Soybean Bioactive Peptide Supplementation Affects the Intestinal Immune Antioxidant Function, Microbial Diversity, and Reproductive Organ Development in Roosters
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diets, and Experimental Design
2.2. Animal Management
2.3. Measurement and Calculation of Growth Performance
2.4. Serum Collection and Indicator Determination
2.5. Intestinal and Testis TissueSample Collection
2.6. Intestinal and Testis Histomorphology
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Detection of Intestine-Related Gene Expression
2.9. Semen Quality Determination
2.10. Cecal Microbial Sequencing Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SBP Supplementation Improves the Growth Performance of Roosters
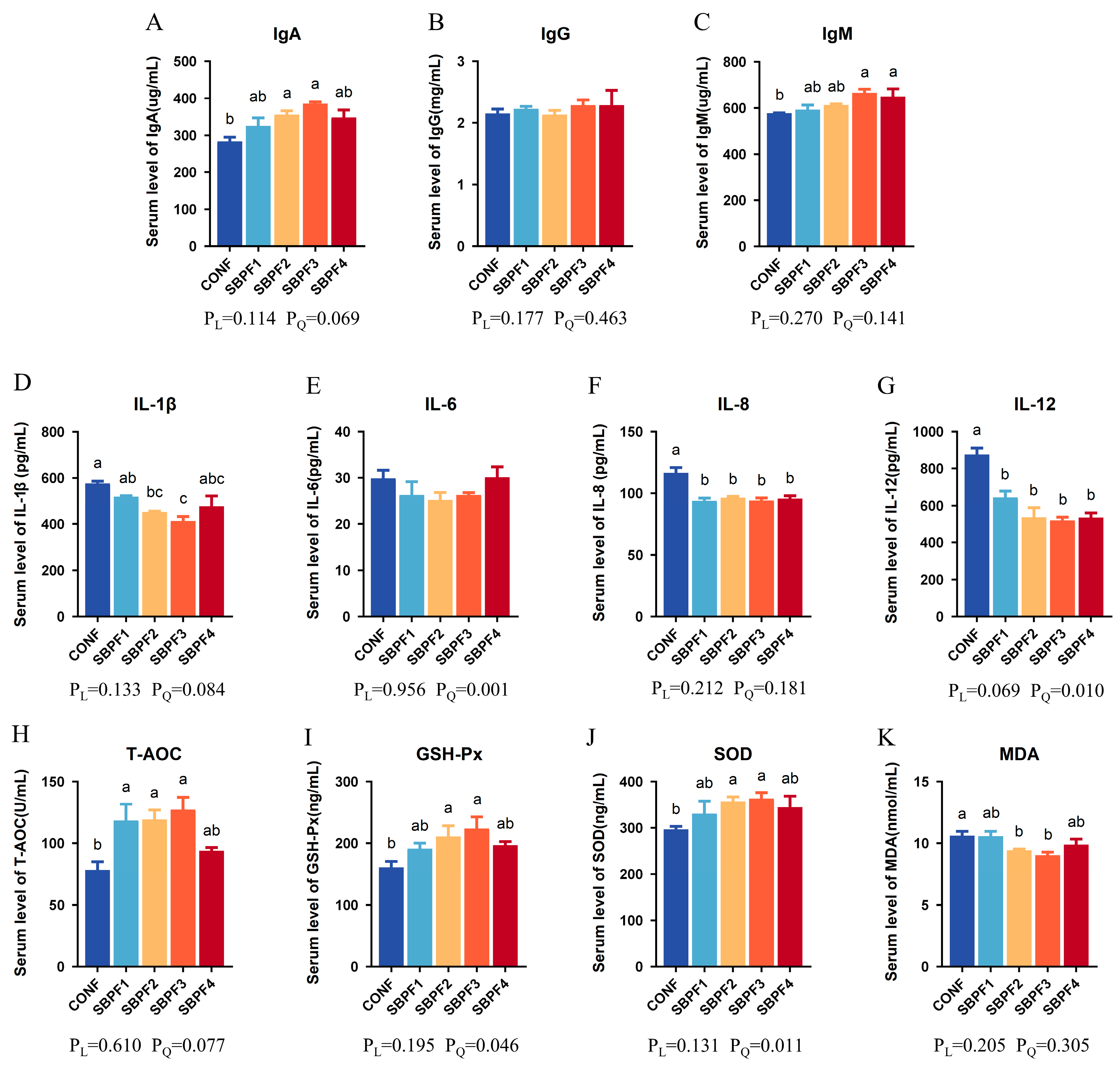
3.2. SBP Supplementation Increases the Serum Immune-, Inflammatory-, and Antioxidant-Related Indices of Roosters
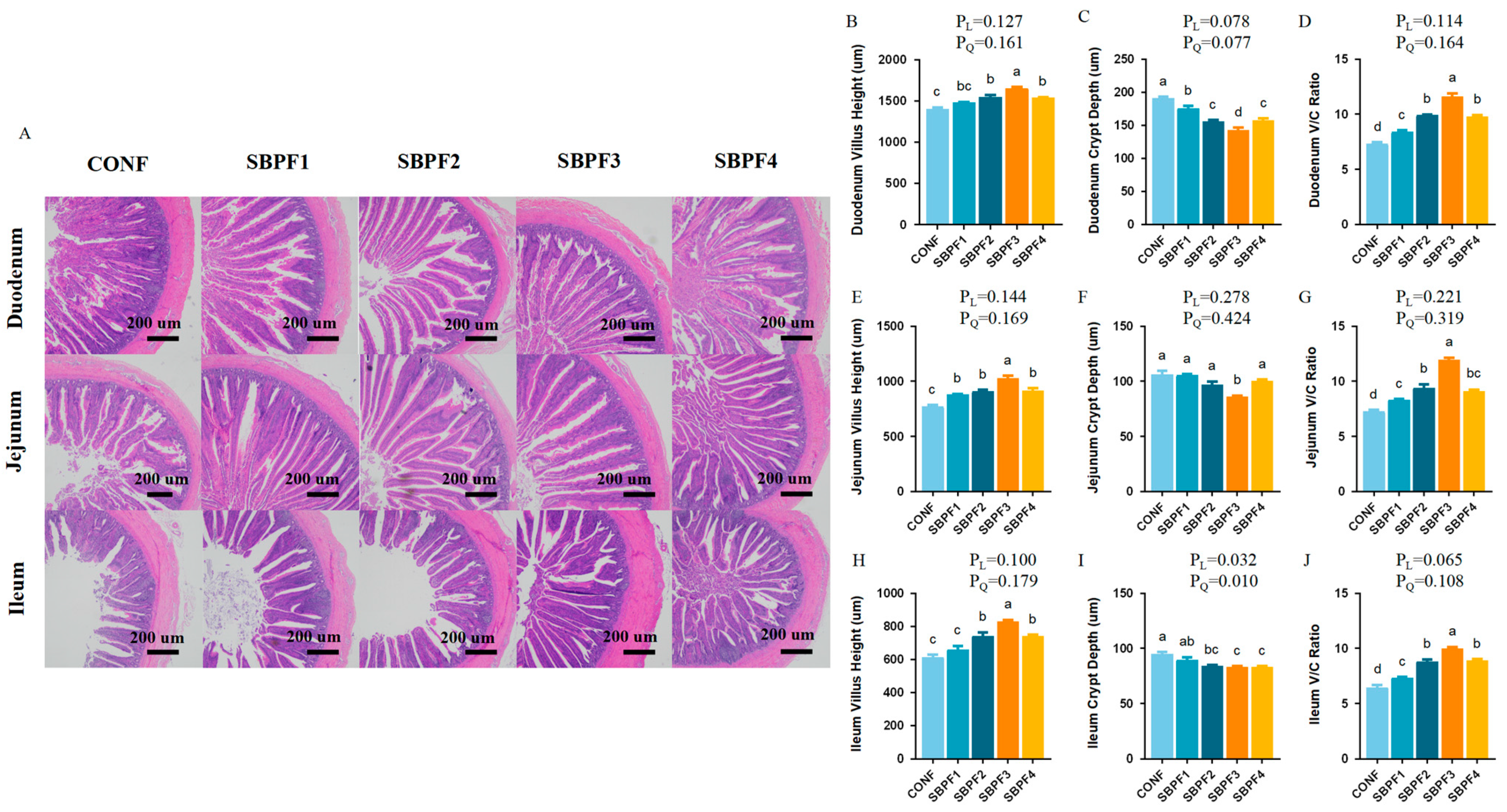
3.3. SBP Supplementation Improves the Intestinal Morphology of Roosters
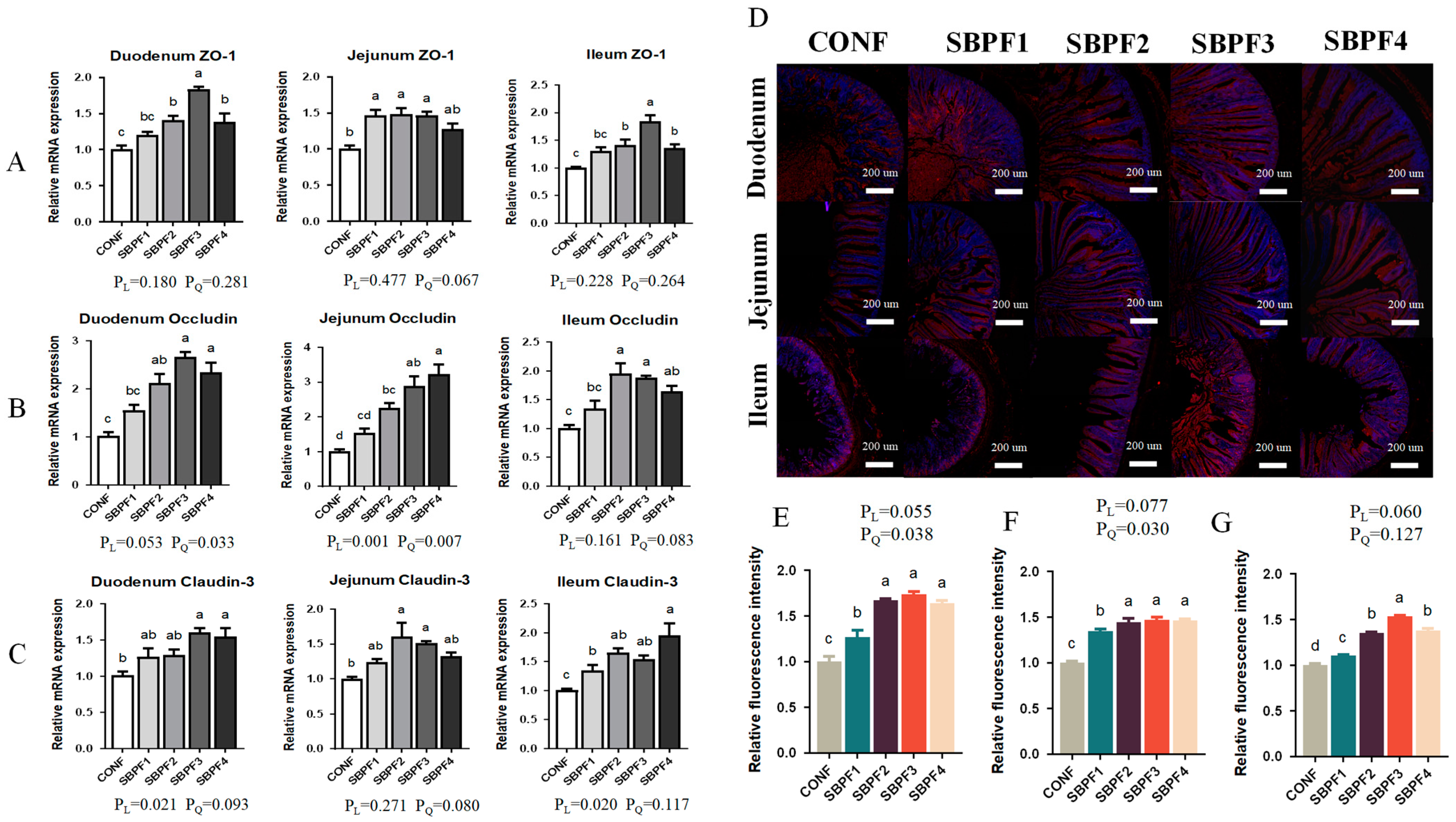
3.4. SBP Supplementation Increases the Intestinal Tight Junction-Gene Expression of Roosters
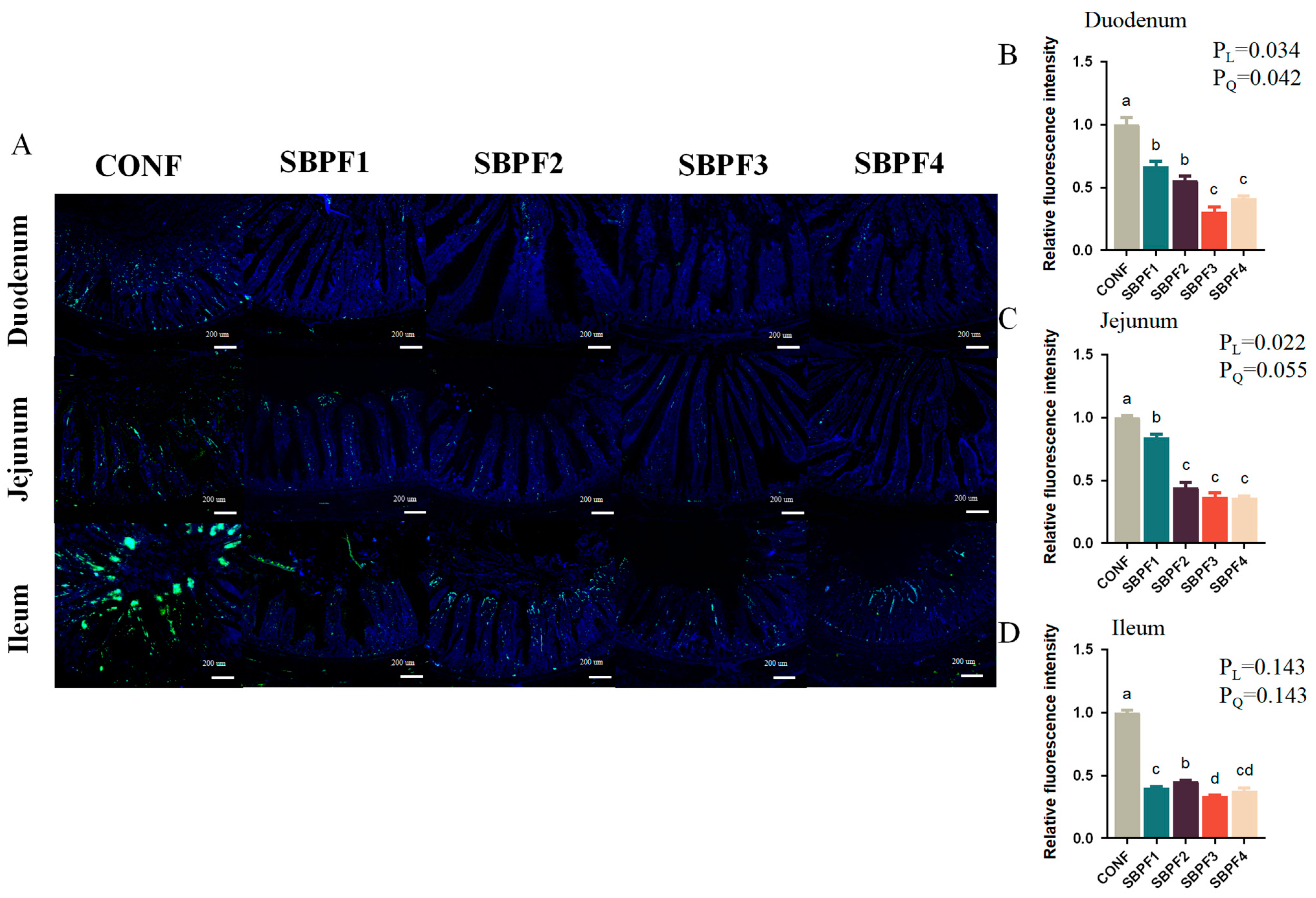
3.5. SBP Supplementation Prevents the Intestinal Cell Apoptosis of Roosters
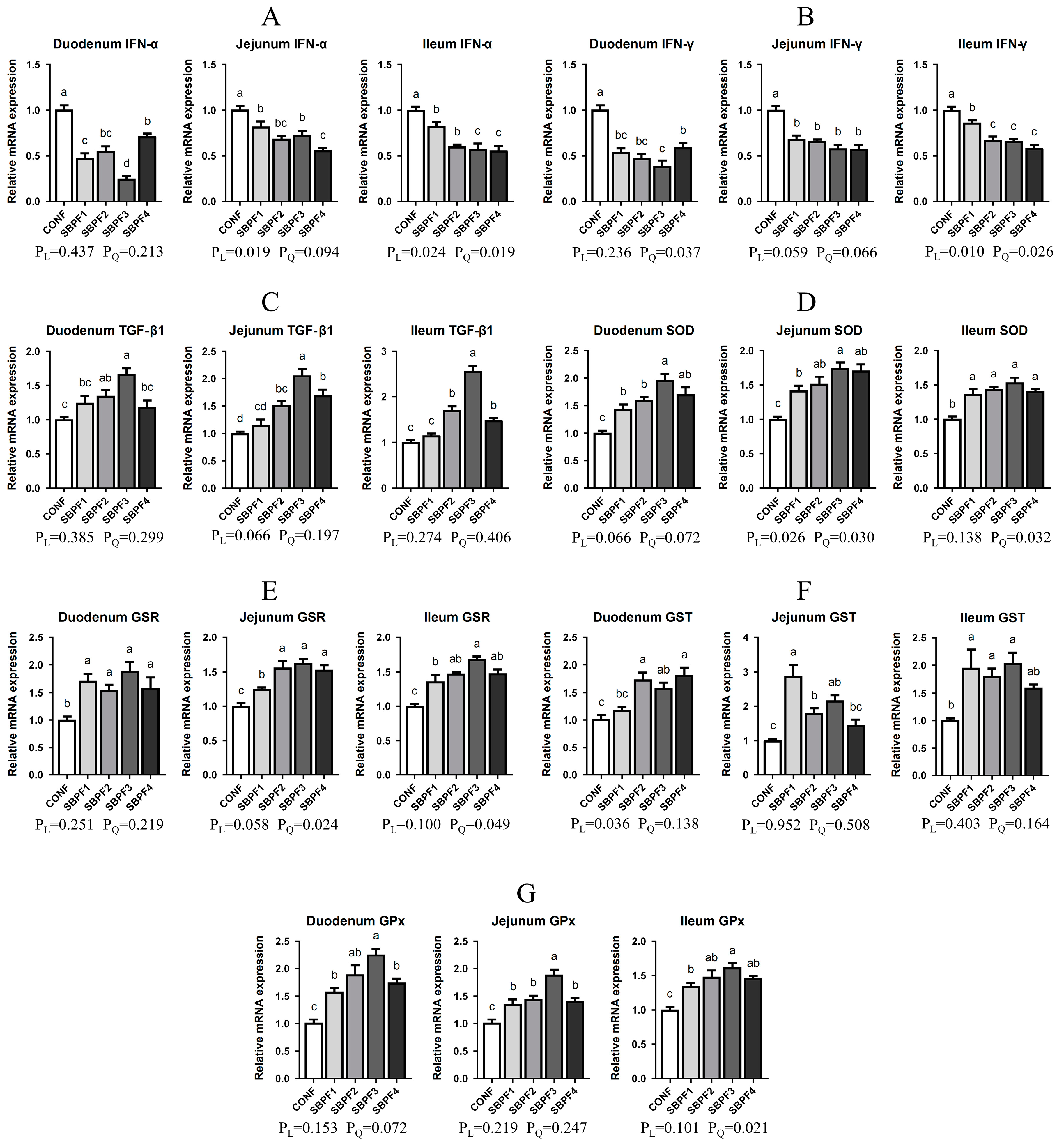
3.6. SBP Supplementation Enhances the Intestinal Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Roosters
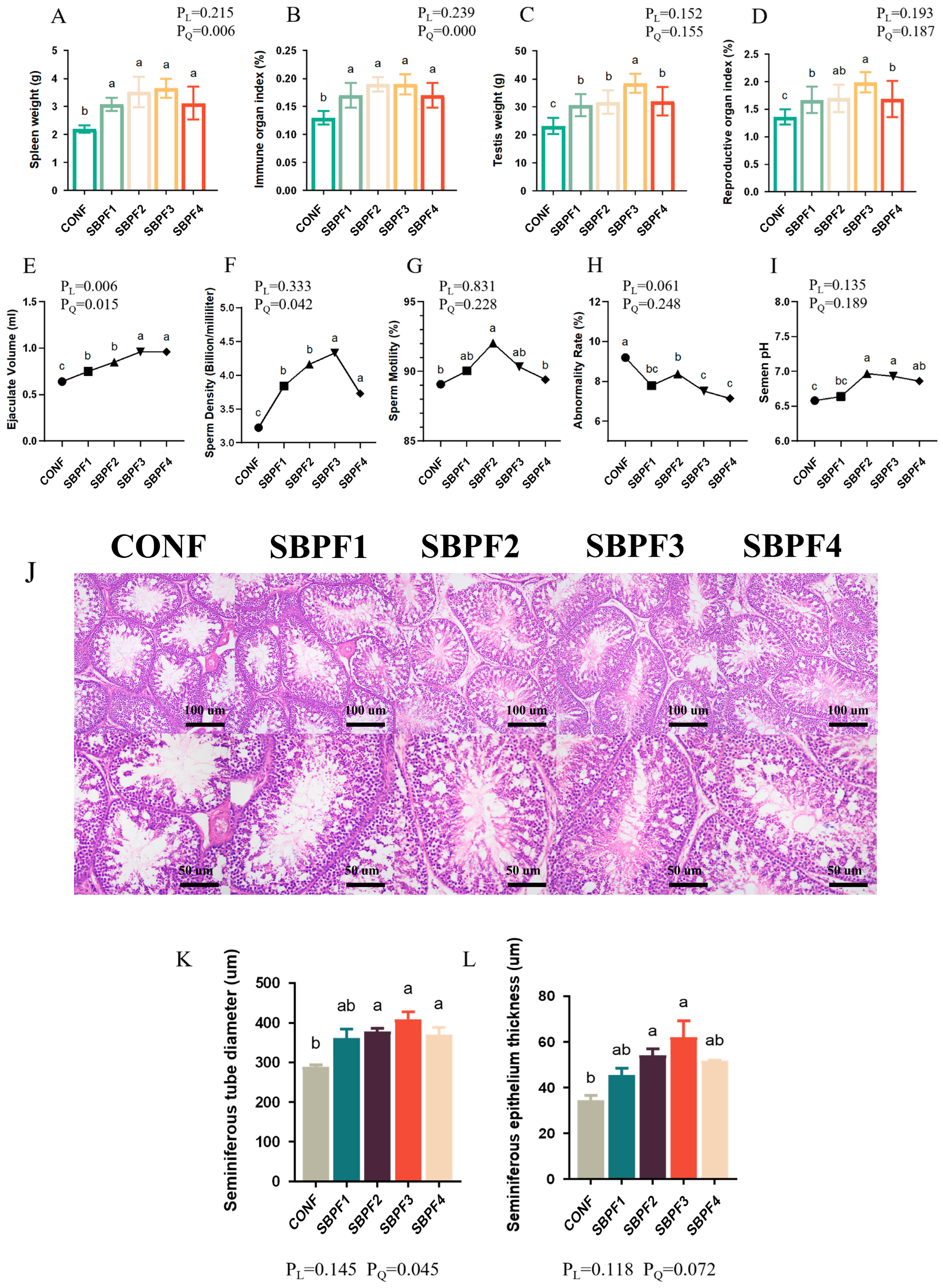
3.7. SBP Supplementation Enhances the Reproductive Performance of Roosters
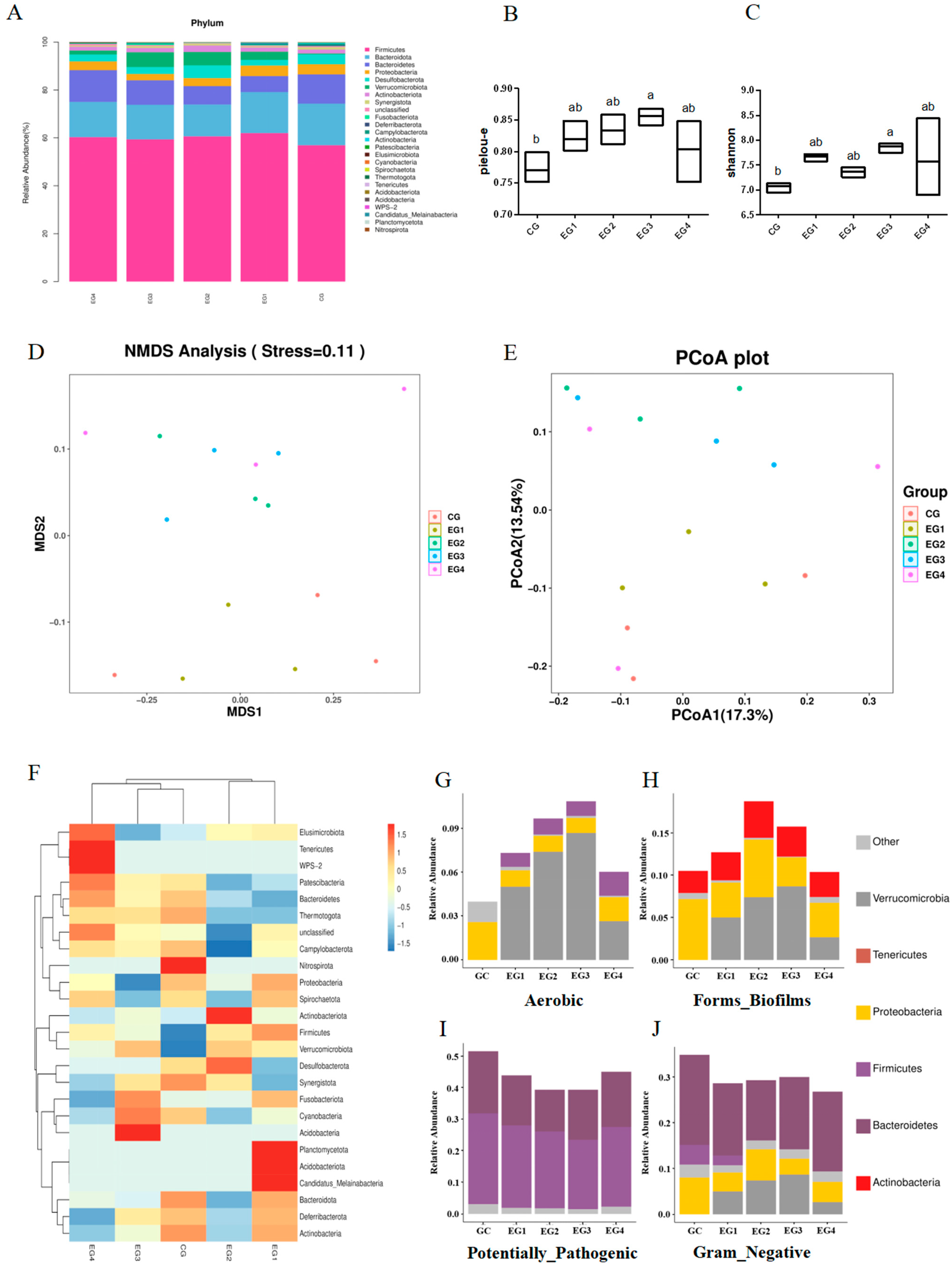
3.8. SBP Supplementation Improves the Cecal Microbiome Composition of Roosters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Molecular Weight Range (Da) | Peptides Fraction (%) |
|---|---|
| <1000 | 54.00 |
| 1000–3000 | 8.00 |
| 3000–10,000 | 6.5 |
| >10,000 | 31.50 |
| Ingredients | Contents % | Analyzed Nutrient Content | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn grain | 62.00 | AMEn 2 (kcal/kg) | 2677.99 |
| Soybean bran | 20.40 | Crude protein (CP)% | 16.36 |
| Wheat bran | 3.00 | Available phosphorus% | 0.32 |
| Calcitic limestone | 9.82 | Calcium% | 4.05 |
| Meat and bone meal (40% CP) | 4.00 | Sodium% | 0.18 |
| Nacl | 0.38 | Digestible lysine% | 0.75 |
| Vitamin and mineral supplement 1 | 0.20 | Digestible Met + Cys% | 0.59 |
| DL-methionine | 0.14 | Digestible methionine% | 0.37 |
| L-Lysine | 0.04 | Digestible threonine% | 0.54 |
| Total | 100.00 | ||
| Age (Week) | Light Period (h) | Light Intensity (Lux) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–2 d | 23 | 20–30 |
| 1 | 22 | 20–30 |
| 2 | 20 | 10–20 |
| 3 | 18 | 10 |
| 4 | 16 | 4–5 |
| 5 | 14 | 4–5 |
| 6 | 12 | 4–5 |
| 7 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 8 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 9 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 10 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 11 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 12 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 13 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 14 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 15 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 16 | 10 | 4–5 |
| 17 | 12 | 5–10 |
| 18 | 12.5 | 10–15 |
| 19 | 13 | 10–15 |
| 20 | 13.5 | 10–15 |
| 21–30 | 14 | 10–15 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | GenBank Number |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | F: GTCCACCGCAAATGCTTCTAA | K02259.1 |
| R: TGCGCATTTATGGGTTTTGTT | ||
| SOD | F: GGTGCTCACTTTAATCCTG | NM_205064.2 |
| R: CTACTTCTGCCACTCCTCC | ||
| GST | F: CATCCGATGGCTGCTGTCTGC | NM_001396288.1 |
| R: TCTGCACTGCACCAACTTCATCC | ||
| GPx | F: ACGGCGCATCTTCCAAAG | NM_001277853.3 |
| R: TGTTCCCCCAACCATTTCTC | ||
| GSR | F: GACTACAGCAACATCCCCAC | XM_015276627.4 |
| R: GTCCTTCCCATACACAGAGATG | ||
| ZO-1 | F: GCCTGAATCAAACCCAGCAA | XM_040706827.2 |
| R: TATGCGGCGGTAAGGATGAT | ||
| Claudin-3 | F: GAAGGGCTGTGGATGAACTG | NM_204202.2 |
| R: GAGACGATGGTGATCTTGGC | ||
| IFN-α | F: CCAGCACCTCGAGCAAT | NM_205427.1 |
| R: GGCGCTGTAATCGTTGTCT | ||
| IFN-γ | F: ATCATACTGAGCCAGATTGTTTCG | NM_205149.2 |
| R: TCTTTCACCTTCTTCACGCCAT | ||
| TGF-β1 | F: CGGGACGGATGAGAAGAA | NM_001318456.1 |
| R: TCGGCGCTCCAGATGTAC |
References
- Vulpiani, M.; Iannetti, L.; Romagnoli, S.; Cotturone, G.; Vincifori, G. Antibiotic-free farming for poultry meat production: Impact on animal welfare. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31, ckab165.279. [Google Scholar]
- Ayalew, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Qiu, K.; Qi, G.; Tekeste, A.; Wassie, T.; Chanie, D. Potential Feed Additives as Antibiotic Alternatives in Broiler Production. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 916473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, E.; Pilolli, R.; Bavaro, S.L.; Monaci, L. Insight into the gastro-duodenal digestion resistance of soybean proteins and potential implications for residual immunogenicity. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lule, V.K.; Garg, S.; Pophaly, S.D.; Hitesh Tomar, S.K. Potential health benefits of lunasin: A multifaceted soy-derived bioactive peptide. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, R485–R494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P.; Vij, S.; Hati, S. Functional significance of bioactive peptides derived from soybean. Peptides 2014, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, F.; Zhang, R.; Fang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Comparative effects of enzymatic soybean, fish meal and milk powder in diets on growth performance, immunological parameters, SCFAs production and gut microbiome of weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoni, A.O.; Aluko, R.E. Soybean foods and their benefits: Potential mechanisms of action. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dia, V.P.; Vasconez, M.; de Mejia, E.G.; Nelson, R.L. Analysis of soybean protein-derived peptides and the effect of cultivar, environmental conditions, and processing on lunasin concentration in soybean and soy products. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarian, M.; Khani, A.; Eghbalpour, S.; Uversky, V.N. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C. Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H.; Genovese, K.J.; He, H.; Swaggerty, C.L.; Jiang, Y. Modulation of chicken intestinal immune gene expression by small cationic peptides as feed additives during the first week posthatch. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, M.; Zaefarian, F.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Jia, J.; Ravindran, V. Influence of soybean bioactive peptides on growth performance, nutrient utilisation, digestive tract development and intestinal histology in broilers. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osho, S.O.; Xiao, W.W.; Adeola, O. Response of broiler chickens to dietary soybean bioactive peptide and coccidia challenge. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5669–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Soy bioactive peptides and the gut microbiota modulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9009–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Rezaei, M.; Teimouri Yansari, A. Effects of Canola Bioactive Peptides on Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activities, Nutrient Digestibility, Intestinal Morphology and Gut Microflora in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2016, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O. New concepts in the generation and functions of IgA. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W., Jr.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, K.A.; Gibbs, M.A.; Friedman, E.J. The Immune System Game. Am. Biol. Teach. 2015, 77, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Netea, M.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Joosten, L.A. Inflammasome activation and IL-1β and IL-18 processing during infection. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Gauldie, J.; Cox, G.; Baumann, H.; Jordana, M.; Lei, X.F.; Achong, M.K. IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.P.; Garrett, M.R.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Carnosine: A versatile antioxidant and antiglycating agent. Sci. Aging Knowl. Environ. 2005, 2005, pe12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, L.; Wu, C.; Yao, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Xie, Z.; et al. The Effect of the Antimicrobial Peptide Plectasin on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Immune Function of Yellow-Feathered Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 688611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.R.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liu, J.X. Effects of fermented soybean meal on digestive enzyme activities and intestinal morphology in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, H.; Barmeyer, C.; Fromm, M.; Runkel, N.; Foss, H.D.; Bentzel, C.J.; Riecken, E.O.; Schulzke, J.D. Altered tight junction structure contributes to the impaired epithelial barrier function in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Li, H.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y. Effects of antibacterial peptide combinations on growth performance, intestinal health, and immune function of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6481–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Leng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of dietary Artemisia annua supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune function, and gut microbiota of geese. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Shindo, M.; Gunshin, H.; Noguchi, T.; Naito, H. Characterization of phosphopeptide derived from bovine beta-casein: An inhibitor to intra-intestinal precipitation of calcium phosphate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1077, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Krishnan, H.B.; Pham, Q.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, T.T. Soy and Gut Microbiota: Interaction and Implication for Human Health. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2016, 64, 8695–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer-Englar, T.; Barlow, G.; Mathur, R. Obesity, diabetes, and the gut microbiome: An updated review. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajeda-Iglesias, C.; Durand, S.; Daillère, R.; Iribarren, K.; Lemaitre, F.; Derosa, L.; Aprahamian, F.; Bossut, N.; Nirmalathasan, N.; Madeo, F.; et al. Oral administration of Akkermansia muciniphila elevates systemic antiaging and anticancer metabolites. Aging 2021, 13, 6375–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Pei, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z. Akkermansia muciniphila and its outer protein Amuc_1100 regulates tryptophan metabolism in colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10184–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Age | CONF | SBPF1 | SBPF2 | SBPF3 | SBPF4 | SEM | PL | PQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW (g) | 0 | 33.40 | 33.74 | 34.34 | 33.84 | 34.18 | 1.83 | 0.150 | 0.200 |
| 6 | 370.40 b | 385.40 a | 402.40 a | 413.00 a | 405.00 a | 16.27 | 0.042 | 0.036 | |
| 18 | 1419.00 c | 1495.00 bc | 1570.00 ab | 1653.00 a | 1559.00 ab | 57.44 | 0.111 | 0.118 | |
| 30 | 1648.00 c | 1726.00 bc | 1807.00 ab | 1896.00 a | 1798.00 ab | 48.72 | 0.106 | 0.120 | |
| Tibia length (mm) | 0 | 27.45 | 26.08 | 27.06 | 26.83 | 27.85 | 0.84 | 0.544 | 0.357 |
| 6 | 66.77 b | 68.55 ab | 69.17 ab | 70.02 a | 70.78 a | 2.19 | 0.004 | 0.017 | |
| 18 | 96.49 b | 100.03 ab | 99.04 ab | 100.19 a | 98.52 ab | 2.39 | 0.450 | 0.250 | |
| ADG (g/d) | 1–6 | 8.04 c | 8.37 bc | 8.73 ab | 9.05 a | 8.82 a | 0.38 | 0.057 | 0.043 |
| 7–18 | 12.45 d | 13.24 c | 13.93 b | 14.73 a | 13.75 bc | 0.77 | 0.132 | 0.121 | |
| 19–30 | 2.75 | 2.77 | 2.81 | 2.86 | 2.85 | 0.10 | 0.013 | 0.075 | |
| ADFI (g/d/bird) | 1–6 | 11.79 | 12.09 | 12.1 | 12.11 | 12.17 | 0.30 | 0.087 | 0.138 |
| 7–18 | 57.17 | 57.74 | 58.00 | 57.98 | 57.72 | 0.63 | 0.252 | 0.001 | |
| 19–30 | 90.33 | 90.84 | 90.9 | 90.91 | 90.76 | 0.53 | 0.275 | 0.049 | |
| F/G (g/g) | 1–6 | 1.47 a | 1.45 ab | 1.38 ab | 1.34 b | 1.38 ab | 0.06 | 0.070 | 0.145 |
| 7–18 | 4.60 a | 4.36 ab | 4.17 bc | 3.94 c | 4.20 b | 0.23 | 0.113 | 0.104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, T.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H. Soybean Bioactive Peptide Supplementation Affects the Intestinal Immune Antioxidant Function, Microbial Diversity, and Reproductive Organ Development in Roosters. Animals 2024, 14, 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131954
Wei Y, Zhao X, Xu T, Liu Z, Zuo Y, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Yin H. Soybean Bioactive Peptide Supplementation Affects the Intestinal Immune Antioxidant Function, Microbial Diversity, and Reproductive Organ Development in Roosters. Animals. 2024; 14(13):1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131954
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yimeng, Xiyu Zhao, Tao Xu, Zhenyan Liu, Yalan Zuo, Mingxue Zhang, Yao Zhang, and Huadong Yin. 2024. "Soybean Bioactive Peptide Supplementation Affects the Intestinal Immune Antioxidant Function, Microbial Diversity, and Reproductive Organ Development in Roosters" Animals 14, no. 13: 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131954
APA StyleWei, Y., Zhao, X., Xu, T., Liu, Z., Zuo, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., & Yin, H. (2024). Soybean Bioactive Peptide Supplementation Affects the Intestinal Immune Antioxidant Function, Microbial Diversity, and Reproductive Organ Development in Roosters. Animals, 14(13), 1954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131954





