Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Microbial Hazards
2.2. Nonmicrobial Hazards
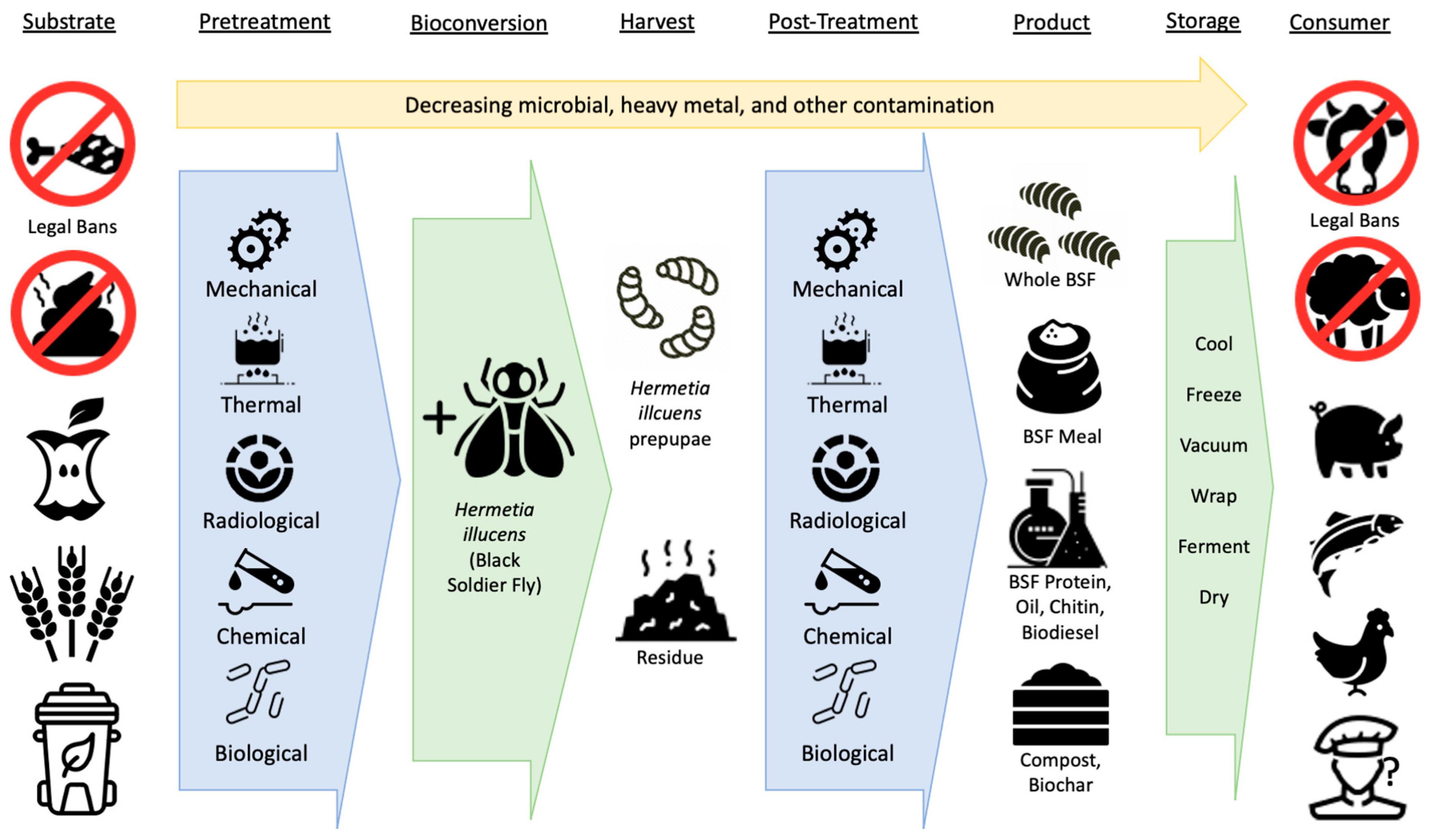
3. Pretreatment of Substrate before Bioconversion
4. Post-Treatment of Larvae after Bioconversion
5. Legal Restrictions on BSFL Bioconversion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PhI, C.P.V.; Walraven, M.; Bézagu, M.; Lefranc, M.; Ray, C. Industrial Symbiosis in Insect Production—A Sustainable Eco-Efficient and Circular Business Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowles, T.M.; Nansen, C. Insect-Based Bioconversion: Value from Food Waste. In Food Waste Management: Solving the Wicked Problem; Närvänen, E., Mesiranta, N., Mattila, M., Heikkinen, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 321–346. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as animal feed and human food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, S.; Bußler, S.; Schlüter, O.K. Food waste valorisation and circular economy concepts in insect production and processing. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.G.; Yong, J.W.H.; Lalander, C. Frass derived from black soldier fly larvae treatment of biodegradable wastes. A critical review and future perspectives. Waste Manag. 2022, 142, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, L.W.; Pieterse, E.; Marais, J.; Dhanani, K.; Hoffman, L.C. Food Safety of Consuming Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: Microbial, Heavy Metal and Cross-Reactive Allergen Risks. Foods 2021, 10, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.; Senecal, J.; Gros Calvo, M.; Ahrens, L.; Josefsson, S.; Wiberg, K.; Vinnerås, B. Fate of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in fly larvae composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulak, P.; Polakowski, C.; Nowak, K.; Waśko, A.; Wiącek, D.; Bieganowski, A. Hermetia illucens as a new and promising species for use in entomoremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Med. Writ. 2015, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.T.; Denniss, A.R. An Introduction to Writing Narrative and Systematic Reviews—Tasks, Tips and Traps for Aspiring Authors. Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Thorne, S.; Malterud, K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Pitsouni, E.I.; Malietzis, G.A.; Pappas, G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhera, J. Narrative Reviews in Medical Education: Key Steps for Researchers. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, L.; Lecocq, A.; Jensen, A.B.; Haenen, O.; Schmitt, E.; Eilenberg, J. Review of insect pathogen risks for the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) and guidelines for reliable production. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 168, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Xiao, Q.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wu, C.; Huang, F.; Cai, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; ur Rehman, K.; et al. Isolated and identified pathogenic bacteria from black soldier fly larvae with “soft rot” reared in mass production facilities and its incidence characteristics. Waste Manag. 2023, 163, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, D.; Montali, A.; Mastore, M.; Brivio, M.F.; Mohamed, A.; Tian, L.; Grimaldi, A.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G. Insights Into the Immune Response of the Black Soldier Fly Larvae to Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Ge, C.; Yao, H. Antimicrobial Peptides from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Potential Antimicrobial Factors Representing an Alternative to Antibiotics in Livestock Farming. Animals 2021, 11, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Caccia, S.; Sgambetterra, G.; Cappellozza, S.; Jucker, C.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M. Structural and Functional Characterization of Hermetia illucens Larval Midgut. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of biowaste macronutrients, microbes, and chemicals in black soldier fly larval treatment: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretta, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Di Somma, A.; Vogel, H.; Pucci, P.; Sgambato, A.; Wolff, M.; Falabella, P. A bioinformatic study of antimicrobial peptides identified in the Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, M.; Shah, P.N.; Voulgari-Kokota, A.; Maistrou, S.; Aartsma, Y.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Salles, J.F.; Loon, J.J.A.V.; Dicke, M.; Wertheim, B. Health of the black soldier fly and house fly under mass-rearing conditions: Innate immunity and the role of the microbiome. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 857–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xie, P.; Ding, Z.; Niu, G.; Wen, T.; Gu, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, W.; Zeng, J.; et al. Inhibition of pathogenic microorganisms in solid organic waste via black soldier fly larvae-mediated management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhag, O.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Jordan, H.R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Inhibition of Zoonotic Pathogens Naturally Found in Pig Manure by Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Their Intestine Bacteria. Insects 2022, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.H.; Diener, S.; Magri, M.E.; Zurbrugg, C.; Lindstrom, A.; Vinneras, B. Faecal sludge management with the larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—from a hygiene aspect. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Islam, M.; Sheppard, C.; Liao, J.; Doyle, M.P. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in chicken manure by larvae of the black soldier fly. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Brady, J.A.; Sanford, M.R.; Yu, Z.N. Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Reduce Escherichia coli in Dairy Manure. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrens, E.; Looveren, N.V.; Moll, L.V.; Vandeweyer, D.; Lachi, D.; Smet, J.D.; Campenhout, L.V. Staphylococcus aureus in Substrates for Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Its Dynamics during Rearing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e02183-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Liu, T.; Awasthi, S.K.; Duan, Y.; Pandey, A.; Zhang, Z. Manure pretreatments with black soldier fly Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae): A study to reduce pathogen content. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Klammsteiner, T.; Dregulo, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. Black soldier fly larvae for organic manure recycling and its potential for a circular bioeconomy: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.G.; Lalander, C.; Vidotti, R.M.; Vinnerås, B. Reduction of Bacteria in Relation to Feeding Regimes When Treating Aquaculture Waste in Fly Larvae Composting. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 545258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Elhag, O.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Jordan, H.R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Sze, S.-H.; Yu, Z.; et al. Hermetia illucens L. larvae–associated intestinal microbes reduce the transmission risk of zoonotic pathogens in pig manure. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, J.; Vandeweyer, D.; Van Moll, L.; Lachi, D.; Van Campenhout, L. Dynamics of Salmonella inoculated during rearing of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Wiedmer, S.; Kurth, M. Risk Evaluation of Passive Transmission of Animal Parasites by Feeding of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Prepupae. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiri, M.; Marin, C.; Garzón, R.; Rosell, C.M.; Rodrigo, D.; Martínez, A. Use of high hydrostatic pressure to inactivate natural contaminating microorganisms and inoculated E. coli O157:H7 on Hermetia illucens larvae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Roncolini, A.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Aquilanti, L.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Jamshidi, E.; et al. Microbial dynamics in rearing trials of Hermetia illucens larvae fed coffee silverskin and microalgae. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Crauwels, S.; Verreth, C.; De Smet, J.; Sandrock, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Van Schelt, J.; Depraetere, S.; Lievens, B. Assessing the microbiota of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) reared on organic waste streams on four different locations at laboratory and large scale. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecocq, A.; Olesen, A.S.; Lazov, C.M.; Rajiuddin, S.M.; Jensen, A.B.; Lohse, L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A. Bioexposure assays to assess uptake and survival of viruses in mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) and black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, A.S.; Lazov, C.M.; Lecocq, A.; Accensi, F.; Jensen, A.B.; Lohse, L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A. Uptake and Survival of African Swine Fever Virus in Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) and Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Pathogens 2023, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Vecherskii, M.V.; Khayrullin, D.R.; Stepankov, A.A.; Maximova, I.A.; Kachalkin, A.V.; Ushakova, N.A. Dramatic effect of black soldier fly larvae on fungal community in a compost. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, P.; Man, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X. Appressoria Formation in Phytopathogenic Fungi Suppressed by Antimicrobial Peptides and Hybrid Peptides from Black Soldier Flies. Genes 2023, 14, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinneras, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokwaro, R.; Semiyaga, S.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Nakagiri, A.; Sempewo, J.I.; Muoghalu, C.C.; Manga, M. Application of black soldier fly larvae in decentralized treatment of faecal sludge from pit latrines in informal settlements in Kampala city. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1118635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.B.; Lecocq, A. Diseases of black soldier flies Hermetia illucens L. a future challenge for production? J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Camenzuli, L.; van der Lee, M.K.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. Uptake of Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic by Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens from Contaminated Substrates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; Belghit, I.; Johansen, J.; Leushuis, R.; Lock, E.-J.; Melsen, D.; Kathirampatti Ramasamy Shanmugam, R.; Van Loon, J.; Paul, A. Growth and Safety Assessment of Feed Streams for Black Soldier Fly Larvae: A Case Study with Aquaculture Sludge. Animals 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fels-Klerx, H.J.v.d.; Meijer, N.; Nijkamp, M.M.; Schmitt, E.; Loon, J.J.A.v. Chemical food safety of using former foodstuffs for rearing black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for feed and food use. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, C.; Annibaldi, A.; Girolametti, F.; Giovannini, L.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Olivotto, I.; Illuminati, S. A Chemically Safe Way to Produce Insect Biomass for Possible Application in Feed and Food Production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purschke, B.; Scheibelberger, R.; Axmann, S.; Adler, A.; Jager, H. Impact of substrate contamination with mycotoxins, heavy metals and pesticides on growth performance and composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for use in the feed and food value chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2017, 34, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, A.J.; Dickinson, M.; Wakefield, M.E.; Fitches, E.; Kenis, M.; Han, R.; Zhu, F.; Kone, N.; Grant, M.; Devic, E.; et al. Exploring the chemical safety of fly larvae as a source of protein for animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuel, M.; Kreuzer, M.; Gangnat, I.D.M.; Frossard, E.; Zurbrügg, C.; Egger, J.; Dortmans, B.; Gold, M.; Mathys, A.; Jaster-Keller, J.; et al. Low transfer of cadmium, lead and aflatoxin B1 to eggs and meat of laying hens receiving diets with black soldier fly larvae reared on contaminated substrates. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 304, 115733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Fernando, I.; Nisa’, K.; Shah, M.A.; Rahayu, T.; Rasool, A.; Aidoo, O.F. Effects of undesired substances and their bioaccumulation on the black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)—A literature review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elechi, M.C.; Kemabonta, K.A.; Ogbogu, S.S.; Orabueze, I.C.; Adetoro, F.A.; Adebayo, H.A.; Obe, T.M. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in prepupae of black soldier fly Hermetia Illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) cultured with organic wastes and chicken feed. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Analysis of heavy metals in the conversion of lake sediment and restaurant waste by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1163057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proc, K.; Bulak, P.; Wiącek, D.; Bieganowski, A. Hermetia illucens exhibits bioaccumulative potential for 15 different elements—Implications for feed and food production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Cai, R.; Xie, S. Effects of heavy metals on the bioaccumulation, excretion and gut microbiome of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attiogbe, F.K.; Ayim, N.Y.K.; Martey, J. Effectiveness of black soldier fly larvae in composting mercury contaminated organic waste. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, F.; Calà, E.; Regalli, N.; Meneguz, M. Canteen waste as food for black soldier fly larvae: Risk of heavy metals accumulation? Variability during one year of rearing. J. Insects Food Feed 2024, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Xu, X. Copper stimulates the incidence of antibiotic resistance, metal resistance and potential pathogens in the gut of black soldier fly larvae. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 107, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagappan, S.; Rowland, D.; Barwell, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Mikkelsen, D.; Olarte Mantilla, S.M.; James, P.; Yarger, O.; Hoffman, L. Organic side streams (bioproducts) as substrate for black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) intended as animal feed: Chemical safety issues. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2022, 62, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Tang, Z.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y. Black soldier fly larvae effectively degrade lincomycin from pharmaceutical industry wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, H.; Wang, C. Black Soldier Fly Larvae Can Effectively Degrade Oxytetracycline Bacterial Residue by Means of the Gut Bacterial Community. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J.; Su, J.; Wang, C. Changes in gut bacterial communities and the incidence of antibiotic resistance genes during degradation of antibiotics by black soldier fly larvae. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, N.; de Rijk, T.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Zoet, L.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Effects of insecticides on mortality, growth and bioaccumulation in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, E.A.; El-Bassiony, G.M. Impact of malathion toxicity on the oxidative stress parameters of the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens (Linnaeus, 1758) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbokou Foukmeniok, S.; Ogbon, A.; Bougna Tchoumi, H.H.; Dzepe, D.; Santos, J.C.C.; Riggi, L.; Tonle Kenfack, I.; Djouaka, R. Effect of the Rearing Substrate Contamination with λ-Cyhalothrin Pesticide on the Growth Performance and Survival of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: A Study of Biodegradation Kinetics. Chem. Afr. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, N.; Zoet, L.; de Rijk, T.; Zomer, P.; Rijkers, D.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; van Loon, J.J.A. Effects of pyrethroid and organophosphate insecticides on reared black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Insect Sci. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, G.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Rijk, T.C.d.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. Aflatoxin B1 Tolerance and Accumulation in Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Yellow Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor). Toxins 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leni, G.; Cirlini, M.; Jacobs, J.; Depraetere, S.; Gianotten, N.; Sforza, S.; Dall’Asta, C. Impact of Naturally Contaminated Substrates on Alphitobius diaperinus and Hermetia illucens: Uptake and Excretion of Mycotoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niermans, K. Unravelling Mycotoxin Biotransformation by the Black Soldier Fly and House Fly. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, P.P.J.; Mueller-Maatsch, J.T.L.; Meijer, N.; Bosch, M.; Zoet, L.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Effects of dietary exposure to plant toxins on bioaccumulation, survival, and growth of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae and lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus). Heliyon 2024, 10, e26523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, F.; Johnson, P.E.; Liceaga, A. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on bioactive properties and allergenicity of cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) protein. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peguero, D.A.; Gold, M.; Vandeweyer, D.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. A Review of Pretreatment Methods to Improve Agri-Food Waste Bioconversion by Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 5, 745894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, A.T.W.M.; Zeeman, G. Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Cheng, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tomberlin, J.K. Inoculating Poultry Manure With Companion Bacteria Influences Growth and Development of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heussler, C.D.; Insam, H.; Walter, A.; Steiner, B.C.S.; Steiner, F.M.; Klammsteiner, T. Life-history traits of black soldier fly reared on agro-industrial by-products subjected to three pre-treatments: A pilot-scale study. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; von Allmen, F.; Zurbrügg, C.; Zhang, J.; Mathys, A. Identification of Bacteria in Two Food Waste Black Soldier Fly Larvae Rearing Residues. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Cassar, C.M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Kreuzer, M.; Boulos, S.; Diener, S.; Mathys, A. Biowaste treatment with black soldier fly larvae: Increasing performance through the formulation of biowastes based on protein and carbohydrates. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peguero, D.A.; Mutsakatira, E.T.; Buckley, C.A.; Foutch, G.L.; Bischel, H.N. Evaluating the Microbial Safety of Heat-Treated Fecal Sludge for Black Soldier Fly Larvae Production in South Africa. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Looveren, N.; Verbaet, L.; Frooninckx, L.; Van Miert, S.; Van Campenhout, L.; Van Der Borght, M.; Vandeweyer, D. Effect of heat treatment on microbiological safety of supermarket food waste as substrate for black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Waste Manag. 2023, 164, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isibika, A.; Vinnerås, B.; Kibazohi, O.; Zurbrügg, C.; Lalander, C. Pre-treatment of banana peel to improve composting by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.), Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, C.S.; Mong, G.R.; Lim, J.W.; Raksasat, R.; Rawindran, H.; Hassan, M.A.; Lam, M.K.; Khoo, K.S.; Zango, Z.U. Low-temperature thermal pre-treated sewage sludge for feeding of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae: Protein, lipid and biodiesel profile and characterization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 178, 113241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.-X.; Ma, X.-W.; Fu, F.-X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, L.-X.; Liu, C. Transformation of heavy metal speciation during sludge drying: Mechanistic insights. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, N.S.; Heidelbach, S.; Vestergaard, S.Z.; Nielsen, M.E.; Riisgaard-Jensen, M.; Zeuner, E.J.; Bahrndorff, S.; Eriksen, N.T. Impact of substrate moisture content on growth and metabolic performance of black soldier fly larvae. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peguero, D.A.; Gold, M.; Endara, A.; Niu, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Mathys, A. Evaluation of ammonia pretreatment of four fibrous biowastes and its effect on black soldier fly larvae rearing performance. Waste Manag. 2023, 160, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J. Pretreatment is an important method for increasing the conversion efficiency of rice straw by black soldier fly larvae based on the function of gut microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, L.; Vinnerås, B.; Lalander, C. Process efficiency in relation to enzyme pre-treatment duration in black soldier fly larvae composting. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, C. Effects of Disinfectants on Larval Growth and Gut Microbial Communities of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Insects 2023, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Relationship of black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) gut microbiota and bioconversion efficiency with properties of substrates. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanga, C.M.; Waweru, J.W.; Tola, Y.H.; Onyoni, A.A.; Khamis, F.M.; Ekesi, S.; Paredes, J.C. Organic Waste Substrates Induce Important Shifts in Gut Microbiota of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.): Coexistence of Conserved, Variable, and Potential Pathogenic Microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 635881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klammsteiner, T.; Walter, A.; Bogataj, T.; Heussler, C.D.; Stres, B.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Arthofer, W.; Insam, H. The Core Gut Microbiome of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Raised on Low-Bioburden Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 00993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrens, E.; Van Moll, L.; Frooninckx, L.; De Smet, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Isolation and Identification of Dominant Bacteria From Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Envisaging Practical Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 665546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegtmeier, D.; Hurka, S.; Mihajlovic, S.; Bodenschatz, M.; Schlimbach, S.; Vilcinskas, A. Culture-Independent and Culture-Dependent Characterization of the Black Soldier Fly Gut Microbiome Reveals a Large Proportion of Culturable Bacteria with Potential for Industrial Applications. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelomi, M.; Wu, M.-K.; Chen, S.-M.; Huang, J.-J.; Burke, C.G. Microbes Associated With Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomiidae) Degradation of Food Waste. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Ge, C.; Yao, H. Identification of functional microflora underlying the biodegradation of sulfadiazine-contaminated substrates by Hermetia illucens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somroo, A.A.; ur Rehman, K.; Zheng, L.; Cai, M.; Xiao, X.; Hu, S.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of Lactobacillus buchneri on soybean curd residue co-conversion by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for food and feedstock production. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangena, D.N. Influence of Post-Harvest Techniques on Nutritional and Microbial Quality of Selected Edible Insects. Master’s Thesis, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Juja, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Larouche, J.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Saucier, L.; Lebeuf, Y.; Doyen, A.; Vandenberg, G.W. Effects of Killing Methods on Lipid Oxidation, Colour and Microbial Load of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Animals 2019, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Park, S.H.; Jung, H.J.; You, S.J.; Kim, B.G. Effects of Drying Methods and Blanching on Nutrient Utilization in Black Soldier Fly Larva Meals Based on In Vitro Assays for Pigs. Animals 2023, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, N.F.N.M.; Seok-Kian, A.Y.; Seng, L.L.; Mustafa, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Shapawi, R. Nutritional value of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae processed by different methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Ortuño, J.; Stratakos, A.C.; Linton, M.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Elliott, T.; Koidis, A.; Theodoridou, K. Impact of Thermal and High-Pressure Treatments on the Microbiological Quality and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Animals 2020, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucier, L.; M’ballou, C.; Ratti, C.; Deschamps, M.H.; Lebeuf, Y.; Vandenberg, G.W. Comparison of black soldier fly larvae pre-treatments and drying techniques on the microbial load and physico-chemical characteristics. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Chundang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Vongsangnak, W.; Pruksakorn, C.; Kovitvadhi, A. Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, C.W.; van Kessel, K.; Castelijn, G.A.A.; van der Voort, M.; Meijer, N. Growth and Sporulation of Pathogenic Bacillus Cereus in Rearing Hermetia Illucens (L.). Heliyon, 2023; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.; Crump, A.; Barrett, M.; Sarlak, S.; Birch, J.; Chittka, L. Chapter Three—Can insects feel pain? A review of the neural and behavioural evidence. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Jurenka, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Volume 63, pp. 155–229. [Google Scholar]
- Shelomi, M. Pain, Suffering, and Euthanasia in Insects. Int. J. Appl. Philos. 2021, 35, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunder, H.C.; Wolkers-Rooijackers, J.; Korpela, J.M.; Nout, M.J.R. Microbiological aspects of processing and storage of edible insects. Food Control 2012, 26, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Clementi, F.; Osimani, A. Current knowledge on the microbiota of edible insects intended for human consumption: A state-of-the-art review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrögel, P.; Wätjen, W. Insects for Food and Feed-Safety Aspects Related to Mycotoxins and Metals. Foods 2019, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, M.; Casartelli, M. Gastrointestinal evacuation in black soldier fly larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, E.; Crauwels, S.; Lievens, B.; Luca, S.; Claes, J.; Borremans, A.; Bruyninckx, L.; Van Campenhout, L. Effect of post-harvest starvation and rinsing on the microbial numbers and the bacterial community composition of mealworm larvae (Tenebrio molitor). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 42, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, R.; Smetana, S.; Wiktor, A.; Parniakov, O.; Pobiega, K.; Rybak, K.; Nowacka, M. The selected quality aspects of infrared-dried black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) and yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) larvae pre-treated by pulsed electric field. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Bußler, S.; Psarianos, M.; Rossi, G.; Schlüter, O.K. Edible insect processing pathways and implementation of emerging technologies. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 877–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Bai, Z.; Ma, L. A novel variable power microwave (VPM) drying technology for lowering energy consumption and improving the in vitro protein digestibility of black solider fly larvae. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 89, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorstkii, I.; Comiotto Alles, M.; Parniakov, O.; Smetana, S.; Aganovic, K.; Sosnin, M.; Toepfl, S.; Heinz, V. Optimization of pulsed electric field assisted drying process of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniakov, O.; Mikhrovska, M.; Wiktor, A.; Alles, M.; Ristic, D.; Bogusz, R.; Nowacka, M.; Devahastin, S.; Mujumdar, A.; Heinz, V.; et al. Insect processing for food and feed: A review of drying methods. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Feng, W.; Xiong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F. Impact of drying method on the nutritional value of the edible insect protein from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae: Amino acid composition, nutritional value evaluation, in vitro digestibility, and thermal properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornsuwan, R.; Pootthachaya, P.; Bunchalee, P.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Cherdthong, A.; Tengjaroenkul, B.; Boonkum, W.; Wongtangtintharn, S. Evaluation of the Physical Characteristics and Chemical Properties of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae as a Potential Protein Source for Poultry Feed. Animals 2023, 13, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selaledi, L.; Mabelebele, M. The Influence of Drying Methods on the Chemical Composition and Body Color of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.). Insects 2021, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmad, M.; Hidra, N.; Lhomme, P.; Mghazli, S.; El Hachimi, Y.; Abdenouri, N. Environmental, economic and quality assessment of hybrid solar-electric drying of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Renew. Energy 2024, 226, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapiki, P. Evaluating the Efficiency of Oven and Sun-Drying Traditional Processing Methods at Bacterial Quality Improvement for Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Master’s Thesis, The University of Zambia School of Veterinary Medicine, Lusaka, Zambia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Hu, R.; Zhang, K.; Ma, S.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Resistance of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae to combined heavy metals and potential application in municipal sewage sludge treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyangena, D.N.; Mutungi, C.; Imathiu, S.; Kinyuru, J.; Affognon, H.; Ekesi, S.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Fiaboe, K.K.M. Effects of Traditional Processing Techniques on the Nutritional and Microbiological Quality of Four Edible Insect Species Used for Food and Feed in East Africa. Foods 2020, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj Saadoun, J.; Luparelli, A.V.; Caligiani, A.; Macavei, L.I.; Maistrello, L.; Neviani, E.; Galaverna, G.; Sforza, S.; Lazzi, C. Antimicrobial Biomasses from Lactic Acid Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Prepupae and Related By-Products. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panikkar, P.; Parakkandi, J.; Khan, F.; Das, B.K.; Udayakumar, A.; Eregowda, V.M.; Yandigeri, M. Use of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on organic waste as feed or as an ingredient in a pellet-feed formulation for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 72968–72978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Campenhout, L.; Lachi, D.; Vandeweyer, D. Potential of Fermentation and Vacuum Packaging Followed by Chilling to Preserve Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Insects 2021, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, E.; Mutungi, C.; Kinyuru, J.; Imathiu, S.; Affognon, H.; Ekesi, S.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Fiaboe, K.K.M. Changes in chemical and microbiological quality of semi-processed black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larval meal during storage. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiku, E.K. Physicochemical and Microbiological Stability of Semi-Processed Edible Crickets (Acheta domesticus) and Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) during Storage. Master’s Thesis, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Juja, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Swinscoe, I.; Oliver, D.M.; Gilburn, A.S.; Lunestad, B.; Lock, E.-J.; Ørnsrud, R.; Quilliam, R.S. Seaweed-fed black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae as feed for salmon aquaculture: Assessing the risks of pathogen transfer. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 5, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/893 of 24 May 2017 amending Annexes I and IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Annexes X, XIV and XV to Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as regards the provisions on processed animal protein. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 138, 92–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Grmelová, N.; Hénault-Ethier, L.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Vandenberg, G.W.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Nemane, V. Insects as Food and Feed: Laws of the European Union, United States, Canada, Mexico, Australia, and China. Eur. Food Feed Law Rev. 2017, 12, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Alagappan, S.; Rowland, D.; Barwell, R.; Mantilla, S.M.O.; Mikkelsen, D.; James, P.; Yarger, O.; Hoffman, L.C. Legislative landscape of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohri, C.R.; Diener, S.; Zabaleta, I.; Mertenat, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Treatment technologies for urban solid biowaste to create value products: A review with focus on low- and middle-income settings. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 81–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J. Prion diseases of humans and animals: Their causes and molecular basis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.; Cembran, A.; Fernandez-Funez, P. Insight From Animals Resistant to Prion Diseases: Deciphering the Genotype—Morphotype—Phenotype Code for the Prion Protein. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenza, E.C.; Carreño, I. Edible Insects and Insect-based Products in the EU: Safety Assessments, Legal Loopholes and Business Opportunities. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 2015, 6, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Scientific Committee. Risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.R.D.; Butler, D.A.; Bredesen, D.E.; Wälchli, M.; Hsiao, K.K.; Prusiner, S.B. Prion protein gene expression in cultured cells. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1988, 2, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupi, O. Could ectoparasites act as vectors for prion diseases? Int. J. Dermatol. 2003, 42, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupi, O. Myiasis as a risk factor for prion diseases in humans. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetana, S.; Palanisamy, M.; Mathys, A.; Heinz, V. Sustainability of insect use for feed and food: Life Cycle Assessment perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Mondello, G.; Giannetto, A.; Fasulo, S.; Savastano, D. Environmental impact of food waste bioconversion by insects: Application of Life Cycle Assessment to process using Hermetia illucens. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Hou, Y.F.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z.N. Biodiesel production from rice straw and restaurant waste employing black soldier fly assisted by microbes. Energy 2012, 47, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye-Yiadom, K.A.; Ilari, A.; Duca, D. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Life Cycle Assessment on the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michishita, R.; Shimoda, M.; Furukawa, S.; Uehara, T. Inoculation with black soldier fly larvae alters the microbiome and volatile organic compound profile of decomposing food waste. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basri, N.E.A.; Azman, N.A.; Ahmad, I.K.; Suja, F.; Jalil, N.A.A.; Amrul, N.F. Potential Applications of Frass Derived from Black Soldier Fly Larvae Treatment of Food Waste: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Le, T.M.; Pham, C.D.; Duong, Y.; Le, P.T.K.; Tran, T.V. Valorization of Black Soldier Flies at Different Life Cycle Stages. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 97, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, A.; Triunfo, M.; Scieuzo, C.; Ianniciello, D.; Tafi, E.; Hahn, T.; Zibek, S.; Salvia, R.; De Bonis, A.; Falabella, P. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan from different developmental stages of the bioconverter insect Hermetia illucens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelomi, M. Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion. Animals 2024, 14, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111590
Shelomi M. Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion. Animals. 2024; 14(11):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111590
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelomi, Matan. 2024. "Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion" Animals 14, no. 11: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111590
APA StyleShelomi, M. (2024). Mitigation Strategies against Food Safety Contaminant Transmission from Black Soldier Fly Larva Bioconversion. Animals, 14(11), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111590




