A Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic and Vascular Activity Effects of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) and Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venoms Using a Chick Embryo Model
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Venom Collection
2.2. The Chick Embryotoxicity Screening Test (CHEST)
2.3. The Hen’s Egg Test on the Chorioallantoic Membrane (HET-CAM)
2.4. Analysis of Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CHEST Test
3.2. Vasoactivity
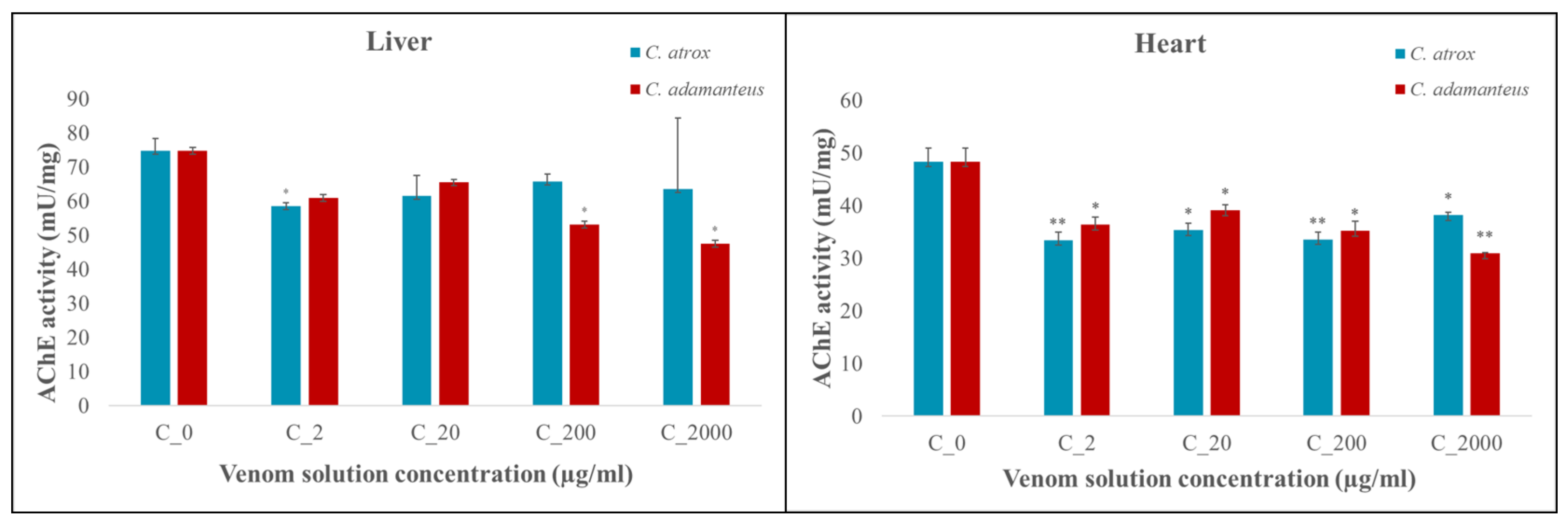
3.3. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruha, A.-M. Rattlesnakes and Other North American Crotalids. In Critical Care Toxicology; Brent, J., Burkhart, K., Dargan, P., Hatten, B., Megarbane, B., Palmer, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, L.R.V.; Quental, T.B.; Grazziotin, F.G.; Alfaro, M.L.; Martins, M.; Venzon, M.; Zaher, H. Diversification in Vipers: Phylogenetic Relationships, Time of Divergence and Shifts in Speciation Rates. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 105, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, L.R.; Martins, M.; Greene, H.W. Evolutionary History of Vipers. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.F.A.; Ferreira, R.S. Antineoplastic Properties and Pharmacological Applications of Crotalus durissus terrificus Snake Venom. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55, e0323-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoe, T.A.; Spencer, C.L.; Parkinson, C.L. Phylogeographic Structure and Historical Demography of the Western Diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox): A Perspective on North American Desert Biogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 42, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.; Means, D. Distribution and Habitat Relationships of the Eastern Diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus). Herpetol. Nat. Hist. 2000, 7, 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kocholaty, W.F.; Ledford, E.B.; Daly, J.G.; Billings, T.A. Toxicity and Some Enzymatic Properties and Activities in the Venoms of Crotalidae, Elapidae and Viperidae. Toxicon 1971, 9, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, J.L.; Straight, R.C.; Wolfe, M.C.; Hardy, D.L. Geographical Variation in Crotalus scutulatus scutulatus (Mojave rattlesnake) Venom Properties. Toxicon 1983, 21, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, P.; Deshwal, A.; McMahon, T.A.; Slikas, M.; Andrews, E.; Becker, B.; Kumar, T.K.S. A Review of Rattlesnake Venoms. Toxins 2024, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meik, J.M.; Pires-daSilva, A. Evolutionary Morphology of the Rattlesnake Style. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and Snake Venom Evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, A.; Pook, C.E.; Harrison, R.A.; Wüster, W. Coevolution of Diet and Prey-Specific Venom Activity Supports the Role of Selection in Snake Venom Evolution. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2443–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano-Martins, I.S.; Tomy, S.C.; Campolina, D.; Dias, M.B.; de Castro, S.C.B.; de Sousa-e-Silva, M.C.C.; Amaral, C.F.S.; Rezende, N.A.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Warrell, D.A.; et al. Coagulopathy Following Lethal and Non-lethal Envenoming of Humans by the South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus) in Brazil. QJM Int. J. Med. 2001, 94, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, L.H.; Teixeira, L.F.; Zaqueo, K.D.; Bastos, J.F.; Nery, N.M.; Setúbal, S.S.; Pontes, A.S.; Butzke, D.; Cavalcante, W.; Gallacci, M.; et al. Local and Systemic Effects Caused by Crotalus durissus terrificus, Crotalus durissus collilineatus, and Crotalus durissus cascavella Snake Venoms in Swiss Mice. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, J.B.; Hamilton, D.; Fox, J.W. Studies on the Mechanism of Hemorrhage Production by Five Proteolytic Hemorrhagic Toxins from Crotalus atrox Venom. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1988, 369, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Retzios, A.D.; Markland, F.S. Fibrinolytic Enzymes from the Venoms of Agkistrodon contortrix contortrix and Crotalus basiliscus basiliscus: Cleavage Site Specificity towards the α-Chain of Fibrin. Throm. Res. 1994, 74, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.G.; Ownby, C.L. Pathogenesis of Hemorrhage Induced by Proteinase H from Eastern Diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venom. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.E. Snake Bite: Pit Vipers. Clin. Tech. Small. Anim. Pract. 2006, 21, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, A.L. Metal and Nonprotein Constituents in Snake Venoms. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Lee, C.-Y., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; Volume 52, pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carregari, V.C.; Rosa-Fernandes, L.; Baldasso, P.; Bydlowski, S.P.; Marangoni, S.; Larsen, M.R.; Palmisano, G. Snake Venom Extracellular Vesicles (SVEVs) Reveal Wide Molecular and Functional Proteome Diversity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkis, I.; Silva, F.d.S.; Pereira, A.; Kerkis, A.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Biological Versatility of Crotamine—A Cationic Peptide from the Venom of a South American rattlesnake. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 19, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snakebite Envenoming—A Strategy for Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-151564-1. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241515641 (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Sells, P.G.; Ioannou, P.; Theakston, R.D. A Humane Alternative to the Measurement of the Lethal Effects (LD50) of Non-Neurotoxic Venoms Using Hens’ Eggs. Toxicon 1998, 36, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.G.; Towers, M.; Vargesson, N.; Tickle, C. The Chick Limb: Embryology, Genetics and Teratology. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachholz, G.E.; Rengel, B.D.; Vargesson, N.; Fraga, L.R. From the Farm to the Lab: How Chicken Embryos Contribute to the Field of Teratology. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.B.; Dvorcakova, S.; Luptakova, L.; Vdoviakova, K.; Petrilla, V.; Petrovova, E. Evaluation of Vasoactivity after Haemotoxic Snake Venom Administration. Toxicon 2019, 158, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polláková, M.; Petrilla, V.; Andrejčáková, Z.; Petrillová, M.; Sopková, D.; Petrovová, E. Spitting Cobras: Experimental Assay Employing the Model of Chicken Embryo and the Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane for Imaging and Evaluation of Effects of Venom from African and Asian Species (Naja ashei, Naja nigricollis, Naja siamensis, Naja sumatrana). Toxicon 2021, 189, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrilla, V.; Polláková, M.; Bekešová, B.; Andrejčáková, Z.; Vlčková, R.; Marcinčáková, D.; Petrillová, M.; Petrovová, E.; Sopková, D.; Legáth, J. A Comprehensive Study Monitoring the Venom Composition and the Effects of the Venom of the Rare Ethiopian Endemic Snake Species Bitis parviocula. Toxins 2021, 13, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hati, R.; Mitra, P.; Sarker, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.K. Snake Venom Hemorrhagins. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1999, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luepke, N.P.; Kemper, F.H. The HET-CAM Test: An Alternative to the Draize Eye Test. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1986, 24, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovova, E.; Sedmera, D.; Lesnik, F.; Luptakova, L. Bendiocarb Effect on Liver and Central Nervous System in the Chick Embryo. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2009, 44, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, R.; Peterka, M.; Rychter, Z. Chick Embryotoxicity Screening Test—130 Substances Tested. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1985, 23, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Neubert, D.; Merker, H.J.; Kwasigroch, T.E. Methods in prenatal toxicology. Evaluation of embryotoxic effects in experimental animals: Teratology Workshop April 1977 Berlin. In Methods in Prenatal Toxicology: Evaluation of Embryotoxic Effects in Experimental Animals; Georg Thieme Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1977; 474p, ISBN 3-13-558201-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek, R.; Peterka, M. Morphogenetic systems and in vitro techniques in teratology. In Culture Techniques: Applicability for Studies on Prenatal Differentiation and Toxicity; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1981; pp. 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Deichmann, W.B.; Radomski, J.L.; Farrell, J.J.; Macdonald, W.E.; Keplinger, M.L. Acute Toxicity and Treatment of Intoxications Due to Crotalus adamanteus (Rattlesnake Venom). Am. J. Med. Sci. 1958, 236, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Padrón, O.; Cruz-Pérez, M.S.; Castro-Guillén, J.L.; García-Arredondo, J.A.; Mendiola-Olaya, E.; Saldaña-Gutiérrez, C.; Herrera-Paniagua, P.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Hybridization between Crotalus aquilus and Crotalus polystictus Species: A Comparison of Their Venom Toxicity and Enzymatic Activities. Biology 2022, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, R.; Cury, Y.; Capela e Ara, A.L.d.S.; Bonamin, L.V.; Bernardi, M.M. Embriotoxic effects of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom. Rev. Inst. Ciências Saúde 2008, 26, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Zancolli, G.; Baker, T.G.; Barlow, A.; Bradley, R.K.; Calvete, J.J.; Carter, K.C.; De Jager, K.; Owens, J.B.; Price, J.F.; Sanz, L.; et al. Is Hybridization a Source of Adaptive Venom Variation in Rattlesnakes? A Test, Using a Crotalus scutulatus × viridis Hybrid Zone in Southwestern New Mexico. Toxins 2016, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowsky, E.R.; Saviola, A.J.; Alvarado-Díaz, J.; Mascareñas, A.Q.; Hansen, K.C.; Yates, J.R.; Mackessy, S.P. Montane Rattlesnakes in México: Venoms of Crotalus tancitarensis and Related Species within the Crotalus intermedius Group. Toxins 2023, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. Venom composition in rattlesnakes: Trends and biological significance. In The Biology of Rattlesnakes; Hayes, W.K., Beaman, K.R., Cardwell, M.D., Bush, S.P., Eds.; Loma Linda University Press: Loma Linda, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 495–510. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz-Sousa, R.; Caldeira, C.A.d.S.; Pereira, S.S.; Da Silva, S.L.; Fernandes, P.A.; Teixeira, L.M.C.; Zuliani, J.P.; Soares, A.M. Therapeutic Applications of Snake Venoms: An Invaluable Potential of New Drug Candidates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frare, B.T.; Silva Resende, Y.K.; Dornelas, B.d.C.; Jorge, M.T.; Souza Ricarte, V.A.; Alves, L.M.; Izidoro, L.F.M. Clinical, Laboratory, and Therapeutic Aspects of Crotalus durissus (South American rattlesnake) Victims: A Literature Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1345923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.E.; Reyes, G.; Albrecht, E.A. Crotalus atrox Venom-Induced Cellular Toxicity: Early Wound Progression Involves Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesar, P.H.S.; Braga, M.A.; Trento, M.V.C.; Menaldo, D.L.; Marcussi, S. Snake Venom Disintegrins: An Overview of Their Interaction with Integrins. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas Mercado, E.; Neri Castro, E.; Bénard Valle, M.; Rucavado-Romero, A.; Olvera Rodríguez, A.; Zamudio Zuñiga, F.; Alagón Cano, A.; Garza Ocañas, L. Disintegrins Extracted from Totonacan Rattlesnake (Crotalus totonacus) Venom and Their Anti-Adhesive and Anti-Migration Effects on MDA-MB-231 and HMEC-1 Cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 65, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Herrera, C. Hemorrhage Caused by Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: A Journey of Discovery and Understanding. Toxins 2016, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, C.; Jamora, C.; Yamanouye, N.; Zorn, T.M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Mechanisms of Vascular Damage by Hemorrhagic Snake Venom Metalloproteinases: Tissue Distribution and In Situ Hydrolysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombet, D.; Rivas-Calero, R.; Salcedo, L.; Rodríguez, M.; Mogollón, A.; Mendoza, J.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A.; Rodriguez, H. Experimental Cardiac Toxicity Induced by the Injection of Uracoan Rattlesnake (Crotalus vegrandis) and the Black Rattlesnake (Crotalus pifanorum) Venoms. Toxicol. Forensic Med. 2022, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.G. Ruthenium-Based Antivenom Attenuates Crotalus atrox Venom Mediated Coagulopathy in Rabbits. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2024, 35, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, R.F.; Vieira, R.P.; Ferrari, E.F.; Souza, R.A.; Osorio, R.A.; Prianti, A.C.G., Jr.; Hyslop, S.; Zamuner, S.R.; Cogo, J.C.; Ribeiro, W. Acute Hepatotoxicity of Crotalus durissus terrificus (South American rattlesnake) Venom in Rats. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 15, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
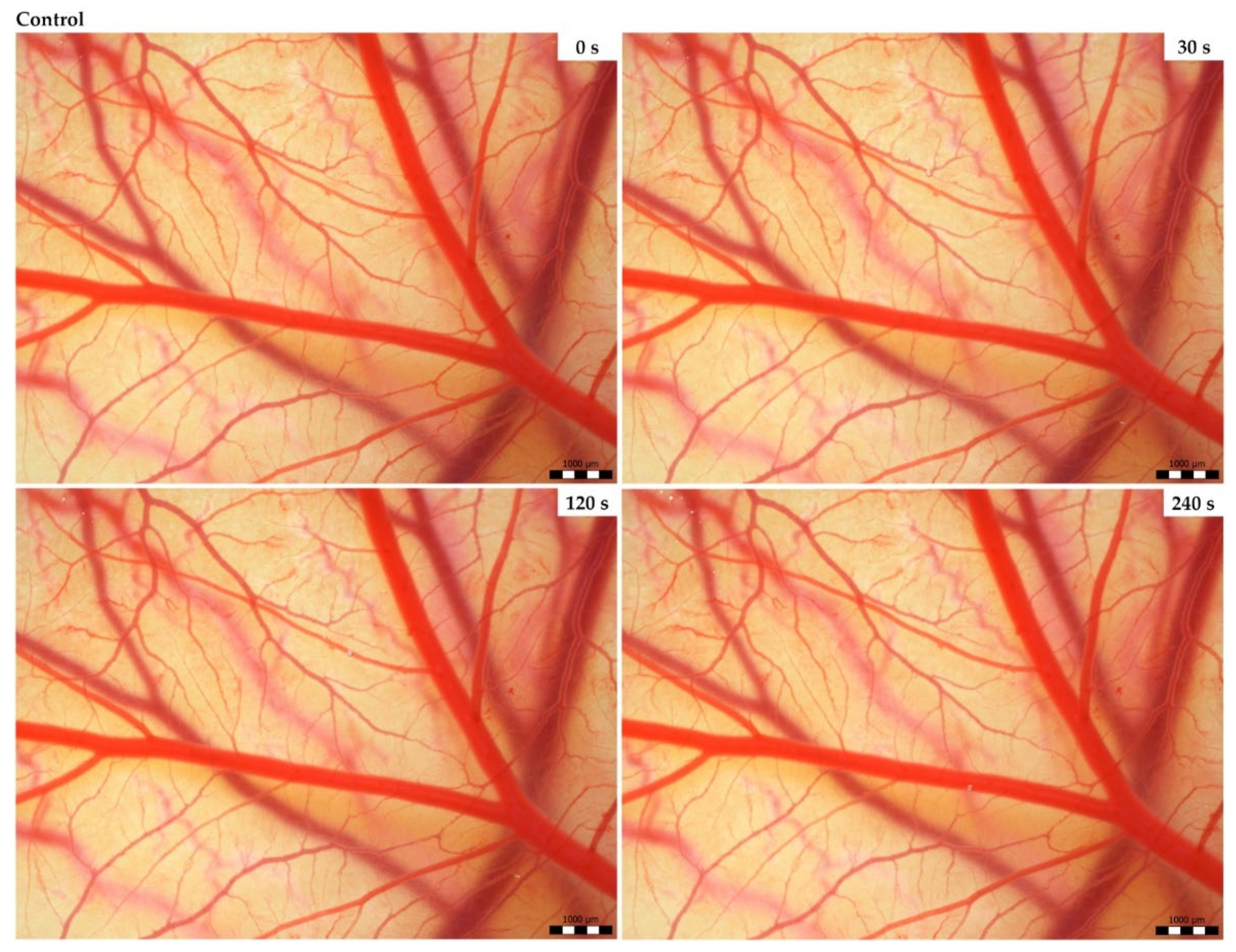
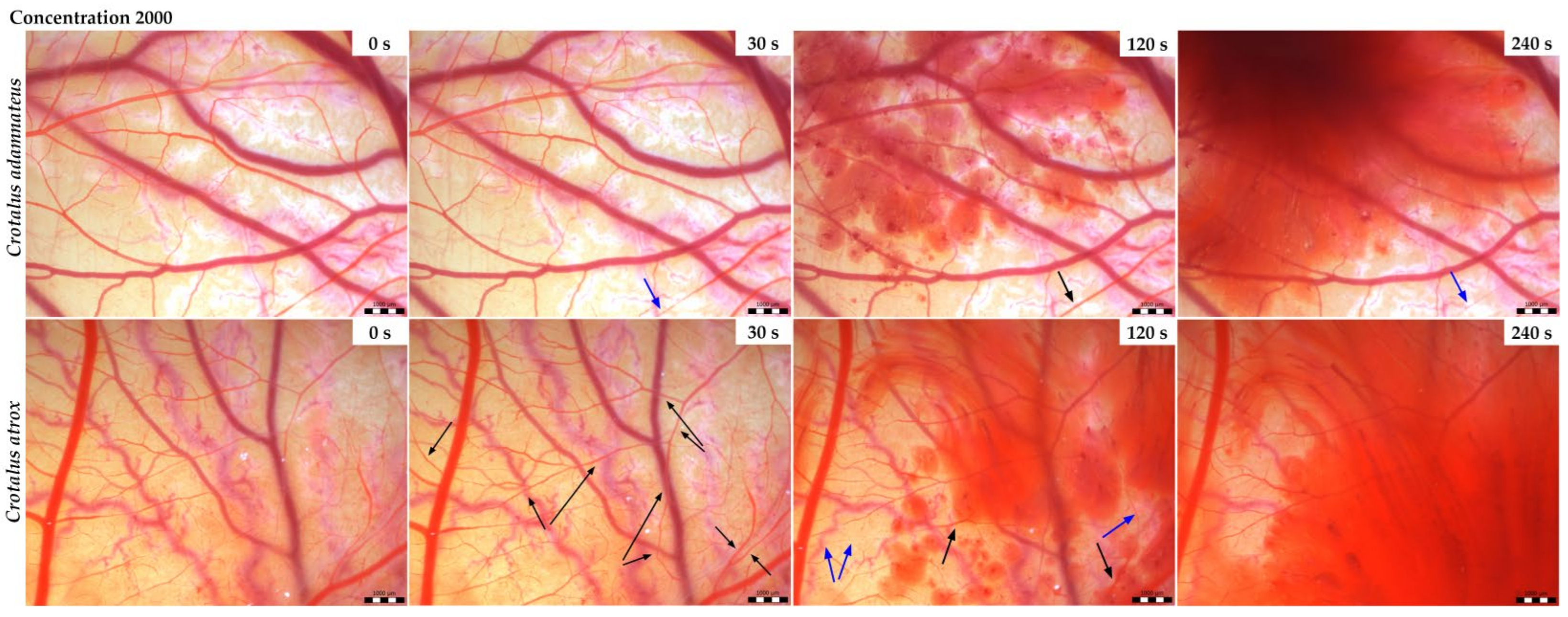
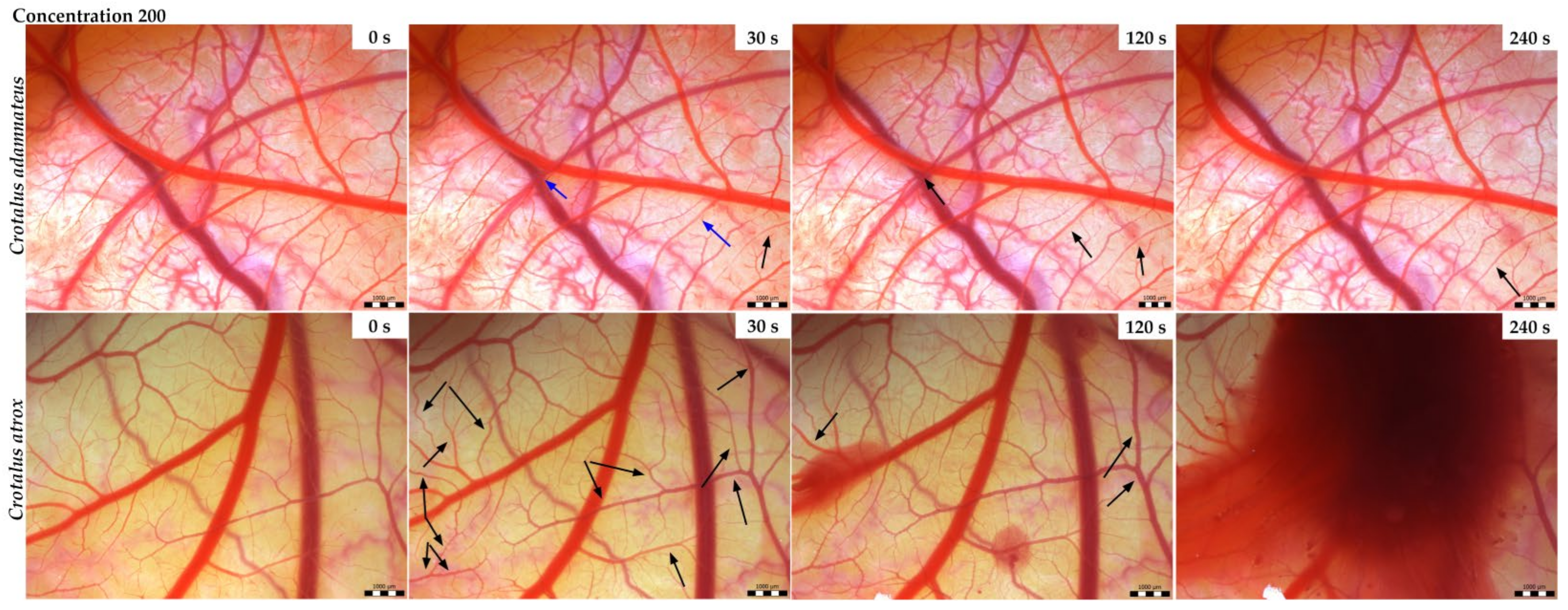
| Snake Venom | Conc. (µg/mL) | n | Live Embryos | Dead Embryos | Mortality (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None (Control) | 0 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Crotalus adamanteus | 2 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 7.69 |
| 20 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 15.38 | |
| 200 | 13 | 10 | 3 | 23.07 | |
| 2000 | 13 | 10 | 3 | 23.07 | |
| Crotalus atrox | 2 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| 20 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 15.38 | |
| 200 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 7.69 | |
| 2000 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 7.69 |
| Snake Venom | Conc. (µg/mL) | Embryo Weight (g) | Heart Weight (g) | Liver Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None (control) | 0 | 0.886 ± 0.014 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.010 ± 0.001 |
| Crotalus adamanteus | 2 | 0.898 ± 0.023 | 0.007 ± 0.000 | 0.010 ± 0.001 |
| 20 | 0.897 ± 0.028 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.001 * | |
| 200 | 0.887 ± 0.053 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.010 ± 0.001 | |
| 2000 | 0.819 ± 0.032 * | 0.009 ± 0.001 ** | 0.009 ± 0.001 | |
| Crotalus atrox | 2 | 1.047 ± 0.026 *** | 0.008 ± 0.001 ** | 0.012 ± 0.001 |
| 20 | 1.078 ± 0.050 *** | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.012 ± 0.001 | |
| 200 | 1.093 ± 0.028 *** | 0.008 ± 0.001 ** | 0.013 ± 0.001 | |
| 2000 | 1.002 ± 0.033 ** | 0.009 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.001 |
| Snake Venom | Conc. (µg/mL) | Hyperemia | Hemorrhage | Blood Clotting | Total Average (Cumulative Score) | Irritant Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None (Control) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Crotalus adamanteus | 200 | 0 | 3.5 | 0 | 3.5 | Slight |
| 2000 | 0 | 5.5 | 0 | 5.5 | Moderate | |
| Crotalus atrox | 200 | 0 | 4.0 | 0 | 4.0 | Slight |
| 2000 | 0 | 5.0 | 0 | 5.0 | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekešová, B.; Petrilla, V.; Polláková, M.; Andrejčáková, Z.; Vlčková, R.; Dyba, B.; Sopková, D.; Petrillová, M.; Petrovová, E.; Legáth, J. A Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic and Vascular Activity Effects of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) and Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venoms Using a Chick Embryo Model. Animals 2024, 14, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111634
Bekešová B, Petrilla V, Polláková M, Andrejčáková Z, Vlčková R, Dyba B, Sopková D, Petrillová M, Petrovová E, Legáth J. A Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic and Vascular Activity Effects of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) and Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venoms Using a Chick Embryo Model. Animals. 2024; 14(11):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111634
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekešová, Barbora, Vladimír Petrilla, Magdaléna Polláková, Zuzana Andrejčáková, Radoslava Vlčková, Barbara Dyba, Drahomíra Sopková, Monika Petrillová, Eva Petrovová, and Jaroslav Legáth. 2024. "A Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic and Vascular Activity Effects of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) and Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venoms Using a Chick Embryo Model" Animals 14, no. 11: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111634
APA StyleBekešová, B., Petrilla, V., Polláková, M., Andrejčáková, Z., Vlčková, R., Dyba, B., Sopková, D., Petrillová, M., Petrovová, E., & Legáth, J. (2024). A Comparative Analysis of the Cytotoxic and Vascular Activity Effects of Western Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) and Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus) Venoms Using a Chick Embryo Model. Animals, 14(11), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14111634






