Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Relatedness, and Safety Assessment of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) Used as Live Feed in Fish Larviculture
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation, Sampling, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Direct Antimicrobial Activity
2.3. Taxonomic Identification of Selected Isolates
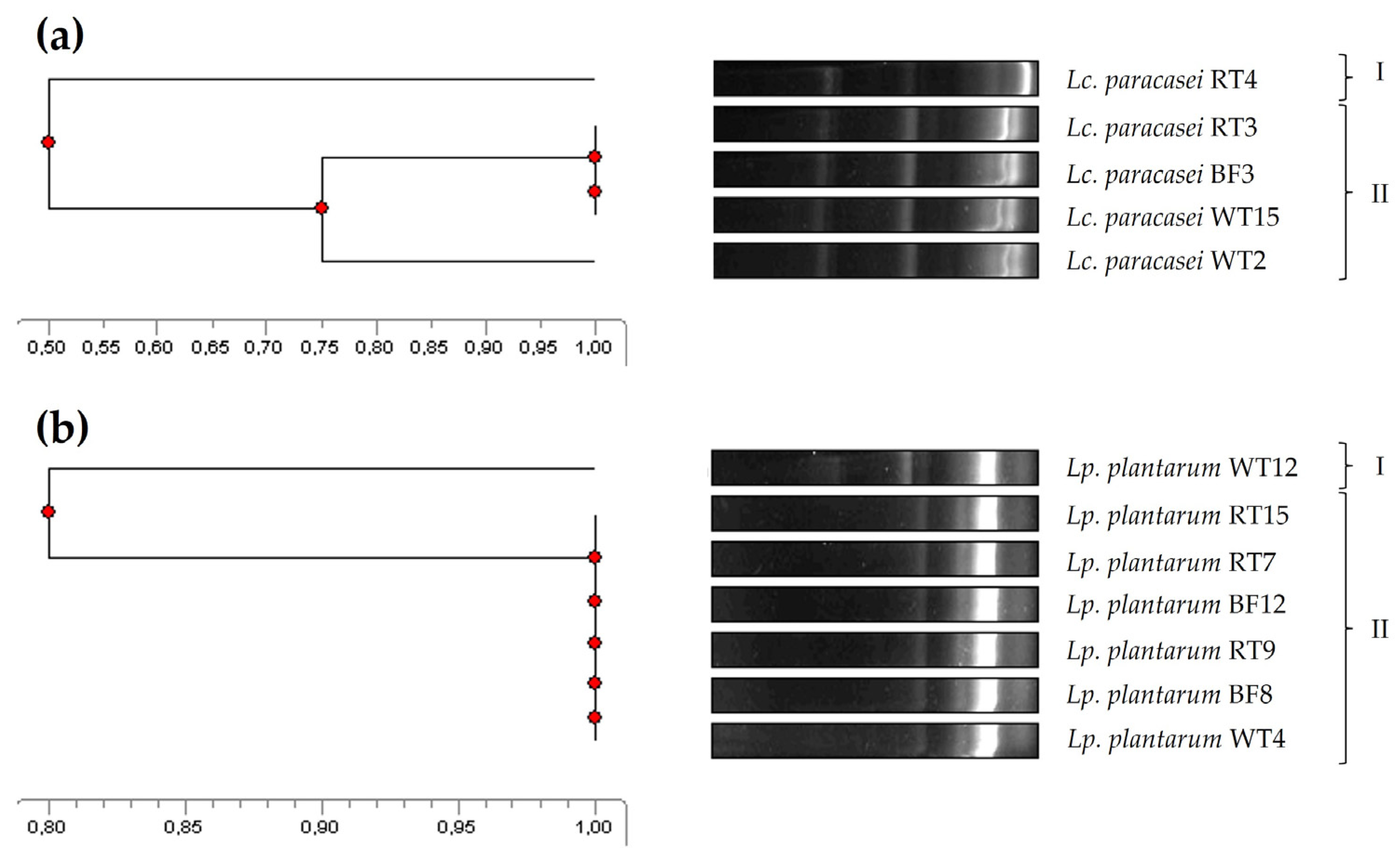
2.4. Molecular Typing and Genetic Relatedness: Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus-PCR (ERIC-PCR)
2.5. In Vitro Safety Assessment
2.5.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.5.2. Hemolytic and Gelatinase Activities
2.5.3. Bile Salt Deconjugation
2.5.4. Mucin Degradation
2.5.5. Biogenic Amine Production PCR-Detection
2.6. Biofilm Formation Assays
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity, Taxonomic Identification, and Molecular Typing of Five Lacticaseibacillus Paracasei and Seven Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Isolates
3.2. In Vitro Safety Assessment of the Four Selected LAB Strains
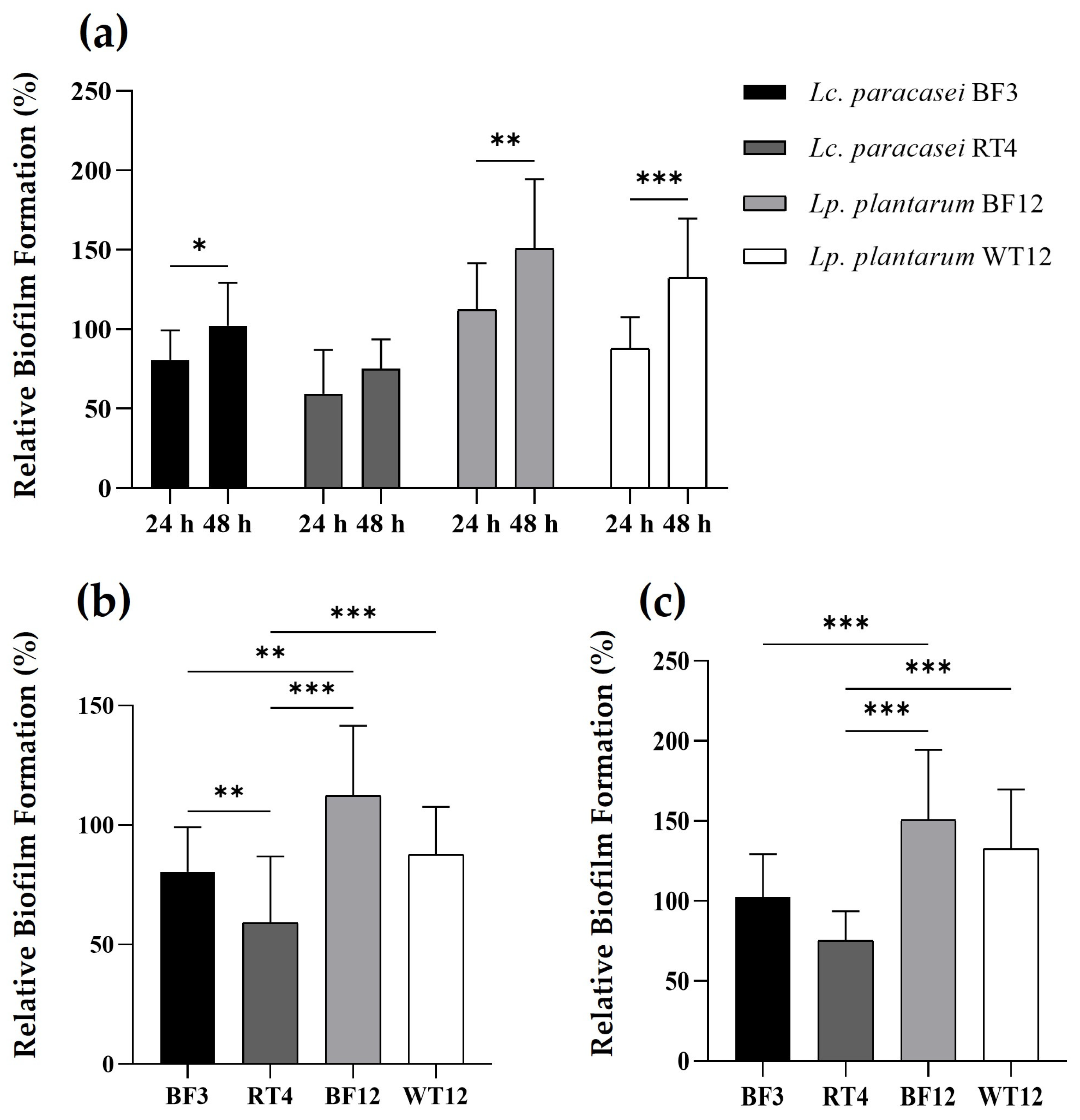
3.3. Biofilm Formation by the Four Selected LAB Strains
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmann, K.K.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Melchiorsen, J.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, B. Changes in microbiome of mariculture feed organisms after treatment with a potentially probiotic strain of Phaeobacter inhibens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00499-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makridis, P.; Fjellheim, A.J.; Skjermo, J.; Vadstein, O. Colonization of the gut in first feeding turbot by bacterial strains added to the water or bioencapsulated in rotifers. Aquac. Int. 2000, 8, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, M.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Hjelm, M.; Gram, L.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Bergh, Ø.; Pintado, J. Probiotic effect in vivo of Roseobacter strain 27-4 against Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum infections in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) larvae. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Schryver, P.; Vadstein, O. Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenschein, E.C.; Jimenez, G.; Castex, M.; Gram, L. The Roseobacter-group bacterium Phaeobacter as a safe probiotic solution for aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02581-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjermo, J.; Vadstein, O. Techniques for the microbial control in the intensive rearing of marine larvae. Aquaculture 1999, 177, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T. Ozonation and UV irradiation—and introduction and examples of current applications. Aquac. Eng. 2003, 28, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, K.K.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Castex, M.; Gram, L.; Bentzon-Tilia, M. The aquaculture microbiome at the center of business creation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, lactic acid bacteria and bacilli: Interesting supplementation for aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, J.; Contente, D.; Ponce-Alonso, M.; Díaz-Formoso, L.; Araújo, C.; Peña, N.; Borrero, J.; Gómez-Sala, B.; del Campo, R.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; et al. Draft genome sequence of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris WA2-67: A promising nisin-producing probiotic strain isolated from the rearing environment of a Spanish rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) farm. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contente, D.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Feito, J.; Díaz-Formoso, L.; Docando, F.; Simón, R.; Borrero, J.; Hernández, P.E.; Poeta, P.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of bacteriocinogenic and non-bacteriocinogenic Lactococcus cremoris of aquatic origin on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, D.; Bradley, G.; Harper, G.M.; Baker, R.T.M.; Munn, C.B.; Davies, S.J. Assessment of the effects of vegetative and lyophilized Pediococcus acidilactici on growth, feed utilization, intestinal colonization and health parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac. Nutr. 2010, 17, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; de Blas, I.; Balcázar, J.L. Probiotics in aquaculture: A current assessment. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, S.; Skírnisdóttir, S.; Dubois, M.; Kolypczuk, L.; Leroi, F.; Leeper, A.; Passerini, D.; Marteinsson, V.Þ. Impact of putative probiotics on growth, behavior, and the gut microbiome of farmed arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 912473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Li, X.; van Doan, H.; Ghosh, K. Interesting probiotic bacteria other than the more widely used lactic acid bacteria and bacilli in finfish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 848037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Løvmo, L.; Kristiansen, M.; Bakken, Y.; Salinas, I.; Myklebust, R.; Olsen, R.E.; Mayhew, T.M. Lactic acid bacteria vs. pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract of fish: A review. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Nahuelquín, Y.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Inhibition of fish pathogens by the microbiota from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Ramírez, M.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Safety assessment, genetic relatedness and bacteriocin activity of potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis strains from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. Eur. Food. Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, T. Enrichment of rotifers and its effect on growth and survival of fish larvae. In Rotifers, Fisheries Science Series; Hagiwara, A., Yoshinaga, T., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2017; pp. 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Samat, N.A.; Yusoff, F.M.; Rasdi, N.W.; Karim, M. Enhancement of live food nutritional status with essential nutrients for improving aquatic animal health: A review. Animals 2020, 10, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.; Woolley, L.; Partridge, G.; Chen, M.; Haney, E.F.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Buller, N.; Currie, A. Assessing the activity of antimicrobial peptides against common marine bacteria located in rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis) cultures. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatesoupe, F.J. The effect of three strains of lactic acid bacteria on the production rate of rotifers, Brachionus plicatilis, and their dietary value for larval turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Aquaculture 1991, 96, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vine, N.G.; Leukes, W.D.; Kaiser, H. Probiotics in marine larviculture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 404–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, C.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.; Rodríguez, C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; de la Banda, I.G. Dietary probiotic supplementation (Shewanella putrefaciens Pdp11) modulates gut microbiota and promotes growth and condition in Senegalese sole larviculture. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintas, L.M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, M.F.; Sletten, K.; Nes, I.F.; Hernández, P.E.; Holo, H. Isolation and characterization of pediocin L50, a new bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici with a broad inhibitory spectrum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullen, M.J.; Sanozky-Dawes, R.B.; Crowell, D.C.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Use of the DNA sequence of variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene for rapid and accurate identification of bacteria in the Lactobacillus acidophilus complex. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klare, I.; Konstabel, C.; Müller-Bertling, S.; Reissbrodt, R.; Huys, G.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Goossens, H.; Witte, W. Evaluation of new broth media for microdilution antibiotic susceptibility testing of Lactobacilli, Pediococci, Lactococci, and Bifidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8982–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FEEDAP. Guidance on the characterization of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05206. [Google Scholar]
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rheman, S.; Debnath, N.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Islam, K.; Islam, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; et al. Antibiotics usage practices in aquaculture in Bangladesh and their associate factors. One Health 2022, 15, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Reviews of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, T.J.; Gasson, M.J. Molecular screening of Enterococcus virulence determinants and potential for genetic exchange between food and medical isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Araújo, C.; Campanero, C.; del Campo, R.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial activity, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence factors of Lactic Acid Bacteria of aquatic origin intended for use as probiotics in aquaculture. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, L.; Cuevas, I.; Margolles, A.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Deconjugation and bile salts hydrolase activity by Bifidobacterium strains with acquired resistance to bile. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.S.; Gopal, P.K.; Gill, H.S. Potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus (HN001), Lactobacillus acidophilus (HN017) and Bifidobacterium lactis (HN019) do not degrade gastric mucin in vitro. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 63, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Jeune, C.; Lonvaud-Funel, A.; ten Brink, B.; Hofstra, H.; van der Vossen, J.M. Development of a detection system for histidine decarboxylating lactic acid bacteria based on DNA probes, PCR and activity test. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 78, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coton, M.; Coton, E.; Lucas, P.; Lonvaud, A. Identification of the gene encoding a putative tyrosine decarboxylase of Carnobacterium divergens 508. Development of molecular tools for the detection of tyramine-producing bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, Á.; de las Rivas, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Muñoz, R. Multiplex PCR method for the simultaneous detection of histamine-, tyramine-, and putrescine-producing Lactic acid bacteria in foods. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, J.; Araújo, C.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Contente, D.; Campanero, C.; Arbulu, S.; Saralegui, C.; Peña, N.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Borrero, J.; et al. Antimicrobial activity, molecular typing and in vitro safety assessment of Lactococcus garvieae isolates from healthy cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum) and rearing environment. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 162, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Correia, E.; Pereira, J.E.; González-Machado, C.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus from pets, livestock, and wild animals: Relationship with clonal lineages and antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, E.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Comparison of multiple methods for quantification of microbial biofilms grown in microtiter plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscelli, G.A.; Bermúdez, R.; Losada, A.P.; Faílde, L.D.; Santos, Y.; Quiroga, M.I. Acute Aeromonas salmonicida infection in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies. Aquaculture 2014, 430, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Cong, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Control of Edwardsiella tarda infection in turbot Scophthalmus maximus (L.) using phage vB_EtaM_ET-ABTNL-9. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3010–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dong, X.; Hu, G. Transcriptome analysis of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) head kidney and liver reveals immune mechanism in response to Vibrio anguillarum infection. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Mo, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Zhu, M.; Li, J. Isolation, identification and vaccine development of serotype III Streptococcus parauberis in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) in China. Aquaculture 2021, 538, 736525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruparelia, J.P.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Duttagupta, S.P.; Mukherji, S. Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, B.L.; Bansal, G.; Hewlett, K.H.; Arora, A.; Schaffer, S.D.; Kamau, E.; Bennett, J.W.; Merrell, D.S. Antimicrobial activity of clinically isolated bacterial species against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Araújo, C.; del Campo, R.; Hernández, P.E.; Herranz, C.; Cintas, L.M. Safety assessment and molecular genetic profiling by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and PCR-based techniques of Enterococcus faecium strains of food origin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, R.; Docando, F.; Nuñez-Ortiz, N.; Tafalla, C.; Díaz-Rosales, P. Mechanisms used by probiotics to confer pathogen resistance to teleost fish. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 653025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Fotedar, R.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Tay, A. Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. plantarum improve health status, modulate gut microbiota and innate immune response of marron (Cherax cainii). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.A.; Tyagi, A.; Khairnar, S.O. Oral feed-based administration of Lactobacillus plantarum enhances growth, haematological and immunological responses in Cyprinus carpio. Emerg. Anim. Species 2022, 3, 100003. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Xue, R.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z. Effects of the exopolysaccharide from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HMX2 on the growth performance, immune response, and intestinal microbiota of juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Foods 2023, 12, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Albanese, G.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Lombardi, S.J.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E. Probiotic potentiality from versatile Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains as resource to enhance freshwater fish health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.-H.; Liang, M.; Yang, Y.-H.; Xue, J.; Suo, H.-Y. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum SHY21-2 protected zebrafish against Aeromonas hydrophila infection by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative stress responses, and regulating intestinal microbiome. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongnum, K.; Hongpattarakere, T. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from digestive tract of wild shrimp on growth and survival of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doan, H.; Lumsangkul, C.; Jaturasitha, S.; Meidong, R.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dawood, M.A.O. Modulation of growth, skin mucus and serum immunities, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia fed host-associated probiotic (Lactobacillus paracasei l61-27b). Aquac Nutr 2022, 27, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-T.; Hu, Y.-F.; Lee, B.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-R.; Huang, S.-N.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chang, J.-J.; Nan, F.-H. Dietary of Lactobacillus paracasei and Bifidobacterium longum improve nonspecific immune responses, growth performance, and resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Penaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Xing, Y.; Gao, J.; Jin, R.; Lin, R.; Weng, W.; Xie, Y.; Aweya, J.J. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei fermentation broth identified peptide, Y2Fr, and its antibacterial activity on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 182, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, J.; Vukotic, G.; Stanisavljevic, N.; Kosanovic, D.; Molnar, Z.; Begovic, J.; Terzic-Vidojevic, A.; Jeney, G.; Ljubobratovic, U. Solid state treatment with Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei BGHN14 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus BGT10 improves nutrient bioavailability in granular fish feed. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, M.; Altinok, I.; Capkin, E. Comparison of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus PCR and biochemical tests to characterize Lactococcus garvieae. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 38, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, L.; Rombaut, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W. Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenyogbe, E. Application of probiotics for sustainable and environment-friendly aquaculture management—A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Fu, B.; Mu, X. Improvement of aquaculture water quality by mixed Bacillus and its effects on microbial community structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69731–69742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Update of the list of qualified presumption of safety (QPS) recommended microbiological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 18: Suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2023. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08092. [Google Scholar]
- Muziasari, W.I.; Pärnänen, K.; Johnson, T.A.; Lyra, C.; Karkman, A.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Tamminen, M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Virta, M. Aquaculture changes the profile of antibiotic resistance and mobile genetic element associated genes in Baltic Sea sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastauskienė, E.; Valskys, V.; Stankevičiūtė, J.; Kalcienė, V.; Gėgžna, V.; Kavoliūnas, J.; Ružauskas, M.; Armalytė, J. The impact of intensive fish farming on pond sediment microbiome and antibiotic resistance gene composition. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 673756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, H.; Kannimuthu, D. Comparative resistome analysis of Aeromonas species in aquaculture reveals antibiotic resistance patterns and phylogeographic distribution. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogrovejo, D.C.; Perini, L.; Gostinčar, C.; Sepčić, K.; Turk, M.; Ambrožič-Avguštin, J.; Brill, F.H.H.; Gunder-Cimerman, N. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance and hemolytic phenotypes in culturable arctic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 00570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurlow, L.R.; Thomas, V.C.; Narayanan, S.; Olson, S.; Fleming, S.D.; Hancock, L.E. Gelatinase contributes to the pathogenesis of endocarditis caused by Enterococcus faecalis. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4936–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biji, K.B.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Mohan, C.O.; Gopal, T.K.S. Biogenic amines in seafood: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Sadiq, F.A.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, G.; Sang, Y. Biofilm-based delivery approaches and specific enrichment strategies of probiotics in the human gut. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2126274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzabekyan, S.; Harutyunyan, N.; Manvelyan, A.; Malkhasyan, L.; Balayan, M.; Miralimova, S.; Chikindas, M.L.; Chistyakov, V.; Pepoyan, A. Fish probiotics: Cell surface properties of fish intestinal Lactobacilli and Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, N.C.; Ramiro, J.M.P.; Quecan, B.X.V.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G. Use of potential probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) biofilms for the control of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella typhimurium, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilms formation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 00863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Jara, M.J.; Ilabaca, A.; Vega, M.; García, A. Biofilm forming Lactobacillus: New challenges for the development of probiotics. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Azzaz, J.; Al Tarraf, A.; Heumann, A.; Barreira, D.S.; Laurent, J.; Assifaoui, A.; Rieu, A.; Guzzo, J.; Lapaquette, P. Resveratrol favors adhesion and biofilm formation of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei Strain ATCC334. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.; Garcia, J.G.; Williams, R.; Elmassry, M.; West, A.; Hamood, A.; Hurtado, D.; Gudenkauf, B.; Ventolini, G.; Schlabritz-Loutsevich, N. Lactobacilli spp.: Real-time evaluation of biofilm growth. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z.; Khanzadi, S.; Salari, A. Biofilm formation and antagonistic activity of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (PTCC1712) and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (PTCC1745). AMB Expr. 2021, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
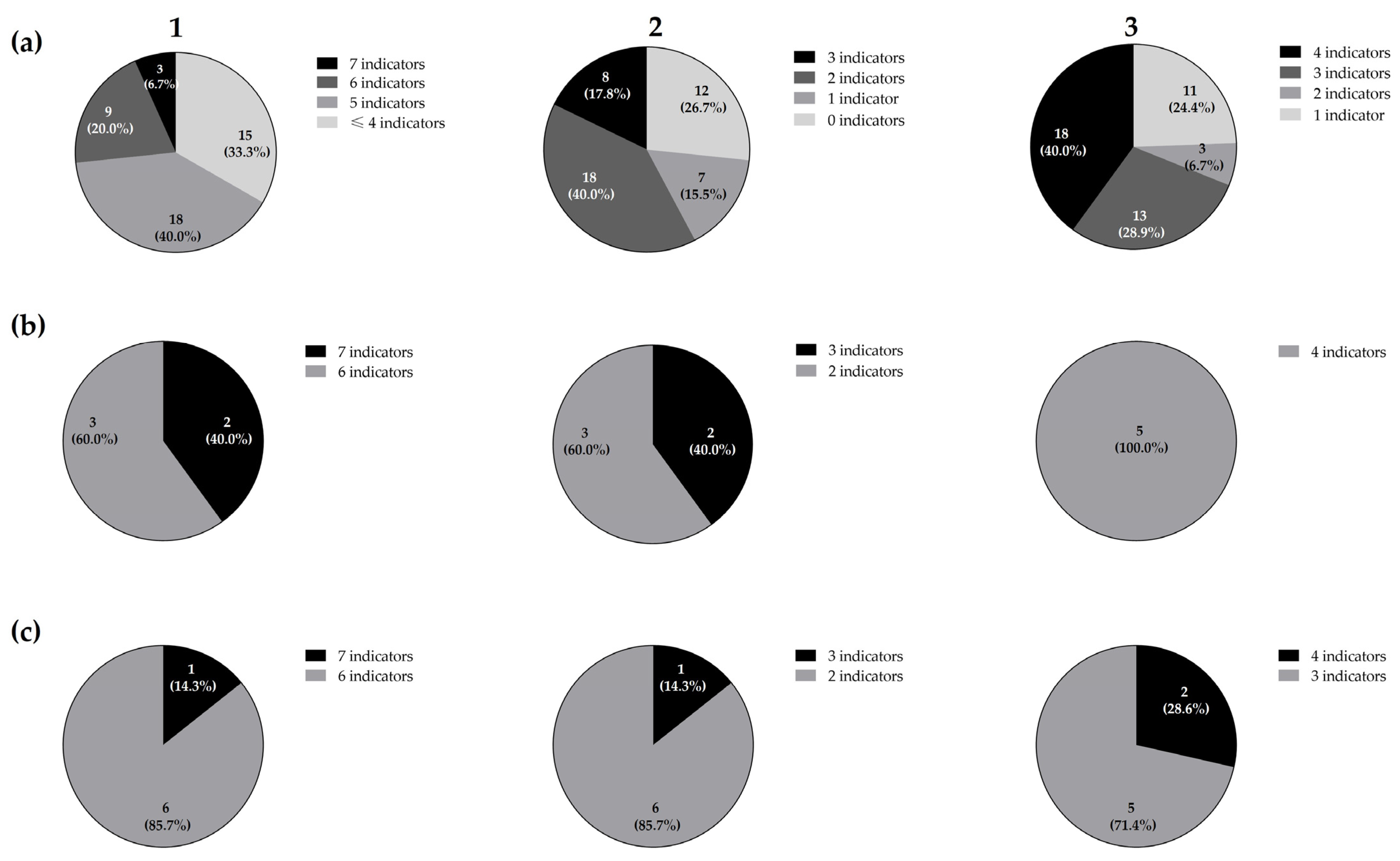
| Isolates | Indicator Micro-Organisms | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. hydrophila CECT839 | A. hydrophila CECT5734 | A. salmonicida CECT4237 | A. salmonicida CECT894 | A. salmonicida CLFP23 | E. tarda CECT886 | V. anguillarum CECT4344 | Y. ruckeri LMG3279 | L. garvieae CF00021 | L. garvieae CLG4 | St. parauberis LMG225 | |
| Biofilm (BF) | |||||||||||
| BF1 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF2 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF3 | - | - | + | - | + | + | +++ | - | + | + | ++ |
| BF4 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF5 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF6 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF7 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF8 | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | ++ | + | + |
| BF9 | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| BF10 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF11 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF12 | - | - | + | - | +++ | + | +++ | - | - | + | ++ |
| BF13 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| BF14 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BF15 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + |
| Tank water with rotifers (RT) | |||||||||||
| RT1 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | - |
| RT2 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| RT3 | - | - | + | - | + | + | ++ | - | - | ++ | + |
| RT4 | - | - | + | - | +++ | + | ++ | - | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| RT5 | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + |
| RT6 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RT7 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + |
| RT8 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | - |
| RT9 | - | - | + | - | ++ | - | + | - | + | + | + |
| RT10 | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RT11 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| RT12 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| RT13 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| RT14 | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | - |
| RT15 | - | - | + | - | ++ | - | + | - | + | ++ | + |
| Tank water without rotifers (WT) | |||||||||||
| WT1 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT2 | - | - | + | - | + | + | ++ | - | - | ++ | + |
| WT3 | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| WT4 | - | - | + | - | - | + | ++ | - | + | ++ | + |
| WT5 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT6 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT7 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT8 | - | - | + | - | + | + | ++ | - | - | ++ | - |
| WT9 | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| WT10 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT11 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT12 | - | - | + | - | +++ | ++ | ++ | - | + | ++ | ++ |
| WT13 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT14 | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - |
| WT15 | - | - | + | - | ++ | + | ++ | - | - | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contente, D.; Díaz-Formoso, L.; Feito, J.; Gómez-Sala, B.; Costas, D.; Hernández, P.E.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Borrero, J.; Poeta, P.; Cintas, L.M. Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Relatedness, and Safety Assessment of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) Used as Live Feed in Fish Larviculture. Animals 2024, 14, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101415
Contente D, Díaz-Formoso L, Feito J, Gómez-Sala B, Costas D, Hernández PE, Muñoz-Atienza E, Borrero J, Poeta P, Cintas LM. Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Relatedness, and Safety Assessment of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) Used as Live Feed in Fish Larviculture. Animals. 2024; 14(10):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101415
Chicago/Turabian StyleContente, Diogo, Lara Díaz-Formoso, Javier Feito, Beatriz Gómez-Sala, Damián Costas, Pablo E. Hernández, Estefanía Muñoz-Atienza, Juan Borrero, Patrícia Poeta, and Luis M. Cintas. 2024. "Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Relatedness, and Safety Assessment of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) Used as Live Feed in Fish Larviculture" Animals 14, no. 10: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101415
APA StyleContente, D., Díaz-Formoso, L., Feito, J., Gómez-Sala, B., Costas, D., Hernández, P. E., Muñoz-Atienza, E., Borrero, J., Poeta, P., & Cintas, L. M. (2024). Antimicrobial Activity, Genetic Relatedness, and Safety Assessment of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Rearing Tank of Rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) Used as Live Feed in Fish Larviculture. Animals, 14(10), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14101415









