Protein, Essential Amino Acid, and Fatty Acid Composition of Five Target Fishery Species of Central Mediterranean Sea
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Strategy and Collection
2.2. Protein and Amino Acids Content
2.3. Fatty Acids Profile Determination
2.4. Nutritional Quality Indexes
| IA: [C12:0 + (4 × C14:0) + C16:0]/ΣUFA |
| IT: (C14:0 + C16:0 + C18:0)/[(0.5 × ΣMUFA) + (0.5 × Σn-6 PUFA) + (3 × Σn-3 PUFA) + (n-3/n-6)] |
| HH: (cis-C18:1 + ΣPUFA)/(C12:0 + C14:0 + C16:0) |
| FLQ: 100 × (C22:6 n-3 + C20:5 n-3)/ΣFA |
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein Content and Essential Amino Acids
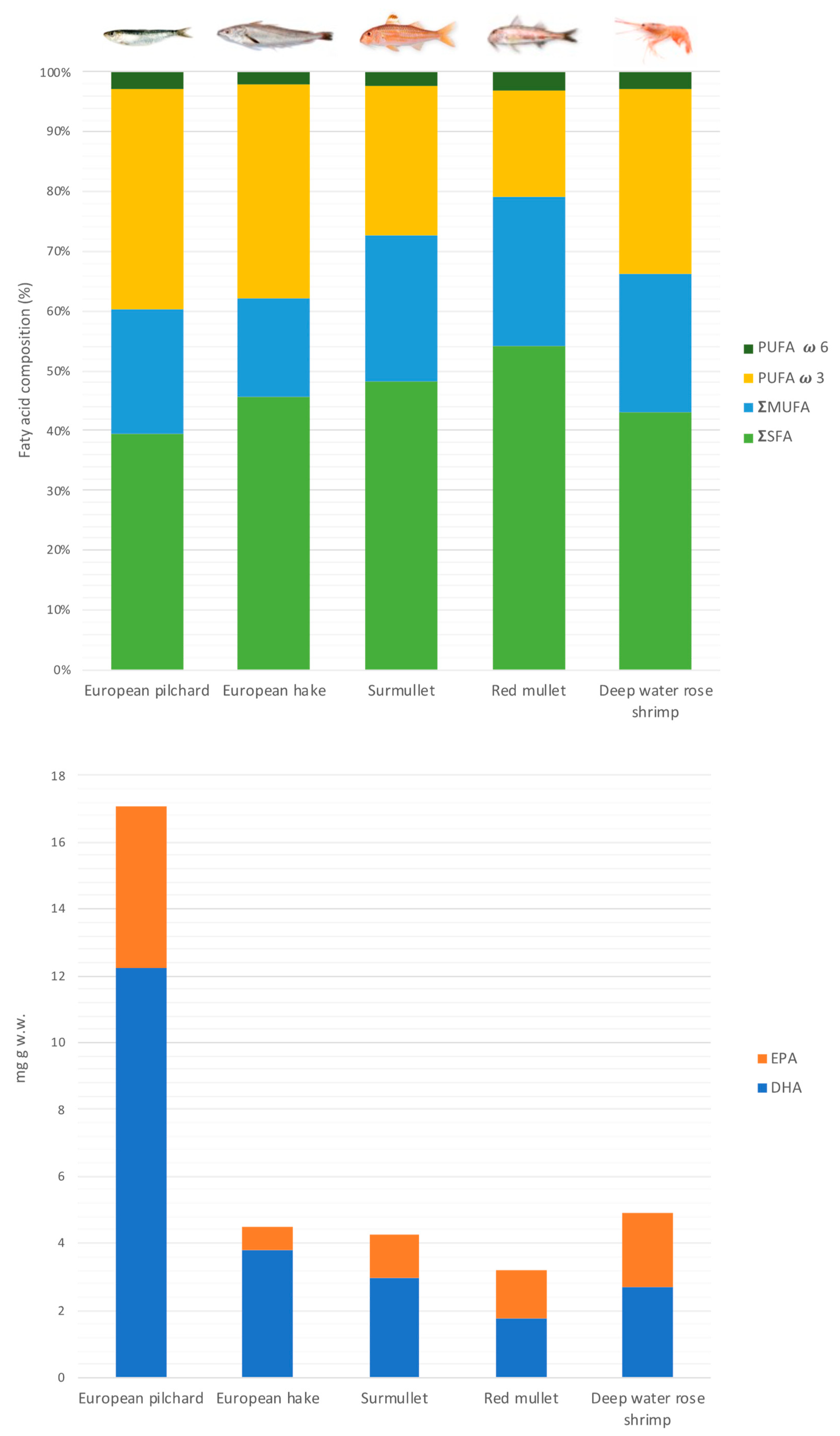
3.2. Fatty Acids Profile
3.3. Nutritional Quality Indices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohanty, B.P.; Ganguly, S.; Mahanty, A.; Mitra, T.; Patra, S.; Karunakaran, D.; Mathew, S.; Chakraborty, K.; Paul, B.N.; Sarma, D.; et al. Fish in Human Health and Nutrition. Adv. Fish. Res. 2019, 7, 189–218. [Google Scholar]
- Iko Afé, O.H.; Assogba, M.F.; Anihouvi, D.G.H.; Boukari, B.; Douny, C.; Kpoclou, Y.E.; Amoussou Fagla, B.; Igout, A.; Mahillon, J.; Anihouvi, V.B.; et al. Consumption and Physico-chemical Characteristics of Smoked and Smoked-dried Fish Commonly Produced in South Benin and Contribution to Recommended Nutrient Intakes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4822–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoussou, N.; Marengo, M.; Iko Afé, O.H.; Lejeune, P.; Durieux, É.D.H.; Douny, C.; Scippo, M.L.; Gobert, S. Comparison of Fatty Acid Profiles of Two Cultivated and Wild Marine Fish from Mediterranean Sea. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, M.; Reale, A.; Ziino, M.; Romeo, V.; Lembo, E.; Manganaro, A. Chemical Composition and Nutritional Value of Engraulis Encrasicolus (Linnaeus, 1758) Caught by Driftnet “Menaide” along Sicilian Coast: A Natural Food for Mediterranean Diet. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, Z.; Louchami, K.; Sener, A.; Malaisse, W.J.; Yahia, D.A. Dietary Sardine Protein Lowers Insulin Resistance, Leptin and TNF-α and Beneficially Affects Adipose Tissue Oxidative Stress in Rats with Fructose-Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, G.; Ruzzin, J.; Rioux, L.E.; Lavigne, C.; White, P.J.; Frøyland, L.; Jacques, H.; Bryl, P.; Beaulieu, L.; Marette, A. Differential Effects of Various Fish Proteins in Altering Body Weight, Adiposity, Inflammatory Status, and Insulin Sensitivity in High-Fat-Fed Rats. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarojnalini, C.; Hei, A. Fish as an Important Functional Food for Quality Life. In Functional Foods; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, B.; Mahanty, A.; Ganguly, S.; Sankar, T.V.; Chakraborty, K.; Rangasamy, A.; Paul, B.; Sarma, D.; Mathew, S.; Asha, K.K.; et al. Amino Acid Compositions of 27 Food Fishes and Their Importance in Clinical Nutrition. J. Amino Acids 2014, 2014, 269797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.A.; Abolude, D.S.; Ega, R.A. Nutrient Quality of Four Oven Dried Freshwater Catfish Species in Northern Nigeria. J. Trop. Biosci. 2001, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sankar, T.V.; Ramachandran, A. Changes in Biochemical Composition in Indian Major Carps in Relation to Size. Fish. Technol. 2001, 38, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, B.P.; Mahanty, A.; Ganguly, S.; Mitra, T.; Karunakaran, D.; Anandan, R. Nutritional Composition of Food Fishes and Their Importance in Providing Food and Nutritional Security. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Amino Acids: Metabolism, Functions, and Nutrition. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Essential Fatty Acids in Health and Chronic Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 560S–569S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverría, F.; Valenzuela, R.; Catalina Hernandez-Rodas, M.; Valenzuela, A. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA), a Fundamental Fatty Acid for the Brain: New Dietary Sources. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2017, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorell, I.; Perelló, G.; Martí-Cid, R.; Castell, V.; Llobet, J.M.; Domingo, J.L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in Foods and Estimated PAH Intake by the Population of Catalonia, Spain: Temporal Trend. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Guan, R.; Ding, G.; Chen, Q.; Lou, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xing, M.; Han, J.; Wu, Y. Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins/Furans (PCDD/Fs) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Zhejiang Foods (2006–2015): Market Basket and Polluted Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traina, A.; Bono, G.; Bonsignore, M.; Falco, F.; Giuga, M.; Quinci, E.M.; Vitale, S.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy Metals Concentrations in Some Commercially Key Species from Sicilian Coasts (Mediterranean Sea): Potential Human Health Risk Estimation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, A.; Chenet, T.; Bono, G.; Geraci, M.L.; Vaccaro, C.; Munari, C.; Mistri, M.; Cavazzini, A.; Pasti, L. Adverse Effects of Plastic Ingestion on the Mediterranean Small-Spotted Catshark (Scyliorhinus Canicula). Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 155, 104876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasbalg, T.L.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Ramsden, C.E.; Majchrzak, S.F.; Rawlings, R.R. Changes in Consumption of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids in the United States during the 20th Century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.A.; King, D.J.; Zibrik, D.; Innis, S.M. Decreasing Linoleic Acid with Constant α-Linolenic Acid in Dietary Fats Increases (n-3) Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Plasma Phospholipids in Healthy Men. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, J.E.; Lokesh, B.; Stone, R.A. Dietary N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Amelioration of Cardiovascular Disease: Possible Mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The Importance of the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio in Cardiovascular Disease and Other Chronic Diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, R.M.; Petenuci, M.E.; Maistrovicz, F.C.; Galuch, M.B.; Montanher, P.F.; Pizzo, J.S.; Gualda, I.P.; Visentainer, J.V. Lipid Profile and Fatty Acid Composition of Marine Fish Species from Northeast Coast of Brazil. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, S.K.; Psota, T.L.; Harris, W.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. N-3 Fatty Acid Dietary Recommendations and Food Sources to Achieve Essentiality and Cardiovascular Benefits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1526S–1535S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.E.; da Silva Vasconcelos, M.A.; de Almeida Ribeiro, M.; Sarubbo, L.A.; Andrade, S.A.C.; de Melo Filho, A.B. Nutritional and Lipid Profiles in Marine Fish Species from Brazil. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, S.; Cannizzaro, L.; Bono, G.; Beltrano, A.M.; Milazzo, A.; Norrito, G. Catch Composition of Decapoda Crustaceans from Trawl Fishery Catches in the Central Mediterranean Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 39, 1798–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, S.; Cannizzaro, L.; Bono, G.; Beltrano, A.M.; Milazzo, A. Catch Composition and Biodiversity Fish Community from Trawl Fishery Catches in the Central Mediterranean Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 39, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, J.G. Zero Hunger and Territories of Citizenship: Promoting Food Security in Brazil’s Rural Areas. In The Poorest and Hungry: Assessments, Analyses, and Actions; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Béné, C.; Macfayden, G.; Allison, E.H. Increasing the Contribution of Small-Scale Fisheries to Poverty Alleviation and Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ariño, A.; Beltrán, J.A.; Herrera, A.; Roncalés, P. Fish and Seafood: Nutritional Value. In Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemist. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemist: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Khuhawar, M.Y.; Majidano, S.A. GC Analysis of Amino Acids Using Trifluoroacetylacetone and Ethyl Chloroformate as Derivatizing Reagents in Skin Samples of Psoriatic and Arsenicosis Patients. Chromatographia 2011, 73, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosuè, C.; D’Agostino, F.; Maniaci, G.; Avellone, G.; Sciortino, M.; De Caro, V.; Bonanno, A.; Ponte, M.; Alabiso, M.; Di Grigoli, A. Persistent Organic Pollutants and Fatty Acid Profile in a Typical Cheese from Extensive Farms: First Assessment of Human Exposure by Dietary Intake. Animals 2022, 12, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary Heart Disease: Seven Dietary Factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, J.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Santos-Silva, F. Effect of Genotype, Feeding System and Slaughter Weight on the Quality of Light Lambs. II. Fatty Acid. Composition of Meat. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 77, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrami, G.; Natiello, F.; Bronzi, P.; McKenzie, D.; Bolis, L.; Agradi, E. A Comparison of Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acid Levels in Wild and Farmed Eels (Anguilla Anguilla). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Comp. Biochem. 1992, 101, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 2nd ed.; Developments in Environmental Modelling, 20; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition; WHO Technical Report Series 935; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Young, V.R.; Pellett, P.L. Background Paper 5: Amino Acid Composition in Relation to Protein Nutritional Quality of Meat and Poultry Products. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackman, R.G. Seafood Lipids and Fatty Acids. Food Rev. Int. 1990, 6, 617–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornaritis, M.; Peraki, E.; Georgulli, M.; Kafatos, A.; Charalambakis, G.; Divanack, P.; Kentouri, M.; Yiannopoulos, S.; Frenaritou, H.; Argyrides, R. Fatty Acid Composition and Total Fat Content of Eight Species of Mediterranean Fish. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1994, 45, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F. Total Lipid Content and Fatty Acid Composition of Commercially Important Fish Species from the Mediterranean, Mar Grande Sea. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Rampacci, M.; Casini, I.; Caproni, R.; Orban, E. Proximate Composition and Lipid Profile of Red Mullet (Mullus Barbatus) from Two Sites of the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Seas (Italy): A Seasonal Differentiation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 45, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Fanelli, G.; Parlapiano, I.; Biandolino, F. Bioactive Fatty Acids in Seafood from Ionian Sea and Relation to Dietary Recommendations. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F.; Çiçek, E.; Polat, A.; Kuley, E. Fat Content and Fatty Acid Compositions of 34 Marine Water Fish Species from the Mediterranean Sea. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Fatty Acid Profiles of Commercially Important Fish Species from the Mediterranean, Aegean and Black Seas. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatanos, S.; Laskaridis, K. Seasonal Variation in the Fatty Acid Composition of Three Mediterranean Fish—Sardine (Sardina Pilchardus), Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicholus) and Picarel (Spicara Smaris). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Taylor, K.D.A.; Zubcov, E.; Shahidi, F.; Alexis, M. Differentiation of Cultured and Wild Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax): Total Lipid Content, Fatty Acid and Trace Mineral Composition. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Kuzu, S.; Özyurt, G.; Tokur, B. Fatty Acid Composition of Red Mullet (Mullus Barbatus): A Seasonal Differentiation. J. Muscle Foods 2009, 20, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biton-Porsmoguer, S.; Bou, R.; Lloret, E.; Alcaide, M.; Lloret, J. Research Article Fatty Acid Composition and Parasitism of European Sardine (Sardina Pilchardus) and Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Populations in the Northern Catalan Sea in the Context of Changing Environmental Conditions. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coaa121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Fats, Including Saturated Fatty Acids, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Monounsaturated Fatty Acids, Trans Fatty Acids, and Cholesterol. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1461. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, G.; Ecker, J. The Opposing Effects of N−3 and N−6 Fatty Acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, Z.; Lai, C. Significance of Increasing N-3 PUFA Content in Pork on Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digiacomo, R.A.; Kremer, J.M.; Shah, D.M. Fish-Oil Dietary Supplementation in Patients with Raynaud’s Phenomenon: A Double-Blind, Controlled, Prospective Study. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Soranna, D.; Catapano, A.L.; Corrao, G. Long-Term Effect of High Dose Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation for Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Trials. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2013, 14, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crupi, R.; Marino, A.; Cuzzocrea, S. N-3 Fatty Acids: Role in Neurogenesis and Neuroplasticity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2953–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, R.; Gagnon, C.; Swist, E.; Rondeau, I.; Massarelli, I.; Cheung, W.; Ratnayake, W.M.N. EPA and DHA Status of South Asian and White Canadians Living in the National Capital Region of Canada. Lipids 2014, 49, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyall, S.C. Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids and the Brain: A Review of the Independent and Shared Effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, M.A.; Petersen, K.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Saturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Replacements for Saturated Fat to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Healthcare 2017, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Che, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative Study of Different Polar Groups of EPA-Enriched Phospholipids on Ameliorating Memory Loss and Cognitive Deficiency in Aged SAMP8 Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Mayyas, F.; Abu Zamzam, H.I. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Protects against Chronic Sleep-Deprivation Induced Memory Impairment. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, W.E. Importance of N-3 Fatty Acids in Health and Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 171S–175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.M. Dietary Fatty Acids and Human Health. Anim. Res. 2000, 49, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. N-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence Explained and Mechanisms Explored. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernichow, S.; Thomas, D.; Bruckert, E. N-6 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Health: A Review of the Evidence for Dietary Intake Recommendations. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, B.L.; Canto, A.C.V.D.C.S.; Da Costa, M.P.; Da Silva, F.A.; Mársico, E.T.; Conte, C.A. Fatty Acid Profiles of Five Farmed Brazilian Freshwater Fish Species from Different Families. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocher, D.R. Fatty Acid Requirements in Ontogeny of Marine and Freshwater Fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.; Barreira, L.; Figueiredo, F.; Custódio, L.; Vizetto-Duarte, C.; Polo, C.; Rešek, E.; Aschwin, E.; Varela, J. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids of Marine Macroalgae: Potential for Nutritional and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, S.; Peltomaa, E.; Salmi, P. Variation in ω-3 and ω-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Produced by Different Phytoplankton Taxa at Early and Late Growth Phase. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneedorferová, I.; Tomčala, A.; Valterová, I. Effect of Heat Treatment on the N-3/n-6 Ratio and Content of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Fish Tissues. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoltsidis, P.A.; Zotos, A.; Constantinides, S.M. Composition of the Commercially Important Mediterranean Finfish, Crustaceans, and Molluscs. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1995, 8, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidos, I.; Van der Padt, A.V.; Luten, J.B.; Boom, R.M. Seasonal Changes in Crude and Lipid Composition of Herring Fillets, Byproducts, and Respective Produced Oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4589–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzia, L.A.; Sampaio, G.R.; Castellucci, C.M.N.; Torres, E.A.F.S. The Influence of Season on the Lipid Profiles of Five Commercially Important Species of Brazilian Fish. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, J.; Galzin, R.; Gil De Sola, L.; Souplet, A.; Demestre, M. Habitat Related Differences in Lipid Reserves of Some Exploited Fish Species in the North-Western Mediterranean Continental Shelf. J. Fish. Biol. 2005, 67, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufan, B.; Koral, S.; Köse, S. Changes during Fishing Season in the Fat Content and Fatty Acid Profile of Edible Muscle, Liver and Gonads of Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Caught in the Turkish Black Sea. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.N.; Jacobsen, C.; Nielsen, H.H. Fatty Acid Composition of Herring (Clupea Harengus L.): Influence of Time and Place of Catch on n-3 PUFA Content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, G.; Gai, F.; Peiretti, P.G.; Badalucco, C.; Brugiapaglia, A.; Siragusa, G.; Palmegiano, G.B. Chemical and Nutritional Characterisation of the Central Mediterranean Giant Red Shrimp (Aristaeomorpha Foliacea): Influence of Trophic and Geographical Factors on Flesh Quality. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, X.; He, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, R.Q.; Wu, Y. Fatty Acid Composition Analyses of Commercially Important Fish Species from the Pearl River Estuary, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty Acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmso, U. Nutritional Aspects of Cardiovascular Disease; Report on Health and Social Subjects No. 46; H.M. Stationery Office: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe, M.G.; Siano, F.; Paolucci, M.; Sacco, A.; Sorrentino, A.; Malinconico, M.; Varricchio, E. Active Edible Coating Effectiveness in Shelf-Life Enhancement of Trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss) Fillets. LWT 2015, 60, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Mahmoudzadeh, L.; Khaksar, R.; Khosroshahi, N.K.; Babakhani, A. Effect of Different Cooking Methods on Minerals, Vitamins and Nutritional Quality Indices of Kutum Roach (Rutilus Frisii Kutum). Food Chem. 2014, 148, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testi, S.; Bonaldo, A.; Gatta, P.P.; Badiani, A. Nutritional Traits of Dorsal and Ventral Fillets from Three Farmed Fish Species. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncarati, A.; Brambilla, G.; Meluzzi, A.; Iamiceli, A.L.; Fanelli, R.; Moret, I.; Ubaldi, A.; Miniero, R.; Sirri, F.; Melotti, P.; et al. Fatty Acid Profile and Proximate Composition of Fillets from Engraulis Encrasicholus, Mullus Barbatus, Merluccius Merluccius and Sarda Sarda Caught in Tyrrhenian, Adriatic and Ionian Seas. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 28, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
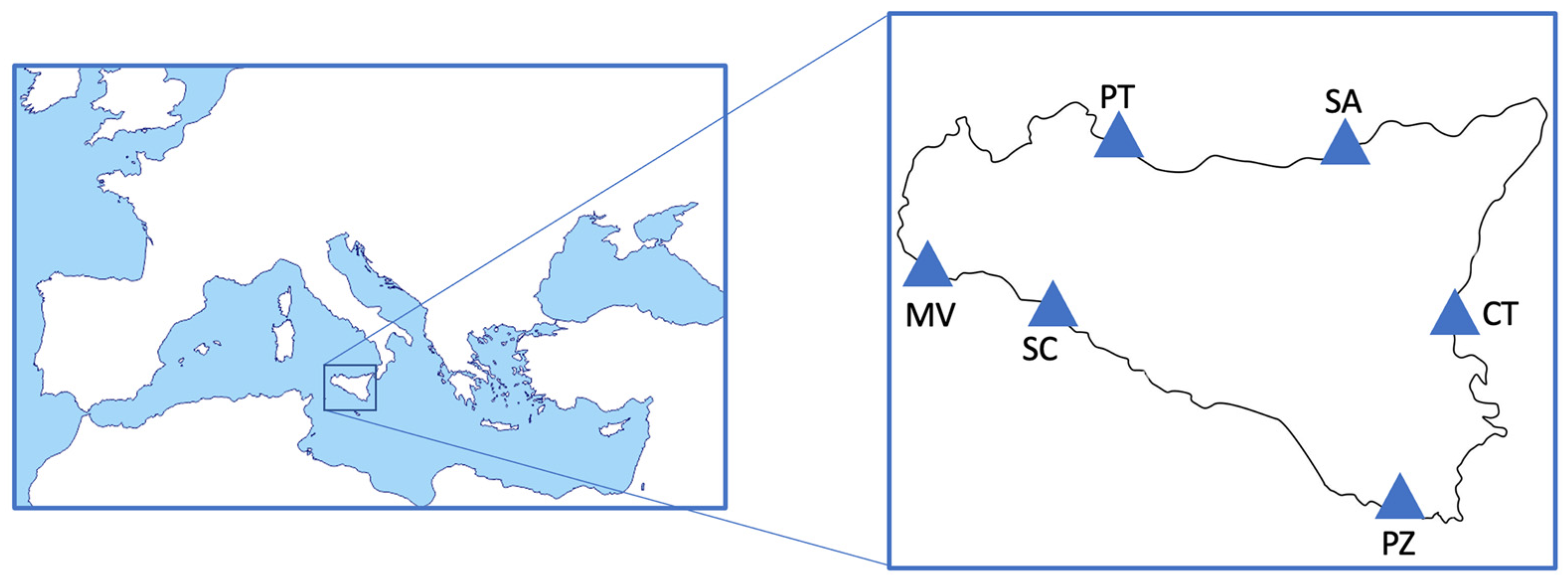

| Scientific Name | Individuals per Site | Length | Weight | Habitat | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Common Name) | PT Porticello | SA S. Agata | CT Catania | PZ Pozzallo | SC Sciacca | MV Mazara del Vallo | (cm) | (g) | |
| Sardina pilchardus | 46 | 50 | 50 | 55 | 59 | / | 15.3 ± 1.3 | 26.7 ± 7.9 | pelagic |
| (European pilchard) | |||||||||
| Merluccius merluccius | 11 | 3 | 9 | 26 | 17 | 14 | 23.5 ± 4.8 | 123.5 ± 128.1 | demersal |
| (European hake) | |||||||||
| Mullus surmuletus | 15 | 8 | 18 | / | / | 16 | 17.9 ± 2.1 | 73.1 ± 26.1 | demersal |
| (Surmullet) | |||||||||
| Mullus barbatus | / | 15 | / | 15 | 34 | / | 16.6 ± 1.9 | 53.8 ± 20 | demersal |
| (Red mullet) | |||||||||
| Parapenaeus longirostris | 126 | 88 | 130 | 104 | 158 | 111 | 3.8 ± 0.7 * | 5.8 ± 2.6 | demersal |
| (Deep water rose shrimp) | |||||||||
| Amino Acid Fractions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Area | Total Protein | EAA | Val | Leu | ILe | Thr | Phen | Lys | Try |
| European pilchard | PT | 24.6 | 11.2 | 1.8 | 3.3 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.6 |
| SA | 25.4 | 13.6 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 1.8 | |
| CT | 23.9 | 12.5 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | |
| PZ | 25.8 | 13.9 | 2.3 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 2.3 | |
| SC | 24.1 | 12.4 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 2.8 | |
| Mean ± Dev.St | 24.8 ± 0.8 | 12.72 ± 1.06 | 1.94 ± 0.4 | 3.15 ± 0.26 | 1.69 ± 0.29 | 1.63 ± 0.27 | 0.45 ± 0.16 | 1.84 ± 0.71 | 2.02 ± 0.5 | |
| European hake | PT | 18.4 | 9.6 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 1.5 |
| SA | 19.6 | 6.4 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.7 | |
| CT | 17.3 | 9.0 | 1.4 | 2.6 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | |
| PZ | 20.3 | 10.3 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 1.3 | |
| SC | 20.8 | 11.9 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 2.9 | |
| MV | 23.1 | 12.3 | 2.0 | 3.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.5 | |
| Mean ± Dev.St | 19.9 ± 2 | 9.91 ± 2.15 | 1.42 ± 0.3 | 2.39 ± 0.75 | 1.27 ± 0.28 | 1.12 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.11 | 1.8 ± 0.77 | 1.51 ± 0.75 | |
| Surmullet | PT | 24.0 | 12.0 | 2.0 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.8 |
| SA | 23.1 | 12.5 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 2.0 | |
| CT | 24.3 | 12.8 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 1.7 | |
| MV | 19.8 | 10.1 | 1.7 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Mean ± Dev.St | 22.8 ± 2.1 | 9.93 ± 1.21 | 1.52 ± 0.26 | 2.42 ± 0.51 | 1.39 ± 0.12 | 1.21 ± 0.2 | 0.41 ± 0.18 | 1.69 ± 1.09 | 1.53 ± 0.25 | |
| Red mullet | SA | 23.3 | 10.9 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 2.4 |
| PZ | 23.4 | 12.9 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 2.0 | |
| SC | 23.0 | 10.3 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.7 | |
| Mean ± Dev.St | 23.2 ± 0.2 | 11.34 ± 1.35 | 1.71 ± 0.14 | 2.82 ± 0.43 | 1.48 ± 0.13 | 1.35 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 1.57 ± 0.66 | 2.04 ± 0.32 | |
| Deep water rose shrimp | PT | 20.7 | 10.8 | 1.5 | 2.6 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| SA | 21.3 | 8.2 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 1.3 | |
| CT | 20.3 | 9.2 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| PZ | 18.3 | 9.3 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| SC | 18.0 | 8.3 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 | |
| MV | 22.2 | 10.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 1.1 | |
| Mean ± Dev.St | 20.1 ± 1.7 | 9.37 ± 1.06 | 1.4 ± 0.15 | 2.16 ± 0.34 | 1.31 ± 0.13 | 1.56 ± 0.31 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 1.49 ± 0.37 | 1.35 ± 0.22 | |
| Specie | Area | Total FA | ΣSFA | ΣMUFA | ΣPUFA | C20:5n3 (EPA) | C22:6n3 (DHA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European pilchard | CT | 8.96 ± 1.32 | 26.8 ± 4.16 | 19.8 ± 2.89 | 51.9 ± 6.05 | 15.2 ± 2.62 | 29.9 ± 2.68 |
| MV | 4.69 ± 1.13 | 38.6 ± 14.4 | 19.8 ± 3.75 | 40.3 ± 11.0 | 9.18 ± 2.58 | 25.9 ± 7.22 | |
| PT | 5.87 ± 1.03 | 38.1 ± 9.67 | 20.5 ± 3.00 | 40.4 ± 6.00 | 11.8 ± 1.33 | 22.8 ± 3.50 | |
| PZ | 2.63 ± 1.82 | 51.3 ± 3.99 | 16.0 ± 4.39 | 32.5 ± 3.61 | 5.55 ± 1.26 | 22.1 ± 3.98 | |
| SA | 3.17 ± 0.74 | 50.4 ± 3.52 | 17.9 ± 1.32 | 31.2 ± 3.73 | 6.44 ± 0.71 | 20.0 ± 2.80 | |
| European hake | CT | 1.07 ± 0.45 | 45.4 ± 3.21 | 16.0 ± 2.67 | 36.4 ± 1.73 | 4.61 ± 0.46 | 25.8 ± 1.05 |
| MV | 1.64 ± 0.44 | 43.3 ± 1.50 | 14.6 ± 0.85 | 38.6 ± 2.52 | 6.19 ± 0.41 | 27.3 ± 2.05 | |
| PT | 0.97 ± 0.24 | 53.1 ± 2.96 | 16.1 ± 2.71 | 24.0 ± 2.55 | 3.71 ± 0.55 | 16.3 ± 1.78 | |
| PZ | 1.69 ± 1.13 | 42.5 ± 5.57 | 12.1 ± 2.18 | 44.0 ± 4.56 | 5.29 ± 0.63 | 33.2 ± 4.21 | |
| SA | 1.79 ± 0.31 | 38.1 ± 2.47 | 10.9 ± 0.85 | 50.7 ± 1.94 | 4.74 ± 0.76 | 41.0 ± 0.54 | |
| SC | 1.97 ± 0.46 | 44.4 ± 1.91 | 15.4 ± 3.32 | 37.7 ± 2.96 | 5.36 ± 0.51 | 27.0 ± 2.72 | |
| Surmullet | CT | 2.86 ± 0.58 | 47.8 ± 1.94 | 34.4 ± 2.47 | 16.1 ± 2.63 | 4.60 ± 0.39 | 5.29 ± 2.45 |
| MV | 1.51 ± 0.59 | 45.6 ± 3.18 | 10.1 ± 2.23 | 44.3 ± 3.72 | 8.45 ± 1.00 | 27.1 ± 3.86 | |
| PT | 2.35 ± 0.33 | 50.4 ± 1.73 | 29.4 ± 1.86 | 17.0 ± 1.00 | 4.08 ± 0.32 | 5.47 ± 0.37 | |
| SA | 2.10 ± 0.36 | 50.7 ± 3.72 | 23.1 ± 3.87 | 23.3 ± 3.19 | 6.01 ± 1.95 | 10.2 ± 1.70 | |
| Red mullet | PZ | 2.19 ± 1.37 | 55.9 ± 8.68 | 22.1 ± 6.62 | 20.2 ± 8.66 | 5.52 ± 2.44 | 7.79 ± 4.38 |
| SA | 2.75 ± 0.73 | 52.7 ± 2.20 | 22.2 ± 1.38 | 23.2 ± 2.53 | 6.88 ± 1.47 | 8.50 ± 1.87 | |
| SC | 2.10 ± 1.19 | 52.5 ± 2.98 | 25.6 ± 4.90 | 19.4 ± 2.15 | 5.24 ± 0.48 | 6.48 ± 1.38 | |
| Deep water rose shrimp | CT | 2.03 ± 0.50 | 44.3 ± 3.61 | 23.1 ± 3.15 | 30.9 ± 2.47 | 10.7 ± 1.17 | 12.7 ± 1.79 |
| MV | 1.38 ± 0.37 | 49.4 ± 8.11 | 20.4 ± 0.95 | 28.1 ± 6.97 | 10.6 ± 3.26 | 11.7 ± 3.98 | |
| PT | 2.37 ± 0.39 | 36.8 ± 0.51 | 22.8 ± 1.26 | 39.9 ± 1.34 | 14.0 ± 0.83 | 16.0 ± 1.08 | |
| PZ | 1.75 ± 0.29 | 45.1 ± 1.38 | 21.9 ± 2.22 | 30.5 ± 2.86 | 10.4 ± 0.39 | 10.7 ± 1.32 | |
| SA | 1.78 ± 0.34 | 40.5 ± 1.68 | 21.6 ± 2.61 | 37.1 ± 1.19 | 12.3 ± 0.27 | 13.9 ± 0.76 | |
| SC | 2.09 ± 0.05 | 42.8 ± 1.29 | 20.3 ± 1.21 | 36.8 ± 0.37 | 11.1 ± 1.23 | 18.3 ± 1.98 |
| Nutritional Indexes | European Pilchard | European Hake | Surmullet | Red Mullet | Deep Water Rose Shrimp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n6/n3 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.09 |
| PUFA/SFA | 1.21 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.41 | 0.84 |
| FLQ | 33.83 | 31.20 | 19.85 | 13.48 | 25.52 |
| IA | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.58 |
| IT | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.30 |
| HH | 3.37 | 1.96 | 1.54 | 1.27 | 2.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Traina, A.; Quinci, E.M.; Sabatino, N.; Del Core, M.; Bellante, A.; Bono, G.; Giuga, M.; Avellone, G.; Sprovieri, M.; D’Agostino, F. Protein, Essential Amino Acid, and Fatty Acid Composition of Five Target Fishery Species of Central Mediterranean Sea. Animals 2024, 14, 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14152158
Traina A, Quinci EM, Sabatino N, Del Core M, Bellante A, Bono G, Giuga M, Avellone G, Sprovieri M, D’Agostino F. Protein, Essential Amino Acid, and Fatty Acid Composition of Five Target Fishery Species of Central Mediterranean Sea. Animals. 2024; 14(15):2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14152158
Chicago/Turabian StyleTraina, Anna, Enza Maria Quinci, Nadia Sabatino, Marianna Del Core, Antonio Bellante, Gioacchino Bono, Marta Giuga, Giuseppe Avellone, Mario Sprovieri, and Fabio D’Agostino. 2024. "Protein, Essential Amino Acid, and Fatty Acid Composition of Five Target Fishery Species of Central Mediterranean Sea" Animals 14, no. 15: 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14152158
APA StyleTraina, A., Quinci, E. M., Sabatino, N., Del Core, M., Bellante, A., Bono, G., Giuga, M., Avellone, G., Sprovieri, M., & D’Agostino, F. (2024). Protein, Essential Amino Acid, and Fatty Acid Composition of Five Target Fishery Species of Central Mediterranean Sea. Animals, 14(15), 2158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14152158







