Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis: New Genetic Signals from the Past of a Species on the Brink of Extinction
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic and Phylogeographic Analyses
2.4. Estimation of the Divergence Time Analyses
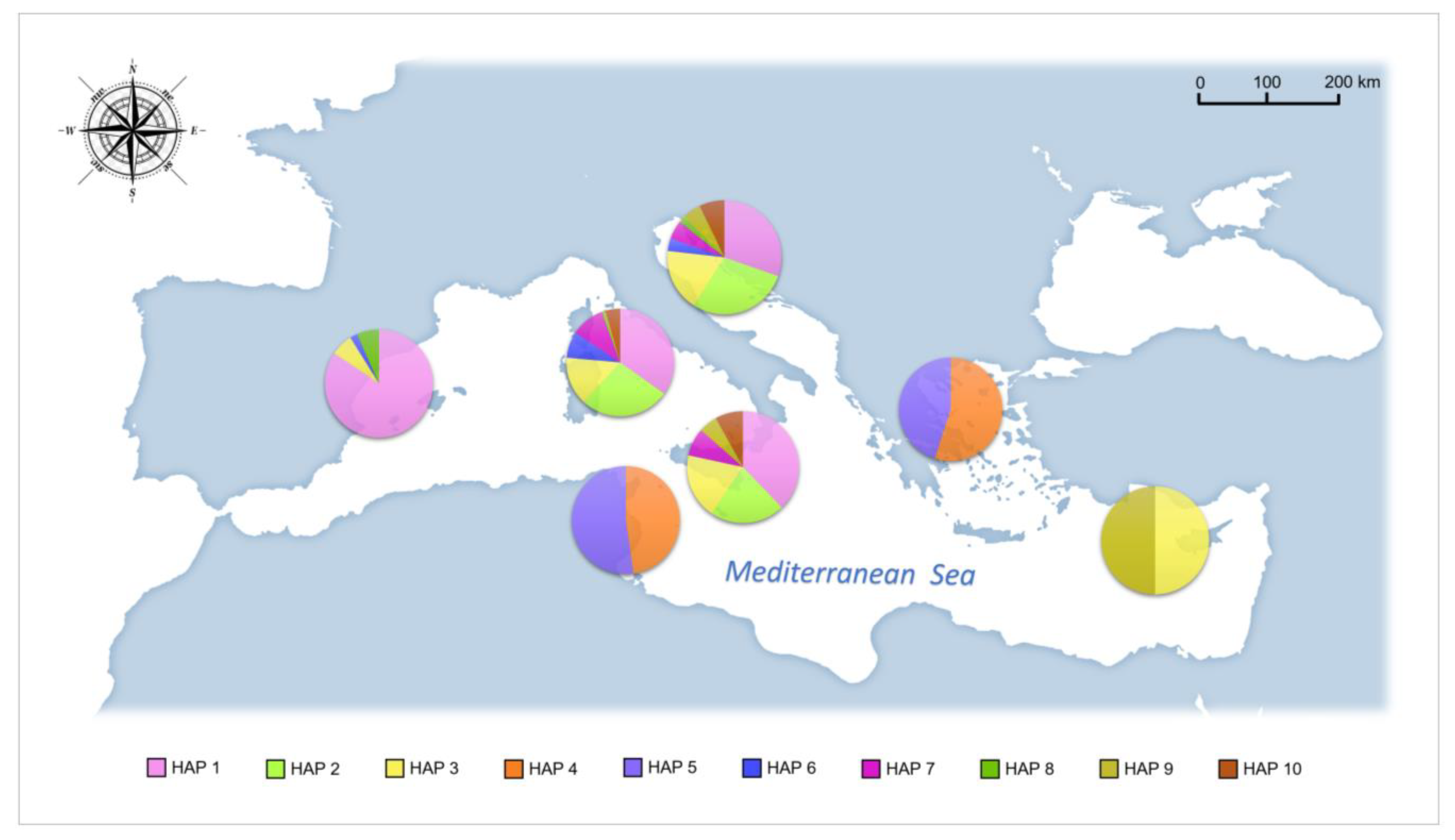
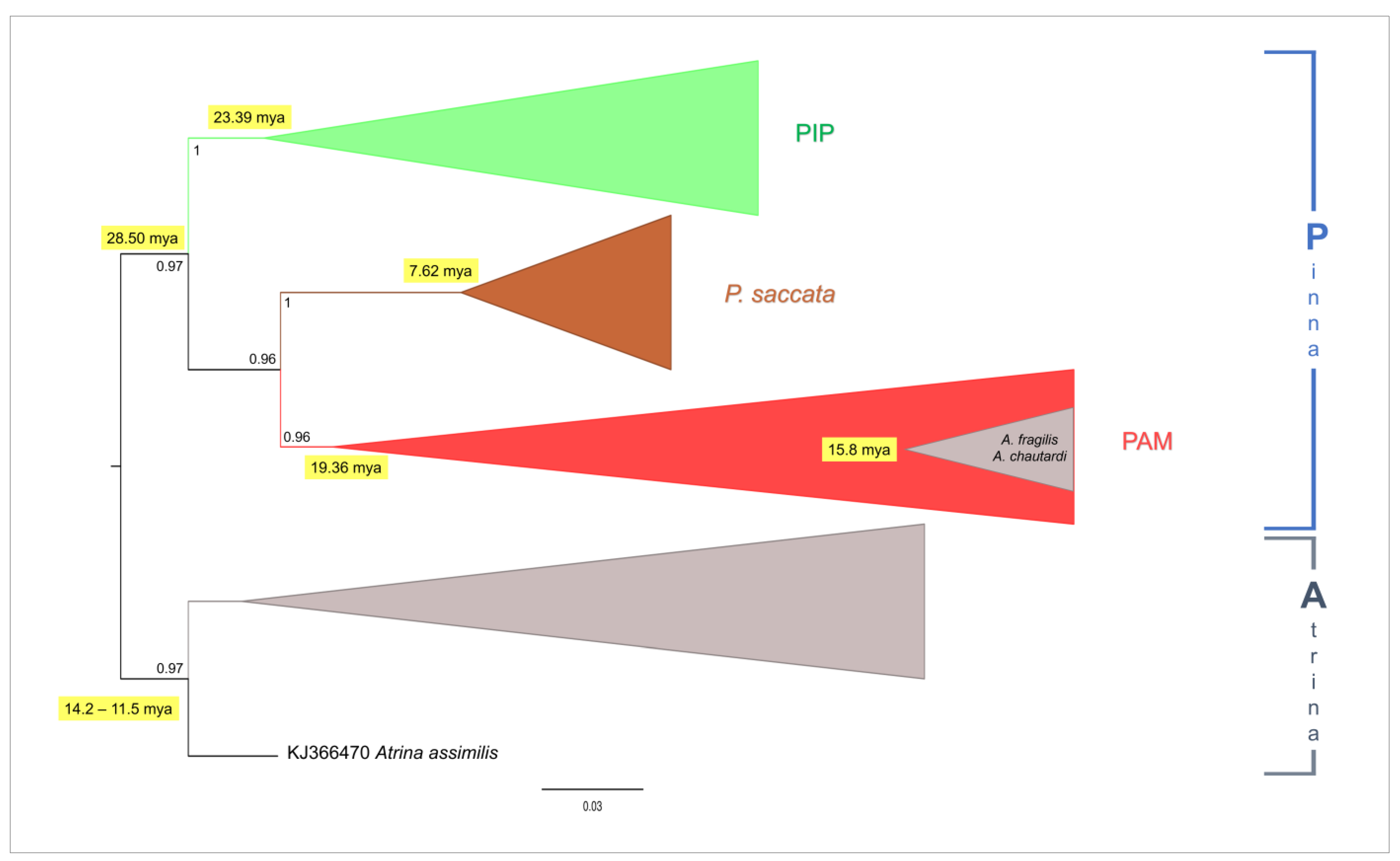
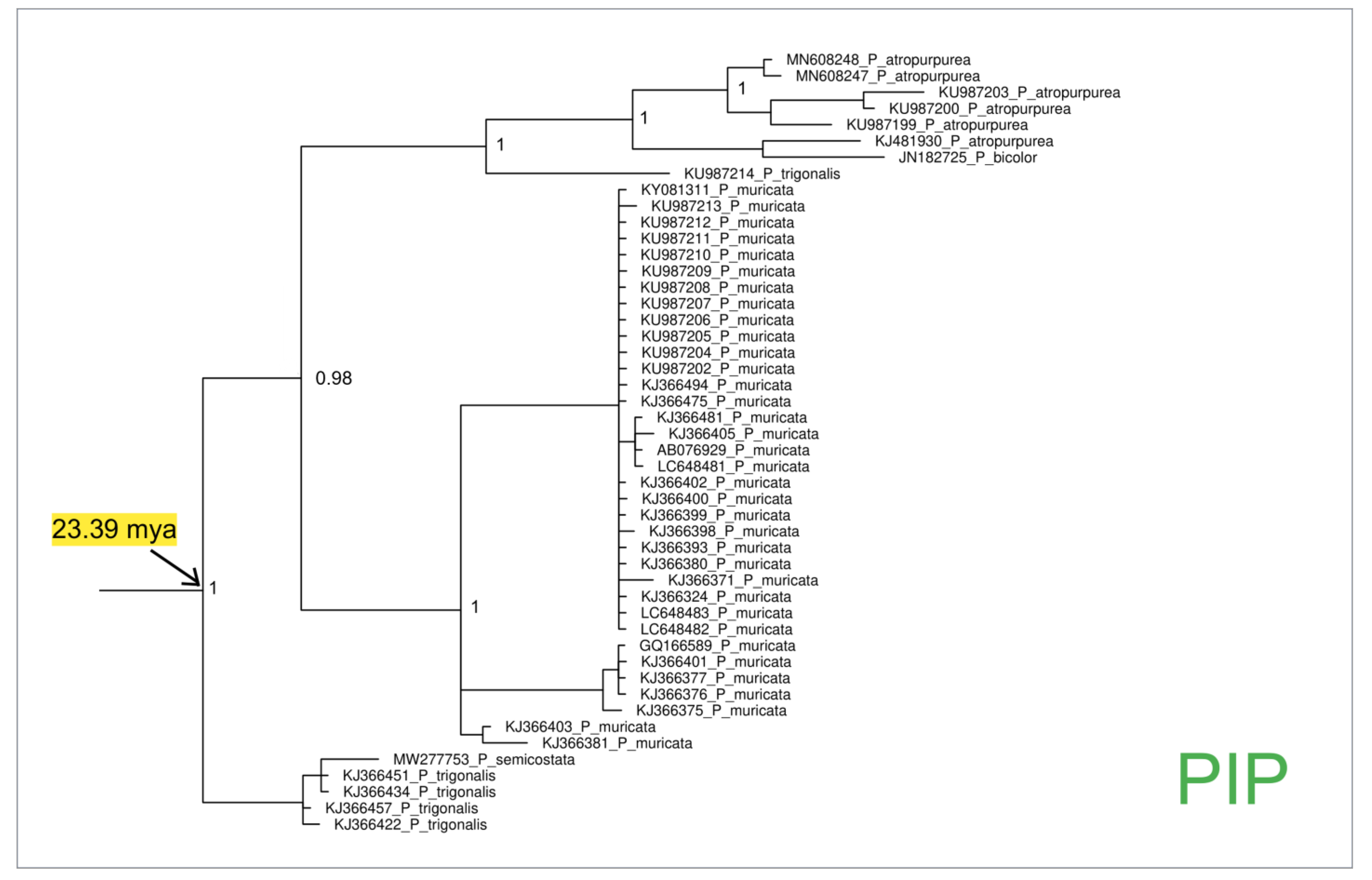
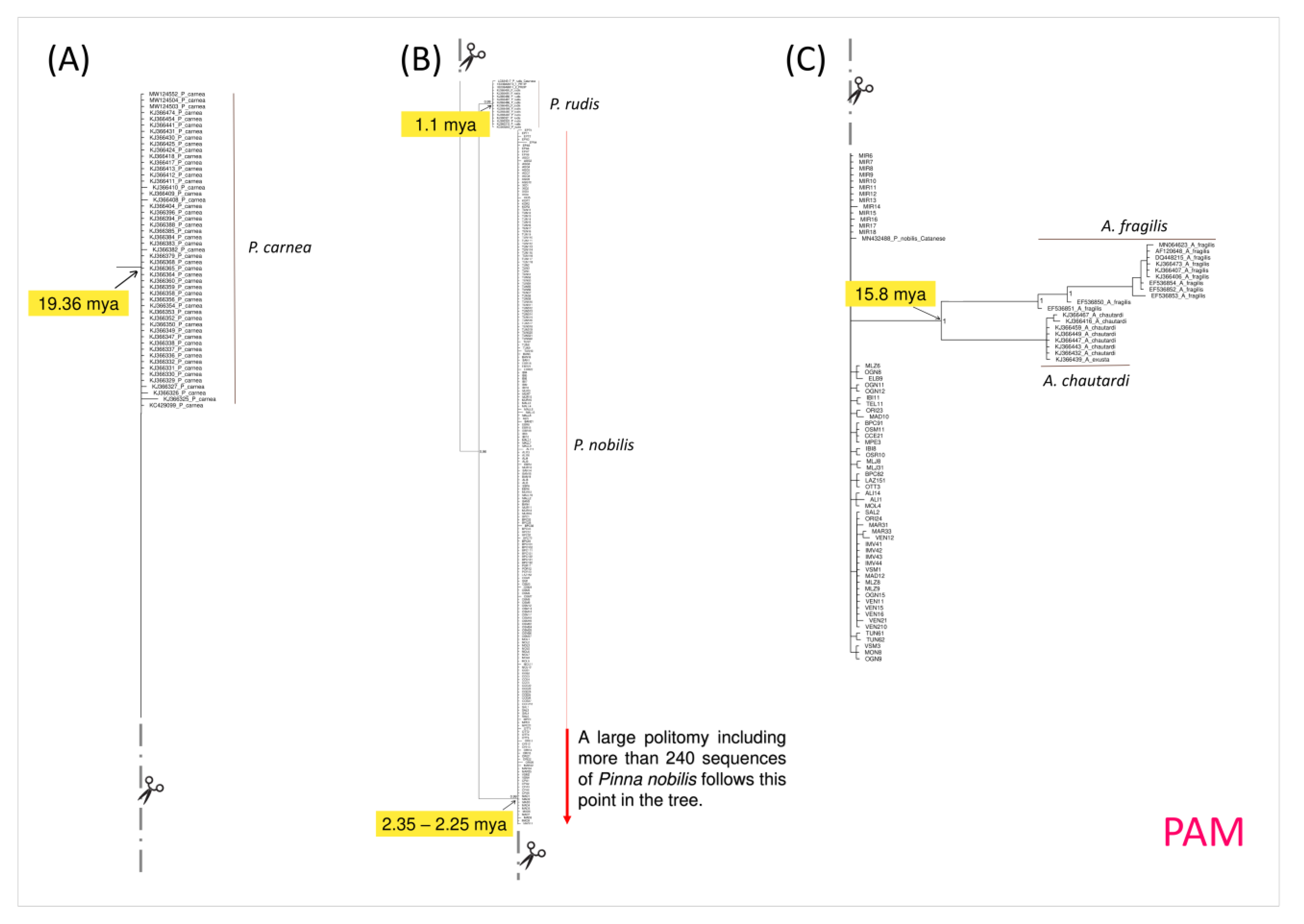
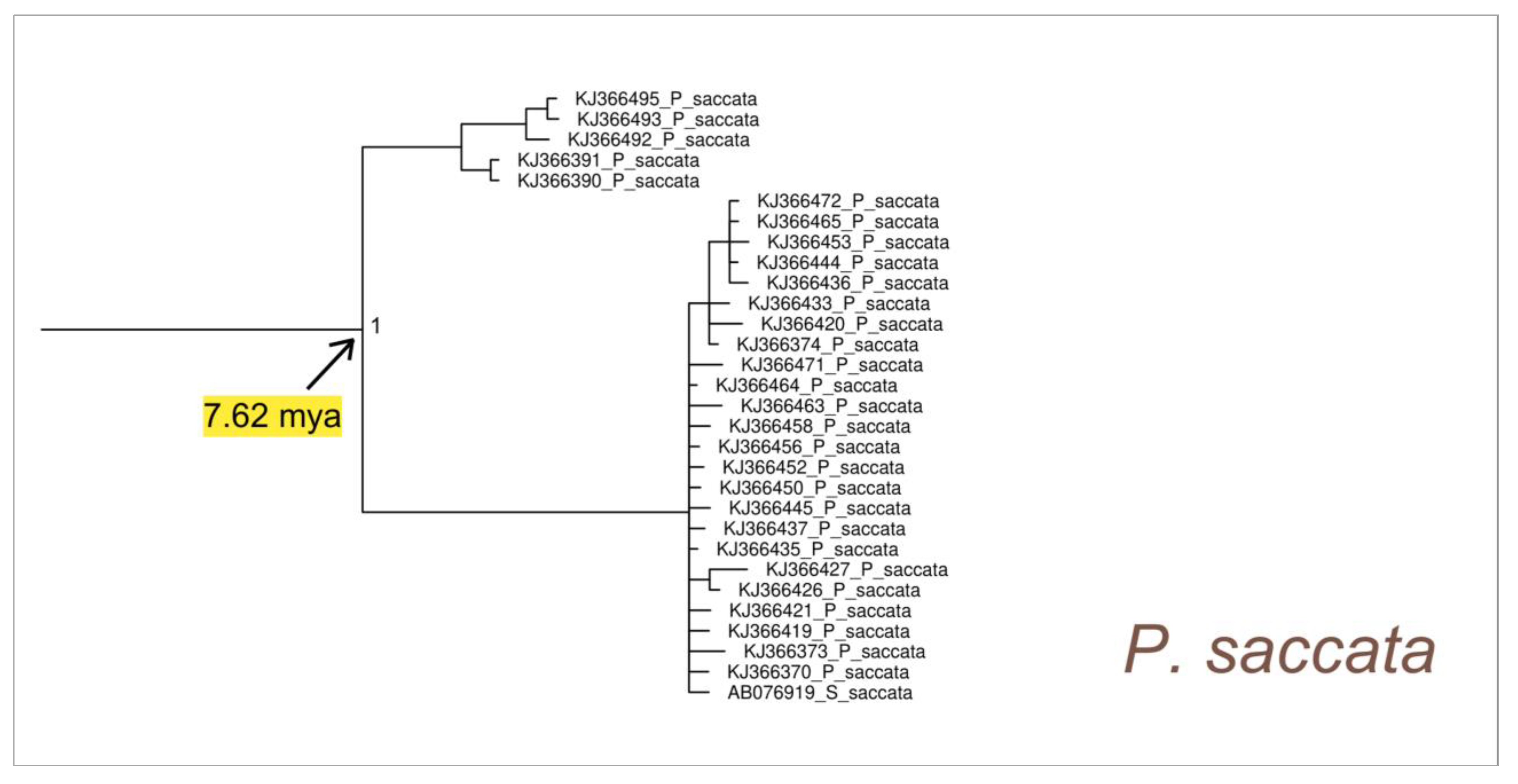
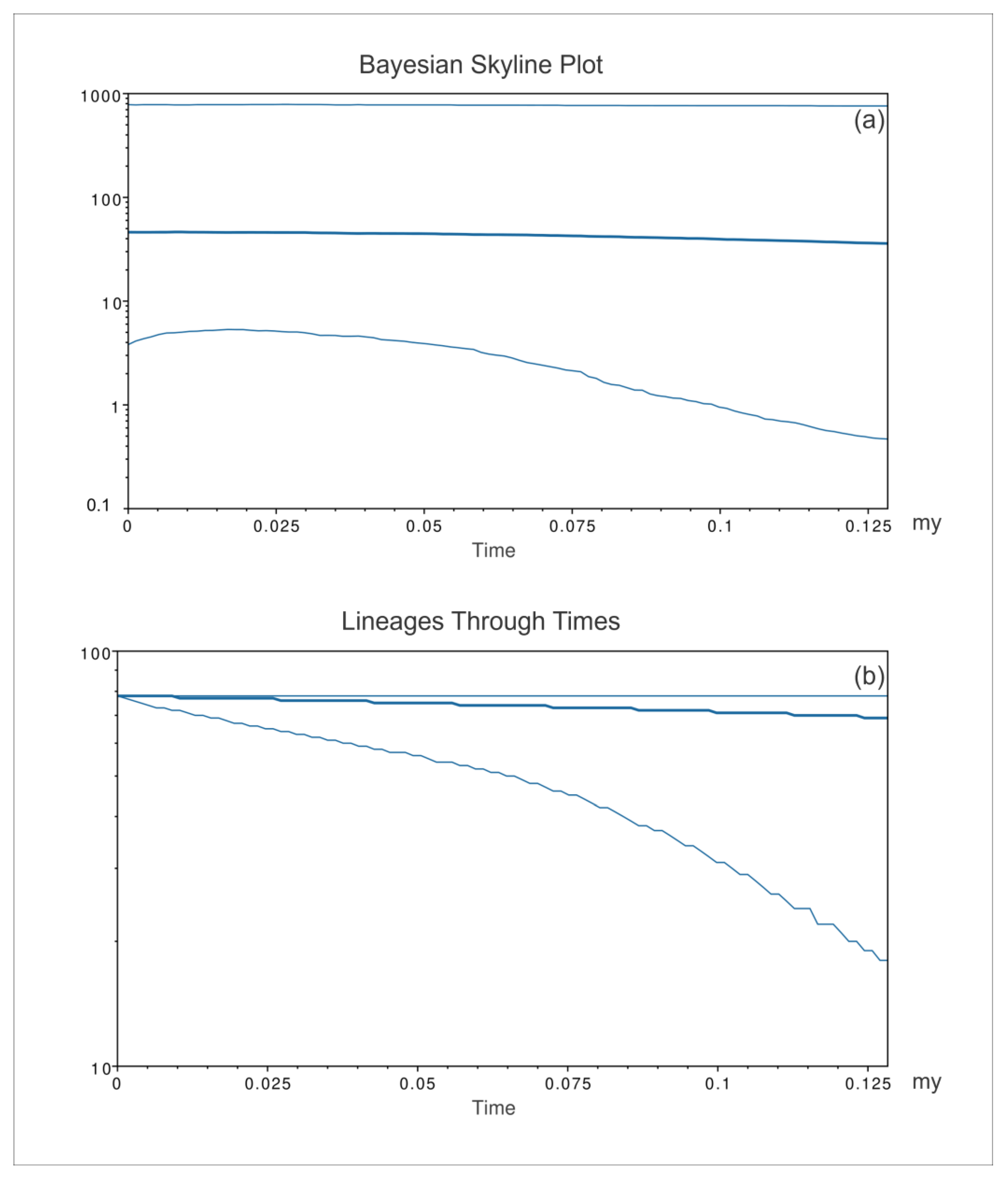
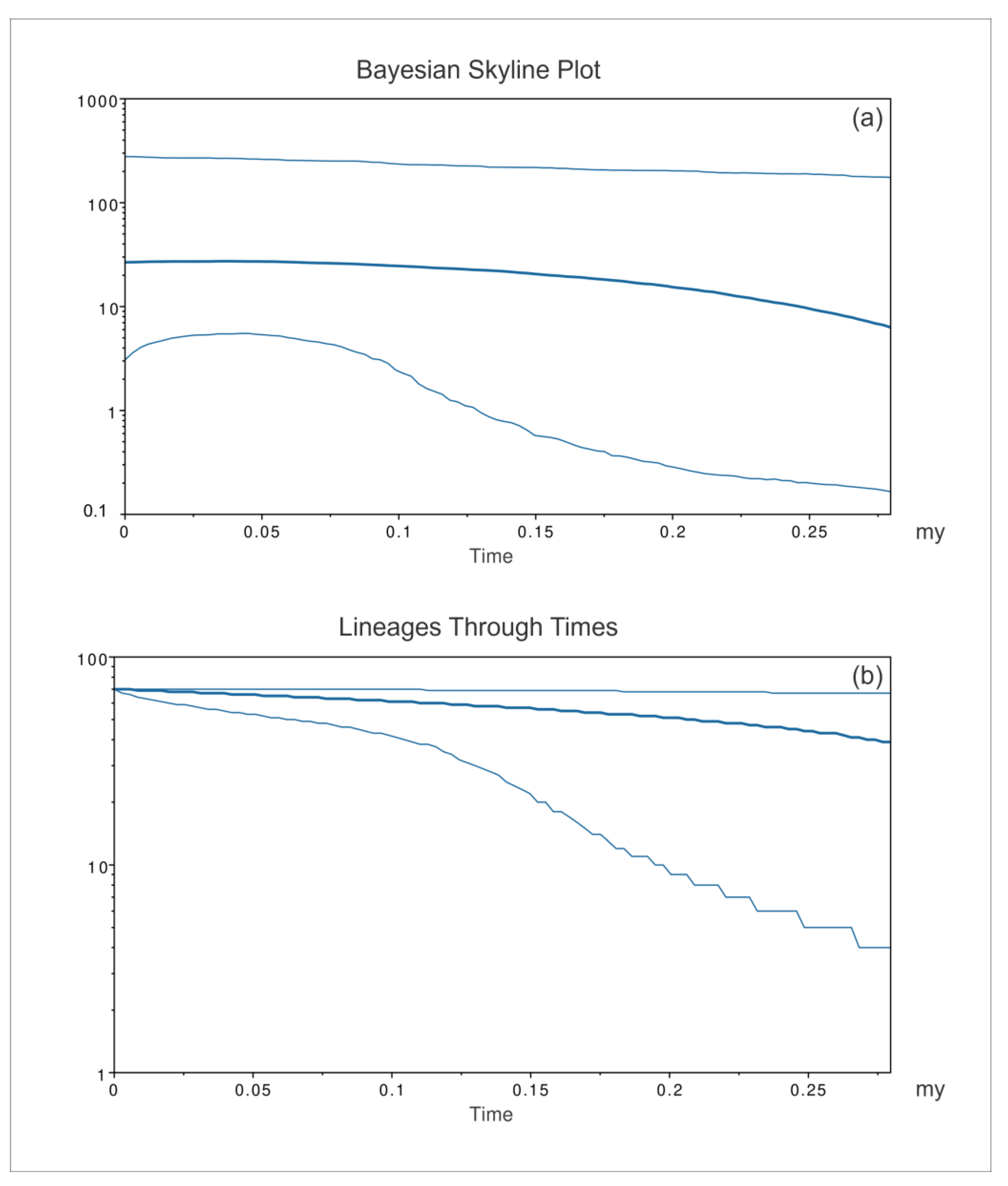
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Phylogeography and Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis
4.2. Phylogeny of Pinna nobilis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Butler, A.; Vicente, N.; de Gaulejac, B. Ecology of the pterioid bivalves Pinna bicolor Gmelin. Mar Life 1993, 3, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lemer, S.; Buge, B.; Bemis, A.; Giribet, G. First molecular phylogeny of the circumtropical bivalve family Pinnidae (Mollusca, Bivalvia): Evidence for high levels of cryptic species diversity. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 75, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Alba, J. Guía de Campo de los Fósiles de España y de Europa; Ediciones Omega: Barcelona, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.R.G. Aportaciones al conocimiento de la Biología de Pinna nobilis Linneo, 1758 (Mollusca: Bivalvia) en el Litoral Mediterráneo Ibérico. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaoui, L.; Tlig-Zouari, S.; Katsanevakis, S.; Ben Hassine, O.K. Modelling population density of Pinna nobilis (Bivalvia) on the eastern and southeastern coast of Tunisia. J. Molluscan Stud. 2010, 76, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, L.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; García-March, J.R.; Deudero, S.; Alvarez, E.; Vicente, N.; Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E. The pen shell, Pinna nobilis: A review of population status and recommended research priorities in the Mediterranean Sea. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2015, 71, 109–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Cossu, P.; Casu, M. From dark to light and back again: Is Pinna nobilis, the largest Mediterranean shellfish, on the brink of extinction? What about Pinna nobilis. Veterinaria 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald, M. The Cruising Chef Cookbook; Paradise Cay Publication: Middletown, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Centoducati, G.; Tarsitano, E.; Bottalico, A.; Marvulli, M.; Lai, O.R.; Crescenzo, G. Monitoring of the endangered Pinna nobilis Linne, 1758 in the Mar Grande of Taranto (Ionian sea, Italy). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; Borg, J.A.; Morell, C.; Banach-Esteve, G.; Deudero, S. Influence of boat anchoring on Pinna nobilis: A field experiment using mimic units. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 66, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öndes, F.; Kaiser, M.J.; Güçlüsoy, H. Human impacts on the endangered fan mussel, Pinna nobilis. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öndes, F.; Alan, V.; Akçalı, B.; Güçlüsoy, H. Mass mortality of the fan mussel, Pinna nobilis in Turkey (eastern Mediterranean). Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Mugetti, D.; Cerruti, F.; Hosseini, S.; Cossu, P.; Pinna, S.; Grech, D.; Cabana, D.; et al. Multiple Non-Species-Specific Pathogens Possibly Triggered the Mass Mortality in Pinna nobilis. Life 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, D.; Cossu, P.; Dedola, G.L.; Scarpa, F.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A.; Franzoi, P.; Lai, T.; Cristo, B.; Curini-Galletti, M.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA Reveals Genetic Structuring of Pinna nobilis across the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, P.; Secci, M.; Brundu, G.; Manunza, A.; Corrias, S.; Cau, A. Density, size structure, shell orientation and epibiontic colonization of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis L. 1758 (Mollusca: Bivalvia) in three contrasting habitats in an estuarine area of Sardinia (W Mediterranean). Sci. Mar. 2009, 73, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combelles, S.; Moreteau, J.C.; Vicente, N. Contribution a la connaissance de l’ecologie de Pinna nobilis L. (mollusque eulamellibranche). Sci. Rep. Port-Cros Nat. Park 1986, 12, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Coppa, S.; Guala, I.; de Lucia, G.A.; Massaro, G.; Bressan, M. Density and distribution patterns of the endangered species Pinna nobilis within a Posidonia oceanica meadow in the Gulf of Oristano (Italy). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U.K. 2010, 90, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiletić, T.; Peharda, M. Population study of the fan shell Pinna nobilis L. in Malo and Veliko Jezero of the Mljet National Park (Adriatic Sea). Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S. Population ecology of the endangered fan mussel Pinna nobilis in a marine lake. Endanger. Species Res. 2005, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaoui, L.; Tlig Zouari, S.; Katsanevakis, S.; Ben Hassine, O.K. Comparison of absolute and relative growth patterns among five Pinna nobilis populations along the Tunisian coastline: An information theory approach. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-March, J.R.; Pérez-Rojas, L.; García-Carrascosa, A.M. Influence of hydrodynamic forces on population structure of Pinna nobilis L., 1758 (Mollusca: Bivalvia): The critical combination of drag force, water depth, shell size and orientation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 342, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsares, V.; Tsiora, A.; Galinou-Mitsoudi, S.; Imsiridou, A. Genetic structure of the endangered species Pinna nobilis (Mollusca: Bivalvia) inferred from mtDNA sequences. Biologia 2008, 63, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S. Population dynamics of the endangered fan mussel Pinna nobilis in a marine lake: A metapopulation matrix modeling approach. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1715–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Thessalou-Legaki, M. Spatial distribution, abundance and habitat use of the protected fan mussel Pinna nobilis in Souda Bay, Crete. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 8, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaoui, L.; Mejri, R.; Tlig-Zouari, S.; Bahri, L.; Ben Hassine, O.K.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S. Genetic variation among populations of the endangered fan mussel Pinna nobilis (Mollusca: Bivalvia) along the Tunisian coastline. Hydrobiologia 2011, 678, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Caiola, N.; Ibáñez, C. Habitat use by a large population of Pinna nobilis in shallow waters. Sci. Mar. 2014, 78, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; March, D.; Alvarez, E.; Alvarez-Berastegui, D.; Deudero, S. Spatial distribution modelling of the endangered bivalve Pinna nobilis in a Marine Protected Area. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafidis, D.; Antoniadou, C.; Voultsiadou, E.; Chintiroglou, C. Population structure of the protected fan mussel Pinna nobilis in the south Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. U. K. 2014, 94, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; Álvarez, E.; Barrajón, A.; García-March, J.R.; Grau, A.; Hendriks, I.E.; Jiménez, S.; Kersting, D.; Moreno, D.; Pérez, M.; et al. S.O.S. Pinna nobilis: A Mass Mortality Event in Western Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Valencia, J.M.; Garcia-March, J.R.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Alvarez, E.; Deudero, S.; Darriba, S.; Carballal, M.J.; Villalba, A. Haplosporidium pinnae sp. nov., a haplosporidan parasite associated with mass mortalities of the fan mussel, Pinna nobilis, in the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 157, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanžek-Turnšek, H. Ugotavljanje Gostote Populacije Velikega Leščurja (Pinna nobilis) z Metodo Podvodnih Videotransektov: Zaključna Naloga. Doctoral dissertation, Univerza na Primorskem, Fakulteta za Matematiko, Naravoslovje in Informacijske Tehnologije, Koper, Slovenia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tsirintanis, K.; Tsaparis, D.; Doukas, D.; Sini, M.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Κolygas, M.N.; Tontis, D.; Koutsoubas, D.; Bakopoulos, V. The cryptogenic parasite Haplosporidium pinnae invades the Aegean Sea and causes the collapse of Pinna nobilis populations. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarese, R.; Tedesco, P.; Chimienti, G.; Latrofa, M.S.; Quaglio, F.; Passantino, G.; Buonavoglia, C.; Gustinelli, A.; Tursi, A.; Otranto, D. Haplosporidium pinnae associated with mass mortality in endangered Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus 1758) fan mussels. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 164, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanellas-Reboredo, M.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Mourre, B.; Álvarez, E.; Deudero, S.; Amores, Á.; Addis, P.; Ballesteros, E.; Barrajón, A.; Coppa, S.; et al. Tracking a mass mortality outbreak of pen shell Pinna nobilis populations: A collaborative effort of scientists and citizens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čižmek, H.; Čolić, B.; Gračan, R.; Grau, A.; Catanese, G. An emergency situation for pen shells in the Mediterranean: The Adriatic Sea, one of the last Pinna nobilis shelters, is now affected by a mass mortality event. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 173, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Michaelidis, B. First detection of the invasive Haplosporidian and Mycobacteria parasites hosting the endangered bivalve Pinna nobilis in Thermaikos Gulf, North Greece. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 155, 104889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarić, T.; Župan, I.; Aceto, S.; Villari, G.; Palić, D.; De Vico, G.; Carella, F. Epidemiology of Noble Pen Shell (Pinna nobilis L. 1758) Mass Mortality Events in Adriatic Sea Is Characterised with Rapid Spreading and Acute Disease Progression. Pathogens 2020, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čelebičić, M.; Gradaščević, N.; Viteškić, V. Is Pinna nobilis L. critically endangered in Neum bay, Bosnia and Herzegovina? Veterinaria 2020, 69, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Künili, I.E.; Ertürk Gürkan, S.; Aksu, A.; Turgay, E.; Çakir, F.; Gürkan, M.; Altinağaç, U. Mass mortality in endangered fan mussels Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus 1758) caused by co-infection of Haplosporidium pinnae and multiple Vibrio infection in Çanakkale Strait, Turkey. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, S. First haplosporidan parasite reported infecting a member of the Superfamily Pinnoidea (Pinna nobilis) during a mortality event in Alicante (Spain, Western Mediterranean). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 148, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sanmartín, M.; López-Sanmartín, M.; Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Valencia, J.M.; García-March, J.R.; Navas, J.I. Real-Time PCR based test for the early diagnosis of Haplosporidium pinnae affecting fan mussel Pinna nobilis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiscar, P.G.; Rubino, F.; Fanelli, G.; Paoletti, B.; Della Salda, L. Mass mortality of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis in Apulia (Ionian Sea) caused by Haplosporidium pinnae. Rapp. Comm. Int. Pour L’exploration Sci. De La Mer Mediterranée 2019, 42, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Carella, F.; Aceto, S.; Pollaro, F.; Miccio, A.; Iaria, C.; Carrasco, N.; Prado, P.; De Vico, G. A mycobacterial disease is associated with the silent mass mortality of the pen shell Pinna nobilis along the Tyrrhenian coastline of Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Antuofermo, E.; Farina, S.; Salati, F.; Mandas, D.; Prado, P.; Panarese, R.; Marino, F.; Fiocchi, E.; Pretto, T.; et al. In the Wake of the Ongoing Mass Mortality Events: Co-occurrence of Mycobacterium, Haplosporidium and Other Pathogens in Pinna nobilis Collected in Italy and Spain (Mediterranean Sea). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, P.; Carrasco, N.; Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Cabanes, P.; Carella, F.; García-March, J.R.; Tena, J.; Roque, A.; Bertomeu, E.; et al. Presence of Vibrio mediterranei associated to major mortality in stabled individuals of Pinna nobilis L. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiscar, P.G.; Rubino, F.; Paoletti, B.; Di Francesco, C.E.; Mosca, F.; Della Salda, L.; Hattab, J.; Smoglica, C.; Morelli, S.; Fanelli, G. New insights about Haplosporidium pinnae and the pen shell Pinna nobilis mass mortality events. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 190, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupé, S.; Giantsis, I.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Scarpa, F.; Foulquié, M.; Prévot, J.M.; Lattos, A.; Casu, M.; Michaelidis, B.; Sanna, D.; et al. Toll-like receptor polymorphism in fan mussels: Does the resistance of Pinna nobilis to Haplosporidium pinnae only depends on its hybridization with Pinna rudis? Authorea Prepr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Palić, D.; Šarić, T.; Župan, I.; Gorgoglione, B.; Prado, P.; Andree, K.B.; Giantsis, I.A.; Michaelidis, B.; Lattos, A.; et al. Multipathogen infections and multifactorial pathogenesis involved in noble pen shell (Pinna nobilis) mass mortality events: Background and current pathologic approaches. Vet. Pathol. 2023, 60, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebot-Colomer, E.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Boissin, E.; Peyran, C.; Deudero, S.; Planes, S. Inferred family structure and dispersal patterns of a Critically Endangered species, Pinna nobilis, using molecular analyses: Implications for conservation. Endanger. Species Res. 2022, 49, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-March, J.R.; Tena, J.; Henandis, S.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; López, D.; Téllez, C.; Prado, P.; Navas, J.I.; Bernal, J.; Catanese, G.; et al. Can we save a marine species affected by a highly infective, highly lethal, waterborne disease from extinction? Biol. Conserv. 2020, 243, 108498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafidou, G.; Tsaparis, D.; Issaris, Y.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Grigoriou, P.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Pavloudi, C. Insights on Pinna nobilis population genetic structure in Greece. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Yokeş, M.B.; Güçlüsoy, H.A.R.U.N. The last fortress fell: Mass mortality of Pinna nobilis in the Sea of Marmara. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Carella, F.; Çınar, M.; Čižmek, H.; Jiménez, C.; Kersting, D.; Moreno, D.; Rabaoui, L.; Vicente, N. The fan mussel Pinna nobilis on the brink of extinction in the Mediterranean. In Imperiled: The Encyclopedia of Conservation; DellaSala, D.A., Goldstein, M.I., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volumes 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, P.; Grau, A.; Catanese, G.; Cabanes, P.; Carella, F.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Andree, K.B.; Añón, T.; Hernandis, S.; Tena, J.; et al. Pinna nobilis in suboptimal environments are more tolerant to disease but more vulnerable to severe weather phenomena. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 163, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.; Benabdi, M.; Cizmek, H.; Grau, A.; Jimenez, C.; Katsanevakis, S.; Oztürk, B.; Tuncer, S.; Tunesi, L.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; et al. Pinna nobilis . IUCN 2019, e.T160075998A160081499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberle, I.; Marn, N.; Geček, S.; Klanjšček, T. Dynamic energy budget of endemic and critically endangered bivalve Pinna nobilis: A mechanistic model for informed conservation. Ecol. Modell. 2020, 434, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, D.; Dedola, G.; Scarpa, F.; Lai, T.; Cossu, P.; Curini-Galletti, M.; Francalacci, P.; Casu, M. New mitochondrial and nuclear primers for the Mediterranean marine bivalve Pinna nobilis. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselmann, M.; González-Wangüemert, M.; Serrão, E.A.; Engelen, A.H.; Renault, L.; García-March, J.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E. Genetic and oceanographic tools reveal high population connectivity and diversity in the endangered pen shell Pinna nobilis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Wangüemert, M.; Basso, L.; Balau, A.; Costa, J.; Renault, L.; Serrão, E.A.; Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E. Gene pool and connectivity patterns of Pinna nobilis in the Balearic Islands (Spain, Western Mediterranean Sea): Implications for its conservation through restocking. Aquatic Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyran, C.; Boissin, E.; Morage, T.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Iwankow, G.; Planes, S. Genetic homogeneity of the critically endangered fan mussel, Pinna nobilis, throughout lagoons of the Gulf of Lion (North-Western Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyran, C.; Boissin, E.; Morage, T.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Iwankow, G.; Planes, S. Investigating population dynamics from parentage analysis in the highly endangered fan mussel Pinna nobilis. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Wanguemert, M.; Costa, J.; Basso, L.; Duarte, C.M.; Serrão, E.; Hendriks, I. Highly polymorphic microsatellite markers for the Mediterranean endemic fan mussel Pinna nobilis. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 16, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costedoat, C.; Gilles, A. Quaternary pattern of freshwater fishes in Europe: Comparative phylogeography and conservation perspective. Open Conserv. Biol. J. 2009, 3, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machordom, A.; Araujo, R.; Erpenbeck, D.; Ramos, M.Á. Phylogeography and conservation genetics of endangered European Margaritiferidae (Bivalvia: Unionoidea). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 78, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.F.; Jones, H.A.; Klunzinger, M.W. Bivalves in a bottleneck: Taxonomy, phylogeography and conservation of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionoida) in Australasia. Hydrobiologia 2014, 735, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladoukakis, E.D.; Zouros, E. Evolution and inheritance of animal mitochondrial DNA: Rules and exceptions. J. Biol. Res. 2017, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracchi, V.A.; Bulegato, S.; Basso, D. Palaeoecology of the Pinna nobilis biofacies along the Stirone River (Early Pleistocene, Northern Italy). Boll. Soc. Paleontol. Ital. 2020, 59, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Estrada, F.; Jiménez-Munt, I.; Gorini, C.; Fernández, M.; Vergés, J.; De Vicente, R. Catastrophic flood of the Mediterranean after the Messinian salinity crisis. Nature 2009, 462, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, C.N. Biodiversity issues for the forthcoming tropical Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, Accurate Alignment of Very Large Numbers of Sequences. In Multiple Sequence Alignment Methods; Russell, D., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1079, pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavaré, S. Some probabilistic and statistical problems in the analysis of DNA sequences. In Some Mathematical Questions in Biology—DNA Sequence Analysis; Miura, R.M., Ed.; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1986; pp. 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Rohl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Thi, G.; Azzena, I.; Scarpa, F.; Cossu, P.; Danh Le, C.; Ton Nu, P.A.; Chau Ngo, T.M.; Sanna, D.; Casu, M. Molecular Identification and Appraisal of the Genetic Variation of Taenia saginata in Central Regions of Vietnam. Life 2022, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Cossu, P.; Sanna, D.; Lai, T.; Norenburg, J.L.; Curini-Galletti, M.; Casu, M. An 18S and 28S-based clock calibration for marine Proseriata (Platyhelminthes). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 463, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Cossu, P.; Lai, T.; Casu, M.; Curini-Galletti, M. How to achieve internal fertilization without a vagina: The study case of the genus Archilina Ax, 1959 (Platyhelminthes, Proseriata) from Canary Islands. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2057–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luttikhuizen, P.C.; Drent, J.; Baker, A.J. Disjunct distribution of highly diverged mitochondrial lineage clade and population subdivision in a marine bivalve with pelagic larval dispersal. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 2215–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gernhard, T.J. The conditioned reconstructed process. J. Theor. Biol. 2008, 253, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yule, G.U. II.—A mathematical theory of evolution, based on the conclusions of Dr. J. C. Willis, F.R.S. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1925, 213, 21–87. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa, F.; Cossu, P.; Lai, T.; Sanna, D.; Curini-Galletti, M.; Casu, M. Meiofaunal cryptic species challenge species delimitation: The case of the Monocelis lineata (Platyhelminthes: Proseriata) species complex. Contrib. Zool. 2016, 85, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.W.; Huber, M. Revision of the Worldwide Recent Pinnidae and Some Remarks on Fossil European Pinnidae; Acta Conchyliorum 13; ConchBooks: Harxheim Germany, 2013; pp. 1–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Chiantore, M.; Montefalcone, M.; Parravicini, V.; Rovere, A. Mediterranean Sea biodiversity between the legacy from the past and a future of change. In Life in the Mediterranean Sea: A Look at Habitat Changes, 1st ed.; Stambler, N., Ed.; Bar Ilan University: Ramat Gan, Israel, 2012; pp. 1, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Crippa, G.; Azzarone, M.; Bottini, C.; Crespi, S.; Felletti, F.; Marini, M.; Petrizzo, M.R.; Scarponi, S.; Raffi, S.; Raineri, G. Bio-and lithostratigraphy of lower Pleistocene marine successions in western Emilia (Italy) and their implications for the first occurrence of Arctica islandica in the Mediterranean Sea. Quat. Res. 2019, 92, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, S. Taphonomy and paleoecology of shallow marine macrofossil assemblages in a collisional setting (late Pliocene–early Pleistocene, western Emilia, Italy). Palaios 2001, 16, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervesler, P.; Uchman, A.; Hohenegger, J.; Dominici, S. Ichnological record of environmental changes in early Quaternary (Gelasian–Calabrian) marine deposits of the Stirone Section, northern Italy. Palaios 2011, 26, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril Hernández, J.M.; Periáñez Rodríguez, R. Revisiting the time scale and size of the Zanclean flood of the Mediterranean (5.33 Ma) from CFD simulations. Mar. Geol. 2016, 382, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, G.; Maars, J.; Andreetto, F.; Hernández-Molina, F.J.; Rodríguez-Tovar, F.J.; Krijgsman, W. A terminal Messinian flooding of the Mediterranean evidenced by contouritic deposits on Sicily. Sedimentology 2023, 70, 1195–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periáñez Rodríguez, R.; Abril Hernández, J.M.; García Castellanos, D.; Estrada, F.; Ercilla, G. An exploratory modelling study on sediment transport during the Zanclean flood of the Mediterranean. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyran, C.; Morage, T.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Iwankow, G.; Planes, S. Unexpected residual habitats raise hope for the survival of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis along the Occitan coast (Northwest Mediterranean Sea). Endanger. Species Res. 2022, 48, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, C.D. Evolution of Blennioidel in the Mediterranean Sea. Rev. Des Trav. De L’institut Des Pêches Marit. 1973, 37, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Thunell, R.; Rio, D.; Sprovieri, R.; Vergnaud-Grazzini, C. An overview of the post-Messinian paleoenvironmental history of the western Mediterranean. Paleoceanography 1991, 6, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboth, S.; Grunert, P.; Lourens, L. Mediterranean Outflow Water variability during the early Pleistocene. Clim. Past 2017, 13, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdenović, S.; Mačić, V.; Pešić, V.; Nikolić, M.; Peraš, I.; Mandić, M. Review on pinna rudis (Linnaeus, 1758) (bivalvia: Pinnidae) presence in the Mediterranean. Agric. For. 2019, 65, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Ballesteros, E. Is the local extinction of Pinna nobilis facilitating Pinna rudis recruitment? Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Deudero, S.; Planes, S.; Boissin, E. Natural hybridization between pen shell species: Pinna rudis and the critically endangered Pinna nobilis may explain parasite resistance in P. nobilis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allmon, W.D. Nutrients, temperature, disturbance, and evolution: A model for the late Cenozoic marine record of the western Atlantic. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2001, 166, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.S.; Coates, A.G.; Berggren, W.A.; Aubry, M.P.; Zhang, J. The late Miocene Panama Isthmian strait. Geology 1996, 24, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.B.C.; Budd, A.F.; Coates, A.G. (Eds.) Evolution and Environment in Tropical America; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1996; Volumes 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, N.; Weigt, L.A. New dates and new rates for divergence across the Isthmus of Panama. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornacchia, I.; Brandano, M.; Agostini, S. Miocene paleoceanographic evolution of the Mediterranean area and carbonate production changes: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 221, 103785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Smith, D.G.; Funnell, B.M. Atlas of Mesozoic and Cenozoic Coastlines; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Duque-Caro, H. Neogene stratigraphy, paleoceanography and paleobiogeography in northwest South America and the evolution of the Panama Seaway. Palaeog. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1990, 77, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, G.D., Jr. Late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic reef-building organisms and paleogeography: The Tethyan-North American connection. Cour. Forsch. Inst. Senckenb. 1994, 172, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rosewater, J. The family Pinnidae in the Indo-Pacific. Indo-Pacific Moll. 1961, 1, 175–226. [Google Scholar]
- Pauls, S.U.; Nowak, C.; Bálint, M.; Pfenninger, M. The impact of global climate change on genetic diversity within populations and species. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 925–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetjen, M.; Hübner, D.; Seehausen, O.; Schulz, R. Genetic diversity of endangered Chondrostoma nasus in the River Rhine system: Conservation genetics considerations on stocking and reintroduction. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2020, 421, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetjen, M.; Schmidt, T.; Schrimpf, A.; Schulz, R. Genetic diversity and population structure of burbot Lota lota in Germany: Implications for conservation and management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2020, 27, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | Sampling Year | Sampling Area | Specimens | GenBank Code | Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARDINIA | |||||
| OSR | 2013 | Ossario (Asinara) | 12 | OR782596–OR782633 | Present Study |
| ASI | 2015 | Cala di Scombro di Dentro and Cala Reale (Asinara) | 38 | OR782634–OR782645 | |
| BPC | 2010 | Baia di Porto Conte | 18 | JX854788–JX854805 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| POR | 2010 | Torre del Porticciolo | 3 | JX854806–JX854808 | |
| LAZ | 2010 | Lazzareto | 2 | JX854809–JX854810 | |
| OSM | 2010 | Ospedale Marino | 21 | JX854811–JX854831 | |
| MOL | 2010 | Molara | 11 | JX854832–JX854842 | |
| CCE | 2010 | Capo Ceraso | 13 | JX854843–JX854855 | |
| SAL | 2011 | Le Saline | 5 | JX854856–JX854860 | |
| MPE | 2010 | Monte Petrosu (Sassi piatti and Isola Cava) | 4 | JX854861–JX854864 | |
| OTT | 2011 | Porto Ottiolu | 5 | JX854865–JX854869 | |
| ORI | 2011 | Oristano | 10 | JX854870–JX854879 | |
| MAR | 2011 | Marceddì | 5 | JX854880–JX854884 | |
| IMV | 2011 | Isola di Mal di Ventre | 4 | JX854885–JX854888 | |
| VMS | 2011 | Villasimius (Capo Caterina) | 4 | JX854889–JX854892 | |
| CPA | 2011 | Costa Paradiso | 5 | JX854893–JX854897 | |
| MAD | 2011 | Isola di La Maddalena (Cala Camiciotto) | 18 | JX854898–JX854915 | |
| CORSICA | |||||
| IPI | 2011 | Isola Piana | 13 | JX854916–JX854928 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| CPC | 2011 | Cala Pesciu Cane | 12 | JX854929–JX854940 | |
| ELBA ISLAND | |||||
| ELB | 2011 | Capo Enfola | 10 | JX854992–JX855001 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| SICILY | |||||
| SVC | 2011 | San Vito lo Capo (Secca di Cala Rossa) | 7 | JX854941–JX854947 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| MON | 2011 | Mondello | 11 | JX854948–JX854958 | |
| MLZ | 2011 | Milazzo | 10 | JX854959–JX854968 | |
| PAC | 2011 | Pachino (Capo Passero) | 8 | JX854969–JX854976 | |
| OGN | 2011 | Ognina di Siracusa | 15 | JX854977–JX854991 | |
| ADRIATIC SEA | |||||
| VEN | 2011 | Ottagono Alberoni and Santa Maria del Lago | 20 | JX855002–JX855021 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| MIR | 2018 | Miramare (Gulf of Trieste) | 18 | OR782678–OR782695 | Present study |
| TEL | 2015 | Telašćica–Island Buč | 14 | OR782646–OR782659 | |
| MLJ | 2015 | Mljet–Lake Malo Jezero | 18 | OR782660–OR782677 | |
| CYPRUS | |||||
| CYP | 2011 | Karaoglanoglu | 2 | JX855022–JX855023 | Sanna et al. [14] |
| AEGEAN SEA | |||||
| EPA–EPT | 2006-2007 | Epanomi | 9 | DQ448215–DQ448217 EF536827–EF536832 | Katsares et al. [22] |
| AGG | 2007 | Aggelochori | 9 | EF536833–EF536841 | |
| XIO | 2007 | Xios Island | 5 | EF536842–EF536846 | |
| KOR | 2007 | Korinthiakos Gulf | 3 | EF536847–EF536849 | |
| TUNISIAN COASTLINES | |||||
| N | 2010 | Bizerta Lagoon | 7 | HM998857–HM998866 * | Rabaoui et al. [25] |
| M | 2010 | Monastir (Stah Jaber) | 9 | ||
| S | 2010 | Kerkennah Island | 7 | ||
| B | 2010 | El Bibane Lagoon | 9 | ||
| K | 2010 | El Ketef | 17 | ||
| BIZ | 2013 | Bizerta Lagoon | 1 | KF612603 | Sanna et al. [57] |
| IBERIAN COASTLINES | |||||
| BAN | 2014 | Banyuls (France) | 9 | KY321755–KY321811 | Wesselmann et al. [58] |
| EBR | 2014 | Ebro Delta (Spain) | 9 | ||
| IBI | 2011 | Ibiza (Spain) | 10 | ||
| MUR | 2014 | Murcia (Spain) | 9 | ||
| MALL | 2011 | Mallorca (Spain) | 10 | ||
| ALI | 2014 | Alicante (Spain) | 10 | ||
| Sample | N | S | H | h | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSR | 12 | 7 | 6 | 0.848 | 0.005 |
| ASI | 38 | 7 | 6 | 0.691 | 0.004 |
| BPC | 18 | 10 | 7 | 0.725 | 0.005 |
| POR | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.667 | 0.006 |
| LAZ | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1.000 | 0.012 |
| OSM | 21 | 9 | 8 | 0.829 | 0.006 |
| MOL | 11 | 6 | 6 | 0.873 | 0.006 |
| CCE | 13 | 5 | 5 | 0.705 | 0.005 |
| SAL | 5 | 3 | 3 | 0.700 | 0.003 |
| MPE | 4 | 5 | 3 | 0.833 | 0.007 |
| OTT | 5 | 6 | 4 | 0.900 | 0.008 |
| ORI | 10 | 8 | 7 | 0.911 | 0.007 |
| MAR | 5 | 7 | 4 | 0.900 | 0.009 |
| IMV | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| VMS | 4 | 5 | 4 | 1.000 | 0.008 |
| CPA | 5 | 4 | 3 | 0.700 | 0.005 |
| MAD | 18 | 11 | 10 | 0.895 | 0.007 |
| Sardinia | 178 | 28 | 31 | 0.830 | 0.006 |
| IPI | 13 | 12 | 9 | 0.949 | 0.009 |
| CPC | 12 | 7 | 6 | 0.803 | 0.005 |
| Corsica | 25 | 13 | 11 | 0.890 | 0.007 |
| Elba Island—ELB | 10 | 7 | 6 | 0.889 | 0.008 |
| SVC | 7 | 5 | 4 | 0.714 | 0.005 |
| MON | 11 | 6 | 6 | 0.836 | 0.007 |
| MLZ | 10 | 6 | 5 | 0.867 | 0.007 |
| PAC | 8 | 8 | 7 | 0.964 | 0.007 |
| OGN | 15 | 7 | 9 | 0.886 | 0.007 |
| Sicily | 51 | 13 | 16 | 0.882 | 0.007 |
| VEN | 20 | 10 | 10 | 0.895 | 0.006 |
| MIR | 18 | 5 | 7 | 0.791 | 0.004 |
| TEL | 14 | 9 | 8 | 0.890 | 0.006 |
| MLJ | 18 | 5 | 5 | 0.752 | 0.005 |
| Adriatic Sea | 70 | 16 | 21 | 0.870 | 0.007 |
| Cyprus—CYP | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1.000 | 0.003 |
| EP | 9 | 9 | 6 | 0.833 | 0.007 |
| AG | 9 | 2 | 3 | 0.667 | 0.002 |
| XI | 5 | 2 | 3 | 0.700 | 0.002 |
| KO | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Aegean Sea | 26 | 11 | 8 | 0.720 | 0.004 |
| N | 7 | 2 | 3 | 0.667 | 0.002 |
| BIZ | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| M | 9 | 4 | 4 | 0.694 | 0.004 |
| S | 7 | 2 | 3 | 0.667 | 0.002 |
| B | 9 | 1 | 2 | 0.556 | 0.002 |
| K | 17 | 1 | 2 | 0.382 | 0.001 |
| Tunisian coastlines | 50 | 7 | 7 | 0.621 | 0.003 |
| BAN | 9 | 3 | 4 | 0.750 | 0.004 |
| EBR | 9 | 2 | 3 | 0.417 | 0.002 |
| IBI | 10 | 3 | 4 | 0.533 | 0.002 |
| MUR | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MALL | 10 | 4 | 4 | 0.533 | 0.003 |
| ALI | 10 | 9 | 7 | 0.867 | 0.010 |
| Iberian coastlines | 57 | 15 | 15 | 0.555 | 0.004 |
| Whole dataset | 469 | 36 | 49 | 0.631 | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Locci, C.; Ankon, P.; Kružić, P.; Manfrin, C.; Pallavicini, A.; Ciriaco, S.; Segarich, M.; Batistini, E.; et al. Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis: New Genetic Signals from the Past of a Species on the Brink of Extinction. Animals 2024, 14, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010114
Sanna D, Azzena I, Locci C, Ankon P, Kružić P, Manfrin C, Pallavicini A, Ciriaco S, Segarich M, Batistini E, et al. Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis: New Genetic Signals from the Past of a Species on the Brink of Extinction. Animals. 2024; 14(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanna, Daria, Ilenia Azzena, Chiara Locci, Pavel Ankon, Petar Kružić, Chiara Manfrin, Alberto Pallavicini, Saul Ciriaco, Marco Segarich, Edoardo Batistini, and et al. 2024. "Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis: New Genetic Signals from the Past of a Species on the Brink of Extinction" Animals 14, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010114
APA StyleSanna, D., Azzena, I., Locci, C., Ankon, P., Kružić, P., Manfrin, C., Pallavicini, A., Ciriaco, S., Segarich, M., Batistini, E., Scarpa, F., & Casu, M. (2024). Reconstructing the Evolutionary History of Pinna nobilis: New Genetic Signals from the Past of a Species on the Brink of Extinction. Animals, 14(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010114












