Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of the Proteomes of Rabbit and Human Sex Chromosomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets Obtention and Filtering
2.2. Functional Annotation
2.2.1. UniProt Database
2.2.2. eggNOG-Mapper
2.3. Protein Topology Prediction
2.4. Identification of Proteins Associated with the Plasma Membrane
2.5. Statistical Overrepresentation Test of the Rabbit X Chromosome Proteome
2.6. Cross-Species Analysis: Identification of Human Targets in the Rabbit Proteome
2.6.1. Data Extraction
2.6.2. Alignment and Similarity
2.6.3. Manual Curation
2.7. Cross-Reference of the Common Human and Rabbit Targets with Human Spermatozoa Proteins
3. Results
3.1. Proteomes Filtering Process
3.2. Analysis of the Sex Chromosomes Proteome
3.2.1. Characterization of the Rabbit X Chromosome Proteome
Overrepresentation Analysis of the Rabbit X Chromosome Proteome
3.2.2. Characterization of the Human X and Y Chromosomes Proteome
3.3. Cross-Species Analysis: Identification of Human Targets in the Rabbit Proteome
3.4. Cross-Reference of the Common Human and Rabbit Targets with Human Spermatozoa Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelfand, B.D.; Ambati, J. Y Chromosome Proteins in Female Tissues. Science 2023, 382, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cao, J.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lee, Y.; Duarte, M.L.; Zhou, X. Sex Specific Molecular Networks and Key Drivers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, F.; Tesoriere, A.; Plotegher, N.; Dalla Valle, L. Sex and Brain: The Role of Sex Chromosomes and Hormones in Brain Development and Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, S.; Caramia, F.; Klein, S.L.; Rubin, J.B.; Haupt, Y. Sex Disparities Matter in Cancer Development and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; McClusky, R.; Chen, J.; Beaven, S.W.; Tontonoz, P.; Arnold, A.P.; Reue, K. The Number of x Chromosomes Causes Sex Differences in Adiposity in Mice. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, C.; Dejager, L.; Pinheiro, I. The X Chromosome in Immune Functions: When a Chromosome Makes the Difference. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Gangwar, D.K.; Singh, J.; Tikadar, C.K.; Khanna, V.V.; Saini, S.; Dholpuria, S.; Palta, P.; Manik, R.S.; Singh, M.K. An Immunological Approach of Sperm Sexing and Different Methods for Identification of X-and Y-Chromosome Bearing Sperm. Vet. World 2017, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wizemann, T.M.; Pardue, M.-L. Every Cell Has a Sex. In Exploring the Biological Contributions to Human Health: Does Sex Matter? National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Quelhas, J.; Pinto-Pinho, P.; Lopes, G.; Rocha, A.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Fardilha, M.; Colaço, B.J.A. Sustainable Animal Production: Exploring the Benefits of Sperm Sexing Technologies in Addressing Critical Industry Challenges. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1181659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.D.; Peña, A.I.; Gullón, J.; Prieto, C.; Barrio, M.; Becerra, J.J.; Herradón, P.G.; Quintela, L.A. Sex Ratio in Rabbits Following Modified Artificial Insemination. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 103, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Pinho, P.; Ferreira, A.F.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Fardilha, M.; Colaço, B. The History and Prospects of Rabbit Sperm Sexing. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Pang, M.G. New Biological Insights on X and Y Chromosome-Bearing Spermatozoa. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrogiacomo, R.; D′ Ambrosio, C.; Niccolini, A.; Serra, A.; Gazzano, A.; Scaloni, A.; Pelosi, P. An Odorant-Binding Protein Is Abundantly Expressed in the Nose and in the Seminal Fluid of the Rabbit. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusco, G.; Słowińska, M.; Di Iorio, M.; Cerolini, S.; Maffione, A.B.; Ciereszko, A.; Iaffaldano, N. Proteomic Analysis of Rabbit Fresh and Cryopreserved Semen Provides an Important Insight into Molecular Mechanisms of Cryoinjuries to Spermatozoa. Theriogenology 2022, 191, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, A.-J.; Cheng, L.; Diao, H.; Wang, P.; Gu, Y.-H.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, G.-W.; Zhou, S.-M.; Guo, S.-J. Comprehensive Profiling of Accessible Surface Glycans of Mammalian Sperm Using a Lectin Microarray. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares-Crespo, L.; Fernández-Serrano, P.; Viudes-de-Castro, M.P. Proteomic Characterization of Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) Sperm from Two Different Genotypes. Theriogenology 2019, 128, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares-Crespo, L.; Fernández-Serrano, P.; Vicente, J.S.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Viudes-de-Castro, M.P. Rabbit Seminal Plasma Proteome: The Importance of the Genetic Origin. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 189, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.J.B.; Arruda-Alencar, J.M.; Martins, J.A.M.; Viana, A.G.A.; Neto, A.M.V.; Rêgo, J.P.A.; Oliveira, R.V.; Lobo, M.; Moreira, A.C.O.; Moreira, R.A. Major Seminal Plasma Proteome of Rabbits and Associations with Sperm Quality. Theriogenology 2019, 128, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares-Crespo, L.; Talaván, A.M.; Viudes-de-Castro, M.P. Can the Genetic Origin Affect Rabbit Seminal Plasma Protein Profile along the Year? Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2016, 51, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Proteomes · Oryctolagus Cuniculus (Rabbit). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/UP000001811 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- NCBI Genome|Oryctolagus Cuniculus (Rabbit). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/genome/?taxon=9986 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- UniProt Proteomes · Homo Sapiens (Human). Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/proteomes/UP000005640 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Soares, J.; Pinheiro, A.; Esteves, P.J. The Rabbit as an Animal Model to Study Innate Immunity Genes: Is It Better than Mice? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 981815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón, T.; Koonin, E.V. Functional and Evolutionary Implications of Gene Orthology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Retrieve/ID Mapping. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/id-mapping (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Ensembl BioMart. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/biomart/martview/a6763ed18bfc217c68f09070ab50e1f1 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Ensembl Transcript Flags. Available online: http://www.ensembl.org/info/genome/genebuild/transcript_quality_tags.html (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- eggNOG EggNOG-Mapper. Available online: http://eggnog-mapper.embl.de/ (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Hernández-Plaza, A.; Szklarczyk, D.; Botas, J.; Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Giner-Lamia, J.; Mende, D.R.; Kirsch, R.; Rattei, T.; Letunic, I.; Jensen, L.J. EggNOG 6.0: Enabling Comparative Genomics across 12 535 Organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D389–D394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. EggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical University of Denmark DeepTMHMM. Available online: https://dtu.biolib.com/DeepTMHMM (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Hallgren, J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Pedersen, M.D.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Marcatili, P.; Nielsen, H.; Krogh, A.; Winther, O. DeepTMHMM Predicts Alpha and Beta Transmembrane Proteins Using Deep Neural Networks. BioRxiv 2022, 2022–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, Z.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Sentiment Classification Using a Single-Layered BiLSTM Model. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 73992–74001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Pinho, P. Gene-Ontology-Analysis 2022. Available online: https://github.com/PATRICIAPINHO/Gene-Ontology-analysis (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Gene Ontology AmiGO 2. Available online: https://amigo.geneontology.org/amigo (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander, S.A.; Balhoff, J.; Carbon, S.; Cherry, J.M.; Drabkin, H.J.; Ebert, D.; Feuermann, M.; Gaudet, P.; Harris, N.L. The Gene Ontology Knowledgebase in 2023. Genetics 2023, 224, iyad031. [Google Scholar]
- Carbon, S.; Ireland, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Shu, S.; Marshall, B.; Lewis, S.; Hub, A.; Group, W.P.W. AmiGO: Online Access to Ontology and Annotation Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PANTHER Classification System|PANTHER 18.0. Available online: https://pantherdb.org/ (accessed on 29 October 2023).
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Huang, X.; Ebert, D.; Mills, C.; Guo, X.; Thomas, P.D. Protocol Update for Large-Scale Genome and Gene Function Analysis with the PANTHER Classification System (v. 14.0). Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangar, V.; Blankenberg, D.J.; Altman, N.; Lesk, A.M. Quantitative Sequence-Function Relationships in Proteins Based on Gene Ontology. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, T.; Xu, D. Quantitative Assessment of Relationship between Sequence Similarity and Function Similarity. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higdon, R.; Louie, B.; Kolker, E. Modeling Sequence and Function Similarity between Proteins for Protein Functional Annotation. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Symposium on High Performance Distributed Computing, Chicago, IL, USA, 21–25 June 2010; pp. 499–502. [Google Scholar]
- Queirós, B. Impact of Sperm Protein Translation on Motility; University of Aveiro: Aveiro, Portugal, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, F.; Marques, J.P.; Areal, H.; Pinto-Pinho, P.; Colaço, B.; Melo-Ferreira, J.; Fardilha, M.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J. TLR7 and TLR8 Evolution in Lagomorphs: Different Patterns in the Different Lineages. Immunogenetics 2022, 74, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Yu, G.Y.; Maa, M.C.; Leu, T.H.; Xu, C.; Luo, Y.; Xiang, R.; Chuang, T.H. TLR7/8 Agonists Activate a Mild Immune Response in Rabbits through TLR8 but Not TLR7. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5593–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI Interleukin-3 Receptor Subunit Alpha Isoform X1 [Oryctolagus cuniculus—Protein]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/XP_008246682 (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Bai, Y.; Lin, W.; Xu, J.; Song, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, Y.E.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Improving the Genome Assembly of Rabbits with Long-Read Sequencing. Genomics 2021, 113, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.E.; Chen, F.; Saven, J.G.; Roos, D.S.; Babbitt, P.C.; Sali, A. Evolutionary Constraints on Structural Similarity in Orthologs and Paralogs. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirny, L.A.; Gelfand, M.S. Using Orthologous and Paralogous Proteins to Identify Specificity Determining Residues. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Forslund, K.; Coelho, L.P.; Szklarczyk, D.; Jensen, L.J.; Von Mering, C.; Bork, P. Fast Genome-Wide Functional Annotation through Orthology Assignment by EggNOG-Mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. The Human Transmembrane Proteome. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collombet, S.; Rall, I.; Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Heckert, A.; Halavatyi, A.; Le Saux, A.; Dailey, G.; Darzacq, X.; Heard, E. RNA Polymerase II Depletion from the Inactive X Chromosome Territory Is Not Mediated by Physical Compartmentalization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langton, M.J. Engineering of Stimuli-Responsive Lipid-Bilayer Membranes Using Supramolecular Systems. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyen, D.; Poët, M.; Jarretou, G.; Pisani, D.F.; Tauc, M.; Cougnon, M.; Argentina, M.; Bouret, Y.; Counillon, L. Intracellular PH Control by Membrane Transport in Mammalian Cells. Insights into the Selective Advantages of Functional Redundancy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 825028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Rahimi, N.; Dimri, M. Biochemistry, G Protein Coupled Receptors. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, K.; Ravelich, S. Materials and Methods for Sperm Sex Selection 2009. WO 2009/014456 A1, 29 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Quelhas, J.; Santiago, J.; Matos, B.; Rocha, A.; Lopes, G.; Fardilha, M. Bovine Semen Sexing: Sperm Membrane Proteomics as Candidates for Immunological Selection of X- and Y-Chromosome-Bearing Sperm. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Verma, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Pandey, D.; Sharma, M. Differential Proteomic Profile of X- and Y-Sorted Sahiwal Bull Semen. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 144, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmivandana, R.; Patole, C.; Sharma, T.R.; Sharma, K.K.; Naskar, S. Differential Proteins Associated with Plasma Membrane in X- and/or Y-chromosome Bearing Spermatozoa in Indicus Cattle. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Zhou, C.; Cao, M.; Cai, W.; Yin, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, S. Differential Membrane Protein Profile in Bovine X- and Y-Sperm. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3031–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaletsky, H.; Kuroda-Kawaguchi, T.; Minx, P.J.; Cordum, H.S.; Hillier, L.; Brown, L.G.; Repping, S.; Pyntikova, T.; Ali, J.; Bieri, T.; et al. The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 2003, 423, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Skaletsky, H.; Brown, L.G.; Zaghlul, S.; Rock, S.; Graves, T.; Auger, K.; Warren, W.C.; Wilson, R.K.; Page, D.C. Independent Specialization of the Human and Mouse X Chromosomes for the Male Germ Line. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanesi, L.; Scotti, E.; Russo, V. Differences of the Porcine Amelogenin X and Y Chromosome Genes (AMELX and AMELY) and Their Application for Sex Determination in Pigs. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.M.; Mannucci, A.; Kimpton, C.P.; Gill, P. A Rapid and Quantitative DNA Sex Test: Fluorescence-Based PCR Analysis of X-Y Homologous Gene Amelogenin. Biotechniques 1993, 15, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Colaco, S.; Modi, D. Genetics of the Human Y Chromosome and Its Association with Male Infertility. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



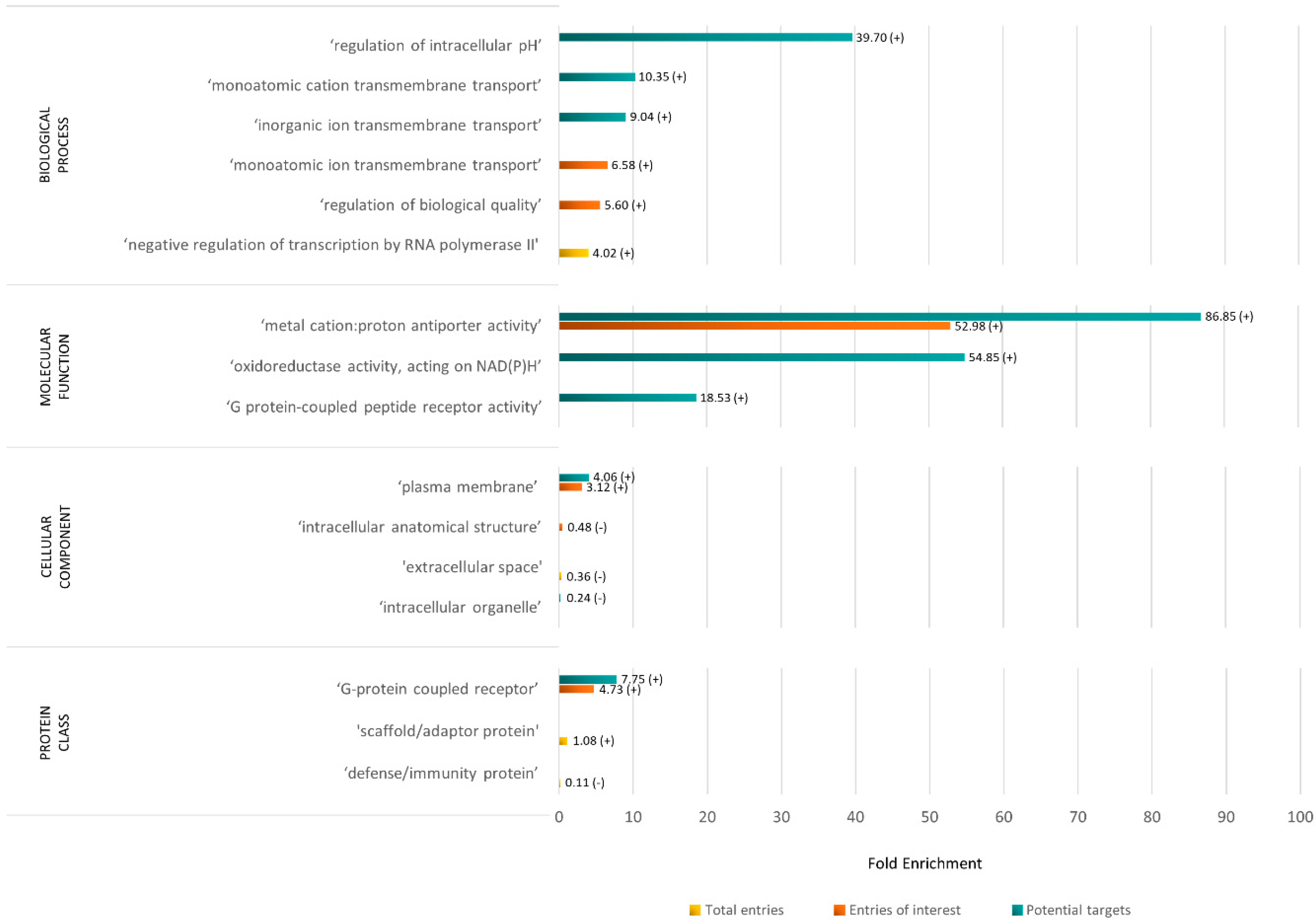

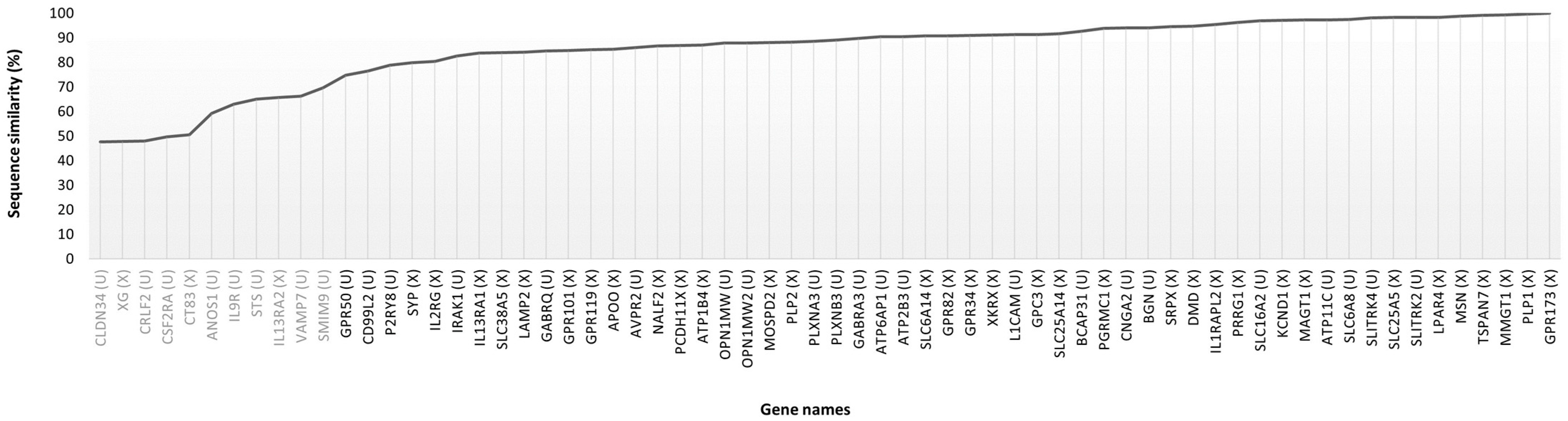
| Protein ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Topology | GO Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1TEF4 | ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme | SP+TM | CS, PM, ES † |
| G1SSU5 | ADGRG2 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G2 | SP+TM | PM † |
| Q8MKE9 | AGTR2 | Type-2 angiotensin II receptor | TM | PM † |
| G1SMQ1 | AMOT | Angiomotin | GLOB | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| G1T923 | ATP6AP2 | Renin receptor | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| G1T6U3 | ATP7A | P-type Cu(+) transporter | TM | PM † |
| G1TUV0 | BRS3 | Bombesin receptor subtype-3 | TM | PM † |
| G1SNI0 | CACNA1F | Calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 F | TM | PM † |
| G1SV48 | CD24 * | CD24 molecule | SP | CS, PM, ESPM, ACPM, ACESPM † |
| G1SKP7 | CD40LG | CD40 ligand | TM | CS, PM, ESPM, ES † |
| Q9TTU3 | CLCN5 | H(+)/Cl(−) exchange transporter 5 | TM | PM † |
| G1TSU9 | CLDN2 | Claudin 2 | TM | PM |
| G1T4N6 | CLTRN | Collectrin, amino acid transport regulator | SP+TM | PM † |
| A0A5F9CEX7 | CXCR3 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3 | TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| A0A5F9CNI6 | CYBB | Cytochrome b-245 beta chain | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1TB31 | CYSLTR1 | Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1T9S6 | EDA | Ectodysplasin A | TM | PM, ES, ICPM † |
| A0A5F9D0L9 | EDA2R | Ectodysplasin A2 receptor | SP+TM | PM |
| A0A5F9CVB5 | EFNB1 | Ephrin B1 | SP+TM | PM† |
| G1TPG8 | ENOX2 | Ecto-NOX disulfide-thiol exchanger 2 | GLOB | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| A0A5F9CPD1 | GDPD2 | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 2 | TM | PM † |
| G1TMB8 | GJB1 | Gap junction protein | TM | PM † |
| G1T1J4 | GLRA2 | Glycine receptor alpha 2 | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1T836 | GLRA4 * | Glycine receptor alpha 4 | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| A0A5F9DIT5 | GPC4 | Glypican 4 | TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| G1SN36 | GPR174 | G protein-coupled receptor 174 | TM | PM |
| G1SD16 | GRIA3 | Glutamate receptor | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1T4A8 | GRPR | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1SXP0 | GUCY2F | Guanylate cyclase | SP+TM | PM † |
| A0A5F9C5Z9 | HEPH | Hephaestin | SP+TM | PM † |
| A0A5F9DJ94 | HNRNPM * | RRM domain-containing protein | GLOB | CS† |
| G1TAG7 | HTR2C | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM, ICPM † |
| G1TBS6 | IL1RAPL1 | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| G1TPE7 | IL2RG * | Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma | TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| G1SVL1 | ITM2A | Integral membrane protein 2 | TM | PM |
| G1TSW5 | KCNE5 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E regulatory subunit 5 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| U3KP42 | MMGT1 * | Membrane magnesium transporter | TM | PM † |
| G1SCP8 | MSN * | Moesin | GLOB | CS, PM † |
| G1TU56 | NDP | Norrin cystine knot growth factor NDP | SP | CS, ES † |
| G1TYL9 | NLGN3 | Neuroligin 3 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ICPM † |
| G1SPD7 | NOX1 | NADPH oxidase 1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1T124 | OR13H1 | Olfactory receptor family 13 subfamily H member 1 | TM | PM |
| G1TCY0 | P2RY4 | P2Y purinoceptor 4 | TM | PM † |
| A0A5F9DQS9 | PCDH11X * | Cadherin domain-containing protein | SP+TM | PM |
| G1TAD7 | PCDH19 | Protocadherin 19 | SP+TM | PM |
| G1SQ59 | PHEX | Phosphate-regulating endopeptidase homolog X-linked | TM | CS † |
| G1T949 | PORCN | Porcupine O-acyltransferase | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| G1T7A1 | PTCHD1 | Patched domain-containing 1 | TM | PM † |
| G1SZZ7 | RS1 | Retinoschisin 1 | SP | PM, ESPM, ES |
| G1SZJ1 | SLC7A3 | Solute carrier family 7 member 3 | TM | PM † |
| G1T4W3 | SLC9A6 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger | SP+TM | PM † |
| G1SLC9 | SLC9A7 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger | SP+TM | PM |
| G1T0T4 | SRPX2 | Sushi repeat containing protein X-linked 2 | SP | CS, PM, ES † |
| G1SN13 | TENM1 | Teneurin transmembrane protein 1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| O62852 | TRPC5 | Short transient receptor potential channel 5 | TM | PM |
| A0A5F9CK03 | VSIG1 | V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 1 | SP+TM | PM † |
| G1SR92 | XK | XK-related protein | TM | PM |
| A0A5F9CW02 | - | Transmembrane protein 182 | TM | PM |
| G1THX1 | - | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger | TM | PM |
| G1TL60 | - | Olfactory receptor | TM | PM |
| U3KP07 | - | receptor protein-tyrosine kinase | TM | PM |
| Protein ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Topology | GO Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9BYF1 | ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ES †† |
| Q8IZP9 | ADGRG2 | Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor G2 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| P50052 | AGTR2 | Type-2 angiotensin II receptor | TM | PM † |
| Q99217 | AMELX | Amelogenin, X isoform | SP | CS † |
| Q4VCS5 | AMOT | Angiomotin | GLOB | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| P23352 | ANOS1 | Anosmin-1 | SP | CS, PM, ESPM, ES † |
| Q9BUR5 | APOO | MICOS complex subunit MIC26 | TM | ES |
| Q8NB49 | ATP11C | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IG | TM | PM † |
| Q9UN42 | ATP1B4 | Protein ATP1B4 | TM | PM |
| Q16720 | ATP2B3 | Plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 3 | TM | PM † |
| Q15904 | ATP6AP1 | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 | SP+TM | PM † |
| O75787 | ATP6AP2 | Renin receptor | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| Q04656 | ATP7A | Copper-transporting ATPase 1 | TM | PM† |
| P30518 | AVPR2 | Vasopressin V2 receptor | TM | PM |
| P51572 | BCAP31 | B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P21810 | BGN | Biglycan | SP | CS, PM, ES † |
| P32247 | BRS3 | Bombesin receptor subtype-3 | TM | PM † |
| O60840 | CACNA1F | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1F | TM | PM † |
| P29965 | CD40LG | CD40 ligand | TM | CS, PM, ESPM, ES † |
| P14209 | CD99 | CD99 antigen | SP+TM | PM |
| Q8TCZ2 | CD99L2 | CD99 antigen-like protein 2 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| P51795 | CLCN5 | H(+)/Cl(−) exchange transporter 5 | TM | PM † |
| P57739 | CLDN2 | Claudin-2 | TM | PM |
| H7C241 | CLDN34 | Claudin-34 | TM | PM |
| Q9HBJ8 | CLTRN | Collectrin | SP+TM | PM † |
| A0A3B3IT09 | CLTRN * | Collectrin domain-containing protein | TM | PM |
| Q16280 | CNGA2 | Cyclic nucleotide-gated olfactory channel | TM | PM |
| Q9HC73 | CRLF2 | Cytokine receptor-like factor 2 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| P15509 | CSF2RA | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor subunit alpha | SP+TM | PM, ESPM † |
| Q5H943 | CT83 | Kita-kyushu lung cancer antigen 1 | TM | PM |
| P49682 | CXCR3 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3 | TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| P04839 | CYBB | Cytochrome b-245 heavy chain | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| Q9Y271 | CYSLTR1 | Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P11532 | DMD | Dystrophin | GLOB | CS, PM † |
| Q92838 | EDA | Ectodysplasin-A | TM | PM, ES, ICPM † |
| Q9HAV5 | EDA2R | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 27 | TM | PM |
| P98172 | EFNB1 | Ephrin-B1 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| Q16206 | ENOX2 | Ecto-NOX disulfide-thiol exchanger 2 | GLOB | CS, PM, ESPM, ES † |
| P34903 | GABRA3 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 | SP+TM | PM |
| Q9UN88 | GABRQ | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit theta | SP+TM | PM |
| Q9HCC8 | GDPD2 | Glycerophosphoinositol inositolphosphodiesterase | TM | PM † |
| P08034 | GJB1 | Gap junction beta-1 protein | TM | PM † |
| P23416 | GLRA2 | Glycine receptor subunit alpha-2 | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P51654 | GPC3 | Glypican-3 | SP | CS, PM, ACPM |
| O75487 | GPC4 | Glypican-4 | SP | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| Q13491 | GPM6B | Neuronal membrane glycoprotein M6-b | TM | PM † |
| Q96P66 | GPR101 | Probable G-protein-coupled receptor 101 | TM | PM |
| Q8TDV5 | GPR119 | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor | TM | PM |
| P51810 | GPR143 | G-protein-coupled receptor 143 | TM | PM † |
| Q9NS66 | GPR173 | Probable G-protein-coupled receptor 173 | TM | PM |
| Q9BXC1 | GPR174 | Probable G-protein-coupled receptor 174 | TM | PM |
| Q9UPC5 | GPR34 | Probable G-protein-coupled receptor 34 | TM | PM |
| Q13585 | GPR50 | Melatonin-related receptor | TM | PM † |
| Q96P67 | GPR82 | Probable G-protein-coupled receptor 82 | TM | PM |
| P42263 | GRIA3 | Glutamate receptor 3 | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P30550 | GRPR | Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P51841 | GUCY2F | Retinal guanylyl cyclase 2 | SP+TM | PM † |
| Q9BQS7 | HEPH | Hephaestin | SP+TM | PM † |
| P28335 | HTR2C | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM, ICPM † |
| P78552 | IL13RA1 | Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-1 | SP+TM | PM, ESPM |
| Q14627 | IL13RA2 | Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2 | SP+TM | ESPM, ES |
| Q9NZN1 | IL1RAPL1 | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| Q9NP60 | IL1RAPL2 | X-linked interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 | SP+TM | PM |
| P31785 | IL2RG | Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| A0A2R8YE73 | IL2RG * | Fibronectin type-III domain-containing protein | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| P26951 | IL3RA | Interleukin-3 receptor subunit alpha | SP+TM | PM, ESPM |
| Q01113 | IL9R | Interleukin-9 receptor | SP+TM | PM, ESPM, ES |
| P51617 | IRAK1 | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 | GLOB | CS, PM |
| O43736 | ITM2A | Integral membrane protein 2A | TM | PM |
| Q9NSA2 | KCND1 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 1 | TM | PM |
| Q9UJ90 | KCNE5 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E regulatory beta subunit 5 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P32004 | L1CAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| P13473 | LAMP2 | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 | SP+TM | PM, ES † |
| Q99677 | LPAR4 | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 | TM | PM † |
| Q9H0U3 | MAGT1 | Magnesium transporter protein 1 | SP+TM | PM |
| Q8N4V1 | MMGT1 | ER membrane protein complex subunit 5 | TM | PM † |
| Q8NHP6 | MOSPD2 | Motile sperm domain-containing protein 2 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P26038 | MSN | Moesin | GLOB | CS, PM, ES † |
| O75949 | NALF2 | NALCN channel auxiliary factor 2 | TM | PM |
| Q00604 | NDP | Norrin | SP | CS, ES † |
| Q9NZ94 | NLGN3 | Neuroligin-3 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ICPM † |
| Q8N0W4 | NLGN4X | Neuroligin-4, X-linked | SP+TM | CS, PM, ICPM † |
| Q9Y5S8 | NOX1 | NADPH oxidase 1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P04000 | OPN1LW | Long-wave-sensitive opsin 1 | TM | PM |
| P04001 | OPN1MW | Medium-wave-sensitive opsin 1 | TM | PM |
| P0DN77 | OPN1MW2 | Medium-wave-sensitive opsin 2 | TM | PM |
| P0DN78 | OPN1MW3 | Medium-wave-sensitive opsin 3 | TM | PM |
| Q8NG92 | OR13H1 | Olfactory receptor 13H1 | TM | PM |
| O00398 | P2RY10 | Putative P2Y purinoceptor 10 | TM | PM |
| P51582 | P2RY4 | P2Y purinoceptor 4 | TM | PM† |
| Q86VZ1 | P2RY8 | P2Y purinoceptor 8 | TM | PM |
| Q9BZA7 | PCDH11X | Protocadherin-11 X-linked | SP+TM | PM |
| Q8TAB3 | PCDH19 | Protocadherin-19 | SP+TM | PM |
| O00264 | PGRMC1 | Membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 1 | TM | PM |
| P78562 | PHEX | Phosphate-regulating neutral endopeptidase PHEX | TM | CS, PM † |
| P60201 | PLP1 | Myelin proteolipid protein | TM | PM † |
| Q04941 | PLP2 | Proteolipid protein 2 | TM | PM † |
| P51805 | PLXNA3 | Plexin-A3 | SP+TM | PM † |
| Q9ULL4 | PLXNB3 | Plexin-B3 | SP+TM | CS, PM † |
| Q9H237 | PORCN | Protein-serine O-palmitoleoyltransferase porcupine | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| O14668 | PRRG1 | Transmembrane gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein 1 | TM | PM, ES |
| Q9BZD7 | PRRG3 | Transmembrane gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein 3 | TM | ES |
| Q96NR3 | PTCHD1 | Patched domain-containing protein 1 | TM | PM † |
| O15537 | RS1 | Retinoschisin | SP | PM, ESPM, ES |
| P36021 | SLC16A2 | Monocarboxylate transporter 8 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| O95258 | SLC25A14 | Brain mitochondrial carrier protein 1 | TM | PM |
| P05141 | SLC25A5 | ADP/ATP translocase 2 | TM | PM |
| Q8WUX1 | SLC38A5 | Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 5 | TM | PM |
| Q9UN76 | SLC6A14 | Sodium- and chloride-dependent neutral and basic amino acid transporter B(0+) | TM | PM |
| P48029 | SLC6A8 | Sodium- and chloride-dependent creatine transporter 1 | TM | PM |
| Q8WY07 | SLC7A3 | Cationic amino acid transporter 3 | TM | PM † |
| Q92581 | SLC9A6 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 6 | SP+TM | PM † |
| Q96T83 | SLC9A7 | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 7 | SP+TM | PM |
| Q9H156 | SLITRK2 | SLIT- and NTRK-like protein 2 | SP+TM | PM |
| Q8IW52 | SLITRK4 | SLIT- and NTRK-like protein 4 | SP+TM | PM |
| A6NGZ8 | SMIM9 | Small integral membrane protein 9 | SP+TM | PM |
| P78539 | SRPX | Sushi repeat-containing protein SRPX | SP | CS |
| O60687 | SRPX2 | Sushi repeat-containing protein SRPX2 | SP | CS, PM, ES † |
| P08842 | STS | Steryl-sulfatase | SP+TM | PM |
| P08247 | SYP | Synaptophysin | TM | PM † |
| P51864 | TDGF1P3 | Putative teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 3 | SP | CS, PM, ES † |
| Q9UKZ4 | TENM1 | Teneurin-1 | TM | PM, ICPM † |
| Q9NYK1 | TLR7 | Toll-like receptor 7 | SP+TM | PM † |
| Q9NR97 | TLR8 | Toll-like receptor 8 | SP+TM | CS, PM, ESPM † |
| Q9BQJ4 | TMEM47 | Transmembrane protein 47 | TM | PM † |
| Q9UL62 | TRPC5 | Short transient receptor potential channel 5 | TM | PM |
| P41732 | TSPAN7 | Tetraspanin-7 | TM | PM |
| P51809 | VAMP7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | TM | CS, PM † |
| Q86XK7 | VSIG1 | V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 1 | SP+TM | PM † |
| P55808 | XG | Glycoprotein Xg | SP+TM | PM, ICPM † |
| P51811 | XK | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane adapter protein XK | TM | PM |
| Q6PP77 | XKRX | XK-related protein 2 | TM | PM |
| Protein ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | Topology | GO Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q99218 | AMELY | Amelogenin, Y isoform | SP | CS † |
| Q8NFZ3 | NLGN4Y | Neuroligin-4, Y-linked | SP+TM | CS, PM |
| Q9BZA8 | PCDH11Y | Protocadherin-11, Y-linked | SP+TM | PM |
| RefSeq_Human | RefSeq_Rabbit | Gene Name | Protein Description | Similarity (%) | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XP_054183011 | XP_051689653 | ANOS1 | anosmin-1 | 59.2 | Unplaced |
| XP_054183834 | XP_051683595 | APOO | MICOS complex subunit MIC26 | 85.4 | X |
| XP_054182860 | XP_051687539 | ATP11C | phospholipid-transporting ATPase IG | 97.3 | Unplaced |
| XP_016884870 | XP_008271374 | ATP1B4 | protein ATP1B4 | 87.0 | X |
| XP_016885042 | XP_051693419 | ATP2B3 | plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 3 | 90.5 | Unplaced |
| NP_001174 | NP_001164848 | ATP6AP1 | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 precursor | 90.4 | Unplaced |
| NP_000045 | XP_008248538 | AVPR2 | vasopressin V2 receptor | 86.0 | Unplaced |
| NP_001132929 | XP_008248542 | BCAP31 | B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 | 92.7 | Unplaced |
| XP_054183538 | XP_051693405 | BGN | biglycan | 94.0 | Unplaced |
| XP_047298518 | XP_008273252 | CD99L2 | CD99 antigen-like protein 2 | 76.5 | Unplaced |
| NP_005131 | XP_051689801 | CNGA2 | cyclic nucleotide-gated olfactory channel | 94.0 | Unplaced |
| XP_011544483 | XP_008273625 | CRLF2 | cytokine receptor-like factor 2 | 47.9 | Unplaced |
| XP_047297804 | XP_008249542 | CSF2RA | granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor subunit alpha | 49.6 | Unplaced |
| NP_001017978 | XP_008271135 | CT83 | kita-kyushu lung cancer antigen 1 | 50.5 | X |
| XP_006724531 | XP_051683632 | DMD | dystrophin | 94.6 | X |
| XP_054182733 | XP_051689815 | GABRA3 | gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 | 89.7 | Unplaced |
| XP_011529486 | XP_002721381 | GABRQ | gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit theta | 84.7 | Unplaced |
| XP_054182809 | XP_002720349 | GPC3 | glypican-3 | 91.3 | X |
| NP_473362 | XP_017205202 | GPR101 | probable G-protein-coupled receptor 101 | 84.8 | X |
| NP_848566 | XP_002720339 | GPR119 | glucose-dependent insulinotropic receptor | 85.1 | X |
| XP_054183230 | XP_008270867 | GPR173 | probable G-protein-coupled receptor 173 | 100.0 | X |
| XP_005272654 | XP_002719905 | GPR34 | probable G-protein-coupled receptor 34 | 90.9 | X |
| XP_011529518 | XP_008273247 | GPR50 | melatonin-related receptor | 74.7 | Unplaced |
| XP_047297947 | XP_051682990 | GPR82 | probable G-protein-coupled receptor 82 | 90.8 | X |
| XP_054183006 | XP_008271141 | IL13RA1 | interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-1 | 83.8 | X |
| XP_054183007 | XP_051683230 | IL13RA2 | interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2 | 65.7 | X |
| XP_011529207 | XP_008271052 | IL1RAPL2 | X-linked interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 | 95.4 | X |
| XP_047298053 | XP_051693453 | IRAK1 | interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 | 82.7 | Unplaced |
| NP_004970 | XP_002719951 | KCND1 | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 1 | 97.1 | X |
| NP_000416 | XP_051693407 | L1CAM | neural cell adhesion molecule L1 | 91.3 | Unplaced |
| NP_001116078 | XP_008271376 | LAMP2 | lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 | 84.2 | X |
| XP_016884927 | XP_008271183 | LPAR4 | lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 | 98.4 | X |
| NP_001354845 | XP_008271178 | MAGT1 | magnesium transporter protein 1 | 97.3 | X |
| NP_689794 | XP_051683552 | MOSPD2 | motile sperm domain-containing protein 2 | 88.0 | X |
| XP_054182806 | XP_051683121 | NALF2 | NALCN channel auxiliary factor 2 | 86.7 | X |
| NP_000504 | NP_001309193 | OPN1MW | medium-wave-sensitive opsin 1 | 87.9 | Unplaced |
| XP_005274486 | XP_002724295 | P2RY8 | P2Y purinoceptor 8 | 78.9 | Unplaced |
| XP_047297954 | XP_008271184 | P2RY10 | putative P2Y receptor family member 10 | 87.9 | X |
| NP_006658 | XP_002720306 | PGRMC1 | membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 1 | 93.8 | X |
| NP_000524 | XP_008271259 | PLP1 | myelin proteolipid protein | 99.6 | X |
| NP_002659 | NP_001075566 | PLP2 | proteolipid protein 2 | 88.2 | X |
| XP_047298203 | XP_008248506 | PLXNA3 | plexin-A3 | 88.5 | Unplaced |
| NP_005384 | XP_017194059 | PLXNB3 | plexin-B3 | 89.0 | Unplaced |
| NP_001135867 | XP_008270716 | PRRG1 | transmembrane gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein 1 | 96.3 | X |
| NP_006508 | XP_051691041 | SLC16A2 | monocarboxylate transporter 8 | 96.8 | Unplaced |
| XP_011529704 | XP_008271409 | SLC25A14 | brain mitochondrial carrier protein 1 | 91.6 | X |
| NP_001143 | XP_002720308 | SLC25A5 | ADP/ATP translocase 2 | 98.3 | X |
| XP_054184094 | XP_051682846 | SLC38A5 | sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 5 | 83.9 | X |
| NP_009162 | XP_002720288 | SLC6A14 | sodium- and chloride-dependent neutral and basic amino acid transporter B(0+) | 90.8 | X |
| NP_005620 | NP_001075866 | SLC6A8 | sodium- and chloride-dependent creatine transporter 1 | 97.5 | Unplaced |
| XP_047298533 | XP_051687602 | SLITRK2 | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 2 | 98.3 | Unplaced |
| XP_054182427 | XP_008271667 | SLITRK4 | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 4 | 98.1 | Unplaced |
| NP_001156408 | XP_051691991 | SMIM9 | small integral membrane protein 9 | 69.7 | Unplaced |
| XP_016885382 | XP_051682971 | SRPX | sushi repeat-containing protein SRPX, partial | 94.6 | X |
| XP_047298063 | XP_008247483 | STS | steryl-sulfatase | 65.1 | Unplaced |
| NP_003170 | XP_051682874 | SYP | synaptophysin | 79.8 | X |
| NP_004606 | XP_017205349 | TSPAN7 | tetraspanin-7 | 99.2 | X |
| XP_011529490 | XP_002722247 | VAMP7 | vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | 66.3 | Unplaced |
| XP_005274644 | XP_008271435 | XG | glycoprotein Xg | 47.8 | X |
| XP_011529256 | XP_002720425 | XKRX | XK-related protein 2 | 91.2 | X |
| Entry | Gene Name | Protein Name |
|---|---|---|
| Q9BYF1 | ACE2 *† | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| Q8IZP9 | ADGRG2 *† | Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor G2 |
| Q4VCS5 | AMOT *† | Angiomotin |
| P23352 | ANOS1 | Anosmin-1 |
| Q9BUR5 | APOO * | MICOS complex subunit MIC26 |
| Q8NB49 | ATP11C | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IG |
| Q16720 | ATP2B3 | Plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 3 |
| Q15904 | ATP6AP1 | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 |
| O75787 | ATP6AP2 *† | Renin receptor |
| Q04656 | ATP7A *† | Copper-transporting ATPase 1 |
| P51572 | BCAP31 | B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 |
| P21810 | BGN | Biglycan |
| P32247 | BRS3 *† | Bombesin receptor subtype-3 |
| O60840 | CACNA1F *† | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1F |
| P51795 | CLCN5 *† | H(+)/Cl(−) exchange transporter 5 |
| P57739 | CLDN2 *† | Claudin-2 |
| Q9HC73 | CRLF2 | Cytokine receptor-like factor 2 |
| Q5H943 | CT83 * | Kita-kyushu lung cancer antigen 1 |
| P04839 | CYBB *† | Cytochrome b-245 heavy chain |
| P11532 | DMD * | Dystrophin |
| Q92838 | EDA *† | Ectodysplasin-A |
| Q16206 | ENOX2 *† | Ecto-NOX disulfide-thiol exchanger 2 |
| P34903 | GABRA3 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 |
| Q9HCC8 | GDPD2 *† | Glycerophosphoinositol inositolphosphodiesterase GDPD2 |
| P51654 | GPC3 * | Glypican-3 |
| O75487 | GPC4 *† | Glypican-4 |
| Q14627 | IL13RA2 * | Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2 |
| Q9NZN1 | IL1RAPL1 *† | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 |
| P51617 | IRAK1 | Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 |
| P32004 | L1CAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 |
| P13473 | LAMP2 * | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 |
| Q9H0U3 | MAGT1 * | Magnesium transporter protein 1 |
| Q8N4V1 | MMGT1 *† | ER membrane protein complex subunit 5 |
| Q8NHP6 | MOSPD2 * | Motile sperm domain-containing protein 2 |
| P26038 | MSN *† | Moesin |
| Q00604 | NDP *† | Norrin |
| Q9Y5S8 | NOX1 *† | NADPH oxidase 1 |
| O00264 | PGRMC1 * | Membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 1 |
| Q04941 | PLP2 * | Proteolipid protein 2 |
| Q96NR3 | PTCHD1 *† | Patched domain-containing protein 1 |
| O95258 | SLC25A14 * | Brain mitochondrial carrier protein 1 |
| P05141 | SLC25A5 * | ADP/ATP translocase 2 |
| Q9UN76 | SLC6A14 * | Sodium- and chloride-dependent neutral and basic amino acid transporter B(0+) |
| Q92581 | SLC9A6 *† | Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 6 |
| Q9H156 | SLITRK2 | SLIT and NTRK-like protein 2 |
| P78539 | SRPX * | Sushi repeat-containing protein SRPX |
| P08842 | STS | Steryl-sulfatase |
| P08247 | SYP * | Synaptophysin |
| Q9UKZ4 | TENM1 *† | Teneurin-1 |
| P41732 | TSPAN7 * | Tetraspanin-7 |
| P51809 | VAMP7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 |
| Q86XK7 | VSIG1 *† | V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 1 |
| P51811 | XK *† | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane adapter protein XK |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto-Pinho, P.; Soares, J.; Esteves, P.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Fardilha, M.; Colaço, B. Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of the Proteomes of Rabbit and Human Sex Chromosomes. Animals 2024, 14, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14020217
Pinto-Pinho P, Soares J, Esteves P, Pinto-Leite R, Fardilha M, Colaço B. Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of the Proteomes of Rabbit and Human Sex Chromosomes. Animals. 2024; 14(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14020217
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto-Pinho, Patrícia, João Soares, Pedro Esteves, Rosário Pinto-Leite, Margarida Fardilha, and Bruno Colaço. 2024. "Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of the Proteomes of Rabbit and Human Sex Chromosomes" Animals 14, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14020217
APA StylePinto-Pinho, P., Soares, J., Esteves, P., Pinto-Leite, R., Fardilha, M., & Colaço, B. (2024). Comparative Bioinformatic Analysis of the Proteomes of Rabbit and Human Sex Chromosomes. Animals, 14(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14020217







