How Much Sea Turtle Bycatch Is Too Much? A Stationary Age Distribution Model for Simulating Population Abundance and Potential Biological Removal in the Mediterranean. Endanger. Species Res. 2016, 29, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P.; Broderick, A.; Camiñas, J.; Cardona, L.; Carreras, C.; Demetropoulos, A.; Fuller, W.; Godley, B.; Hochscheid, S.; Kaska, Y.; et al. Mediterranean Sea Turtles: Current Knowledge and Priorities for Conservation and Research. Endanger. Species Res. 2018, 36, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jribi, I.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouain, A. Impact of Trawl Fishery on Marine Turtles in the Gulf of Gabès. Tunisia 2007, 17, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bradai, M.N.; Bentivegna, F.; Jribi, I.; El Ouaer, A.; Maatoug, K.; El Abed, A.; Bradai, M.N.; Bentivegna, F.; Jribi, I.; El Ouaer, A.; et al. Monitoring of Loggerhead Sea Turtle Caretta caretta, in the Central Mediterranean via Satellite Telemetry. In Proceedings of the Second Mediterranean Conference on Marine Turtles, Kemer, Turkey, 4–7 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Casale, P.; Laurent, L.; De Metrio, G. Incidental Capture of Marine Turtles by the Italian Trawl Fishery in the North Adriatic Sea. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 119, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez de Segura, A.; Tomás, J.; Pedraza, S.N.; Crespo, E.A.; Raga, J.A. Abundance and Distribution of the Endangered Loggerhead Turtle in Spanish Mediterranean Waters and the Conservation Implications. Anim. Conserv. 2006, 9, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritoulis, D.; Argano, R.; Baran, I.; Bentivegna, F.; Bradai, M.; Camiñas, J.; Casale, P.; Metrio, G.; Demetropoulos, A.; Gerosa, G. Loggerhead Turtles in the Mediterranean Sea: Present Knowledge and Conservation Perspectives. In Loggerhead Sea Turtles (editors: AB Bolten, BE Witherington); Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, B.P.; Heppell, S.S.; Lewison, R.L.; Kelez, S.; Crowder, L.B. Impacts of Fisheries Bycatch on Loggerhead Turtles Worldwide Inferred from Reproductive Value Analyses. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, L.; Antonello, S. An Overview of Loggerhead Sea Turtle (Caretta caretta) Bycatch and Technical Mitigation Measures in the Mediterranean Sea. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2010, 20, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P. Sea Turtle By-catch in the Mediterranean. Fish Fish. 2011, 12, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: Https://Dx.Doi.Org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T3897A119333622.En (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Jribi, I.; Echwikhi, K.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouain, A. Incidental Capture of Sea Turtles by Longlines in the Gulf of Gabès (South Tunisia): A Comparative Study between Bottom and Surface Longlines. Sci. Mar. 2008, 72, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echwikhi, K.; Imed, J.; Bradai, M.; Bouain, A. Effect of Type of Bait on Pelagic Longline Fishery-Loggerhead Interactions in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echwikhi, K.; Imed, J.; Bradai, M.; Bouain, A. Interactions of loggerhead turtle with bottom longline fishery in the Gulf of Gabés, Tunisia. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradai, M.N. Les Captures Accidentelles de Caretta caretta au Chalut Benthique Dans Le Golfe de Gabès. Rapp. Comm. Int. Pour L’exploration Sci. Mer Médit. 1992, 33, 285. [Google Scholar]
- Bradai, M.N. La Tortue Marine Caretta caretta Dans Le Sud-Est de La Tunisie (Peche Accidentelle—Utilisation—Législation). MAP, RAC/SPA, UNEP: Athens, Greece, 1993; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Echwikhi, K.; Jribi, I.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouain, A. Gillnet Fishery-Loggerhead Turtle Interactions in the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Herpetol. J. 2010, 20, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Echwikhi, K.; Imed, J.; Bradai, M.; Bouain, A. Overview of Loggerhead Turtles Coastal Nets Interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2012, 22, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderburn, R.W.M. Generalized Linear Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1989; ISBN 978-0412317606. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.M.; Hastie, T.J.; Hastie, T. Statistical Models in S; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1992; p. 608. ISBN 978-0-534-16764-6. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-387-95457-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jackman, S. Pscl: Classes and Methods for R Developed in the Political Science Computational Laboratory, Stanford University; Department of Political Science, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, R Package Version 0.95; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H.A. New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Monitoring the Incidental Catch of Vulnerable Species in Mediterranean and Black Sea Fisheries: Methodology for Data Collection; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper: Roma, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Echwikhi, K. Loggerhead Turtle Bycatch in the Gulf of Gabès, Tunisia: An Overview. MTN 2011, 131, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Nada, M.; Casale, P. Sea Turtle Bycatch and Consumption in Egypt Threatens Mediterranean Turtle Populations. Oryx 2011, 45, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godley, B.J.; Gücü, A.C.; Broderick, A.C.; Furness, R.W.; Solomon, S.E. Interaction between Marine Turtles and Artisanal Fisheries in the Eastern Mediterranean: A Probable Cause for Concern? Zool. Middle East 1998, 16, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiè, G. Incidental Capture of Caretta caretta in Trammel Nets off the Western Coast of Sardinia (Italy): Statistical Models of Capture Abundance and Immediate Survival. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2011, 21, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, C.; Cardona, L.; Aguilar, A. Incidental catch of the loggerhead turtle Caretta caretta off the Balearic Islands (western Mediterranean). Biol. Conserv. 2004, 117, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, A.; Vasapollo, C.; Virgili, M. An Interview-Based Approach to Assess Sea Turtle Bycatch in Italian Waters. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerosa, G.; Casale, P. Interaction of Marine Turtles with Fisheries in the Mediterranean; UNEP/MAP, RAC/SPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 1999; 59p. [Google Scholar]
- Bradai, M.N.; Jribi, I. Tunisia. In Sea Turtles in the Mediterranean: Distribution, Threats and Conservation Priorities; Casale, P., Margaritoulis, D., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; 294 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Crouse, D.T.; Crowder, L.B.; Caswell, H. A stage based population model for loggerhead sea turtles and implications for conservation. Ecology 1987, 68, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, L.; Clobert, J.; Lescure, J. The demographic modeling of the Mediterranean loggerhead sea turtle population: First results. Rapp. Comm. Int. Pour I ‘Explor. Sci. Mer Mediterr. 1992, 33, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Crowder, L.B.; Deborah, T.C.; Heppell, S.S.; Martin, T.H. Predicting the Impact of Turtle Excluder Devices on Loggerhead Sea Turtle Populations. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppel, S.S.; Limpus, C.J.; Crouse, D.T.; Frazer, N.B.; Crowder, L.B. Population Model Analysis for the Loggerhead Sea Turtle, Caretta Caretta, in Queensland. Wildl. Res 1996, 23, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argano, R.; Basso, R.; Cocco, M.; Gerosa, G. Nuovi Dati Sugli Spostamenti Di Tartaruga Marina Comune (Caretta caretta) in Mediterraneo. Boll. Dei Musei Degli Ist. Biol. Dell’Università Genova 1992, 56–57, 137–164. [Google Scholar]
- Margaritoulis, D. Post-Nesting Movement of Loggerhead Sea Turtles Tagged in Greece. Rapp. Comm. Int. Pour L’exploration Sci. Mer Méditerranée 1988, 31, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, L.; Nouira, S.; Jeudy De Grissac, A.; Bradai, M.N. Les Tortues Marines de Tunisie: Premières Données. Bull. Soc. Herpétol. Fr. 1990, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, L.; Lescure, J. L’hivernage Des Tortues Caouannes Caretta caretta (L.) Dans Le Sud Tunisien. Rev. Ecol. Terre Vie 1994, 49, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jribi, I.; Bradai, M.N.; Bouain, A. Etude de l’Interaction Tortue Marine Caretta Caretta. Chalut Bentique Dans Le Golfe de Gabés (Tunisie). Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Médit 2004, 37, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Zbinden, J.A.; Aebischer, A.; Margaritoulis, D.; Arlettaz, R. Important Areas at Sea for Adult Loggerhead Sea Turtles in the Mediterranean Sea: Satellite Tracking Corroborates Findings from Potentially Biased Sources. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, S. Hare, S. Turtles Caught Incidental to Demersal Finfish Fishery in Oman. MTN 1991, 53, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Caillouet, C.W.; Duronslet, M.J.; Landry, A.M.; Revera, D.B.; Shaver, D.J.; Stanley, K.M.; Heinly, R.W.; Stabenau, E.K. Sea Turtle Strandings and Shrimp Fishing Effort in the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Bull 1991, 89, 712–718. [Google Scholar]
- Bradai, M.N. Bradai, M.N. Observations Sur La Tortue Marine Caretta caretta En Tunisie. Actes Des Premiéres Journées Tunisiennes Des Sciences de La Mer, Kerkennah. Bull. Inst. Nat. Sci. Techn. Mer 1994, 3, 2–34. [Google Scholar]
- Epperly, S.P.; Braun, J.; Chester, A.J.; Cross, F.A.; Merriner, J.V.; Tester, P.A. Winter Distribution of Sea Turtles in the Vicinity of Cape Hatteras and Their Interactions with the Summer Flounder Trawl Fishery. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1995, 56, 547–568. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, A.C.; Coyne, M.S.; Fuller, W.J.; Glen, F.; Godley, B.J. Fidelity and Over-Wintering of Sea Turtles. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci 2007, 274, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.; Gearhart, J.; Price, B.; Eckert, S.; Milliken, H.; Wang, J.; Swimmer, Y.; Shiode, D.; Abe, O.; Peckham, S.H.; et al. Mitigating Sea Turtle Bycatch in Coastal Passive Net Fisheries; International Union for the Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2009; ISBN 978-2-8317-1128-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, E.; Bianchi, G. Guidelines to Reduce Sea Turtle Mortality in Fishing Operations; FAO Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries: Roma, Italy, 2010; ISBN 978-92-106226-5. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, A.; Louvinguila, H.D.; Breheret, N.; Monsinjon, J.; Charra, M.; Protat, E.; Roche, H.; Ngokaka, C.; Girondot, M. Les engins et techniques de pêche utilisés dans la baie de Loango, République du Congo, et leurs incidences sur les prises accessoires. Cybium 2014, 38, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.W.; Epperly, S.P.; Shah, A.K.; Foster, D.G. Fishing Methods to Reduce Sea Turtle Mortality Associated with Pelagic Longlines. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Kiyota, M.; Okamura, H. Effect of Bait Species and Color on Sea Turtle Bycatch and Fish Catch in a Pelagic Longline Fishery. Fish. Res. 2009, 97, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, M.C.; Solomon, J.N.; Blank, S.G. Measuring and Monitoring Illegal Use of Natural Resources. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jančič, M.; Holcer, D.; Casale, P.; Lazar, B. Evaluating Post-Release Survival of Loggerhead Sea Turtles Bycaught in Bottom Trawls. Assessing the Effectiveness of a Low-Cost Conservation Method. In Proceedings of the 7th Sea Turtle Med Conference, Tetouan, Marocco, 18–22 October 2022. [Google Scholar]

| N_Loggerhead_Month | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Incidence Rate Ratios | CI | p |
| Count Model | |||
| (Intercept) | 0.04 | 0.00–0.55 | 0.016 |
| Type of nets [trammel nets] | 0.39 | 0.22–0.70 | 0.002 |
| Type of nets [Garrasia] | 10.01 | 3.00–33.43 | <0.001 |
| Gulf [Gabes]*cos(PseudoFourier) | 0.64 | 0.49–0.85 | 0.002 |
| Observations | 3795 | ||
| Dependent Variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Incidence Rate Ratios | CI | p |
| Count Model | |||
| (Intercept) | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | <0.001 |
| Longline type [pelagic] | 2.84 | 1.44–5.59 | 0.003 |
| Hook size [1st degree] | - | 0.00–0.01 | 0.008 |
| Hook size [2nd degree] | - | 0.00–0.78 | 0.044 |
| Gulf [Hammamet]*cos(PseudoFourier) | 0.39 | 0.27–0.57 | <0.001 |
| Gulf [Hammamet]*sin(PseudoFourier) | 0.56 | 0.40–0.78 | 0.001 |
| Observations | 429 | ||
| Dependent Variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Incidence Rate Ratios | CI | p |
| Count Model | |||
| (Intercept) | 0.01 | 0.00–0.09 | <0.001 |
| Gulf [Hammamet] | 0.22 | 0.11–0.45 | <0.001 |
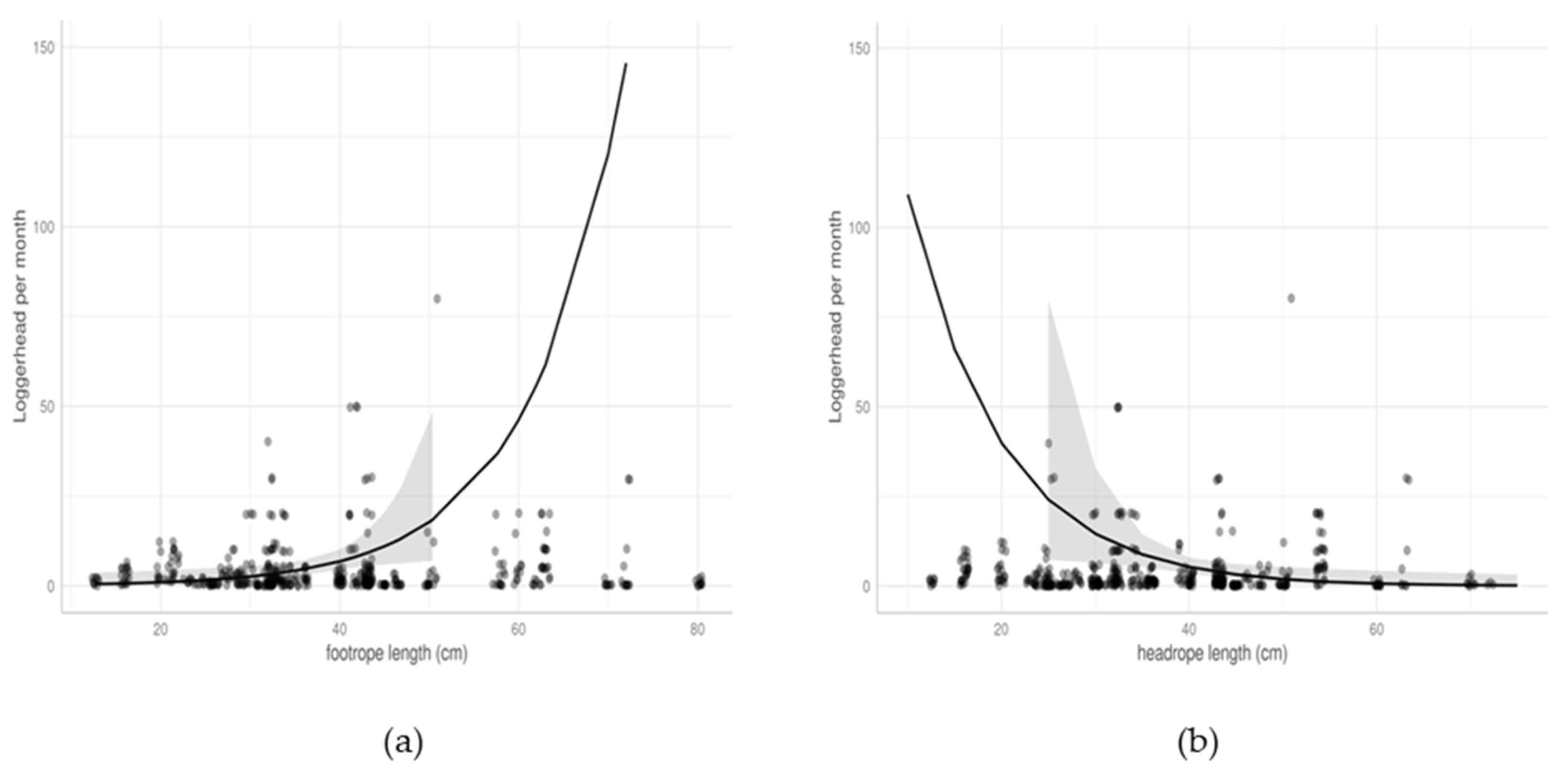
| Length of footrope | 1.10 | 1.02–1.19 | 0.014 |
| Length of headrope | 0.90 | 0.83–0.98 | 0.017 |
| Gulf [Hammamet] * cos(PseudoFourier) | 0.34 | 0.18–0.62 | <0.001 |
| Gulf [Gabes] * sin(PseudoFourier) | 1.29 | 1.05–1.58 | 0.014 |
| Observations | 637 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Louhichi, M.; Girard, A.; Jribi, I. Fishermen Interviews: A Cost-Effective Tool for Evaluating the Impact of Fisheries on Vulnerable Sea Turtles in Tunisia and Identifying Levers of Mitigation. Animals 2023, 13, 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091535
Louhichi M, Girard A, Jribi I. Fishermen Interviews: A Cost-Effective Tool for Evaluating the Impact of Fisheries on Vulnerable Sea Turtles in Tunisia and Identifying Levers of Mitigation. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091535
Chicago/Turabian StyleLouhichi, Maissa, Alexandre Girard, and Imed Jribi. 2023. "Fishermen Interviews: A Cost-Effective Tool for Evaluating the Impact of Fisheries on Vulnerable Sea Turtles in Tunisia and Identifying Levers of Mitigation" Animals 13, no. 9: 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091535
APA StyleLouhichi, M., Girard, A., & Jribi, I. (2023). Fishermen Interviews: A Cost-Effective Tool for Evaluating the Impact of Fisheries on Vulnerable Sea Turtles in Tunisia and Identifying Levers of Mitigation. Animals, 13(9), 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091535








