Effect of Dietary Riboflavin Levels on Reproductive Performance of Pigeon Breeders, and Growth Performance and Carcass Traits of Offspring Squabs
Abstract
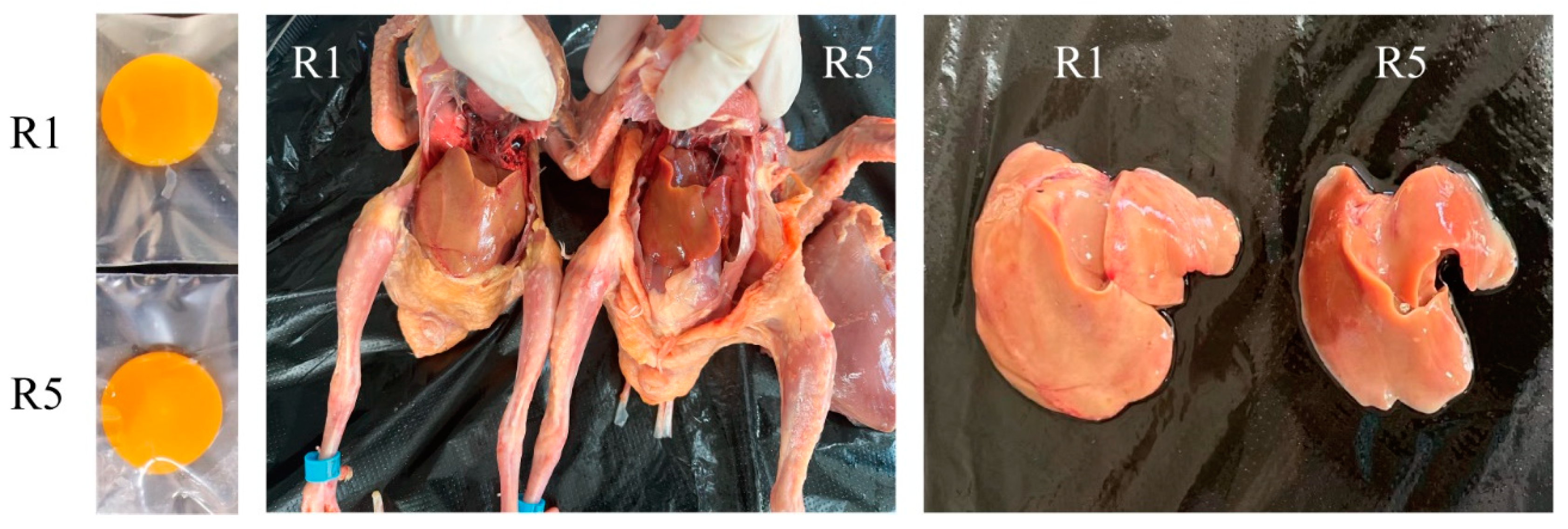
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Diets
2.3. Productivity and Reproductive Performance
2.4. Egg Quality
2.5. Growth Performance, Carcass Trait, and Organ Index
2.6. Riboflavin Concentration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reproductive Performance
3.2. Egg Quality
3.3. Growth Performance and Carcass Trait
3.4. Organ Weight and Index
3.5. Riboflavin Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.; He, Y.X.; Ye, J. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components of Columaba domesticus. Food Ind. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 447–448. [Google Scholar]
- Northrop-Clewes, C.A.; Thurnham, D.I. The discovery and characterization of riboflavin. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Bacher, A. Biosynthesis of flavocoenzymes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 324–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogburn, L.A.; Smarsh, D.N.; Wang, X.; Trakooljul, N.; Carre, W.; White, H.B., 3rd. Transcriptional profiling of liver in riboflavin-deficient chicken embryos explains impaired lipid utilization, energy depletion, massive hemorrhaging, and delayed feathering. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Hu, J.; Xue, M.; Guo, Z.B.; Xie, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Z.K.; Huang, W.; Hou, S.S. Maternal diet deficient in riboflavin induces embryonic death associated with alterations in the hepatic proteome of duck embryos. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naber, E.C.; Squires, M.W. Research note: Early detection of the absence of a vitamin premix in layer diets by egg albumen riboflavin analysis. Poult. Sci. 1993, 72, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, M.W.; Naber, E.C. Vitamin profiles of eggs as indicators of nutritional status in the laying hen riboflavin study. Poult. Sci. 1993, 72, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.B.; Cao, J.T.; Xing, G.N.; Sun, P.X.; Huang, W.; Xie, M.; Hou, S.S. Effects of riboflavin deficiency on the lipid metabolism of duck breeders and duck embryos. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maw, A.J.G. Inherited riboflavin deficiency in chicken eggs. Poult. Sci. 1954, 33, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, V.A.; Han, C.C. Riboflavin-deficient chicken embryos: Hypoglycemia without dicarboxylic aciduria. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 1995, 111, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.B. Sudden death of chicken embryos with hereditary riboflavin deficiency. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 1303S–1307S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, R.; Fouad, A.M.; Wu, Y.B.; Sun, P.X.; Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Xie, M.; Tang, J.; Hou, S.S. Effects of riboflavin on reproductive performance and antioxidant status of duck breeders. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY/T 823–2004; Performance Terms and Measurement for Poultry. The Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Tang, J.; Xie, M.; Yang, J.; Wen, Z.G.; Zhu, Y.W.; Huang, W.; Hou, S.S. Riboflavin requirements of white Pekin ducks from hatch to 21 d of age. Br. Poult. Sci. 2013, 54, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, N.L.; Riter, K.L.; Smallidge, R.L. Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic determination of riboflavin in feeds. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petteys, B.J.; Frank, E.L. Rapid determination of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) in plasma by HPLC. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batey, D.W.; Eckhert, C.D. Identification of FAD, FMN, and riboflavin in the retina by microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 188, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, H.R.; Saxton, A.M.; Southern, L.L. Estimation of nutrient requirements using broken-line regression analysis. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, E155–E165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry: Ninth Revised Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture of China. Nutrient Requirements of Meat-Type Chicken of China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture of China. Nutrient Requirements of Meat-Type Ducks of China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, R.D.; Tung, H.T.; Donaldson, W.E.; Hamilton, P.B. A New Description of Riboflavin Deficiency Syndrome in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 1973, 52, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hegeman, M.A.; Hu, J.; Xie, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, Y.; de Boer, V.; Guo, Y.; Hou, S.; Keijer, J. Severe riboflavin deficiency induces alterations in the hepatic proteome of starter Pekin ducks. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.P.; Buss, E.G.; Clagett, C.O.; Boucher, R.V. The nature of the biochemical lesion in avian renal riboflavinuria—II. The inherited change of a riboflavin-binding protein from blood and eggs. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 1967, 22, 897–906. [Google Scholar]
- White, H.B.; Nuwaysir, E.F.; Komara, S.P.; Anderson, D.A. Effect of riboflavin-binding protein deficiency on riboflavin metabolism in the laying hen. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 295, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, N.; Harms, R.H. Riboflavin requirement of broiler chicks fed a corn-soybean diet. Poult. Sci. 1988, 67, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegsted, D.M. The determination of minimum vitamin requirements for growth. J. Nutr. 1948, 35, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchenko, P.E.; Lemaire, M.; Fneich, S.; Voisin, S.; Jouin, M.; Junien, C.; Gabory, A. Epigenetics and Nutrition: Maternal nutrition impacts on placental development and health of offspring. Biol. Aujourdhui. 2015, 209, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Gomez, M.; Garcia-Contreras, C.; Torres-Rovira, L.; Astiz, S.; Ovilo, C.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A.; Isabel, B. Maternal undernutrition and offspring sex determine birth-weight, postnatal development and meat characteristics in traditional swine breeds. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth-Maier, D.A.; Kettlter, S.I.; Hirschvogl, G.; Kirchgessner, M. Investigations on the effect of maternal dietary riboflavin supplementation during gravidity and lactation on riboflavin concentrations in blood, liver, and total body of rat offspring. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 83, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, A.; Kent, J.P. Double and single yolked duck eggs: Their contents and dimensions compared and the mechanical stimulation hypothesis for albumen secretion is supported. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2013, 12, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.X.; Kim, W.K.; Wu, B.; Liu, G.M.; Wang, J.P.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; Song, J.P.; et al. Effects of selenium supplementation on the ion homeostasis in the reproductive organs and eggs of laying hens fed with the diet contaminated with cadmium, lead, mercury, and chromium. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 902355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawand, D.; Wahli, W.; Kaessmann, H. Loss of egg yolk genes in mammals and the origin of lactation and placentation. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelekan, D.A.; Thurnham, D.I. The influence of riboflavin deficiency on absorption and liver storage of iron in the growing rat. Br. J. Nutr. 1986, 56, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamji, M.S.; Sharada, D. Hepatic glutathione reductase and riboflavin concentration in experimental deficiency of thiaminand riboflavin in rats. J. Nutr. 1972, 102, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, J. Glutathione and related indices in rat lenses, liver and red cells during riboflavin deficiency and its correction. Exp. Eye Res. 1991, 53, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, P.S.; Brady, L.J.; Parsons, M.J.; Ullrey, D.E.; Miller, E.R. Effects of Riboflavin Deficiency on Growth and Glutathione Peroxidase System Enzymes in the Baby Pig. J. Nutr. 1979, 109, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Zhao, R.; Wu, Y.B.; Sun, P.X.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, S.S. Effect of riboflavin deficiency of duck breeders on birth weight, organ indexes, body shape indexes and plasma biochemical indexes of offspring. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 32, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, M.; Nakamura, M. Effects of riboflavin deficiency on the lipids of rat liver. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1975, 22, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, M. Effects of riboflavin deficiency on the lipids of rat liver mitochondria and microsomes. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1978, 24, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olpin, S.E.; Bates, C.J. Lipid metabolism in riboflavin-deficient rats. 2. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and the microsomal desaturation pathway. Br. J. Nutr. 1982, 47, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olpin, S.E.; Bates, C.J. Lipid metabolism in riboflavin-deficient rats. 1. Effect of dietary lipids on riboflavin status and fatty acid profiles. Br. J. Nutr. 1982, 47, 577–596. [Google Scholar]
- Siles, E.; Villalobos, M.; Jones, L.; Guerrero, R.; Eady, J.J.; Valenzuela, M.T.; Nunez, M.I.; McMillan, T.J.; Ruiz, D.; Almodovar, J.M. Apoptosis after gamma irradiation. Is it an important cell death modality? Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 1594–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredient | Content |
|---|---|
| Corn | 400.0 |
| Soybean meal (44% CP) | 68.0 |
| Pea | 180.0 |
| Wheat | 128.0 |
| Corn gluten meal (50% CP) | 50 |
| Sorghum | 104.0 |
| Soybean oil | 7.0 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 22.3 |
| Limestone | 25 |
| Sodium chloride | 4.0 |
| Vitamin premix 1 | 0.3 |
| Choline chloride | 0.4 |
| Mineral premix 2 | 1.0 |
| DL-Methionine | 6.0 |
| Lysine hydrochloride | 4.0 |
| Calculated composition | |
| Metabolizable energy, Mcal/kg | 2.99 |
| Crude protein 3 | 159.1 |
| Calcium | 15.2 |
| Non-phytate phosphorus | 5.4 |
| Lysine | 6.4 |
| Methionine | 2.5 |
| Methionine + cysteine | 5.0 |
| Threonine | 5.3 |
| Tryptophan | 1.5 |
| Arginine | 9.5 |
| Riboflavin 4, mg/kg | 1.20 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (g/pair) 1 | 1182 | 1177 | 1189 | 1188 | 1202 | 6.86 | 0.363 | -- | 0.956 | 1.00 | 0.884 | 0.717 |
| Final body weight (g/pair) 1 | 1237 | 1217 | 1252 | 1203 | 1182 | 13.7 | 0.901 | -- | 0.934 | 1.00 | 0.902 | 0.851 |
| Total feed intake of nursing (g/pair·28d) 1 | 3908 | 3910 | 3908 | 3909 | 3907 | 2.30 | 0.081 | -- | 0.667 | 0.840 | 0.785 | 0.693 |
| Laying interval (d) 1 | 39.0 | 40.7 | 40.1 | 43.2 | 40.8 | 0.703 | 1.14 | -- | 0.305 | 0.373 | 0.476 | 0.356 |
| Egg production (%) 1 | 90.2 | 93.5 | 92.3 | 93.2 | 90.9 | 0.860 | 0.329 | -- | 0.883 | 0.946 | 0.562 | 0.679 |
| Egg fertility (%) 1 | 92.3 | 98.8 | 94.7 | 94.4 | 93.9 | 0.553 | 0.733 | -- | 0.945 | 1.00 | 0.895 | 0.956 |
| Egg hatchability (%) 2 | 59.9b | 60.1 b | 67.9 ab | 77.7 a | 77.6 a | 0.044 | -- | 17.15 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.022 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg weight (g) | 24.5 | 23.0 | 24.5 | 24.6 | 23.8 | 0.241 | 1.56 | -- | 0.193 | 0.354 | 0.984 | 0.602 |
| Egg shape index (vertical diameter, cm) | 43.5 | 43.0 | 43.6 | 44.0 | 43.3 | 0.172 | 0.726 | -- | 0.577 | 0.907 | 0.709 | 0.402 |
| Egg shape index (horizontal diameter, cm) | 31.9 | 31.4 | 32.0 | 31.9 | 32.2 | 0.173 | 0.599 | -- | 0.664 | 0.913 | 0.306 | 0.780 |
| Eggshell color (%) | 66.2 | 66.2 | 65.6 | 64.7 | 66.5 | 0.825 | 0.377 | -- | 0.484 | 1.00 | 0.862 | 0.298 |
| Eggshell strength (kg) | 1.19 | 1.24 | 1.11 | 1.18 | 1.13 | 0.021 | 1.15 | -- | 0.342 | 0.577 | 0.272 | 0.860 |
| Egg albumen height | 3.22 | 2.84 | 3.18 | 2.66 | 2.62 | 0.104 | 1.54 | -- | 0.203 | 0.319 | 0.051 | 0.920 |
| Egg yolk color | 7.28 b | 7.68 b | 7.94 ab | 8.71 a | 8.78 a | 0.152 | 4.49 | -- | 0.003 | 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.356 |
| Haugh units | 67.1 | 57.3 | 57.9 | 56.7 | 60.7 | 2.12 | 0.938 | -- | 0.447 | 1.00 | 0.512 | 0.148 |
| Egg yolk weight (g) | 4.04 | 3.90 | 4.37 | 3.81 | 3.69 | 0.121 | 0.866 | -- | 0.488 | 1.00 | 0.262 | 0.455 |
| Eggshell weight (g) | 4.83 | 5.39 | 4.79 | 5.56 | 5.13 | 0.136 | 1.19 | -- | 0.323 | 0.395 | 0.416 | 0.440 |
| Eggshell thickness (mm) | 0.250 | 0.262 | 0.262 | 0.243 | 0.247 | 0.003 | 1.58 | -- | 0.187 | 0.411 | 0.175 | 0.463 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d BW (g) 2 | 19.2 b | 19.3 b | 20.8 ab | 21.7 a | 21.9 a | 0.316 | -- | 17.15 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.002 | 0.371 |
| 7 d BW (g) 2 | 140 | 139 | 148 | 144 | 171 | 0.673 | -- | 2.602 | 0.521 | 0.627 | 0.203 | 0.523 |
| 14 d BW (g) 1 | 361 | 356 | 362 | 363 | 381 | 3.90 | 1.24 | -- | 0.303 | 0.682 | 0.050 | 0.496 |
| 28 d BW (g) 1 | 459 | 440 | 519 | 512 | 522 | 14.8 | 1.62 | -- | 0.169 | 0.466 | 0.149 | 0.502 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcass weight (g) 1 | 412 | 404 | 418 | 417 | 426 | 6.34 | 0.261 | -- | 0.827 | 0.902 | 0.440 | 0.854 |
| Eviscerated weight (g) 2 | 319 b | 310 b | 336 ab | 359 a | 368 a | 5.78 | -- | 8.99 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.106 | 0.439 |
| Eviscerated percentage (%) 2 | 66.3 | 66.4 | 67.1 | 67.3 | 69.3 | 0.693 | -- | 3.83 | 0.227 | 0.421 | 0.238 | 0.716 |
| Half-eviscerated weight (g) 1 | 342 | 341 | 363 | 387 | 397 | 6.05 | 3.10 | -- | 0.018 | 0.066 | 0.009 | 0.680 |
| Half-eviscerated percentage (%) 2 | 69.9 | 71.8 | 72.5 | 74.8 | 74.6 | 0.637 | -- | 5.76 | 0.115 | 0.218 | 0.211 | 0.835 |
| Breast muscle weight (g) 2 | 59.5 b | 72.7 a | 74.5 a | 77.1 a | 78.2 a | 1.92 | -- | 10.4 | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.029 | 0.202 |
| Breast muscle percentage (%) 2 | 19.7 b | 22.9 a | 23.4 a | 23.5 a | 24.0 a | 0.357 | -- | 14.8 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.044 | 0.107 |
| Leg muscle weight (g) 1 | 21.5 | 22.0 | 22.6 | 23.4 | 24.8 | 0.432 | 1.26 | -- | 0.287 | 0.395 | 0.054 | 0.585 |
| Leg muscle percentage (%) 1 | 6.82 | 7.04 | 6.76 | 6.78 | 6.74 | 0.0980 | 0.290 | -- | 0.884 | 0.912 | 0.517 | 0.941 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver weight (g) | 16.6 a | 13.7 b | 13.1 b | 12.7 b | 12.7 b | 0.345 | -- | 16.5 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.021 |
| Liver index (%) | 3.44 a | 2.80 b | 2.62 b | 2.58 b | 2.45 b | 0.066 | -- | 18.2 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 |
| Spleen weight (g) | 0.406 | 0.442 | 0.434 | 0.454 | 0.448 | 0.023 | -- | 0.345 | 0.826 | 0.987 | 0.654 | 0.737 |
| Spleen index (%) | 0.0854 | 0.0885 | 0.0861 | 0.0912 | 0.0838 | 0.004 | -- | 0.384 | 0.817 | 0.984 | 0.963 | 0.696 |
| Bursa weight (g) | 0.569 | 0.713 | 0.708 | 0.718 | 0.841 | 0.037 | -- | 5.55 | 0.158 | 0.236 | 0.100 | 0.862 |
| Bursa percentage (%) | 0.115 | 0.139 | 0.141 | 0.142 | 0.158 | 0.006 | -- | 4.05 | 0.333 | 0.400 | 0.222 | 0.646 |
| Dietary Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 1.20 | 3.70 | 6.20 | 11.2 | 16.2 | SEM | F-Value | H-Value | p-Value | p-Value Adjustment | p-Value Riboflavin Linear | p-Value Riboflavin Quadratic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parental plasma (♀, μmol/L) | 0.947 d | 2.47 c | 3.50 b | 4.09 a | 4.25 a | 0.199 | -- | 36.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parental plasma (♂, μmol/L) | 0.546 d | 0.918 c | 1.35 b | 1.63 a | 1.66 a | 0.070 | -- | 35.1 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Egg yolk (μg/g) | 6.93 c | 10.5 b | 13.9 a | 14.5 a | 14.7 a | 0.486 | -- | 32.5 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Squab plasma (μmol/L) | 0.765 c | 1.56 b | 2.36 a | 2.55 a | 2.56 a | 0.115 | -- | 31.9 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Squab liver riboflavin (μg/g) | 2.59 c | 3.68 b | 4.21 a | 4.33 a | 4.39 a | 0.111 | -- | 31.6 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Squab liver FAD (μg/g) | 0.844 d | 0.949 c | 1.29 b | 1.45 a | 1.52 a | 0.045 | -- | 34.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Squab liver FMN (μg/g) | 2.61 d | 3.92 c | 4.35 b | 4.58 a | 4.66 a | 0.124 | -- | 34.3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Shen, L.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, Z. Effect of Dietary Riboflavin Levels on Reproductive Performance of Pigeon Breeders, and Growth Performance and Carcass Traits of Offspring Squabs. Animals 2024, 14, 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162414
Zhang B, Gao Y, Shao Y, Shen L, Liu W, Li H, Li Y, Li J, Ma T, Wang Z. Effect of Dietary Riboflavin Levels on Reproductive Performance of Pigeon Breeders, and Growth Performance and Carcass Traits of Offspring Squabs. Animals. 2024; 14(16):2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162414
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Yusheng Gao, Yuxin Shao, Li Shen, Wenli Liu, Haoxuan Li, Yipu Li, Jing Li, Tenghe Ma, and Zheng Wang. 2024. "Effect of Dietary Riboflavin Levels on Reproductive Performance of Pigeon Breeders, and Growth Performance and Carcass Traits of Offspring Squabs" Animals 14, no. 16: 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162414
APA StyleZhang, B., Gao, Y., Shao, Y., Shen, L., Liu, W., Li, H., Li, Y., Li, J., Ma, T., & Wang, Z. (2024). Effect of Dietary Riboflavin Levels on Reproductive Performance of Pigeon Breeders, and Growth Performance and Carcass Traits of Offspring Squabs. Animals, 14(16), 2414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162414





