Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Visual System (Vision)

3. Auditory System (Hearing)
3.1. Innervation of the Cochlea
3.2. Central Auditory Pathways
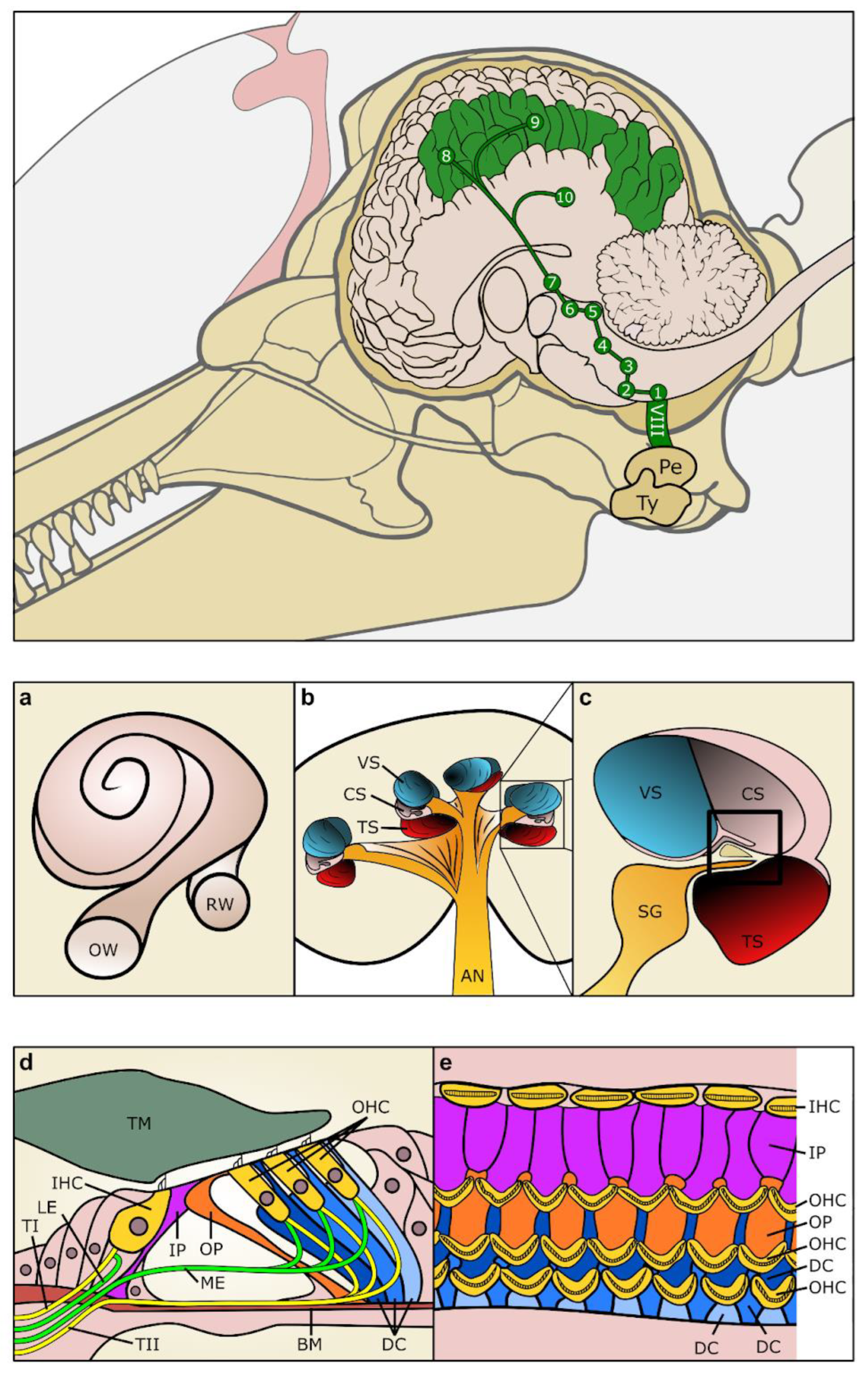
4. Vestibular System (Spatial Orientation)
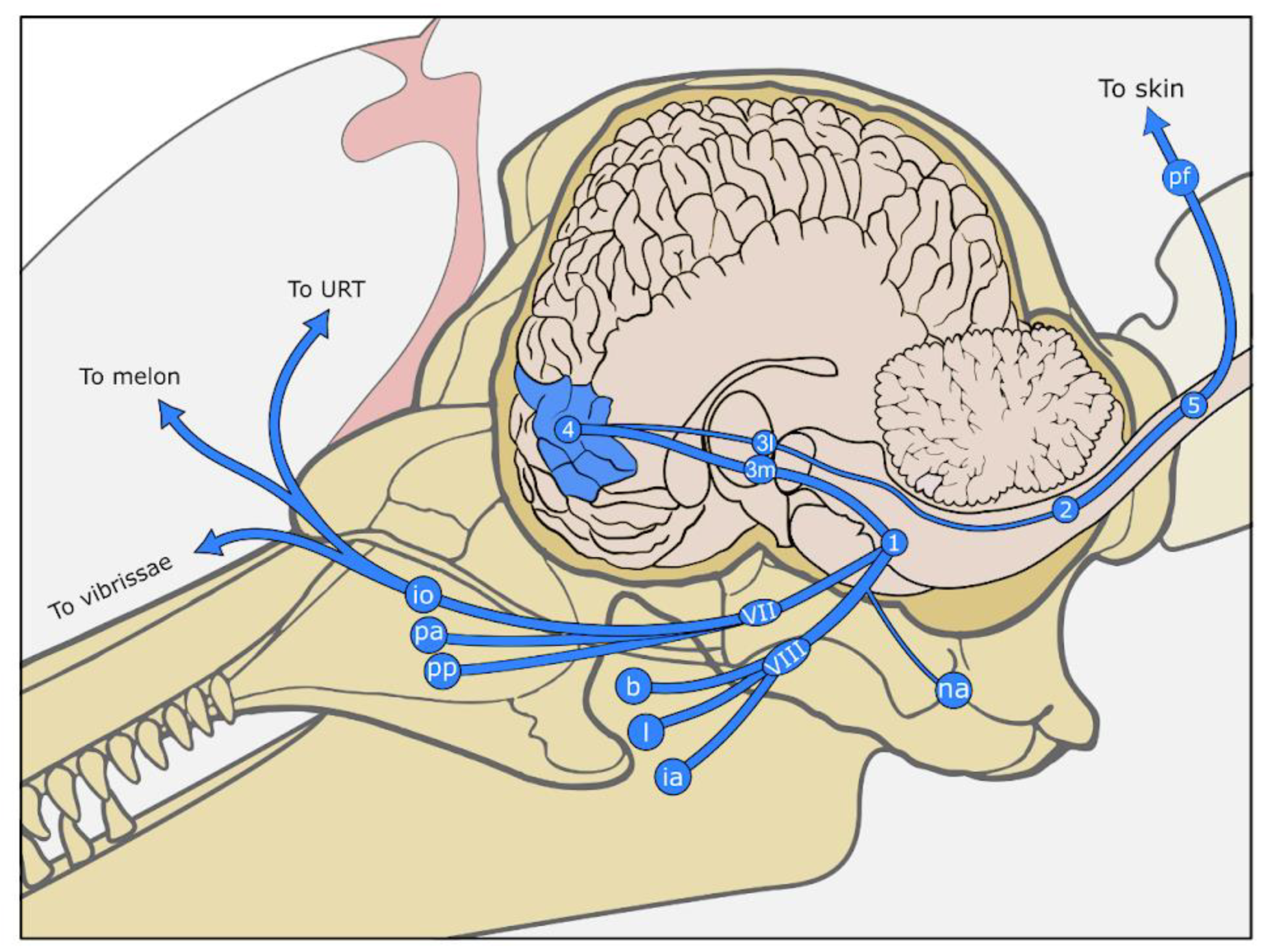
5. Somatosensory System (Somatosensation)
5.1. Continuations of the Skin
5.1.1. Nasal Sac System
5.1.2. External Ear Canal
5.1.3. Vibrissae, Crypts, Tubercles
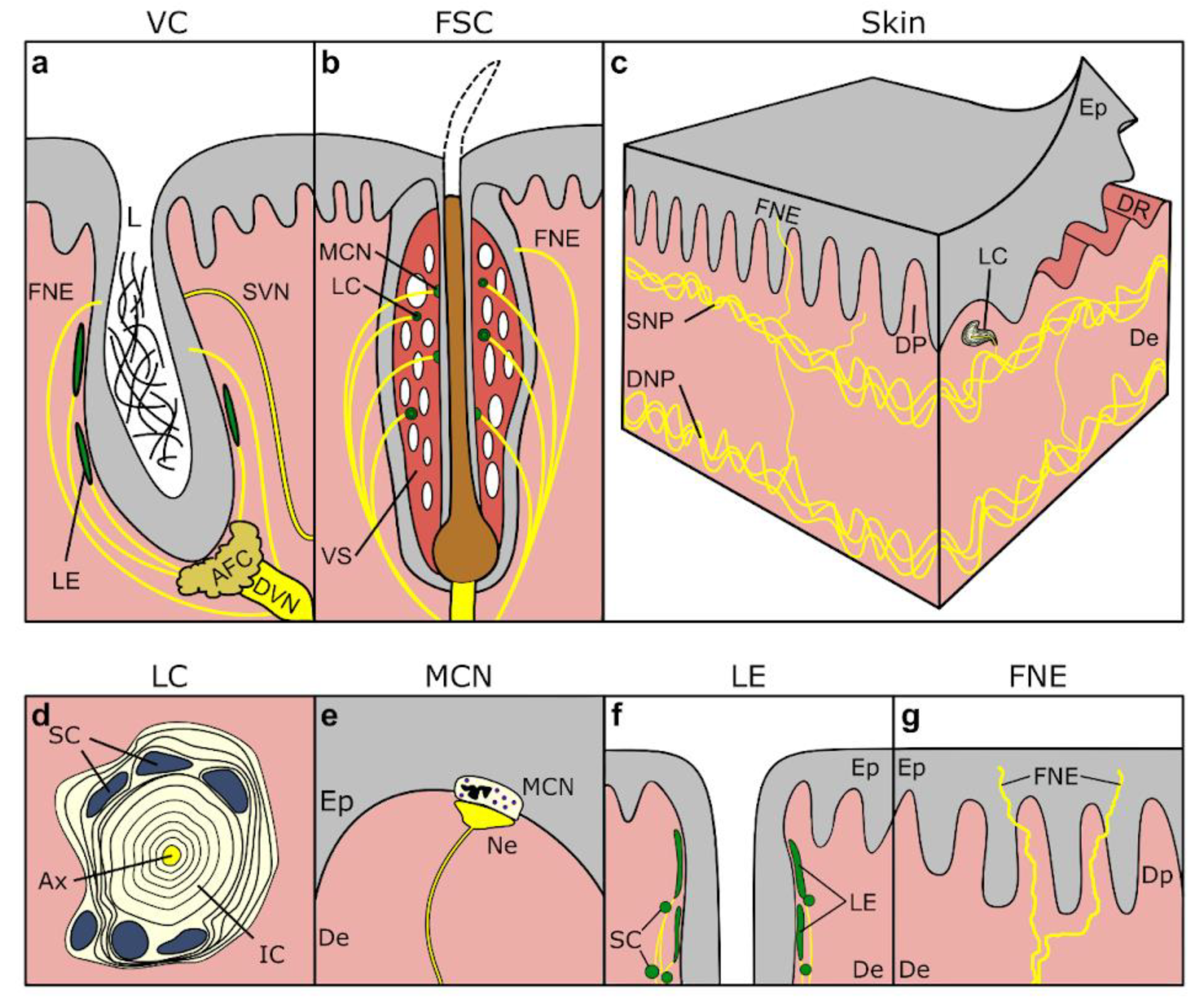
| Name | Species | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamellar corpuscles | |||
| Ciliary corpuscles that resemble Pacinian corpuscles | Megaptera novaeangliae | Iridocorneal angle of the eye | [208] |
| Corpuscles of Rochon–Duvigneaud | Inia geoffrensis, Mesoplodon bidens, Ziphius cavirostris, Kogia breviceps, Delphinapterus leucas, Delphinus delphis, Tursiops truncatus, Stenella attenuata | [10] | |
| Encapsulated corpuscles | [10] | ||
| Skin of trunk, flippers and fluke | [146] | ||
| Nasal sac system | [151] and Khomenko, 1974 therein | ||
| Complex encapsulated terminals, resembling Vater–Pacini corpuscles | Tursiops truncatus, Balaenoptera physalus | Skin of the body and head | [149] |
| Small Vater–Pacini corpuscles | Balaenoptera physalus | Skin of entire body | [209] |
| Encapsulated, lamellated (mechano-) receptor organs | Tursiops truncatus, Pseudorca crassidens | Blowhole lips | [147] |
| (Simple) Lamellar corpuscles | Stenella coeruleoalba, Delphinus delphis, Tursiops truncatus, Ziphius cavirostris, Grampus griseus, Globicephalus macrorhynchus, Berardius bairdii, Physeter macrocephalus, Kogia breviceps, Balaenoptera physalus, Balaenoptera acutorostrata | External ear canal | [152,186,187] |
| Laminated corpuscles | Balaenoptera spp. | Oral cavity and lips | Ogawa Shida, 1950, In: [186] |
| Lamellar corpuscles, similar to Herbst’s corpuscles | B. borealis | Vibrissae | [207] |
| Lamellated corpuscles | B. acutorostrata | Ventral pouch | [210] |
| Pacinian corpuscles | Balaena mysticetus, Delphinapterus leucas | Circumorbital skin | [153] |
| Pacchionian bodies | T. truncatus | Mammary glands | [159] |
| Krause bulbs | T. truncatus | Flippers, snout, clitoris | [159] |
| Golgi–Mazzoni and Pacinian-type lamellated corpuscles | E. robustus | Vibrissae | [155] |
| Lamellar bodies/corpuscles | Balaenopteridae P. blainvillei T. truncatus | Vibrissae | [195] [156,157] [158] |
| Other SNF | |||
| Lanceolate endings | S. guianensis, P. blainvillei T. truncatus | Vibrissae | [156] [158] |
| Merkel cell-Neurite Complexes | S. coeruleoalba S. guianensis | SkinVibrissae | [161] [157] |
| Intraepithelial ‘free’ nerve endings | All species studied to date | Skin and adnexa, like vibrissae, external ear canal, etc. | E.g., [157,158,162] |
| Intrapapillary myelinated endings (IMEs) | Stenella coeruleoalba, Delphinus delphis, Tursiops truncatus | External ear canal | [152] |
| Muscle spindles | 15 species of toothed and baleen whales | Skeletal muscle | [211,212] |
| Myo-elastic sphincters | Tursiops truncatus, Stenella coeruleoalba | Lungs | [213] |
6. Chemoreception
6.1. Gustation
6.2. Vomeronasal Organ
6.3. Olfaction
7. Magneto-Sensation
8. Proprioception and Interoception
Internal Organs
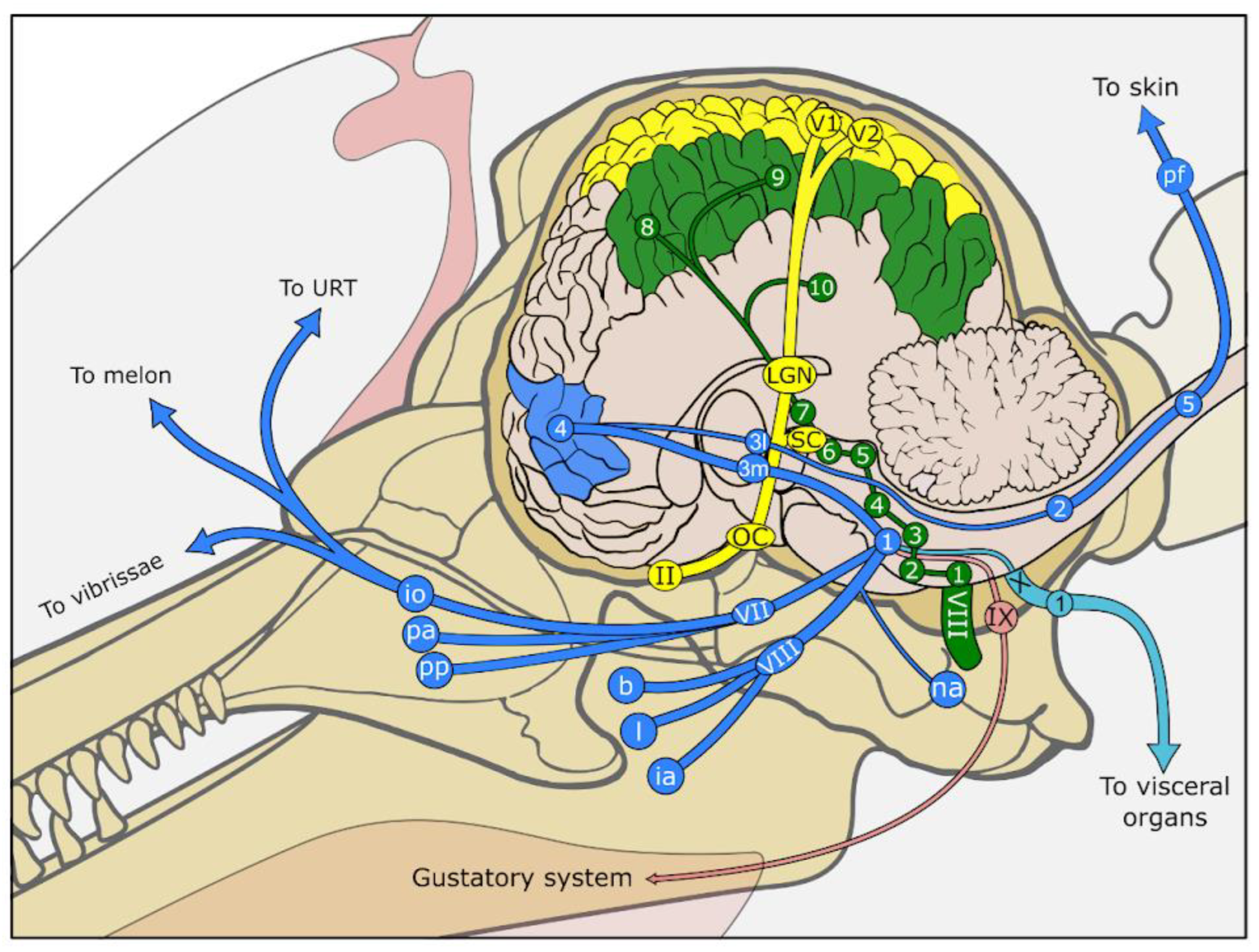
9. Central Nervous System Signal Processing
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cozzi, B.; Huggenberger, S.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. Anatomy of Dolphins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.W. Marine Mammals: Adaptations for an Aquatic Life; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-98278-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hanke, F.D.; Mooney, A.T.; Janik, V.M. Sensory physiology in dolphinids. In The Physiology of Dolphins, 1st ed.; Fahlman, A., Hooker, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 193–215. [Google Scholar]
- De Vreese, S.; Sørensen, K.; Biolsi, K.; Fasick, J.I.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Hanke, F.D. Open Questions in Marine Mammal Sensory Research. Biol. Open 2023, 12, bio059904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, D.; Célérier, A.; Schaal, B.; Campagna, S.; Trabalon, M.; Böye, M.; Hausberger, M.; Lemasson, A. Sensory Perception in Cetaceans: Part I—Current Knowledge about Dolphin Senses As a Representative Species. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, A.M.; Supin, A.Y. Ganglion Cell Topography and Retinal Resolution in the Bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops Truncatus at an Early Stage of Postnatal Development. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2020, 47, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, A.M.; Supin, A.Y.A. Adaptive Features of Aquatic Mammals’ Eye. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2007, 290, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, A.M.; Supin, A. Vision. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Kovacs, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press (Elsevier): London, UK, 2018; pp. 1035–1044. ISBN 978-0-12-804327-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya, H.; Imamura, E.; Inomata, T. Comparative Anatomy of the Ophthalmic Rete and Its Relationship to Ocular Blood Flow in Three Species of Marine Mammal. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2014, 17, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, M.G. Irido-Corneal Angle of Mammalian Eyes: Comparative Morphology of Encapsulated Corpuscles in Odontocete Cetaceans. Cell Tissue Res. 1980, 210, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Samuelson, D.; Dubielzig, R. Anatomic Features of the Cetacean Globe. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2013, 16, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.M.; Silva, F.M.O.; Trompieri-Silveira, A.C.; Vergara-Parente, J.E.; Miglino, M.A.; Guimarães, J.P. Morphology of the Eyeball from the Humpback Whale (Megaptera Novaeangliae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2014, 77, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshida, K.; Lin, S.; Domning, D.P.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Wang, P.; Gilland, E. Cetacean Orbital Muscles: Anatomy and Function of the Circular Layers. Anat. Rec. 2020, 303, 1792–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshida, K.; Lin, S.; Domning, D.P.; Wang, P.; Gilland, E. The Oblique Extraocular Muscles in Cetaceans: Overall Architecture and Accessory Insertions. J. Anat. 2021, 238, 917–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshida, K.; Lin, S.; Domning, D.P.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Wang, P.C.; Gilland, E. The Unique Rectus Extraocular Muscles of Cetaceans: Homologies and Possible Functions. J. Anat. 2022, 240, 1075–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, A.M.; Supin, A.Y.; Abramov, A.V.; Mukhametov, L.M.; Rozanova, E.I. Ocular Anatomy, Ganglion Cell Distribution and Retinal Resolution of a Killer Whale (Orcinus Orca). Brain Behav. Evol. 2013, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peichl, L.; Behrmann, G.; Kröger, R.H.H. For Whales and Seals the Ocean Is Not Blue: A Visual Pigment Loss in Marine Mammals. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, R.W.; Gatesy, J.; Emerling, C.A.; York, V.M.; Springer, M.S. Rod Monochromacy and the Coevolution of Cetacean Retinal Opsins. PLOS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasick, J.I.; Robinson, P.R. Adaptations of Cetacean Retinal Pigments to Aquatic Environments. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, S.Z.; Kosyakov, A.; Chang, B.S.W. Spectral Tuning of Killer Whale (Orcinus Orca) Rhodopsin: Evidence for Positive Selection and Functional Adaptation in a Cetacean Visual Pigment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, S.Z.; Chang, B.S.W. Ancient Whale Rhodopsin Reconstructs Dim-Light Vision over a Major Evolutionary Transition: Implications for Ancestral Diving Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118145119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, N.; Nickle, B.; Cronin, T.W.; Velasquez, S.; Fasick, J.I. Deep-Sea and Pelagic Rod Visual Pigments Identified in the Mysticete Whales. Vis. Neurosci. 2012, 29, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengual, R.; García, M.; Segovia, Y.; Pertusa, J.F. Ocular Morphology, Topography of Ganglion Cell Distribution and Visual Resolution of the Pilot Whale (Globicephala Melas). Zoomorphology 2015, 134, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivamonte, L.A. Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus) Double-Slit Pupil Asymmetries Enhance Vision. Aquat. Mamm. 2009, 35, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, A.M.; Supin, A.Y. Topography of the Ganglion Retinal Layer and Retinal Resolution in the Rough-Toothed Dolphin Steno Bredanensis (Cetacea: Delphinidae). J. Evol. Biochem. Phys. 2021, 57, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisney, T.J.; Collin, S.P. Retinal Topography in Two Species of Baleen Whale (Cetacea: Mysticeti). Brain Behav. Evol. 2019, 92, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzafa, N.; Pereiro, X.; Vecino, E. Immunohistochemical Characterisation of the Whale Retina. Front. Neuroanat. 2022, 16, 813369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, W.W.; Hawthorne, M.N.; Jenkins, R.L.; Goldston, R.T. Giant Neural Systems in the Inner Retina and Optic Nerve of Small Whales. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 205, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, W.W.; Hope, G.M.; Ulshafer, R.J. Contents of the Optic Nerve of a Small Cetacean. Aquat. Mamm. 1983, 10, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Caleo, M.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Maffei, L. A Comparative Morphometric Analysis of the Optic Nerve in Two Cetacean Species, the Striped Dolphin (Stenella Coeruleoalba) and Fin Whale (Balaenoptera Physalus). Vis. Neurosci. 2001, 18, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.S.; Morgane, P.J.; McFarland, W.L. Degeneration of Visual Pathways in the Bottlenose Dolphin. Brain Res. 1975, 88, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.S.; Morgane, P.J. Retino-Hypothalamic Connexions in Cetacea. Nature 1964, 203, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatschek, R. Sehnervenatrophie Bei Einem Delphin. In Arbeiten aus dem Neurologischen Institut an der Wiener Universität (Osterr. Interakademisches Zentralinstitut Für Hinforschung); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1903; Volume 10, pp. 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.H. The Central Nervous System of the Bottlenose Dolphin. In The Bottlenose Dolphin; Leatherwood, S., Reeves, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 69–98. ISBN 978-0-12-440280-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kruger, L. The Thalamus of the Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus) and Comparison with Other Mammals. J. Comp. Neurol. 1959, 111, 133–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, L. Specialized Features of the Cetacean Brain. In Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises; Norris, K.S., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1966; pp. 232–254. [Google Scholar]
- Glezer, I.I.; Hof, P.R.; Istomin, V.V.; Morgane, P.J. Comparative Immunocytochemistry of Calcium-Binding Protein-Positive Neurons in Visual and Auditory Systems of Cetacean and Primate Brains. In Sensory Systems of Aquatic Mammals; Kastelein, R.A., Thomas, J.A., Nachtigall, P.E., Eds.; De Spil Publishers: Woerden, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 477–513. [Google Scholar]
- Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Haas-Rioth, M.; Fung, C.; Ridgway, S.H.; Knauth, M. Morphology and Evolutionary Biology of the Dolphin (Delphinus Sp.) Brain–MR Imaging and Conventional Histology. Brain Behav. Evol. 2007, 71, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, G. Uberstrukturelle Eigenheiten Am Vorderen Zweihiigel Des Seiwals (Balaenoptera Borealis Less.). Arb. Anat. Inst. Sendai 1935, 17, 203–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fuse, G. Uber Ein Bisher Unbekannten, Den Nucleus Olivaris Corporis Quadrigemini Anterioris Gleichstellbaren Kern, Bei Einigen Delphinen. Arb. Anat. Inst. Sendai 1938, 31, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, V.E.; Ladygina, F.; Supin, A. Localization of Sensory Zones in the Dolphin Cerebral Cortex. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1972, 202, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graïc, J.-M.; Peruffo, A.; Grandis, A.; Cozzi, B. Topographical and Structural Characterization of the V1–V2 Transition Zone in the Visual Cortex of the Long-Finned Pilot Whale Globicephala Melas (Traill, 1809). Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgane, P.J.; Glezer, I.I.; Jacobs, M.S. Visual Cortex of the Dolphin: An Image Analysis Study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 273, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supin, A.Y.; Popov, V.V.; Mass, A.M. Vision in Aquatic Mammals. In The Sensory Physiology of Aquatic Mammals; Supin, A.Y., Popov, V.V., Mass, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 229–284. ISBN 978-1-4615-1647-7. [Google Scholar]
- Graïc, J.-M.; Peruffo, A.; Corain, L.; Finos, L.; Grisan, E.; Cozzi, B. The Primary Visual Cortex of Cetartiodactyls: Organization, Cytoarchitectonics and Comparison with Perissodactyls and Primates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 1195–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supin, A.Y.; Popov, V.V.; Mass, A.M. The Sensory Physiology of Aquatic Mammals; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-4613-5658-5. [Google Scholar]
- Glezer, I.I.; Hof, P.R.; Leranth, C.; Morgane, P.J. Calcium-Binding Protein-Containing Neuronal Populations in Mammalian Visual Cortex: A Comparative Study in Whales, Insectivores, Bats, Rodents, and Primates. Cereb. Cortex 1993, 3, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.G.; Manger, P.R. Clarifying Homologies in the Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: The Case of the Third Visual Area (V3). Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerussi, T.; Graïc, J.-M.; Peruffo, A.; Behroozi, M.; Schlaffke, L.; Huggenberger, S.; Güntürkün, O.; Cozzi, B. The Prefrontal Cortex of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus Montagu, 1821): A Tractography Study and Comparison with the Human. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketten, D.R. Cetacean Ears. In Hearing by Whales and Dolphins; Au, W.W.L., Popper, A.N., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 43–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dudok van Heel, W.H. Sound and Cetacea. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1962, 1, 407–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, F.C.; Purves, P.E. Anatomy and Function of the Cetacean Ear. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1960, 152, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, J.G.; Wever, E.G.; Palin, J.; Ridgway, S.H. Sound Conduction in the Dolphin Ear. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 48, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reysenbach de Haan, F.W. De Ceti Auditu: Over de Gehoorzin Bij Walvissen. Ph.D. Thesis, Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Solntseva, G.N. The Auditory Organ of Mammals in Relation to the Acoustic Properties of the Habitat and Frequency Tuning. In Sensory Systems of Aquatic Mammals, Proceedings of the “Marine Mammal Sensory Symposium; Kastelein, R.A., Thomas, J.A., Nachtigall, P.E., Eds.; De Spil Publishers: Woerden, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 455–475. ISBN 978-90-72743-05-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R.; Simmons, J.A.; Riquimaroux, H.; Simmons, A.M. Functional Analyses of Peripheral Auditory System Adaptations for Echolocation in Air vs. Water. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 661216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummela, S.; Reuter, T.; Hemilä, S.; Holmberg, P.; Paukku, P. The Anatomy of the Killer Whale Middle Ear (Orcinus Orca). Hear. Res. 1999, 133, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, D.S.; Gomez-Rubio, A.; Finneran, J.J. Evoked Potential Audiometry of 13 Pacific Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus Gilli). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2008, 24, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Helder-Hoek, L.; Van de Voorde, S. Hearing Thresholds of a Male and a Female Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena Phocoena). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shen, W.; He, D.Z.; Long, K.B.; Madison, L.D.; Dallos, P. Prestin Is the Motor Protein of Cochlear Outer Hair Cells. Nature 2000, 405, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Békésy, G. Experiments in Hearing; Mcgraw Hill: Oxford, UK, 1960; p. 745. [Google Scholar]
- Manley, G.A. Travelling Waves and Tonotopicity in the Inner Ear: A Historical and Comparative Perspective. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2018, 204, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad, J.A.; Shepherd, G.M.; Corey, D.P. Tip-Link Integrity and Mechanical Transduction in Vertebrate Hair Cells. Neuron 1991, 7, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, P.G.; Müller, U. Mechanotransduction by Hair Cells: Models, Molecules, and Mechanisms. Cell 2009, 139, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, P.G.; Walker, R.G. Molecular Basis of Mechanosensory Transduction. Nature 2001, 413, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickles, J.O.; Comis, S.D.; Osborne, M.P. Cross-Links between Stereocilia in the Guinea Pig Organ of Corti, and Their Possible Relation to Sensory Transduction. Hear. Res. 1984, 15, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wever, E.G.; McCormick, J.G.; Palin, J.; Ridgway, S.H. Cochlear Structure in the Dolphin, Lagenorhynchus Obliquidens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wever, E.G.; McCormick, J.G.; Palin, J.; Ridgway, S.H. The Cochlea of the Dolphin, Tursiops Truncatus: General Morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2381–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, E.G.; McCormick, J.G.; Palin, J.; Ridgway, S.H. Cochlea of the Dolphin, Tursiops Truncatus: The Basilar Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2708–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, E.G.; McCormick, J.G.; Palin, J.; Ridgway, S.H. The Cochlea of the Dolphin, Tursiops Truncatus: Hair Cells and Ganglion Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2908–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhou, K. Fiber Analysis of the Optic and Cochlear Nerves of Small Cetaceans. In Marine Mammal Sensory Systems; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Supin, A.Y., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 39–52. ISBN 978-1-4615-3406-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R. The Marine Mammal Ear: Specializations for Aquatic Audition and Echolocation. In The Evolutionary Biology of Hearing; Webster, D.B., Fay, R.R., Popper, A.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 717–750. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R. Functional Analyses of Whale Ears: Adaptations for Underwater Hearing. In Proceedings of the OCEANS’94 ’Oceans Engineering for Today’s Technology and Tomorrow’s Preservation ’ Proceedings, Brest, France, 13–16 September 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Ketten, D.R.; Wartzok, D. Three-Dimensional Reconstructions of the Dolphin Ear. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 81–105. [Google Scholar]
- Girdlestone, C.D.; Piscitelli-Doshkov, M.A.; Ostertag, S.K.; Morell, M.; Shadwick, R.E. Description of Cochlear Morphology and Hair Cell Variation in the Beluga Whale. Arct. Sci. 2018, 4, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M. Ultrastructural Analysis of Odontocete Cochlea. Doctoral Thesis, Universitat Politécnica de Catalunya: Vilanova i la Geltrú, Barcelona, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morell, M.; Lenoir, M.; Shadwick, R.E.; Jauniaux, T.; Dabin, W.; Begeman, L.; Ferreira, M.; Maestre, I.; Degollada, E.; Hernandez-Milian, G.; et al. Ultrastructure of the Odontocete Organ of Corti: Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy: Odontocete Organ of Corti Ultrastructure: SEM and TEM. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.; Brownlow, A.; McGovern, B.; Raverty, S.A.; Shadwick, R.E.; André, M. Implementation of a Method to Visualize Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Mass Stranded Cetaceans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.; IJsseldijk, L.L.; Piscitelli-Doshkov, M.; Ostertag, S.; Estrade, V.; Haulena, M.; Doshkov, P.; Bourien, J.; Raverty, S.A.; Siebert, U.; et al. Cochlear Apical Morphology in Toothed Whales: Using the Pairing Hair Cell—Deiters’ Cell as a Marker to Detect Lesions. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 622–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.; Raverty, S.A.; Mulsow, J.; Haulena, M.; Barrert-Lennard, L.; Nordstrom, C.A.; Venail, F.; Shadwick, R.E. Combining Cochlear Analysis and Auditory Evoked Potentials in a Beluga Whale With High-Frequency Hearing Loss. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, M.; Vogl, A.W.; IJsseldijk, L.L.; Piscitelli-Doshkov, M.; Tong, L.; Ostertag, S.; Ferreira, M.; Fraija-Fernandez, N.; Colegrove, K.M.; Puel, J.-L.; et al. Echolocating Whales and Bats Express the Motor Protein Prestin in the Inner Ear: A Potential Marker for Hearing Loss. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vater, M.; Lenoir, M.; Pujol, R. Ultrastructure of the Horseshoe Bat’s Organ of Corti. II. Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 318, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, Y.; Altschuler, R.A. Structure and Innervation of the Cochlea. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 60, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fettiplace, R. Hair Cell Transduction, Tuning, and Synaptic Transmission in the Mammalian Cochlea. In Comprehensive Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1197–1227. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sensor, J.D.; Suydam, R.; George, J.C.; Liberman, M.C.; Lovano, D.; Rhaganti, M.A.; Usip, S.; Vinyard, C.J.; Thewissen, J.G.M. The Spiral Ganglion and Rosenthal’s Canal in Beluga Whales. J. Morphol. 2015, 276, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Glowatzki, E.; Fuchs, P.A. Unmyelinated Type II Afferent Neurons Report Cochlear Damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14723–14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, J.J. Olivocochlear Efferents: Their Action, Effects, Measurement and Uses, and the Impact of the New Conception of Cochlear Mechanical Responses. Hear. Res. 2018, 362, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, S.F.; Usubuchi, H.; Liberman, M.C. Efferent Feedback Minimizes Cochlear Neuropathy from Moderate Noise Exposure. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5542–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maison, S.F.; Liberman, M.C. Predicting Vulnerability to Acoustic Injury with a Noninvasive Assay of Olivocochlear Reflex Strength. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 4701–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.W.; Keil, A. The Biological Role of the Medial Olivocochlear Efferents in Hearing: Separating Evolved Function from Exaptation. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finneran, J.J. Conditioned Attenuation of Auditory Brainstem Responses in Dolphins Warned of an Intense Noise Exposure: Temporal and Spectral Patterns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, P.E.; Supin, A.Y.; Pacini, A.F.; Kastelein, R.A. Four Odontocete Species Change Hearing Levels When Warned of Impending Loud Sound. Integr. Zool. 2018, 13, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, P.E.; Supin, A.Y. A False Killer Whale Reduces Its Hearing Sensitivity When a Loud Sound Is Preceded by a Warning. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, P.E.; Supin, A.Y. Conditioned Hearing Sensitivity Reduction in a Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogoslovskaya, L.S. Ultra-Structure of the Spiral Ganglion and Auditory Nerve of the Bottlenose Dolphin; Kiev, Ukraine, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 41–43. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Solntseva, G.N. Morphology of the Auditory and Vestibular Organs in Mammals, with Emphasis on Marine Species; Russian Academy of Sciences & Pensoft Publishers & Brill Academic Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Zhou, K. The Number of Fibers and Range of Fiber Diameters in the Cochlear Nerve of Three Odontocete Species. Can. J. Zool. 1991, 69, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.S. Further Fiber Counts of Cetacean Cranial Nerves. Proc. Eighty Sixth Annu. Sess. Am. Assoc. Anat. 1973, 175, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhova, K. Multimodal Assessment of Cetacean Central Nervous Auditory Pathways with Emphasis on Forensic Diagnostics of Acoustic Trauma. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, M.S.; Jensen, A.V. Gross Aspects of the Brain and a Fiber Analysis of Cranial Nerves in the Great Whale. J. Comp. Neurol. 1964, 123, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgane, P.T.; Jacobs, M.S. Comparative Anatomy of the Cetacean Nervous System. In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach, A.S. The Cetacean Central Nervous System. Biol. Rev. 1960, 35, 187–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, A.S. Anatomical Aspects of the Cetacean Brain Stem; Van Gorcum & Comp.: Assen, The Netherlands, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.M.; Irving, R. Visual and Nonvisual Auditory Systems in Mammals. Anatomical Evidence Indicates Two Kinds of Auditory Pathways and Suggests Two Kinds of Hearing in Mammals. Science 1966, 154, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatschek, R.; Schlesinger, H. Der Hirnstamm Des Delphins (Delphinus Delphis). In Arbeiten aus dem Neurologischen Institut an der Wiener Universität (Osterr. Interakademisches Zentralinstitut Für Hinforschung); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1902; Volume 9, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, F. Die Obere Olive Der Saeugetiere, Nebst Bemerkungen Ueber Die Lage Der Cochleariskerne, Eine Vergleichende Anatomische Studie. Arb. Aus Dem Neurol. Inst. Der Univ. Wien 1908, 14, 326–328. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.; Jansen, J.K.S. The Nervous System of Cetacea. In The Biology of Marine Mammals; Andersen, H.A., Ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 175–252. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Arifuku, S. On the Acoustic System in the Cetacean Brains. Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo 1948, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Osen, K.K.; Jansen, J. The Cochlear Nuclei in the Common Porpoise, Phocaena Phocaena. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 125, 223–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petelina, E.V. Structure and topography of the superior olive complex in the dolphin. Arkhiv Anat. Gistol. I Émbriologii 1973, 65, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Schulmeyer, F.J. Morphologische Untersuchungen Am Hirnstamm Der Delphine Unter Besonderer Berücksichtigung Des La Plata-Delphins, Pontoporia Blainvillei. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Human Medicine, Johann Wolfgang Goethe University, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Schulmeyer, F.J.; Adams, J.C.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. Specialized Sound Reception in Dolphins—A Hint for the Function of the Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus in Mammals. Hist. Biol. 2000, 14, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvorykin, V. Morfologicheskie Osnovy Ul’trazvukovykh i Lokatsionnykh Kachestv Del’fina (Morphological Principles of the Ultrasonic and Location Properties of the Dolphin). Arkhiv Anat. Gistol. I Embriol. 1963, 45, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Batigália, F.; Boer, N.P.; Bankoff, A.; Simonato, L.; Boer, A.; Chacon, E. Computational Macroscopical Patterning of the Medullary Striae of Fourth Ventricle. Braz. J. Morphol. Sci. 2009, 26, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Malkemper, E.P.; Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Huggenberger, S. The Dolphin Cochlear Nucleus: Topography, Histology and Functional Implications. J. Morphol. 2012, 273, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Rosene, D.L.; Mortazavi, F.; Oblak, A.L.; Ketten, D.R. Morphology and Unbiased Stereology of the Lateral Superior Olive in the Short-beaked Common Dolphin, Delphinus delphis (Cetacea, Delphinidae). J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhova, K.; Selmanovic, E.; De Gasperi, R.; Gama Sosa, M.A.; Wicinski, B.; Maloney, B.; Seifert, A.; Alipour, A.; Balchandani, P.; Gerussi, T.; et al. Multimodal Assessment of Bottlenose Dolphin Auditory Nuclei Using 7-Tesla MRI, Immunohistochemistry and Stereology. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.W.B.; Pawloski, D.A.; Dankiewicz, L. Harderwijk Marine Mammal Park Interaural Time and Intensity Difference Thresholds in the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). In Sensory Systems of Aquatic Mammals; Kastelein, R.A., Thomas, J.A., Nachtigall, P.E., Eds.; Proceedings of the “Marine Mammal Sensory Symposium”; De Spil Publishers: Woerden, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 11–24. ISBN 90-72743-05-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zook, J.M.; DiCaprio, R.A. A Potential System of Delay-Lines in the Dolphin Auditory Brainstem. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 181–193. ISBN 978-1-4899-0858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhoruchenko, M.N. Selective Hearing Adaptation to Paired Pulses in Tursiops Truncatus. In Marine Mammal Sensory Systems; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Supin, A.Y., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, T.H.; Ridgway, S.H. Evoked Potentials in the Central Auditory System of Alert Porpoises to Their Own and Artificial Sounds. J. Neurobiol. 1972, 3, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zook, J.M.; Jacobs, M.S.; Glezer, I.; Morgane, P.J. Some Comparative Aspects of Auditory Brainstem Cytoarchitecture in Echolocating Mammals: Speculations on the Morphological Basis of Time-Domain Signal Processing. In Animal Sonar: Processes and Performance; Nachtigall, P.E., Moore, P.W.B., Eds.; NATO ASI Science; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 311–316. ISBN 978-1-4684-7493-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Bullock, T.H.; Carder, D.A.; Seeley, R.L.; Woods, D.; Galambos, R. Auditory Brainstem Response in Dolphins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, T.H.; Gurevich, V.S. Soviet Literature on the Nervous System and Psychobiology of Cetacea. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 1979, 21, 47–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H. The Auditory Central Nervous System of Dolphins. In Hearing by Whales and Dolphins; Au, W.W.L., Fay, R.R., Popper, A.N., Eds.; Springer Handbook of Auditory Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 12, pp. 273–293. ISBN 978-1-4612-7024-9. [Google Scholar]
- Houser, D.S.; Moore, P.W.; Johnson, S.; Lutmerding, B.; Branstetter, B.; Ridgway, S.H.; Trickey, J.; Finneran, J.J.; Jensen, E.; Hoh, C. Relationship of Blood Flow and Metabolism to Acoustic Processing Centers of the Dolphin Brain. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Ridgway, S.H.; Knauth, M. Cetacean Brain Evolution: Dwarf Sperm Whale (Kogia Sima) and Common Dolphin (Delphinus Delphis)—An Investigation with High-Resolution 3D MRI. Brain Behav. Evol. 2010, 75, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supin, A.Y.; Mukhametov, L.M.; Ladygina, F.; Popov, V.V.; Mass, A.M.; Poliakova, E.G. Electrophysiological Study of the Dolphin Brain; Nauka, Moscow, 1978. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Revishchin, A.V.; Garey, L.J. The Thalamic Projection to the Sensory Neocortex of the Porpoise, Phocoena Phocoena. J. Anat. 1990, 169, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hof, P.R.; Glezer, I.I.; Archin, N.; Janssen, W.G.; Morgane, P.J.; Morrison, J.H. The Primary Auditory Cortex in Cetacean and Human Brain: A Comparative Analysis of Neurofilament Protein-Containing Pyramidal Neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 146, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, P.R.; Chanis, R.; Marino, L. Cortical Complexity in Cetacean Brains. Anat. Rec. A Discov. Mol. Cell Evol. Biol. 2005, 287, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, P.R.; Van Der Gucht, E. Structure of the Cerebral Cortex of the Humpback Whale, Megaptera Novaeangliae (Cetacea, Mysticeti, Balaenopteridae). Anat. Rec. 2007, 290, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, G.S.; Cook, P.F.; Foxley, S.; Jbabdi, S.; Miller, K.L.; Marino, L. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of Dolphin Brains Reveals Direct Auditory Pathway to Temporal Lobe. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.K.; Theilmann, R.J.; Ridgway, S.H.; Scadeng, M. Diffusion Tractography Reveals Pervasive Asymmetry of Cerebral White Matter Tracts in the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, R. Laminar and Cytoarchitectonic Features of the Cerebral Cortex in the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus Griseus), Striped Dolphin (Stenella Coeruleoalba), and Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). J. Anat. 2008, 213, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, A.; Siebert, U.; Cozzi, B.; Hof, P.R.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. Stereology of the Neocortex in Odontocetes: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Functional Implications. Brain Behav. Evol. 2011, 77, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, H.S.; Pakkenberg, B.; Dam, M.; Dietz, R.; Sonne, C.; Mikkelsen, B.; Eriksen, N. Quantitative Relationships in Delphinid Neocortex. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf, J.P.; Hof, P.R.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. The Neocortex of Indian River Dolphins (Genus Platanista): Comparative, Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis. Brain Behav. Evol. 2016, 88, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solntseva, G.N. Comparative Analysis of Vestibular System Development in Various Groups of Mammals Living under Different Environmental Conditions. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2001, 32, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketten, D.R. Structure and Function in Whale Ears. Bioacoustics 1997, 8, 103–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoor, F.; Bajpai, S.; Hussain, S.T.; Kumar, K.; Thewissen, J.G. Vestibular Evidence for the Evolution of Aquatic Behaviour in Early Cetaceans. Nature 2002, 417, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Zhou, K. Fiber Analysis of the Vestibular Nerve of Small Cetaceans. In Sensory Systems of Aquatic Mammals; Proceedings of the “Marine Mammal Sensory Symposium”; Kastelein, R.A., Thomas, J.A., Nachtigall, P.E., Eds.; De Spil Publishers: Woerden, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 447–453. ISBN 978-90-72743-05-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, A.; Seidel, K.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. The Central Vestibular Complex in Dolphins and Humans: Functional Implications of Deiters’ Nucleus. Brain Behav. Evol. 2009, 73, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langworthy, O.R. A Description of the Central Nervous System of the Porpoise (Tursiops Truncatus). J. Comp. Neurol. 1932, 54, 437–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.B.; Reep, R.L.; Marshall, C.D. The Tactile Senses of Marine Mammals. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2018, 31, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, E.; Weddell, G. The Relationship Between Structure, Innervation and Function of the Skin of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1964, 143, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, M.M.; Molyneux, G.S. Ultrastructure of Encapsulated Mechanoreceptor Organs in the Region of the Nares. In Research on Dolphins; Bryden, M.M., Harrison, R., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.J.; Thurley, K.W. Structure of the Epidermis in Tursiops, Delphinus, Orcinus and Phocoena. In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; pp. 45–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.K. The Integument of Marine Mammals. In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, L.; Tavolga, W. The Communication Systems of Cetaceans. In Cetacean Behavior: Mechanisms and Functions; Herman, L.M., Ed.; Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 149–209. [Google Scholar]
- Degollada Bastos, E. Functional Anatomy and Histology of the Nasal Sac System in Odontocetes (Superfamily Delphinoidea). Ph.D. Thesis, Autonomous University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- De Vreese, S.; André, M.; Cozzi, B.; Centelleghe, C.; van der Schaar, M.; Mazzariol, S. Morphological Evidence for the Sensitivity of the Ear Canal of Odontocetes as Shown by Immunohistochemistry and Transmission Electron Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehorek, S.J.; Stimmelmayr, R.; George, J.C.; Suydam, R.; McBurney, D.M.; Thewissen, J. Whale Tear Glands in the Bowhead and the Beluga Whales: Source and Function. J. Morphol. 2020, 281, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.F.; McLellan, W.A.; Rommel, S.A.; Costidis, A.M.; Harms, C.A.; Thewissen, J.G.M.; Rotstein, D.S.; Gay, M.D.; Potter, C.W.; Taylor, A.R.; et al. Gross and Histological Morphology of the Cervical Gill Slit Gland of the Pygmy Sperm Whale (Kogia Breviceps). Anat. Rec. 2021, 305, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berta, A.; Ekdale, E.G.; Zellmer, N.T.; Deméré, T.A.; Kienle, S.S.; Smallcomb, M. Eye, Nose, Hair, and Throat: External Anatomy of the Head of a Neonate Gray Whale (Cetacea, Mysticeti, Eschrichtiidae). Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, N. Functional Morphology and Postnatal Transformation of Vibrissal Crypts in Toothed Whales (Odontoceti). Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Biologie und Biotechnologie der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Czech-Damal, N.U.; Liebschner, A.; Miersch, L.; Klauer, G.; Hanke, F.D.; Marshall, C.; Dehnhardt, G.; Hanke, W. Electroreception in the Guiana Dolphin (Sotalia Guianensis). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerussi, T.; Graïc, J.; De Vreese, S.; Grandis, A.; Tagliavia, C.; De Silva, M.; Huggenberger, S.; Cozzi, B. The Follicle-sinus Complex of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Functional Anatomy and Possible Evolutional Significance of Its Somato-sensory Innervation. J. Anat. 2020, 238, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yablokov, A.V.; Bel’kovich, V.M.; Borisov, V.I. Whales and Dolphins (Translated from Kity I Del’finy, 1972, Acad. Sci. USSR, Nauka, Moscow, Russia, pp. 472); National Technical Information Service, U.S. Department of Commerce: Springfield, VA, USA, 1974; p. 540. [Google Scholar]
- Geraci, J.R.; St Aubin, D.J.; Hicks, B.D. The Epidermis of Odontocetes: A View from Within. In Research on Dolphins; Bryden, M.M., Harrison, R.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lauriano, E.R.; Pergolizzi, S.; Aragona, M.; Spanò, N.; Guerrera, M.C.; Capillo, G.; Faggio, C. Merkel Cells Immunohistochemical Study in Striped Dolphin (Stenella Coeruleoalba) Skin. Tissue Cell 2019, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, S.A.; Mortazavi, F.; Rice, F.L.; Ketten, D.R.; Wiley, D.N.; Lyman, E.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Hanke, F.D.; De Vreese, S.; Strobel, S.M.; et al. Specializations of Somatosensory Innervation in the Skin of Humpback Whales (Megaptera Novaeangliae). Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Shida, T. On the Sensory Tubercles of Lips and of Oral Cavity in the Sei and the Fin Whale. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. 1950, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lillie, M.A.; Vogl, A.W.; Gil, K.N.; Gosline, J.M.; Shadwick, R.E. Two Levels of Waviness Are Necessary to Package the Highly Extensible Nerves in Rorqual Whales. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.B. Tissue Biomechanics: Whales Have Some Nerve. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R177–R179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vogl, A.W.; Lillie, M.A.; Piscitelli, M.A.; Goldbogen, J.A.; Pyenson, N.D.; Shadwick, R.E. Stretchy Nerves Are an Essential Component of the Extreme Feeding Mechanism of Rorqual Whales. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R360–R361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Carder, D.A. Tactile Sensitivity, Somatosensory Responses, Skin Vibrations, and the Skin Surface Ridges of the Bottle-Nose Dolphin, Tursiops Truncatus. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lende, R.A.; Welker, W.I. An Unusual Sensory Area in the Cerebral Neocortex of the Bottlenose Dolphin, Tursiops Truncatus. Brain Res. 1972, 45, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Carder, D.A. Features of Dolphin Skin with Potential Hydrodynamic Importance. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1993, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolchin, S.; Bel’kovich, V. Tactile Sensitivity in Delphinus Delphis. Zool. Zhurnal 1973, 52, 620–622. [Google Scholar]
- Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Oelschläger, J.S. Brain. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 134–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lende, R.A.; Akdikmen, S. Motor Field in Cerebral Cortex of the Bottlenose Dolphin. J. Neurosurg. 1968, 29, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, A. Der Neokortex Der Säugetiere: Evolution Und Funktion. Ph.D. Thesis, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- van Kann, E.; Cozzi, B.; Hof, P.R.; Oelschläger, H.H.A. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Primary Neocortical Areas in Selected Mammals. Brain Behav. Evol. 2017, 90, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, S.; Mortazavi, F.; Rosene, D. The Hydrodynamic Sensory System in the Skin of Cetaceans. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, F.E. The Myth and Reality of Gray’s Paradox: Implication of Dolphin Drag Reduction for Technology. Bioinspir Biomim 2006, 1, R17–R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnhardt, G.; Mauck, B. Mechanoreception in Secondarily Aquatic Vertebrates. In Sensory Evolution on the Threshold: Adaptations in Secondarily Aquatic Vertebrates; Thewissen, J.G.M., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 295–316. ISBN 978-0-520-25278-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wartzok, D.; Ketten, D.R. Marine Mammal Sensory Systems. In Biology of Marine Mammals; Reynolds, J., Rommel, S., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 117–175. [Google Scholar]
- Slijper, E.J. De Verdwaalde Walvissen; Hilversum-den Helder: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1958; p. 524. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, P.W. Hydrodynamics of Dolphin Skin and Other Compliant Surfaces. In WIT Transactions on State of the Art in Science and Engineering; Liebe, R., Ed.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 447–456. ISBN 978-1-84564-095-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright, D.K.; Fish, F.E.; Ingersoll, S.; Williams, T.M.; St Leger, J.; Smits, A.J.; Lauder, G.V. How Smooth Is a Dolphin? The Ridged Skin of Odontocetes. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20190103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzinski, K.M.; Gregg, J.D. Communication. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Kovacs, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 210–215. ISBN 978-0-12-804327-1. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.M.; Norris, K.S. Delphinid Social Organization and Social Behavior. In Dolphin Cognition and Behavior: A Comparative Approach; Schusterman, R.J., Thomas, J.A., Wood, F.G., Eds.; Psychology Press: London, UK, 1986; pp. 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Prahl, S.; Huggenberger, S.; Schliemann, H. Histological and Ultrastructural Aspects of the Nasal Complex in the Harbour Porpoise, Phocoena Phocoena. J. Morphol. 2009, 270, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, E. Anatomical Notes on Pinnipedia and Cetacea. Carnegie Inst. Washington Publ. 1934, 447, 105–136. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, M. Contribution to the Anatomy of the Organ of Hearing of Whales. Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. 1953, 8, 79. [Google Scholar]
- De Vreese, S.; Doom, M.; Haelters, J.; Cornillie, P. Heeft de Uitwendige Gehoorgang van Walvisachtigen Nog Enige Functie? Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschr. 2014, 83, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vreese, S. Morpho-Functionality of the Toothed Whale External Ear Canal. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, J.G.; Fordyce, R.E. The Therian Skull A Lexicon with Emphasis on the Odontocetes. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 2009, 627, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosetto, V.; Damarco, P.; Daniello, R.; Pavia, M.; Carnevale, G.; Bisconti, M. Cranial Material of Long-Snouted Dolphins (Cetacea, Odontoceti, Eurhinodelphinidae) from the Early Miocene of Rosignano Monferrato, Piedmont (NW Italy): Anatomy, Paleoneurology, Phylogenetic Relationships and Paleobiogeography. Diversity 2023, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisconti, M.; Damarco, P.; Tartarelli, G.; Pavia, M.; Carnevale, G. A Natural Endocast of an Early Miocene Odontocete and Its Implications in Cetacean Brain Evolution. J. Comp. Neurol. 2021, 529, 1198–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisconti, M.; Daniello, R.; Damarco, P.; Tartarelli, G.; Pavia, M.; Carnevale, G. High Encephalization in a Fossil Rorqual Illuminates Baleen Whale Brain Evolution. Brain Behav. Evol. 2021, 96, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschmann, M.A. Morphologie des Kopfes beim Schlanken Delphin Stenella attenuata mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Hirnnerven. Makroskopische Präparation und moderne bildgebende Verfahren-Dissertation. Ph.D. Thesis, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Barthelmess, N.G. Topographic Anatomy and Course of Cranial Nerves in the Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus Griseus). Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.K. Vibrissae of Marine Mammals. In Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 3, pp. 387–415. [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg, J.S.; Laitman, J.T. Cetacean Prenatal Development. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Perrin, W.F., Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 220–230. ISBN 978-0-12-373553-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner, T.; Fersen, L.; Miersch, L.; Czech, N.U.; Dehnhardt, G. Behavioral and Anatomical Evidence for Electroreception in the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Anat. Rec. 2021, 305, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnhardt, G.; Hanke, F.D. Whiskers. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 3rd ed.; Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Kovacs, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1074–1077. ISBN 978-0-12-804327-1. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, S.E.; Crish, S.D.; George, J.C.; Stimmelmayr, R.; Thewissen, J.G.M. Sensory Hairs in the Bowhead Whale, Balaena Mysticetus (Cetacea, Mammalia): Sensory Hairs in the Bowhead Whale. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado III, E. Tubercles: What Sense Is There? Aquat. Mamm. 2014, 40, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, C.; Casey, C.; Friedlaender, A. In-Situ Observations of the Sensory Hairs of Antarctic Minke Whales (Balaenoptera Bonaerensis). Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yablokov, A.V.; Klevezal, G.A. Vibrissae of Whales and Seals, Their Distribution, Structure and Significance. In Morphological Features of Aquatic Mammals; Kleynenberg, S.E., Ed.; The Science Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 1969; pp. 48–81. [Google Scholar]
- Mynett, N.; Mossman, H.L.; Huettner, T.; Grant, R.A. Diversity of Vibrissal Follicle Anatomy in Cetaceans. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüttner, T.; von Fersen, L.; Miersch, L.; Dehnhardt, G. Passive Electroreception in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus): Implication for Micro- and Large-Scale Orientation. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb245845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldiman, J.T.; Henk, W.G.; Henry, R.W.; Albert, T.F.; Abdelbaki, Y.Z.; Duffield, D.W. Epidermal and Papillary Dermal Characteristics of the Bowhead Whale (Balaena Mysticetus). Anat. Rec. 1985, 211, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japha, A. Die Haare Der Waltiere. Zool. Jahrbücher. Abt. Für Anat. Und Ontog. Der Tiere 1912, 32, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Shida, T. Sinus-Hairs of the Sei-Whale (Balaenoptera Borealis). Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. 1948, 1, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rochon-Duvigneaud, A.J.F. L’oeil Des Cétacés. Arch. Mus. Hist. Nat. Paris 1940, 16, 57–90. [Google Scholar]
- Giacometti, L. The Skin of the Whale (Balaenoptera Physalus). Anat. Rec. 1967, 159, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, M.A.G.; Dubbeldam, J.L.; Kastelein, R.A. Histology of the Grooved Ventral Pouch of the Minke Whale, Balaenoptera Acutorostrata, with Special Reference to the Occurrence of Lamellated Corpuscles. Can. J. Zool. 1997, 75, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, E.; Fernández, A.; Espinosa de los Monteros, A.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Bernaldo de Quirós, Y.; García-Álvarez, N.; Arbelo, M.; Herráez, P. Comparative Histology of Muscle in Free Ranging Cetaceans: Shallow versus Deep Diving Species. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulsi, R.S. Observations on the Structure of the Dorsal Muscle in the Bottle-Nose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). J. Anat. 1975, 119, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otero-Sabio, C.; Centelleghe, C.; Corain, L.; Graïc, J.-M.; Cozzi, B.; Rivero, M.; Consoli, F.; Peruffo, A. Microscopic Anatomical, Immunohistochemical, and Morphometric Characterization of the Terminal Airways of the Lung in Cetaceans. J. Morphol. 2021, 282, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, B.; Barnagaud, J.-Y.; Verborgh, P.; Gauffier, P.; Campagna, S.; Célérier, A. A Field Study of Chemical Senses in Bottlenose Dolphins and Pilot Whales. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, D.C.; Wang, A.; Nicolas, J.; Pfeiffer, C.J. Lingual Ultrastructure of the Long-Finned Pilot Whale (Globicephala Melas). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2001, 30, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachetti, I.; MacLeod, P. Olfactory Input to the Thalamus: Evidence for a Ventroposteromedial Projection. Brain Res. 1977, 125, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetzov, V.B. Chemical Sense of Dolphins: Quasi-Olfaction. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 481–503. ISBN 978-1-4899-0858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, V.B. Quasi-Olfaction of Dolphins. In Chemical Signals in Vertebrates 6; Doty, R.L., Müller-Schwarze, D., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 543–549. ISBN 978-1-4757-9655-1. [Google Scholar]
- Oelschläger, H.A.; Buhl, E.H. Development and Rudimentation of the Peripheral Olfactory System in the Harbor Porpoise Phocoena Phocoena (Mammalia: Cetacea). J. Morphol. 1985, 184, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschläger, H.H.A.; Kemp, B. Ontogenesis of the Sperm Whale Brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 399, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, A.; Ekdale, E.G.; Cranford, T.W. Review of the Cetacean Nose: Form, Function, and Evolution. Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, J.G.M.; George, J.; Rosa, C.; Kishida, T. Olfaction and Brain Size in the Bowhead Whale (Balaena Mysticetus). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2011, 27, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, S.J.; Geisler, J.; Fitzgerald, E.M.G. On the Olfactory Anatomy in an Archaic Whale (Protocetidae, Cetacea) and the Minke Whale Balaenoptera Acutorostrata (Balaenopteridae, Cetacea). Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnkopf, I.C.; George, J.C.; Kishida, T.; Hillmann, D.J.; Suydam, R.S.; Thewissen, J.G.M. Olfactory Epithelium and Ontogeny of the Nasal Chambers in the Bowhead Whale (Balaena Mysticetus). Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 643–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, A.; Kishida, T.; Nakamura, G. Nasal Mucosa Resembling an Olfactory System in the Common Minke Whale. Cetacean Popul. Stud. CPOPS 2018, 1, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kishida, T.; Thewissen, J.; Hayakawa, T.; Imai, H.; Agata, K. Aquatic Adaptation and the Evolution of Smell and Taste in Whales. Zool. Lett. 2015, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishida, T.; Thewissen, J.G.M.; Usip, S.; Suydam, R.S.; George, J.C. Organization and Distribution of Glomeruli in the Bowhead Whale Olfactory Bulb. PeerJ 2015, 3, e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, B.; Barnagaud, J.-Y.; Poupard, M.; Glotin, H.; Gauffier, P.; Ortiz, S.T.; Lisney, T.J.; Campagna, S.; Rasmussen, M.; Célérier, A. Behavioural Responses of Humpback Whales to Food-Related Chemical Stimuli. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, C.J.; Rogers, T.L.; Shorter, A.; Barton, K.; Miller, P.J.O.; Nowacek, D. Determination of Steroid Hormones in Whale Blow: It Is Possible. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2009, 25, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philström, H. Comparative Anatomy and Physiology of Chemical Senses in Aquatic Mammals. In Sensory Evolution on the Threshold: Adaptations in Secondary Aquatic Vertebrates; Thewissen, J.G.M., Nummela, S., Eds.; University of California Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 95–109. ISBN 978-0-520-25278-3. [Google Scholar]
- Barboza, M.L.B.; Reyno, B. Taste Receptors in Aquatic Mammals: Potential Role of Solitary Chemosensory Cells in Immune Responses. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker’, M.M.; Kirschvink’, J.L.; Ahmed, G.; Dizon’, A.E. Evidence That Fin Whales Respond to the Geomagnetic Field During Migration. J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 171, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.H.; Wilkens, L.A. Magnetoreception. In Sensory Evolution on the Threshold: Adaptations in Secondarily Aquatic Vertebrates; Thewissen, J.G.M., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 317–324. ISBN 978-0-520-25278-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zoeger, J.; Dunn, J.R.; Fuller, M. Magnetic Material in the Head of the Common Pacific Dolphin. Science 1981, 213, 892–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschvink, J.L.; Jones, D.S.; MacFadden, B.J. Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Houser, D.; Finneran, J.; Carder, D.; Keogh, M.; Van Bonn, W.; Smith, C.; Scadeng, M.; Dubowitz, D.; Mattrey, R.; et al. Functional Imaging of Dolphin Brain Metabolism and Blood Flow. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrits, N.M.; Kastelein, R.A. A. A Potential Neural Substrate for Geomagnetic Sensibility in Cetaceans. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 196, pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tuthill, J.C.; Azim, E. Proprioception. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R194–R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.G.; Schloesser, D.; Arensdorf, A.M.; Simmons, J.M.; Cui, C.; Valentino, R.; Gnadt, J.W.; Nielsen, L.; Hillaire-Clarke, C.S.; Spruance, V.; et al. The Emerging Science of Interoception: Sensing, Integrating, Interpreting, and Regulating Signals within the Self. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.N.; Dawson, S.D.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Berta, A. Neuromuscular Anatomy and Evolution of the Cetacean Forelimb. Anat. Rec. 2007, 290, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyenson, N.D.; Goldbogen, J.A.; Vogl, A.W.; Szathmary, G.; Drake, R.L.; Shadwick, R.E. Discovery of a Sensory Organ That Coordinates Lunge Feeding in Rorqual Whales. Nature 2012, 485, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, D.J. The Spinal Nervous System of the Porpoise and Dolphin. J. Anat. Physiol. 1877, 11, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte, H.V.W.; Smith, M.D.F. The External Characters, Skeletal Muscles, and Peripheral Nerves of Kogia Breviceps. Bulletin American Museum of Natural History 1918, 38, 7–72. [Google Scholar]
- Agarkov, G.B.; Veselovsky, M.V. Investigation of the Peripheral Nervous System in Cetaceans. Investig. Cetacea 1987, 20, 192–227. [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen, H.K. Fiber Spectra of Spinal Nerve Roots in Cetacea (Balaenoptera Physalus). J. Comp. Neurol. 1964, 123, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.E. On the Cardiac Nerves of Some Cetacea, with Special Reference to Those of Berardius Bairdii Stejneger. Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo 1952, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fanning, J.C. The Submicroscopic Structure of the Dolphin Lung; University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Dell, L.-A.; Patzke, N.; Bhagwandin, A.; Bux, F.; Fuxe, K.; Barber, G.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization and Number of Orexinergic Neurons in the Hypothalamus of Two Species of Cetartiodactyla: A Comparison of Giraffe (Giraffa Camelopardalis) and Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena Phocoena). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2012, 44, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dell, L.-A.; Karlsson, K.Æ.; Patzke, N.; Spocter, M.A.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization of the Sleep-Related Neural Systems in the Brain of the Minke Whale (Balaenoptera Acutorostrata). J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 2018–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyamin, O.I.; Manger, P.R.; Ridgway, S.H.; Mukhametov, L.M.; Siegel, J.M. Cetacean Sleep: An Unusual Form of Mammalian Sleep. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 1451–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, P.R.; Ridgway, S.H.; Siegel, J.M. The Locus Coeruleus Complex of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus) as Revealed by Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunohistochemistry. J. Sleep Res. 2003, 12, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, P.R.; Fuxe, K.; Ridgway, S.H.; Siegel, J.M. The Distribution and Morphological Characteristics of Catecholaminergic Cells in the Diencephalon and Midbrain of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Brain Behav. Evol. 2004, 64, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhaas, R.; Chung, S. Role of the Preoptic Area in Sleep and Thermoregulation. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 664781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillie, M.A.; Vogl, A.W.; Gerard, S.G.; Raverty, S.; Shadwick, R.E. Retia Mirabilia: Protecting the Cetacean Brain from Locomotion-Generated Blood Pressure Pulses. Science 2022, 377, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgane, P.J.; Jacobs, M.S.; McFarland, W.L. The Anatomy of the Brain of the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Surface Configurations of the Telencephalon of the Bottlenose Dolphin with Comparative Anatomical Observations in Four Other Cetacean Species. Brain Res. Bull. 1980, 5, 1–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Koester, J.D.; Mack, S.H.; Siegelbaum, S.A. Principles of Neural Science, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garey, L.J.; Revishchin, A.V. Structure and Thalamocortical Relations of the Cetacean Sensory Cortex: Histological, Tracer and Immunocytochemical Studies. In Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans; Thomas, J.A., Kastelein, R.A., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 196. [Google Scholar]
- Morgane, P.T.; Glezer, I.I.; Thomas, J.A.; Kastelein, R.A. Sensory Neocortex in Dolphin Brain. In Sensory Abilities of Cetceans; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 196. [Google Scholar]
- Kot, B.C.W.; Tsui, H.C.L.; Chung, T.Y.T.; Lau, A.P.Y. Postmortem Neuroimaging of Cetacean Brains Using Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 544037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtfeger, W.K.; Oelschläger, H.A.; Stephan, H. Quantitative Neuroanatomy of the Brain of the La Plata Dolphin, Pontoporia Blainvillei. Anat. Embryol. 1984, 170, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Jeong, B.; Polcari, A.; Rohan, M.L.; Teicher, M.H. Reduced Fractional Anisotropy in the Visual Limbic Pathway of Young Adults Witnessing Domestic Violence in Childhood. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latini, F. New Insights in the Limbic Modulation of Visual Inputs: The Role of the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus and the Li-Am Bundle. Neurosurg. Rev. 2015, 38, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F.C.; Koch, C. What Is the Function of the Claustrum? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirone, A.; Graïc, J.-M.; Grisan, E.; Cozzi, B. The Claustrum of the Sheep and Its Connections to the Visual Cortex. J. Anat. 2021, 238, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, B.; Roncon, G.; Granato, A.; Giurisato, M.; Castagna, M.; Peruffo, A.; Panin, M.; Ballarin, C.; Montelli, S.; Pirone, A. The Claustrum of the Bottlenose Dolphin Tursiops Truncatus (Montagu 1821). Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Brownson, R.H. Relative Brain Sizes and Cortical Surface Areas in Odontocetes. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1984, 172, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Delfour, F.; Marten, K. Lateralized Visual Behavior in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus) Performing Audio–Visual Tasks: The Right Visual Field Advantage. Behav. Process. 2006, 71, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, S.H. Physiological Observations on Dolphin Brains. Dolphin Cogn. Behav. 2013, 44–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Fersen, L.; Schall, U.; Güntürkün, O. Visual Lateralization of Pattern Discrimination in the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops Truncatus). Behav. Brain Res. 2000, 107, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, J.G.M.; Nummela, S. (Eds.) Sensory Evolution on the Threshold: Adaptations in Secondarily Aquatic Vertebrates, 1st ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-520-25278-3. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, L.G. A Sense of Scale: Foraging Cetaceans’ Use of Scale-Dependent Multimodal Sensory Systems. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2017, 33, 1170–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, J.N.; Pack, A.A. Understanding across the Senses: Cross-Modal Studies of Cognition in Cetaceans. Anim. Cogn. 2022, 25, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pack, A.A.; Herman, L.M. Sensory Integration in the Bottlenosed Dolphin: Immediate Recognition of Complex Shapes across the Senses of Echolocation and Vision. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominoni, D.M.; Halfwerk, W.; Baird, E.; Buxton, R.T.; Fernández-Juricic, E.; Fristrup, K.M.; McKenna, M.F.; Mennitt, D.J.; Perkin, E.K.; Seymoure, B.M.; et al. Why Conservation Biology Can Benefit from Sensory Ecology. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Vreese, S.; Orekhova, K.; Morell, M.; Gerussi, T.; Graïc, J.-M. Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems. Animals 2024, 14, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010066
De Vreese S, Orekhova K, Morell M, Gerussi T, Graïc J-M. Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems. Animals. 2024; 14(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Vreese, Steffen, Ksenia Orekhova, Maria Morell, Tommaso Gerussi, and Jean-Marie Graïc. 2024. "Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems" Animals 14, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010066
APA StyleDe Vreese, S., Orekhova, K., Morell, M., Gerussi, T., & Graïc, J.-M. (2024). Neuroanatomy of the Cetacean Sensory Systems. Animals, 14(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14010066







